Research on Vibration Control Technology of Robot Motion Based on Magnetorheological Elastomer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
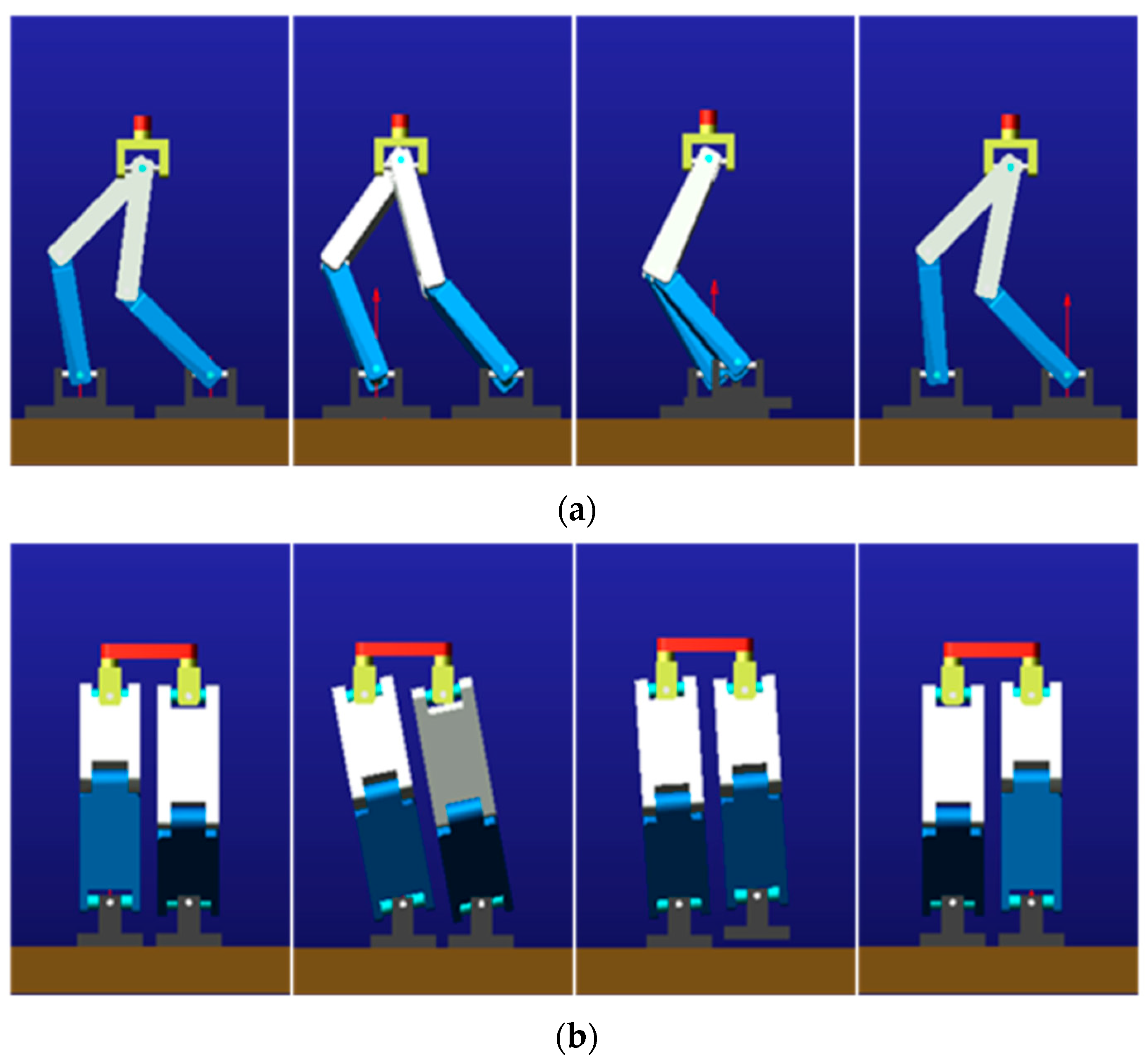
2. Simulation of Bipedal Robot Dynamics
3. Design and Experimentation of MRE Vibration Isolators for Robot Feet
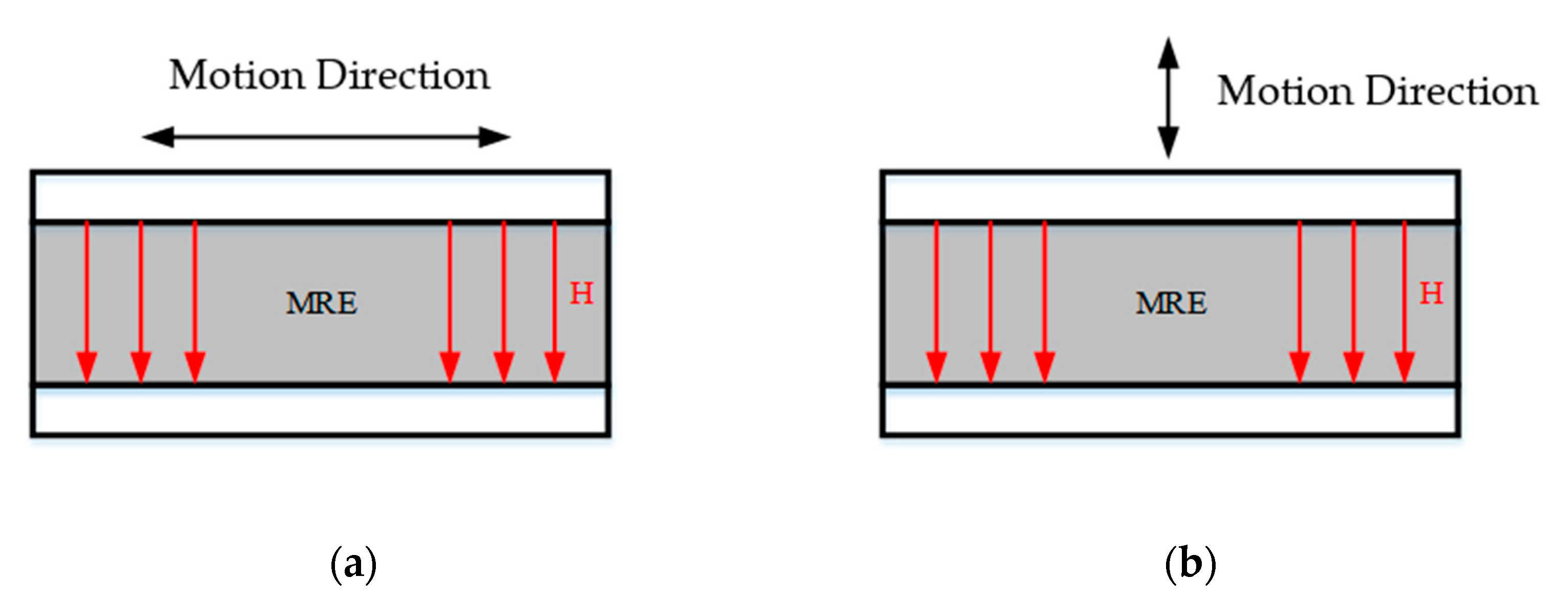
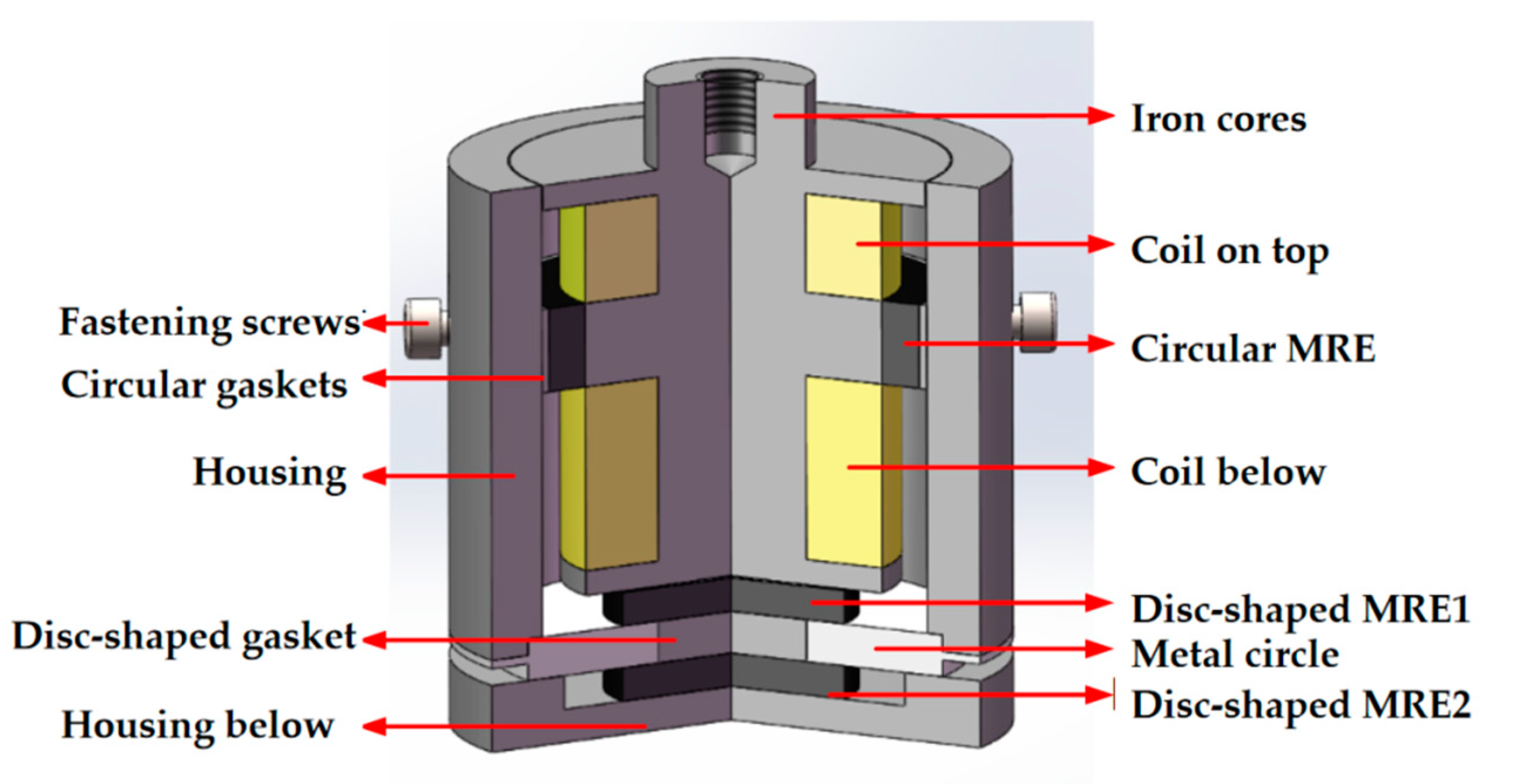
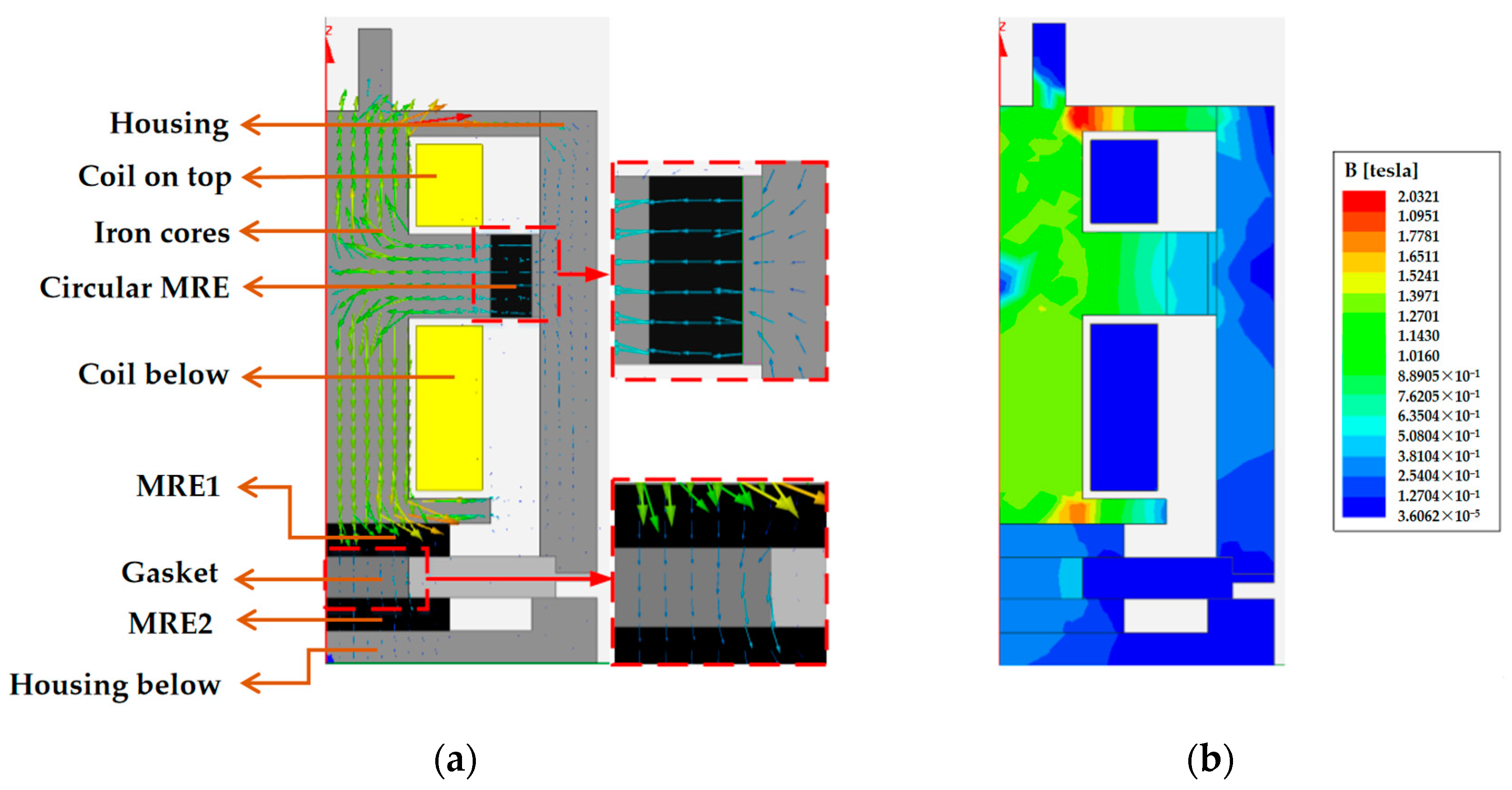
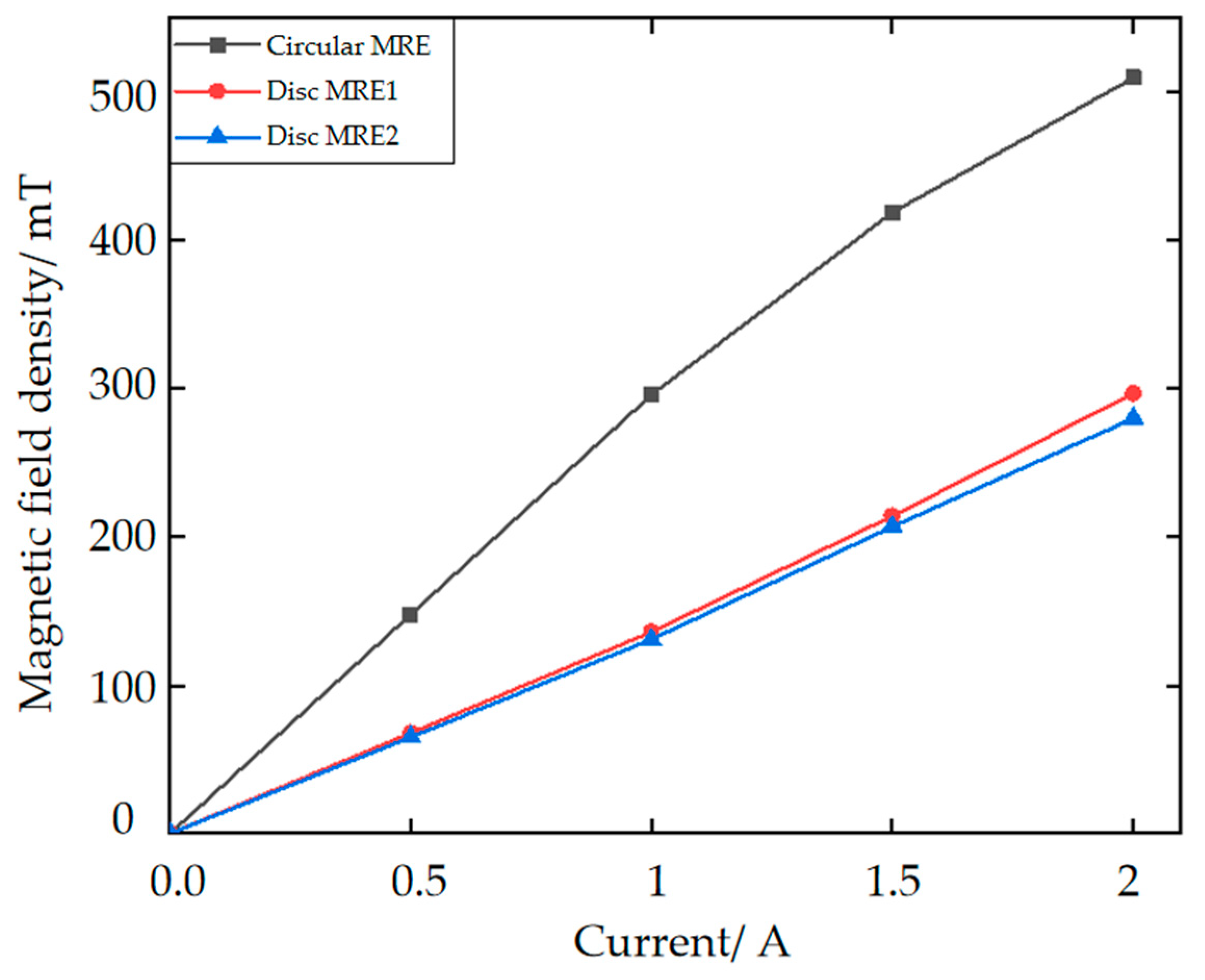
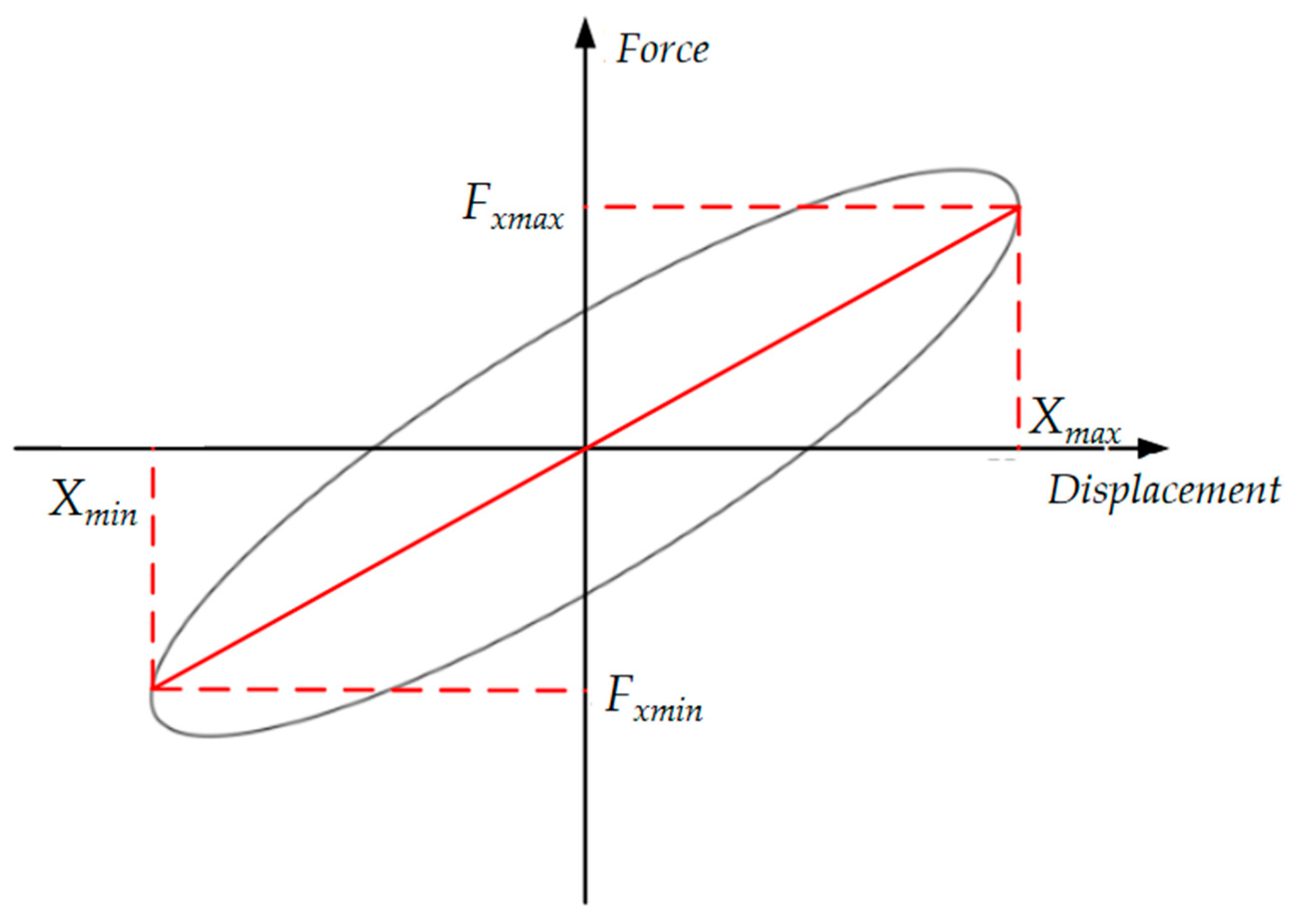
3.1. Magnetorheological Elastomer-Based Vibration Isolator Design and Vibration Damping Performance Testing
3.2. Dynamical Modeling of the Magnetorheological Elastomeric Vibration Isolator
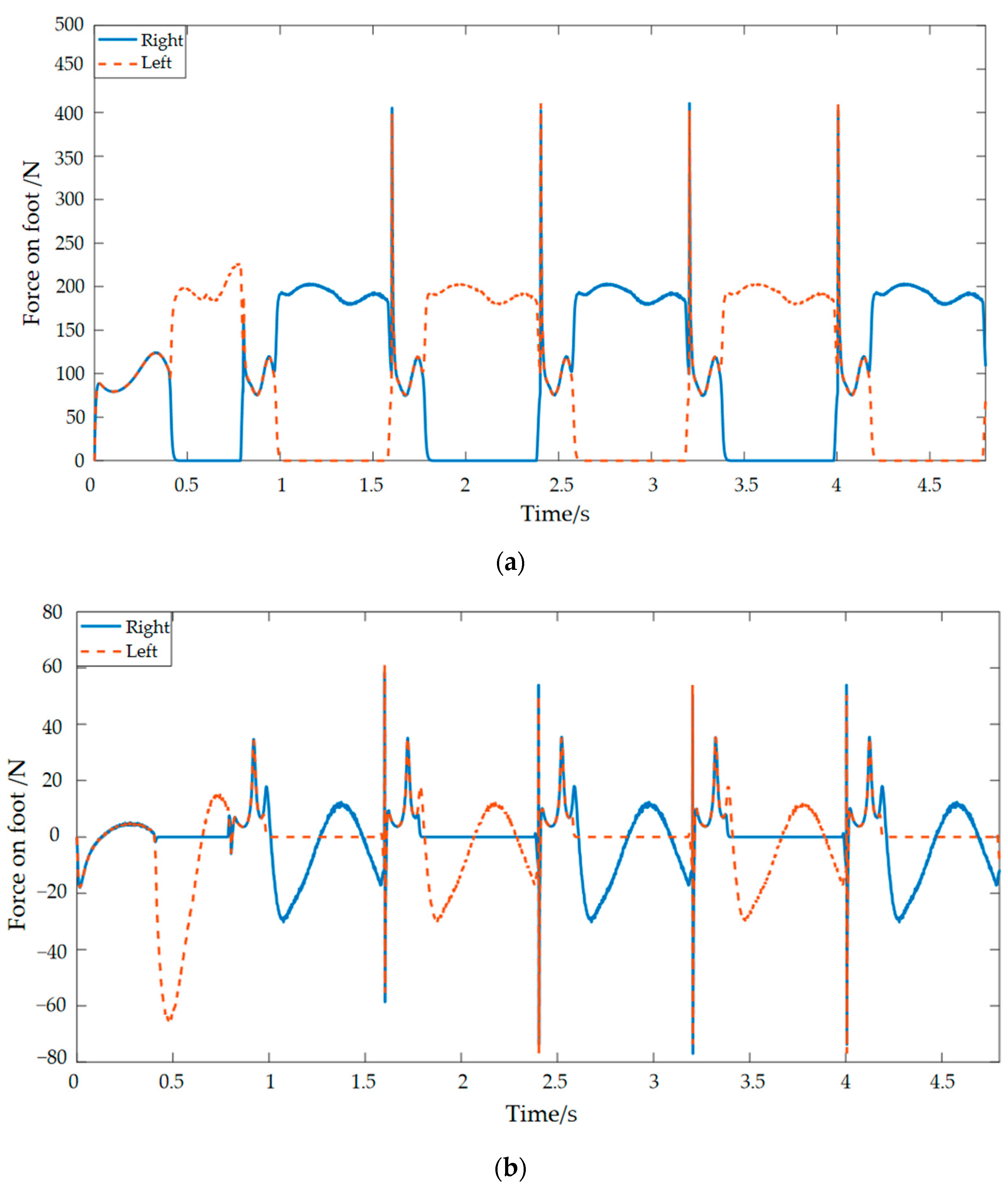
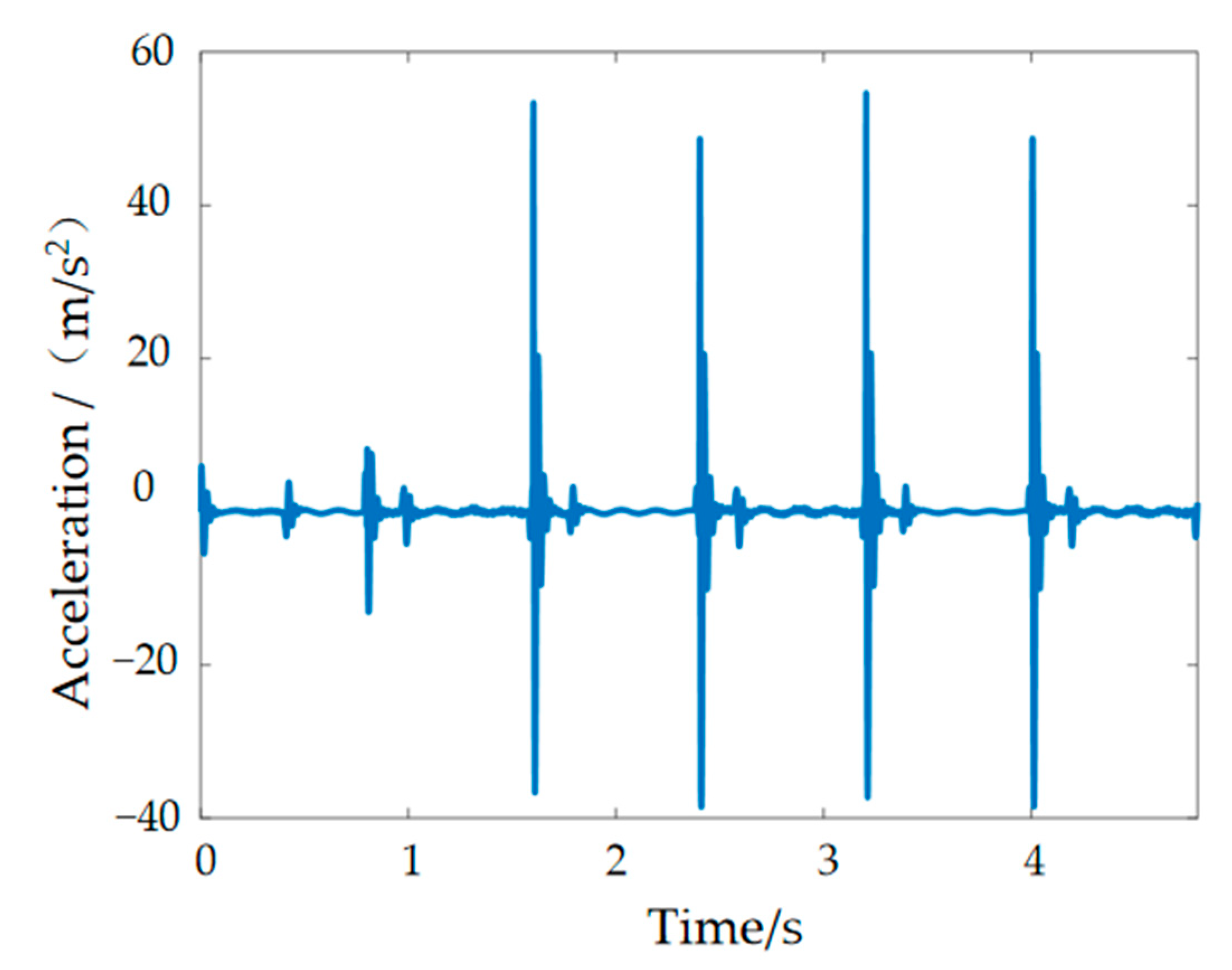
4. Simulation Experiments of Control Algorithms Based on Foot–Ground Signals
4.1. Fuzzy Control
4.2. PID Control
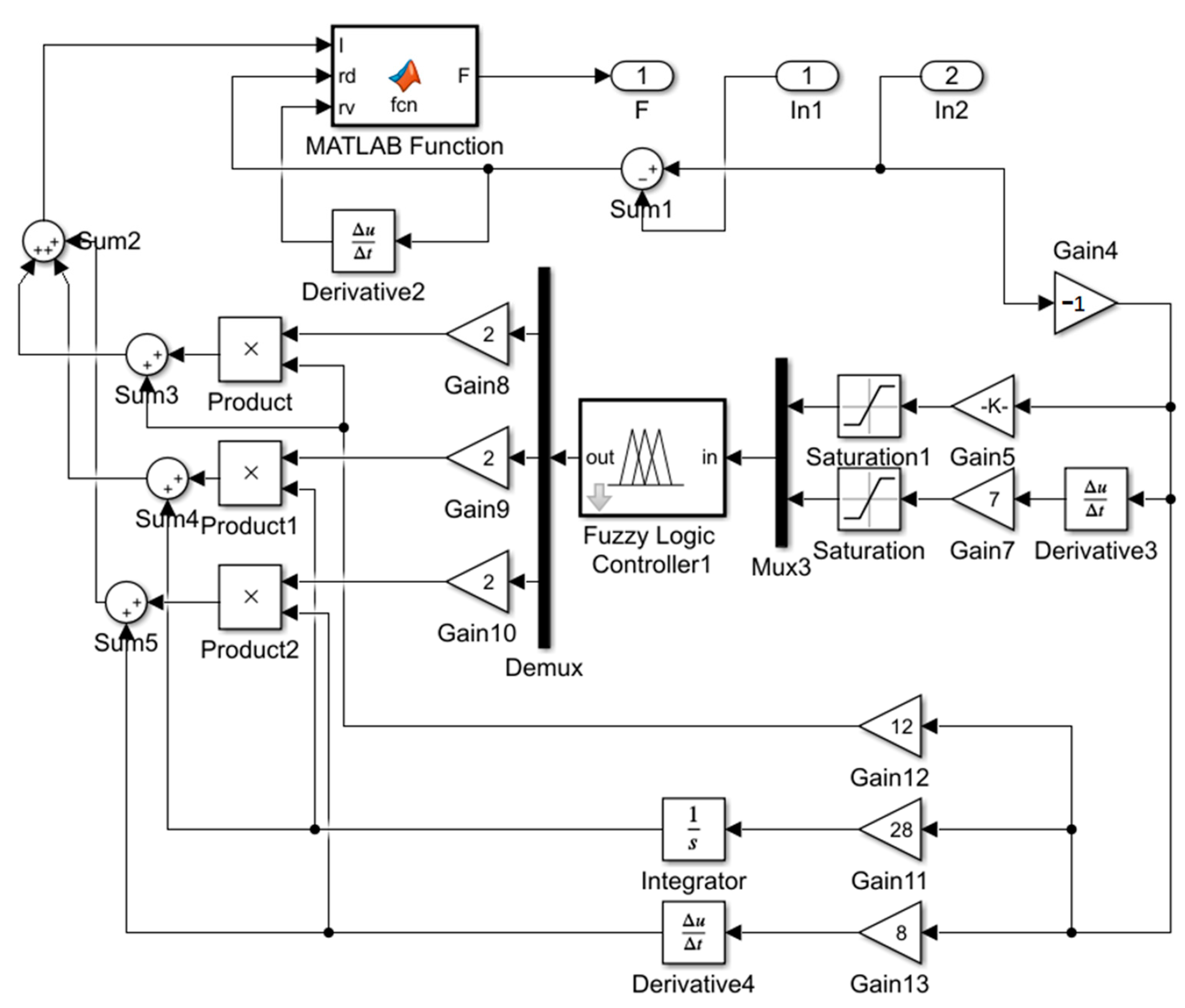
4.3. Fuzzy PID Control
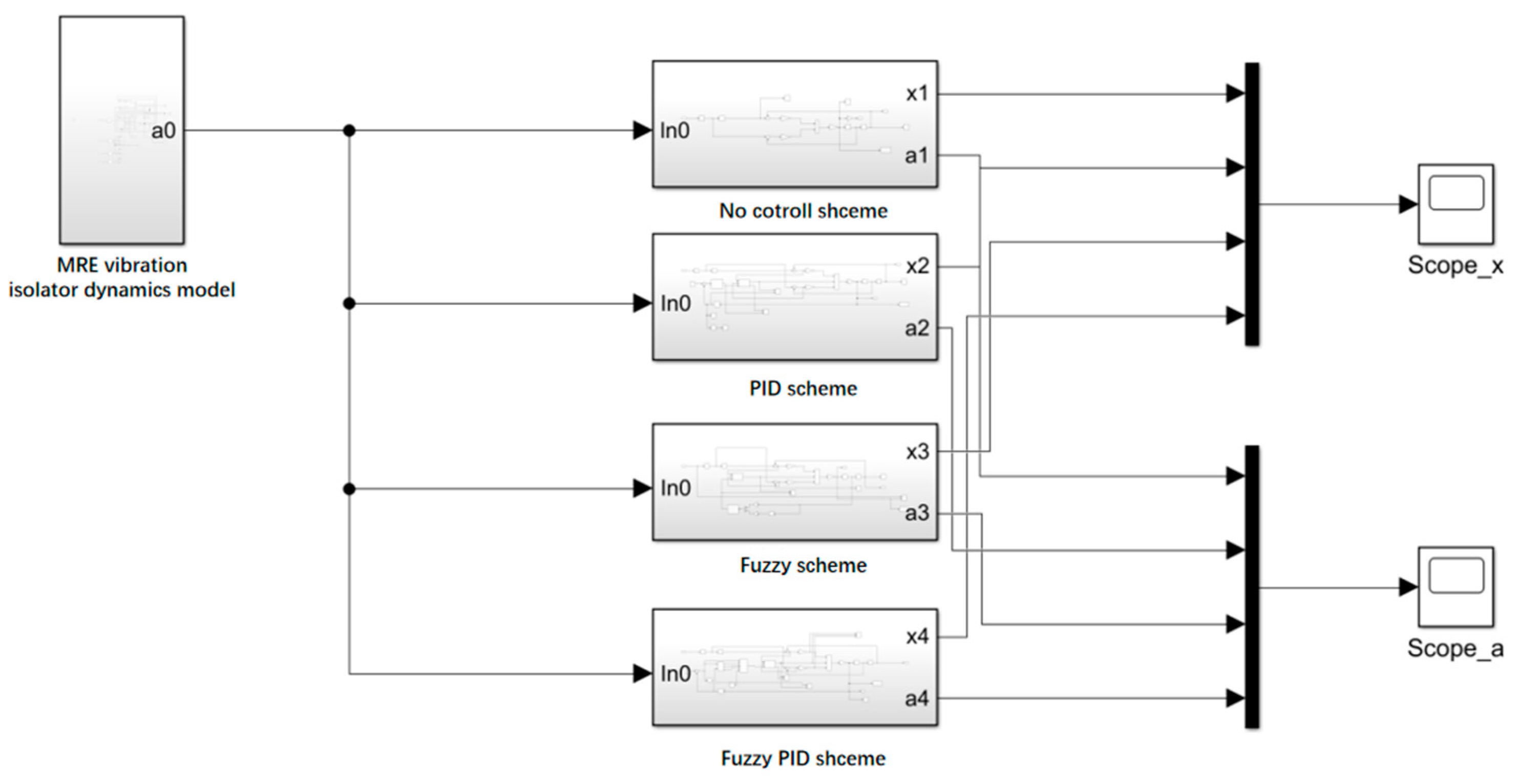
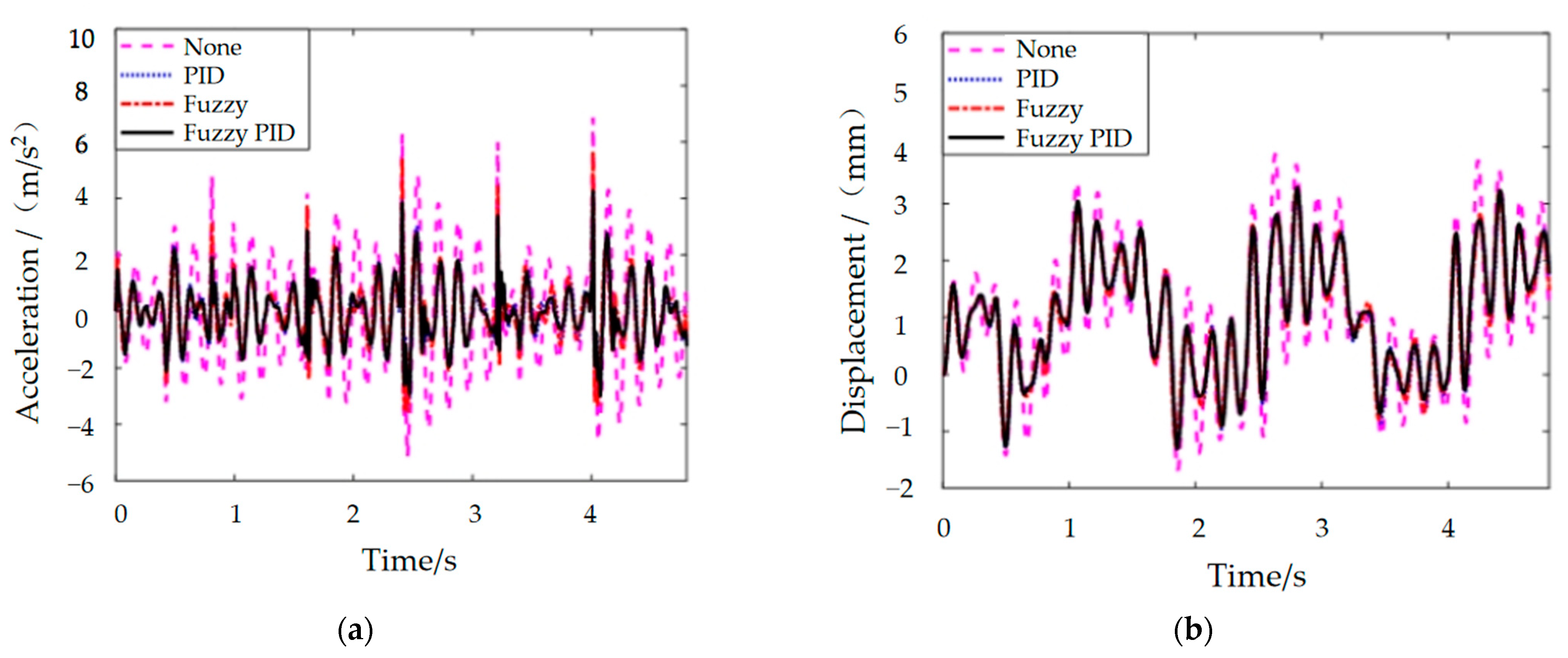
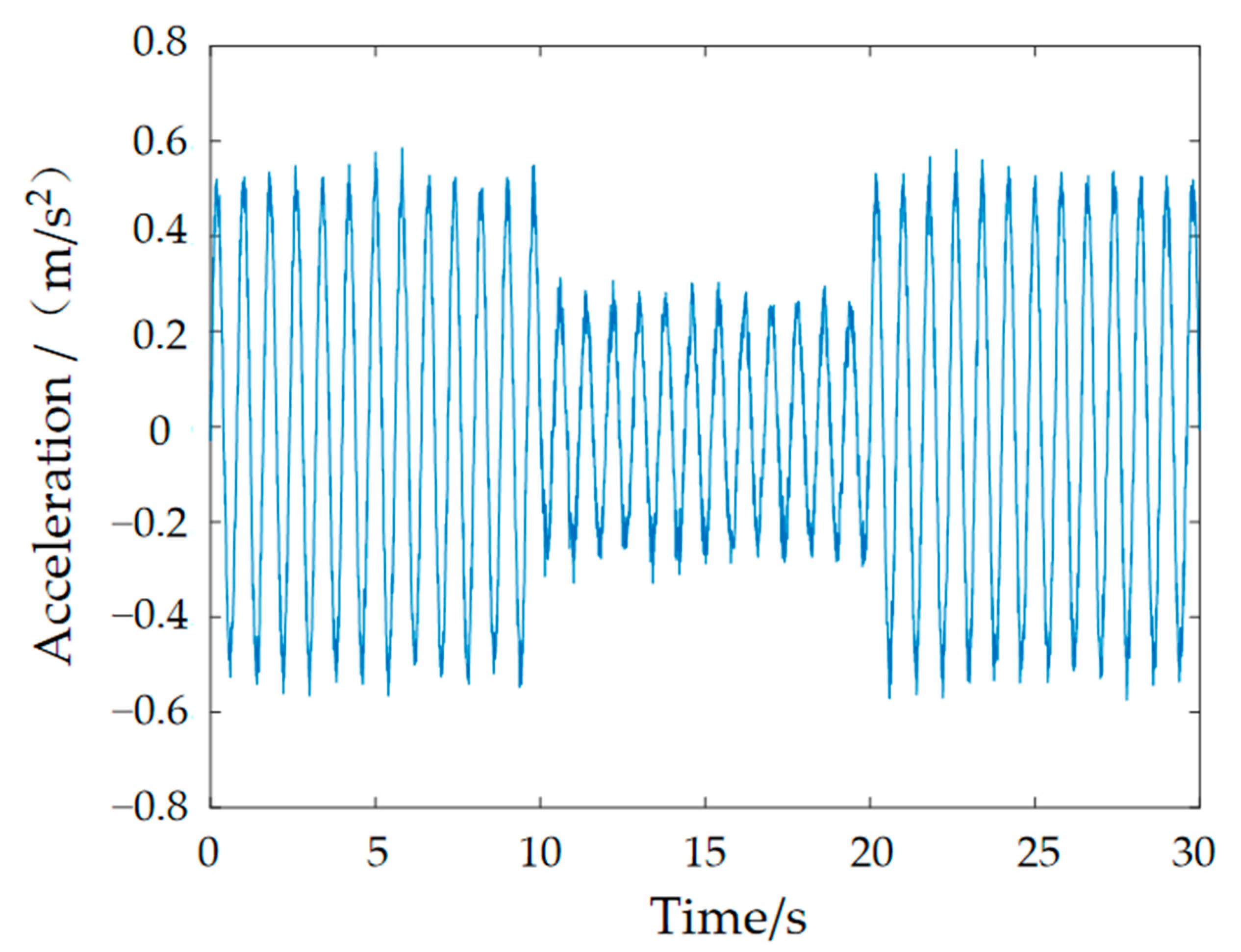
4.4. Semi-Active Control Simulation Results and Analysis
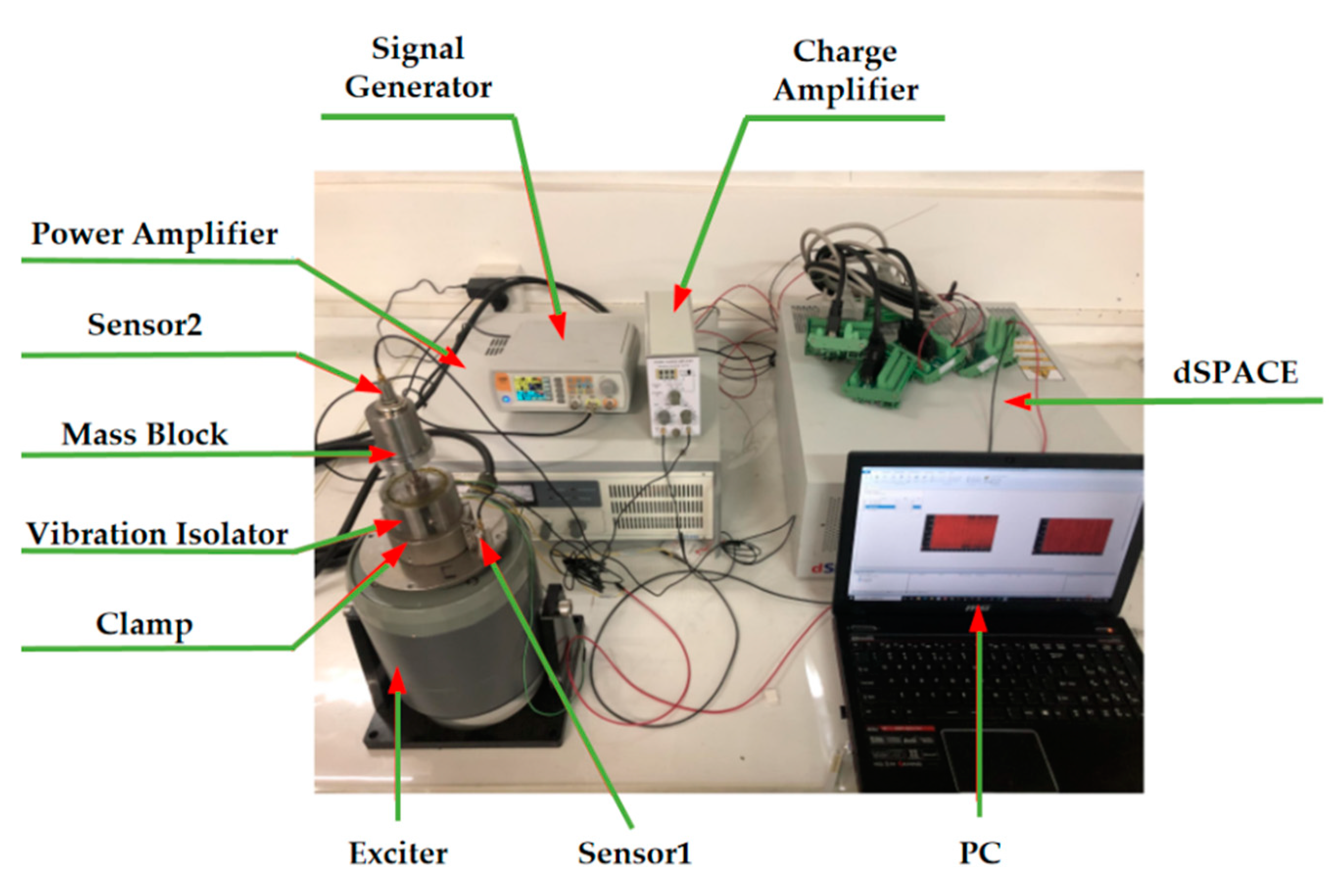
