Green Facile Synthesis of Silver-Doped Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and Evaluation of Their Effect on Drug Release
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
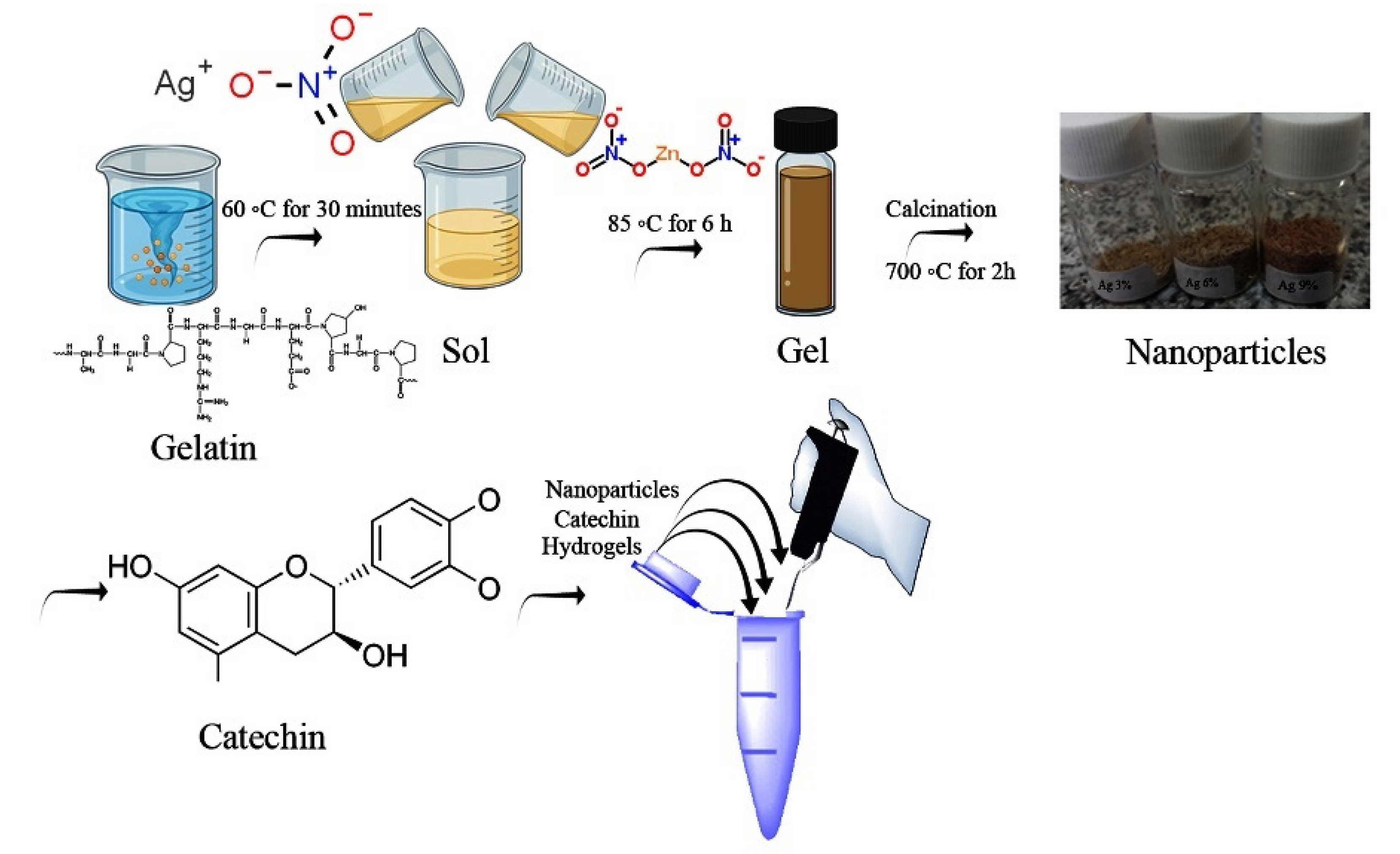
2.2. Green Synthesis of Nanoparticles
2.3. Hydrogel Production
2.3.1. Swelling of Hydrogels
2.3.2. Catechin Loading
2.3.3. Characterization of Nanoparticles
2.3.4. Drug Content
2.3.5. In Vitro Release Studies
3. Results
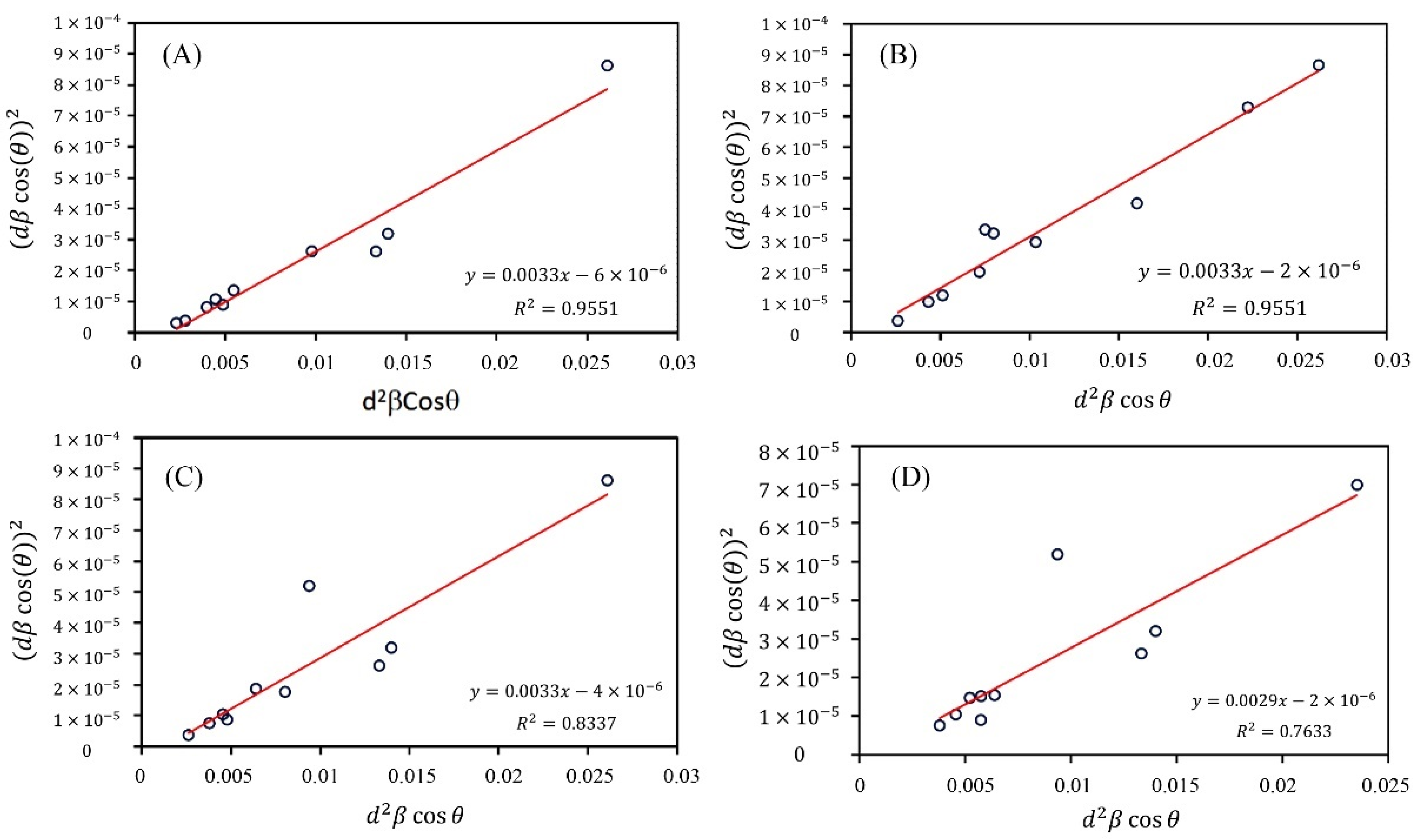
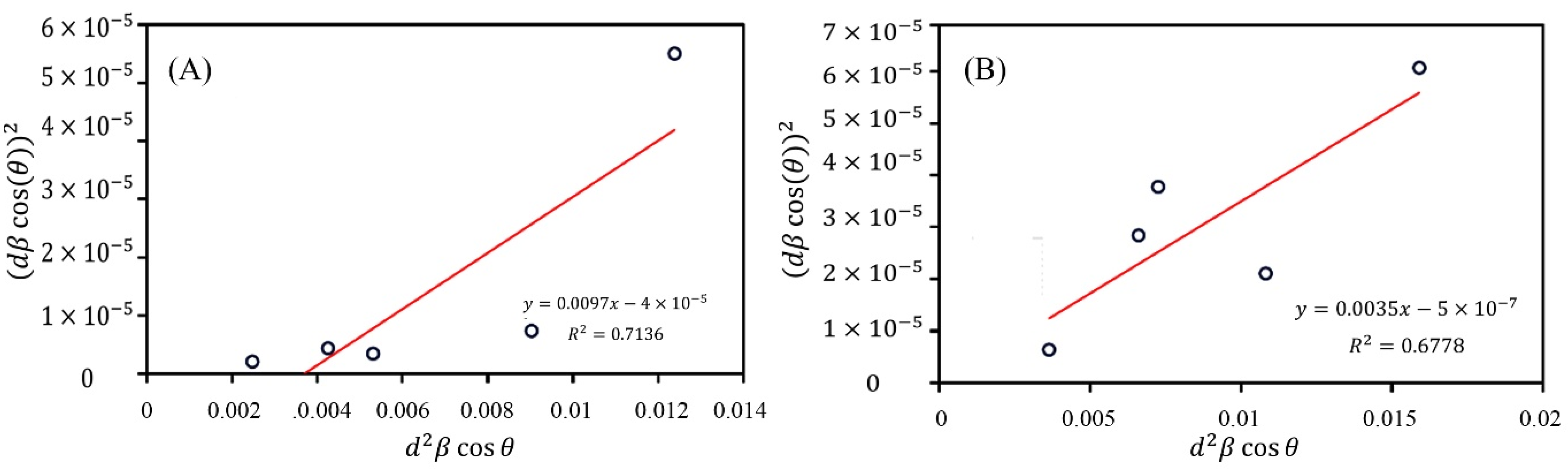
3.1. XRD Characterization
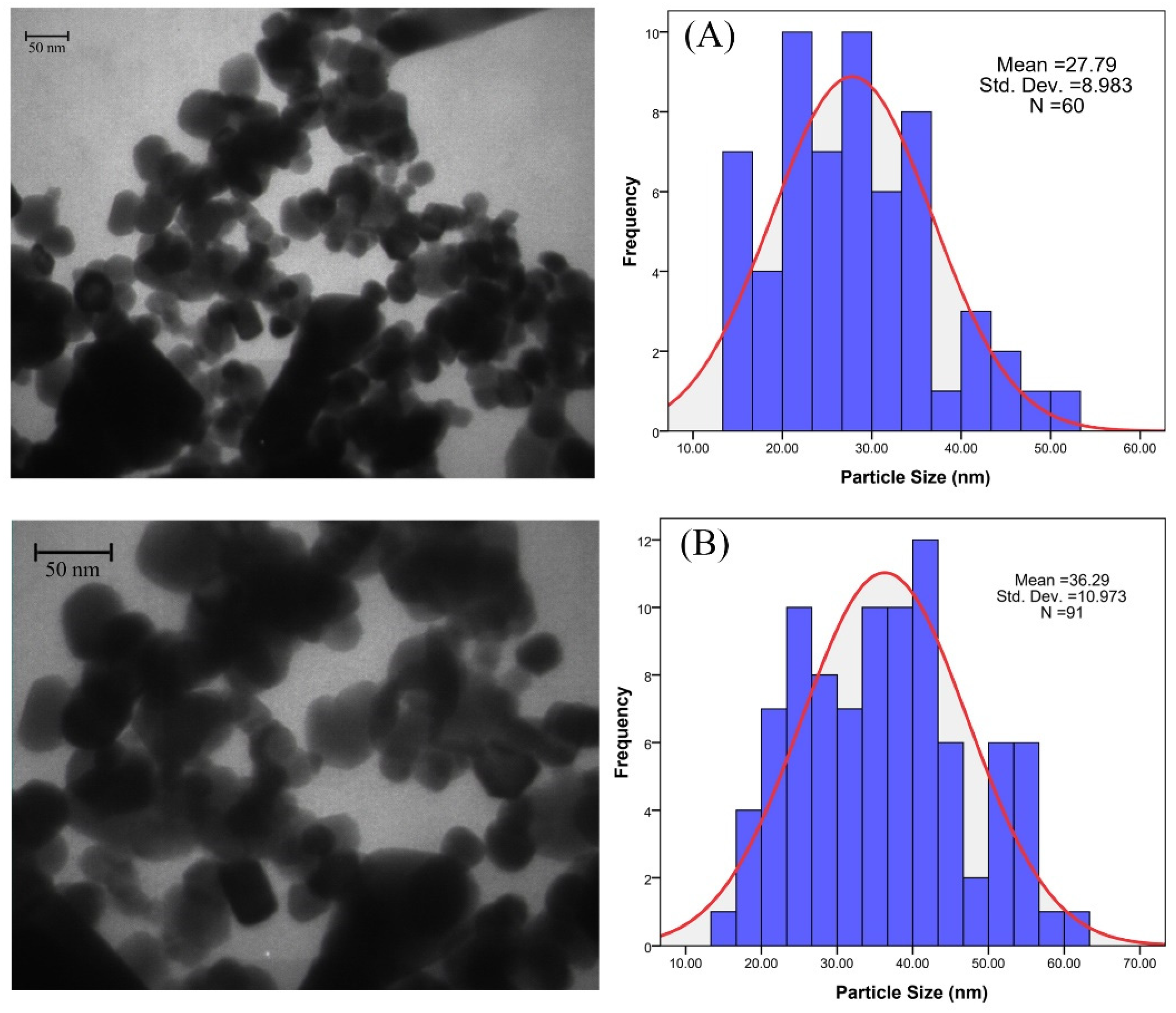
3.2. TEM Analysis
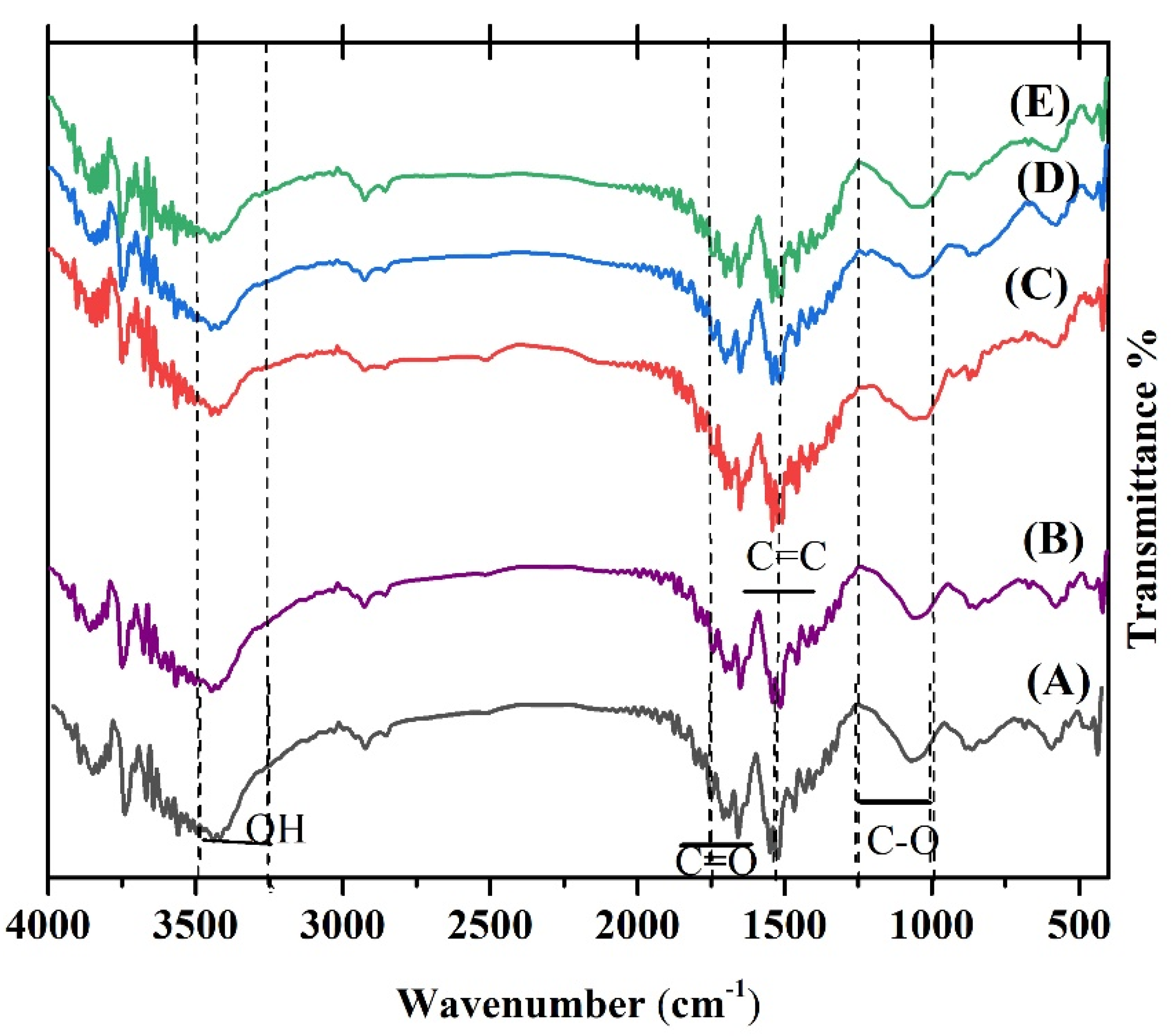
3.3. FTIR
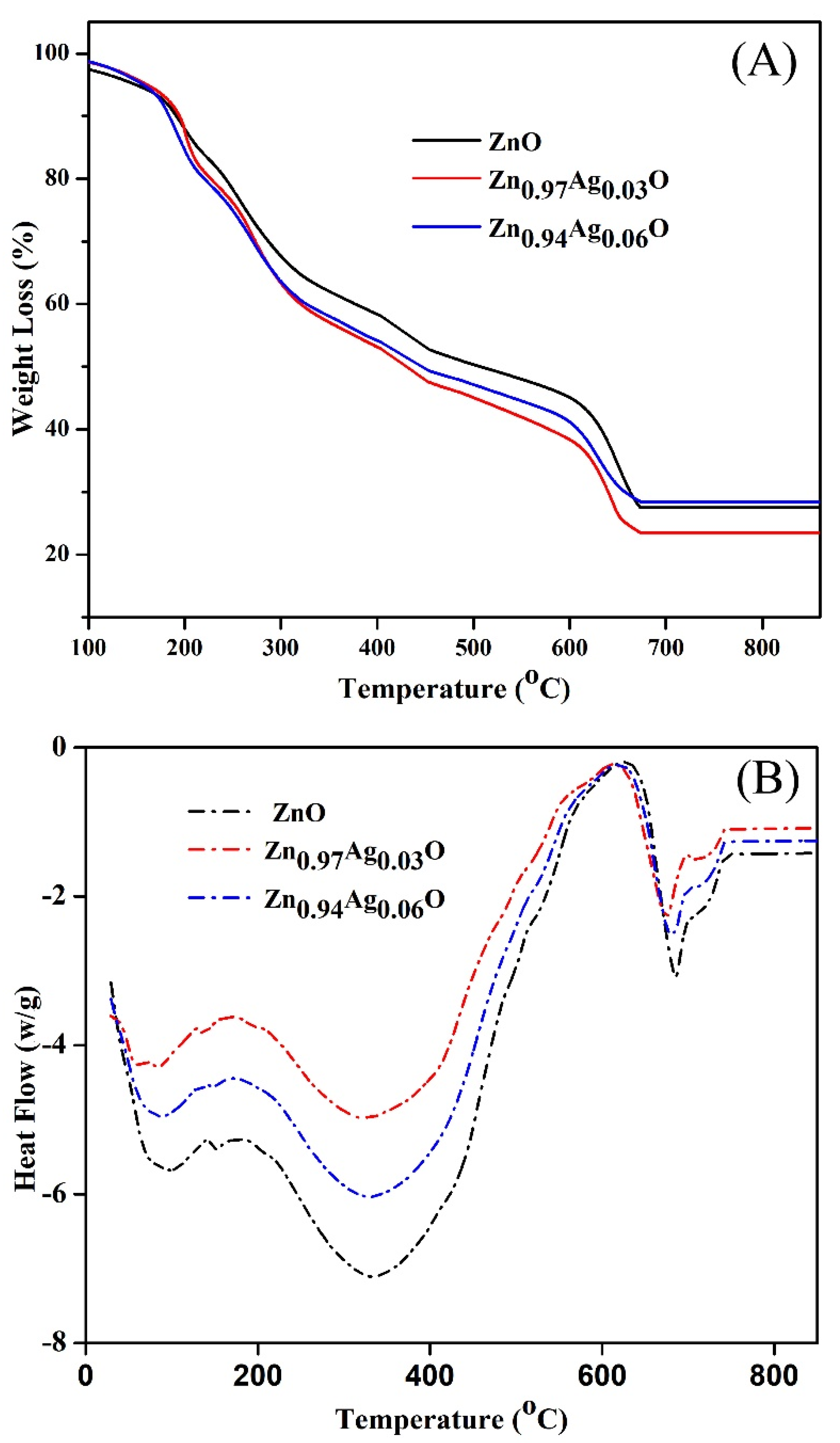
3.4. TGA and DSC Analysis
3.5. Texture
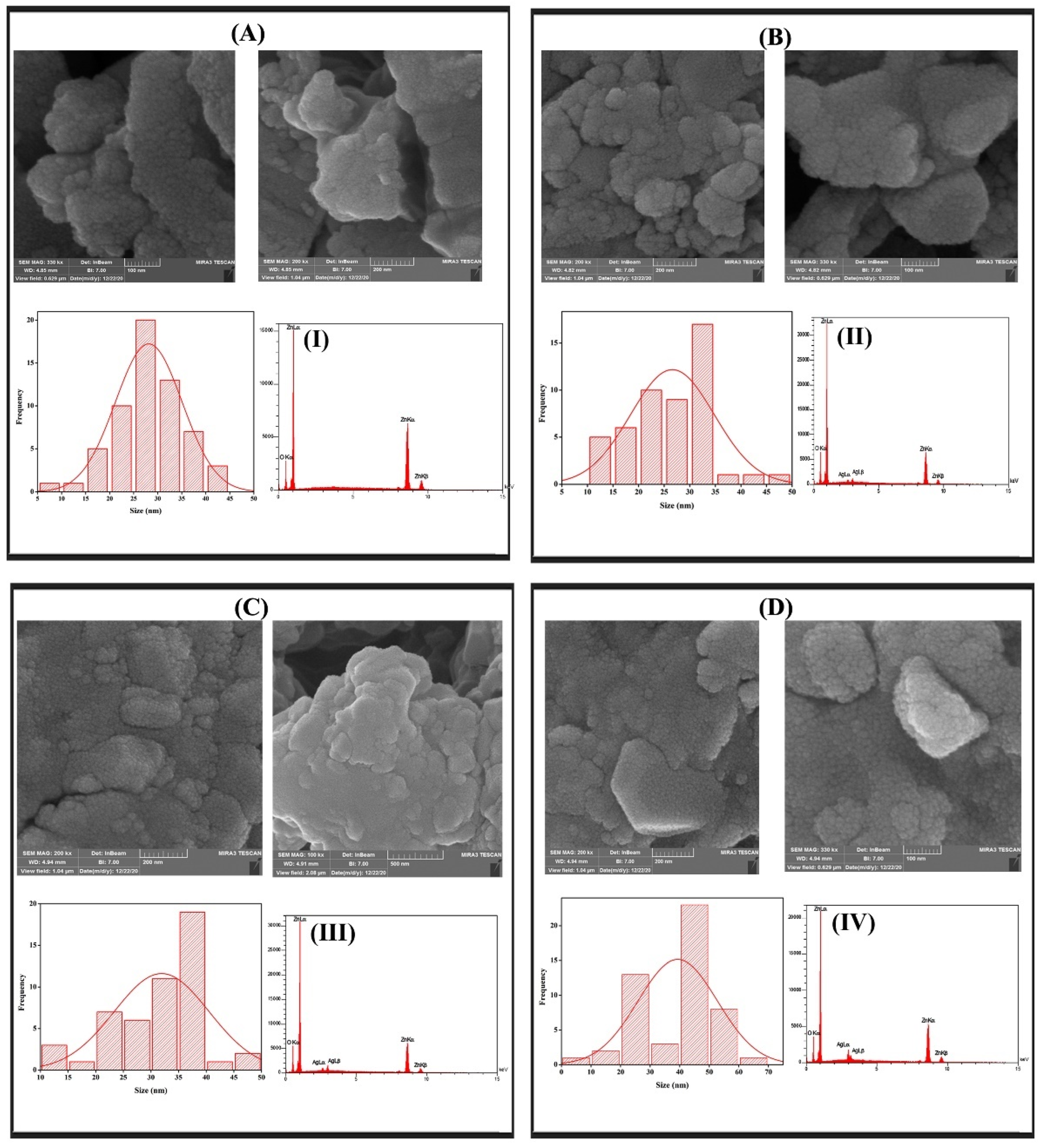
3.6. FESEM and EDS
3.7. Swelling Ratio and In Vitro Release Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Agarwal, H.; Shanmugam, V. A review on anti-inflammatory activity of green synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticle: Mechanism-based approach. Bioorgan. Chem. 2020, 94, 103423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarian, M.; Mahjoub, S.; Elahi, S.M.; Zabihi, E.; Tashakkorian, H. Green synthesis, formulation and biological evaluation of a novel ZnO nanocarrier loaded with paclitaxel as drug delivery system on MCF-7 cell line. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 186, 110686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kołodziejczak-Radzimska, A.; Jesionowski, T. Zinc oxide—From synthesis to application: A review. Materials 2014, 7, 2833–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, S.M.; Ferreira, D.P.; Ferreira, A.; Vaz, F.; Fangueiro, R. Multifunctional flax fibres based on the combined effect of silver and zinc oxide (Ag/ZnO) nanostructures. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojnarowicz, J.; Chudoba, T.; Lojkowski, W. A review of microwave synthesis of zinc oxide nanomaterials: Reactants, process parameters and morphologies. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.A.; Abu-Elghait, M.; Ahmed, N.E.; Salem, S.S. Eco-friendly mycogenic synthesis of ZnO and CuO nanoparticles for in vitro antibacterial, antibiofilm, and antifungal applications. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2021, 199, 2788–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavi, M.; Nokhodchi, A. Synthesis and modification of bio-derived antibacterial Ag and ZnO nanoparticles by plants, fungi, and bacteria. Drug Discov. Today 2021, 26, 1953–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faisal, S.; Jan, H.; Shah, S.A.; Shah, S.; Khan, A.; Akbar, M.T.; Rizwan, M.; Jan, F.; Wajidullah; Akhtar, N. Green synthesis of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles using aqueous fruit extracts of Myristica fragrans: Their characterizations and biological and environmental applications. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 9709–9722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighat, M.; Alijani, H.Q.; Ghasemi, M.; Khosravi, S.; Borhani, F.; Sharifi, F.; Iravani, S.; Najafi, K.; Khatami, M. Cytotoxicity properties of plant-mediated synthesized K-doped ZnO nanostructures. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 45, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, C.V.; Repp, S.; Thomann, R.; Krueger, M.; Weber, S.; Erdem, E. Charge transfer and surface defect healing within ZnO nanoparticle decorated graphene hybrid materials. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 9682–9687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhu, L.; Cao, W.; Li, P.; Zhan, Z.; Chen, Z.; Yuan, X.; Wang, J. Defect-related optical properties of Mg-doped ZnO nanoparticles synthesized via low temperature hydrothermal method. J. Alloy. Compd. 2021, 858, 157654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saqib, A.N.S.; Huong, N.T.T.; Kim, S.-W.; Jung, M.-H.; Lee, Y.H. Structural and magnetic properties of highly Fe-doped ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by one-step solution plasma process. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 853, 157153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simanjuntak, F.M.; Panda, D.; Wei, K.-H.; Tseng, T.-Y. Status and Prospects of ZnO-Based Resistive Switching Memory Devices. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.; Yang, D.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wu, B.; Zong, Y.; Feng, Q. ZnO ultraviolet photodetector based on flexible polyester fibre substrates by low-temperature hydrothermal approach. Micro Nano Lett. 2019, 14, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagha, G.; Mersagh, M.R.; Naffakh-Moosavy, H.; Matin, L.F. The role of rGO sheet and Ag dopant in reducing ZnO electron transport layer recombination in planar perovskite solar cells. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 16111–16123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.; Bahadur, A.; Javed, M.; Hakami, O.; Irfan, R.M.; Ahmad, Z.; AlObaid, A.; Al-Anazy, M.M.; Baghdadi, H.B.; Abd-Rabboh, H.S. Design Ag-doped ZnO heterostructure photocatalyst with sulfurized graphitic C3N4 showing enhanced photocatalytic activity. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2021, 272, 115320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusdianto, K.; Sari, T.; Laksono, M.; Madhania, S.; Winardi, S. Fabrication and Application of ZnO-Ag Nanocomposite Materials Prepared by Gas-Phase Methods; IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; p. 012023. [Google Scholar]
