Shedding Light on Roman Glass Consumption on the Western Coast of the Black Sea
Abstract
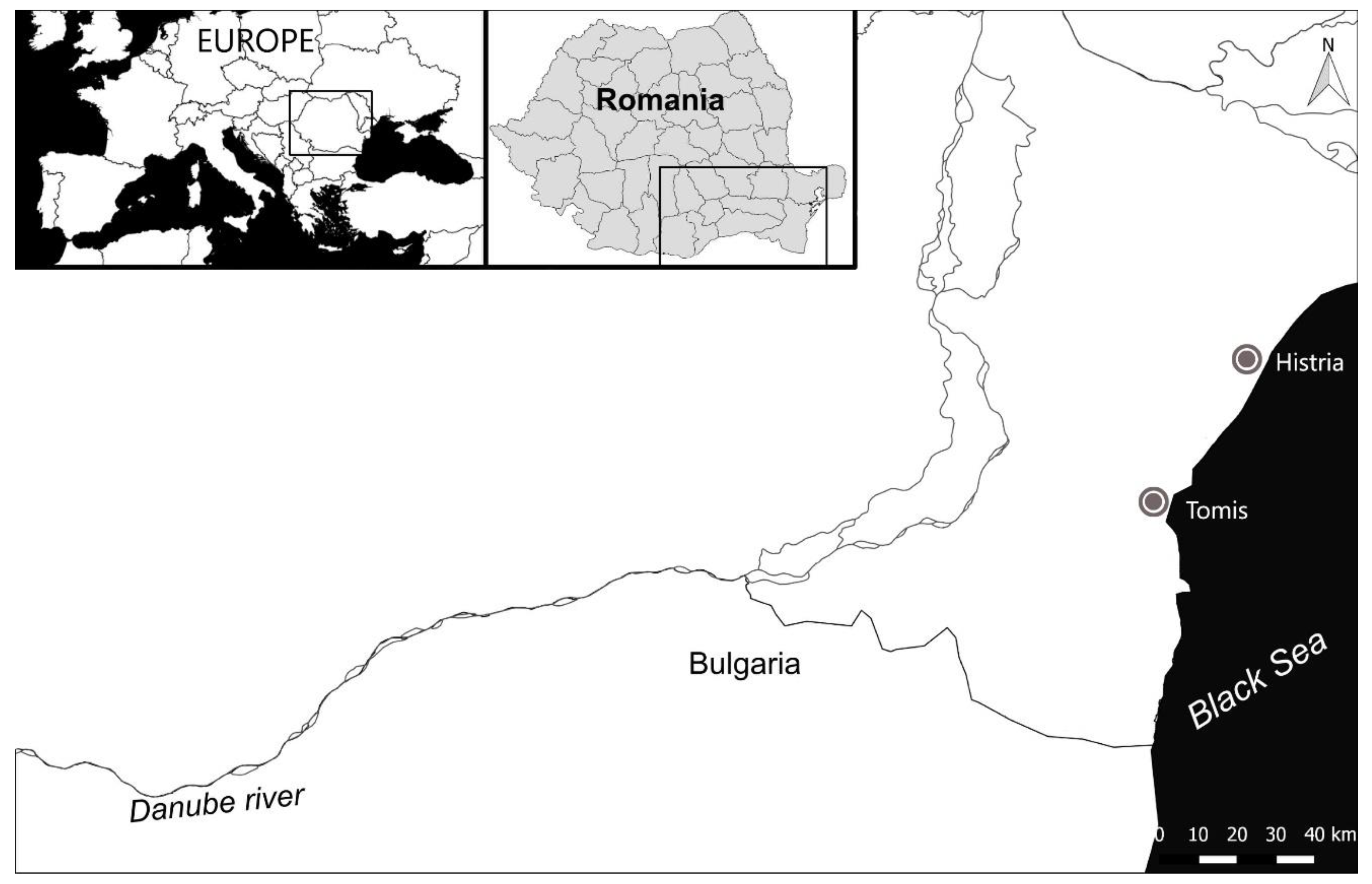
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Archaeological Background and Analyzed Samples
3. Experimental
4. Results and Discussions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shortland, A.J.; Rehren, T. Glass. In Archaeological Science—An Introduction; Richards, M.P., Britton, K., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2020; pp. 347–364. [Google Scholar]
- Freestone, I.C. Glass production in the first millennium CE: A compositional perspective. In Ancient Glass and Glass Production, Edition TOPOI; Klimscha, F., Ed.; Berlin Studies of the Ancient World 67: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 243–262. [Google Scholar]
- Nenna, M.D.; Vichy, M.; Picon, M. L’atelier de verrier de Lyon du 1er siècle après J.-C. et l’origine des verres “romains”. Revue d’Archéométrie 1997, 21, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayre, E.V.; Smith, R.W. Compositional categories of ancient glass. Science 1961, 133, 1824–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvestri, A.; Gallo, F.; Maltoni, F.; Degryse, P.; Ganio, M.; Longinelli, A.; Molin, G. Things that Travelled: A Review of the Roman Glass from Northern Adriatic Italy in Things That Travelled. Mediterranean Glass in the First Millennium AD; Rosenow, D., Phelps, M., Meek, A., Freestone, I.C., Eds.; UCL Press: London, UK, 2018; pp. 346–367. [Google Scholar]
- Gorin-Rosen, Y. The ancient glass industry in Israel: Summary of the finds and new discoveries. In La route du Verre: Ateliers Primaires et Secondaires du Second Millénaire Av J-C au Moyen Âge; Nenna, M.D., Ed.; Maison de l’Orient Méditerranéen: Lyon, France, 2000; Volume 33, pp. 49–63. [Google Scholar]
- Nenna, M.D. Primary glass workshops in Graeco-Roman Egypt: Preliminary report on the excavations of the site of Beni Salama, Wadi Natrun (2003, 2005–2009). In Glass of the Roman World; Bayley, J., Freestone, I.C., Jackson, C.M., Eds.; Oxbow Books: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Tal, O.; Jackson-Tal, R.E.; Freestone, I.C. New evidence of the production of raw glass at late Byzantine Apollonia-Arsuf, Israel. J. Glass Stud. 2004, 46, 51–66. [Google Scholar]
- Fontaine, S.D.; Foy, D. L’épave Ouest-Embiez 1, Var: Le commerce maritime du verre brut et manufacturé en Méditerranée occidentale dans l’Antiquité. Rev. Archéol. Narbonn. 2007, 40, 235–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirion-Merle, V.; Nenna, M.D.; Picon, M.; Vichy, M. Un Nouvel Atelier Primaire Dans le Wadi Natrun (Egypte) et les Compositions des Verres Produits Dans Cette Région; Bulletin de l’AFAV: Dijon, France, 2002–2003; pp. 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Silvestri, A.; Molin, G.; Salviulo, G. The colourless glass of Iulia Felix. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2008, 35, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freestone, I.C. The recycling and reuse of Roman glass: Analytical approaches. J. Glass Stud. 2015, 57, 29–40. [Google Scholar]
