Emerging Glass Industry Patterns in Late Antiquity Balkans and Beyond: New Analytical Findings on Foy 3.2 and Foy 2.1 Glass Types
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Evolution and Characteristics of Foy 3.2-Type Glass
3. Characteristics of Iron-Rich Foy 2.1 Glass and Source of Increased Iron
4. Discussion
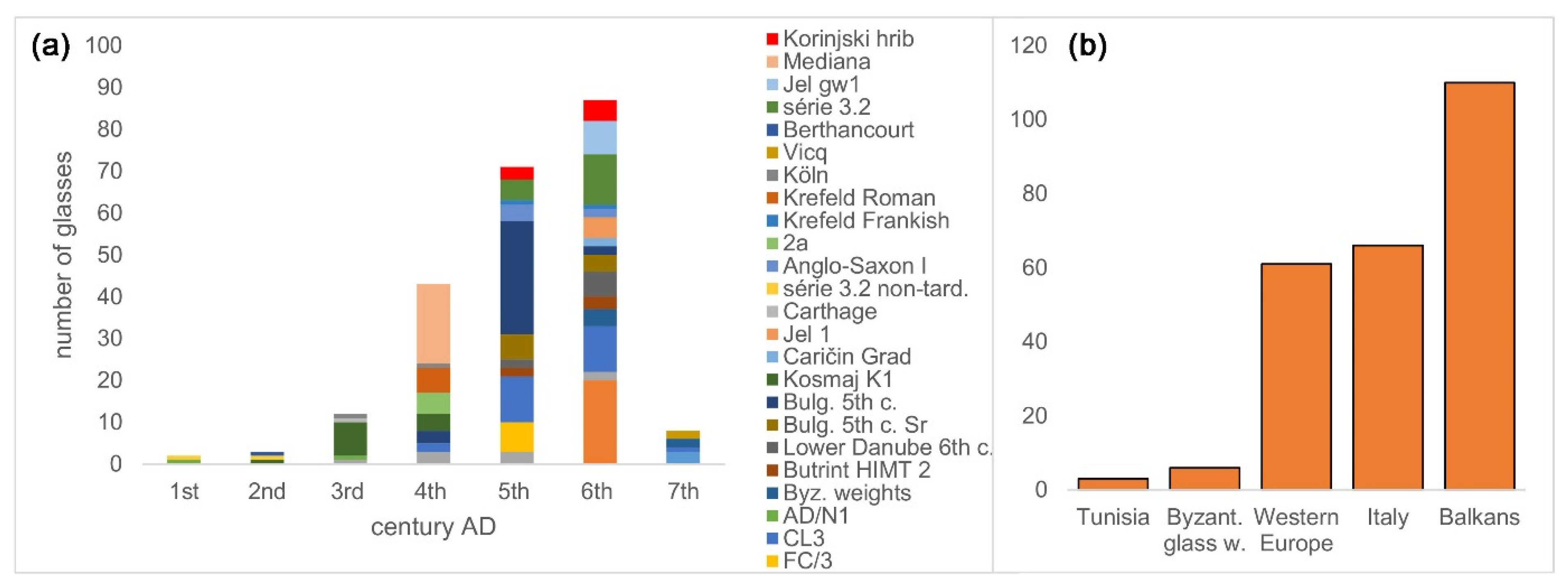
4.1. Changes in Distribution of Glass Types from Fourth to Sixth Century AD in the Balkans
4.2. Evolving Chemical Composition of Série 3.2
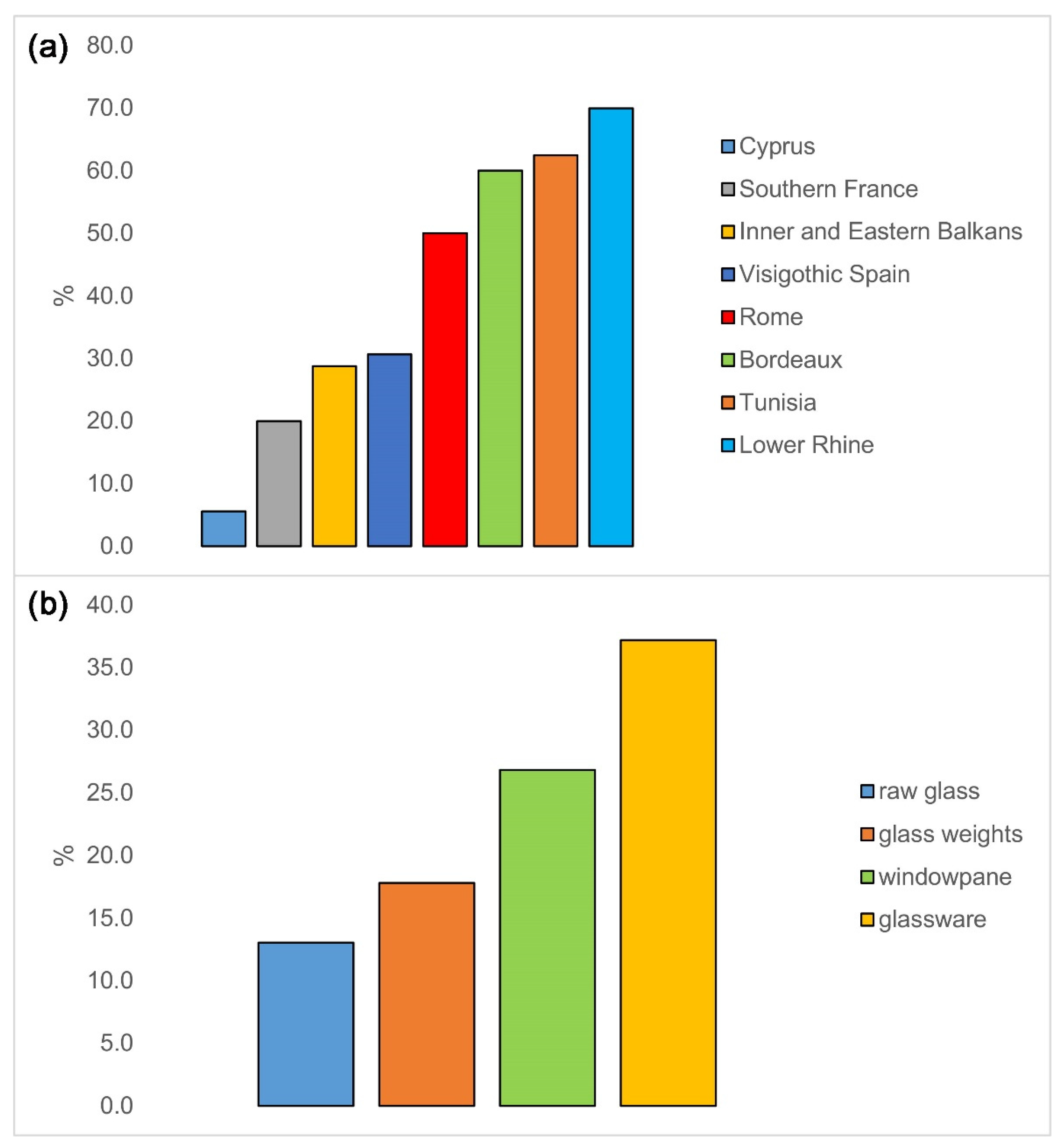
4.3. Distribution of Fe-Rich 2.1
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balvanović, R.; Stojanović, M.M.; Šmit, Ž. Exploring the unknown Balkans: Early Byzantine glass from Jelica Mt in Serbia and its contemporary neighbours. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2018, 317, 1175–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balvanović, R.; Šmit, Ž. Sixth-century AD glassware from Jelica, Serbia—an increasingly complex picture of late antiquity glass composition. Archaeol. Anthr. Sci. 2020, 12, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foy, D.; Picon, M.; Vichy, M.; Thirion-Merle, V. Caractérisation des verres de la fin de l’Antiquité en Méditerranée occidentale: L’émergence de nouveaux courants commerciaux. In Échanges et Commerce du Verre Dans le Monde Antique: Actes du Colloque International de l’Association Française pour l’Archéologie du Verre; Montagnac, Ed.; Mergoil: Drémil-Lafage, France, 2003; pp. 41–86. [Google Scholar]
- Stojanović, M.M.; Šmit, Ž.; Glumac, M.; Mutić, J. PIXE–PIGE investigation of Roman Imperial vessels and window glass from Mt. Kosmaj, Serbia (Moesia Superior). J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2015, 1, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drauschke, J.; Greiff, S. Early Byzantine glass from Caričin Grad/Iustiniana Prima (Serbia): First results concerning the composition of raw glass chunks. In Glass along the Silk Road from 2000 BC to AD 1000; Zorn, B., Hilgner, A., Eds.; Verlag des Römisch-Germanisches Zentralmuseums: Mainz, Germany, 2010; pp. 53–67. [Google Scholar]
- Cholakova, A.; Rehren, T.; Freestone, I.C. Compositional identification of 6th c AD glass from the Lower Danube. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2016, 7, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cholakova, A.; Rehren, T. A Late Antiquity manganese-decolourised glass composition: Interpreting patterns and mechanisms of distribution. In Things that Travelled: Mediterranean Glass in the First Millennium ce; Rosenow, D., Phelps, M., Meek, A., Freestone, I., Eds.; UCL Press: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, S.; Chinni, T.R.; Arletti, R.; Vandini, M. Butrint (Albania) between eastern and western Mediterranean glass production: EMPA and LA-ICP-MS of late antique and early medieval finds. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2014, 49, 6–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milavec, T.; Šmit, Ž. Analyses of glass from late antique hilltop site Korinjski hrib above Veliki Korinj (Slovenia). Arheol. Vestn. 2020, 71, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schibille, N.; Sterrett-Krause, A.; Freestone, I.C. Glass groups, glass supply and recycling in late Roman Carthage. Archeol. Antrhropol. Sci. 2016, 9, 1223–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ceglia, A.; Cosyns, P.; Schibille, N.; Meulebroeck, W. Unravelling provenance and recycling of late antique glass from Cyprus with trace elements. Archaeol. Anthropol. Sci. 2017, 11, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schibille, N.; Meek, A.; Tobias, B.; Entwistle, C.; Avisseau-Broustet, M.; Da Mota, H.; Gratuze, B. Comprehensive chemical characterisation of Byzantine glass weights. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ares, J.J.; Guirado, V.E.; Gutiérrez, Y.C.; Schibille, N. Changes in the supply of eastern Mediterranean glasses to Visigothic Spain. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2019, 107, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, F.; Silvestri, A.; Molin, G. Glass from the Archaeological Museum of Adria (North-East Italy): New insights into Early Roman production technologies. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2013, 40, 2589–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestri, A. The coloured glass of Iulia Felix. J. Archeol. Sci. 2008, 35, 1489–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestri, A.; Molin, G.; Salviulo, G. The colourless glass of Iulia Felix. J. Archeol. Sci. 2008, 35, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, C.M. Making colourless glass in the Roman period. Archaeometry 2005, 47, 763–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nenna, M.D.; Vichy, M.; Picon, M. L’atelier de verrier de Lyon du 1er siècle après J.-C, et l’origine des verre “romains”. Rev. d’Archaéométrie 1997, 21, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltoni, S.; Chinni, T.; Vandini, M.; Cirelli, E.; Silvestri, A.; Molin, G. Archaeological and archaeometric study of the glass finds from the ancient harbour of Classe (Ravenna- Italy): New evidence. Herit. Sci. 2015, 3, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehren, T.; Brüggler, M. The Late Antique glass furnaces in the Hambach Forest were working glass-not making it. J. Archaeol. Sci. Rep. 2020, 29, 102072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, F.; Marcante, A.; Silvestri, A.; Molin, G. The glass of the “Casa delle Bestie Ferite”: A first systematic archaeometric study on Late Roman vessels from Aquileia. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2014, 41, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barfod, G.H.; Freestone, I.C.; Lesher, C.E.; Lichtenberger, A.; Raja, R. ‘Alexandrian’ glass confirmed by hafnium isotopes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirti, P.; Lepora, A.; Saguì, L. Scientific analysis of fragments from the seventh-century glass Crypta Balbi in Rome. Archaeometry 2000, 42, 359–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velde, B. Aluminum and calcium oxide content of glass found in western and northern Europe, first to ninth centuries. Oxf. J. Archaeol. 1990, 9, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestri, A.; Tonietto, S.; Molin, G. The palaeo-Christian glass mosaic of St. Prosdocimus (Padova, Italy): Archaeometric characterization of ‘gold’ tesserae. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2011, 38, 3402–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltoni, S.; Silvestri, A.; Marcante, A.; Molin, G. The transition from Roman to Late Antiquity glass: New insights from the Domus of Tito Macro in Aquilea (Italy). J. Archaeol. Sci. 2016, 73, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, H.E.; Jackson, C.M. The composition of late Romano-British colourless vessel glass: Glass production and consumption. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2010, 37, 3068–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedepohl, K.H.; Pirling, R.; Hartmann, G. Römische und fränkische Glaäser aus dem Gräberfeld von Krefeld-Gellep. Bonn. Jahrbücher 1997, 197, 177–189. [Google Scholar]
- Stamenković, S.Z. Glass Production Technology and Production Centres in Dacia Mediterranea. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Belgrade, Faculty of Philosophy, Department of Archaeology, Belgrade, Sebia, 2015. Available online: https://nardus.mpn.gov.rs/handle/123456789/4259?locale-attribute=en (accessed on 20 July 2021). (In Serbian).
