Static and Fatigue Mechanical Performance of Abutments Materials for Dental Restorations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
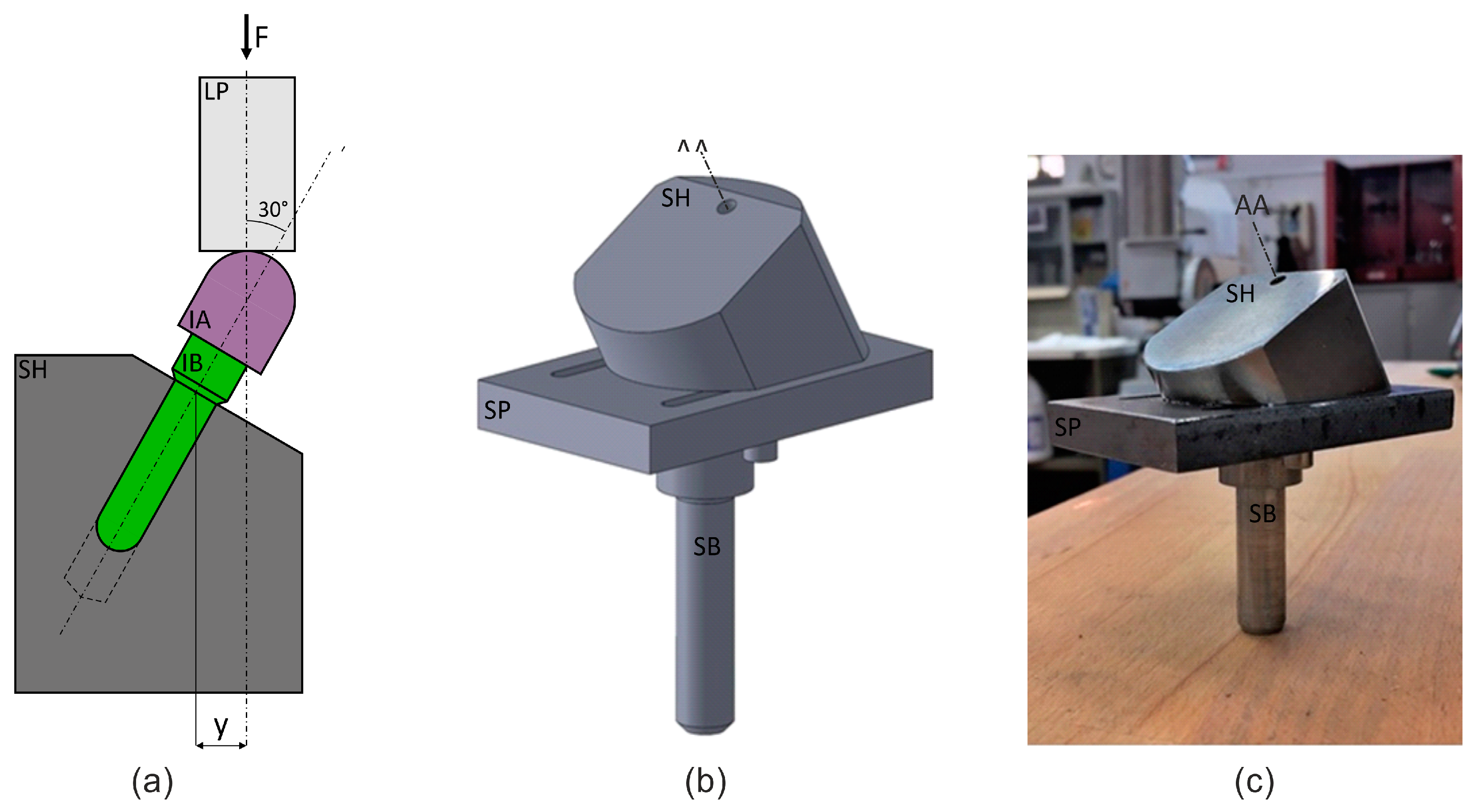
2.1. Experimental Apparatus
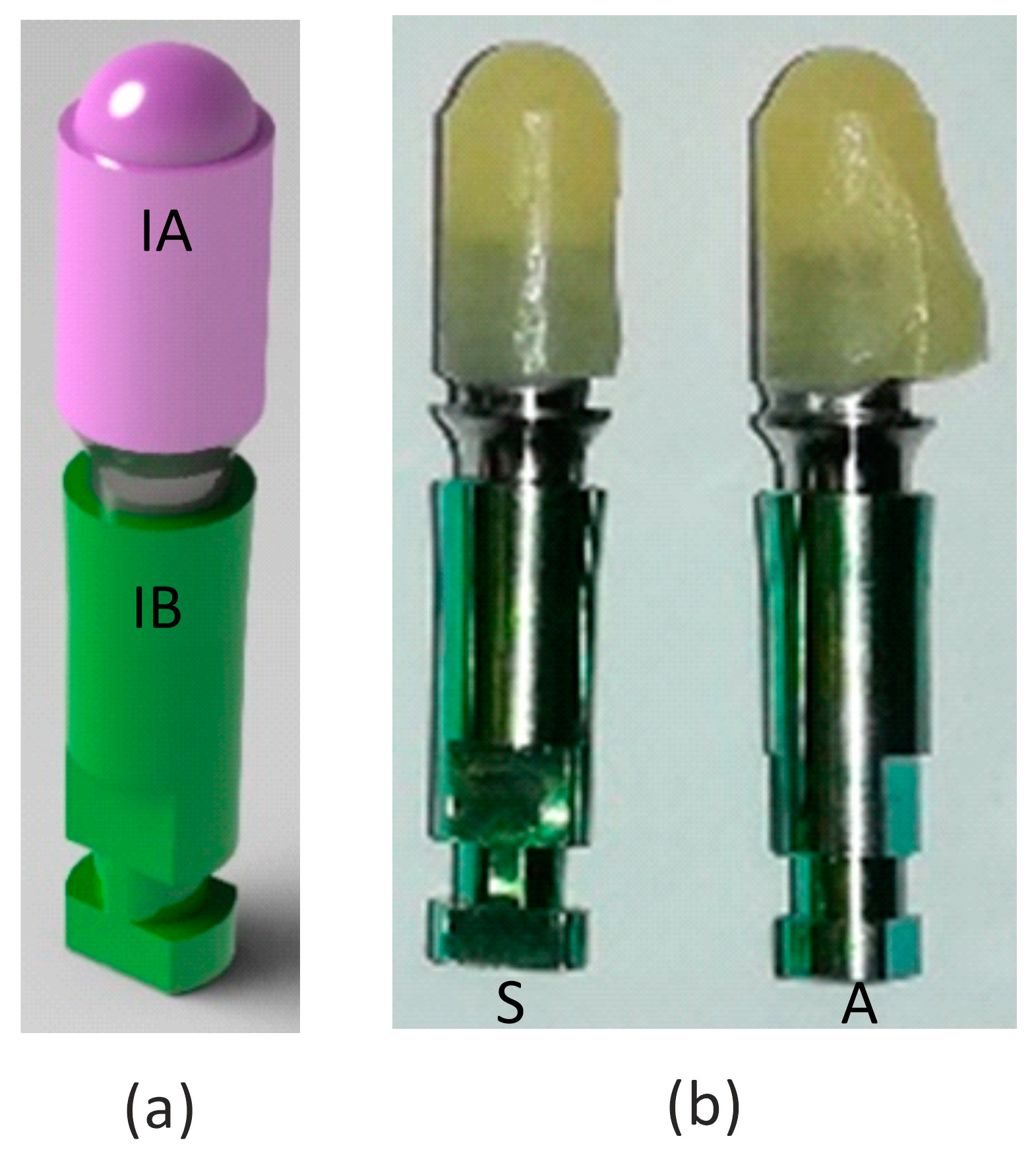
2.2. Specimen
2.3. Testing Protocols
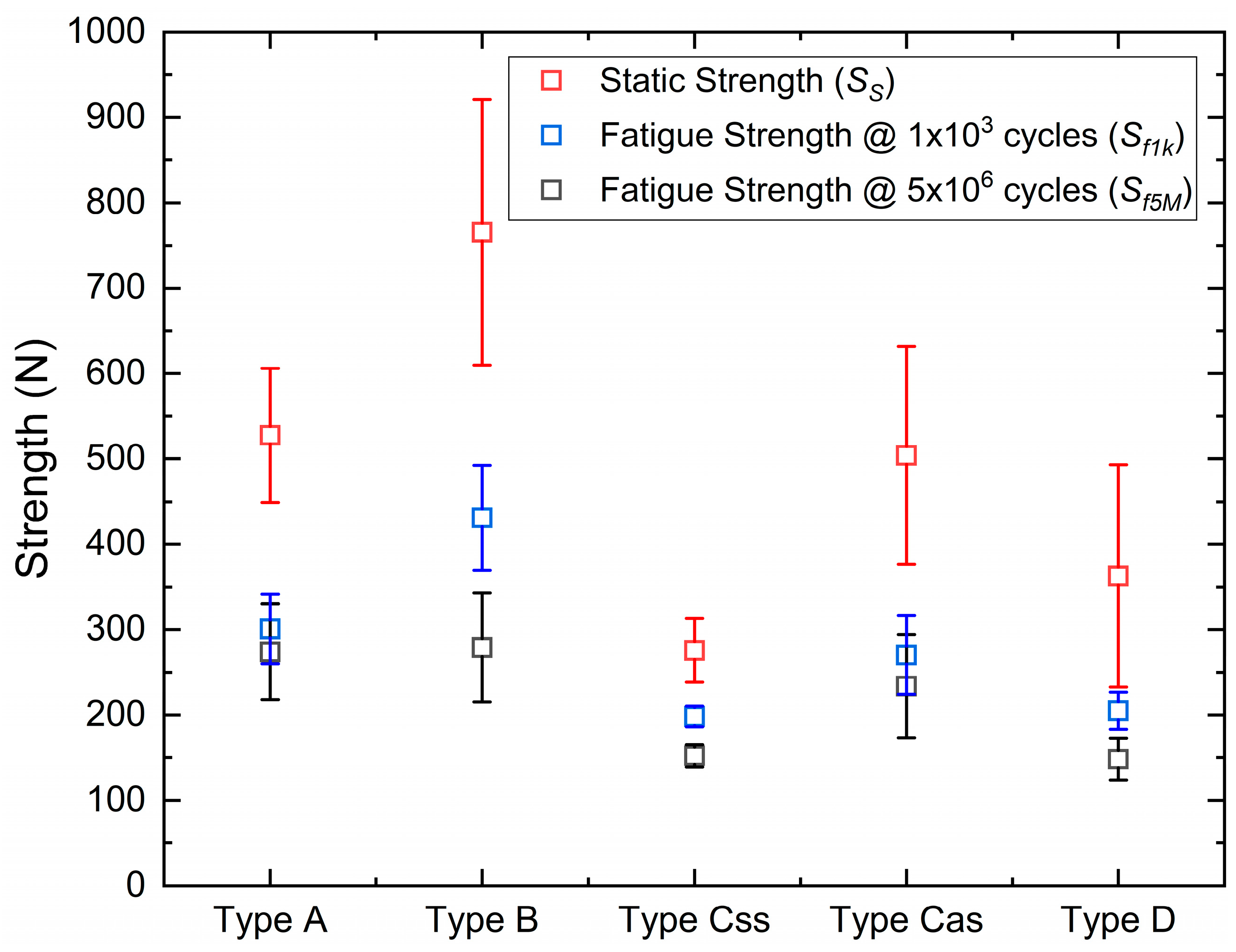
3. Results
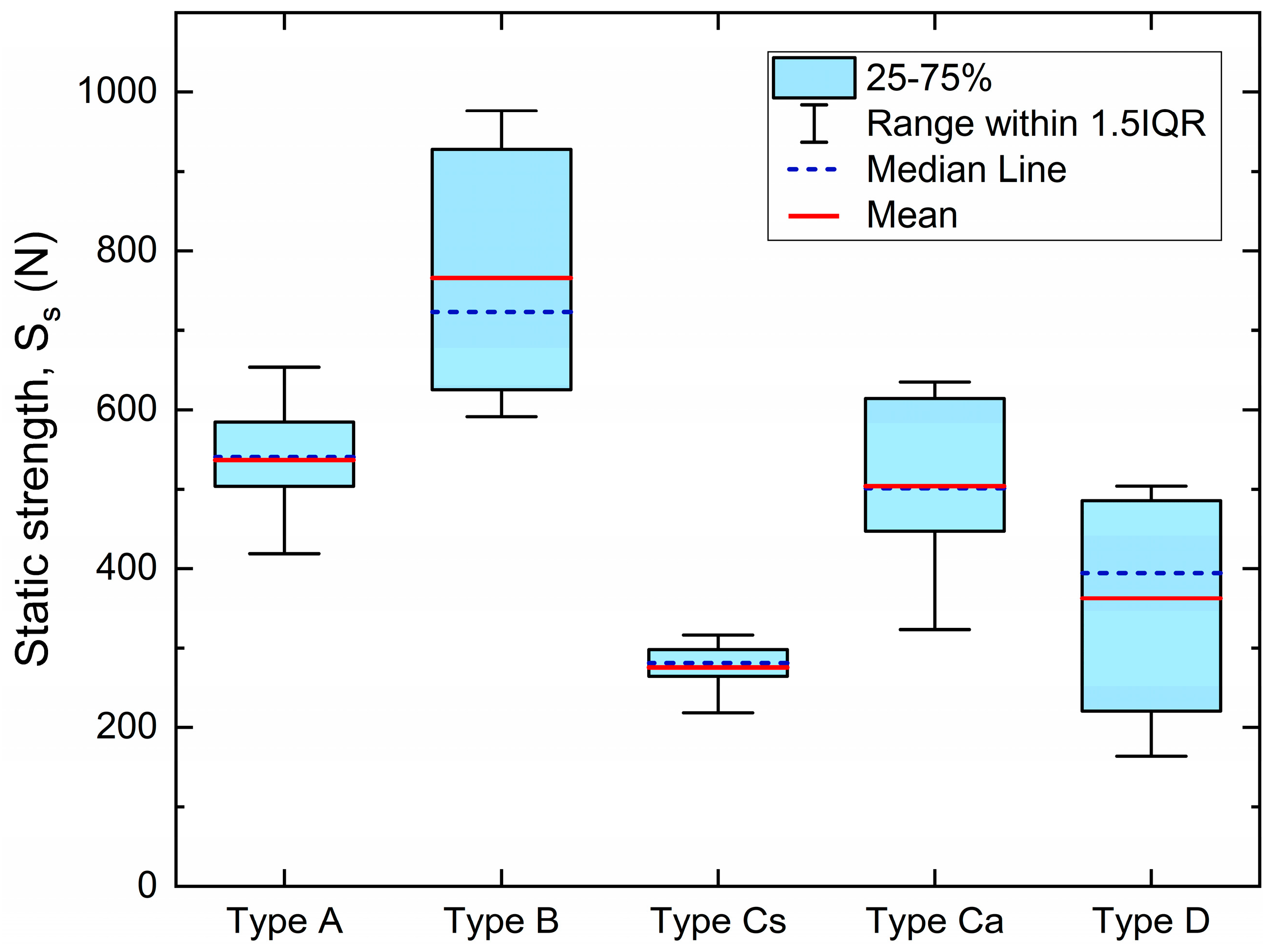
3.1. Static Strength
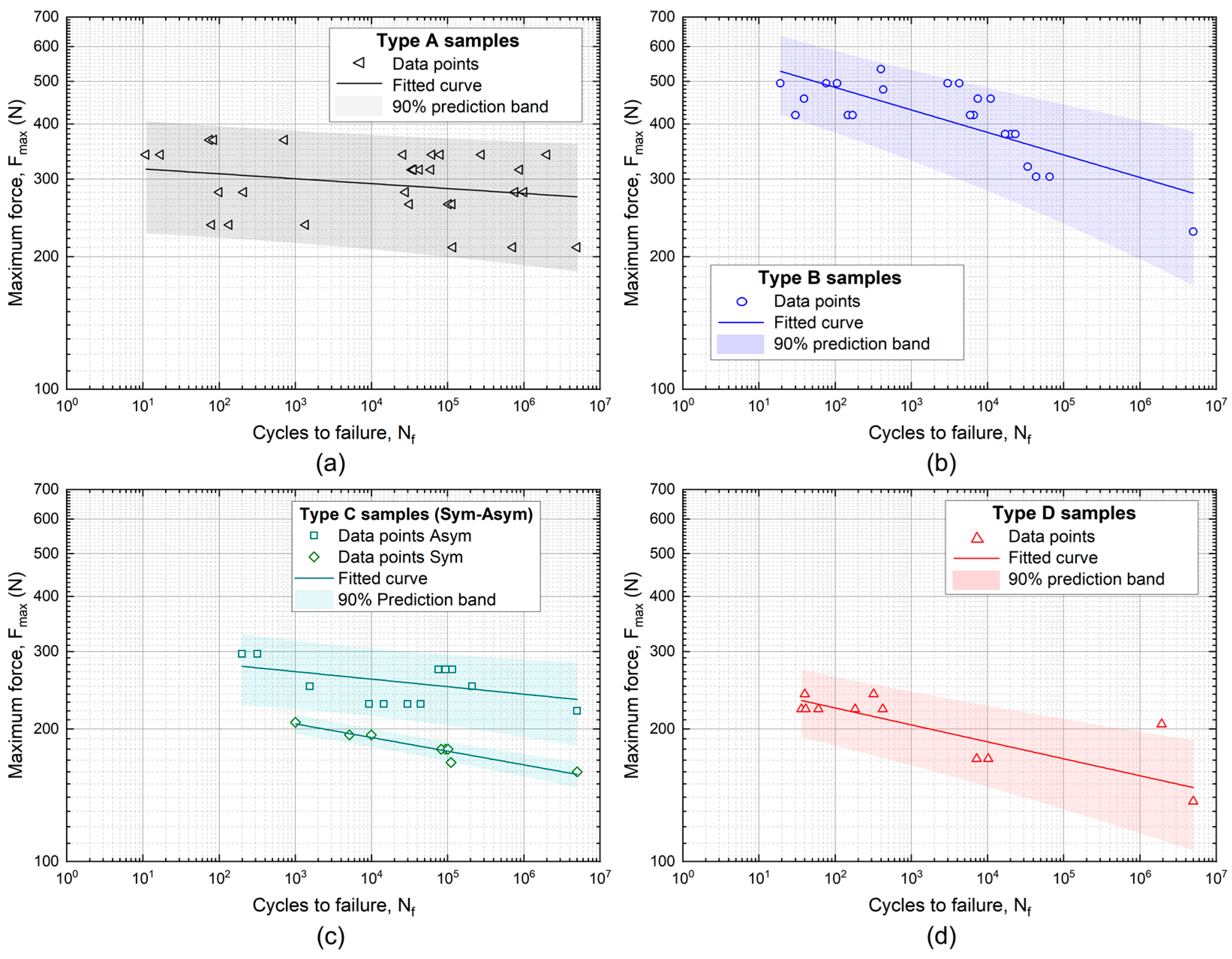
3.2. Fatigue Strength
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- −
- In comparison to polymer-based composites (PMMA and PEEK), ceramics (disilicate and zirconia) demonstrated significantly more static strength, with mean values exceeding 500 N for disilicate and 750 N for zirconia.
- −
- The results of the fatigue tests confirmed the trend observed for static strength, with disilicate and zirconia exhibiting the highest endurance limit values at 5 × 106 cycles, with mean values of around 280 N for both materials.
- −
- The power law fatigue parameters obtained for all materials provided the fatigue strength for a wide range of life cycles and highlighted the sensitivity of each material to fatigue loading conditions.
- −
