Molecular Dynamics Simulation of the Interaction between Graphene Oxide Quantum Dots and DNA Fragment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Computational Details
2.1. System Setup
2.2. MD Simulations
3. Results and Discussion
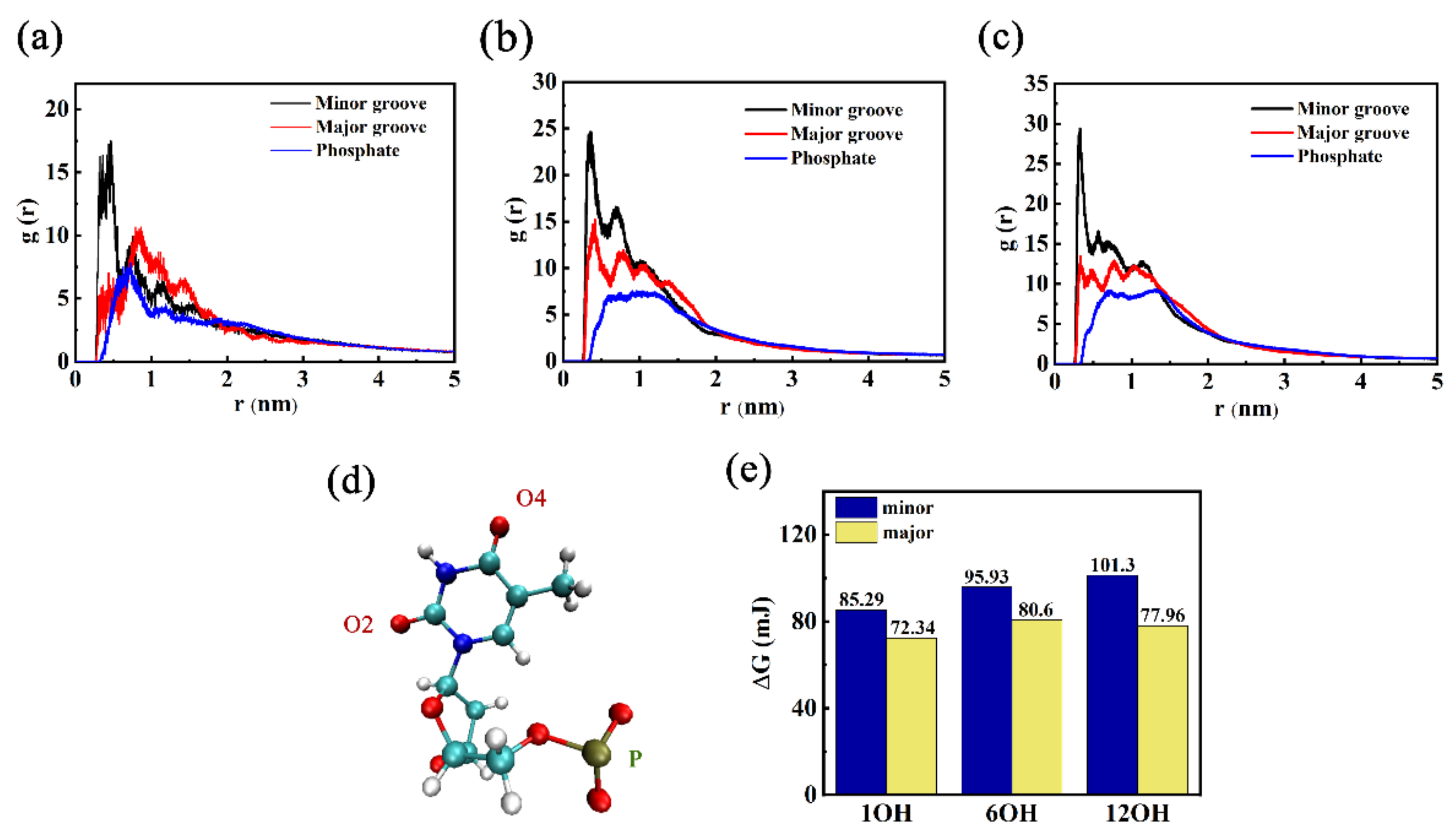
3.1. Effects of Different Oxidation Degrees of GOQDs on the Adsorption Sites of DNA
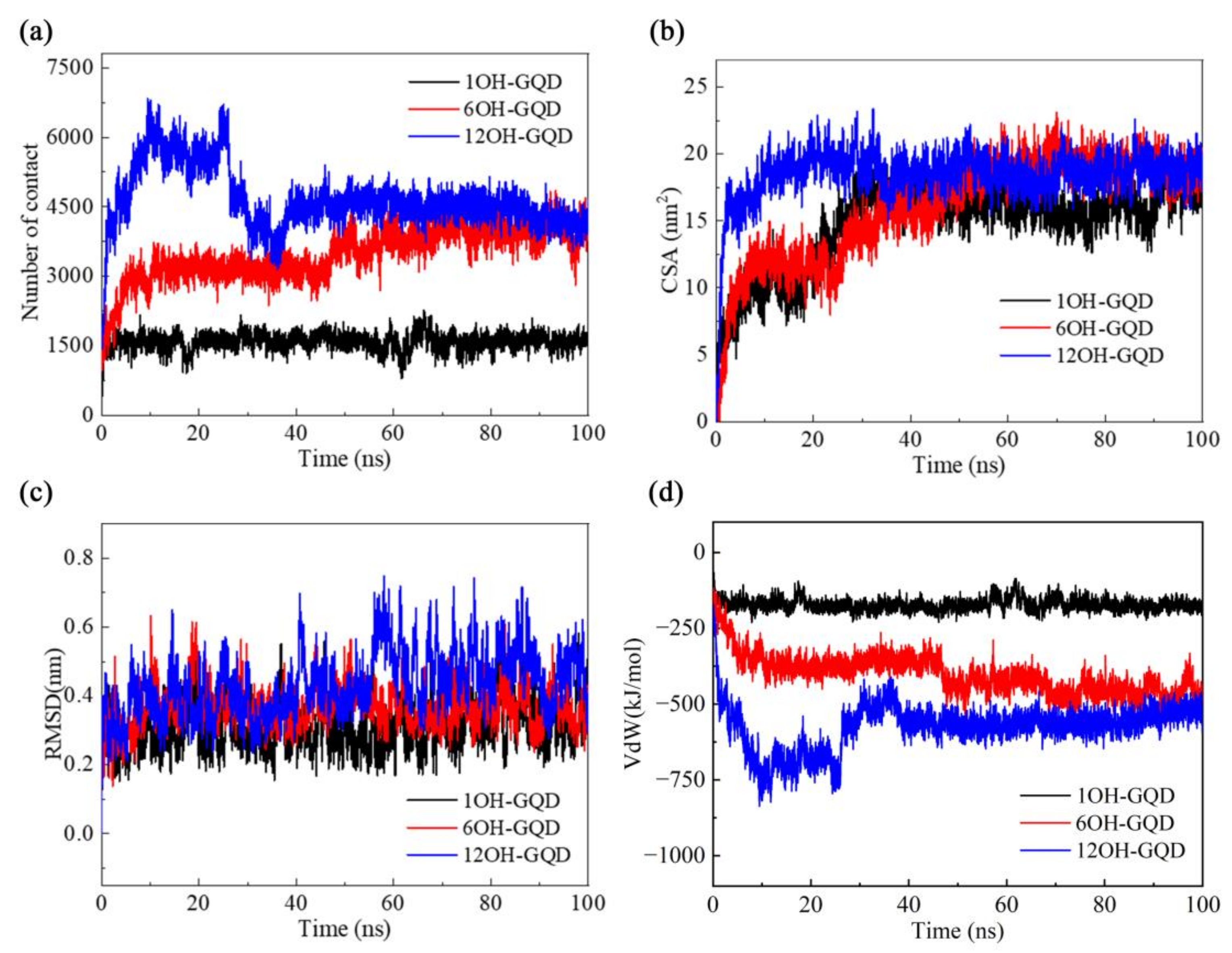
3.2. Effects of Different Oxidation Degrees of GOQDs on DNA Damage
3.3. Effects of the Number of GOQDs on DNA Damage
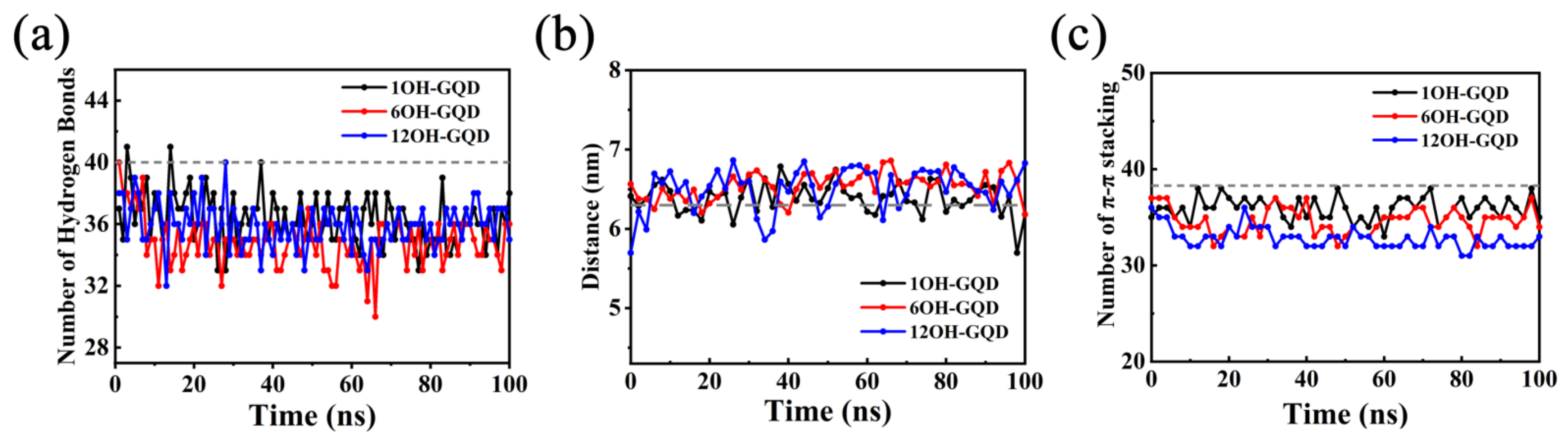
3.4. Effect of Different Functional Groups of GOQDs on DNA Damage
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, Y.; Murali, S.; Cai, W.; Li, X.; Suk, J.W.; Potts, J.R.; Ruoff, R.S. Graphene and Graphene Oxide: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 3906–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, Y.; Bian, Z.-Y.; Zhang, J.-X.; Ding, A.-Z.; Liu, S.-L.; Wang, H. Effect of the oxygen-containing functional group of graphene oxide on the aqueous cadmium ions removal. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 329, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, L.; Song, B.; Liang, H.; Liu, J.; Feng, X.; Deng, B.; Sun, T.; Shao, L. Toxicity of graphene-family nanoparticles: A general review of the origins and mechanisms. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2016, 13, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Yu, Y.; Hou, W.; Zhou, J.; Song, L. Effects of particle size and pH value on the hydrophilicity of graphene oxide. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 273, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathizadeh, M.; Xu, W.L.; Zhou, F.; Yoon, Y.; Yu, M. Graphene Oxide: A Novel 2-Dimensional Material in Membrane Separation for Water Purification. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 4, 1600918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Liu, D.