- Freestone, I.C.; Hughes, M.J.; Stapleton, C.P. The composition and production of Anglo-Saxon glass. In Catalogue of Anglo-Saxon Glass in the British Museum; Evison, V.I., Ed.; BMP: London, UK, 2008; pp. 29–46. [Google Scholar]
- Gorin-Rosen, Y. The Ancient Glass Industry in Israel: Summary of the Finds and New Discoveries. In La Route du Verre: Ateliers Primaires et Secondaires du Second Millénaire av. J.-C. au Moyen Âge; Nenna, M.-D., Ed.; Maison de l’Orient et de la Méditerranée Jean Pouilloux: Lyon, France, 2000; pp. 49–63. [Google Scholar]
- Ceglia, A.; Cosyns, P.; Nys, K.; Terryn, H.; Thienpont, H.; Meulebroeck, W. Late antique glass distribution and consumption in Cyprus: A chemical Study. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2015, 61, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gliozzo, E.; Turchiano, M.; Giannetti, F.; Santagostino, B.A. Late Antique glass vessels and production indicators from the town of Herdonia (Foggia, Italy): New data on CaO-rich/weak HIMT glass. Archaeometry 2015, 58, 81–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gliozzo, E.; Braschi, E.; Giannetti, F.; Langone, A.; Turchiano, M. New geochemical and isotopic insights into the Late Antique Apulian glass and the HIMT1 and HIMT2 glass productions—The glass vessels from San Giusto (Foggia, Italy) and the diagrams for provenance studies. Archaeol. Anthropol. Sci. 2019, 11, 141–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brill, R.H. Scientific investigations of Jalame glass and related finds. In Excavations in Jalame: Site of a Glass Factory in Late Roman Palestine; Weinberg, G.D., Ed.; University of Missouri: Columbia, MO, USA, 1988; pp. 257–294. [Google Scholar]
