Impedance Spectroscopy of Pr-Doped BaBi2Nb2O9 Aurivillius Ceramics
Abstract
1. Introduction
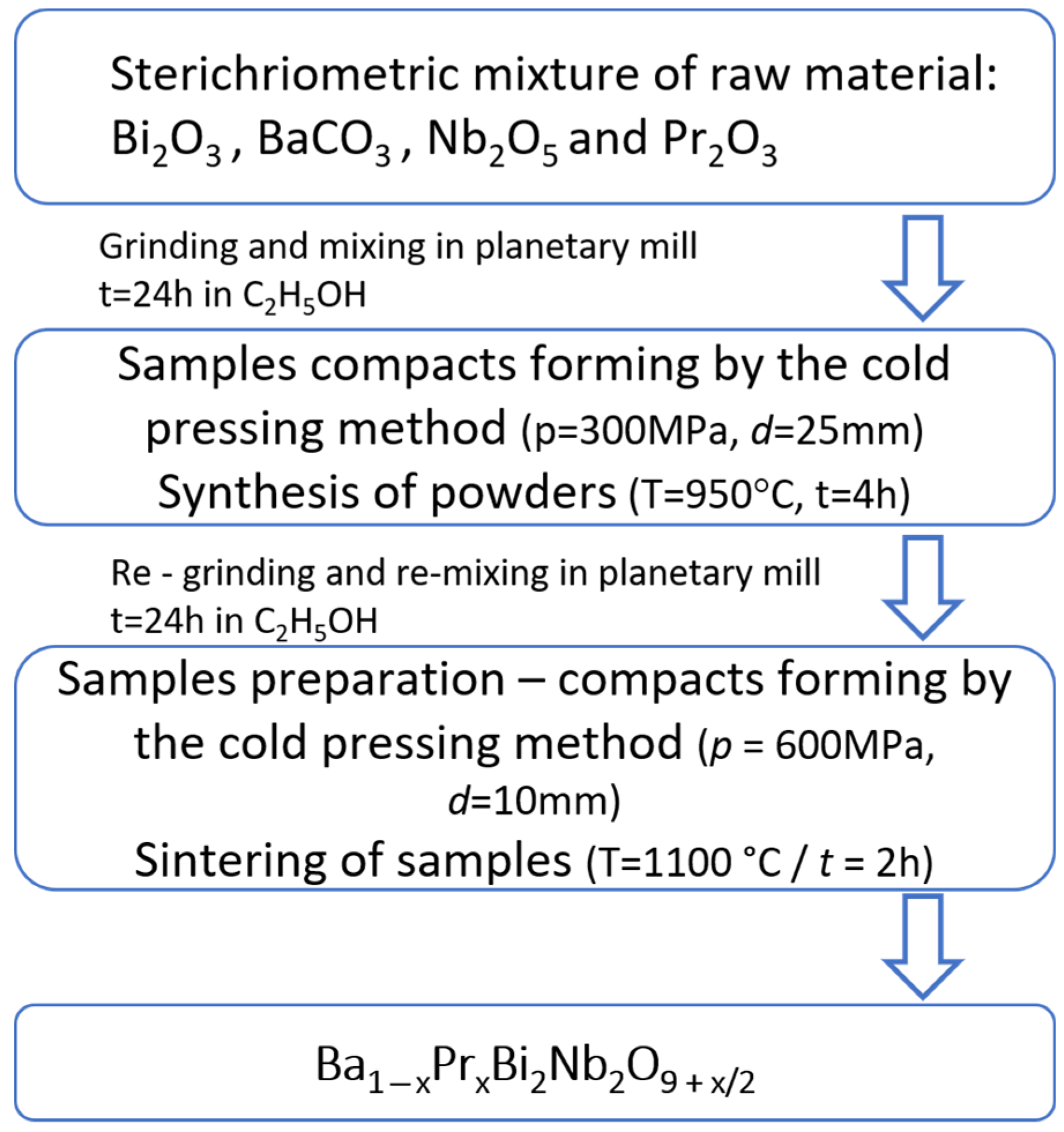
2. Materials and Methods
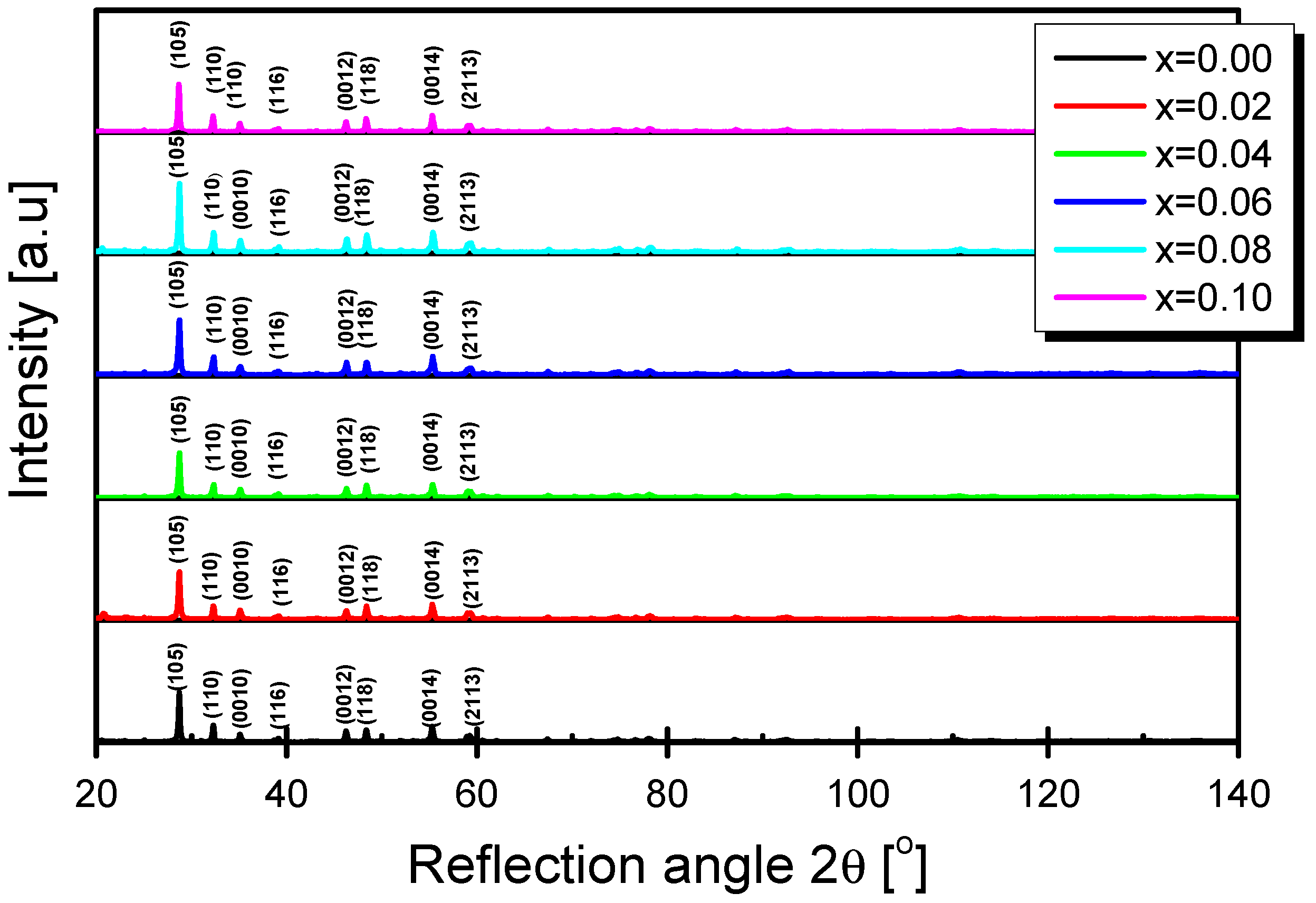
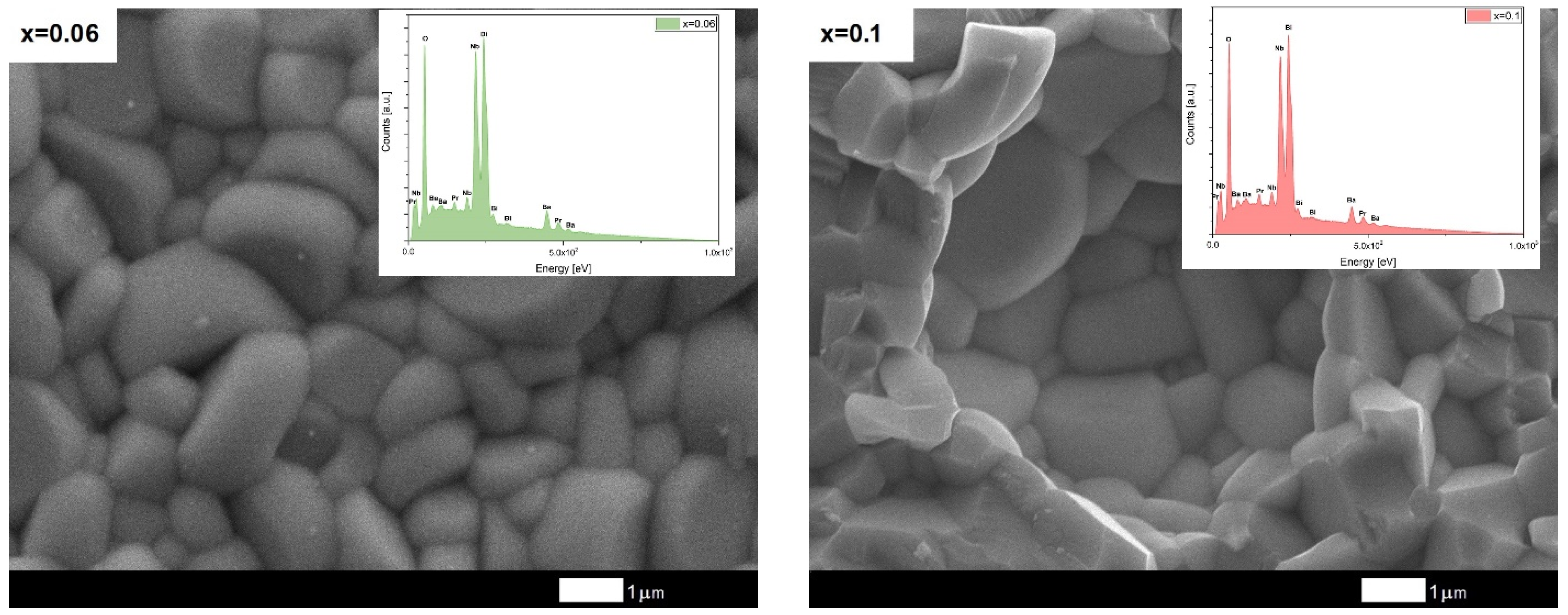
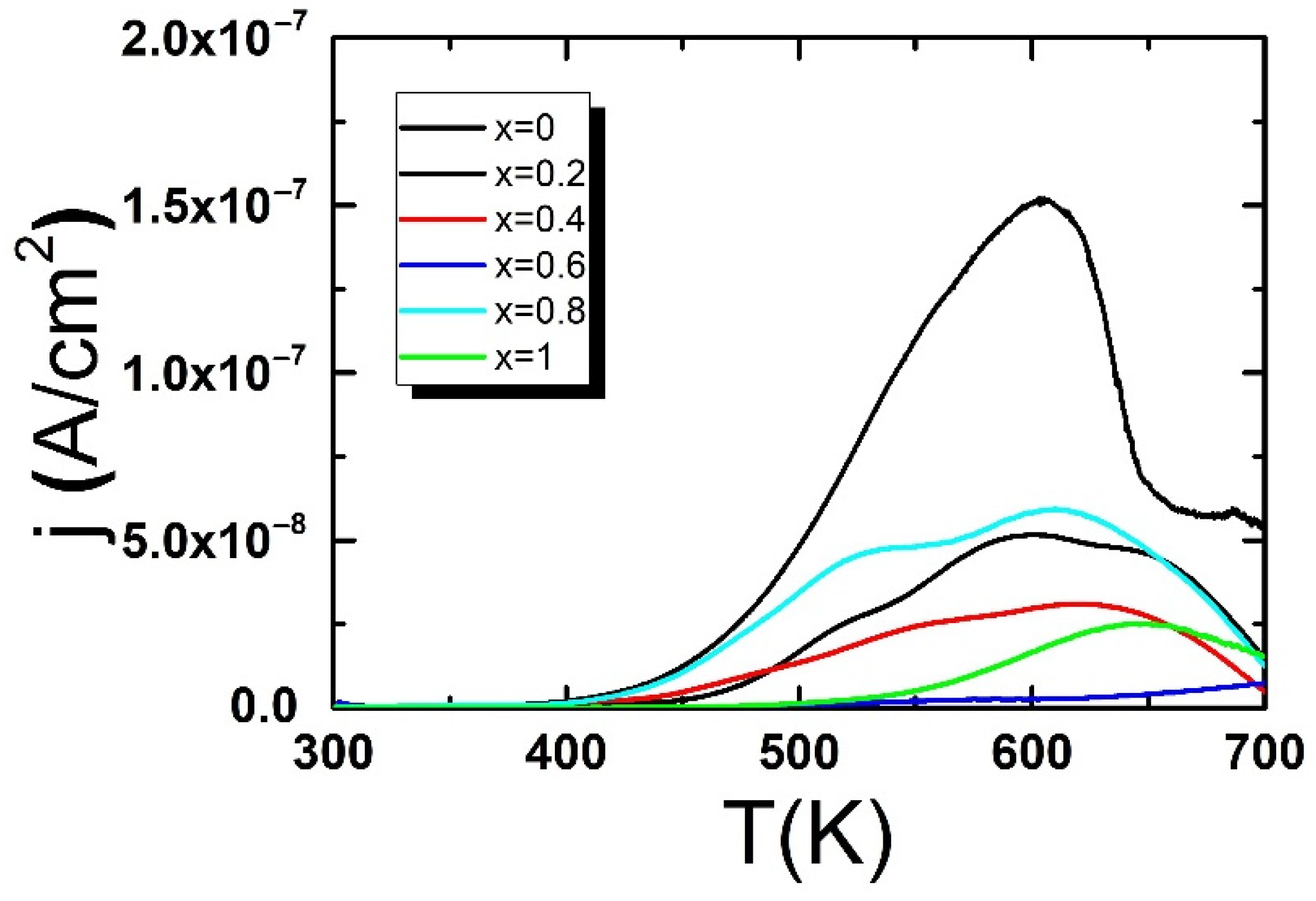
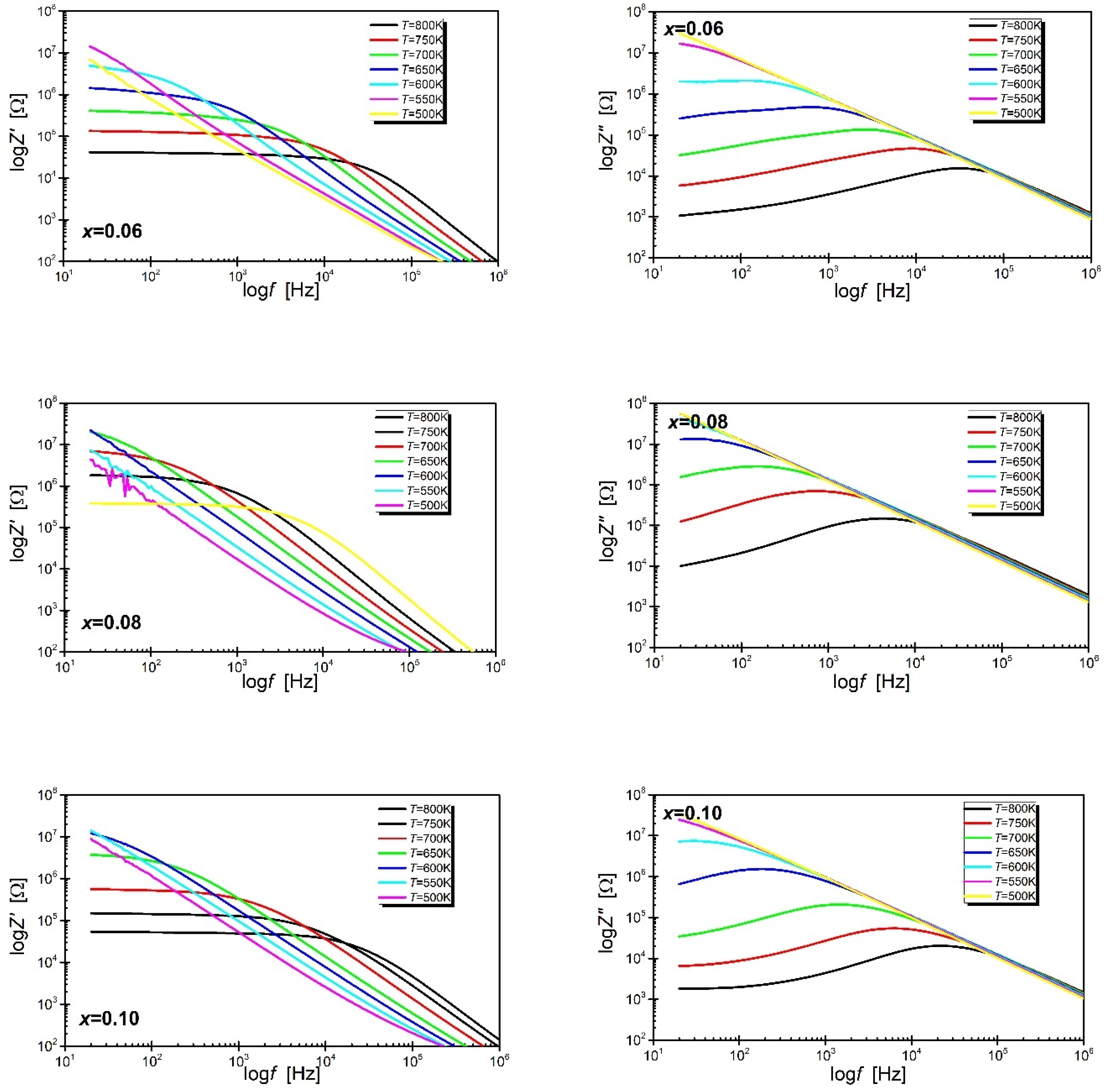
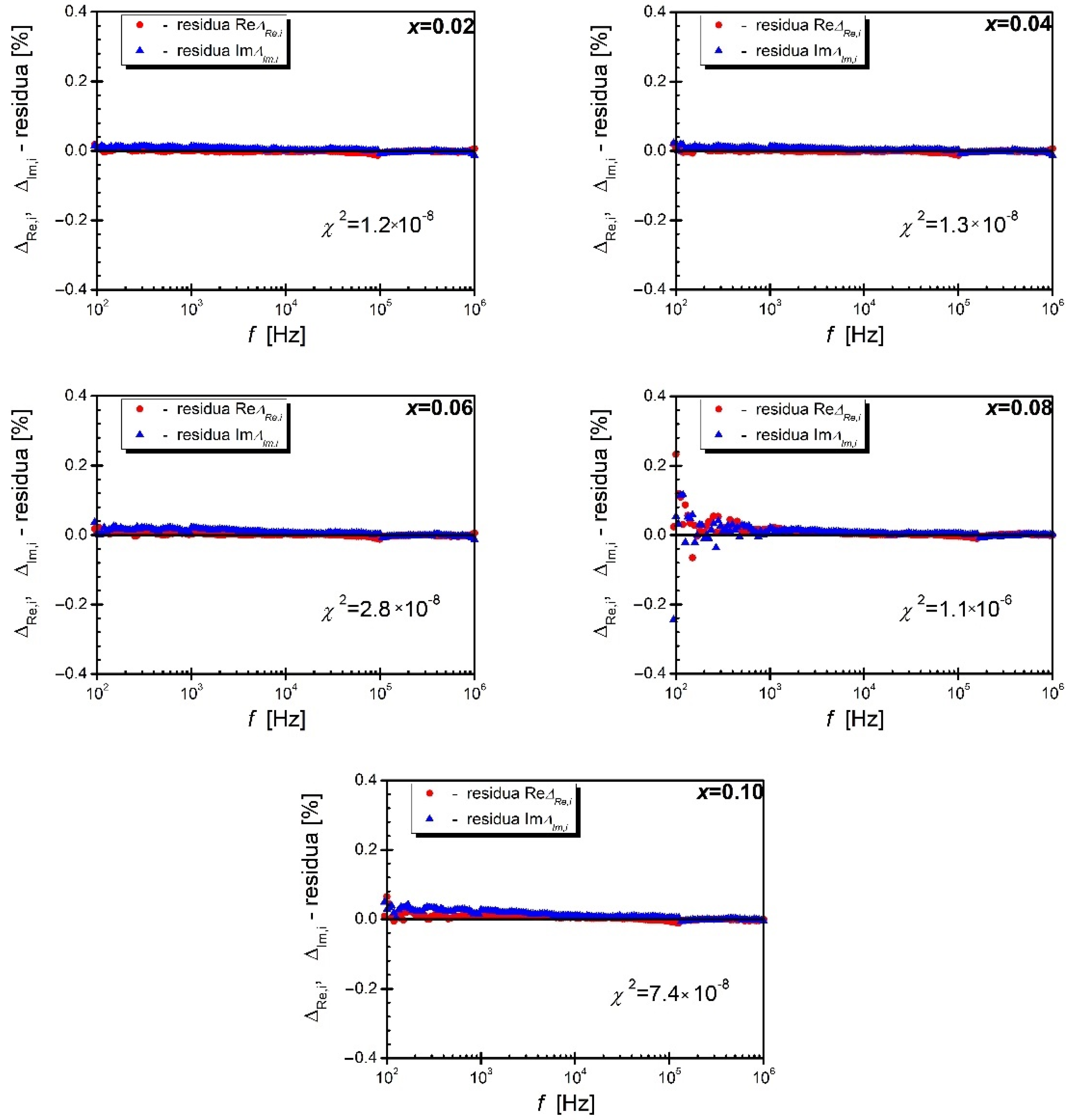
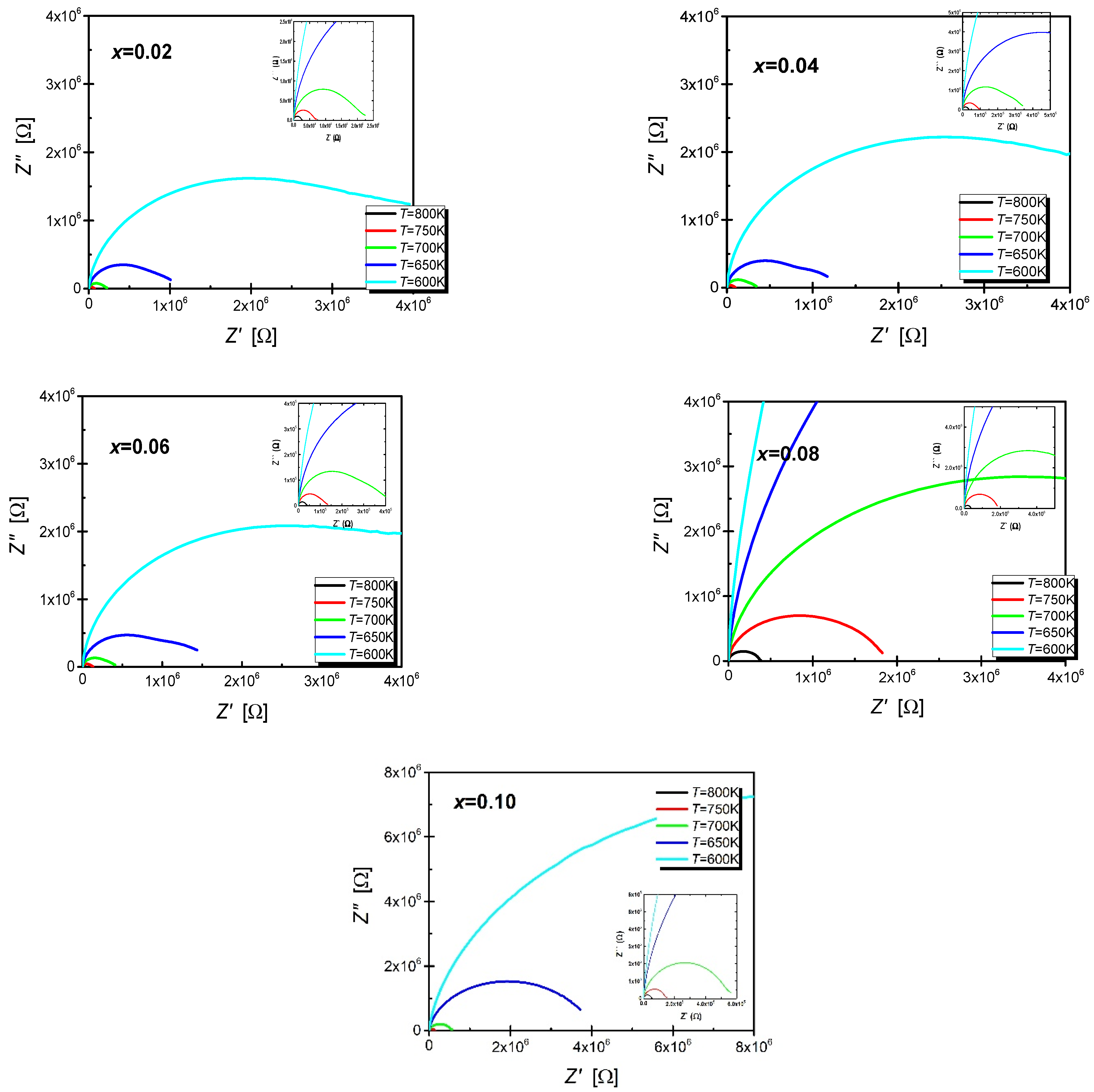
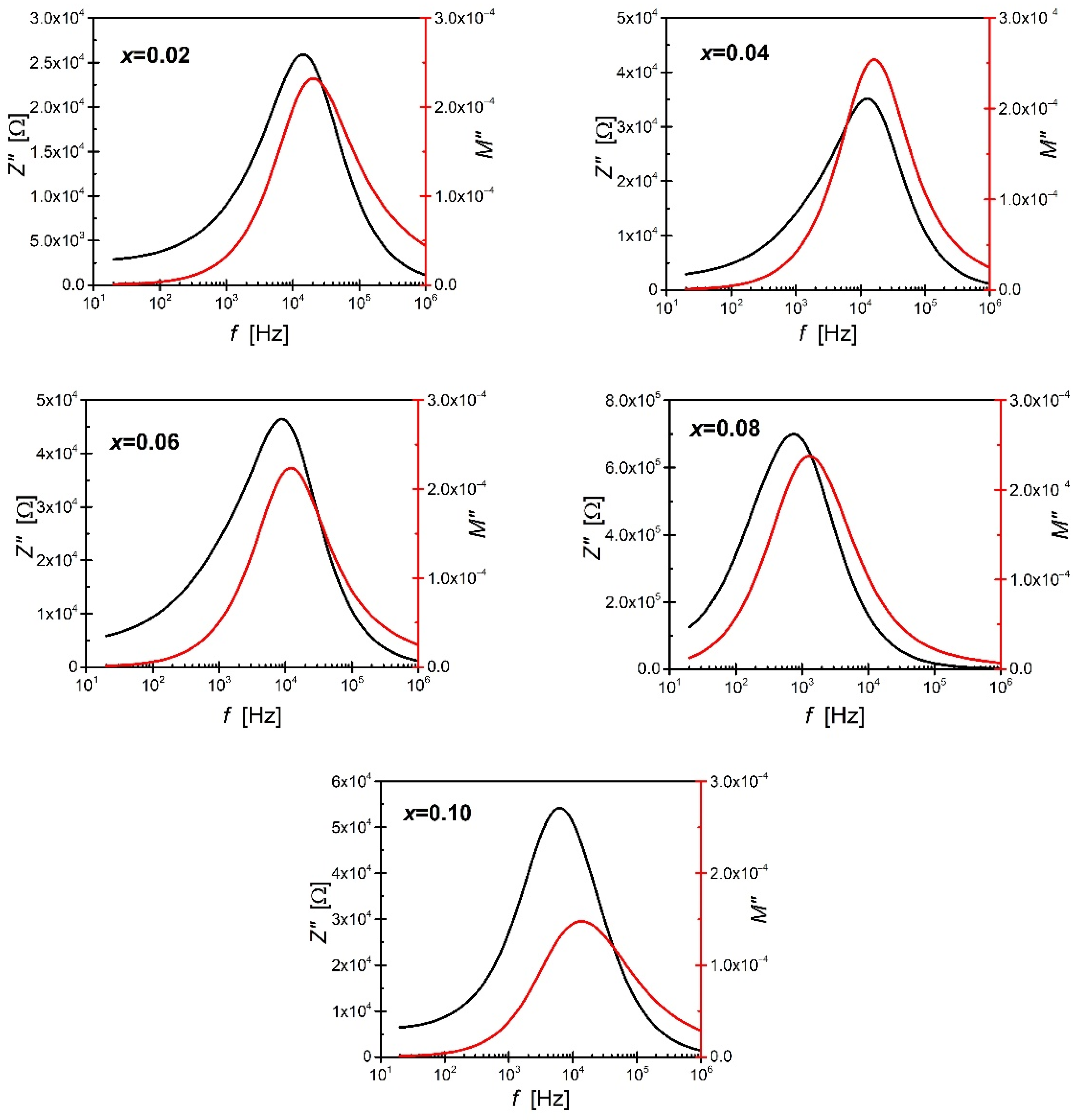
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Assirey, E.A.R. Perovskite synthesis, properties and their related biochemical and industrial application. Saudi Pharm. J. 2019, 27, 817–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhalla, A.S.; Guo, R. The perovskite structure—a review of its role in ceramic science and technology. Mater. Res. Innov. 2000, 4, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Rinke, P. Atomic structue of metal-halide perovskites from first principles: The chicken-and-egg paradox of organic-inorganic interaction. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 94, 045201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochenek, D.; Niemiec, P.; Szafraniak-Wiza, I.; Dercz, G. Comparison of electrophysical properties of PZT-type ceramics obtained by conventional and mechanochemical methods. Materials 2019, 12, 3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bochenek, D. Magnetic and ferroelectric properties of PbFe1/2Nb1/2O3 synthesized by a solution precipitation method. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 504, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossetti, G.A. Structure and bonding in PbZrO3–PbTiO3 (PZT) alloys. Br. Ceram. Trans. 2004, 103, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochenek, D.; Surowiak, Z. Influence of admixtures on the properties of biferroic Pb(Fe0.5Nb0.5)O3 ceramics. Phys. Status Solidi A 2009, 206, 2857–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubkov, S.V. Crystal structure and dielectric properties of layered perovskite-like solid solutions Bi3–xGdxTiTaO9 (x = 0.0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3) with high Curie temperature. J. Adv. Dielectr. 2021, 11, 2160016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalini, G.; Sybbanna, G.N.; Guru Row, T.N. Studies on n=2 phases: Structure of the series Bi3-xLaxTiNbO9 (0≤x≤1). Mater. Chem. Phys. 2003, 82, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Qaiser, M.