Cellulose Nanofibrils as a Damping Material for the Production of Highly Crystalline Nanosized Zeolite Y via Ball Milling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Ball Milling Procedure
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Dye Adsorption Experiment
3. Results and Discussion
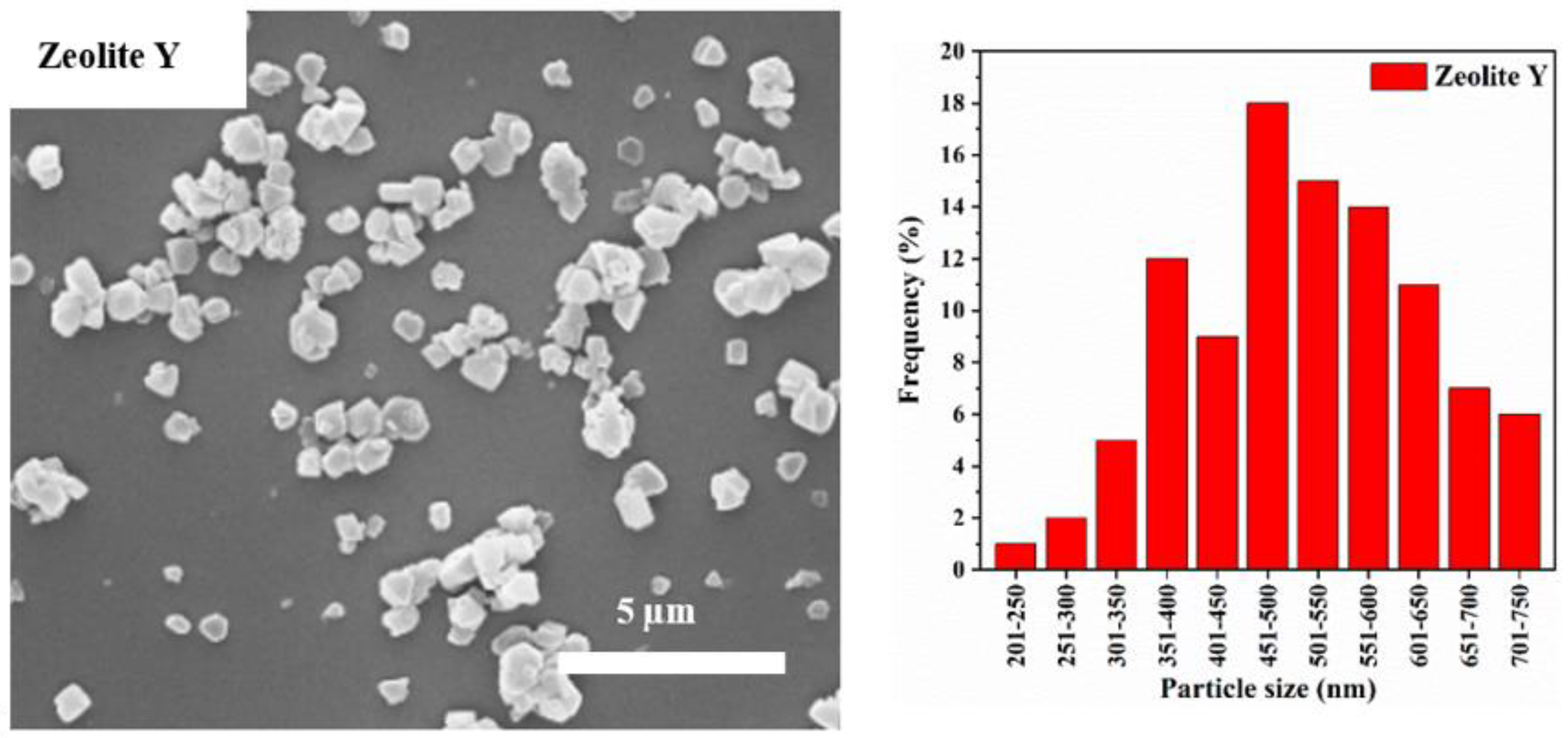
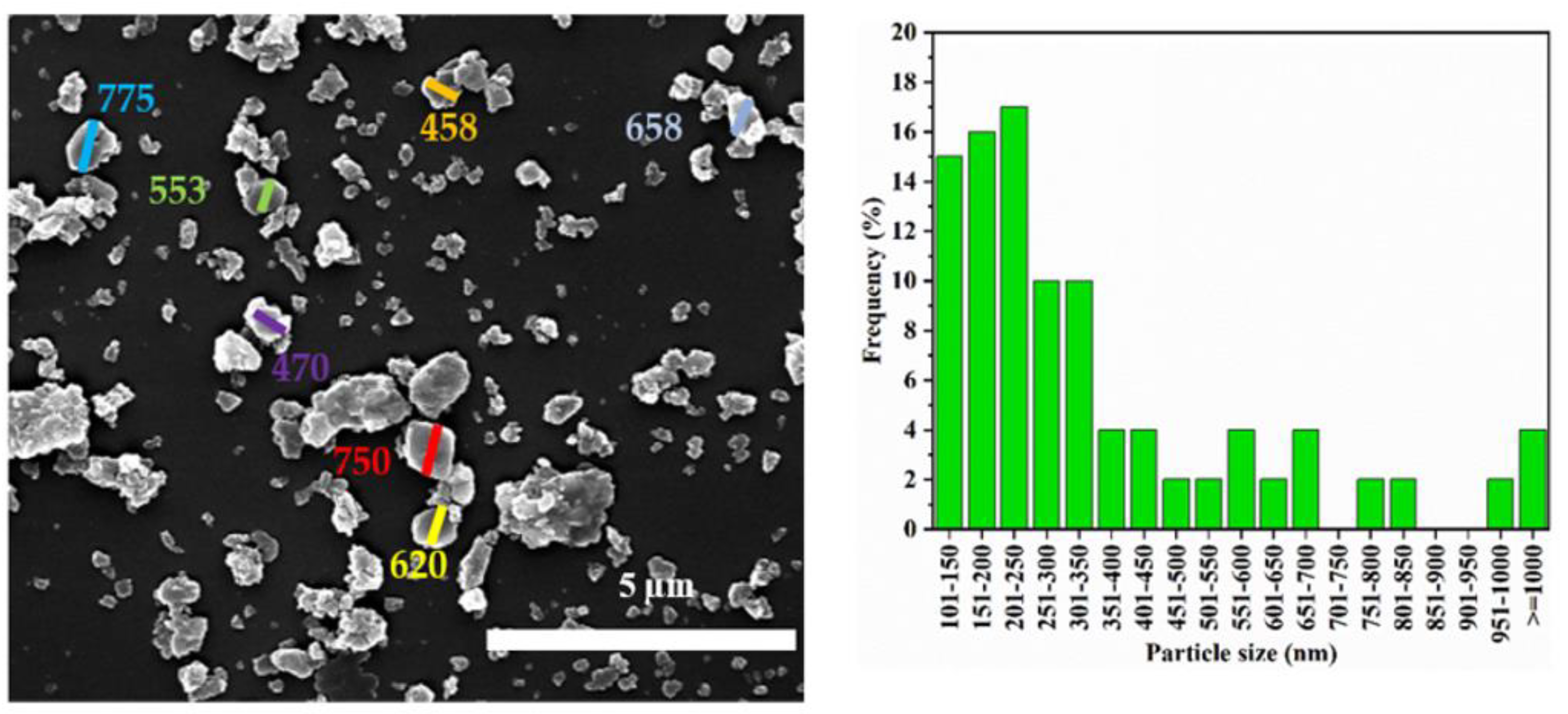
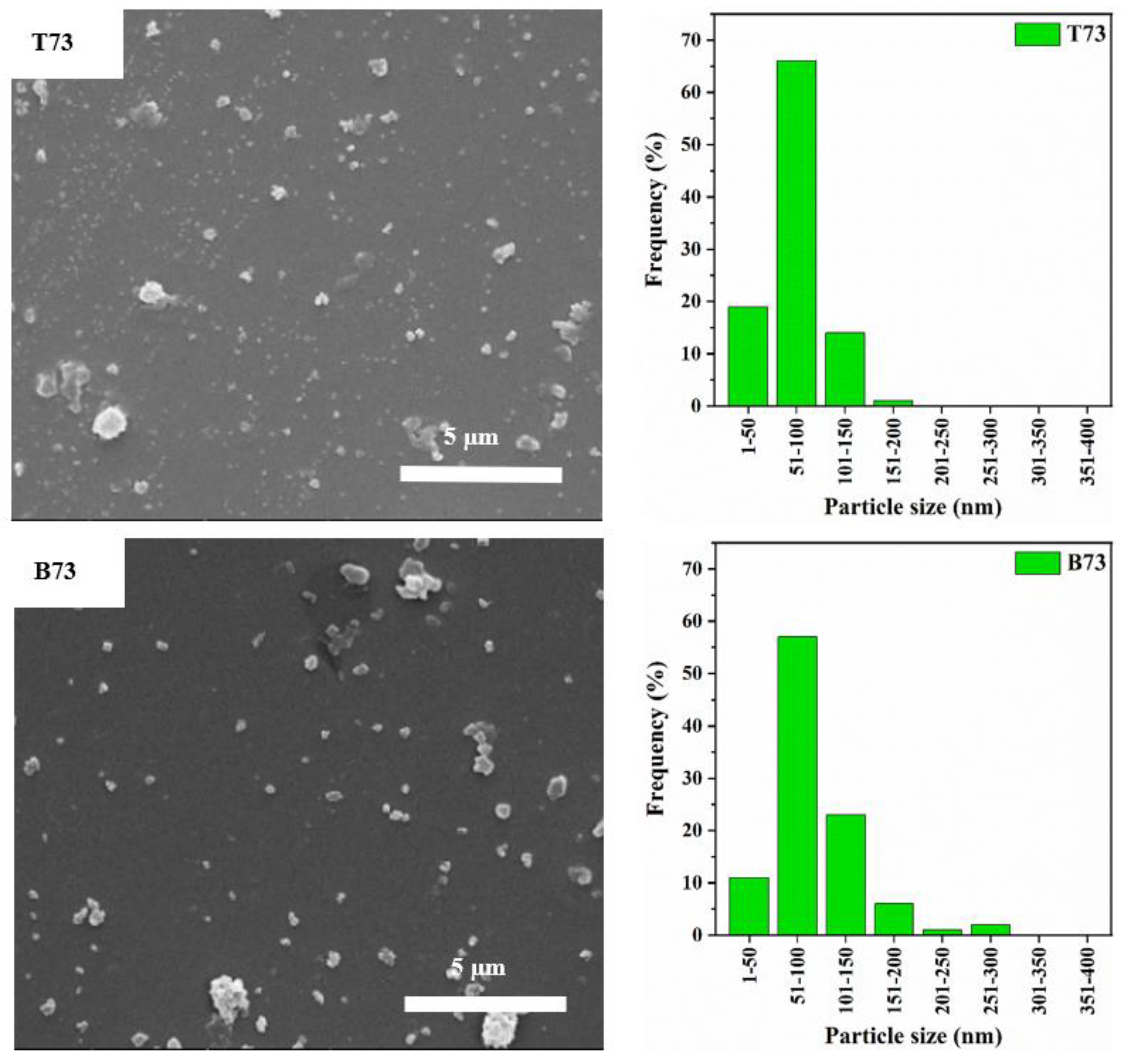
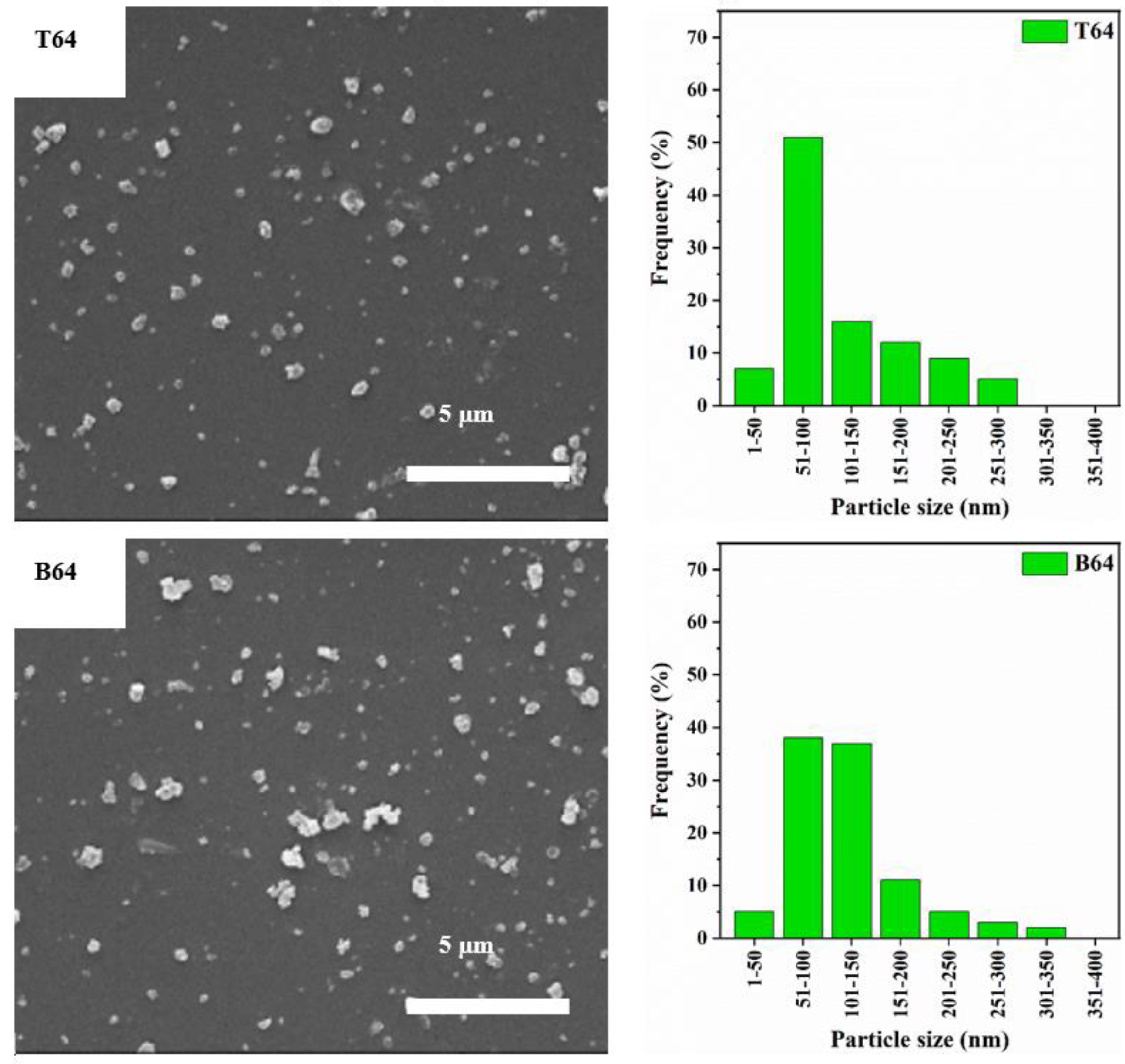
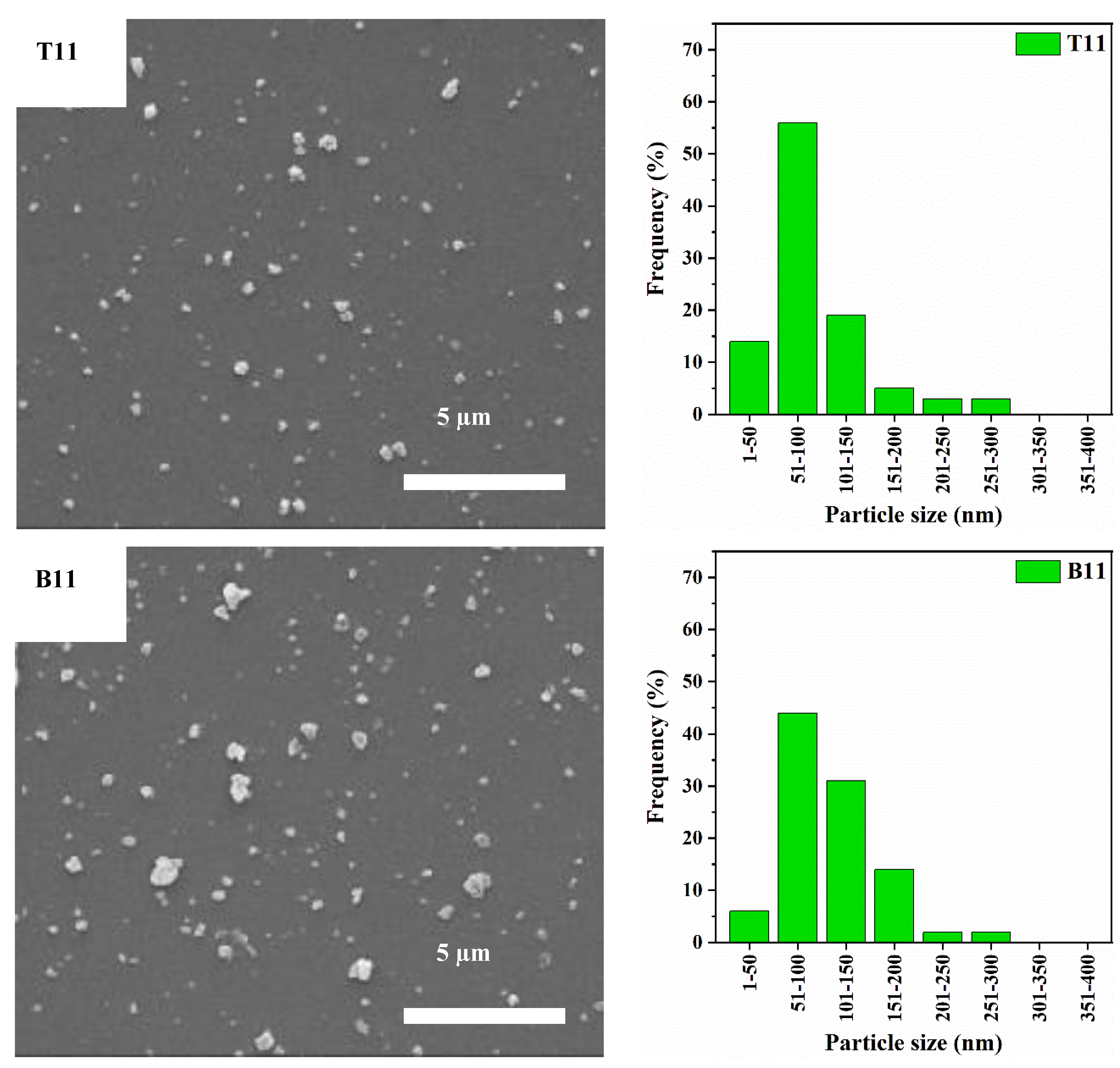
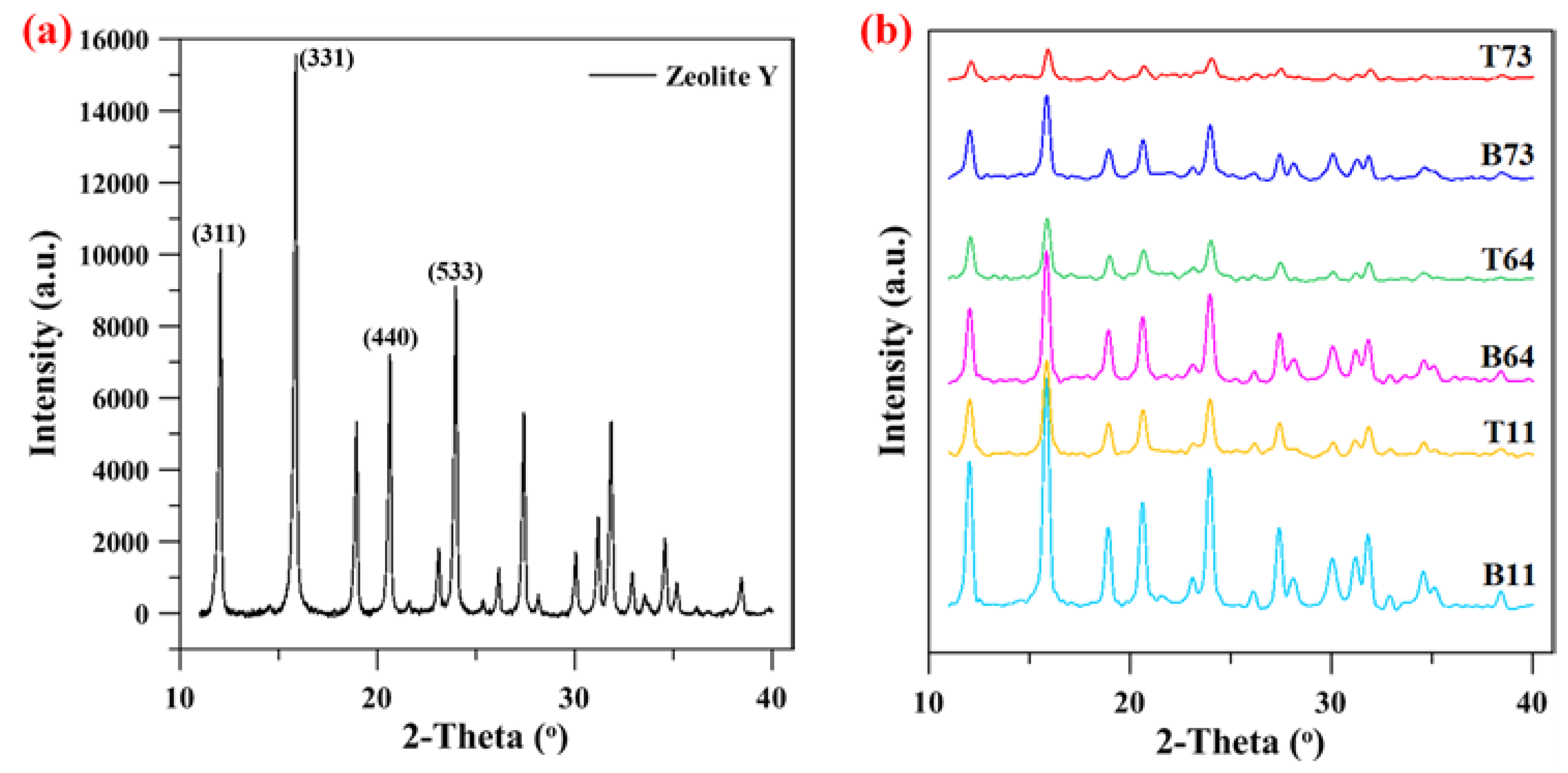
3.1. Particle Size Distribution and XRD Analysis
3.2. Thermal Analysis
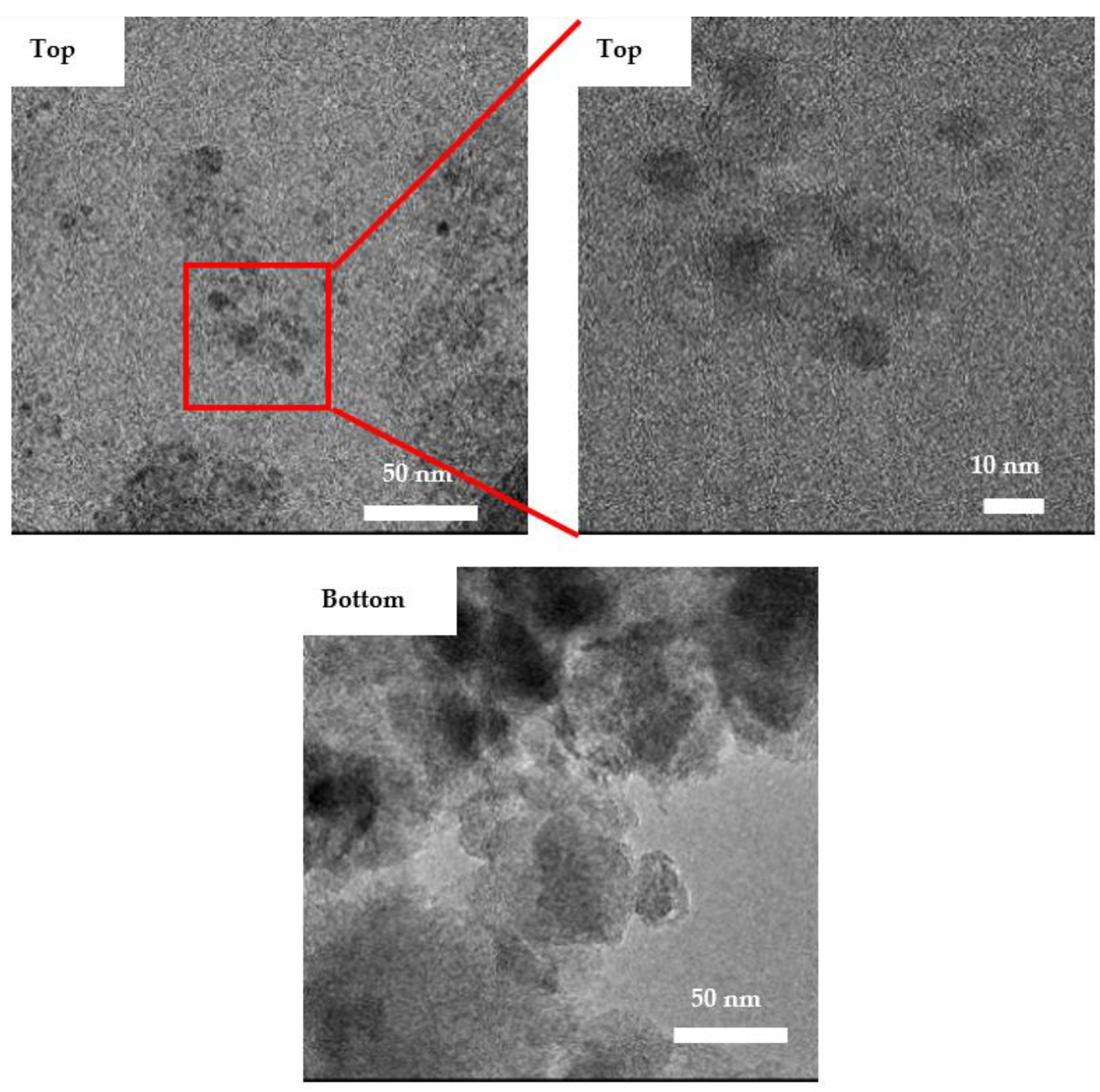
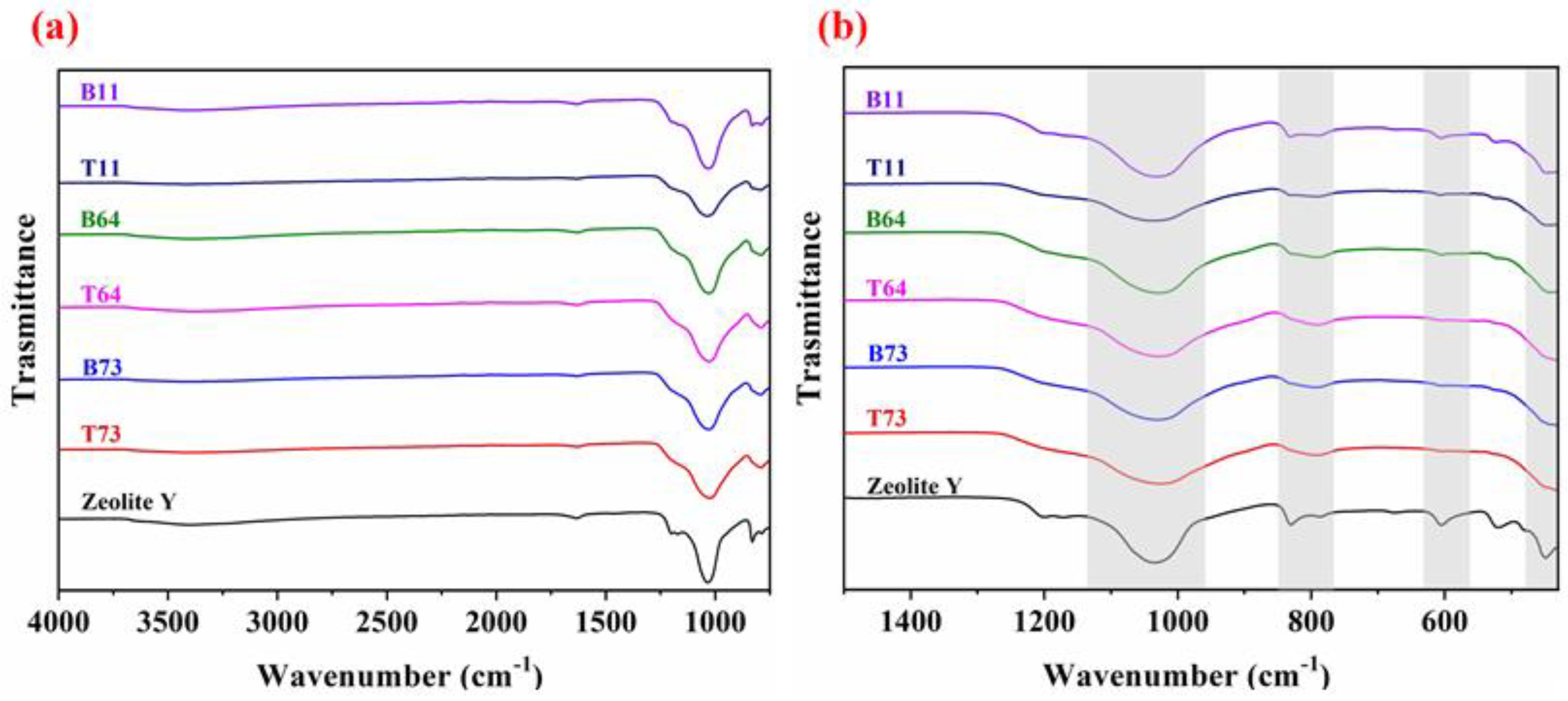
3.3. Surface Morphology and Functionalities
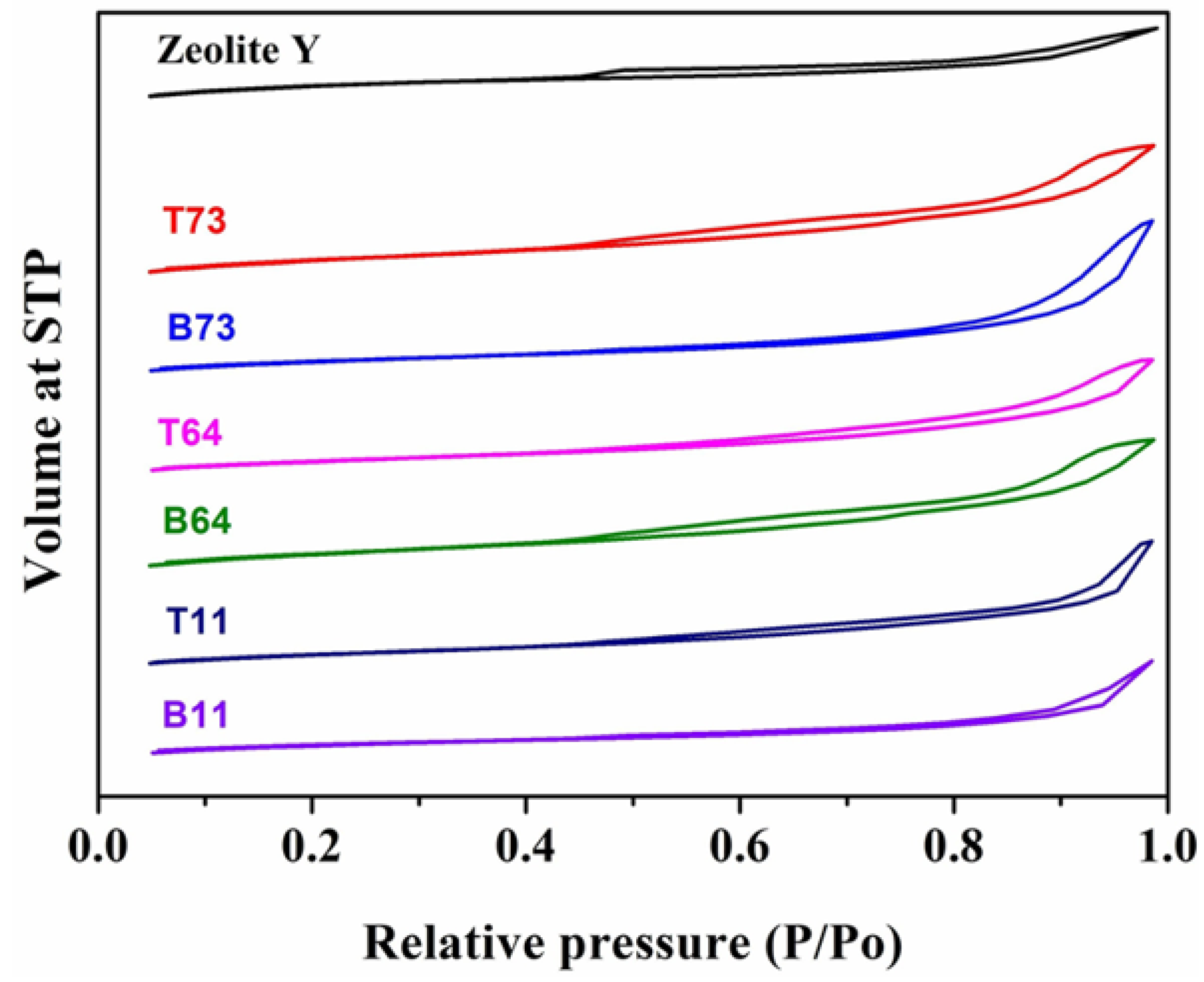
3.4. BET Analysis
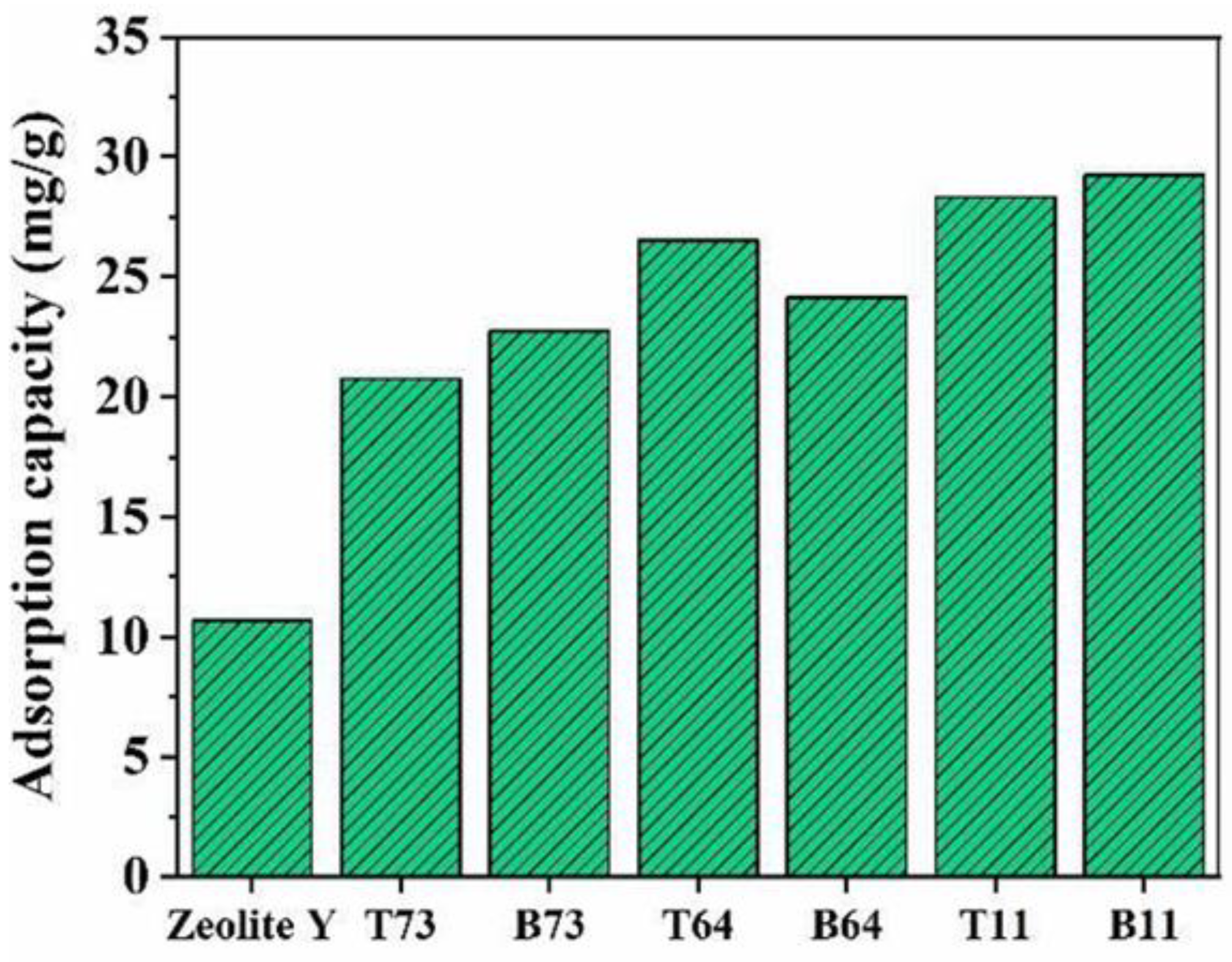
3.5. Dye Adsorption Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rhodes, C.J. Properties and applications of Zeolites. Sci. Prog. 2010, 93, 223–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosheva, L.; Valtchev, V.P. Nanozeolites: Synthesis, Crystallization Mechanism, and Applications. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 2494–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anis, S.F.; Singaravel, G.; Hashaikeh, R. Hierarchical nano zeolite-Y hydrocracking composite fibers with highly efficient hydrocracking capability. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 16703–16715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anis, S.F.; Singaravel, G.; Hashaikeh, R. Electropsun Ni-W/zeolite composite fibers for n-heptane hydrocracking and hydroisomerization. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2017, 200, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminski, T.; Anis, S.F.; Husein, M.M.; Hashaikeh, R. Hydrocracking of Athabasca VR Using NiO-WO3 Zeolite-Based Catalysts. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 2224–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anis, S.F.; Hashaikeh, R. Electrospun zeolite-Y fibers: Fabrication and morphology analysis. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 233, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taufiqurrahmi, N.; Mohamed, A.R.; Bhatia, S. Nanocrystalline zeolite beta and zeolite Y as catalysts in used palm oil cracking for the production of biofuel. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2011, 13, 3177–3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Prins, R.; van Bokhoven, J.A. Synthesis and characterization of mesoporous mordenite. J. Catal. 2009, 262, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konno, H.; Okamura, T.; Kawahara, T.; Nakasaka, Y.; Tago, T.; Masuda, T. Kinetics of n-hexane cracking over ZSM-5 zeolites–Effect of crystal size on effectiveness factor and catalyst lifetime. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 207–208, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anis, S.F.; Lalia, B.S.; Hashaikeh, R.; Hilal, N. Breaking through the selectivity-permeability tradeoff using nano zeolite-Y for micellar enhanced ultrafiltration dye rejection application. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 242, 116824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anis, S.F.; Hashaikeh, R.; Hilal, N. Flux and salt rejection enhancement of polyvinyl(alcohol) reverse osmosis membranes using nano-zeolite. Desalination. 2019, 470, 114104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlence, D.J.; Gosling, K. FCC catalyst performance evaluation. Appl. Catal. 1988, 43, 213–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borel, M.; Dodin, M.; Daou, T.J.; Bats, N.; Harbuzaru, B.; Patarin, J. SDA-Free Hydrothermal Synthesis of High-Silica Ultra-nanosized Zeolite Y. Cryst. Growth Des. 2017, 17, 1173–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akçay, K.; Sirkecioğlu, A.; Tatlıer, M.; Savaşçı, Ö.T.; Erdem-Şenatalar, A. Wet ball milling of zeolite HY. Powder Technol. 2004, 142, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Auroux, A.; Kaliaguine, S. Crystallinity dependence of acid site distribution in HA, HX and HY zeolites. Microporous Materials. 