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, X.; Lu, J.; Cui, F. Molecular Dynamics Study of the Aggregation Process of Graphene Oxide in Water. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 26712–26718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Gao, W.; Yan, F.; Ji, H.; Ju, H. Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer between Quantum Dots and Graphene Oxide for Sensing Biomolecules. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 5511–5517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, T.-F.; Teng, C.-Y.; Chen, S.-J.; Teng, H. Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Oxide Quantum Dots as Photocatalysts for Overall Water-Splitting under Visible Light Illumination. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 3297–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Liao, F.; Wang, T.; Zhu, L.; Shao, M. Tuning surface properties of graphene oxide quantum dots by gamma-ray irradiation. J. Lumin. 2016, 175, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, S.J.; Kroon, R.; Laufersky, G.; Röding, M.; Goreham, R.V.; Gschneidtner, T.; Schroeder, K.; Moth-Poulsen, K.; Andersson, M.; Nann, T. Heterogeneity in the fluorescence of graphene and graphene oxide quantum dots. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Xie, J.; Ma, H.; Zhang, X.; Pan, Y.; Lv, J.; Ge, H.; Ren, N.; Su, H.; Xie, X.; et al. Graphene: From Graphite to Graphene Oxide and Graphene Oxide Quantum Dots. Small 2017, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansuriya, B.D.; Altintas, Z. Applications of Graphene Quantum Dots in Biomedical Sensors. Sensors 2020, 20, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, C. Graphene quantum dots: Emergent nanolights for bioimaging, sensors, catalysis and photovoltaic devices. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 3686–3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonça, M.C.P.; Soares, E.S.; de Jesus, M.B.; Ceragioli, H.J.; Batista, Â.G.; Nyúl-Tóth, Á.; Molnár, J.; Wilhelm, I.; Maróstica, M.R.; Krizbai, I.; et al. PEGylation of Reduced Graphene Oxide Induces Toxicity in Cells of the Blood–Brain Barrier: An in Vitro and in Vivo Study. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 3913–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Shan, S.; Yang, X.; Liu, D.; Cui, F.; Xing, B. Wrinkle- and Edge-Adsorption of Aromatic Compounds on Graphene Oxide as Revealed by Atomic Force Microscopy, Molecular Dynamics Simulation, and Density Functional Theory. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 7689–7697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, X.; Ma, H.; Fang, H. Length feature of ssDNA adsorption onto graphene oxide with both large unoxidized and oxidized regions. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 6699–6707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Wu, G.; Lu, N.; Yuan, X.; Li, B. A miniaturized electrochemical toxicity biosensor based on graphene oxide quantum dots/carboxylated carbon nanotubes for assessment of priority pollutants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 324, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wu, C.; Zhou, X.; Han, T.; Xin, X.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; Guo, S. Enhancing cell nucleus accumulation and DNA cleavage activity of anti-cancer drug via graphene quantum dots. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Pramanik, A.; Tchounwou, C.; Pedraza, F.; Crouch, R.A.; Chavva, S.R.; Vangara, A.; Sinha, S.S.; Jones, S.; Sardar, D.; et al. Multifunctional biocompatible graphene oxide quantum dots decorated magnetic nanoplatform for efficient capture and two-photon imaging of rare tumor cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 10935–10943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.Y.; Baek, S.H.; Chang, S.J.; Song, Y.; Rafique, R.; Lee, K.T.; Park, T.J. Synthesis of upconversion nanoparticles conjugated with graphene oxide quantum dots and their use against cancer cell imaging and photodynamic therapy. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 93, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Xu, B.; Yao, M.; Mao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, G.; Tang, Q.; Wang, X.; Xia, Y. Graphene oxide quantum dots disrupt autophagic flux by inhibiting lysosome activity in GC-2 and TM4 cell lines. Toxicology 2016, 374, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Gu, M.-M.; Tian, X.; Xiao, B.-B.; Lu, S.; Zhu, W.; Yu, L.; Shang, Z.-F. Hydroxylated-Graphene Quantum Dots Induce DNA Damage and Disrupt Microtubule Structure in Human Esophageal Epithelial Cells. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 164, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, Y.; Duo, L. Biochemical toxicity, lysosomal membrane stability and DNA damage induced by graphene oxide in earthworms. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 116225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chng, E.L.; Pumera, M. The toxicity of graphene oxides: Dependence on the oxidative methods used. Chemistry 2013, 19, 8227–8235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golkaram, M.; van Duin, A.C.T. Revealing graphene oxide toxicity mechanisms: A reactive molecular dynamics study. Mater. Discov. 2015, 1, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, K.-H.; Lin, Y.-S.; Macosko, C.W.; Haynes, C.L. Cytotoxicity of Graphene Oxide and Graphene in Human Erythrocytes and Skin Fibroblasts. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 2607–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, L.; Wei, M.; Hu, W.; Li, X.; Huang, Q. Effect of graphene oxide on undifferentiated and retinoic acid-differentiated SH-SY5Y cells line. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 3861–3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hu, W.; Li, J.; Tao, L.; Wei, Y. A comparative study of cellular uptake and cytotoxicity of multi-walled carbon nanotubes, graphene oxide, and nanodiamond. Toxicol. Res. 2012, 1, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhu, L.; Chen, J.