Production, Mechanical Properties and Biomedical Characterization of ZrTi-Based Bulk Metallic Glasses in Comparison with 316L Stainless Steel and Ti6Al4V Alloy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Production of Bulk Metallic Glasses
2.2. Microstructure Investigations
2.3. Investigations of Mechanical Properties
2.4. Corrosion Resistance in SBF
2.5. Biocompatibility Assay
2.5.1. Cell Culture
2.5.2. Cytotoxicity Assays
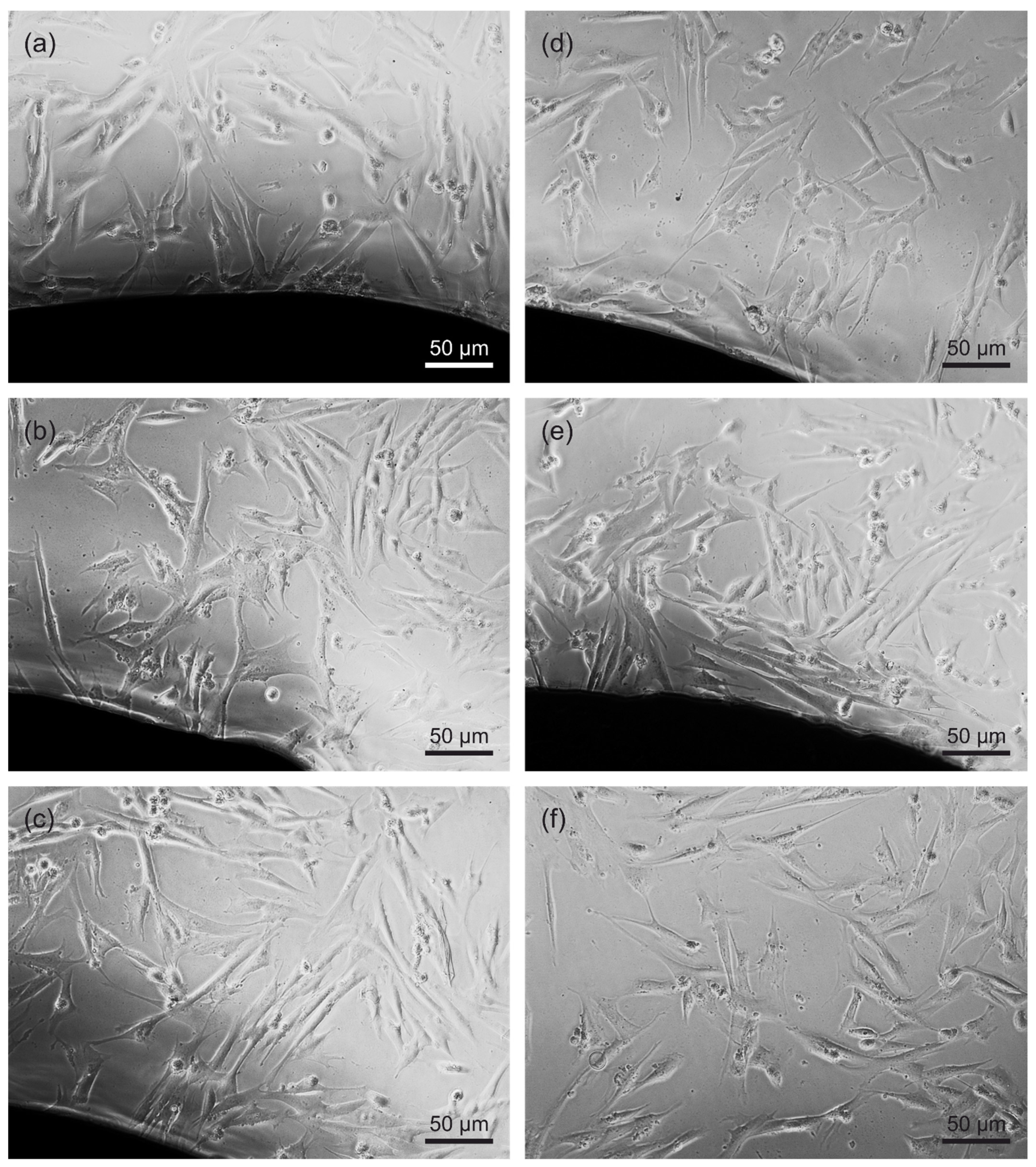
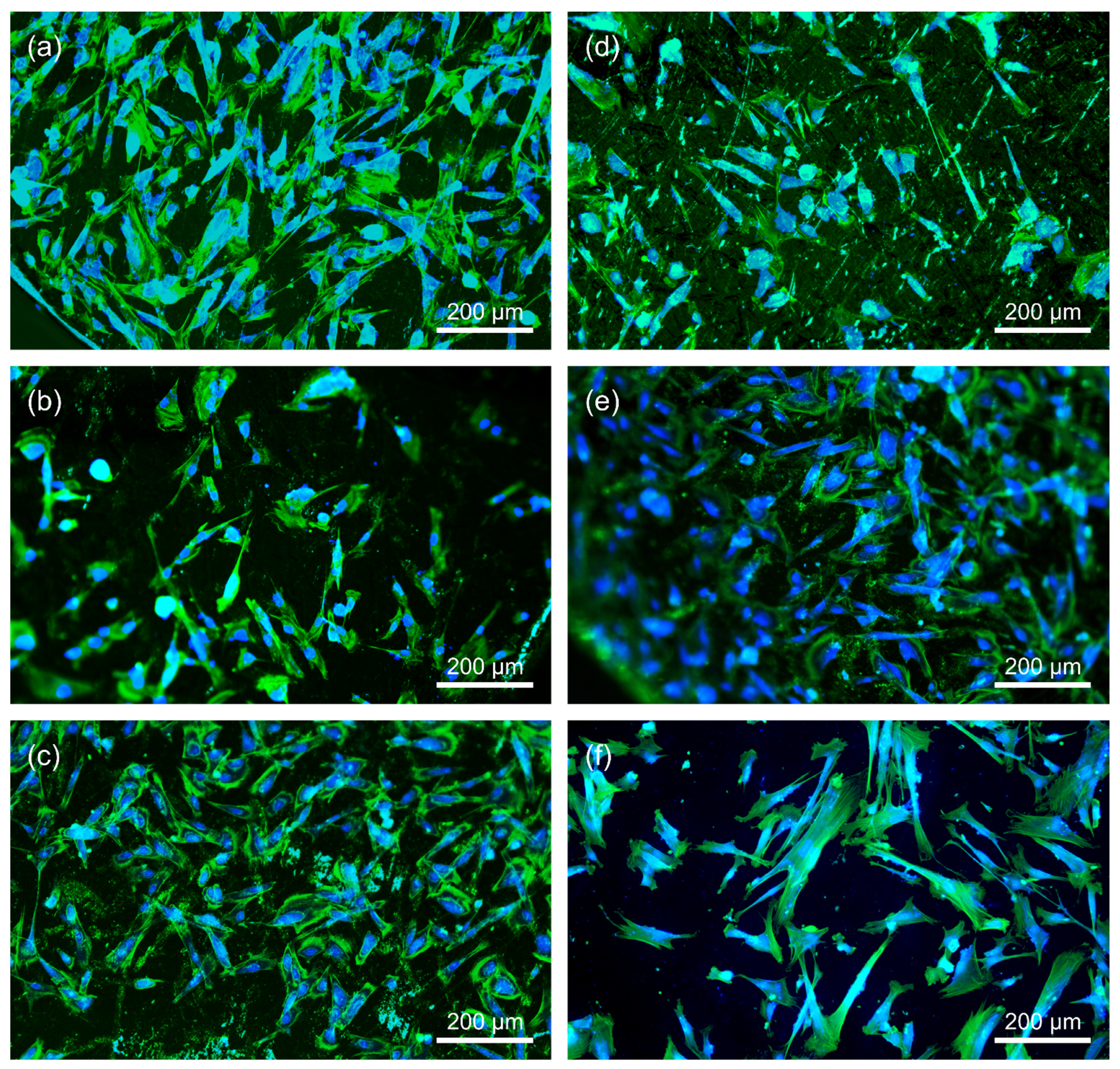
2.5.3. Microscopy
2.5.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microstructure
3.2. Nanoindentation
3.3. Scratch Test
3.4. Corrosion
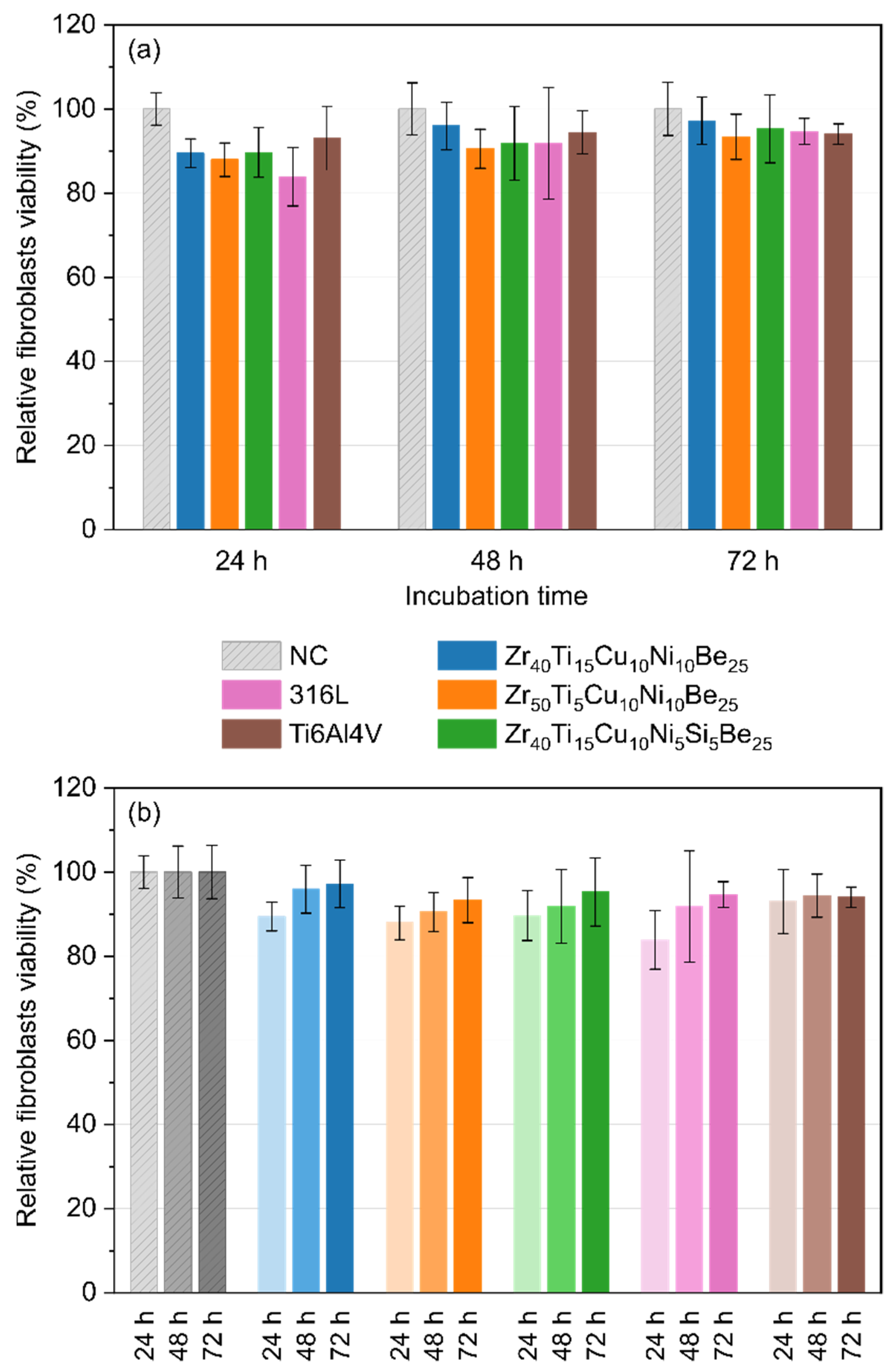
3.5. Direct Cytotoxicity to Fibroblasts
3.6. Indirect Cytotoxicity to Fibroblasts
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klement, W.; Willens, R.H.; Duwez, P. Non-Crystalline Structure in Solidified Gold-Silicon Alloys. Nature 1960, 187, 869–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Xie, G.; Inoue, A. Glass-Forming Ability and Mechanical Properties of the Ternary Cu-Zr-Al and Quaternary Cu-Zr-Al-Ag Bulk Metallic Glasses. Mater. Trans. 2007, 48, 1626–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Takeuchi, A.; Inoue, A. Gd-Co-Al and Gd-Ni-Al Bulk Metallic Glasses with High Glass Forming Ability and Good Mechanical Properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 457, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiflet, G.J.; He, Y.; Poon, S.J. Mechanical Properties of a New Class of Metallic Glasses Based on Aluminum. J. Appl. Phys. 1988, 64, 6863–6865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polk, D.E.; Calka, A.; Giessen, B.C. The Preparation and Thermal and Mechanical Properties of New Titanium Rich Metallic Glasses. Acta Metall. 1978, 26, 1097–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.J.; Poon, S.J.; Shiflet, G.J. Mechanical Properties of Iron-Based Bulk Metallic Glasses. J. Mater. Res. 2007, 22, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peker, A.; Johnson, W.L. A Highly Processable Metallic Glass: Zr41.2Ti13.8Cu12.5Ni10.0Be22.5. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1993, 63, 2342–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavari, A.R.; Lewandowski, J.J.; Eckert, J. Mechanical Properties of Bulk Metallic Glasses. MRS Bull. 2007, 32, 635–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.L.; Duwez, P. Metastable Amorphous Phases in Tellurium-Based Alloys. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1963, 2, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duwez, P.; Willens, R.H.; Crewdson, R.C. Amorphous Phase in Palladium—Silicon Alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 1965, 36, 2267–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, W.L. Bulk Glass-Forming Metallic Alloys: Science and Technology. MRS Bull. 1999, 24, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, A. Recent Progress of Zr-Based Bulk Amorphous Alloys. Sci. Rep. Res. Inst. Tohoku Univ. Ser. A Phys. 1996, 42, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, A. Bulk Amorphous Alloys: Preparation and Fundamental Characteristics; Enfield, N.H., Ed.; Trans Tech Publications: Uetikon-Zuerich, Switzerland, 1998; ISBN 978-0878497959. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, A. Stabilization of Supercooled Liquid and Opening-up of Bulk Glassy Alloys. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 1997, 73, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, A. Stabilization of Metallic Supercooled Liquid and Bulk Amorphous Alloys. Acta Mater. 2000, 48, 279–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, W.L. Thermodynamic and Kinetic Aspects of the Crystal to Glass Transformation in Metallic Materials. Prog. Mater. Sci. 1986, 30, 81–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbull, D. Under what Conditions Can a Glass Be Formed? Contemp. Phys. 1969, 10, 473–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroers, J. Processing of Bulk Metallic Glass. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 1566–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budhani, R.C.; Goel, T.C.; Chopra, K.L. Melt-Spinning Technique for Preparation of Metallic Glasses. Bull. Mater. Sci. 1982, 4, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavernia, E.J.; Srivatsan, T.S. The Rapid Solidification Processing of Materials: Science, Principles, Technology, Advances, and Applications. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 287–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.S. Thermodynamic Considerations on the Formation and Stability of Metallic Glasses. Acta Metall. 1974, 22, 1505–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S. Bulk Metallic Glasses. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 2001, 13, 7723–7736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, A.; Takeuchi, A. Recent Development and Application Products of Bulk Glassy Alloys. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 2243–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuh, C.A.; Hufnagel, T.C.; Ramamurty, U. Mechanical Behavior of Amorphous Alloys. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 4067–4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trexler, M.M.; Thadhani, N.N. Mechanical Properties of Bulk Metallic Glasses. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2010, 55, 759–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, A.L. Metallic Glasses...on the Threshold. Mater. Today 2009, 12, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telford, M. The Case for Bulk Metallic Glass. Mater. Today 2004, 7, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferry, M.; Laws, K.J.; White, C.; Miskovic, D.M.; Shamlaye, K.F.; Xu, W.; Biletska, O. Recent Developments in Ductile Bulk Metallic Glass Composites. MRS Commun. 2013, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ashby, M.F.; Greer, A.L. Metallic Glasses as Structural Materials. Scr. Mater. 2006, 54, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanarayana, C.; Inoue, A. Bulk Metallic Glasses, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Künzi, H.-U. Mechanical properties of metallic glasses. In Glassy Metal II. Topics in Applied Physics; Beck, H., Güntherodt, H.J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1983; Volume 53, pp. 169–216. [Google Scholar]