- For nominally isotropic materials, such as ceramics and PEEK, no geometric effects were observed. However, significant material–geometry coupling was noted for fiber-reinforced PMMA in terms of both static and fatigue strength.
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yazdanian, M.; Alam, M.; Abbasi, K.; Rahbar, M.; Farjood, A.; Tahmasebi, E.; Tebyaniyan, H.; Ranjbar, R.; Hesam Arefi, A. Synthetic Materials in Craniofacial Regenerative Medicine: A Comprehensive Overview. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 987195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pjetursson, B.E.; Fehmer, V. EAO Position Paper: Material Selection for Implant-Supported Restorations. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2022, 35, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pjetursson, B.E.; Brägger, U.; Lang, N.P.; Zwahlen, M. Comparison of Survival and Complication Rates of Tooth-Supported Fixed Dental Prostheses (FDPs) and Implant-Supported FDPs and Single Crowns (SCs). Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2007, 18, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menini, M.; Conserva, E.; Tealdo, T.; Bevilacqua, M.; Pera, F.; Signori, A.; Pera, P. Shock Absorption Capacity of Restorative Materials for Implant Prostheses: An in Vitro Study. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2013, 26, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conserva, E.; Menini, M.; Tealdo, T.; Bevilacqua, M.; Pera, F.; Ravera, G.; Pera, P. Robotic chewing simulator for dental materials testing on a sensor-equipped implant setup. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2008, 21, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Conserva, E.; Menini, M.; Bevilacqua, M.; Tealdo, T.; Ravera, G.; Pera, F.; Pera, P. The Use of a Masticatory Robot to Analyze the Shock Absorption Capacity of Different Restorative Materials for Prosthetic Implants: A Preliminary Report. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2009, 22, 53–55. [Google Scholar]
- Pera, P.; Menini, M.; Pesce, P.; Bevilacqua, M.; Pera, F.; Tealdo, T. Immediate Versus Delayed Loading of Dental Implants Supporting Fixed Full-Arch Maxillary Prostheses: A 10-Year Follow-Up Report. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2019, 32, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menini, M.; Pesce, P.; Bevilacqua, M.; Pera, F.; Tealdo, T.; Barberis, F.; Pera, P. Effect of Framework in an Implant-Supported Full-Arch Fixed Prosthesis: 3D Finite Element Analysis. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2015, 28, 627–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pera, F.; Pesce, P.; Solimano, F.; Tealdo, T.; Pera, P.; Menini, M. Carbon Fibre Versus Metal Framework In Full-Arch Immediate Loading Rehabilitations of The Maxilla—A Cohort Clinical Study. J. Oral Rehabil. 2017, 44, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delucchi, F.; De Giovanni, E.; Pesce, P.; Bagnasco, F.; Pera, F.; Baldi, D.; Menini, M. Framework Materials for Full-Arch Implant-Supported Rehabilitations: A Systematic Review of Clinical Studies. Materials 2021, 14, 3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesce, P.; Lagazzo, A.; Barberis, F.; Repetto, L.; Pera, F.; Baldi, D.; Menini, M. Mechanical Characterisation of Multi vs. Uni-Directional Carbon Fiber Frameworks for Dental Implant Applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 102, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menini, M.; Pesce, P.; Pera, F.; Barberis, F.; Lagazzo, A.; Bertola, L.; Pera, P. Biological and Mechanical Characterization of Carbon Fiber Frameworks for Dental Implant Applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 70, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, T.-Y.; Ogawa, Y.; Akebono, H.; Iwaguro, S.; Sugeta, A.; Shimoe, S. Finite-Element Analysis and Optimization of the Mechanical Properties of Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) Clasps for Removable Partial Dentures. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2020, 64, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.; Liu, Y.; Peng, B.; Chen, M.; Liu, Z.; Li, Z.; Kuang, H.; Gong, B.; Li, Z.; Sun, H. PEEK for Oral Applications: Recent Advances in Mechanical and Adhesive Properties. Polymer 2023, 15, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arieira, A.; Madeira, S.; Rodrigues, F.; Silva, F. Tribological Behavior of TiO2 PEEK Composite and Stainless Steel for Pediatric Crowns. Materials 2023, 16, 2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benalcázar Jalkh, E.B.; Bergamo, E.T.P.; Campos, T.M.B.; de Araújo-Júnior, E.N.S.; Lopes, A.C.O.; Tebcherani, S.M.; Yamaguchi, S.; Genova, L.A.; Gierthmuehlen, P.C.; Witek, L.; et al. Stability of Fatigued and Aged ZTA Compared to 3Y-TZP and Al2O3 Ceramic Systems. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2022, 135, 105451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Li, X.; Zou, L.; He, J.; Zhao, B. Mechanical Properties and Marginal Fit of Prefabricated Versus Customized Dental Implant Abutments: A Comparative Study. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2022, 24, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- On, S.-W.; Yi, S.-M.; Park, I.-Y.; Byun, S.-H.; Yang, B.-E. Fracture and Fatigue of Dental Implants Fixtures and Abutments with a Novel Internal Connection Design: An in Vitro Pilot Study Comparing Three Different Dental Implant Systems. J. Funct. Biomater. 2022, 13, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atalay, P.; Öztas, D.D. Fatigue Resistance and Fracture Strength of Narrow-Diameter One-Piece Zirconia Implants with Angled Abutments. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2022, 34, 1060–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNE EN ISO 14801:2017; Dentistry—Implants—Dynamic Loading Test for Endosseous Dental Implants (ISO 14801:2016). International Organization for Standardization: Plzen, Czech Republic, 2016. Available online: https://www.en-standard.eu/une-en-iso-14801-2017-dentistry-implants-dynamic-loading-test-for-endosseous-dental-implants-iso-14801-2016/ (accessed on 7 January 2019).