- Gliozzo, E. The composition of colourless glass: A review. Archaeol. Anthropol. Sci. 2017, 9, 455–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugoi, R.; Alexandrescu, C.G.; Panaite, A. Chemical composition characterization of ancient glass finds from Troesmis—Turcoaia, Romania. Archaeol. Anthropol. Sci. 2018, 10, 571–586. [Google Scholar]
- Bugoi, R.; Talmaţchi, G.; Szilágyi, V.; Harsányi, I.; Cristea-Stan, D.; Boţan, S.; Kasztovszky, Z. PGAA analyses on Roman glass finds from Tomis. Rom. J. Phys. 2021, 66, 906. [Google Scholar]
- Bugoi, R.; Panaite, A.; Alexandrescu, C.G. Chemical analyses on Roman and Late Roman Empire glass finds from the Lower Danube: The case of Tropaeum Traiani. Archaeol. Anthropol. Sci. 2021, 13, 148. [Google Scholar]
- Bugoi, R.; Ţârlea, A.; Szilágyi, V.; Harsányi, I.; Cliante, L.; Kasztovszky, Z. Colour and beauty at the Black Sea coast: Archaeometric analyses of selected small finds from Histria. Rom. Rep. Phys 2022, 74. [Google Scholar]
- Stawiarska, T. Roman and Early Byzantine Glass from Romania and Northern Bulgaria. Archaeological and Technological Study; Biblioteca Antiqua Volume XXIV, Academia Scientiarum Polona: Warsaw, Poland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bugoi, R.; Poll, I.; Mănucu-Adameşteanu, G.; Neelmeijer, C.; Eder, F. Investigations of Byzantine glass bracelets from Nufăru, Romania using external PIXE-PIGE methods. J. Arch. Sci. 2013, 40, 2881–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugoi, R.; Poll, I.; Manucu-Adamesteanu, G.; Calligaro, T.; Pichon, L.; Pacheco, C. PIXE-PIGE analyses of Byzantine glass bracelets (10th–13th centuries AD) from Isaccea, Romania. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2016, 307, 1021–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugoi, R.; Poll, I.; Mănucu-Adameşteanu, G.; Pacheco, C.; Lehuédé, P. Compositional study of Byzantine glass bracelets discovered at the Lower Danube. Microchem. J. 2018, 137, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugoi, R.; Măgureanu, A.; Măgureanu, D.; Lemasson, Q. IBA analyses on glass beads from the Migration Period. Nucl. Instrum. Method B 2020, 478, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugoi, R.; Mureşan, O. A brief study on the chemistry of some Roman glass finds from Apulum. Rom. Rep. Phys. 2021, 73, 803. [Google Scholar]
- Foy, D.; Picon, M.; Vichy, M.; Thirion-Merle, V. Caractérisation des verres de la fin de l’Antiquité en Mediterranée occidentale: l’émergence de nouveaux courants commerciaux. In Échanges et Commerce du Verre dans le Monde Antique. Actes du Colloque de l’AIHV, Aix-en-Provence et Marseille, Juin 2001. Monographies Instrumentum 24; Foy, D., Nenna, M.D., Eds.; Monique Mergoil: Montagnac, France, 2003; pp. 41–85. [Google Scholar]
- Foy, D.; Thirion-Merle, V.; Vichy, M. Contribution à l’étude des verres antiques décolorés à l’antimoine. Revue d’Archéométrie 2004, 28, 169–177. [Google Scholar]
- Gliozzo, E.; Turchiano, M.; Giannetti, F.; Santagostino Barbone, A. Late Roman Empire glass vessels and production indicators from the town of Herdonia (Foggia, Italy): New data on CaO-rich/weak HIMT glass. Archaeometry 2016, 58, 81–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condurachi, E. (Ed.) Histria. Monografie Arheologică Vol. I; Editura Academiei RPR: Bucureşti, Romania, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Condurachi, E. (Ed.) Histria. Monografie Arheologică Vol. II; Editura Academiei RSR: Bucureşti, Romania, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Băjenaru, C.; Bâltâc, A. Depozitul de candele de sticlă descoperit la basilica episcopală de la Histria. Pontica 2000–2001, 33–34, 469–513. [Google Scholar]