-F.; Dai, L. Can graphene quantum dots cause DNA damage in cells? Nanoscale 2015, 7, 9894–9901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, Y.; Ge, C.; Yang, Z.; Garate, J.A.; Gu, Z.; Weber, J.K.; Liu, J.; Zhou, R. Reduced Cytotoxicity of Graphene Nanosheets Mediated by Blood-Protein Coating. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 5713–5724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan, O.; Ghaderi, E. Toxicity of Graphene and Graphene Oxide Nanowalls Against Bacteria. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 5731–5736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X. Self-Assembly of DNA Segments on Graphene and Carbon Nanotube Arrays in Aqueous Solution: A Molecular Simulation Study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 6181–6189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J. Exploration on the mechanism of DNA adsorption on graphene and graphene oxide via molecular simulations. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2015, 48, 275402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ren, X.; He, L. First-principles study of benzo[a]pyrene-7,8-dione and DNA adducts. J. Chem. Phys. 2021, 154, 175102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Bu, X.; Lu, J.; Xu, C.; Wang, X.; Yang, X. Interaction study of ciprofloxacin with human telomeric DNA by spectroscopy and molecular docking. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2013, 107, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, B.; Hu, J.; Li, P.; Pan, D.; Shen, L. DNA binding graphene quantum dots inhibit dual topoisomerases for cancer chemotherapy. Carbon 2022, 187, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, L.; Lv, X.; Wu, Z.; Xia, W.; Huang, Y.; Chen, L.; Sun, W.; Qi, Y.; Yang, M.; Qi, L. Oxygen content-related DNA damage of graphene oxide on human retinal pigment epithelium cells. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2021, 32, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Guo, R.; Yan, L.