- Reis, T.A.D.; Zancopé, K.; Karam, F.K.; Neves, F.D.D. Biomechanical Behavior of Extra-Narrow Implants After Fatigue and Pull-Out Tests. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2019, 122, 54.e1–54.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivrikaya, E.C.; Guler, M.S.; Bekci, M.L. A comparative study between zirconia and titanium abutments on the stress distribution in parafunctional loading: A 3D finite element analysis. Technol. Health Care Off. J. Eur. Soc. Eng. Med. 2020, 28, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarot, J.R.; Contar, C.M.M.; Cruz, A.C.C.D.; de Souza Magini, R. Evaluation of the stress distribution in CFR-PEEK dental implants by the three-dimensional finite element method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2010, 21, 2079–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Park, J.M.; Park, E.J.; Koak, J.Y.; Kim, S.K.; Heo, S.J. Comparison of Customized Abutments Made from Titanium and a Machinable Precious Alloy. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2016, 31, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Material ID | Material Type | Trade Name/Manufacturer | Manufacturing Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type A | Lithium disilicate | IPS Emax-Ivoclar | Sintering |
| Type B | Translucent zirconia | Katana, Kouraray-Noritake | Sintering |
| Type C | Fiber-reinforced PMMA | Bre.CAM, Multilayer, Bredent | Milling |
| Type D | Ceramic-reinforced PEEK | breCAM.BioHPP, Bredent | Milling |
| Type A | Type B | Type C | Type D | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | A | S | A | S | A | S | A | ||
| Sample ID | 1 | 540.3 | 446.4 | 654.9 | 965.5 | 218.5 | 323.1 | 163.9 | 175.6 |
| 2 | 514.5 | 503.7 | 591.3 | 595.6 | 298.3 | 614.2 | 220.7 | 504.0 | |
| 3 | 434.8 | 574.4 | 741.6 | 625.1 | 316.2 | 501.2 | 496.6 | 403.1 | |
| 4 | 584.5 | 653.4 | 872.6 | 976.5 | 264.6 | 447.0 | 377.9 | 414.0 | |
| 5 | 418.5 | 605.6 | 704.4 | 927.9 | 281.1 | 634.7 | 385.4 | 485.5 | |
| Sample | 498.5 | 556.7 | 713.0 | 818.1 | 275.7 | 504.0 | 328.9 | 396.4 | |
| 70.5 | 82.2 | 105.5 | 190.8 | 37.3 | 127.7 | 134.8 | 131.0 | ||
| p-value | 0.264 | 0.321 | 0.014 | 0.445 | |||||
| Material | 527.6 | 765.5 | N/A | 362.7 | |||||
| 78.4 | 155.6 | N/A | 130.2 | ||||||
| Type A | Type B | Type CS | Type CA | Type D | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Power law parameters | a (N) | 324.6 ± 26.2 | 613.0 ± 45.0 | 245.5 ± 9.8 | 303.8 ± 30.8 | 266.5 ± 15.3 |
| b | −0.011 ± 0.008 | −0.051 ± 0.010 | −0.031 ± 0.003 | −0.017 ± 0.010 | −0.038 ± 0.007 | |
| Fatigue strength | Sf1k (N) | 300.8 ± 42.7 | 431.0 ± 64.7 | 198.2 ± 12.2 | 270.1 ± 46.1 | 205.0 ± 21.7 |
| Sf5M (N) | 273.9 ± 56.1 | 279.1 ± 64.0 | 152.2 ± 13.2 | 233.7 ± 60.2 | 148.3 ± 24.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bruno, L.; Canullo, L.; Mayer, Y.; Schoenbaum, T.; Giuzio, F.; Maletta, C. Static and Fatigue Mechanical Performance of Abutments Materials for Dental Restorations. Materials 2023, 16, 3713. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16103713
Bruno L, Canullo L, Mayer Y, Schoenbaum T, Giuzio F, Maletta C. Static and Fatigue Mechanical Performance of Abutments Materials for Dental Restorations. Materials. 2023; 16(10):3713. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16103713
Chicago/Turabian StyleBruno, Luigi, Luigi Canullo, Yaniv Mayer, Todd Schoenbaum, Francesco Giuzio, and Carmine Maletta. 2023. "Static and Fatigue Mechanical Performance of Abutments Materials for Dental Restorations" Materials 16, no. 10: 3713. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16103713
APA StyleBruno, L., Canullo, L., Mayer, Y., Schoenbaum, T., Giuzio, F., & Maletta, C. (2023). Static and Fatigue Mechanical Performance of Abutments Materials for Dental Restorations. Materials, 16(10), 3713. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16103713









