Fabrication of PDMS@Fe3O4/MS Composite Materials and Its Application for Oil-Water Separation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Instrumentation and Characterization
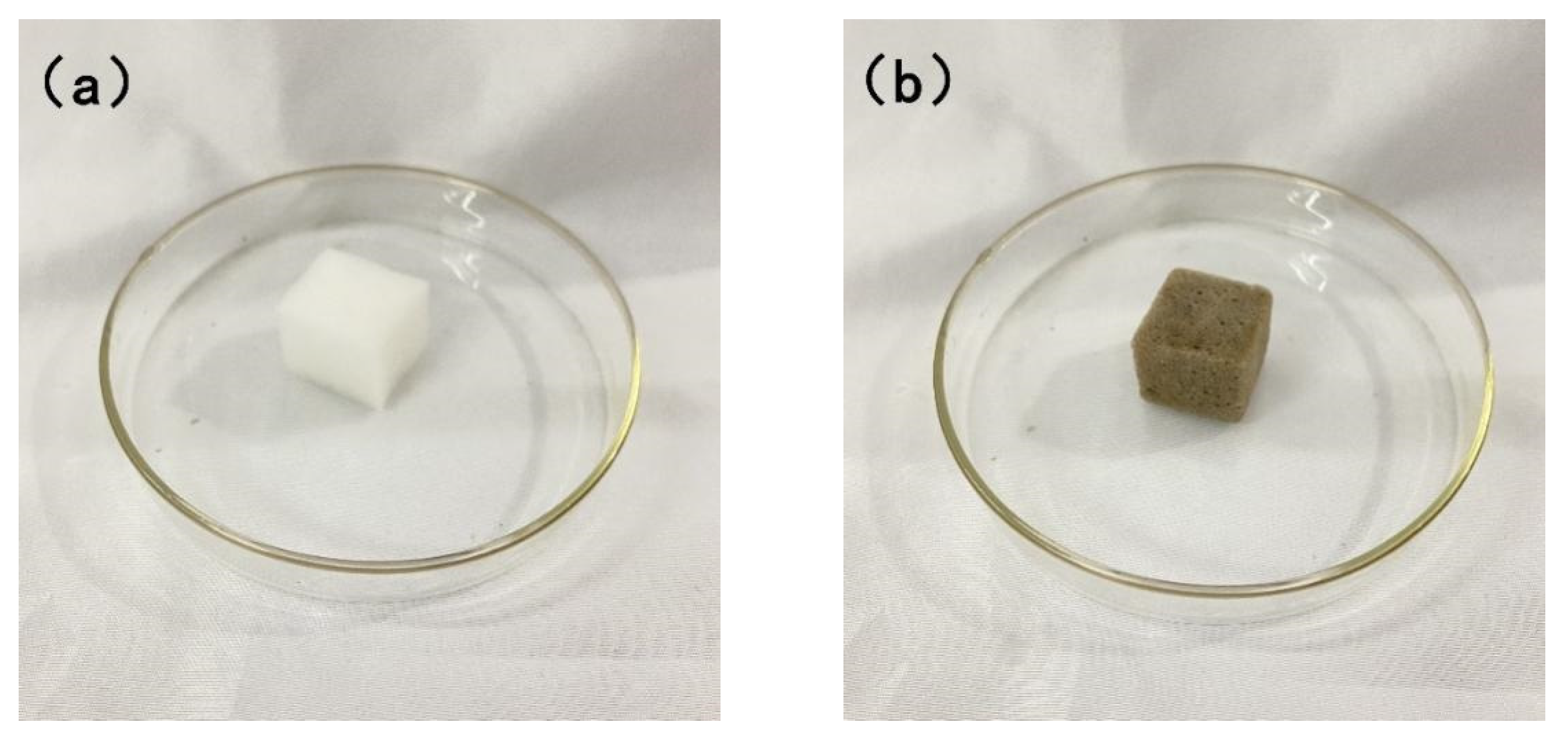