-T. Simulation and analysis of cellular internalization pathways and membrane perturbation for graphene nanosheets. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 6069–6077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, L.; Kang, Z.; Liang, L.; Wang, Q.; Shen, J.-W. Graphene quantum dot assisted translocation of drugs into a cell membrane. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 4503–4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.X.; Chen, Y.G.; Kapral, R. Chemically Propelled Motors Navigate Chemical Patterns. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1800028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, Z.; Liu, F.; Shen, J.W.; He, Z.; Wang, H. DNA fragment translocation through the lipid membrane assisted by carbon nanotube. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 574, 118921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Ying, S.; Ren, H.; Dai, J.; Zhang, L.; Liang, L.; Wang, Q.; Shen, Q.; Shen, J.W. Molecular dynamics study on the encapsulation and release of anti-cancer drug doxorubicin by chitosan. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 580, 119241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Shen, Q.; Shen, J.W.; Jin, L.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Q.; Hu, Q.; Liang, L. Understanding the size effect of graphene quantum dots on protein adsorption. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 174, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Z.; Hu, W.; Jiao, F.; Zhang, P.; Shen, J.; Cui, B.; Wang, H.; Liang, L. Theoretical Evaluation of DNA Genotoxicity of Graphene Quantum Dots: A Combination of Density Functional Theory and Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 9335–9342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanciuc, O. HyperChem Release 4.5 for Windows. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1996, 36, 612–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Wu, C.; Chowdhury, S.; Lee, M.C.; Xiong, G.; Zhang, W.; Yang, R.; Cieplak, P.; Luo, R.; Lee, T.; et al. A point-charge force field for molecular mechanics simulations of proteins based on condensed-phase quantum mechanical calculations. J. Comput. Chem. 2003, 24, 1999–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, M.J.; Murtola, T.; Schulz, R.; Páll, S.; Smith, J.C.; Hess, B.; Lindahl, E. GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX 2015, 1–2, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen-Tanugi, D.; Lin, L.-C.; Grossman, J.C. Multilayer Nanoporous Graphene Membranes for Water Desalination. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 1027–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Wang, X.; Wu, C. Early stage intercalation of doxorubicin to DNA fragments observed in molecular dynamics binding simulations. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2012, 38, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.B.; Zhou, H.Y.; Xiao, X.M. Spectroscopic and viscosity study of doxorubicin interaction with DNA. J. Mol. Struct. 2005, 749, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Roy, S.; Singh, P.C. Groove Switching of Hydroxychloroquine Modulates the Efficacy of Binding and Induced Stability to DNA. J. Phys. Chem. B 2021, 125, 6889–6896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, N.M.; Poleto, M.D.; Steuer, J.; van der Spoel, D. Influence of Na+ and Mg2+ ions on RNA structures studied with molecular dynamics simulations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 4872–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, M.-T.; Glezakou, V.-A.; Lonergan, J.; McNamara, B.; Paviet, P.D.; Rousseau, R. Ab initio molecular dynamics assessment of thermodynamic and transport properties in (K, Li)Cl and (K, Na)Cl molten salt mixtures. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 326, 115262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, D.S.; van der Spoel, D. Screening for the Location of RNA using the Chloride Ion Distribution in Simulations of Virus Capsids. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2012, 8, 2474–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