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.T.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, G. High-temperature piezoelectric properties of 0-3 type CaBi4O15: X wt%BiFeO3 composites. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 10, 3522–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabeen, N.; Hussain, A.; Nawazc, S.; Qaiserd, M.A.; Zafarc, R.; Ishtiaqe, S.; Ahmedf, F.; Masudg, U.; Sultanb, T.; Muntahab, S.T. Thermally Stable Piezoelectric Performance of MnO2 Inserted Pseudo-tetragonal Phase Existent CaBi2Nb2O9-based Ceramics. Mater. Technol. 2022, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabenn, N.; Nawaz, S.; Qaiser, M.A.; Hassan, F.; Abbas, Z. Stable piezoelectric response of 0–3 type CaBi2Nb2O9: X wt%BiFeO3 composites for high–temperature piezoelectric applications. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2021, 9, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qauser, M.A.; Hussain, A.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, L.; Yuan, G. 0-3 type Bi3TaTiO9: 40wt%BiFeO3 composite with improved high-temperature piezoelectric properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 740, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazon, T.; Zaghete, M.A.; Cilense, M.; Varela, J.A. Effect of the excess of bismuth on the morphology and properties of the BaBi2Nb2O9 thin films. Ceram. Int. 2009, 35, 3143–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debasis, D.; Tanmay, G.K.; Panchanan, P. Studies of dielectric characteristics of BaBi2Nb2O9 ferroelectrics prepared by chemical precursor decomposition method. Solid State Sci. 2007, 9, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczyk, M.; Kozielski, L.; Pilch, M. Impedance Spectroscopy of BaBi2Nb2O9 Ceramics. Ferroelectrics 2011, 417, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigyo, T.; Itoh, H.; Takahashi, J. Low-temperature fabrication of BaBi2Nb2O9 ceramics by reaction controlled sintering. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2010, 21, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bochenek, D.; Zachariasz, R. PFN ceramics synthesized by a two-stage method. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2009, 54, 903–910. [Google Scholar]