- Jabeen, S. Facile green synthesis of silver doped ZnO nanoparticles using Tridax Procumbens leaf extract and their evaluation of antibacterial activity. J. Water Environ. Nanotechnol. 2020, 5, 307–320. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, Y.Y.; Pang, Y.L.; Lim, S.; Chong, W.C. Sonocatalytic degradation of Congo red by using green synthesized silver doped zinc oxide nanoparticles. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 46, 1948–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raguvaran, R.; Manuja, B.K.; Chopra, M.; Thakur, R.; Anand, T.; Kalia, A.; Manuja, A. Sodium alginate and gum acacia hydrogels of ZnO nanoparticles show wound healing effect on fibroblast cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 96, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirelkhatim, A.; Mahmud, S.; Seeni, A.; Kaus, N.H.M.; Ann, L.C.; Bakhori, S.K.M.; Hasan, H.; Mohamad, D. Review on zinc oxide nanoparticles: Antibacterial activity and toxicity mechanism. Nano-Micro Lett. 2015, 7, 219–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joorabloo, A.; Khorasani, M.T.; Adeli, H.; Mansoori-Moghadam, Z.; Moghaddam, A. Fabrication of heparinized nano ZnO/poly (vinylalcohol)/carboxymethyl cellulose bionanocomposite hydrogels using artificial neural network for wound dressing application. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 70, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, S.; Jameel, M.H.; Akhtar, N.; Nazir, N.; Ali, A.; Zaman, A.; Rehman, A.; Butt, S.; Sultana, F.; Mushtaq, M. Modification in structural, optical, morphological, and electrical properties of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles (NPs) by metal (Ni, Co) dopants for electronic device applications. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 103518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltakesmez, A.; Tekmen, S.; Köç, P.; Tüzemen, S.; Meral, K.; Onganer, Y. UV-visible detector and LED based n-ZnO/p-Si heterojunction formed by electrodeposition. AIP Adv. 2013, 3, 032125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handral, H.; Ashajyothi, C.; Sriram, G.; Kelmani, C.; Dubey, N.; Cao, T. Cytotoxicity and Genotoxicity of Metal Oxide Nanoparticles in Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Fibroblasts. Coatings 2021, 11, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neupane, G.R.; Kaphle, A.; Hari, P. Microwave-assisted Fe-doped ZnO nanoparticles for enhancement of silicon solar cell efficiency. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2019, 201, 110073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallikarjunaswamy, C.; Lakshmi Ranganatha, V.; Ramu, R.; Nagaraju, G. Facile microwave-assisted green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles: Application to photodegradation, antibacterial and antioxidant. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 1004–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Shui, A.; Wang, X.; He, C.; Qian, J.; Du, B. A facile fabrication and high-performance electromagnetic microwave absorption of ZnO nanoparticles. J. Alloy. Compd. 2020, 842, 155638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharthi, M.N.; Ismail, I.; Bellucci, S.; Khdary, N.H.; Abdel Salam, M. Biosynthesis Microwave-Assisted of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles with ZiziphusJujuba Leaves Extract: Characterization and Photocatalytic Application. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.; Oh, S.-G. Synthesis of amine modified ZnO nanoparticles and their photocatalytic activities in micellar solutions under UV irradiation. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 96, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulcha, B.; Leta Tesfaye, J.; Anatol, D.; Shanmugam, R.; Dwarampudi, L.P.; Nagaprasad, N.; Bhargavi, V.; Krishnaraj, R. Synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles by hydrothermal methods and spectroscopic investigation of ultraviolet radiation protective properties. J. Nanomater. 2021, 2021, 8617290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, N.A.; Matsui, K.; Paskocimas, C.; Bomio, M.; Motta, F. Study of the photocatalysis and increase of antimicrobial properties of Fe3+ and Pb2+ co-doped ZnO nanoparticles obtained by microwave-assisted hydrothermal method. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2019, 93, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasly, H.; Abd El-Sadek, M.; Henini, M. Influence of reaction time and synthesis temperature on the physical properties of ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by the hydrothermal method. Appl. Phys. A 2018, 124, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosowska, J.; Kaszewski, J.; Witkowski, B.; Kuryliszyn-Kudelska, I.; Godlewski, M. The effect of iron content on properties of ZnO nanoparticles prepared by microwave hydrothermal method. Opt. Mater. 2020, 109, 110089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Pedraza, A. Synthesis and alignment of Zn and ZnO nanoparticles by laser-assisted chemical vapor deposition. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 045609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taziwa, R.; Meyer, E.; Katwire, D.; Ntozakhe, L. Influence of carbon modification on the morphological, structural, and optical properties of zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized by pneumatic spray pyrolysis technique. J. Nanomater. 2017, 2017, 9095301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibraheam, A.; Rzaij, J.M.; Fakhri, M.A.; Abdulwahhab, A. Structural, optical and electrical investigations of Al: ZnO nanostructures as UV photodetector synthesized by spray pyrolysis technique. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 055916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiragino, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Takeuchi, H.; Takeuchi, A.; Lin, J.; Yoshida, T.; Fujita, Y. Synthesis of nitrogen-doped ZnO nanoparticles by RF thermal plasma. Solid-State Electron. 2016, 118, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, H.R.; Mehr, F.P.; Pazoki, H.; Rahmani, B.M. Synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles by precipitation method. Orient. J. Chem 2015, 31, 1219–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahouli, M.; Barhoumi, A.; Bouzid, A.; Al-Hajry, A.; Guermazi, S. Structural and optical properties of ZnO nanoparticles prepared by direct precipitation method. Superlattices Microstruct. 