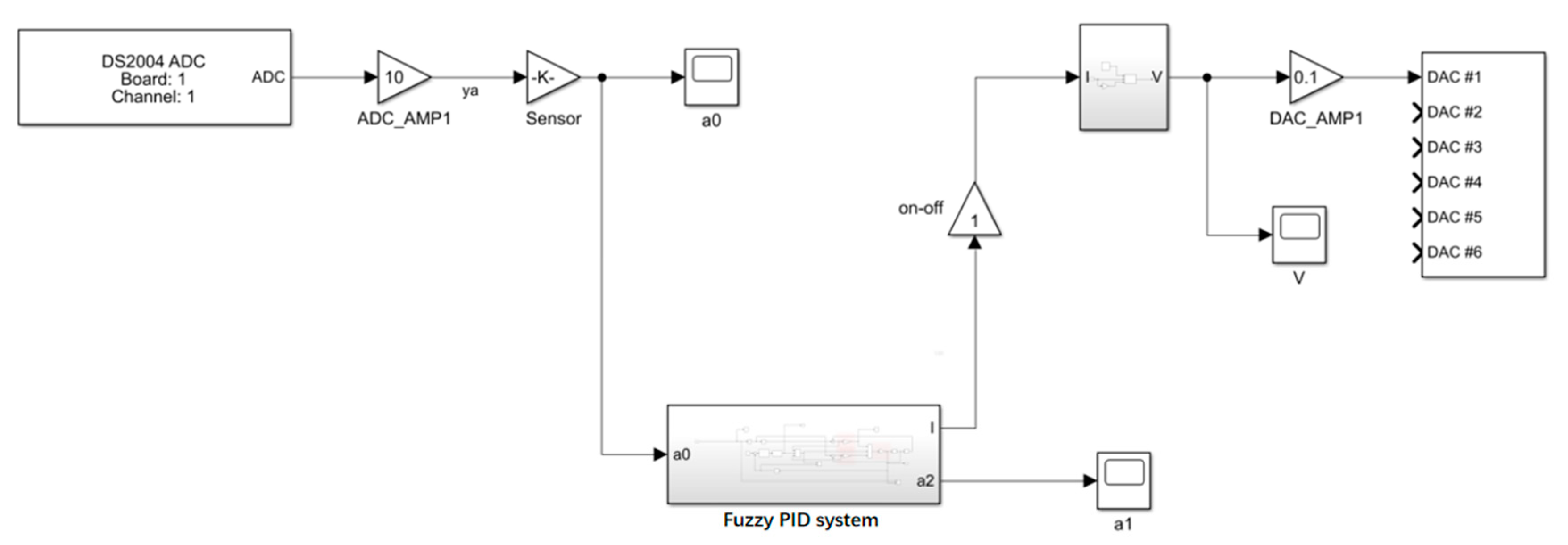
5. Hardware-in-the-Loop-Simulation of Vibration Isolator Damping Control Based on Foot–Ground Signal
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, M. Research on Cushioning and Vibration Damping Mechanism of Goat Hoof Box and Design of Bionic Cushioned Foot for Footed Robot. Master’s Thesis, Jilin University, Jilin, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.H.; Ding, E. A study of the walking stability of a humanoid robot. J. Harbin Eng. Univ. 2004, 04, 536–539. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, L.; Wang, Z.H.; Zhao, L.M. Progress in the study of the mechanical properties of porous metals and their sandwich structures. Mech. Pract. 2015, 37, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, H.B. Multivariate Coupled Cushioning Mechanism of the Canine Leg-Foot System and Its Bionic Study. Ph.D. Thesis, Jilin University, Jilin, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ananthanarayanan, A.; Azadi, M.; Kim, S. Towards a bio-inspired leg design for high-speed running. Bioinspiration Biomim. 