- Băjenaru, C.; Bâltâc, A. Histria—Basilica Episcopală. Catalogul descoperirilor de sticlă (1984–2000). Pontica 2006, 39, 219–247. [Google Scholar]
- Boţan, S.P. Vase de Sticlă în Spaţiul dintre Carpaţi şi Prut (Secolele II a.Chr.–II p.Chr.); Ed. Mega: Cluj-Napoca, Romania, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Chiriac, C.; Boţan, S.P. Sticlăria elenistică şi romană din Pontul Euxin. Între producţie şi import. In Poleis în Marea Neagră. Relaţii Interpontice şi Producţii Locale, Pontica et Mediterranea I; Panait Bîrzescu, F., Birzescu, I., Matei-Popescu, F., Robu, K., Eds.; Ed. Humanitas: Bucureşti, Romania, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Țârlea, A.; Cliante, L. ‘Put the lights on’: Early Byzantine stemmed goblets and lamps from the Acropolis Centre-South Sector in Histria (I). Peuce SN 2020, 18, 301–332. [Google Scholar]
- Achim, I.; Bottez, V.; Angelescu, M.; Cliante, L.; Țârlea, A.; Lițu, A. A city reconfigured: Old and new research concerning Late Roman urbanism in Istros. In The Greeks and Romans in the Black Sea and the Importance of the Pontic Region for the Graeco–Roman World (7th Century BC–5th Century AD): 20 Years On (1997–2017); Tsetskhladze, G.R., Avram, A., Hargrave, J., Eds.; In Proceedings of the Sixth International Congress on Black Sea Antiquities, Constanƫa, Romania, 18–22 September 2017, Dedicated to Prof. Sir John Boardman to Celebrate his Exceptional Achievement and His 90th Birthday; Archaeopress Archaeology: Oxford, UK, 2021; pp. 477–487. [Google Scholar]
- Bottez, V.; Liţu, A.; Ţârlea, A. Preliminary results of the excavations at Histria. The Acropolis Centre-South Sector (2013–2014). MCA SN 2015, 11, 157–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achim, I. La basilique à crypte d’Istros: Dix campagnes de fouilles (2002–2013). MCA 2014, 10, 265–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achim, I.; Dima, M.; Beldiman, C.; Surdu, V.; Băcăran, M.; Munteanu, F. Comuna Istria, jud. Constanța. “Basilica cu criptă”. In Cronica Cercetărilor Arheologice din România, Campania 2013; MInisterul Culturii, Institutul National al Patrimoniului: Oradea, Romania, 2014; pp. 64–66. [Google Scholar]
- Bărbulescu, M.; Buzoianu, L. Tomis. Comentariu Istoric și Arheologic; Ed. Ex Ponto: Constanța, Romania, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bucovală, M. Vase Antice de Sticlă la Tomis; Muzeul de Arheologie: Constanţa, Romania, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Bucovală, M. Tradiţii elenistice în materialele funerare de epocă romană timpurie la Tomis. Pontice 1969, 2, 297–332. [Google Scholar]
- Bucovală, M. Roman glass vessels discovered in Dobrudja. J. Glass Stud. 1984, 26, 59–63. [Google Scholar]
- Drăghici, C. Glassware from Tomis. Chronological and typological aspects. In Annales AIHV Thessaloniki 2009; Drăghici, C., Drăghici, C., Eds.; Ziti Publications: Thessaloniki, Greece, 2012; pp. 211–216. [Google Scholar]
- Lungu, V.; Chera, C. Importuri de vase de sticlă suflate în tipar descoperite în necropolele Tomisului. Pontica 1992, 25, 273–280. [Google Scholar]