1995, 5, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinski, P.A.; Van Neste, A.; Akolekar, D.B.; Kaliaguine, S. Effect of high-energy ball milling on the structural stability, surface and catalytic properties of small-, medium- and large-pore zeolites. Microporous Materials 1995, 5, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saepurahman, C.; Hashaikeh, R. Insight into ball milling for size reduction and nanoparticles production of H-Y zeolite. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 220, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuman, B.; Saepurahman, C.; Anis, S.F.; Hashaikeh, R. Obtaining high crystalline ball milled H-Y zeolite particles with carbon nanostructures as a damping material. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 273, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, C.-w.; James, J.T.; McCluskey, R.; Arepalli, S.; Hunter, R.L. A review of carbon nanotube toxicity and assessment of potential occupational and environmental health risks. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2006, 36, 189–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simate, G.S.; Iyuke, S.E.; Ndlovu, S.; Heydenrych, M.; Walubita, L.F. Human health effects of residual carbon nanotubes and traditional water treatment chemicals in drinking water. Environ. Int. 2012, 39, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Martinez, F.J.; Jin, K.; López Barreiro, D.; Buehler, M.J. The Rise of Hierarchical Nanostructured Materials from Renewable Sources: Learning from Nature. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 7425–7433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, R.J.; Martini, A.; Nairn, J.; Simonsen, J.; Youngblood, J. Cellulose nanomaterials review: Structure, properties and nanocomposites. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 3941–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klemm, D.; Kramer, F.; Moritz, S.; Lindström, T.; Ankerfors, M.; Gray, D.; Dorris, A. Nanocelluloses: A new family of nature-based materials. Angew. Chem. 2011, 50, 5438–5466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rol, F.; Belgacem, M.N.; Gandini, A.; Bras, J. Recent advances in surface-modified cellulose nanofibrils. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2019, 88, 241–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Shahzad, N.; Xiong, C.; Zhao, T.K.; Li, T.; Siddique, F.; Ali, N.; Shahzad, M.; Ullah, H.; Rakha, S.A. Dispersion behavior and the influences of ball milling technique on functionalization of detonated nano-diamonds. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2016, 61, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Abhash, A.; Yadav, B.N.; Shafeeq, M.; Singh, I.B.; Mondal, D.P. Effect of milling time on powder characteristics and mechanical performance of Ti4wt%Al alloy. Powder Technol. 2019, 342, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anis, S.F.; Lalia, B.S.; Khair, M.; Hashaikeh, R.; Hilal, N. Electro-ceramic self-cleaning membranes for biofouling control and prevention in water treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 415, 128395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosanović, C.; Bronić, J.; Subotić, B.; Smit, I.; Stubičar, M.; Tonejc, A.; Yamamoto, T. Mechanochemistry of zeolites: Part 1. Amorphization of zeolites A and X and synthetic mordenite by ball milling. Zeolites 1993, 13, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanigen, E.M.; Khatami, H.; Szymanski, H.A. Infrared Structural Studies of Zeolite Frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1974, 101, 201–229. [Google Scholar]
- Taufiqurrahmi, N.; Mohamed, A.R.; Bhatia, S. Nanocrystalline Zeolite Y: Synthesis and Characterization. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2011, 17, 012030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, K.; Dong, D.; Li, D.; Hill, M.R.; Hill, A.J.; Wang, H. Synthesis of hierarchical porous zeolite NaY particles with controllable particle sizes. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2010, 127, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachse, A.; Wuttke, C.; Díaz, U.; de Souza, M.O. Mesoporous Y zeolite through ionic liquid based surfactant templating. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2015, 217, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, H.; Azizi, S.N.; Cravotto, G. Improved removal of methylene blue on modified hierarchical zeolite Y: Achieved by a “destructive-constructive” method. Green Process. Synth. 2019, 8, 730–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.T. Adsorbents: Fundamentals and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]


| Label | Zeolite Y: CNF | Product Location * |
|---|---|---|
| T73 | 7:3 | Top |
| B73 | 7:3 | Bottom |
| T64 | 6:4 | Top |
| B64 | 6:4 | Bottom |
| T11 | 1:1 | Top |
| B11 | 1:1 | Bottom |
| Label | Crystallinity Index (%) | Median Particle Diameter D50 (nm) | Cumulative Frequency of Particles with Diameter <100 nm (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zeolite Y | 100 | 547 | 0 |
| T73 | 5 | 69 | 85 |
| B73 | 13 | 80 | 67 |
| T64 | 9 | 89 | 58 |
| B64 | 21 | 106 | 43 |
| T11 | 12 | 82 | 70 |
| B11 | 32 | 100 | 51 |
| Sample | Surface Area (m2/g) | VMP (cm3/g) | V (cm3/g) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| St | SMP | |||
| Pristine zeolite Y | 91 | 619 | 0.354 | 0.531 |
| T73 | 238 | 78 | 0.042 | 0.473 |