- Bochenek, D.; Skulski, R.; Wawrzała, P.; Brzezińska, D. Dielectric and ferroelectric properties and electric conductivity of sol-gel derived PBZT ceramics. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 5356–5363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochenek, D.; Niemiec, P.; Skulski, R.; Chrobak, A.; Wawrzała, P. Ferroelectric and magnetic properties of the PMN-PT-nickel-zinc ferrite multiferroic ceramic. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015, 157, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keburis, P.; Kiselev, D.A.; Banys, J.; Costa, M.E.V.; Kholkin, A.L. PFM Studies of Domain Structure of Relaxor Ceramics BaBi2Nb2O9. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference and Exhibition of the European Ceramic Society, Berlin, Germany, 17–21 June 2007; p. 587. [Google Scholar]
- Ismunadar; Kennedy, B.I. Effect of temperature on cation disorder in AB2Nb2O9 (A=Sr, Ba). J. Mater. Chem. 1999, 9, 541–544. [Google Scholar]
- Adamczyk, M.; Kozielski, L.; Zachariasz, R.; Pawełczyk, M.; Szymczak, L. Structural, dielectric spectroscopy and internal friction correlation in BaBi2Nb2O9 ceramics. Arch. Matellurgy Mater. 2014, 59, 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Rajesh Kannan, B.; Harihara Venkataraman, B. Dielectric relaxor and conductivity characteristics of undoped and samarium doped barium bismuth niobiate ferroelectric ceramics. Ferroelectr. Lett. Sestion 2015, 43, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh Kannan, B.; Harihara Venkataraman, B. Effect of rare earth ion doping on te structural, microstructural and diffused phase transition characteristics of BaBi2Nb2O9. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 16365–16369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczyk-Habrajska, M.; Goryczka, T.; Szalbot, D.; Dzik, J.; Rerak, M.; Bochenek, D. Influence of lanthanum dopant on the structure and electric properties of BaBi2Nb2O9 ceramics. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2020, 65, 207–214. [Google Scholar]
- Afqir, M.; Tachafine, A.; Fasquelle, D.; Elaatmani, M.; Carru, J.C.; Zegzauti, A.; Daoud, M.; Sayouri, S.; Lamcharii, T.; Zauhairi, M. Structural, electric and dielectric properties of Eu-doper SrBi2Nb2O9 ceramics obtained by co-precipitation route. Processing Appl. Ceram. 