- Cliante, L.; Ţârlea, A. Secondary glass kilns and local glass production in Tomis during the Roman times. CICSA J. 2020, 6, 117–133. [Google Scholar]
- Szentmiklósi, L.; Belgya, T.; Révay, Z.; Kis, Z. Upgrade of the prompt gamma activation analysis and the neutron-induced prompt gamma spectroscopy facilities at the Budapest research reactor. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2010, 286, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Révay, Z.; Molnár, G.L. Standardisation of the prompt gamma activation analysis method. Radiochim. Acta 2003, 91, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonezawa, C. Quantitative analysis. In Handbook of Prompt Gamma Activation Analysis with Neutron Beams; Molnár, G.L., Ed.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands; Boston, MA, USA; New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 113–135. [Google Scholar]
- Révay, Z.; Belgya, T.; Kasztovszky, Z.; Weil, J.L.; Molnar, G.L. Cold neutron PGAA facility at Budapest. Nucl. Instrum. Method B 2004, 213, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Révay, Z. Determining elemental composition using Prompt γ Activation Analysis. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 6851–6859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinescu, B.; Cristea-Stan, D.; Szőkefalvi-Nagy, Z.; Kovács, I.; Harsányi, I.; Kasztovszky, Z. PIXE and PGAA—Complementary methods for studies on ancient glass artefacts from Byzantine, Late Medieval to modern Murano glass. Nucl. Instrum. Method B 2018, 417, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasztovszky, Z.; Kunicki-Goldfinger, J.J.; Dzierżanowski, P.; Nawrolska, G.; Wawrzyniak, P. (2005) PGAA and EPMA as complimentary nondestructive methods for analysis of boron content in historical glass. In Proceedings of the Art’05–8th International Conference on Non Destructive Investigations and Microanalysis for the Diagnostics and Conservation of the Cultural and Environmental Heritage, Lecce, Italy, 15–19 May 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Moropoulou, A.; Zacharias, N.; Delegou, E.T.; Maróti, B.; Kasztovszky, Z. Analytical and technological examination of glass tesserae from Hagia Sophia. Microchem. J. 2016, 125, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharias, N.; Kaparou, M.; Oikonomou, A.; Kasztovszky, Z. Mycenaean glass from the Argolid, Peloponnese, Greece: A technological and provenance study. Microchem. J. 2018, 141, 404–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adlington, L.W. The Corning archaeological reference glasses: New values for “old” compositions. Pap. Inst. Archaeol. 2017, 27, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Révay, Z. Calculation of uncertainties in Prompt Gamma Activation Analysis. Nucl. Instrum. Method A 2006, 564, 688–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiner, M.; Woisetchlaeger, G.; Schmitz, I.; Wadsak, M. Characterisation of surface layers formed under natural environmental conditions on medieval stained glass and ancient copper alloys using SEM, SIMS and atomic force microscopy. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 1999, 14, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shortland, A.J.; Schachner, L.; Freestone, I.; Tite, M. Natron as a flux in the early vitreous materials industry: Sources, beginnings and reasons for decline. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2006, 33, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bashaireh, K.; Al-Mustafa, S.; Freestone, I.C.; Al-Housan, A.Q. Composition of Byzantine glasses from Umm el-Jimal, northeast Jordan: Insights into glass origins and recycling. J. Cultural Herit. 2016, 21, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freestone, I.C. Appendix: Chemical analysis of “raw” glass fragments. In Excavations at Carthage II, 1. The Circular Harbor, the Site and Finds Other Than Pottery; Hurst, H.R., Ed.; Oxford University Press for British Academy: Oxford, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Brill, R.H. Scientific investigations of the Jalame glass and related finds. In Excavations at Jalame: Site of a Glass Factory in Late Roman Palestine; Weinberg, G.D., Ed.; University of Missouri Press: Columbia, MO, USA, 1988; pp. 257–294. [Google Scholar]
- Ceglia, A.; Cosyns, P.; Nys, K.; Terryn, H.; Thienpont, H.; Meulebroeck, W. Late Roman Empire glass distribution and consumption in Cyprus: A chemical study. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2015, 61, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Juan Ares, J.; Schibille, N.; Molina Vidal, J.; Sanchez de Prado, M.D. The supply of glass at Portus Ilicitanus (Alicante, Spain): A meta-analysis of HIMT glasses. Archaeometry 2019, 61, 647–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freestone, I.C.; Degryse, P.; Lankton, J.; Gratuze, B.; Schneider, J. HIMT, glass composition and commodity branding in the primary glass industry. In Things That Travelled, Mediterranean Glass in the First Millenium CE; Rosenow, D., Phelps, M., Meek, A., Freestone, I., Eds.; UCL Press: London, UK, 2018; pp. 159–190. [Google Scholar]
- Mirti, P.; Casoli, A.; Appolonia, L. Scientific analysis of Roman glass from Augusta Praetoria. Archaeometry 1993, 35, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drauschke, J.; Greiff, S. (Eds.) Chemical aspects of Byzantine glass from Caričin Grad/Iustiniana Prima (Serbia) . In Glass in Byzantium: Production, Usage, Analyses: International Workshop Organised by the Byzantine Archaeology Mainz, 17–18 of January 2008; Verlag des Römisch-Germanischen Zentralmuseums: Mainz, Germany, 2010; pp. 25–46. [Google Scholar]
- Adam-Veleni, P. (Ed.) Glass Cosmos; Archaeological Museum of Thessaloniki: Thessaloniki, Greece, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Antonaras, A. Fire and Sand. Ancient Glass in the Princeton University Art Museum; Princeton University Art Museum: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Arveiller-Dulong, V.; Arveiller, J. La Verre D’epoque Romaine au Musée Archéologique de Strasbourg; Éditions de la Réunion des Musées Nationaux: Strasbourg, France, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Arveiller-Dulong, V.; Nenna, M.D. Les Verres Antiques du Musée du Louvre, Vol. II: Vaisselle et Contenants du Ier Siècle au Début du VIIe Siècle Après J.-C., Musée du Louvre; Editions D’Art Somogy: Paris, France, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Atila, C.; Gürler, B.; Özerler, M.; Ünsalan, D. Glass Objects from Bergama Museum/Bergama Muzesi Cam Eserleri; Zero Books: Izmir, Turkey, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Buljević, Z. Imprints on the bottoms of glass bottles from Dalmatia held in the Archaeological Museum in Split. In Corpus des Signatures et Marques sur Verres Antiques; Foy, D., Nenna, M.D., Eds.; Montagnac: Aix-en-Provence–Lyon, France, 2011; Volume 3, pp. 179–195. [Google Scholar]