- Baxter, M.J.; Buck, C.E. Data handling and statistical analysis. In Modern Analytical Methods in Art and Archaeology; Ciliberto, E., Spoto, G., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 681–746. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, H.; Jackson, C. The composition of ‘naturally coloured’ late Roman vessel glass from Britain and the implications for models of glass production and supply. J. Archeol. Sci. 2009, 36, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehren, T.; Cholakova, A. The early Byzantine HIMT glass from Dichin, Northern Bulgaria, UCL. Interdiscip. Stud. 2010, 22, 81–96. [Google Scholar]
- Shortland, A.; Rogers, N.; Eremin, K. Trace element discriminants between Egyptian and Mesopotamian Late Bronze Age glasses. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2007, 34, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åström, M. Abundance and fractionation patterns of rare earth elements in streams affected by acid sulphate soils. Chem. Geol. 2001, 175, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åström, M.; Corin, N. Distribution of rare earth elements in anionic, cationic and particulate fractions in boreal humus-rich streams affected by acid sulphate soils. Water Res. 2003, 37, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedepohl, K.H.; Baumann, A. The use of marine molluskan shells for Roman glass and local raw glass production in the Eifel area (western Germany). Naturwissenschaften 2000, 87, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wedepohl, K.H.; Gaitzsch, W.; Follmann-Shultz, A.-B. Glassmaking and Glassworking in Six Roman Factories in the Hambach Forest, Germany. Ann. AIHV 2003, 15, 53–55. [Google Scholar]
- Schibille, N.; Freestone, I.C. Composition, production and procurement of glass at San Vincenzo Al Volturno: An early Medieval monastic complex in Southern Italy. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freestone, I.C.; Degryse, P.; Lankton, J.; Gratuze, B.; Schneider, J. HIMT, glass composition and the commodity branding in the primary glass industry. In Things That Travelled, Mediterranean Glass in the First Millennium CE; Rosenow, D., Phelps, M., Meek, A., Freestone, I., Eds.; UCL Press, University College London: London, UK, 2018; pp. 159–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamber, B.S.; Greig, A.; Collerson, K.D. A new estimate for the composition of weathered young upper continental crust from alluvial sediments, Queensland, Australia. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2005, 69, 1041–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arletti, R.; Vezzalini, G.; Benati, S.; Mazzeo Saracino, L.; Gamberini, A. Roman Window Glass: A Comparison of Findings from Three Different Italian Sites. Archaeometry 2010, 52, 252–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.; Henderson, J.; Faber, E.W. Early Byzantine glass supply and consumption: The case of Dichin, Bulgaria. In Recent Advances in the Scientific Research On Ancient Glass And Glaze; Gan, F., Li, Q., Henderson, J., Eds.; World Scientific: Singapore, 2016; pp. 207–231. [Google Scholar]
- Siu, I.; Henderson, J.; Faber, E. The production and circulation of Carthaginian glass under the rule of the romans and the vandals (fourth to sixth century ad): A chemical investigation. Archaeometry 2017, 59, 255–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freestone, I.C. Primary glass sources in the mid first millennium AD. In Proceedings of the Annales du 15e Congrès de l’Association Internationale pour l’Histoire du Verre, Corning, NY, USA, 15–20 October 2003; Nottingham AIHV and Authors, UK. pp. 111–115. [Google Scholar]
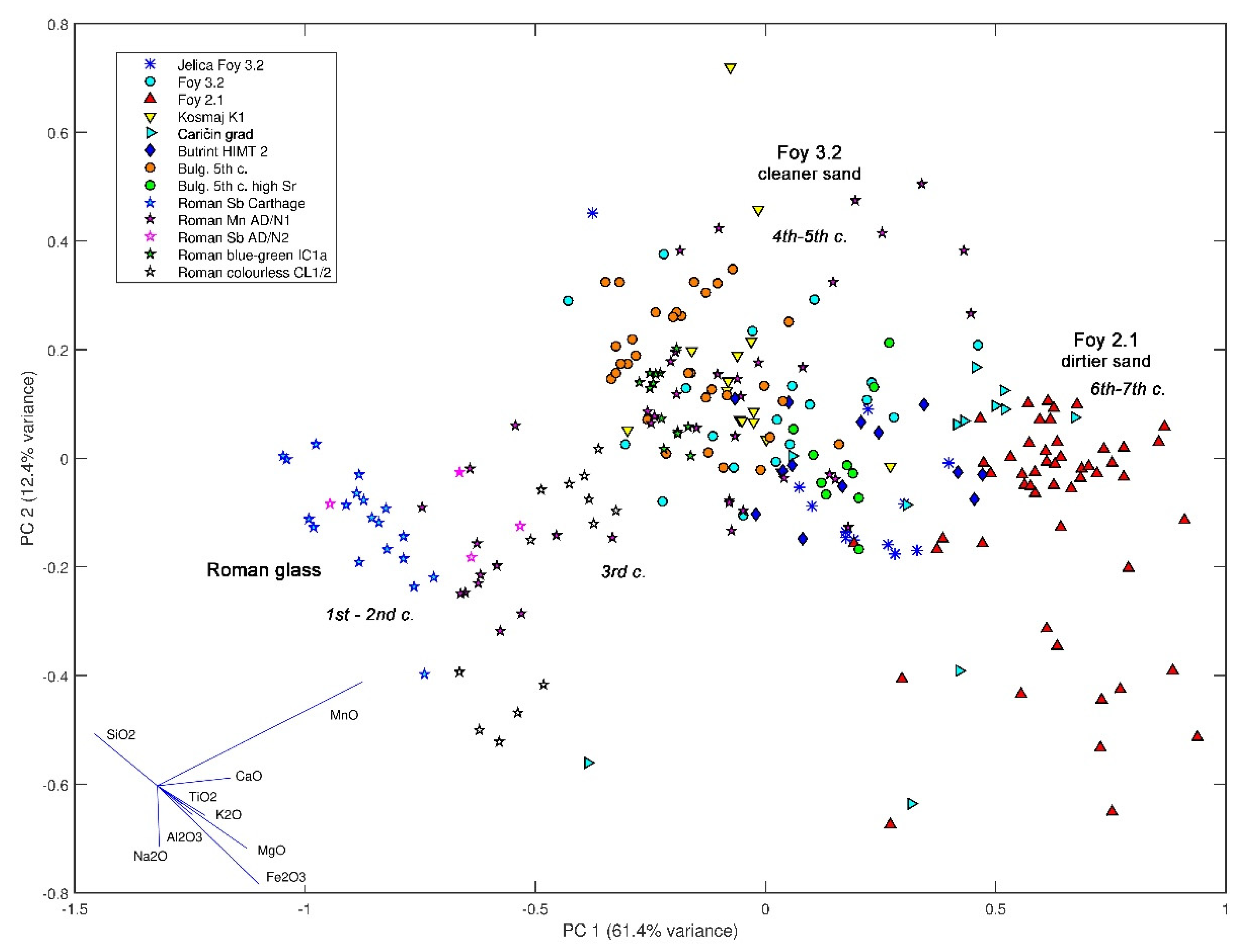
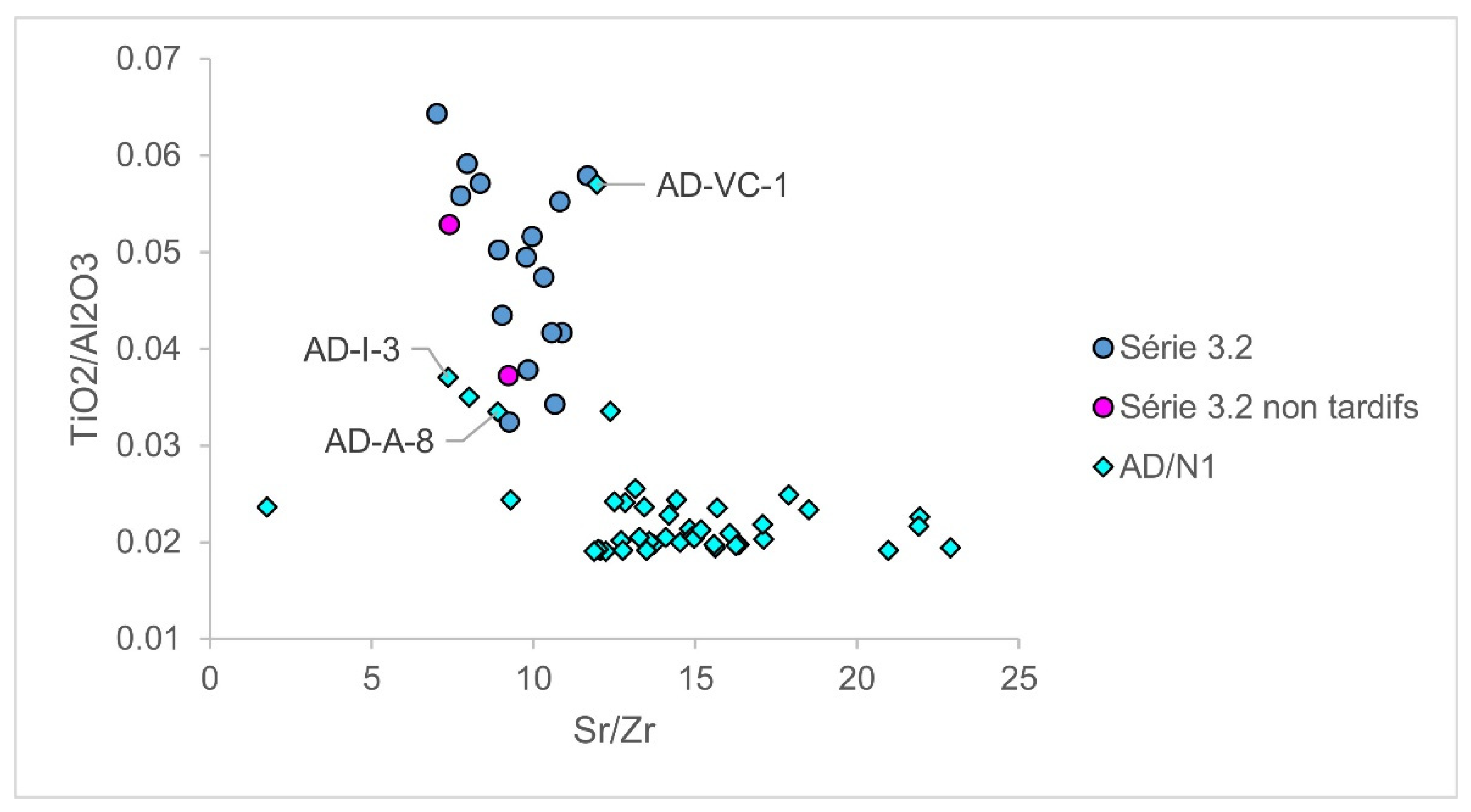
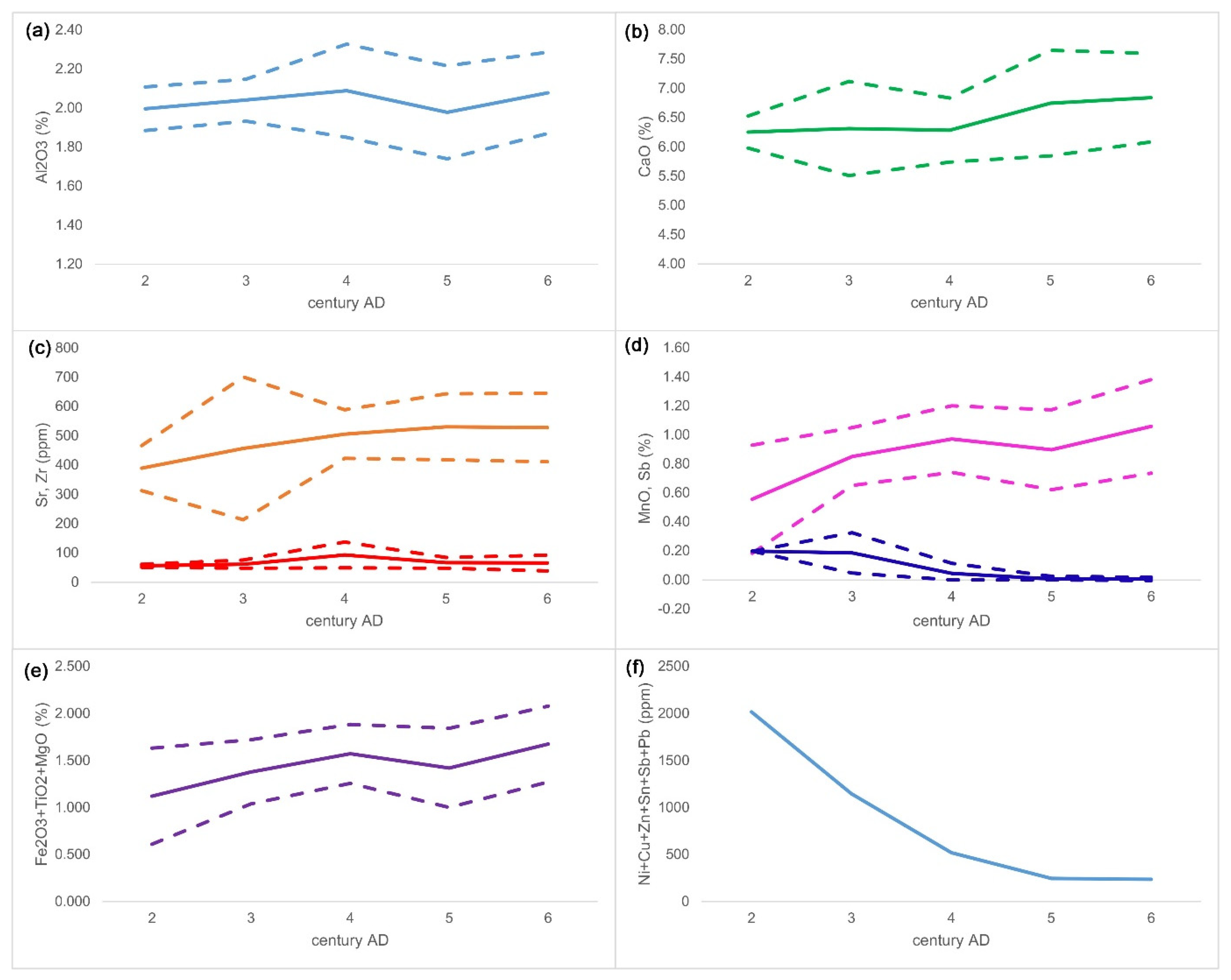
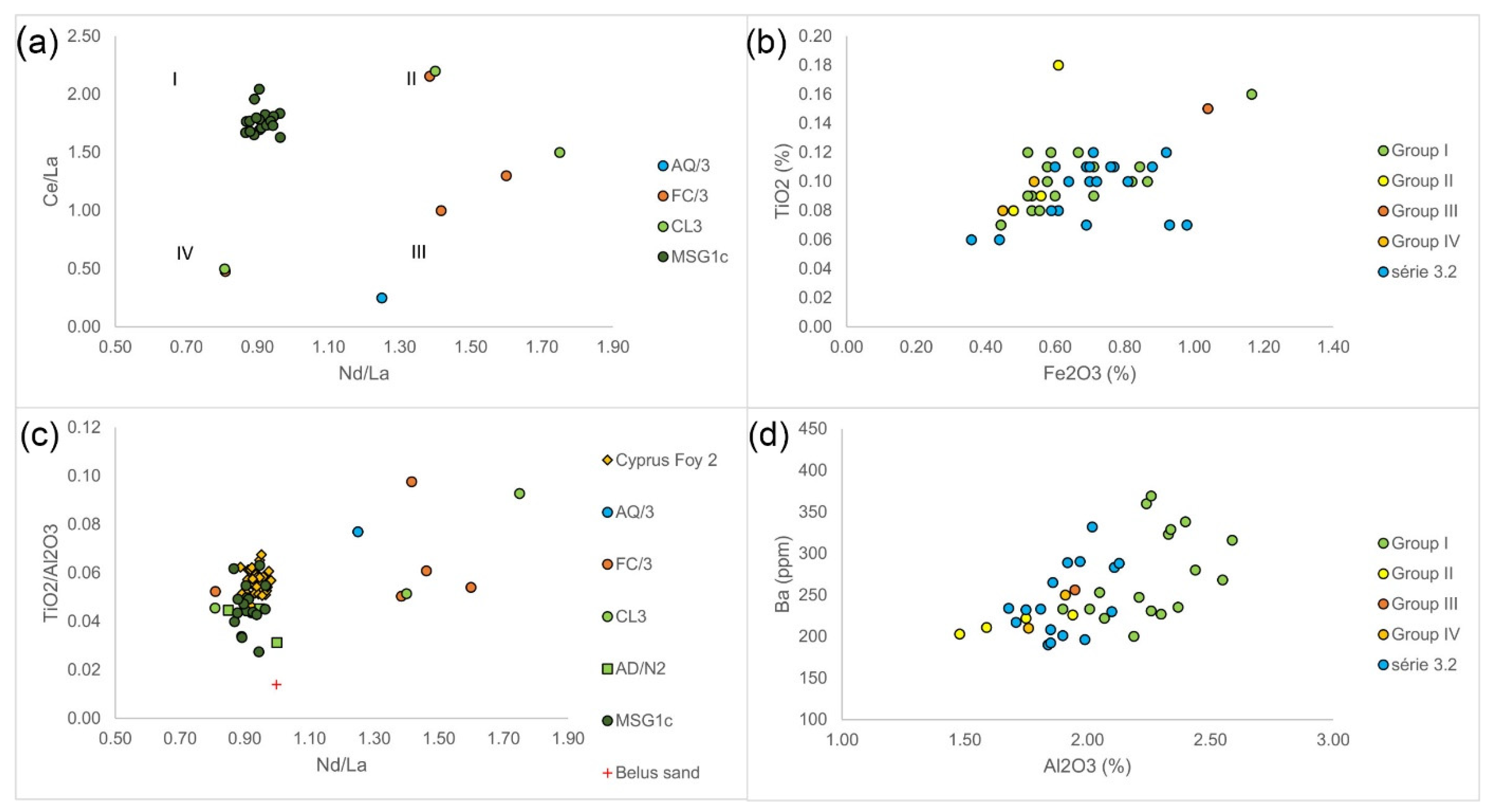
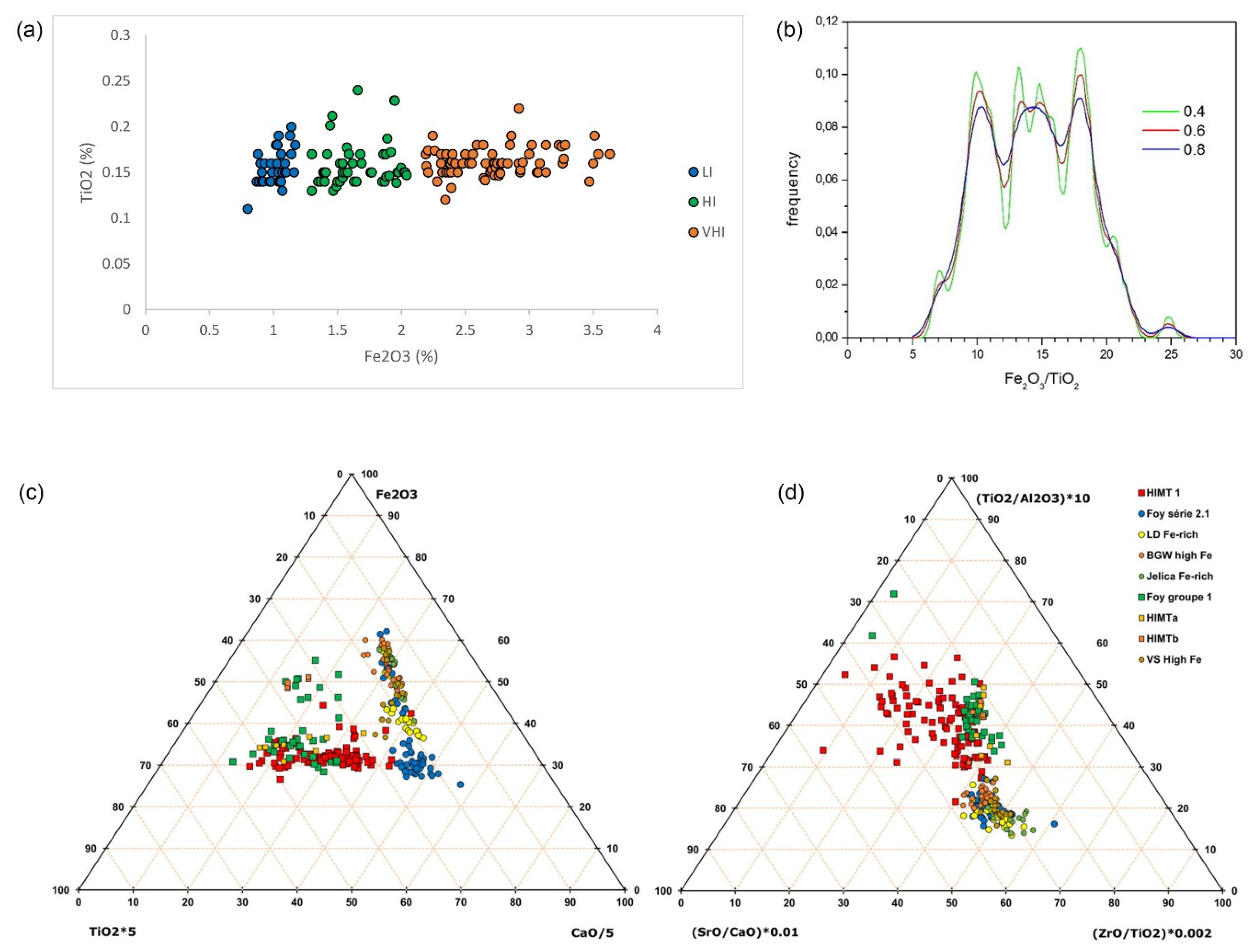
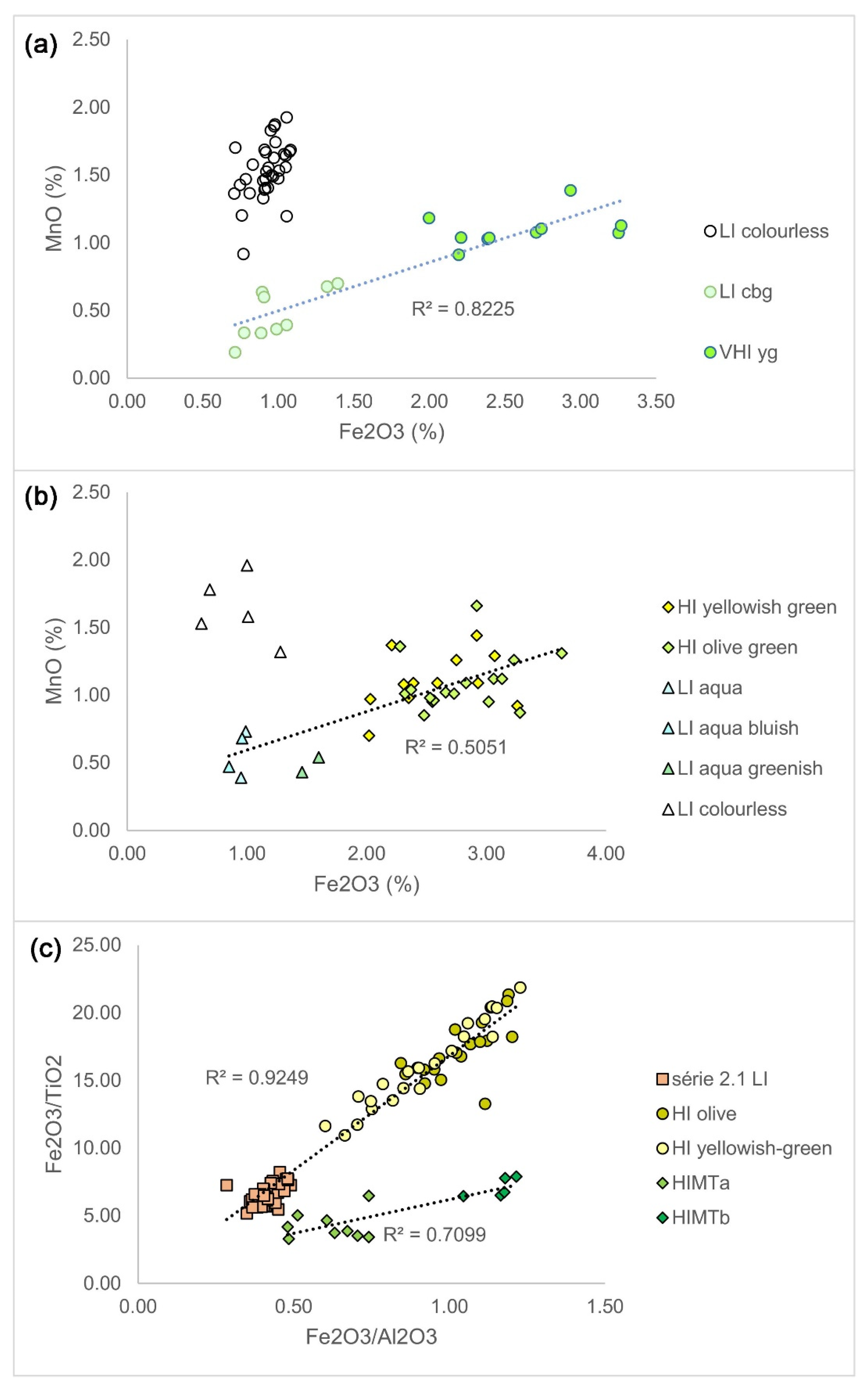
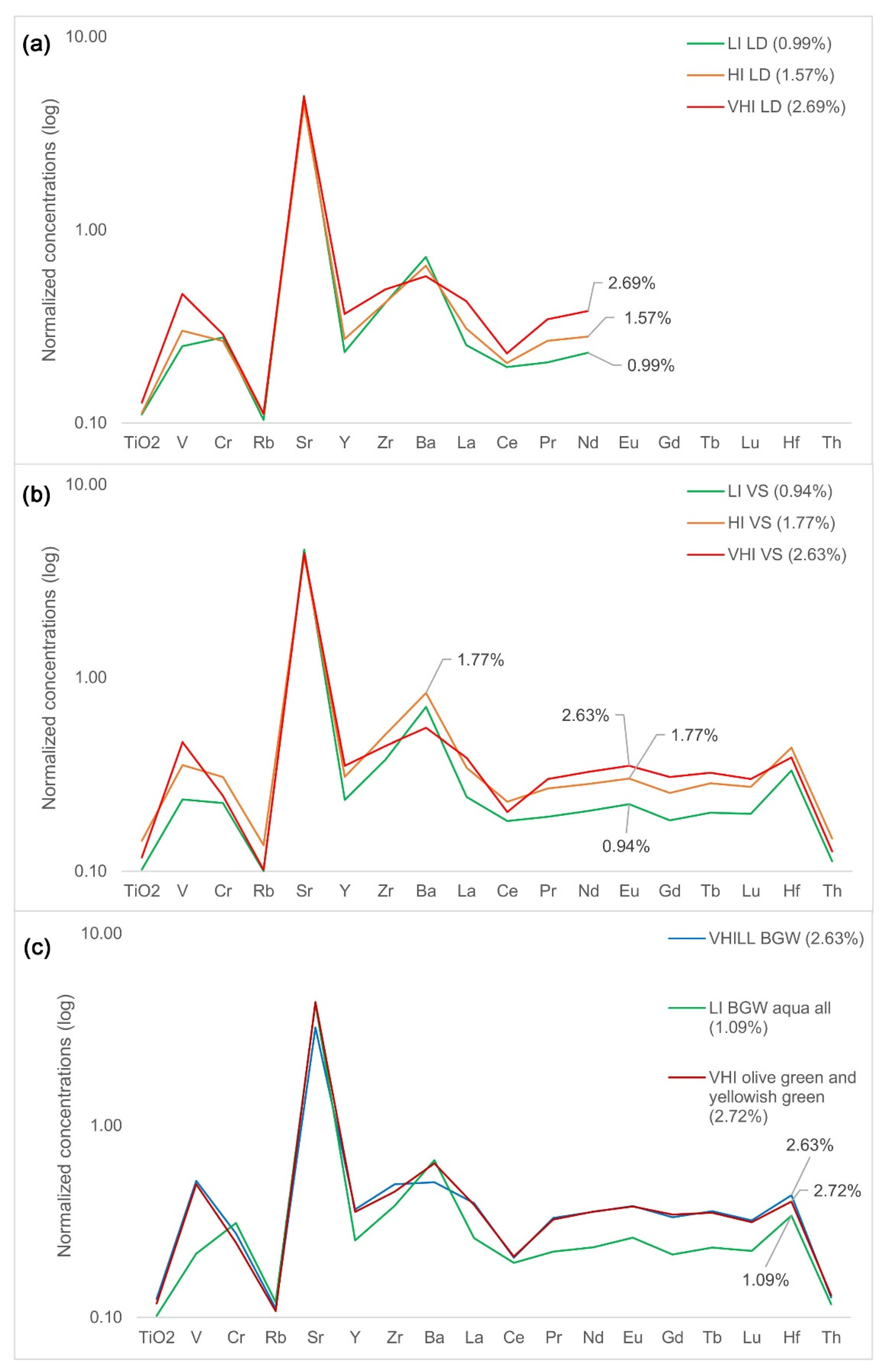
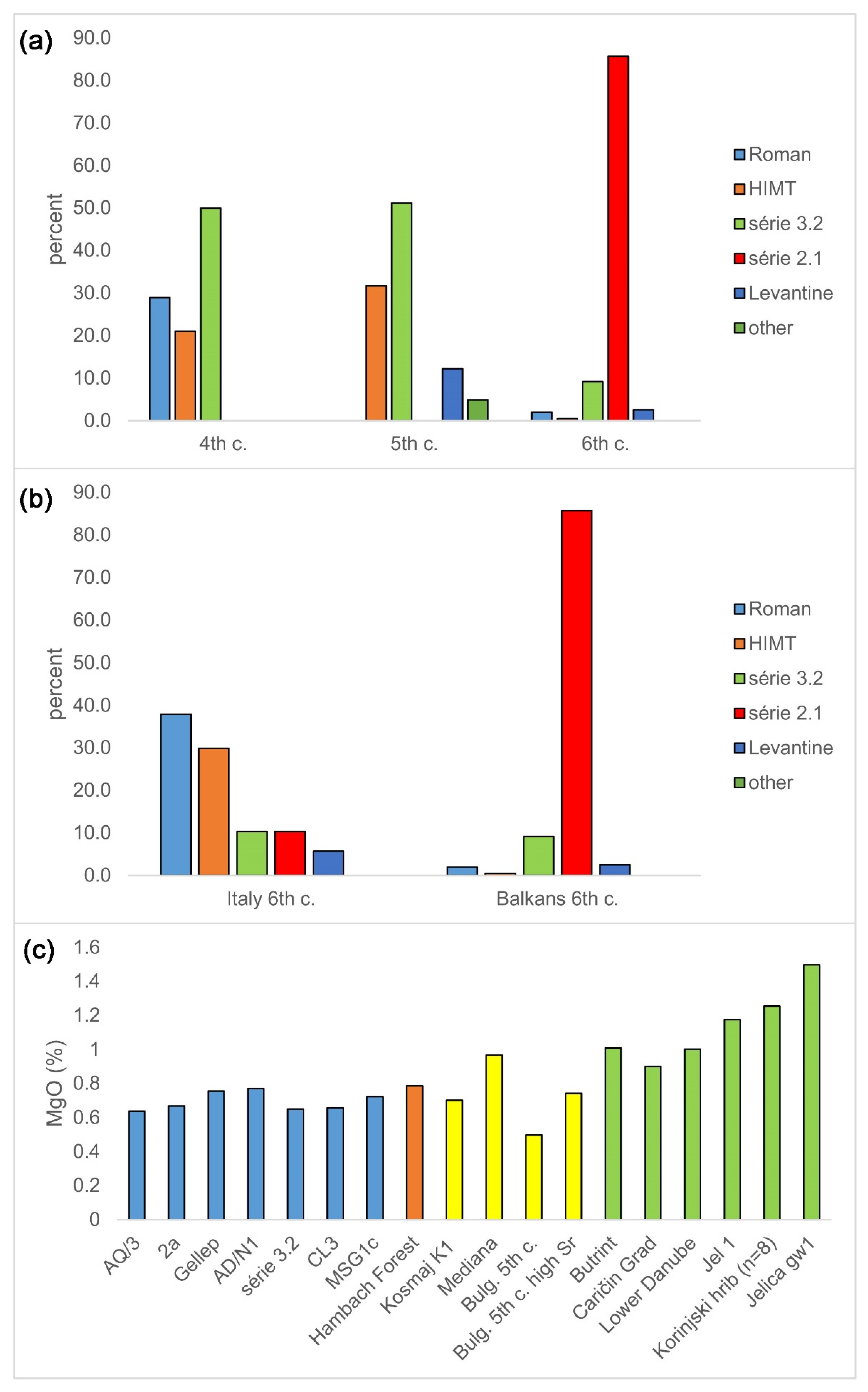