2012, 7, 46005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grizzle, J.; Hurst, J.; Morris, B.; Park, H.W.; Sreenath, K. Mabel, a new robotic bipedal walker and runner. In Proceedings of the 2009 American Control Conference, St. Louis, MO, USA, 10–12 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Y.W.; Zheng, P. Design and dynamic analysis of a flexible vibration isolation structure. J. Dyn. Control. 2021, 19, 16–24. [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham, D.; Davis, P. A multiaxis passive isolation system for a magnetic bearing reaction wheel. Adv. Astronaut. Sci. 1993, 95, 80426. [Google Scholar]
- Verrelst, B.; Ham, R.V.; Vanderborght, B.; Daerden, F.; Lefeber, D. The Pneumatic Biped “Lucy” Actuated with Pleated Pneumatic Artificial Muscles. Auton. Robot. 2005, 18, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchli, J.; Kalakrishnan, M.; Mistry, M.; Pastor, P.; Schaal, S. Compliant quadruped locomotion over rough terrain. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, St. Louis, MO, USA, 10–15 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.K.; Shi, M.X.; Yue, B.K.; Xu, K.; Wang, J.Z. Adaptive impedance control based vibration isolation control for wheeled and footed robots. Trans. Beijing Inst. Technol. 2020, 40, 888–893. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Wang, C.J. Design of multi-dimensional vibration isolator for vibration stress relief robot based on TRIZ theory. South Agric. Mach. 2022, 53, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Sun, H.; Ma, S.S. Design of a kind of multi-dimensional attitude adjustment and vibration isolation platform based on 4-UPS/CPC parallel mechanisms. China Mech. Eng. 2021, 32, 1513–1522. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.F.; Wu, S.; Li, Z.X.; Xu, S. A study on vibration isolation based on a buckled beam quasi-zero-stiffness isolator and active damping. J. Vib. Shock. 2021, 40, 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Z.G.; Zhao, X.G.; Cheng, L.; Wang, Q.M.; Wang, W.Q. Research advances in rehabilitation robotics and intelligent assistive systems. J. Autom. 2016, 42, 1765–1779. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, F.R.; Cao, R.K.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Ma, T. MRE-based variable stiffness variable damping damper design study. Vib. Shock. 2019, 42, 192–198. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Li, P.D.; Liao, G.Y.; Lai, J.J.; Yu, M. Development and Dynamic Characterization of a Mixed Mode Magnetorheological Elastomer Isolator. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 53, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie, M.D.; Sun, S.S.; Ning, D.H.; Du, H.; Zhang, S.W.; Li, W.H. A torsional MRE joint for a C-shaped robotic leg. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 015002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.J.; Huang, X.G.; Wang, H.X.; Zhang, G.; Wang, J. Vibration isolation control and an experimental study of magnetorheological elastomer isolators. J. Vib. Shock. 2020, 39, 118–122. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Du, J.H. Gait planning for bipedal walking robots. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2002, 38, 214–216. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, N.; Lu, W. Gait smulation and results analysis of multi-articular biped walking robot in ADAMS environment. South Agric. Mach. 2021, 52, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L. Bipedal Robot Modelling and Gait Planning Analysis. Master’s Thesis, Shenyang University of Architecture, Shenyang, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C. Design Study of Magnetorheological Elastomers and Their Intelligent Vibration Isolators for Composite Service Conditions. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Du, G.L. Design of Composite Magnetorheological Elastomeric Vibration Isolators and Study of Their Control Systems. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, M. Research on Magnetorheological Elastomer Materials and Devices for Lateral Vibration Control. Master’s Thesis, Chongqing University, Chongqing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Przybylski, M.; Sun, S.S.; Li, W.H. Development and characterization of a multi-layer magnetorheological elastomer isolator based on a Halbach array. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 105015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wang, H.X.; Ma, W.J. Dynamic model identification of MRE vibration isolators based on genetic algorithm. Noise Vib. Control. 2021, 41, 50–57. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.X.; Liu, T.; Ma, W.J.; Zhang, G. Analysis of variable stiffness semi-active vibration isolation system based on MRE isolator. J. Hunan Univ. 2021, 48, 27–36. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Z.L.; Pan, D.Y.; Xiao, P.; Shi, P.C. Analysis of vibration isolation performance of magnetorheological mounting system based on fuzzy control. J. Chongqing Inst. Technol. 2020, 34, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Shen, C.W.; Liu, X.B.; Xie, M.J. Active vibration isolation technology based on fuzzy PID. J. Chang. Univ. Technol. 2020, 41, 67–72. [Google Scholar]
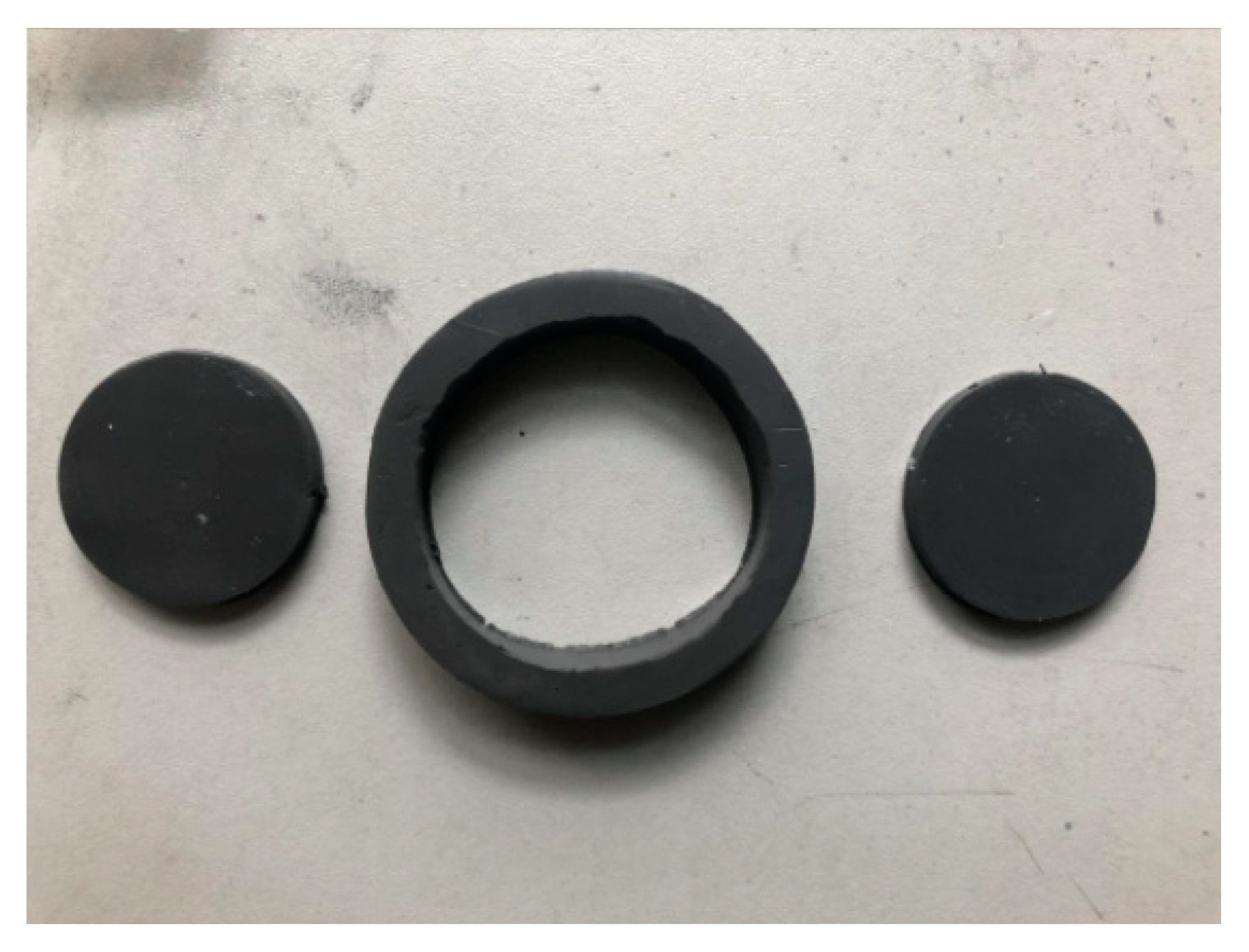

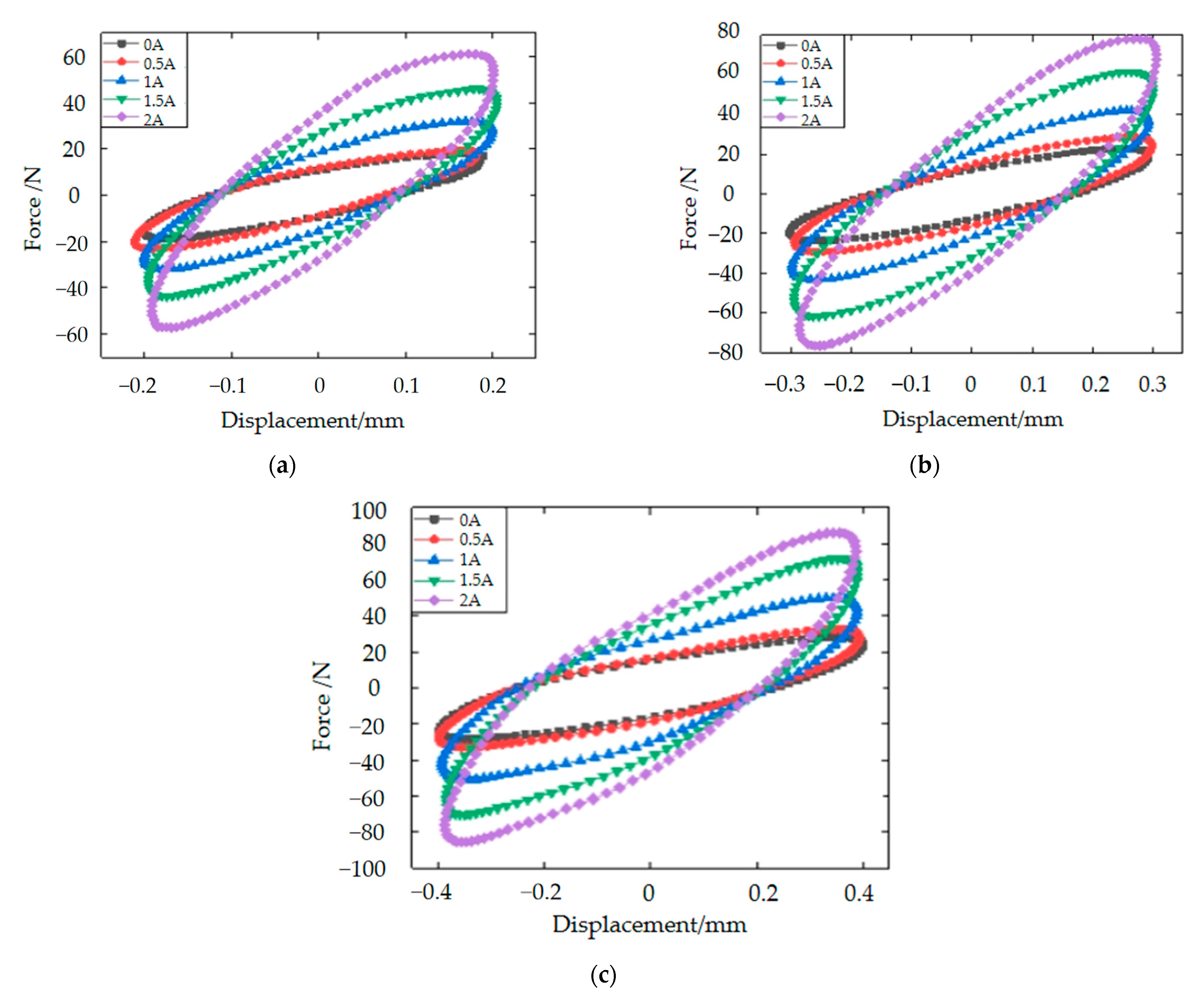
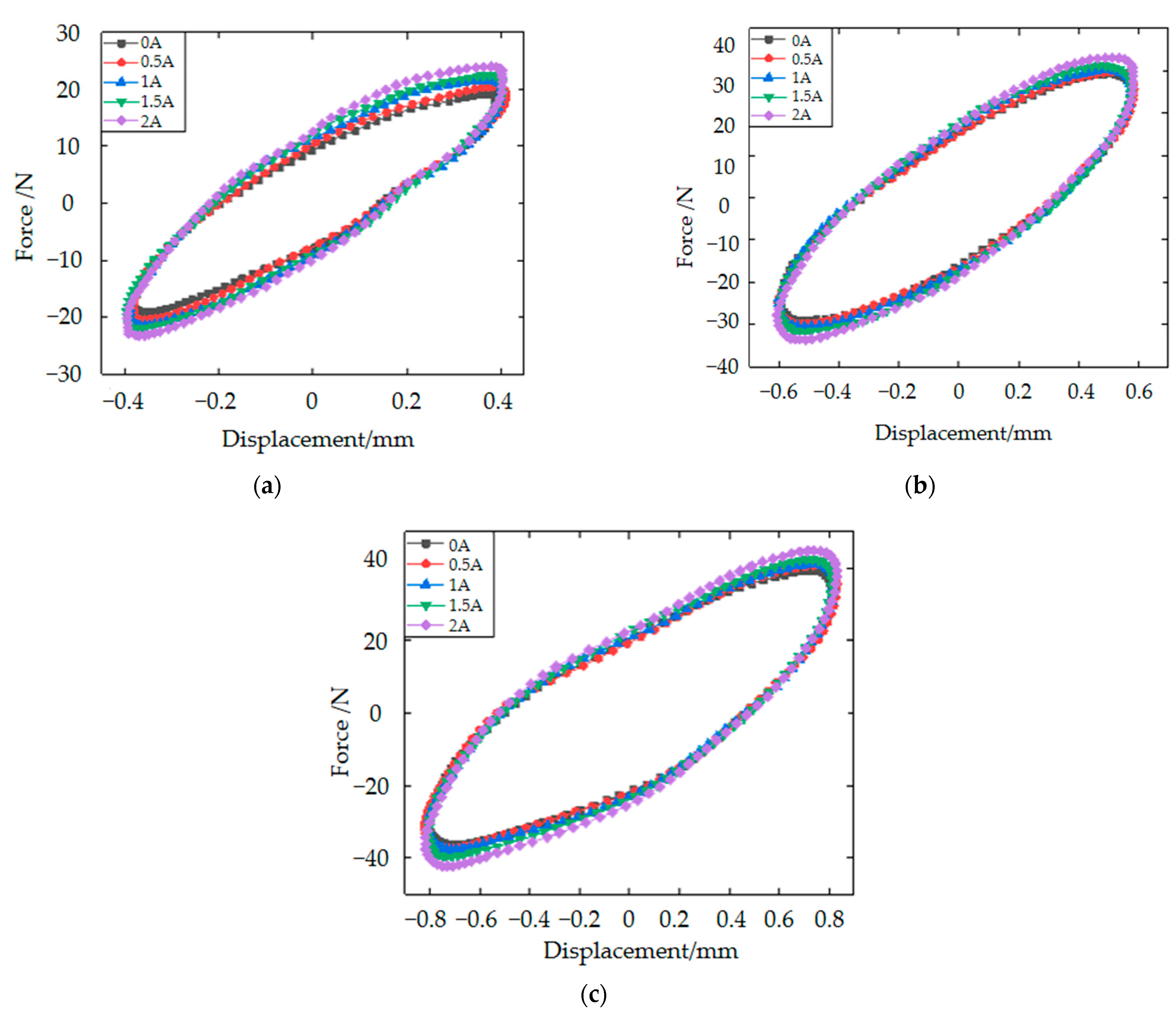
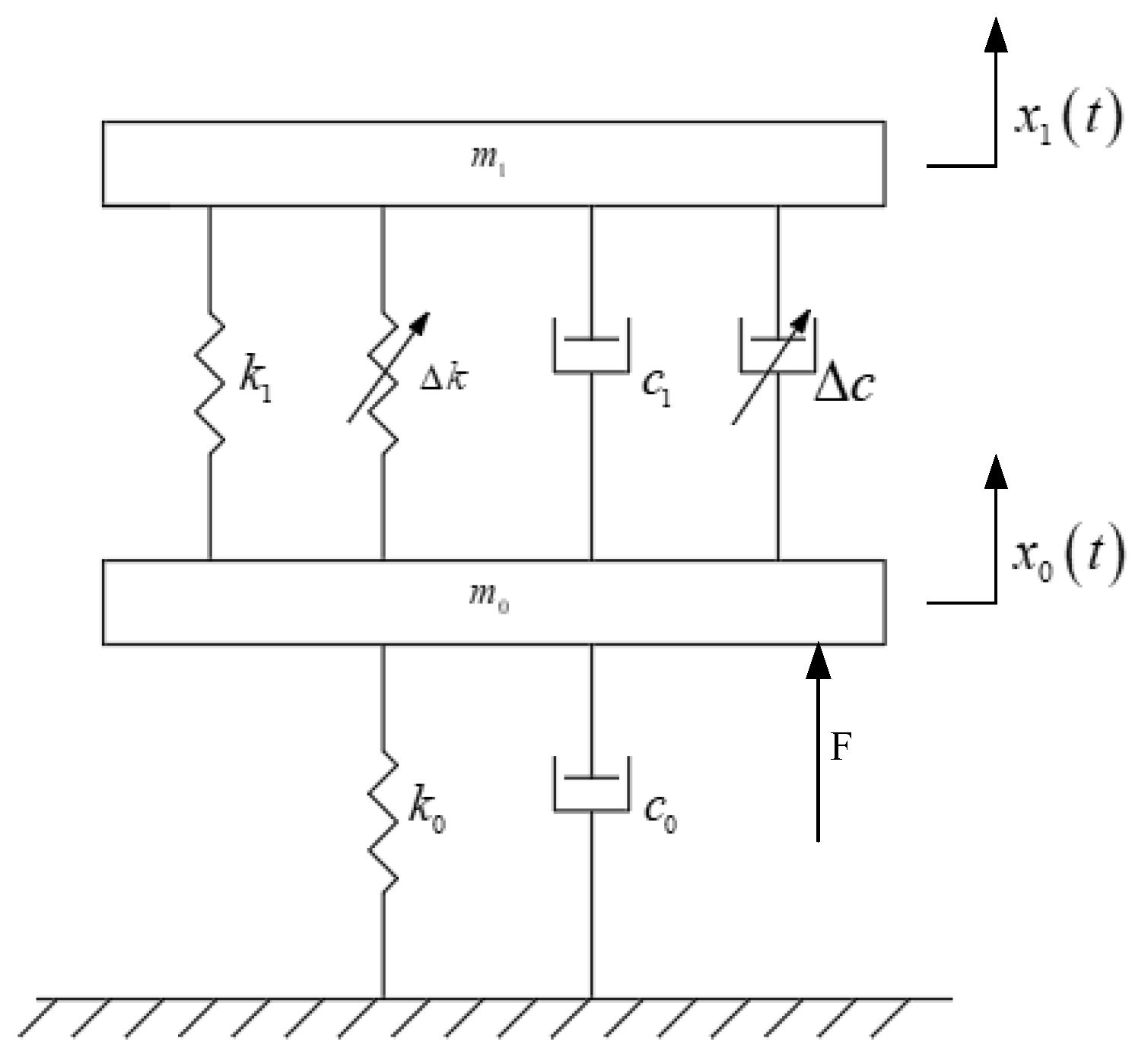
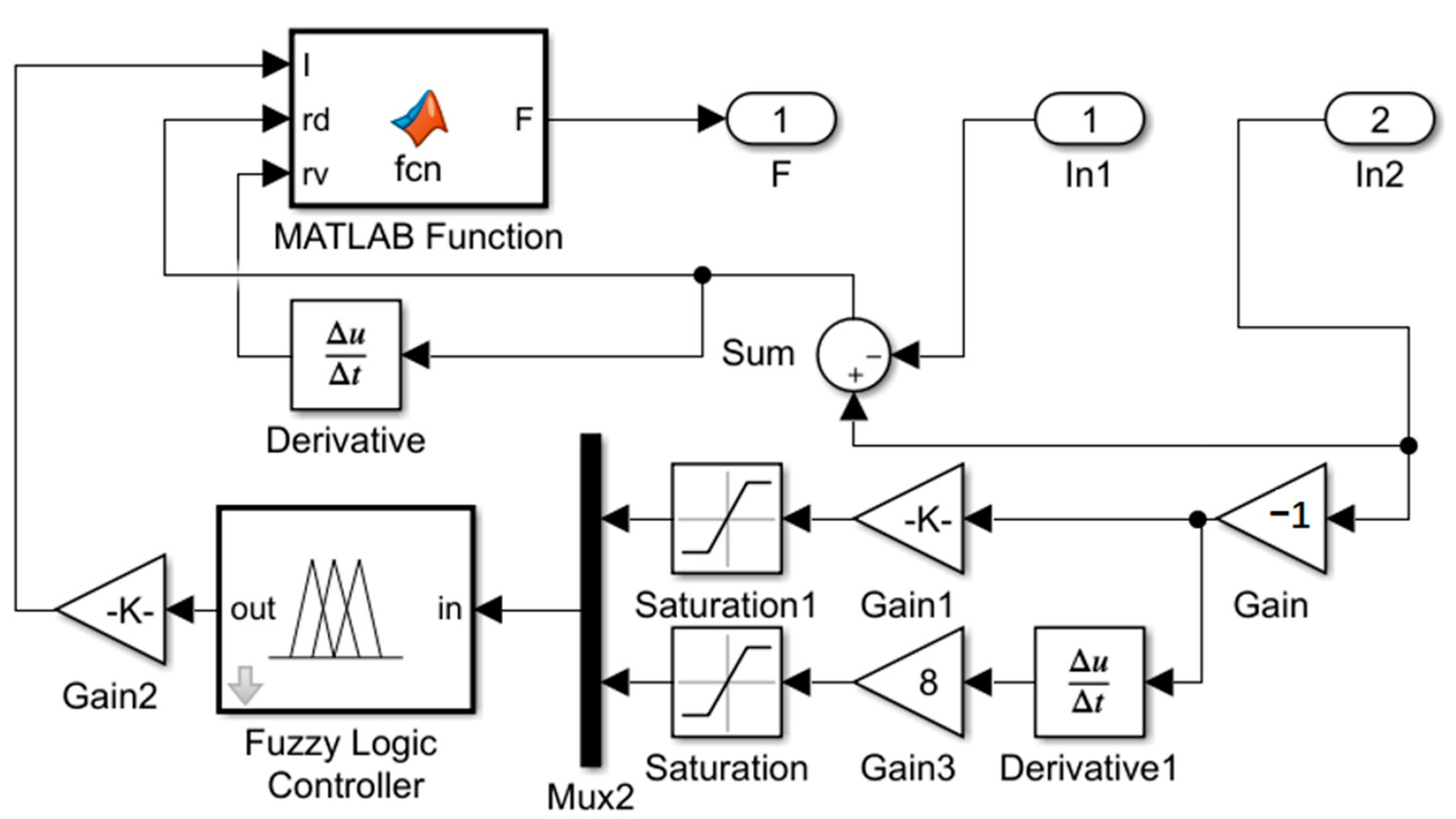
| Parameters | Values and Units |
|---|---|
| Stiffness factor | 105 (N/mm) |
| Force Index | 2.2 |
| Damping factor | 10 (Ns/mm) |
| Penetration depth | 0.1 |
| Coefficient of static friction | 0.5 |
| Coefficient of dynamic friction | 0.3 |
| Size of each foot | 10 × 5 × 3 cm3 |
| Mass of each foot | 100 g |
| Simulation time | 9.6 s |
| None | PID | Fuzzy | Fuzzy PID | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peak | RMS | Peak | RMS | Peak | RMS | Peak | RMS | |
| displacement | 3.871 | 1.604 | 3.214 | 1.4452 | 3.259 | 1.4398 | 3.289 | 1.4536 |
| acceleration | 6.872 | 1.978 | 4.266 | 1.0076 | 5.691 | 1.0623 | 4.267 | 0.997 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, X.; Zhai, Y.; He, G. Research on Vibration Control Technology of Robot Motion Based on Magnetorheological Elastomer. Materials 2022, 15, 6479. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15186479
Huang X, Zhai Y, He G. Research on Vibration Control Technology of Robot Motion Based on Magnetorheological Elastomer. Materials. 2022; 15(18):6479. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15186479
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Xuegong, Yutong Zhai, and Guisong He. 2022. "Research on Vibration Control Technology of Robot Motion Based on Magnetorheological Elastomer" Materials 15, no. 18: 6479. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15186479
APA StyleHuang, X., Zhai, Y., & He, G. (2022). Research on Vibration Control Technology of Robot Motion Based on Magnetorheological Elastomer. Materials, 15(18), 6479. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15186479