- Hufnagel, T.C.; Ott, R.T.; Almer, J. Structural Aspects of Elastic Deformation of a Metallic Glass. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 2006, 73, 064204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowski, J.J.; Wang, W.H.; Greer, A.L. Intrinsic Plasticity or Brittleness of Metallic Glasses. Philos. Mag. Lett. 2005, 85, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieh, T.G. Deformation Behavior. In Bulk Metallic Glasses; Miller, M., Liaw, P., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2008; pp. 147–167. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.H.; Xie, S.H.; Yang, H.P.; Qian, H.X.; Zeng, X.R. Wear Behaviors of Three Typical Bulk Metallic Glasses in Bearing Applications. Metals 2018, 8, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, A.L.; Myung, W.N. Abrasive Wear Resistance of Bulk Metallic Glasses. In MRS Online Proceedings Library. Proceedings of the Materials Research Society Symposium, San Francisco, CA, USA, 16–20 April 2001; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011; Volume 644, pp. L10.4.1–L10.4.12. [Google Scholar]
- Gloriant, T. Microhardness and Abrasive Wear Resistance of Metallic Glasses and Nanostructured Composite Materials. J. Non Cryst. Solids 2003, 316, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, D.C.; Andersen, L.M.; Kolodziejska, J.; Roberts, S.N.; Borgonia, J.P.; Johnson, W.L.; Vecchio, K.S.; Kennett, A. Optimizing Bulk Metallic Glasses for Robust, Highly Wear-Resistant Gears. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2017, 19, 1600541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Chan, K.C.; Liu, L. Tribological Characterisation of Zr-Based Bulk Metallic Glass in Simulated Physiological Media. Philos. Mag. 2011, 91, 3705–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köster, U.; Meinhardt, J. Crystallization of Highly Undercooled Metallic Melts and Metallic Glasses around the Glass Transition Temperature. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1994, 178, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, Y.; Shibata, T.; Inoue, A.; Masumoto, T. Workability of the Supercooled Liquid in the Zr65Al10Ni10Cu15 Bulk Metallic Glass. Acta Mater. 1998, 46, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hays, C.C.; Kim, C.P.; Johnson, W.L. Large Supercooled Liquid Region and Phase Separation in the Zr-Ti-Ni-Cu-Be Bulk Metallic Glasses. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1999, 75, 1089–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaepen, F. A Microscopic Mechanism for Steady State Inhomogeneous Flow in Metallic Glasses. Acta Metall. 1977, 25, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroers, J. On the Formability of Bulk Metallic Glass in Its Supercooled Liquid State. Acta Mater. 