2015, 85, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moharram, A.; Mansour, S.; Hussein, M.; Rashad, M. Direct precipitation and characterization of ZnO nanoparticles. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navas, D.; Ibañez, A.; González, I.; Palma, J.L.; Dreyse, P. Controlled dispersion of ZnO nanoparticles produced by basic precipitation in solvothermal processes. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jay Chithra, M.; Sathya, M.; Pushpanathan, K. Effect of pH on crystal size and photoluminescence property of ZnO nanoparticles prepared by chemical precipitation method. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 2015, 28, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christy, S.R.; Priya, L.S.; Durka, M.; Dinesh, A.; Babitha, N.; Arunadevi, S. Simple combustion synthesis, structural, morphological, optical and catalytic properties of ZnO nanoparticles. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 19, 3564–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaraju, G.; Shivaraju, G.; Banuprakash, G.; Rangappa, D. Photocatalytic activity of ZnO nanoparticles: Synthesis via solution combustion method. Mater. Today Proc. 2017, 4, 11700–11705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irshad, K.; Khan, M.T.; Murtaza, A. Synthesis and characterization of transition-metals-doped ZnO nanoparticles by sol-gel auto-combustion method. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2018, 543, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shkir, M.; Al-Shehri, B.M.; Pachamuthu, M.; Khan, A.; Chandekar, K.V.; AlFaify, S.; Hamdy, M.S. A remarkable improvement in photocatalytic activity of ZnO nanoparticles through Sr doping synthesized by one pot flash combustion technique for water treatments. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 587, 124340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, S.; Mahajan, P.; Mahajan, S.; Khosla, A.; Datt, R.; Gupta, V.; Young, S.-J.; Oruganti, S.K. influence of processing parameters to control morphology and optical properties of Sol-Gel synthesized ZnO nanoparticles. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2021, 10, 023002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.; Menazea, A.; Kabary, H.A.; El-Sherbiny, A.; Samy, A. The influence of calcination temperature on structural and antimicrobial characteristics of zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized by Sol–Gel method. J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1196, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi Khatir, N.; Abdul-Malek, Z.; Zak, A.K.; Akbari, A.; Sabbagh, F. Sol–gel grown Fe-doped ZnO nanoparticles: Antibacterial and structural behaviors. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2016, 78, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbagh, F.; Kiarostami, K.; Mahmoudi Khatir, N.; Rezania, S.; Muhamad, I.I. Green synthesis of Mg0.99 Zn0.01O nanoparticles for the fabrication of κ-Carrageenan/NaCMC hydrogel in order to deliver catechin. Polymers 2020, 12, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perveen, R.; Shujaat, S.; Qureshi, Z.; Nawaz, S.; Khan, M.; Iqbal, M. Green versus sol-gel synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles and antimicrobial activity evaluation against panel of pathogens. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 7817–7827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, V.; Hariram, M.; Vivekanandhan, S.; Muthuramkumar, S. Periconium sp. (endophytic fungi) extract mediated sol-gel synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles for antimicrobial and antioxidant applications. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2020, 105, 104739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramgir, N.S.; Hwang, Y.K.; Mulla, I.S.; Chang, J.-S. Effect of particle size and strain in nanocrystalline SnO2 according to doping concentration of ruthenium. Solid State Sci. 2006, 8, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isemura, M. Catechin in Human Health and Disease; Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute: Basel, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 24, p. 528. [Google Scholar]
- Grzesik, M.; Naparło, K.; Bartosz, G.; Sadowska-Bartosz, I. Antioxidant properties of catechins: Comparison with other antioxidants. Food Chem. 2018, 241, 480–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.-J.; Liu, Q. Molecular structure and physicochemical properties of potato and bean starches as affected by gamma-irradiation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2010, 47, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabbagh, F.; Muhamad, I.I. Acrylamide-based hydrogel drug delivery systems: Release of acyclovir from MgO nanocomposite hydrogel. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 72, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erol, O.; Pantula, A.; Liu, W.; Gracias, D.H. Transformer hydrogels: A review. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1900043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbagh, F.; Kiarostami, K.; Khatir, N.M.; Rezania, S.; Muhamad, I.I.; Hosseini, F. Effect of zinc content on structural, functional, morphological, and thermal properties of kappa-carrageenan/NaCMC nanocomposites. Polym. Test. 2021, 93, 106922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullity, B.D.; Stock, S.R. Elements of X-ray Diffraction; Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Rad, M.S.; Kompany, A.; Zak, A.K.; Abrishami, M.E. The effect of silver concentration and calcination temperature on structural and optical properties of ZnO:Ag nanoparticles. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2015, 29, 1450254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shayani Rad, M.; Kompany, A.; Khorsand Zak, A.; Javidi, M.; Mortazavi, S.M. Microleakage and antibacterial properties of ZnO and ZnO:Ag nanopowders prepared via a sol–gel method for endodontic sealer application. J. Nanopart. Res. 2013, 15, 1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, R.; Jamali-Sheini, F.; Zak, A.K. A Comparative Study of the Properties of ZnO Nano/Microstructures Grown using Two Types of Thermal Evaporation Set-Up Conditions. Chem. Vap. Depos. 2012, 18, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, B.; Huang, P.; Wu, Y.; Wu, F.-Y.; Ma, L. Colorimetric determination of tyrosinase based on in situ silver metallization catalyzed by gold nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-M.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, K.-W.; Ji, V. General compliance transformation relation and applications for anisotropic hexagonal metals. Solid State Commun. 2006, 139, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nye, J.F. Physical Properties of Crystals: Their Representation by Tensors and Matrices; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- Yousefi, R.; Zak, A.K.; Jamali-Sheini, F. The effect of group-I elements on the structural and optical properties of ZnO nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 1371–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, T.; Ara, G.; Khalid, N.; Ijaz, M. Simple synthesis of Ag-doped CdS nanostructure material with excellent properties. Appl. Nanosci. 2020, 10, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraju, G.; Prashanth, S.; Shastri, M.; Yathish, K.; Anupama, C.; Rangappa, D. Electrochemical heavy metal detection, photocatalytic, photoluminescence, biodiesel production and antibacterial activities of Ag–ZnO nanomaterial. Mater. Res. Bull. 2017, 94, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caglar, M.; Caglar, Y.; Aksoy, S.; Ilican, S. Temperature dependence of the optical band gap and electrical conductivity of sol–gel derived undoped and Li-doped ZnO films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 4966–4971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Tejada, M.; Durán, J.; Ontiveros-Ortega, A.; Espinosa-Jimenez, M.; Perea-Carpio, R.; Chibowski, E. Investigation of alumina/(+)-catechin system properties. Part I: A study of the system by FTIR-UV–Vis spectroscopy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2002, 24, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surendra, B.; Swamy, M.M.; Shamala, T.; Rao, S.; Pramila, S. Development of enhanced electrochemical sensor and antimicrobial studies of ZnO NPs synthesized using green plant extract. Sens. Int. 2022, 3, 100176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, A.; Khammar, M.; Taherzadeh, D.; Rajabian, A.; Zak, A.K.; Darroudi, M. Zinc-doped cerium oxide nanoparticles: Sol-gel synthesis, characterization, and investigation of their in vitro cytotoxicity effects. J. Mol. Struct. 2017, 1149, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, P.; Nemati, F.; Gholoobi, A.; Hashemzadeh, A.; Sabouri, Z.; Darroudi, M. Green facile synthesis of silver-doped cerium oxide nanoparticles and investigation of their cytotoxicity and antibacterial activity. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2021, 131, 108762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
