Core–Shell Fe3O4@C Nanoparticles for the Organic Dye Adsorption and Targeted Magneto-Mechanical Destruction of Ehrlich Ascites Carcinoma Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
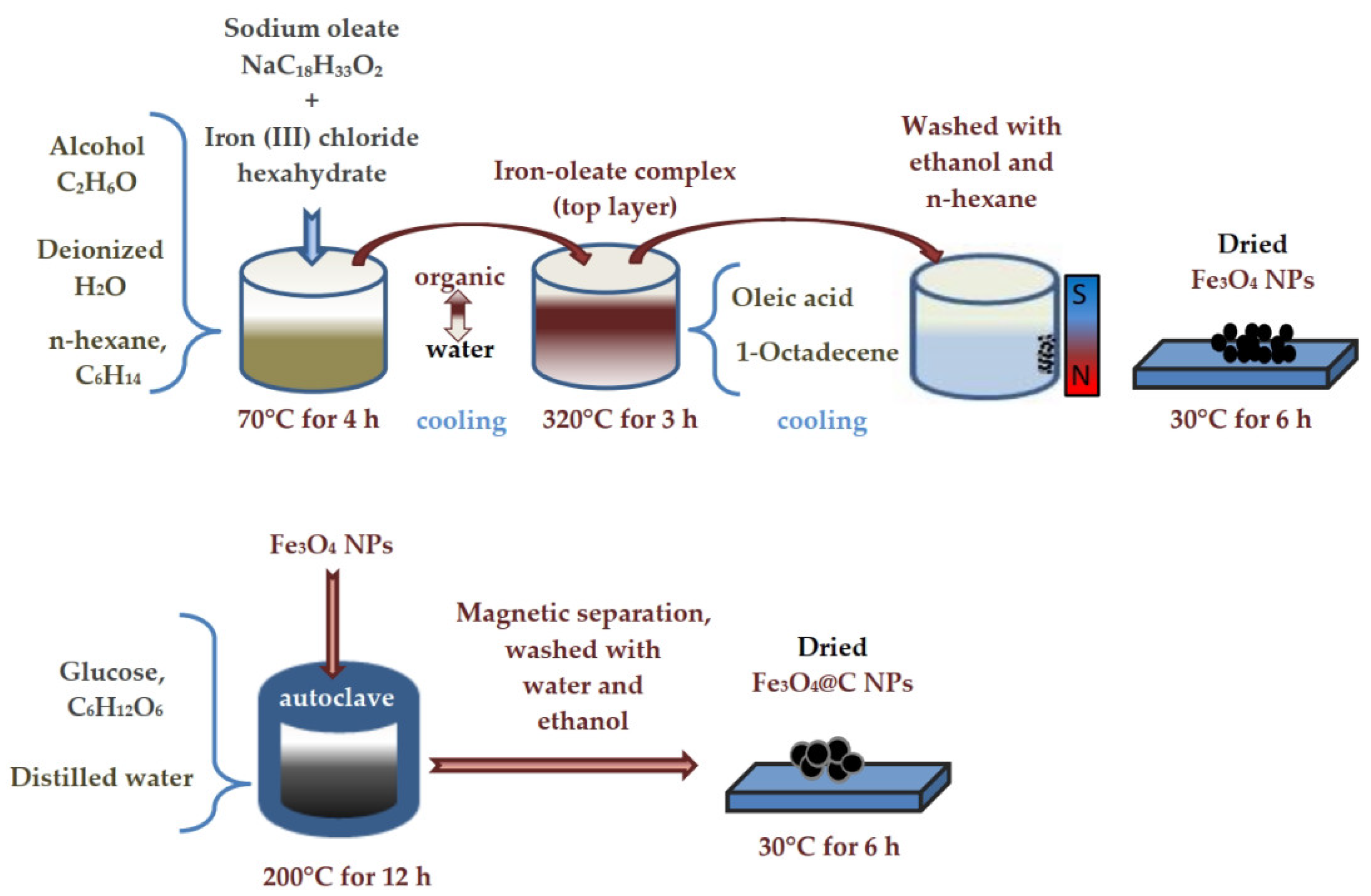
2.1. Synthesis of Nanoparticles
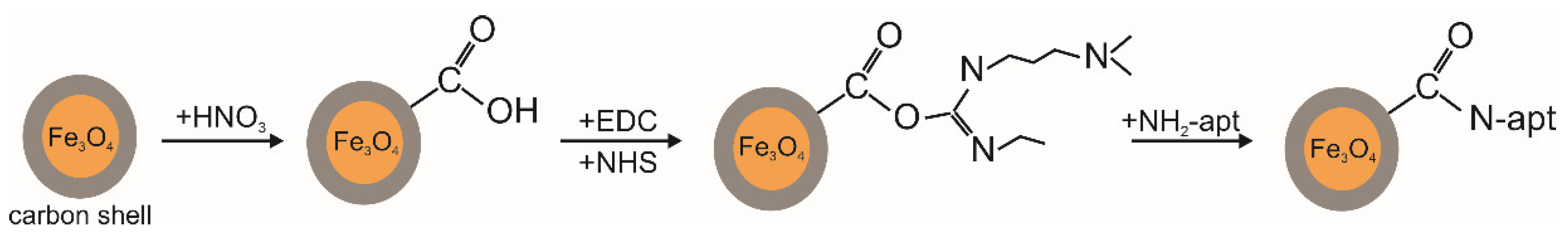
2.2. Functionalization of Fe3O4@C NPs by Aptamers
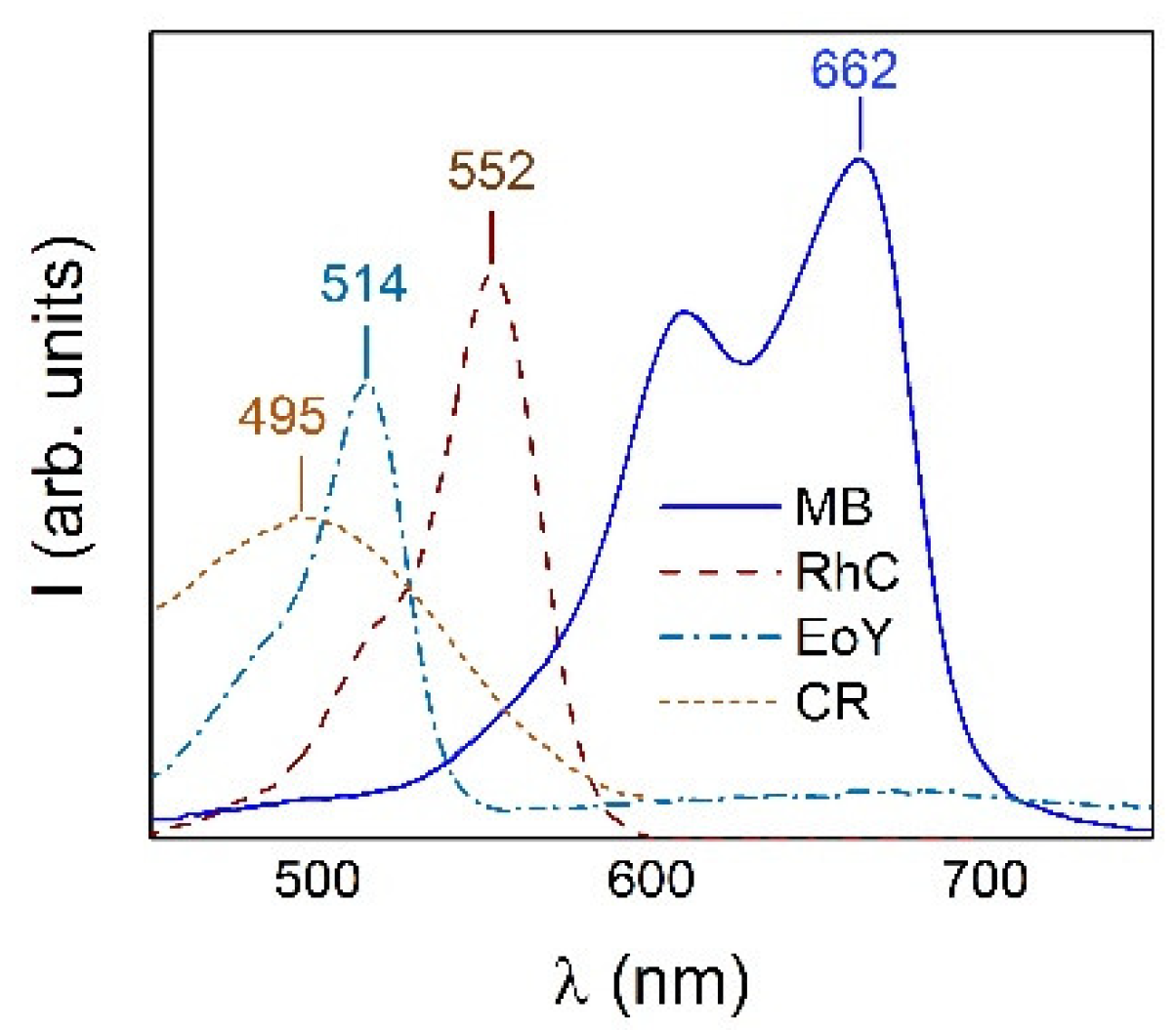
2.3. Dyes
2.4. Characteristic Methods
3. Results and Discussion
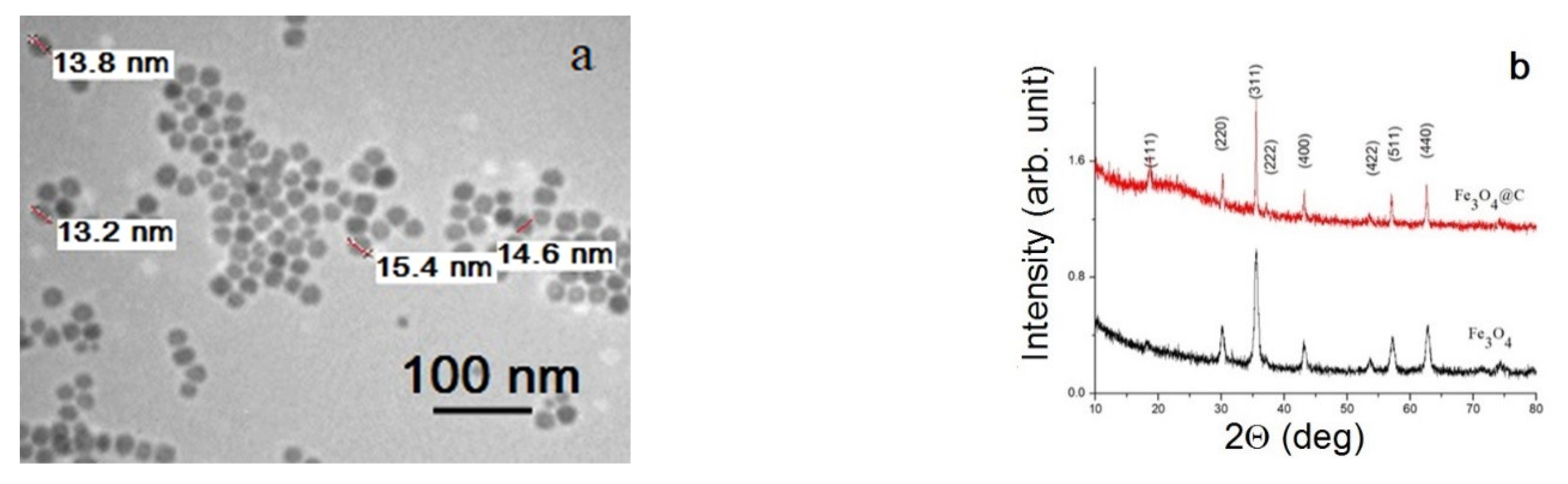
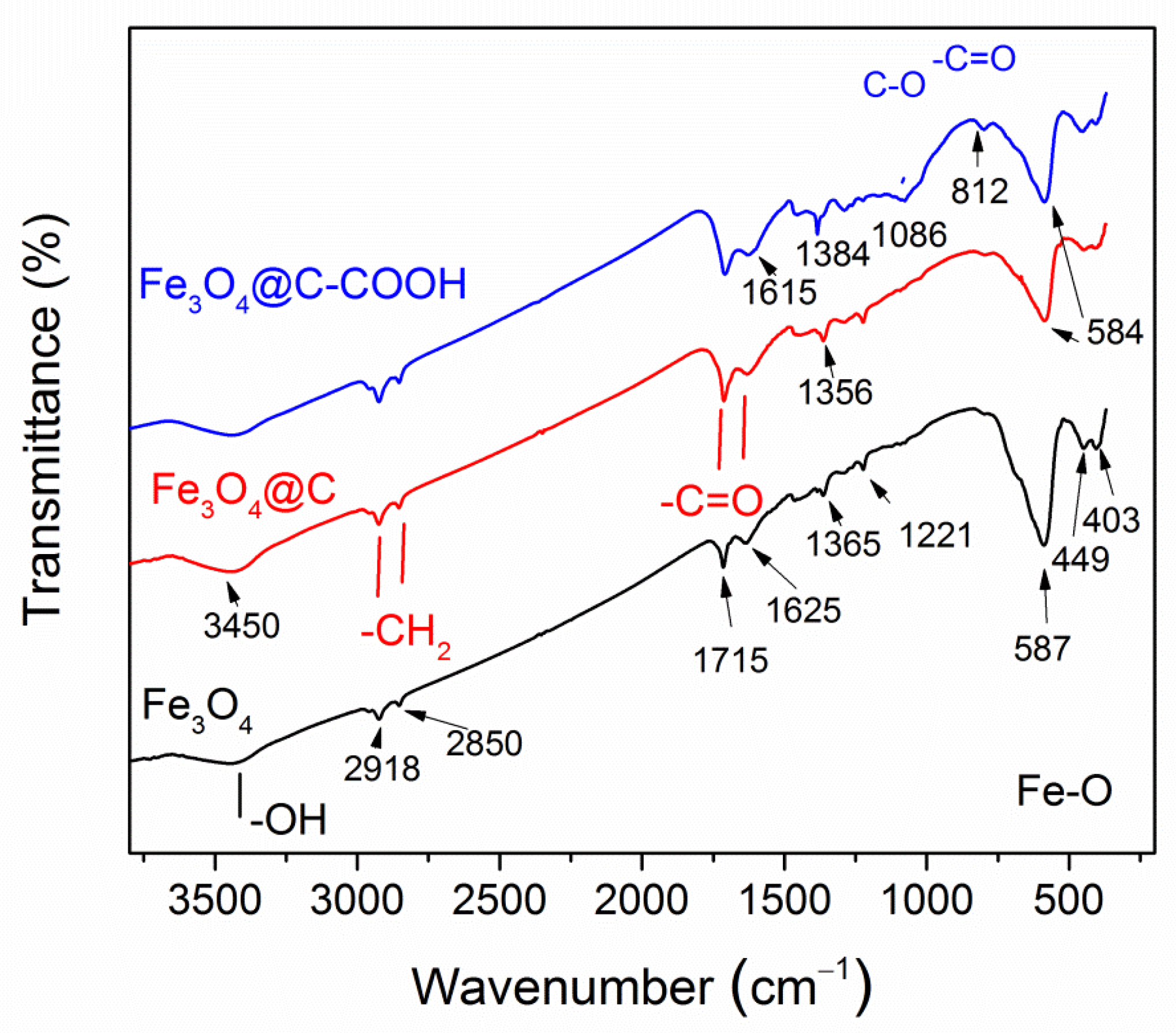
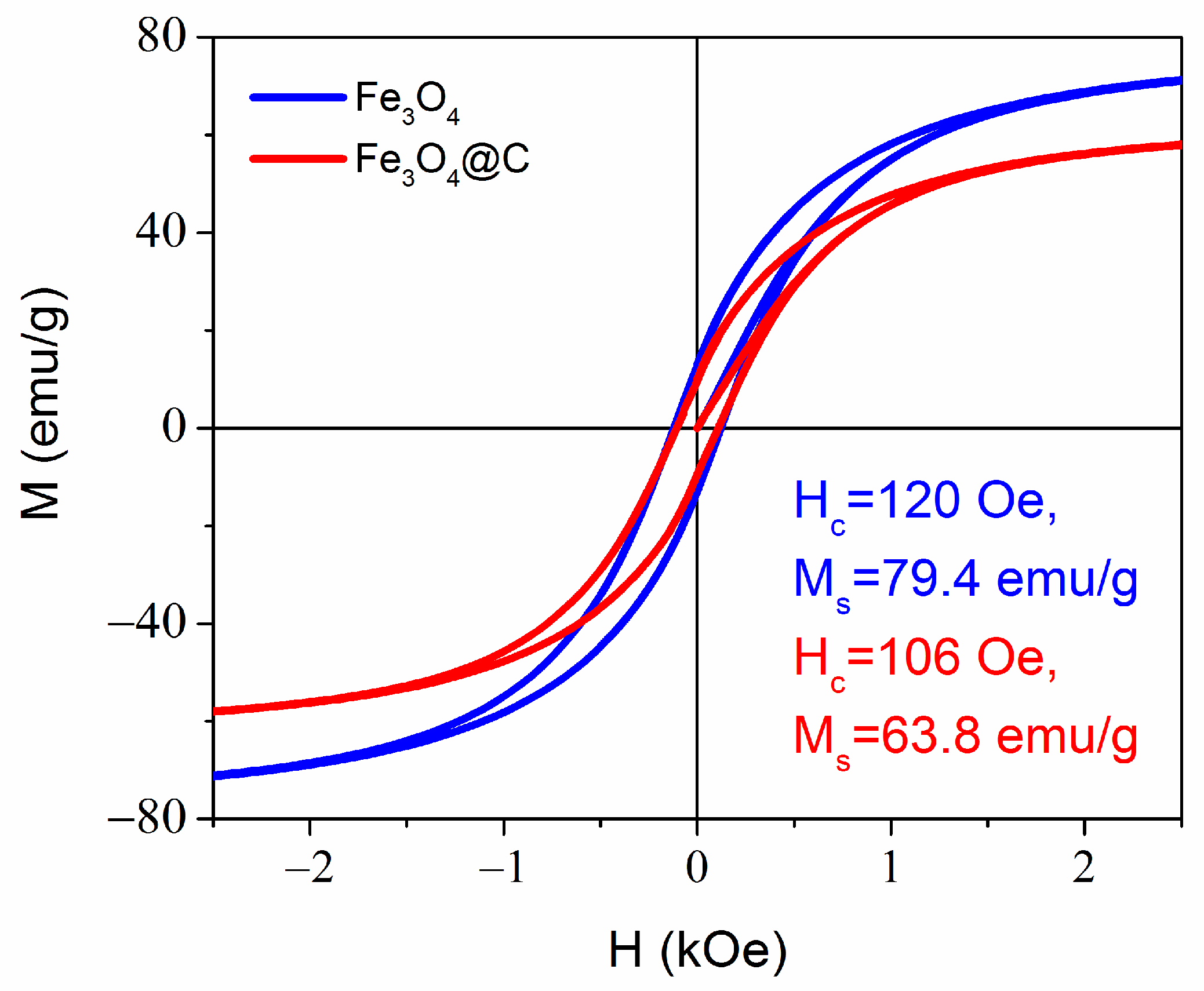
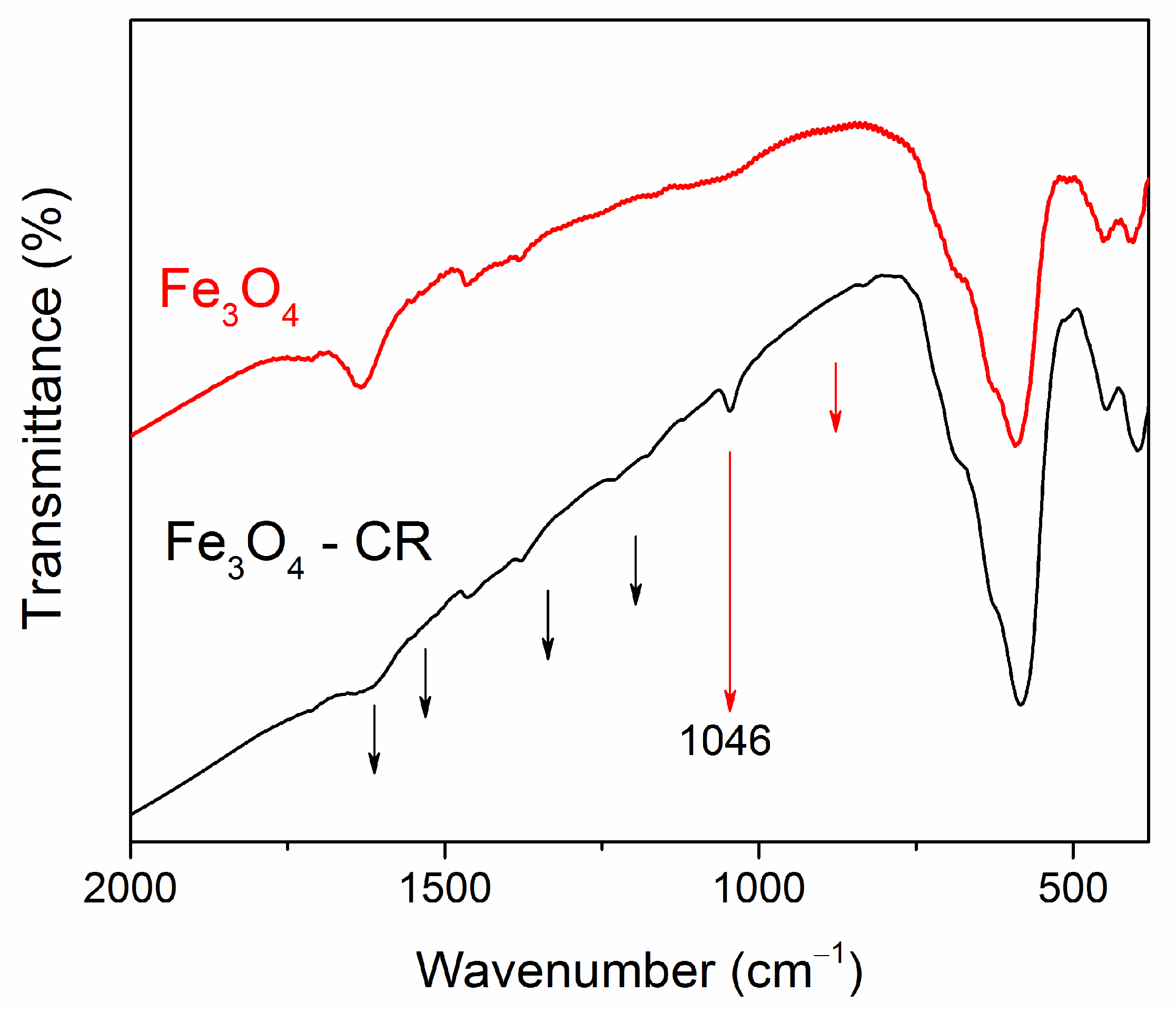
3.1. Morphology, Structure, and Magnetic Properties
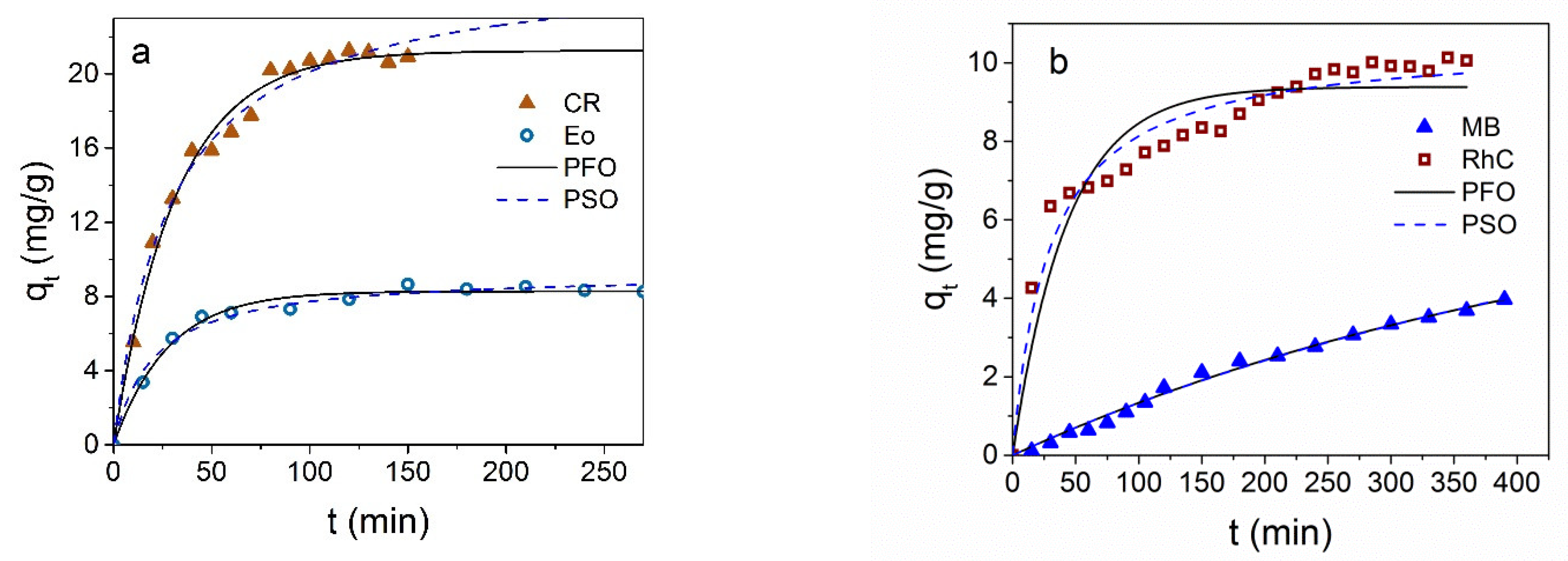
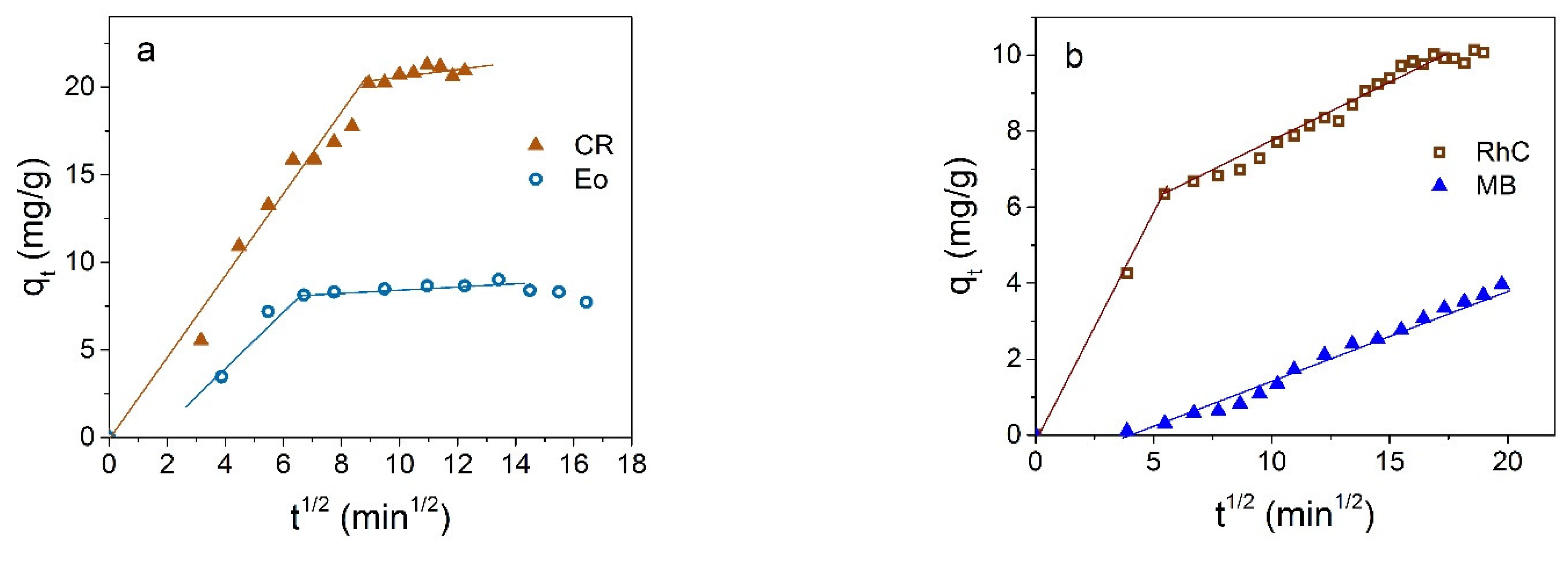
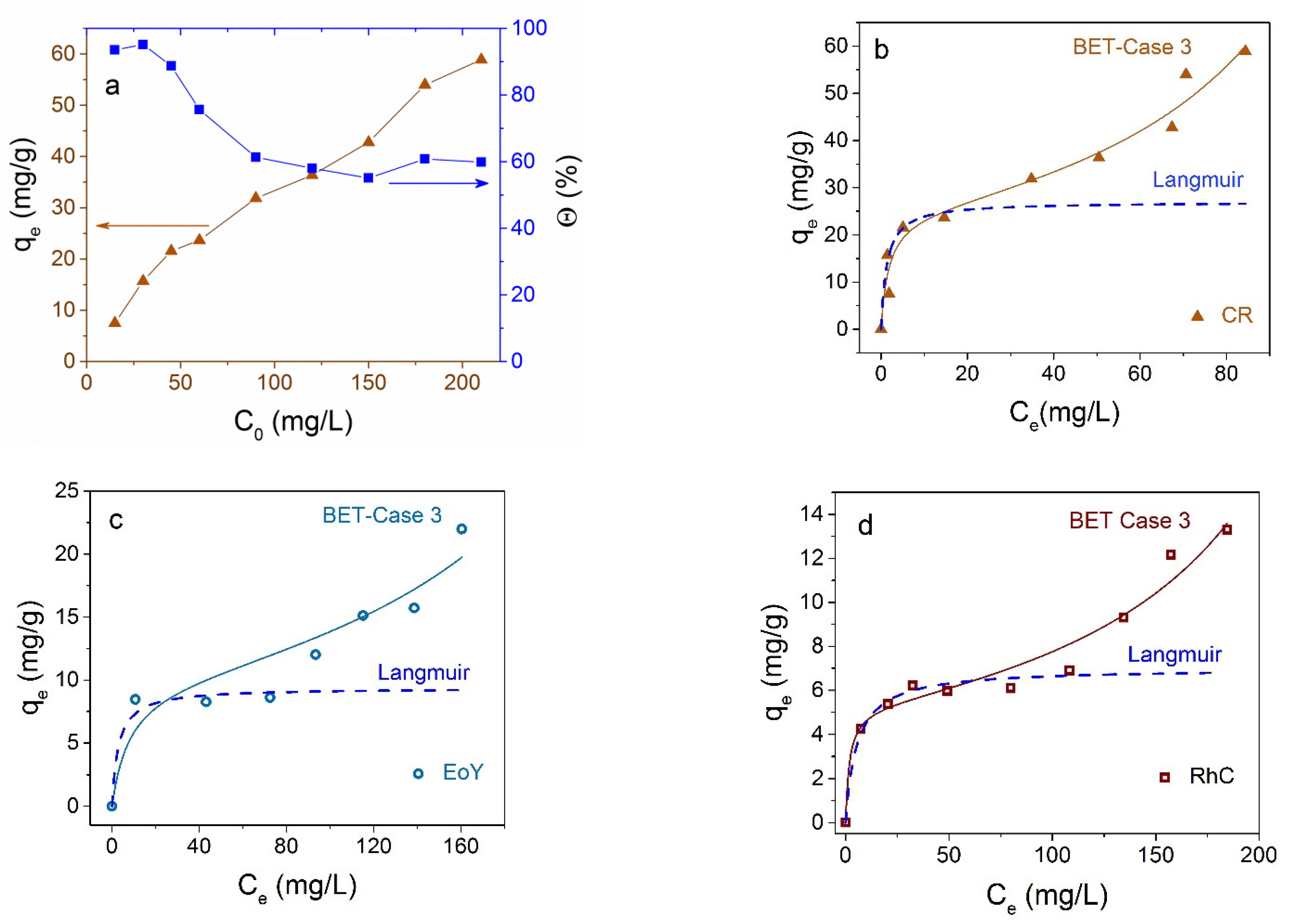
3.2. Dyes Adsorption by Fe3O4 NPs
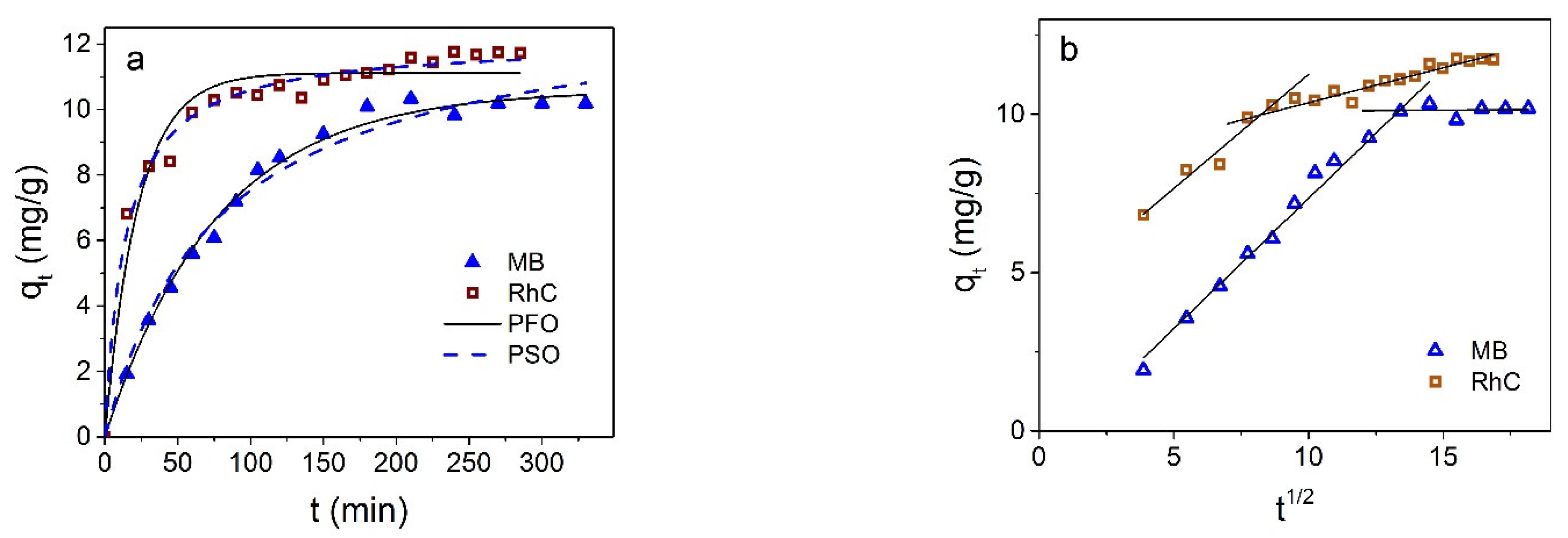
3.3. Dyes Adsorption by Fe3O4@C NPs
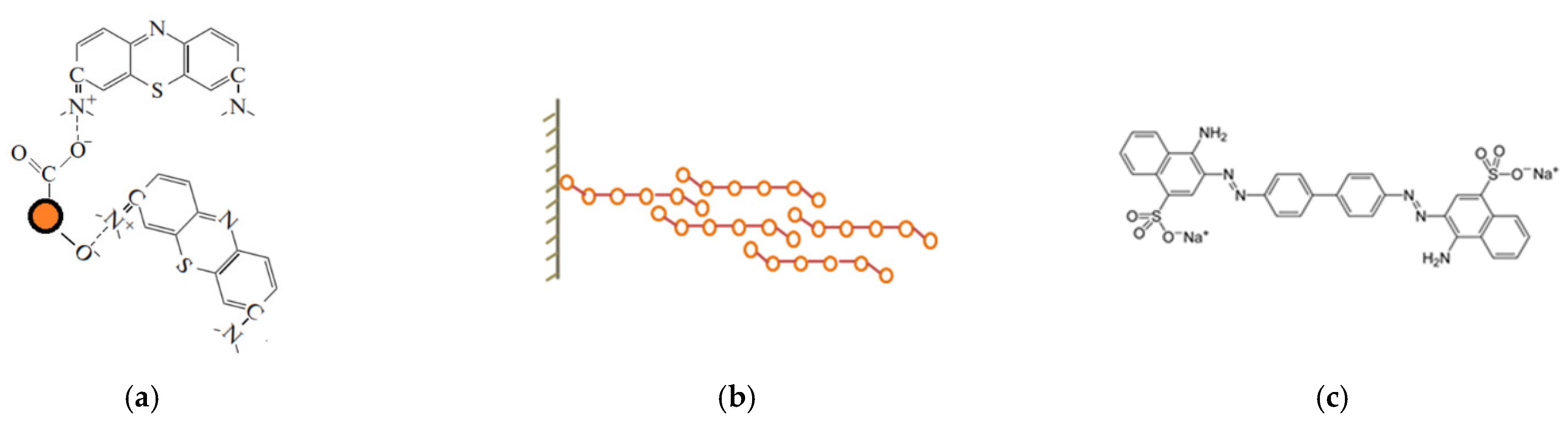
3.4. Comparison and Mechanism
3.5. Desorption and Reusability Studies
3.6. Magneto-Mechanical Destruction of Ehrlich Ascites Carcinoma Cells by Fe3O4@C NPs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khajeh, M.; Laurent, S.; Dastafkan, K. Nanoadsorbents: Classification, preparation, and applications (with emphasis on aqueous media). Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 7728–7768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehrke, I.; Geiser, A.; Somborn-Schulz, A. Innovations in nanotechnology for water treatment. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2015, 8, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Malik, S.; Shah, S.; Ali, N.; Ali, F.; Ghotekar, S.; Dabhane, H.; Bilal, M. Nanoadsorbents for Environmental Remediation. In Nanotechnology for Environmental Remediation; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, M.A.; Najam, T.; Jabeen, S.; Wattoo, M.A.; Bashir, M.S.; Shah, S.S.A.; Rehman, A. Facile synthesis of Tri-metallic layered double hydroxides (NiZnAl-LDHs): Adsorption of Rhodamine-B and methyl orange from water. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 145, 110008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, M.A.; Najam, T.; Bashir, M.S.; Javed, M.S.; Bashir, M.A.; Imran, M.; Azhar, U.; Shah, S.S.A.; Rehman, A. Kinetics, isothermal and mechanistic insight into the adsorption of eosin yellow and malachite green from water via tri-metallic layered double hydroxide nanosheets. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 39, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, M.A.; Najam, T.; Shahzad, K.; Wattoo, M.A.; Hussain, T.; Tufail, M.K.; Shah, S.S.A.; Rehman, A. Heterointerface engineering of water stable ZIF-8@ZIF-67: Adsorption of rhodamine B from water. Surf. Interfaces 2022, 34, 102324. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S246802302200585 (accessed on 2 September 2022). [CrossRef]