2008, 56, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, M.A.; Mykulowycz, N.M.; Shim, J.; Fontana, R.; Schmitt, P.; Roberts, A.; Ketkaew, J.; Shao, L.; Chen, W.; Bordeenithikasem, P.; et al. 3D Printing Metals like Thermoplastics: Fused Filament Fabrication of Metallic Glasses. Mater. Today 2018, 21, 697–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.J.; Lee, J.B.; Jeong, H.G. Superplastic Gas Pressure Forming of Zr65Al10Ni10Cu15 Metallic Glass Sheets Fabricated by Squeeze Mold Casting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 428, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroers, J.; Pham, Q.; Desai, A. Thermoplastic Forming of Bulk Metallic Glass—A Technology for MEMS and Microstructure Fabrication. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2007, 16, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, B.A.; Liaw, P.; Buchanan, R.A. Corrosion Behavior. In Bulk Metallic Glasses; Miller, M., Liaw, P., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2008; pp. 205–234. [Google Scholar]
- Scully, J.R.; Gebert, A.; Payer, J.H. Corrosion and Related Mechanical Properties of Bulk Metallic Glasses. J. Mater. Res. 2007, 22, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudali, U.K.; Scudino, S.; Kühn, U.; Eckert, J.; Gebert, A. Polarisation Behaviour of the Zr57Ti8Nb 2.5Cu13.9Ni11.1Al7.5 Alloy in Different Microstructural States in Acid Solutions. Scr. Mater. 2004, 50, 1379–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meagher, P.; O’Cearbhaill, E.D.; Byrne, J.H.; Browne, D.J. Bulk Metallic Glasses for Implantable Medical Devices and Surgical Tools. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 5755–5762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loye, A.M.; Kwon, H.-K.; Dellal, D.; Ojeda, R.; Lee, S.; Davis, R.; Nagle, N.; Doukas, P.G.; Schroers, J.; Lee, F.Y.; et al. Biocompatibility of Platinum-Based Bulk Metallic Glass in Orthopedic Applications. Biomed. Mater. 2021, 16, 045018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, L.; Cui, C.; Wang, Q.; Bu, S.; Qi, Y. Ti-Zr-Fe-Si System Amorphous Alloys with Excellent Biocompatibility. J. Non Cryst. Solids 2008, 354, 3935–3938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroers, J.; Kumar, G.; Hodges, T.M.; Chan, S.; Kyriakides, T.R. Bulk Metallic Glasses for Biomedical Applications. JOM 2009, 61, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, M.L.; Buchanan, R.A.; Peker, A.; Liaw, P.K.; Horton, J.A. Electrochemical Behavior of a Ti-Based Bulk Metallic Glass. J. Non Cryst. Solids 2007, 353, 2115–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Fu, R.; Liu, X.W.; Xu, L.M.; Wang, G.; Chen, S.Y.; Zhai, Q.J.; Pauly, S. Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis of a Bulk Metallic Glass for Biomedical Implants. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 8, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornell, J.; van Steenberge, N.; Varea, A.; Rossinyol, E.; Pellicer, E.; Suriñach, S.; Baró, M.D.; Sort, J. Enhanced Mechanical Properties and in Vitro Corrosion Behavior of Amorphous and Devitrified Ti 40Zr 10Cu 38Pd 12 Metallic Glass. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2011, 4, 1709–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ketov, S.V.; Shi, X.; Xie, G.; Kumashiro, R.; Churyumov, A.Y.; Bazlov, A.I.; Chen, N.; Ishikawa, Y.; Asao, N.; Wu, H.; et al. Nanostructured Zr-Pd Metallic Glass Thin Film for Biochemical Applications. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 7799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monfared, A.; Vali, H.; Faghihi, S. Biocorrosion and Biocompatibility of Zr–Cu–Fe–Al Bulk Metallic Glasses. Surf. Interface Anal. 2013, 45, 1714–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.L.; Chen, Q.; Liu, L.; Chan, K.C.; Zhou, J.X.; Chen, P.P.; Zhang, S.M. A Novel Ni-Free Zr-Based Bulk Metallic Glass with Enhanced Plasticity and Good Biocompatibility. Scr. Mater. 2006, 55, 605–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, S.; Daiwile, A.; Devi, S.S.; Kramer, M.J.; Besser, M.F.; Murty, B.S.; Bhatt, J. Bio-Corrosion and Cytotoxicity Studies on Novel Zr55Co30Ti15 and Cu60Zr20Ti20 Metallic Glasses. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2015, 46, 2422–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huiskes, R.; Weinans, H.; van Rietbergen, B. The Relationship between Stress Shielding and Bone Resorption around Total Hip Stems and the Effects of Flexible Materials. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1992, 274, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, M.; Michiardi, A.; Castaño, O.; Planell, J.A. Biomaterials in Orthopaedics. J. R. Soc. Interface 2008, 5, 1137–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Thouas, G.A. Metallic Implant Biomaterials. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2015, 87, 1–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.Z.; Sarhan, A.A.D.; Yusuf, F.; Hamdi, M. Biomedical Materials and Techniques to Improve the Tribological, Mechanical and Biomedical Properties of Orthopedic Implants—A Review Article. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 714, 636–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crow, J.E.; Sweedler, A.R. A Simple Casting Device for Use with an Argon Arc Furnace. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1973, 44, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, H.E.N. A Casting Device for Use with an Argon-Arc Furnace. J. Phys. E Sci. Instrum. 1971, 4, 1058–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, J.J.; Fan, C.; Liaw, P.K.; Liu, C.T.; Choo, H. A Combined Drop/Suction-Casting Machine for the Manufacture of Bulk-Metallic-Glass Materials. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2006, 77, 033902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, W.C.; Pharr, G.M. An Improved Technique for Determining Hardness and Elastic Modulus Using Load and Displacement Sensing Indentation Experiments. J. Mater. Res. 1992, 7, 1564–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, W.C.; Pharr, G.M. Measurement of Hardness and Elastic Modulus by Instrumented Indentation: Advances in Understanding and Refinements to Methodology. J. Mater. Res. 2004, 19, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokubo, T.; Takadama, H. How Useful Is SBF in Predicting in Vivo Bone Bioactivity? Biomaterials 2006, 27, 2907–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Prasad, N. Studies of Passivation, Repassivation and Metastable Pitting of 316L Stainless Implant in Bone Solution. Res. Rev. Electrochem. 2014, 4, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Broomfield, J.P. Corrosion of Steel in Concrete. In Uhlig’s Corrosion Handbook; Revie, R.W., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 633–647. [Google Scholar]