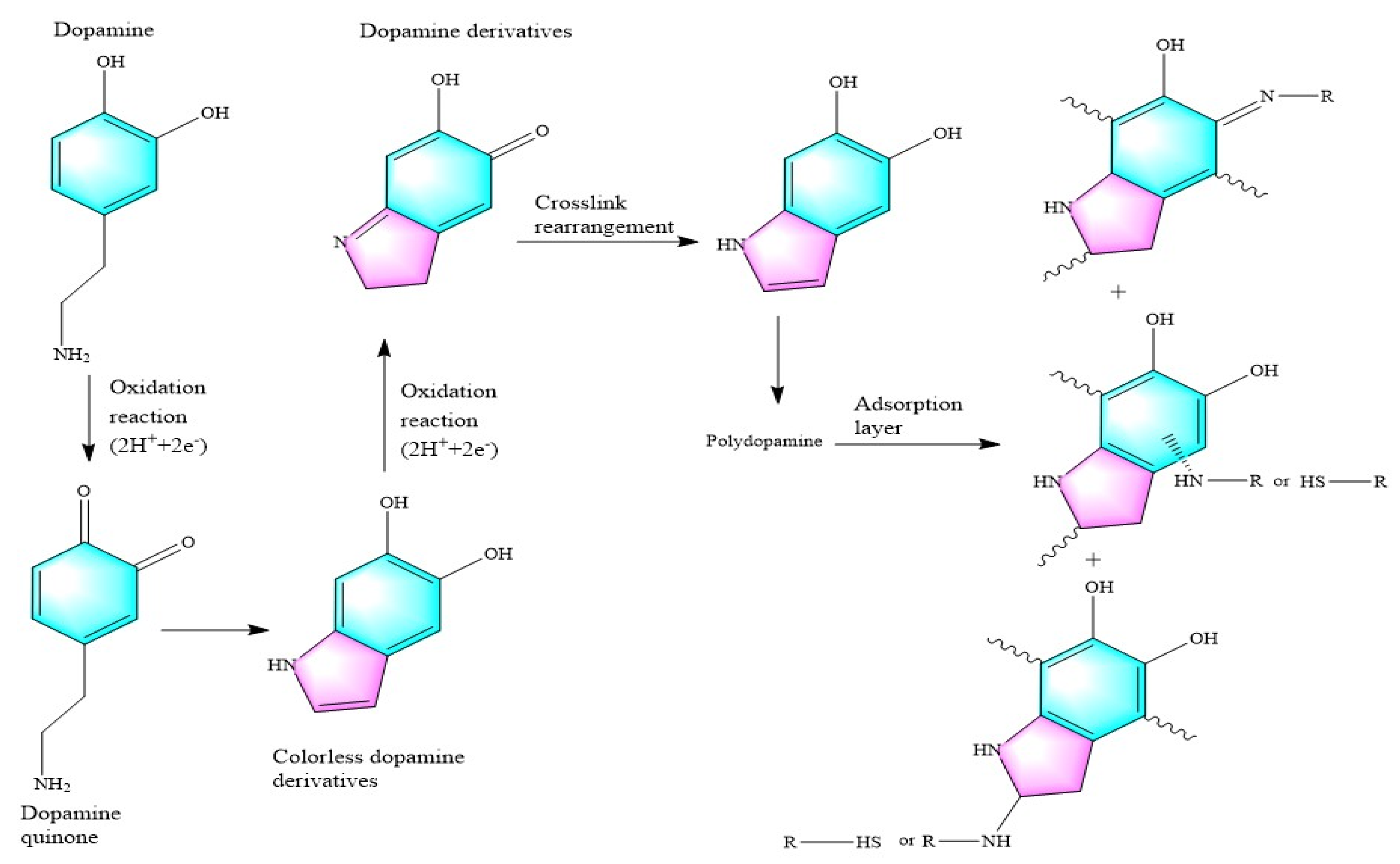
2.3. Preparation of PDMS@Fe3O4/MS
- (1)
- Pretreatment of MS surface.
- (2)
- Polydopamine coating covers the MS skeleton.
- (3)
- Sponge adhesion nano-Fe3O4.
- (4)
- PDMS treats sponge superhydrophobicity.