2018, 12, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Yu, Y.; Li, J.; Cao, Q.; Wang, X.; Hou, J. Photoluminescence enhanced ferroelectric and dielectric properties of Pr3+- doped SrBi2Nb2O9 multifunctrional ceramics. Mater. Res. Bull. 2015, 69, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rerak, M.; Makowska, J.; Osińska, K.; Goryczka, T.; Zawada, A.; Adamczyk-Habrajska, M. The Effect of Pr Doping Contents on the Structural, Microstructure and Dielectric Properties of BaBi2Nb2O9 Aurivillius Ceramics. Materials 2022, 15, 5790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, J.N.; Sreenivasulu, M.; Rao, K.S.; Rao, K.S.; Nagamani, S.; Nagamalleswari, T. Study of structural and mechanical aspect of praseodymium and europium doped SrBi2Nb2O9 ceramics. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 19, 2658–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Feng, C.; Chen, L.; Wen, X. Dielectric properties of SrBi2-xPrxNb2O9. Solid State Commun. 2005, 133, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietveld, H.M. Line profiles of neutron powder diffraction peaks for structure refinement. Acta Cryst. 1967, 22, 151–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.P.; Wang, X.J.; Wen, J.X.; Chen, C.; Tu, N.; Li, X.H. Microstructure and electrical properties of Mn-modified bismuth-layer Na0.25K0.25Bi2.5Nb2O9 ceremics. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 544, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.M.; Wang, J.F.; Zheng, L.M. Enhancement of the piezoelectric properties of sodium lanthanum bismuth titanete (Na0.5La0.5Ni4O15) trough modification with cobalt. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2010, 171, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patri, S.K.; Deepti, P.L.; Choudhary, R.N.P.; Behera, B. Dielectric, impedance and modulus spectroscopy of BaBi2Nb2O9. J. Electroceramics 2018, 40, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczyk, M.; Ujma, Z.; Pawełczyk, M. Dielectric properties of BaBi2Nb2O9 ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 5317–5322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Sun, H.; Wang, X.; Tang, M.; Yao, X. Red emission in Pr doped CaBi4Ti4O15 ferroelectric ceramics. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2011, 176, 1513–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triyono, D.; Fitria, S.N.; Hanifah, U. Dielectric analysis and electrical conduction mechanism of La1-xBixFeO3 ceramics. RSC Adv. 2020, 31, 18323–18338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, L.K.; Prasad, K.; Choudhary, R.N.P. Impedance spectroscopy of (Na0.5Bi0.5)(Zr0.25Ti0.75)O3 lead free ceramic. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 453, 325–331. [Google Scholar]