- International Organization for Standardization. ISO 10993—Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices, 3rd ed.; ISO: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Dal Piva, A.M.O.; Contreras, L.P.C.; Ribeiro, F.C.; Anami, L.C.; Camargo, S.E.A.; Jorge, A.O.C.; Bottino, M.A. Monolithic Ceramics: Effect of Finishing Techniques on Surface Properties, Bacterial Adhesion and Cell Viability. Oper. Dent. 2018, 43, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.H.; Wong, P.C.; Chang, S.F.; Tsai, P.H.; Jang, J.S.C.; Huang, J.C. Biocompatibility Study on Ni-Free Ti-Based and Zr-Based Bulk Metallic Glasses. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 75, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruck, H.A.; Rosakis, A.J.; Johnson, W.L. The Dynamic Compressive Behavior of Beryllium Bearing Bulk Metallic Glasses. J. Mater. Res. 1996, 11, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.L.; Chen, G.; Xu, F.; Du, Y.L.; Li, Y.S.; Liu, C.T. Correlation of the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Zr-Based in-Situ Bulk Metallic Glass Matrix Composites. Intermetallics 2010, 18, 2425–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Li, Y.; Zeng, K. Characterization of Mechanical Properties of a Zr-Based Metallic Glass by Indentation Techniques. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 384, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Yang, F.; Fan, G.; Liaw, P.K. Hardness Variation across a Zr57Ti5Cu 20Ni8Al10 Bulk Metallic Glass. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 2208–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.C.; Pelletier, J.M.; Esnouf, C.; Liu, Y.; Kato, H. Impact of the Structural State on the Mechanical Properties in a Zr-Co-Al Bulk Metallic Glass. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 607, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.C.; Pelletier, J.M. Influence of Thermal Treatments and Plastic Deformation on the Atomic Mobility in Zr50.7Cu28Ni9Al12.3 Bulk Metallic Glass. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 615, S85–S89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, K.K.; Suksawang, N.; Lahiri, D.; Agarwal, A. Evaluating Initial Unloading Stiffness from Elastic Work-of-Indentation Measured in a Nanoindentation Experiment. J. Mater. Res. 2013, 28, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milman, Y.V. Plasticity Characteristic Obtained by Indentation. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2008, 41, 074013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Ozan, S.; Li, Y.; Ping, D.; Tong, X.; Li, G.; Wen, C. Novel Ti-Ta-Hf-Zr Alloys with Promising Mechanical Properties for Prospective Stent Applications. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozan, S.; Lin, J.; Li, Y.; Ipek, R.; Wen, C. Development of Ti-Nb-Zr Alloys with High Elastic Admissible Strain for Temporary Orthopedic Devices. Acta Biomater. 