- Ouachtak, H.; Guerdaoui, A.E.; Haounati, R.; Akhouairi, S.; Haouti, R.E.; Hafid, N.; Addi, A.A.; Šljukić, B.; Santosa, D.M.F.; Taha, M.L. Highly efficient and fast batch adsorption of orange G dye from polluted water using superb organo-montmorillonite: Experimental study and molecular dynamics investigation. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 335, 116560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alakhras, F.; Ouachtak, H.; Alhajri, E.; Rehman, R.; Al-Mazaideh, G.; Anastopoulos, I.; Lima, E.C. Adsorptive Removal of Cationic Rhodamine B Dye from Aqueous Solutions Using Chitosan-Derived Schiff Base. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 542–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Liu, J.; Deng, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, G.; Liao, J.; Yang, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, N.; Sun, Q. Uranium (Ⅵ) adsorption from aqueous solutions by microorganism-graphene oxide composites via an immobilization approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 236, 117624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staroń, P.; Chwastowski, J. Raphia-Microorganism Composite Biosorbent for Lead Ion Removal from Aqueous Solutions. Materials 2021, 14, 7482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Pastora, J.; Bringas, E.; Ortiz, I. Recent progress and future challenges on the use of high performance magnetic nano-adsorbents in environmental applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 256, 187–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, M.M.; Macuvele, D.L.P.; Muller, L.; Nones, J.; Silva, L.L.; Fiori, M.A.; Soares, C.; Riella, H.G. Synthesis and Potential Adsorption of Fe3O4@C Core-Shell Nanoparticles for to Removal of Pollutants in Aqueous Solutions: A Brief Review. J. Adv. Chem. Eng. 2017, 7, 1000172. [Google Scholar]
- Hlongwane, G.N.; Sekoai, P.T.; Meyyappan, M.; Moothi, K. Simultaneous removal of pollutants from water using nanoparticles: A shift from single pollutant control to multiple pollutant control. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 656, 808–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Dief, A.M.; Hamdan, S.K. Functionalization of Magnetic Nano Particles: Synthesis, Characterization and Their Application in Water Purification. Am. J. Nanosci. 2016, 2, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; He, Q.; Jiang, C. Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Surface Functionalization Strategies. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2008, 3, 397–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Li, Y.; Zu, B.; Zhou, C.; Dou, X. AM-DMC-AMPS Multi-Functionalized Magnetic Nanoparticles for Efficient Purification of Complex Multiphase Water System. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehra, P.; Chauhan, R.P.; Garg, N.; Verma, K. Antibacterial and antifungal activity of chitosan coated iron oxide nanoparticles. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2018, 75, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaytulevich, E.A.; Yurmazova, T.A.; Tuan, H.T. Sorbents Based on Magnetite Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. Nanotechnol. Russ. 2019, 14, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.; Ren, G.; Zhong, Y.; Xu, D.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Yang, X. Fe3O4@C Nanoparticles synthesized by In situ solid-phase method for removal of methylene blue. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-R.; Ivanova, O.S.; Edelman, I.S.; Knyazev, Y.V.; Zharkov, S.M.; Petrov, D.A.; Sokolov, A.E.; Svetlitsky, E.S.; Velikanov, D.A.; Solovyov, L.A.; et al. Carbon Double Coated Fe3O4@C@C Nanoparticles: Morphology Features, Magnetic Properties, Dye Adsorption. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.; Han, T.; Luo, Z.; Liu, C.; Mei, Y.; Zhu, T. One-step fabricated Fe3O4@C core-shell composites for dye removal: Kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamics. J. Phys. Chem. Sol. 2015, 78, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, L.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Z. Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution by a solvothermal-synthesized graphene/magnetite composite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 1515–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Ni, P.; Zhu, M.; Yao, Y.; Fu, S. Preparation of Fe3O4@C submicron rods for adsorption of methylene blue and fast separation from water. Micro Nano Lett. 2019, 14, 962–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; He, M.; Liu, J.H.; Liao, R.; Zhao, L.; Xie, J.; Wang, R.; Yang, S.T.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y. Fe3O4@C nanoparticles as high-performance Fenton-like catalyst for dye decoloration. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2014, 59, 3406–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Kong, J. Novel magnetic Fe3O4@C nanoparticles as adsorbents for removal of organic dyes from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 193, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Guan, C.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Lai, X.; Du, H.; Xu, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Qiu, K.; et al. Preparation of a Fe3O4@C magnetic materials with high adsorption capacity of methylene blue. Ferroelectrics 2020, 566, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GOST 4453-74; Active Absorpting Powder Charcoal, Specifications. National Standard of the Russian Federation: Moscow, Russia, 1974.