| Group | Cent. AD | (Fe2O3 + TiO2 + MgO)/SiO2 | (Al2O3 + K2O + CaO)/SiO2 | Sum | TiO2/Al2O3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roman glass n = 227 | 1st–4th | 0.019 | 0.156 | 0.175 | 0.05 |
| AD/N1 (Mn added) n = 45 | 1st–4th | 0.017 ± 0.004 | 0.158 ± 0.014 | 0.174 ± 0.016 | 0.024 ± 0.009 |
| AD/N2 (Sb added) n = 4 | 2nd–3rd | 0.014 ± 0.003 | 0.112 ± 0.007 | 0.127 ± 0.010 | 0.047 ± 0.015 |
| série 3.2 (non-t.) n = 2 | 1st–2nd | 0.023 ± 0.003 | 0.124 ± 0.007 | 0.147 ± 0.009 | 0.045 ± 0.011 |
| série 3.2 n = 17 | 5th/6th | 0.021 ± 0.004 | 0.138 ± 0.016 | 0.159 ± 0.020 | 0.049 ± 0.009 |
| série 2.1 n = 51 | 6th–7th | 0.043 ± 0.011 | 0.173 ± 0.012 | 0.216 ± 0.016 | 0.062 ± 0.007 |
| Original Classification | Group/Location | n | Nd/La ppm/ppm | Ce/La ppm/ppm | Zr/TiO2 ppm/pm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Foy 3.2 | Group IV | 2 | 0.81 ± 0.00 | 0.49 ± 0.02 | 56.88 ± 4.42 |
| Foy 2.1 Fe-rich | Lower Danube | 23 | 0.91 ± 0.03 | 1.44 ± 0.17 | 74.92 ± 4.78 |
| Foy 3.2 | Group I (MSG1c) | 18 | 0.91 ± 0.03 | 1.77 ± 0.10 | 49.98 ± 6.58 |
| Foy 2 High-Fe | Yeroskipou | 2 | 0.92 ± 0.01 | 1.19 ± 0.22 | 52.58 ± 0.88 |
| Foy 2.1 | Lower Danube | 43 | 0.92 ± 0.05 | 1.77 ± 0.12 | 74.71 ± 4.62 |
| Ca-rich HIMT | Herdonia | 4 | 0.93 ± 0.02 | 1.66 ± 0.10 | 72.80 ± 10.10 |
| HIMT 2 | San Giusto | 9 | 0.93 ± 0.03 | 1.69 ± 0.09 | 60.90 ± 2.95 |
| Foy 2 High-Fe | Byz. glass weights | 31 | 0.93 ± 0.04 | 1.19 ± 0.09 | 55.86 ± 2.80 |
| Roman Sb | AD/N2 | 4 | 0.93 ± 0.08 | 1.81 ± 0.04 | 63.70 ± 6.12 |
| Foy 2 | Yeroskipou | 34 | 0.94 ± 0.02 | 1.68 ± 0.07 | 53.44 ± 3.57 |
| Levantine | San Giusto | 21 | 0.94 ± 0.05 | 1.74 ± 0.08 | 62.30 ± 5.86 |
| Foy 2 | Byz. glass weights | 85 | 0.95 ± 0.04 | 1.63 ± 0.10 | 56.78 ± 3.69 |
| HIT | Cyprus | 2 | 0.96 ± 0.00 | 1.90 ± 0.01 | 53.96 ± 9.95 |
| High Mn Lev 1 | Cyprus | 6 | 0.96 ± 0.02 | 1.71 ± 0.07 | 54.58 ± 4.54 |
| Roman Mn | AD/N1 | 43 | 0.96 ± 0.06 | 1.82 ± 0.12 | 69.12 ± 67.43 |
| HIMTb | Cyprus | 5 | 0.98 ± 0.02 | 1.28 ± 0.08 | 45.95 ± 0.77 |