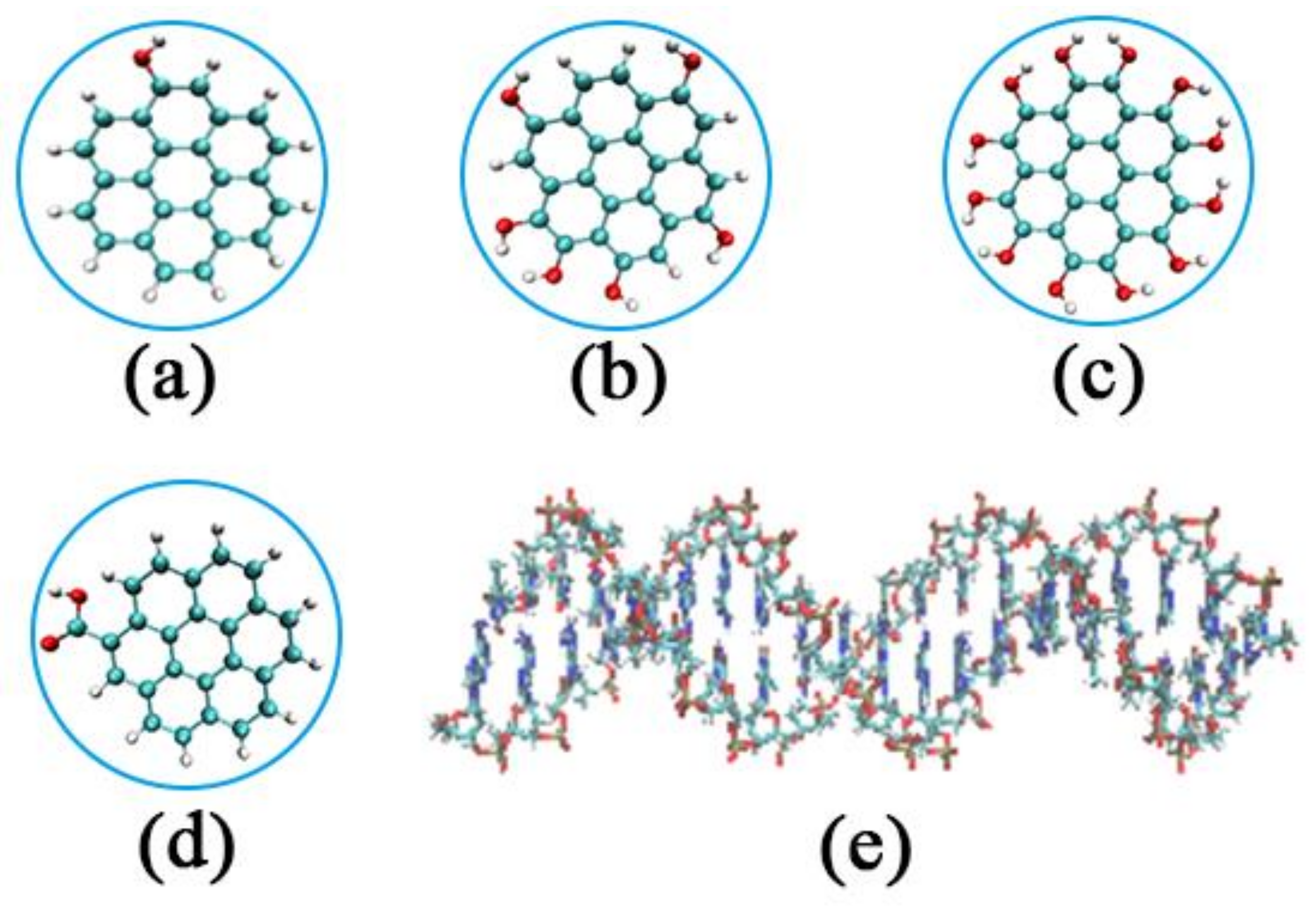
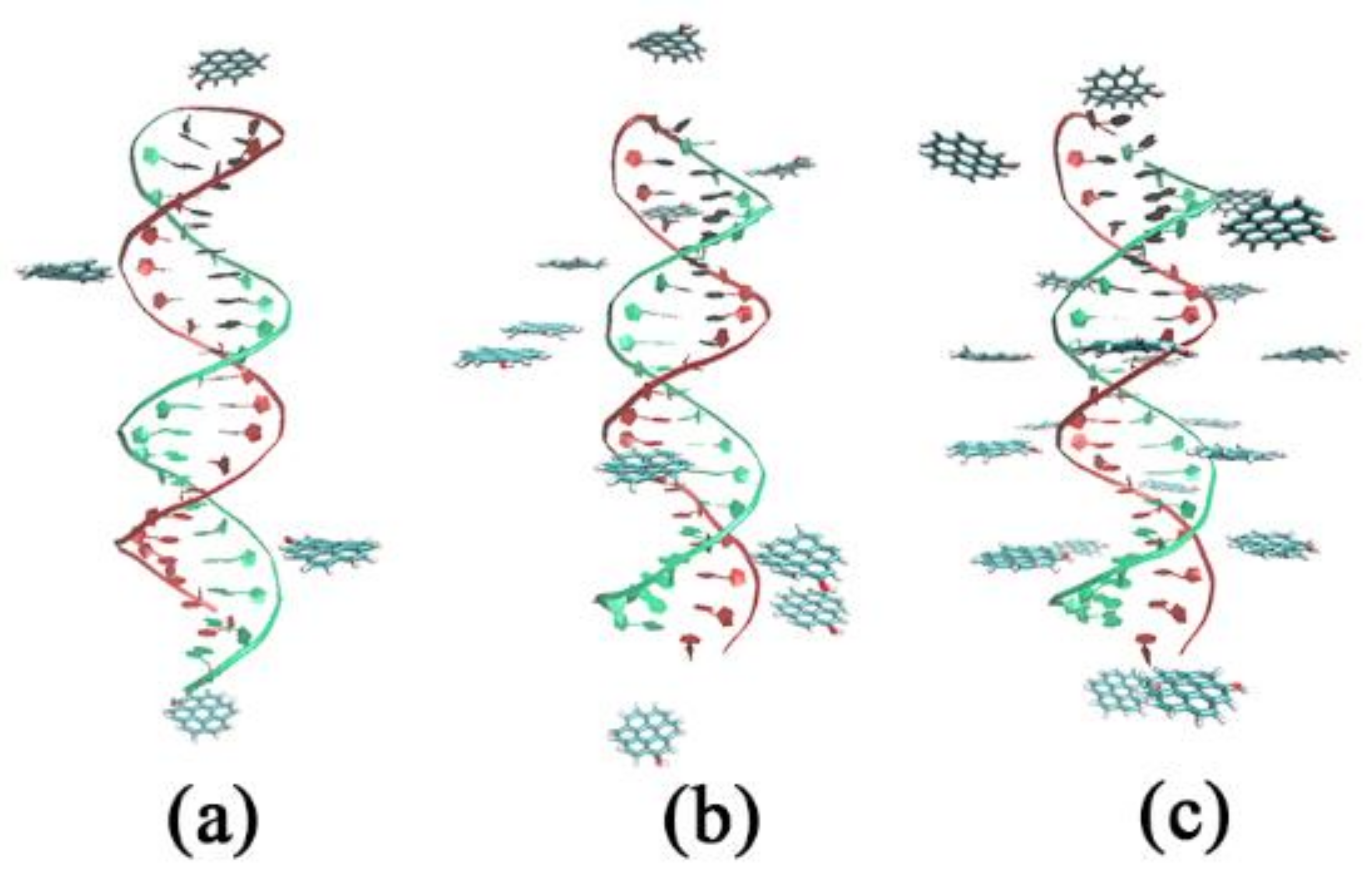
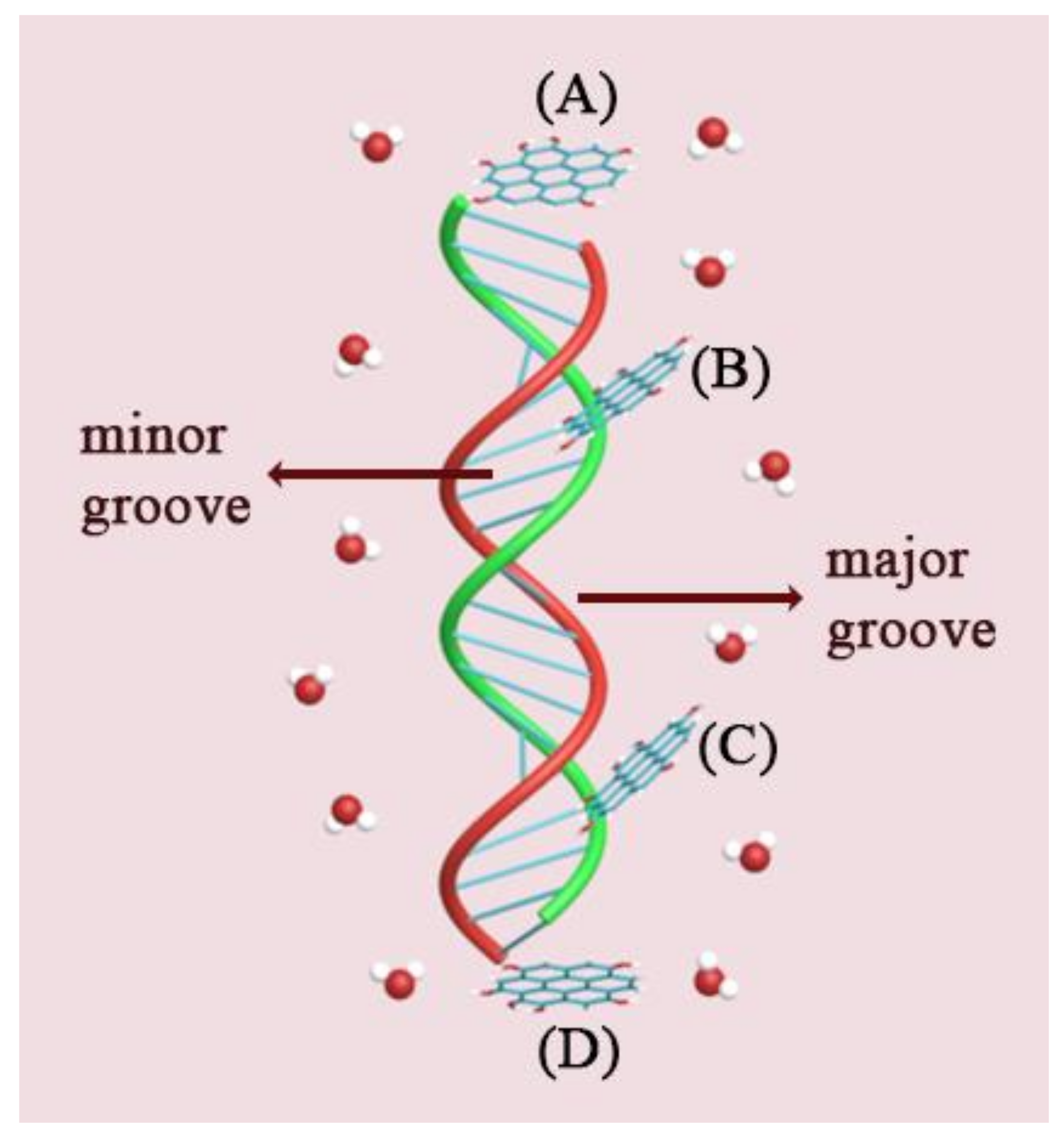
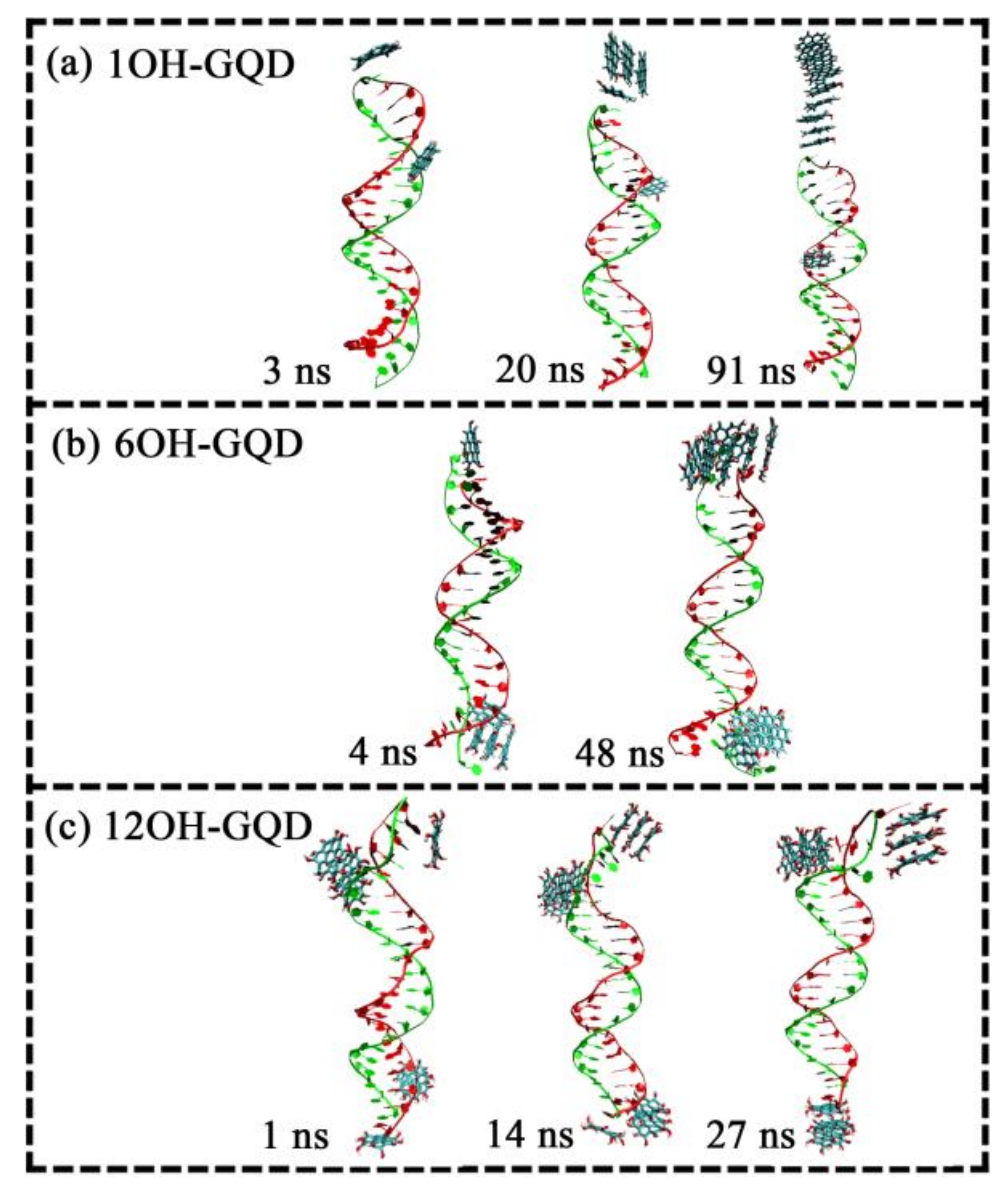

| System | Type of GOQD | Number of GOQDs | Number of Atoms | Simulation Time (ns) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AT-1OH-10 | 1OH-GQD | 10:1 | 131,543 | 100 |
| AT-6OH-10 | 6OH-GQD | 10:1 | 104,140 | 100 |
| AT-12OH-10 | 12OH-GQD | 10:1 | 104,281 | 100 |
| AT-6OH-4 | 6OH-GQD | 4:1 | 89,383 | 100 |
| AT-6OH-20 | 6OH-GQD | 20:1 | 94,915 | 100 |
| AT-1COOH-10 | 1COOH-GQD | 10:1 | 104,392 | 100 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, L.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, H.; Li, J.; Shen, X.; Li, T.; Kong, Z.; Hu, W.; Zhang, Y. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of the Interaction between Graphene Oxide Quantum Dots and DNA Fragment. Materials 2022, 15, 8506. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15238506
Wu L, Zhang P, Zhou H, Li J, Shen X, Li T, Kong Z, Hu W, Zhang Y. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of the Interaction between Graphene Oxide Quantum Dots and DNA Fragment. Materials. 2022; 15(23):8506. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15238506
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Lingxiao, Pengzhen Zhang, Hanxing Zhou, Jing Li, Xin Shen, Tianyu Li, Zhe Kong, Wei Hu, and Yongjun Zhang. 2022. "Molecular Dynamics Simulation of the Interaction between Graphene Oxide Quantum Dots and DNA Fragment" Materials 15, no. 23: 8506. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15238506
APA StyleWu, L., Zhang, P., Zhou, H., Li, J., Shen, X., Li, T., Kong, Z., Hu, W., & Zhang, Y. (2022). Molecular Dynamics Simulation of the Interaction between Graphene Oxide Quantum Dots and DNA Fragment. Materials, 15(23), 8506. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15238506