- Bauerle, J.E. Study of solid electrolyte polarization by a complex admittance method. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1969, 30, 2657–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Choudhary, R.N.P.; Sinha, P.K. Impedance spectroscopy studies on Fe3+ ion modified PLZT ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2007, 33, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, K.; Thomas, J.K.; Loye, H.C. Synthesis and ionic conductivity of a new series of modified Aurivillius phases. Chem. Mater. 1995, 7, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukamp, B.A. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy in Solid State Ionics: Recent advances. Solid State Ion. 2004, 169, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukamp, B.A. A Linear Kronig-Kramers Transform Test for Immittance Data Validation. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1995, 142, 1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukamp, B.A.; Macdonald, J.R. Alternatives to Kronig-Kramers transformation and testing, and estimation of distributions. Solid State Ion. 1994, 74, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahato, D.K.; Sinha, T.P. Electrical conductivity and dielectric relaxation in Pr2CoZrO6 double perovskite. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 634, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omari, L.H.; Moubah, R.; Boutahar, A.; Hajji, L.; El Quatib, R. Analysis of electrical properties using complex impedance spec-troscopy in solid solutions (PbTiO3)0.97-(LaFeO3)0.03 prepared by sol-gel technique. J. Electroceramics 2020, 44, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkoy, E.M.; Berksoy-Yavuz, A. Electrical Properties and Impedance Spectroscopy of Pue and Copper-Oxide-Added Potassium Sodium Niobiate Ceramics. In IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Volume 59, Issue 10; pp. 2121–2128. [Google Scholar]
- Kamal, A.; Rafiq, M.A.; Rafiq, M.N.; Usman, M.; Waqar, M.; Anwar, M.S. Structural and impedance spectroscopic studies of CuO-doped (Ka0.5Na0.5Nb0.995Mn0.005O3) lead free piezoelectric ceramics. Appl. Phys. A 2016, 122, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barranco, A.P.; Tera, A.H.; Monjaras, R.V.; Eiras, J.A.; Garcia, D.; Piñar, F.C.; Martínez, O.P. Influence of synthesis process on the AC response of PLZT (8/65/35), ferroelectric ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2003, 23, 1337–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidner, N.J.; Homrighaus, Z.J.; Ingram, B.J.; Mason, T.O.; Garboczi, E.J. Impedance/Dielectric Spectroscopy of Electroceramics–Part 1, Evaluation of Composite Models for Polycrystalline Ceramics. J. Electroceramics 2005, 14, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiq, M.A.; Zaman, T.U.; Ishfaq, H.A.; Maqbool, A.; Waqr, M.; Muhammad, Q.K.; Anjum, A.; Waris, A. Exploring the con-duction mechanism of multiferroic SrM-BCZT composite. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 2489–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, K.; Dehury, S.K.; Choudhary, R. Electrical, optical and magneto-electric characteristics of BiBaFeCeO6 electronic system. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 225, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, J.R.; Barsoukov, E. Impedance Spectroscopy: Theory, Experiment, and Application, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; Volume 1, pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Bijelić, J.; Tatar, D.; Hajra, S.; Sahu, M.; Kim, S.J.; Jagličić, Z.; Djerdj, I. Nanocrystalline Antiferromagnetic High-k Dielectric Sr2NiMO (M = Te, W) with Double Perovskite Structure Typ. Molecules 2020, 25, 3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mančić, D.; Paunović, V.; Vijatović, M.; Stojanović, B.; Živković, L. Electrical Characterization and Impedance Response of Lanthanum Doped Barium Titanate Ceramics. Sci. Sinter. 2008, 40, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szalbot, D.; Adamczyk, M.; Wodecka-Duś, B.; Dzik, J.; Rerak, M.; Feliksik, K. Influence of calcium doping on microstructure, dielectric and electric properties of BaBi2Nb2O9 ceramics. Processing Appl. Ceram. 2018, 12, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punia, R.; Kundu, R.S.; Dult, M.; Murugavel, S.; Kishore, N. Temperature and frequency dependent conductivity of bismuth zinc vanadate semiconducting glassy system. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 112, 083701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliot, S.R. A theory of a.c. conduction in chalcogenide glasses. Philos. Mag. A J. Theor. Exp. Appl. Phys. 1977, 36, 1291–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliot, S.R. A continuous random network approach to the structure of vitreous boron trioxide. Philos. Mag. B 1978, 37, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