| HIMTa | Cyprus | 14 | 1.00 ± 0.05 | 1.77 ± 0.13 | 48.05 ± 4.29 |
| Foy 3.2 | AQ/3 | 1 | 1.25 ± 0.00 | 0.25 ± 0.00 | 52.67 ± 0.00 |
| Foy 3.2 | FC/3 | 4 | 1.30 ± 0.34 | 1.23 ± 0.70 | 58.19 ± 4.50 |
| Foy 3.2 | CL3 | 3 | 1.32 ± 0.48 | 1.40 ± 0.85 | 54.40 ± 3.11 |
| Foy 3.2 | Group III | 2 | 1.33 ± 0.12 | 0.63 ± 0.53 | 52.08 ± 0.82 |
| Foy 3.2 | Group II | 4 | 1.53 ± 0.17 | 1.79 ± 0.46 | 57.67 ± 4.25 |
| LI Série 2.1 | HI | VHI | VHILL | Total Fe-Rich | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 38 | n = 47 | n = 74 | n = 4 | n = 125 | ||||||
| wto% | aver. | std | aver. | std | aver. | std | aver. | std | aver. | std |
| Na2O | 18.46 | 1.26 | 17.67 | 2.76 | 17.63 | 1.19 | 17.43 | 0.62 | 17.78 | 1.20 |
| MgO | 1.21 | 0.15 | 1.28 | 0.29 | 1.32 | 0.21 | 0.98 | 0.11 | 1.28 | 0.22 |
| Al2O3 | 2.49 | 0.13 | 4.02 | 9.06 | 2.78 | 0.26 | 2.67 | 0.18 | 2.75 | 0.26 |
| SiO2 | 64.50 | 1.08 | 63.81 | 9.55 | 64.61 | 1.22 | 67.88 | 0.79 | 64.93 | 1.48 |
| K2O | 0.76 | 0.14 | 1.00 | 0.87 | 0.91 | 0.17 | 0.66 | 0.03 | 0.89 | 0.17 |
| CaO | 7.97 | 0.65 | 7.34 | 1.21 | 7.48 | 0.59 | 5.43 | 0.20 | 7.42 | 0.68 |
| TiO2 | 0.16 | 0.02 | 0.18 | 0.13 | 0.16 | 0.01 | 0.16 | 0.02 | 0.16 | 0.02 |
| MnO | 1.69 | 0.31 | 1.06 | 0.43 | 1.14 | 0.25 | 1.11 | 0.12 | 1.11 | 0.32 |
| Fe2O3 | 1.03 | 0.11 | 1.64 | 0.21 | 2.69 | 0.41 | 2.57 | 0.15 | 2.29 | 0.61 |
| ppm | ||||||||||
| NiO | 14 | 9 | 30 | 15 | 27 | 17 | 27 | 15 | ||
| CuO | 75 | 25 | 92 | 27 | 115 | 47 | 83 | 12 | 106 | 43 |
| ZnO | 60 | 110 | 48 | 18 | 46 | 14 | 46 | 16 | ||
| SrO | 798 | 86 | 701 | 147 | 715 | 99 | 433 | 222 | 705 | 120 |
| ZrO2 | 111 | 14 | 108 | 24 | 117 | 18 | 100 | 67 | 114 | 20 |
| SnO2 | 16 | 13 | 8 | 8 | 1 | 1 | 10 | 10 | ||
| PbO | 130 | 140 | 87 | 70 | 106 | 92 | 20 | 36 | 97 | 86 |
| Sb2O3 | 188 | 289 | 155 | 75 | 134 | 119 | 12 | 13 | 135 | 107 |
| Site/Collection | Type of Object | Fe-Rich Foy 2.1 | Total Foy 2.1 | Percent Fe-Rich |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jelica | windowpane, glassware | 16 | 63 | 25 |