| B73 | 148 | 135 | 0.074 | 0.541 |
| T64 | 178 | 95 | 0.053 | 0.419 |
| B64 | 105 | 148 | 0.081 | 0.473 |
| T11 | 180 | 101 | 0.059 | 0.462 |
| B11 | 99 | 220 | 0.122 | 0.399 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nassrullah, H.; Anis, S.F.; Lalia, B.S.; Hashaikeh, R. Cellulose Nanofibrils as a Damping Material for the Production of Highly Crystalline Nanosized Zeolite Y via Ball Milling. Materials 2022, 15, 2258. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15062258
Nassrullah H, Anis SF, Lalia BS, Hashaikeh R. Cellulose Nanofibrils as a Damping Material for the Production of Highly Crystalline Nanosized Zeolite Y via Ball Milling. Materials. 2022; 15(6):2258. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15062258
Chicago/Turabian StyleNassrullah, Haya, Shaheen Fatima Anis, Boor Singh Lalia, and Raed Hashaikeh. 2022. "Cellulose Nanofibrils as a Damping Material for the Production of Highly Crystalline Nanosized Zeolite Y via Ball Milling" Materials 15, no. 6: 2258. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15062258
APA StyleNassrullah, H., Anis, S. F., Lalia, B. S., & Hashaikeh, R. (2022). Cellulose Nanofibrils as a Damping Material for the Production of Highly Crystalline Nanosized Zeolite Y via Ball Milling. Materials, 15(6), 2258. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15062258