2015, 20, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Hady Gepreel, M.; Niinomi, M. Biocompatibility of Ti-Alloys for Long-Term Implantation. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2013, 20, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordji, K.; Jouzeau, J.Y.; Mainard, D.; Payan, E.; Delagoutte, J.P.; Netter, P. Evaluation of the Effect of Three Surface Treatments on the Biocompatibility of 316L Stainless Steel Using Human Differentiated Cells. Biomaterials 1996, 17, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.F. On the Mechanisms of Biocompatibility. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 2941–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.G.; Choi, B.W.; Nieh, T.G.; Liu, C.T. Nano-Scratch Behavior of a Bulk Zr–10Al–5Ti–17.9Cu–14.6Ni Amorphous Alloy. J. Mater. Res. 2000, 15, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, A.-E.; Bermúdez, M.-D. Friction and wear. In Tribology for Engineers; Davim, J.P., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 33–63. [Google Scholar]
- Zitter, H.; Plenk, H. The Electrochemical Behavior of Metallic Implant Materials as an Indicator of Their Biocompatibility. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1987, 21, 881–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Qiu, C.L.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, S.M. Corrosion Behavior of Zr-Based Bulk Metallic Glasses in Different Artificial Body Fluids. J. Alloys Compd. 2006, 425, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Qiu, C.L.; Chen, Q.; Chan, K.C.; Zhang, S.M. Deformation Behavior, Corrosion Resistance, and Cytotoxicity of Ni-Free Zr-Based Bulk Metallic Glasses. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2008, 86, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.M.; Pang, H.F.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, L. A Ni-Free ZrCuFeAlAg Bulk Metallic Glass with Potential for Biomedical Applications. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 7043–7053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.H.; Huang, C.H.; Chuang, J.F.; Lee, H.C.; Liu, M.C.; Du, X.H.; Huang, J.C.; Jang, J.S.C.; Chen, C.H. Simulated Body-Fluid Tests and Electrochemical Investigations on Biocompatibility of Metallic Glasses. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2012, 32, 2578–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebert, A.; Buchholz, K.; Leonhard, A.; Mummert, K.; Eckert, J.; Schultz, L. Investigations on the Electrochemical Behaviour of Zr-Based Bulk Metallic Glasses. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1999, 267, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzzi, S.; Jin, K.; Uggowitzer, P.J.; Tosatti, S.; Gerber, I.; Löffler, J.F. Cytotoxicity of Zr-Based Bulk Metallic Glasses. Intermetallics 2006, 14, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, K.; Zhou, X.; Liu, X. Application of Zr and Ti-Based Bulk Metallic Glasses for Orthopaedic and Dental Device Materials. Metals 2020, 10, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanski, D.; Koller, M.; Muller, D.; Muhr, G.; Bram, M.; Buchkremer, H.P.; Stover, D.; Choi, J.; Epple, M. Easy Assessment of the Biocompatibility of Ni-Ti Alloys by in Vitro Cell Culture Experiments on a Functionally Graded Ni-NiTi-Ti Material. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 4549–4555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