| Caričin grad | raw glass | 2 | 24 | 8 |
| Serdica | glassware, raw glass | 4 | 17 | 23 |
| Odartsi | glassware | 21 | 44 | 48 |
| Dichin | glassware, windowpane | 5 | 19 | 26 |
| Cyprus | not specified | 2 | 36 | 6 |
| Krefeld-Gellep | glassware, bead | 5 | 8 | 62 |
| Köln | glassware | 2 | 2 | 100 |
| Crypta Balbi | glassware, windowpane | 4 | 8 | 50 |
| Bordeaux | raw glass | 3 | 5 | 60 |
| Marseille | glassware, raw glass, debris | 1 | 6 | 17 |
| Gémenos | glassware | 4 | 4 | 100 |
| Nabeul | glassware | 4 | 6 | 67 |
| Sidi Jdidi | glassware | 1 | 2 | 50 |
| Maguelone | glassware, raw glass, debris | 1 | 20 | 5 |
| Visigothic Spain | glassware | 19 | 62 | 31 |
| Byzantine glass weights | glass weights | 31 | 174 | 18 |
| Total | 125 | 500 | 25.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Balvanović, R.V.; Šmit, Ž. Emerging Glass Industry Patterns in Late Antiquity Balkans and Beyond: New Analytical Findings on Foy 3.2 and Foy 2.1 Glass Types. Materials 2022, 15, 1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15031086
Balvanović RV, Šmit Ž. Emerging Glass Industry Patterns in Late Antiquity Balkans and Beyond: New Analytical Findings on Foy 3.2 and Foy 2.1 Glass Types. Materials. 2022; 15(3):1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15031086
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalvanović, Roman V., and Žiga Šmit. 2022. "Emerging Glass Industry Patterns in Late Antiquity Balkans and Beyond: New Analytical Findings on Foy 3.2 and Foy 2.1 Glass Types" Materials 15, no. 3: 1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15031086
APA StyleBalvanović, R. V., & Šmit, Ž. (2022). Emerging Glass Industry Patterns in Late Antiquity Balkans and Beyond: New Analytical Findings on Foy 3.2 and Foy 2.1 Glass Types. Materials, 15(3), 1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15031086