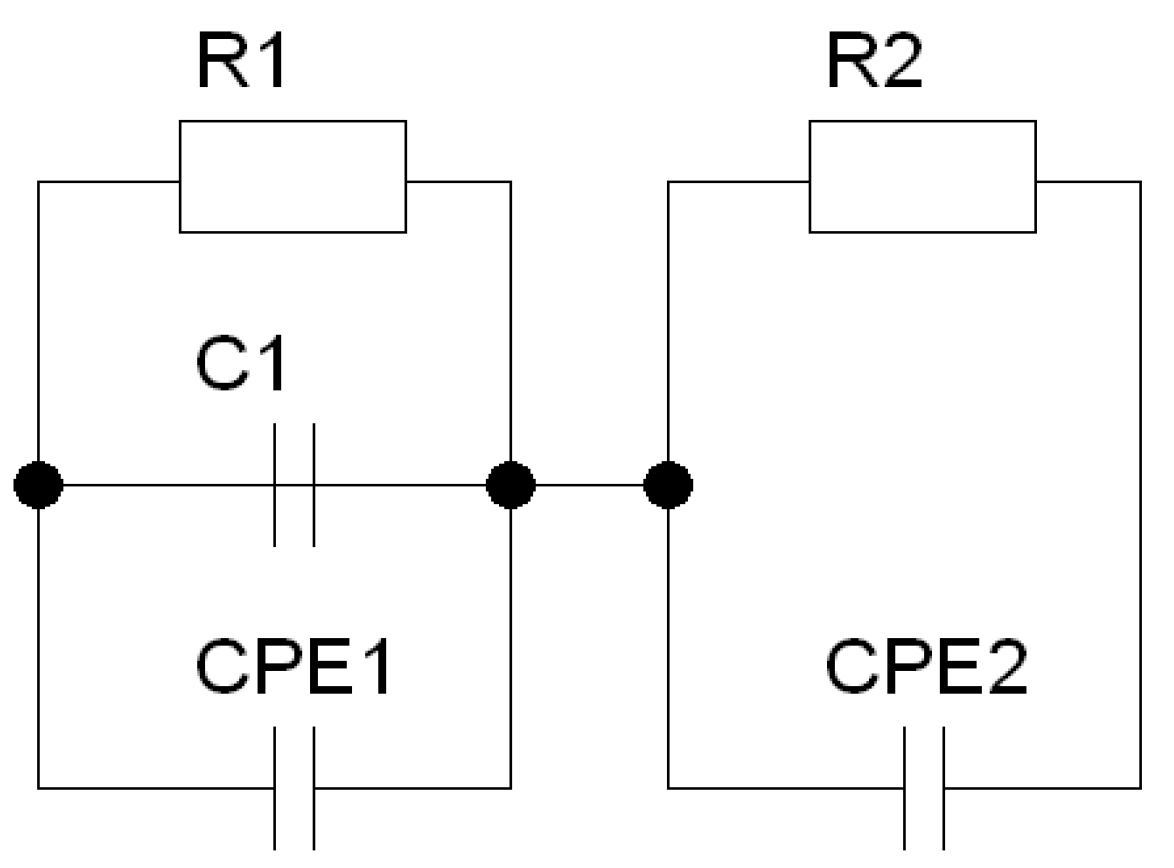


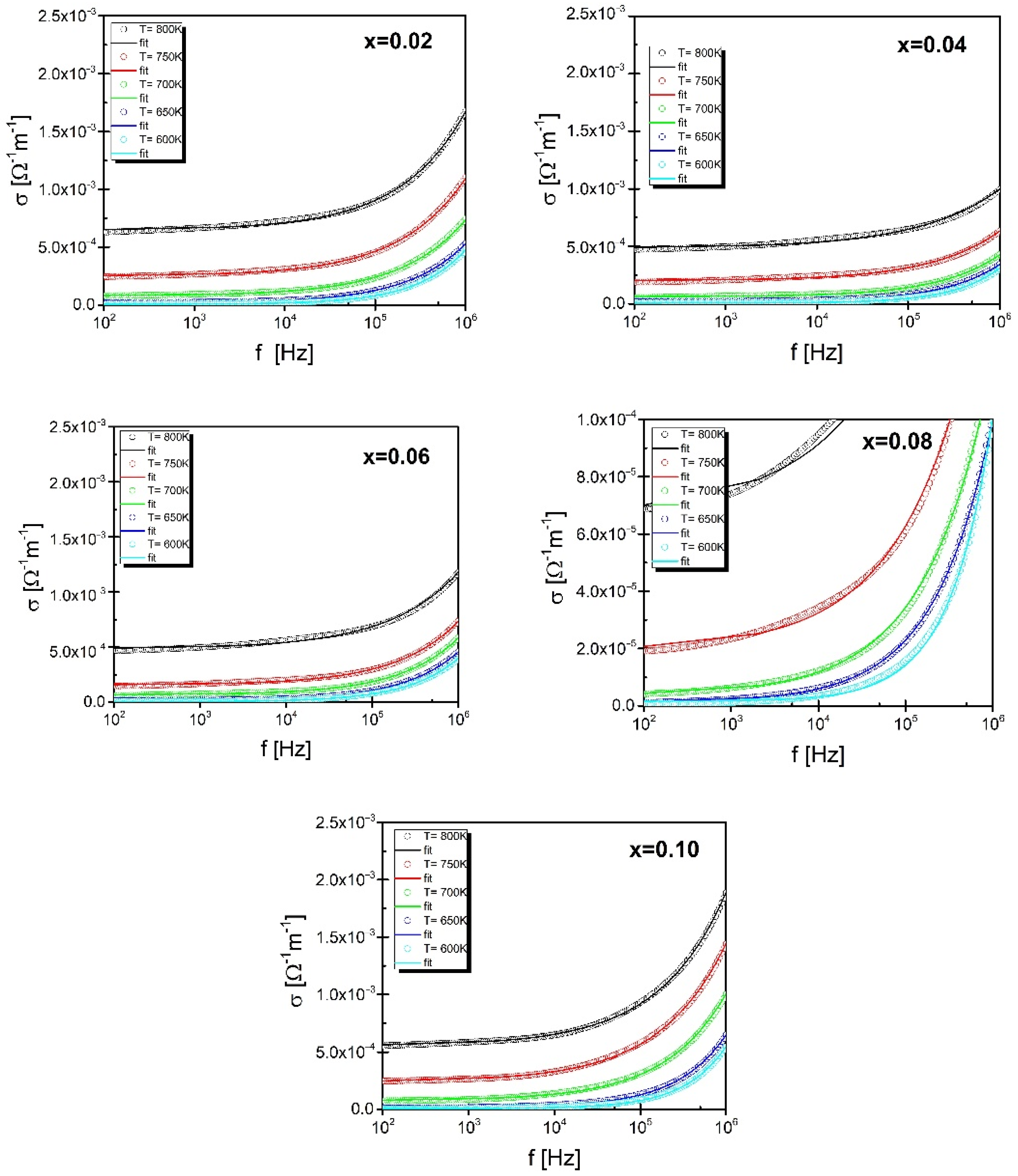

| Element | Parameter | T = 800 K | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x = 0.02 | x = 0.04 | x = 0.06 | x = 0.08 | x = 0.10 | ||
| R1 | Value [Ω] | 13,613 | 20,446 | 26,273 | 314,920 | 36,673 |
| Relative error [Ω] | 58.67 | 178 | 491 | 1693 | 419 | |
| Absolute error [%] | 0.43 | 0.87 | 1.22 | 0.54 | 1.14 | |
| CPE-T | Value [F] | 5.99 × 10−7 | 3.64 × 10−7 | 1.26 × 10−7 | 2.38 × 10−8 | 1.43 × 10−8 |
| Relative error [F] | 2.31 × 10−8 | 1.02 × 10−8 | 7.81 × 10−13 | 9.11 × 10−10 | 5.36 × 10−10 | |
| Absolute error [%] | 3.87 | 2.80 | 0.41 | 3.83 | 3.73 | |
| CPE-P | Value [a.u.] | 0.38 | 0.39 | 0.38 | 0.38 | 0.5451 |
| Relative error [a.u.] | 0.0032 | 0.0029 | 0.008 | 0.0031 | 0.0022 | |
| Absolute error [%] | 0.84 | 0.74 | 6.2 | 0.83 | 0.41 | |
| C | Value [F] | 2.88 × 10−10 | 3.27 × 10−10 | 1.25 × 10−10 | 9.06 × 10−11 | 9.921 × 10−11 |
| Relative error [F] | 61.55 | 5.85 × 10−12 | 5.16 × 10−13 | 3.97 × 10−13 | 3.27 × 10−13 | |
| Absolute error [%] | 0.70 | 1.79 | 0.41 | 0.44 | 0.33 | |
| R2 | Value [Ω] | 13,989 | 18,166 | 23,729 | 79,871 | 22,069 |
| Relative error [Ω] | 61.88 | 169 | 416 | 1850 | 452 | |
| Absolute error [%] | 0.44 | 0.93 | 1.75 | 2.32 | 2.04 | |
| CPE-T | Value [F] | 4.196 × 10−10 | 2.48 × 10−10 | 4.74 × 10−11 | 1.14 × 10−9 | 3.47 × 10−10 |
| Relative error [F] | 4.75 × 10−12 | 2.08 × 10−12 | 1.44 × 10−11 | 2.51 × 10−11 | 6.37 × 10−12 | |
| Absolute error [%] | 1.13 | 0.84 | 30 | 2.20 | 1.84 | |
| CPE-P | Value [a.u.] | 0.96 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.97 |
| Relative error [a.u.] | 0.0007 | 0.0006 | 0.04 | 0.002 | 0.004 | |
| Absolute error [%] | 0.08 | 0.06 | 4.12 | 0.18 | 0.41 | |
| χ2 | 5.5 × 10−6 | 1.71 × 10−5 | 9.7 × 10−5 | 1.6 × 10−5 | 2.45 × 10−5 | |
| Element | Parameter | T = 600 K | ||||
| x = 0.02 | x = 0.04 | x = 0.06 | x = 0.08 | x = 0.10 | ||
| R1 | Value [Ω] | 5.13 × 106 | 5.33 × 106 | 6.7743 × 106 | 2.6679 × 107 | 2.0817 × 107 |
| Relative error [Ω] | 494,494 | 95,650 | 91,936 | 1.24 × 105 | 1.26 × 105 | |
| Absolute error [%] | 0.97 | 1.79 | 1.36 | 0.45 | 0.61 | |
| CPE-T | Value [F] | 2.86 × 10−8 | 3.18 × 10−8 | 1.47 × 10−8 | 6.9 × 10−10 | 1.42 × 10−9 |
| Relative error [F] | 6.44 × 10−10 | 9.21 × 10−10 | 4.24 × 10−10 | 1.62 × 10−11 | 3.16 × 10−11 | |