- Foy, D. Les Verres Antiques d’Arles; La collection du Musée Départamental Arles Antique: Paris, France, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Gorin-Rosen, Y. The glass finds from Horbat Zefat ‘Adi (east). Hadashot Arkheologiyot 2015, 127, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Gorin-Rosen, Y. Glass finds and remains of a glass industry from Miska. Atiqot 2020, 99, 135–168. [Google Scholar]
- Gorin-Rosen, Y.; Jackson-Tal, R. Chapter 9: Area F: The glass finds. In Paneas I, IAA Reports 37; Tzaferis, V., Israeli, S., Eds.; Israel Antiquities Authority Publications Department: Jerusalem, Israel, 2008; pp. 141–154. [Google Scholar]
- Hayes, J.W. Roman and Pre-Roman Glass in the Royal Ontario Museum: A Catalogue; Royal Ontario Museum: Toronto, ON, Canada, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Israeli, Y. Ancient Glass in the Israel Museum; The Eliahu Dobkin Collection and Other Gifts, with Contributions by Dan Barag and Na’ama Brosh; The Israel Museum: Jerusalem, Israel, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Lightfoot, C.S. Ancient Glass in National Museums Scotland; NMSE Publishing Ltd.: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lightfoot, C.S. Cesnola Collection of Cypriot Art; Ancient Glass; The Metropolitan Museum of Art: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lightfoot, C.S.; Arslan, M. Ancient Glass of Asia Minor; The Yüksel Erimtan Collection: Ankara, Turkey, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Whitehouse, D. Roman Glass in the Corning Museum of Glass; Corning: New York, NY, USA, 1997; Volume I. [Google Scholar]
- Whitehouse, D. Roman Glass in the Corning Museum of Glass; Corning: New York, NY, USA, 2001; Volume II. [Google Scholar]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bugoi, R.; Ţârlea, A.; Szilágyi, V.; Harsányi, I.; Cliante, L.; Achim, I.; Kasztovszky, Z. Shedding Light on Roman Glass Consumption on the Western Coast of the Black Sea. Materials 2022, 15, 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15020403
Bugoi R, Ţârlea A, Szilágyi V, Harsányi I, Cliante L, Achim I, Kasztovszky Z. Shedding Light on Roman Glass Consumption on the Western Coast of the Black Sea. Materials. 2022; 15(2):403. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15020403
Chicago/Turabian StyleBugoi, Roxana, Alexandra Ţârlea, Veronika Szilágyi, Ildikó Harsányi, Laurenţiu Cliante, Irina Achim, and Zsolt Kasztovszky. 2022. "Shedding Light on Roman Glass Consumption on the Western Coast of the Black Sea" Materials 15, no. 2: 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15020403
APA StyleBugoi, R., Ţârlea, A., Szilágyi, V., Harsányi, I., Cliante, L., Achim, I., & Kasztovszky, Z. (2022). Shedding Light on Roman Glass Consumption on the Western Coast of the Black Sea. Materials, 15(2), 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15020403