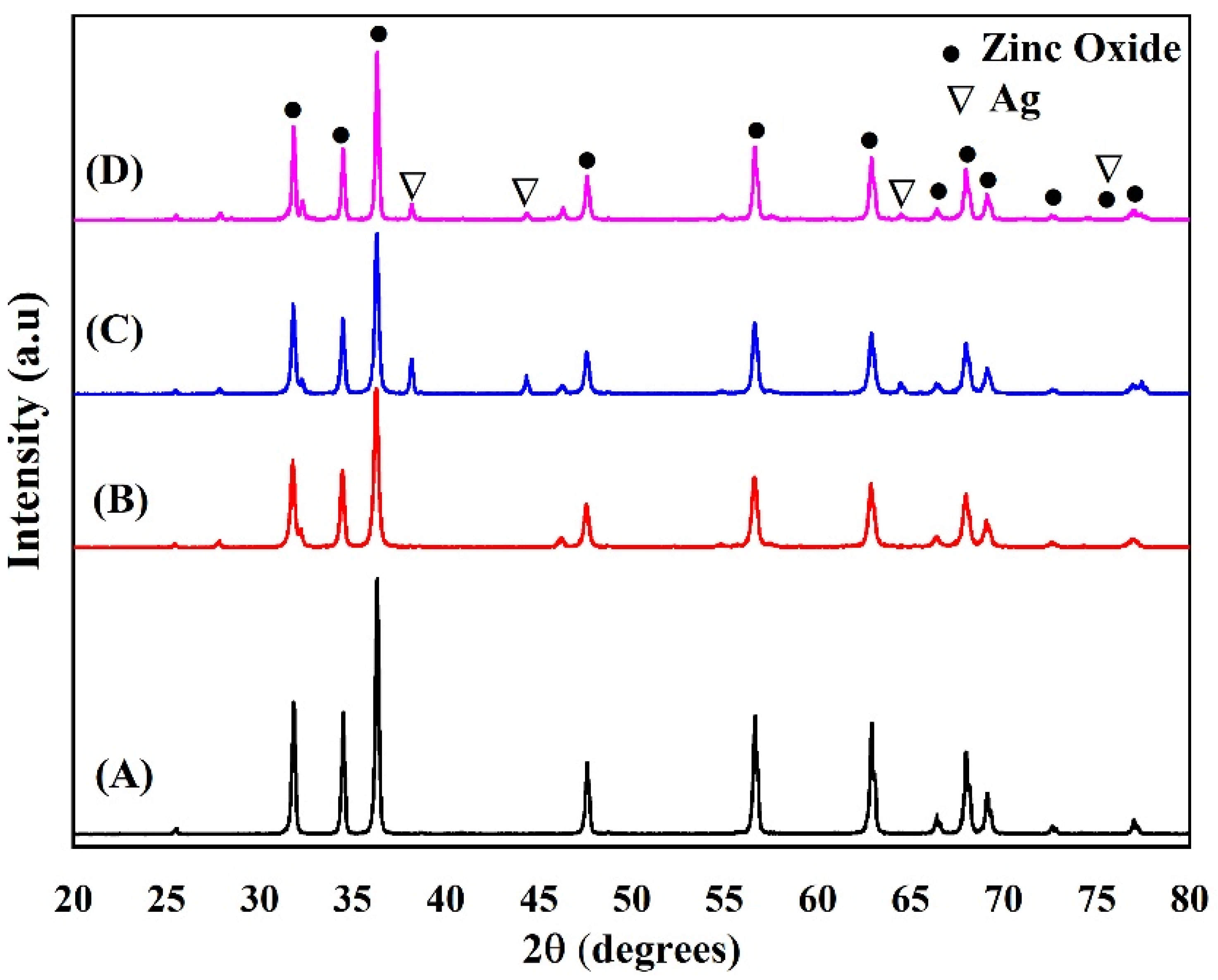



| Compound | hkl | dhk l (nm) ± 0.0005 | Structure | Lattice Parameter (nm) ± 0.0005 | V(Å3) ± 0.0002 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZnONPs | 31.8291 34.4884 | (100) (002) | 0.2811 0.2600 | Hexagonal | a = 0.32465 c = 0.520122 | 0.0474737 |
| Zn0.97Ag0.03O | 31.7693 34.4491 | (100) (002) | 0.2816 0.2603 | Hexagonal | a = 0.325246 c = 0.520696 | 0.0477007 |
| Zn0.94Ag0.06O | 31.8083 34.4688 | (100) (002) | 0.2813 0.2602 | Hexagonal | a = 0.324857 c = 0.520408 | 0.0475603 |
| Zn0.91Ag0.09O | 31.8389 34.4876 | (100) (002) | 0.2810 0.2600 | Hexagonal | a = 0.324553 c = 0.520132 | 0.0474463 |
| Compound | Scherrer | Size Strain Plot | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D (nm) | D (nm) | |||||
| ZnO-NPs | 42 | 28 | 3.46 | 360 | 12.48 | 21.61 |
| Zn0.97Ag0.03O | 45 | 35 | 1.55 | 360 | 55.81 | 43.23 |
| Zn0.94Ag0.06O | 47 | 39 | 1.26 | 360 | 45.57 | 28.82 |
| Zn0.91Ag0.09O | 53 | 48 | 1.55 | 360 | 55.81 | 43.23 |
| Sample | Hardness (g) | Adhesiveness | Springiness (mm) | Adhesion (g.s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn O | 3.40 | 3.40 | 0.52 | 0.12 |
| Zn0.97Ag0.03O | 4.17 | 2.10 | 0.46 | 0.19 |
| Zn0.94Ag0.06O | 3.15 | 4.50 | 0.62 | 0.15 |
| Zn0.91Ag0.09O | 0.06 | 2.13 | 0.73 | 0.16 |
| Sample | Drug Content (%) |
|---|---|
| ZnO-NPs | 97.71 ± 1.02% |
| Zn0.97Ag0.03O | 98.59 ± 2.11% |
| Zn0.94Ag0.06O | 98.41 ± 1.14% |
| Zn0.91Ag0.09O | 97.91 ± 1.32% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khatir, N.M.; Sabbagh, F. Green Facile Synthesis of Silver-Doped Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and Evaluation of Their Effect on Drug Release. Materials 2022, 15, 5536. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15165536
Khatir NM, Sabbagh F. Green Facile Synthesis of Silver-Doped Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and Evaluation of Their Effect on Drug Release. Materials. 2022; 15(16):5536. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15165536
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhatir, Nadia Mahmoudi, and Farzaneh Sabbagh. 2022. "Green Facile Synthesis of Silver-Doped Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and Evaluation of Their Effect on Drug Release" Materials 15, no. 16: 5536. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15165536
APA StyleKhatir, N. M., & Sabbagh, F. (2022). Green Facile Synthesis of Silver-Doped Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and Evaluation of Their Effect on Drug Release. Materials, 15(16), 5536. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15165536