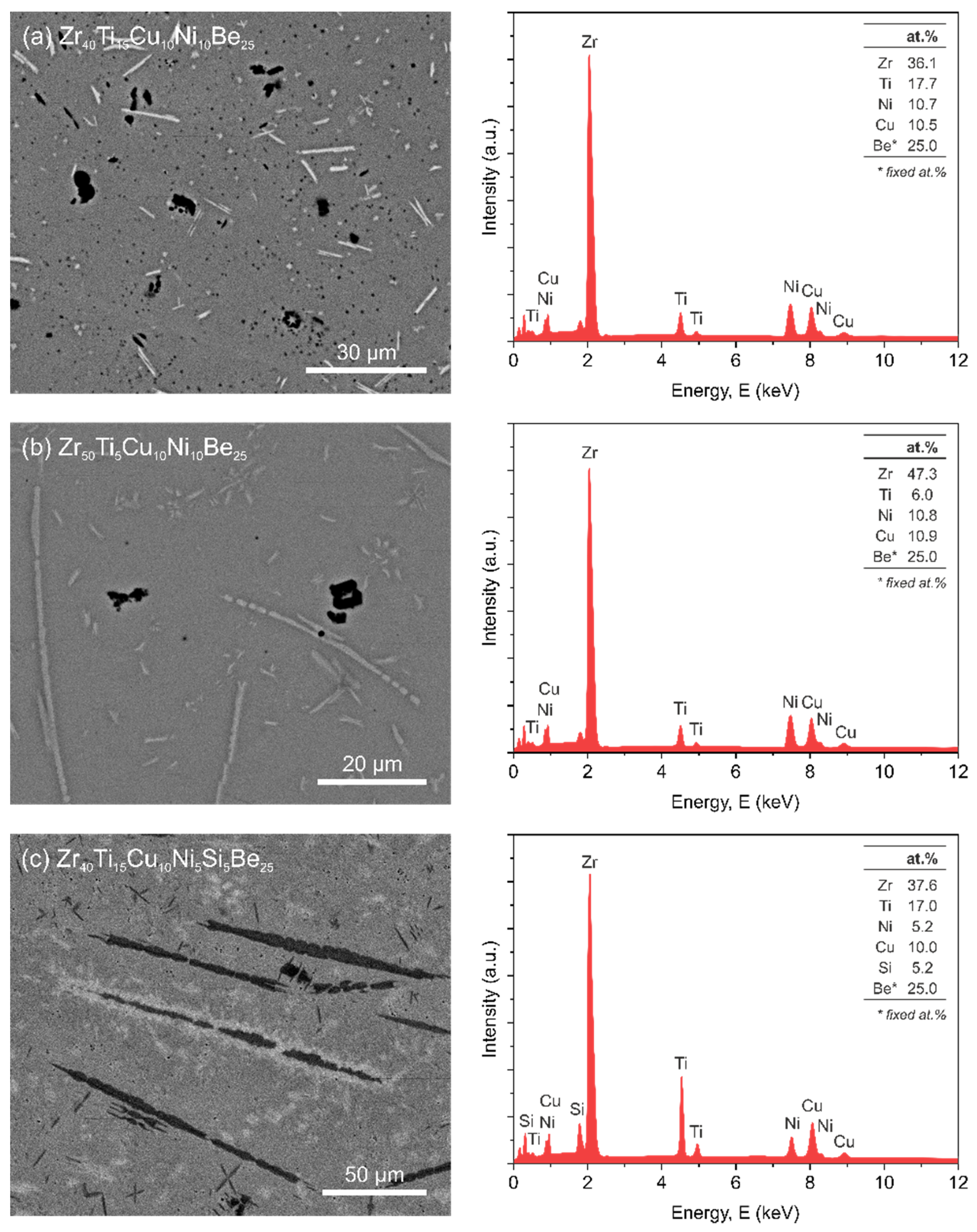
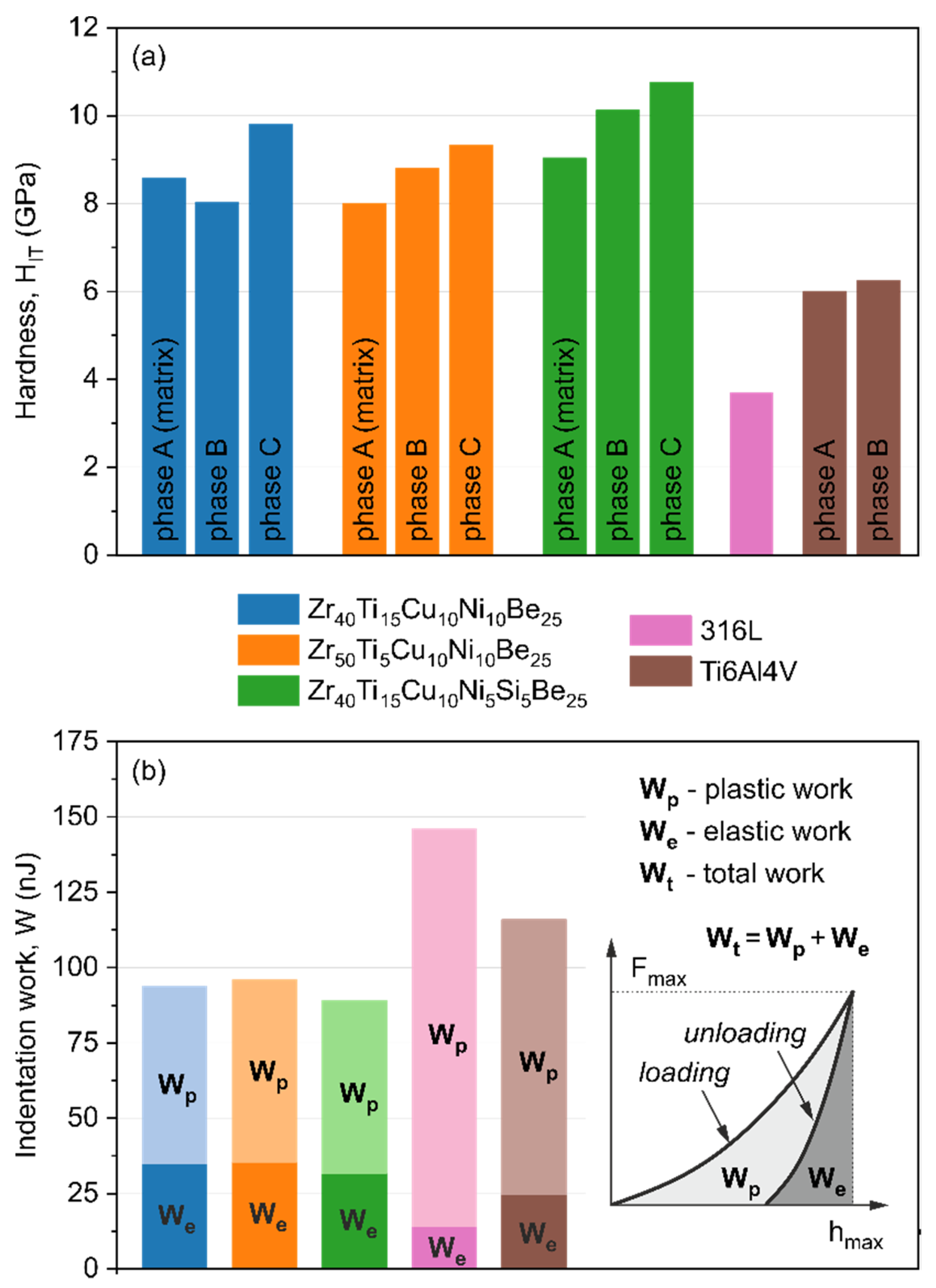
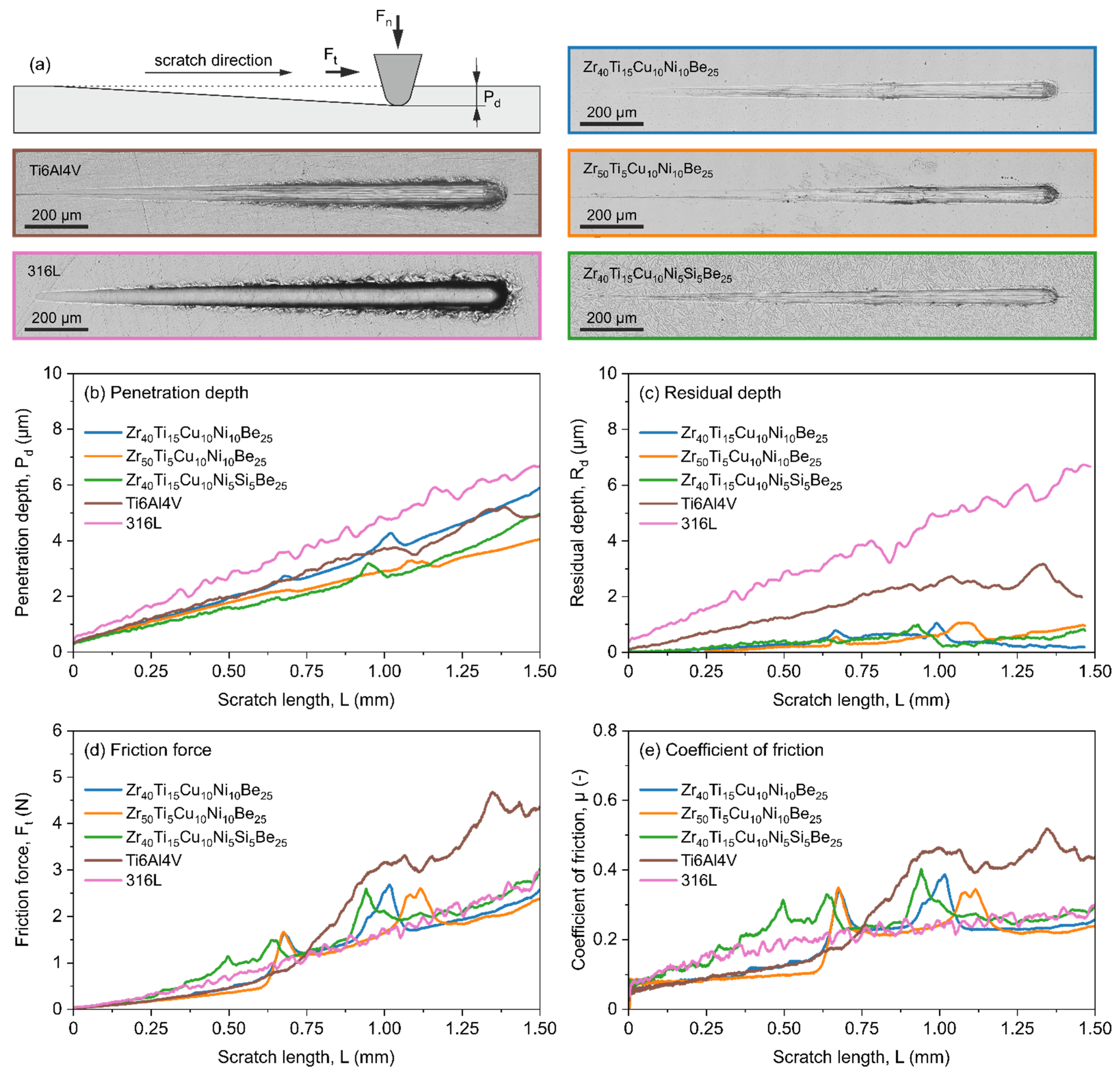
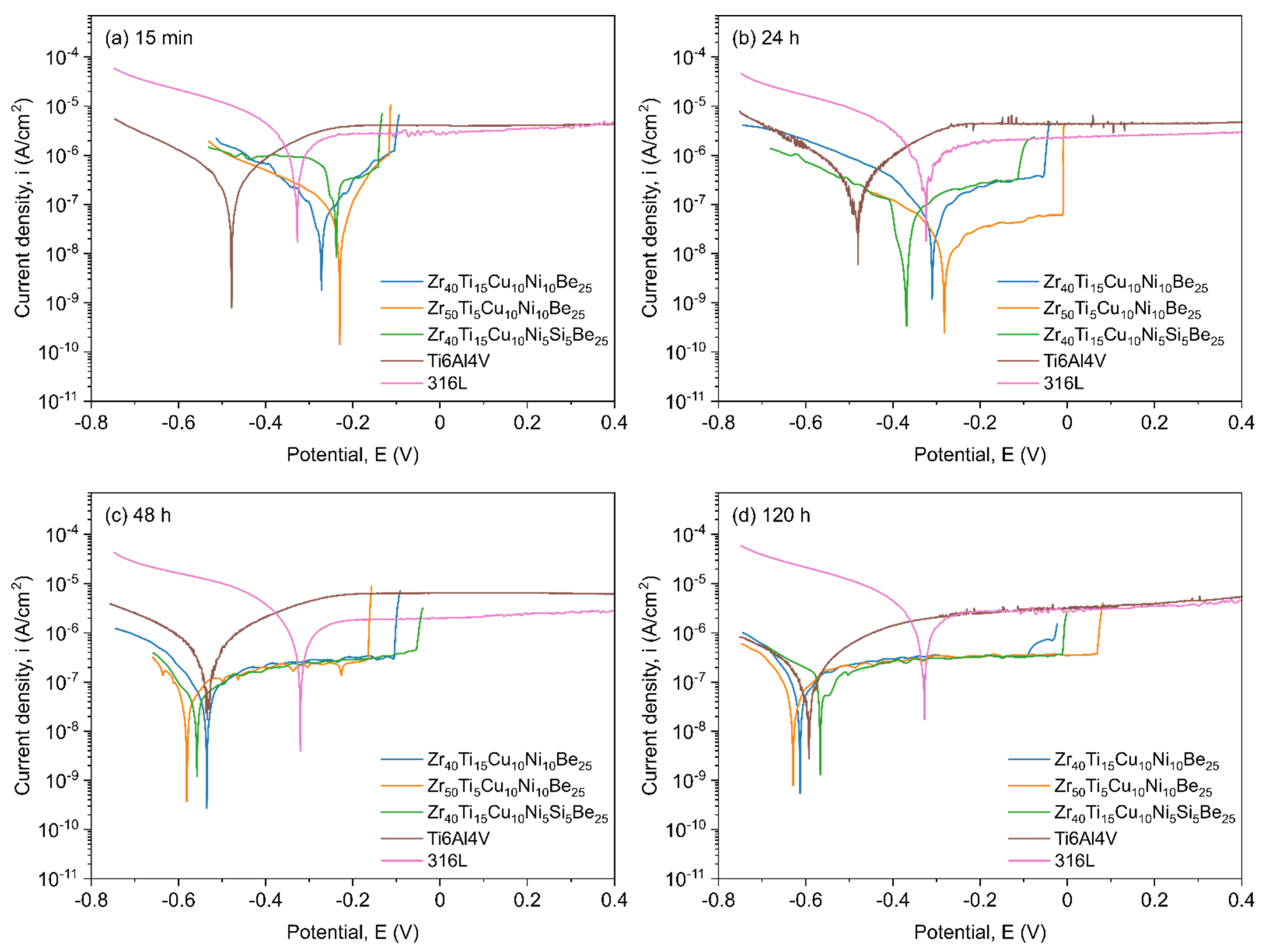

| Alloy Composition | Time (h) | Rp (Ω·cm2) | icorr (A/cm2) | EC-A (mV) | EOC (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zr40Ti15Cu10Ni10Be25 | 0.25 | 2.77 × 105 | 9.42 × 10−8 | −274 | −167 |
| 24 | 3.42 × 105 | 7.62 × 10−8 | −308 | −318 | |
| 48 | 3.09 × 105 | 8.44 × 10−8 | −535 | −348 | |
| 120 | 2.27 × 105 | 1.15 × 10−8 | −612 | −123 | |
| Zr50Ti5Cu10Ni10Be25 | 0.25 | 3.24 × 105 | 8.06 × 10−8 | −229 | −185 |
| 24 | 1.18 × 105 | 2.22 × 10−8 | −280 | −352 | |
| 48 | 6.99 × 104 | 3.73 × 10−7 | −633 | −154 | |
| 120 | 2.72 × 105 | 9.81 × 10−8 | −627 | −91 | |
| Zr40Ti15Cu10Ni5Si5Be25 | 0.25 | 6.32 × 104 | 4.12 × 10−7 | −240 | −187 |
| 24 | 6.27 × 105 | 4.16 × 10−8 | −373 | −267 | |
| 48 | 3.21 × 105 | 8.13 × 10−8 | −558 | −299 | |
| 120 | 1.49 × 105 | 1.70 × 10−7 | −562 | −125 | |
| Ti6Al4V | 0.25 | 9.91 × 104 | 2.63 × 10−7 | −478 | −472 |
| 24 | 9.79 × 104 | 2.66 × 10−7 | −483 | −487 | |
| 48 | 8.05 × 104 | 3.24 × 10−7 | −533 | −476 | |
| 120 | 2.07 × 105 | 1.26 × 10−7 | −593 | −599 | |
| 316L | 0.25 | 3.68 × 104 | 7.08 × 10−7 | −326 | −240 |
| 24 | 3.01 × 104 | 8.68 × 10−7 | −325 | −244 | |
| 48 | 2.89 × 104 | 9.02 × 10−7 | −319 | −241 | |
| 120 | 3.24 × 104 | 8.05 × 10−7 | −327 | −215 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hasiak, M.; Sobieszczańska, B.; Łaszcz, A.; Biały, M.; Chęcmanowski, J.; Zatoński, T.; Bożemska, E.; Wawrzyńska, M. Production, Mechanical Properties and Biomedical Characterization of ZrTi-Based Bulk Metallic Glasses in Comparison with 316L Stainless Steel and Ti6Al4V Alloy. Materials 2022, 15, 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15010252
Hasiak M, Sobieszczańska B, Łaszcz A, Biały M, Chęcmanowski J, Zatoński T, Bożemska E, Wawrzyńska M. Production, Mechanical Properties and Biomedical Characterization of ZrTi-Based Bulk Metallic Glasses in Comparison with 316L Stainless Steel and Ti6Al4V Alloy. Materials. 2022; 15(1):252. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15010252
Chicago/Turabian StyleHasiak, Mariusz, Beata Sobieszczańska, Amadeusz Łaszcz, Michał Biały, Jacek Chęcmanowski, Tomasz Zatoński, Edyta Bożemska, and Magdalena Wawrzyńska. 2022. "Production, Mechanical Properties and Biomedical Characterization of ZrTi-Based Bulk Metallic Glasses in Comparison with 316L Stainless Steel and Ti6Al4V Alloy" Materials 15, no. 1: 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15010252
APA StyleHasiak, M., Sobieszczańska, B., Łaszcz, A., Biały, M., Chęcmanowski, J., Zatoński, T., Bożemska, E., & Wawrzyńska, M. (2022). Production, Mechanical Properties and Biomedical Characterization of ZrTi-Based Bulk Metallic Glasses in Comparison with 316L Stainless Steel and Ti6Al4V Alloy. Materials, 15(1), 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15010252