| Absolute error [%] | 2.25 | 2.90 | 2.87 | 2.34 | 2.22 | |
| CPE-P | Value [a.u.] | 0.41 | 0.46 | 0.52441 | 0.54 | 0.5874 |
| Relative error [a.u.] | 0.003 | 0.0044 | 0.0041 | 0.004 | 0.0028 | |
| Absolute error [%] | 0.73 | 0.97 | 0.79 | 0.66 | 0.47 | |
| C | Value [F] | 3.48 × 10−10 | 4.80 × 10−10 | 3.89 × 10−10 | 1.05 × 10−10 | 1.372 × 10−10 |
| Relative error [F] | 1.17 | 2.63 × 10−12 | 2.44 × 10−12 | 4.68 × 10−13 | 8.59 × 10−13 | |
| Absolute error [%] | 0.34 | 0.55 | 0.63 | 0.44 | 0.62 | |
| R2 | Value [Ω] | 1.6833 × 106 | 2.1603 × 106 | 2.4574 × 106 | 1.2728 × 106 | 1.5381 × 106 |
| Relative error [Ω] | 7437 | 6414 | 9826 | 1.09 × 104 | 1.45 × 104 | |
| Absolute error [%] | 0.44 | 0.30 | 0.4 | 0.86 | 0.92 | |
| CPE-T | Value [F] | 5.60 × 10−10 | 3.14 × 10−10 | 3.74 × 10−10 | 2.84 × 10−8 | 5.636 × 10−8 |
| Relative error [F] | 3.73 × 10−12 | 1.48 × 10−12 | 2.15 × 10−12 | 1.10 × 10−10 | 2.68 × 10−10 | |
| Absolute error [%] | 0.67 | 0.47 | 0.58 | 0.38 | 0.48 | |
| CPE-P | Value [a.u.] | 0.96 | 0.99 | 0.98015 | 0.89929 | 0.81243 |
| Relative error [a.u.] | 0.0003 | 0.0003 | 0.0005 | 0.031 | 0.023 | |
| Absolute error [%] | 0.036 | 0.031 | 0.049 | 3.41 | 2.77 | |
| χ2 | 1.35 × 10−5 | 4.55 × 10−5 | 6.67 × 10−5 | 1.9 × 10−5 | 2.41 × 10−5 | |
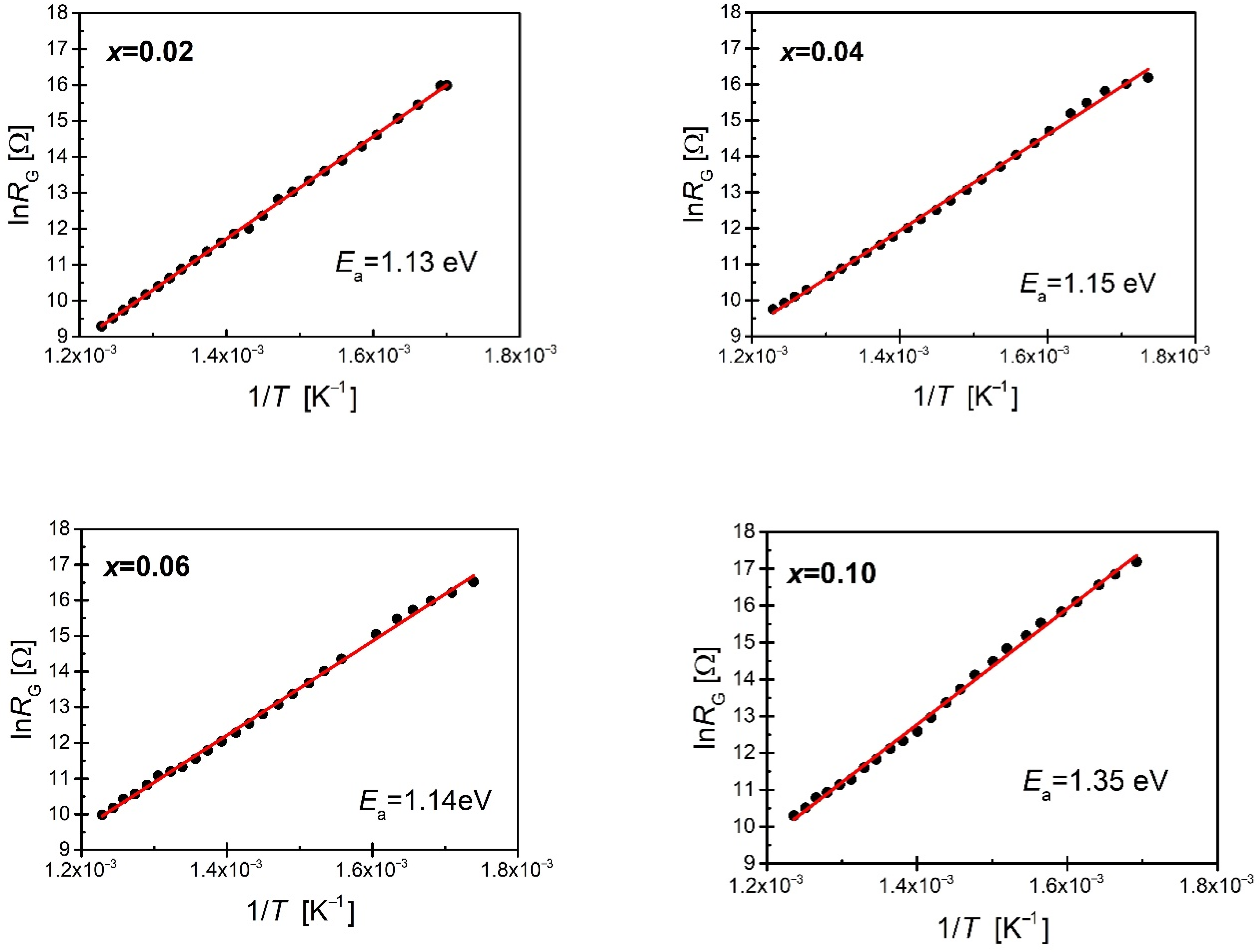
| x (Pr) | EG [eV] | EGB [eV] |
|---|---|---|
| 0.02 | 1.13 | 1.00 |
| 0.04 | 1.15 | 1.00 |
| 0.06 | 1.14 | 0.98 |
| 0.08 | 1.44 | 0.95 |
| 0.10 | 1.35 | 0.85 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rerak, M.; Makowska, J.; Adamczyk-Habrajska, M.; Kozielski, L. Impedance Spectroscopy of Pr-Doped BaBi2Nb2O9 Aurivillius Ceramics. Materials 2022, 15, 6308. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15186308
Rerak M, Makowska J, Adamczyk-Habrajska M, Kozielski L. Impedance Spectroscopy of Pr-Doped BaBi2Nb2O9 Aurivillius Ceramics. Materials. 2022; 15(18):6308. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15186308
Chicago/Turabian StyleRerak, Michał, Jolanta Makowska, Małgorzata Adamczyk-Habrajska, and Lucjan Kozielski. 2022. "Impedance Spectroscopy of Pr-Doped BaBi2Nb2O9 Aurivillius Ceramics" Materials 15, no. 18: 6308. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15186308
APA StyleRerak, M., Makowska, J., Adamczyk-Habrajska, M., & Kozielski, L. (2022). Impedance Spectroscopy of Pr-Doped BaBi2Nb2O9 Aurivillius Ceramics. Materials, 15(18), 6308. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15186308