- Patra, J.K.; Das, G.; Fraceto, L.F.; Campos, E.V.R.; Rodriguez-Torres, M.P.; Acosta-Torres, L.S.; Diaz-Torres, L.A.; Grillo, R.; Swamy, M.K.; Sharma, S.; et al. Nano based drug delivery systems: Recent developments and future prospects. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vangijzegem, T.; Stanicki, D.; Laurent, S. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for drug delivery: Applications and characteristics. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, K.; Eom, K.; Yang, J.; Park, J.; Lee, G.; Jang, K.; Lee, H.; Lee, S.W.; Yoon, D.S.; Lee, C.Y.; et al. Aptamer-functionalized nano-pattern based on carbon nanotube for sensitive, selective protein detection. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 23348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakha, M.; Pal, S.; Samantarrai, D.; Panigrahi, T.K.; Mallick, B.C.; Pramanik, K.; Mallick, B.; Jha, S. Antimicrobial activity of iron oxide nanoparticle upon modulation of nanoparticle-bacteria interface. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alphandéry, E. Biodistribution and targeting properties of iron oxide nanoparticles for treatments of cancer and iron anemia disease. Nanotoxicology 2019, 13, 573–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naud, C.; Thebault, C.; Carrière, M.; Hou, Y.; Morel, R.; Berger, F.; Dieny, B.; Joisten, H. Cancer treatment by magneto-mechanical effect of particles, a review. Nanoscale Adv. 2020, 2, 3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolovskaya, O.S.; Zamay, T.N.; Zamay, G.S.; Babkin, V.A.; Medvedeva, E.N.; Neverova, N.A.; Kirichenko, A.K.; Zamay, S.S.; Lapin, I.N.; Morozov, E.V.; et al. Aptamer-conjugated superparamagnetic ferroarabinogalactan nanoparticles for targeted magnetodynamic therapy of cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golovin, Y.I.; Klyachko, N.L.; Majouga, A.G.; Gribanovskii, S.L.; Golovin, D.Y.; Zhigachev, A.O.; Shuklinov, A.V.; Efremova, M.V.; Veselov, M.M.; Vlasova, K.Y.; et al. New Approaches to Nanotheranostics: Polyfunctional Magnetic Nanoparticles Activated by Non-Heating Low-Frequency Magnetic Field Control Biochemical System with Molecular Locality and Selectivity. Nanotechnol. Russ. 2018, 13, 215–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhu, X.; Lu, P.Y.; Rosato, R.R.; Tan, W.; Zu, Y. Oligonucleotide aptamers: New tools for targeted cancer therapy. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2014, 3, e182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, D.F.; Yang, T.; Yang, J.; Fu, S.; Zhang, S.B. Targeting strategies for superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in cancer therapy. Acta Biomater. 2019, 102, 13–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamay, G.S.; Zamay, T.N.; Lukyanenko, K.A.; Kichkailo, A.S. Aptamers increase biocompatibility and reduce the toxicity of magnetic nanoparticles used in biomedicine. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudłak, B.; Wieczerzak, M. Aptamer based tools for environmental and therapeutic monitoring: A review of developments, applications, future perspectives. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 50, 816–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, S.I.; Herrera, A.; Rossi, J.J.; Zhou, J. Current Advances in Aptamers for Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy. Cancers 2018, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belyanina, I.V.; Zamay, T.N.; Zamay, G.S.; Zamay, S.S.; Kolovskaya, O.S.; Ivanchenko, T.I.; Denisenko, V.V.; Kirichenko, A.K.; Glazyrin, Y.E.; Garanzha, I.V.; et al. In vivo cancer cells elimination guided by aptamer-functionalized gold-coated magnetic nanoparticles and controlled with low frequency alternating magnetic field. Theranostics 2017, 7, 3326–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.R.P.; Rodrigues, R.O.; Barros, L.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Marchesi, L.F.; Koneracka, M.; Jurikova, A.; Zavisova, V.; Gomes, H.T. Carbon-Based Magnetic Nanocarrier for Controlled Drug Release: A Green Synthesis Approach. J. Carbon Res. 2019, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petcharoen, K.; Sirivat, A. Synthesis and characterization of magnetite nanoparticles via the chemical co-precipitation method. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2012, 177, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, J.S.; de Vasconcelos, C.L.; Cabral, F.A.O.; de Araújo, J.H.; Pereira, M.R.; Fonseca, J.L.C. Synthesis and characterization of poly(ethyl methacrylate-co-methacrylic acid) magnetic particles via miniemulsion polymerization. Polymer 2006, 47, 7646–7652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, M.; Namvar, F.; Ahmad, M.B.; Mohamad, R. Green Biosynthesis and Characterization of Magnetic Iron Oxide (Fe3O4) Nanoparticles Using Seaweed (Sargassum muticum) Aqueous Extract. Molecules 2013, 18, 5954–5964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, X.; Qiang, Z.; Chang, J.-H.; Ben, W.; Qu, J. Synthesis of carbon-coated magnetic nanocomposite (Fe3O4@C) and its application for sulfonamide antibiotics removal from water. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellamy, L.J. The Infrared Spectra of Complex Molecules; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1980; p. 290. [Google Scholar]
- Zare, K.; Sadegh, H.; Shahryari-Ghoshekandi, R.; Maazinejad, B.; Ali, V.; Tyagi, I.; Agarwal, S.; Kumar Gupta, V. Enhanced removal of toxic Congo red dye using multi walled carbon nanotubes: Kinetic, equilibrium studies and its comparison with other adsorbents. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 212, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, V.-P.; Huynh, T.-D.-T.; Le, H.M.; Nguyen, V.-D.; Dao, V.-A.N.; Hung, Q.; Tuyen, L.A.; Lee, S.; Yi, J.; Nguyen, T.D.; et al. Insight into the adsorption mechanisms of methylene blue and chromium (III) from aqueous solution onto pomelo fruit peel. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 25847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Kahlout, A.M.; El-Ghamri, H.S.; Al Dahoudi, N.; El-Agez, T.M.; Taya, S.A.; Abdel-Latif, M.S. A comparative study: Synthetic dyes as photosensitizers for dye-sensitized solar cells. Turk. J. Phys. 2015, 39, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nag, A.; Goswami, D. Solvent effect on two-photon absorption and fluorescence of rhodamine dyes. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2009, 206, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopal, R.A.; Song, M.; Yang, D.; Lkhagvaa, T.; Chandrasekaran, S.; Choi, D. Synthesis of Hierarchically Structured γ-Fe2O3–PPy Nanocomposite as Effective Adsorbent for Cationic Dye Removal from Wastewater. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revellame, E.D.; Fortela, D.L.; Sharp, W.; Hernandez, R.; Zappi, M.E. Adsorption kinetic modeling using pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order rate laws: A review. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2020, 1, 100032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, W.J.; Morris, J.C. Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solutions. J. Sanit. Eng. Div. 1963, 89, 31–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunauer, S.; Emmett, P.H.; Teller, E. Adsorption of Gases in Multimolecular Layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1938, 2, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebadi, A.; Mohammadzadeh, J.S.S.; Khudiev, A. What is the correct form of BET isotherm for modeling liquid phase adsorption? Adsorption 2009, 15, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H. Über die Adsorption in Lösungen. Z. Phys. Chem. Stöchiometrie Verwandschaftslehre 1907, 57, 385–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Torrellas, S.; Boutahala, M.; Boukhalfa, N.; Munoz, M. Effective Adsorption of Methylene Blue dye onto Magnetic Nanocomposites. Modeling and Reuse Studies. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksu, Z.; Tezer, S. Equilibrium and Kinetic Modelling of Biosorption of Remazol Black B by Rhizopus arrhizus in a Batch System: Effect of Temperature. Process Biochem. 2000, 36, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harja, M.; Buema, G.; Bucur, D. Recent advances in removal of Congo Red dye by adsorption using an industrial waste. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghereghlou, M.; Esmaeili, A.A.; Darroudi, M. Adsorptive Removal of Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solutions Using Magnetic Fe3O4@C-dots: Removal and kinetic studies. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 2005–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Fan, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhou, X.; Gao, Z.F.; Deng, S.; Wan, S.; Lv, X.; Shi, Y.; Han, W. Fabrication of Nano Iron Oxide–Modified Biochar from Co-Hydrothermal Carbonization of Microalgae and Fe(II) Salt for Efficient Removal of Rhodamine B. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazantsev, S.O.; Glazkova, E.A.; Lozhkomoev, A.S.; Bakina, O.V.; Khorobraya, E.G. Effect of the morphology of γ-Al2O3 nanosized particles on their adsorption properties. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A 2020, 94, 806–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartošová, A.; Blinová, L.; Sirotiak, M.; Michalíková, A. Usage of ftir-atr as non-destructive analysis of selected toxic dyes, Research Papers Faculty of Materials Science and Technology Slovak University of Technology. Sciendo 2017, 25, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-H.; Rozhkova, E.A.; Ulasov, I.V.; Bader, S.D.; Rajh, T.; Lesniak, M.S.; Novosad, V. Biofunctionalized magnetic-vortex microdiscs for targeted cancer-cell destruction. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameters of the Nonlinear Fit | Experiment | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dyes | Kinetic Model | qe (mg/g) | k1 (1/min) k2 (g/(mg*min) | R2 | qe (mg/g) |
| CR | PFO | 21.249 ± 0.319 | 0.031 ± 0.0018 | 0.989 | 21.6 |
| PSO | 25.960 ± 0.70 | 0.00133 ± 0.00016 | 0.988 | ||
| EoY | PFO | 8.28 ± 0.121 | 0.036 ± 0.0025 | 0.987 | 8.3 |
| PSO | 9.265 ± 0.224 | 0.0054 ± 0.0008 | 0.984 | ||
| MB | PFO | 7.2 ± 0.85 | 0.002 ± 0.0003 | 0.992 | 4.5 * |
| PSO | 12.58 ± 1.83 | 0.00009 ± 0.000032 | 0.992 | ||
| RhC | PFO | 9.38 ± 0.206 | 0.023 ± 0.0027 | 0.889 | 10.2 |
| PSO | 10.53 ± 0.222 | 0.003 ± 0.0004 | 0.958 | ||
| CR Dye | BET-Case 3 | Langmuir |
|---|---|---|
| KL (L/mg) | 0.007 ± 0.0005 | – |
| KS (L/mg) | 0.831 ± 0.0 | 0.7608 ± 1.136 |
| qm (mg/g) | 23.73 ± 1.56 | 27.49 ± 20.76 |
| R2 | 0.9695 | 0.3188 |
| Parameters of the Nonlinear Fit | Experiment | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dyes | Kinetic Model | qe (mg/g) | k1 (1/min) k2 (g/(mg*min) | R2 | qe (mg/g) |
| MB | PFO | 10.59 ± 0.159 | 0.013 ± 0.0006 | 0.993 | 11 |
| PSO | 13.33 ± 0.487 | 0.0009 ± 0.00014 | 0.984 | ||
| RhC | PFO | 11.12 ± 0.166 | 0.044 ± 0.0045 | 0.950 | 12 |
| PSO | 12.09 ± 0.137 | 0.0059 ± 0.0005 | 0.987 | ||
| Adsorbent | Dyes | qe [mg/g] | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fe3O4 NPs | Congo Red | 96.46 | [59] |
| Fly ash | 22.12 | [60] | |
| Fe3O4 NPs | 58 | Present work | |
| Fe3O4@C NPs (30 nm with 2 nm carbon shell) | Methylene Blue | 18.52 | [19] |
| Fe3O4@C magnetic materials (particle size, 1~100 μm) | 270.51 | [26] | |
| Fe3O4@C-dots | 124.9 | [61] | |
| B-Fe3O4@C (~3 μm) | 42.11 | [21] | |
| Fe3O4@C NPs | 15 | Present work | |
| NiZnAl-LDH, ZnAl-LDH, NiAl-LDH | RhB | 52–97 | [4] |
| Nano iron oxide–modified biochar | 286.4 | [62] | |
| Fe3O4 NPs | RhC | 14 | Present work |
| Fe3O4@C NPs | 35 | Present work | |
| Nanoplates γ-Al2O3 | EoY | 6 | [63] |
| Fe3O4 NPs | 22 | Present work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ivanova, O.S.; Edelman, I.S.; Lin, C.-R.; Svetlitsky, E.S.; Sokolov, A.E.; Lukyanenko, K.A.; Sukhachev, A.L.; Shestakov, N.P.; Chen, Y.-Z.; Spivakov, A.A. Core–Shell Fe3O4@C Nanoparticles for the Organic Dye Adsorption and Targeted Magneto-Mechanical Destruction of Ehrlich Ascites Carcinoma Cells. Materials 2023, 16, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16010023
Ivanova OS, Edelman IS, Lin C-R, Svetlitsky ES, Sokolov AE, Lukyanenko KA, Sukhachev AL, Shestakov NP, Chen Y-Z, Spivakov AA. Core–Shell Fe3O4@C Nanoparticles for the Organic Dye Adsorption and Targeted Magneto-Mechanical Destruction of Ehrlich Ascites Carcinoma Cells. Materials. 2023; 16(1):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16010023
Chicago/Turabian StyleIvanova, Oxana S., Irina S. Edelman, Chun-Rong Lin, Evgeniy S. Svetlitsky, Alexey E. Sokolov, Kirill A. Lukyanenko, Alexander L. Sukhachev, Nikolay P. Shestakov, Ying-Zhen Chen, and Aleksandr A. Spivakov. 2023. "Core–Shell Fe3O4@C Nanoparticles for the Organic Dye Adsorption and Targeted Magneto-Mechanical Destruction of Ehrlich Ascites Carcinoma Cells" Materials 16, no. 1: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16010023
APA StyleIvanova, O. S., Edelman, I. S., Lin, C.-R., Svetlitsky, E. S., Sokolov, A. E., Lukyanenko, K. A., Sukhachev, A. L., Shestakov, N. P., Chen, Y.-Z., & Spivakov, A. A. (2023). Core–Shell Fe3O4@C Nanoparticles for the Organic Dye Adsorption and Targeted Magneto-Mechanical Destruction of Ehrlich Ascites Carcinoma Cells. Materials, 16(1), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16010023