2.4. Calculation of Adsorption Capacity and Oil-Water Separation Efficiency
2.4.1. PDMS@Fe3O4/MS Adsorption Capacity Calculation
2.4.2. PDMS@Fe3O4/MS Oil-Water Separation Efficiency Calculation
3. Results and Discussion
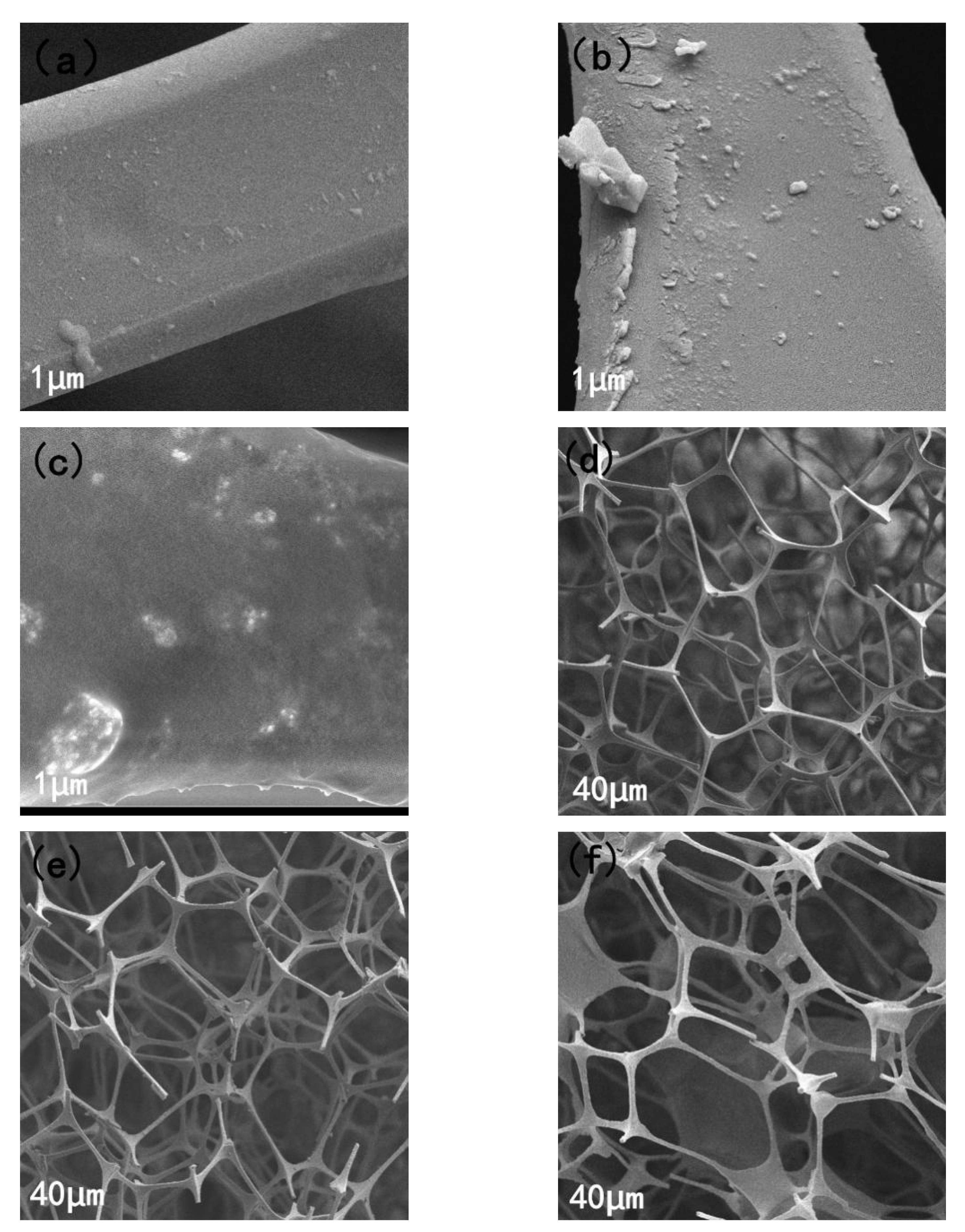
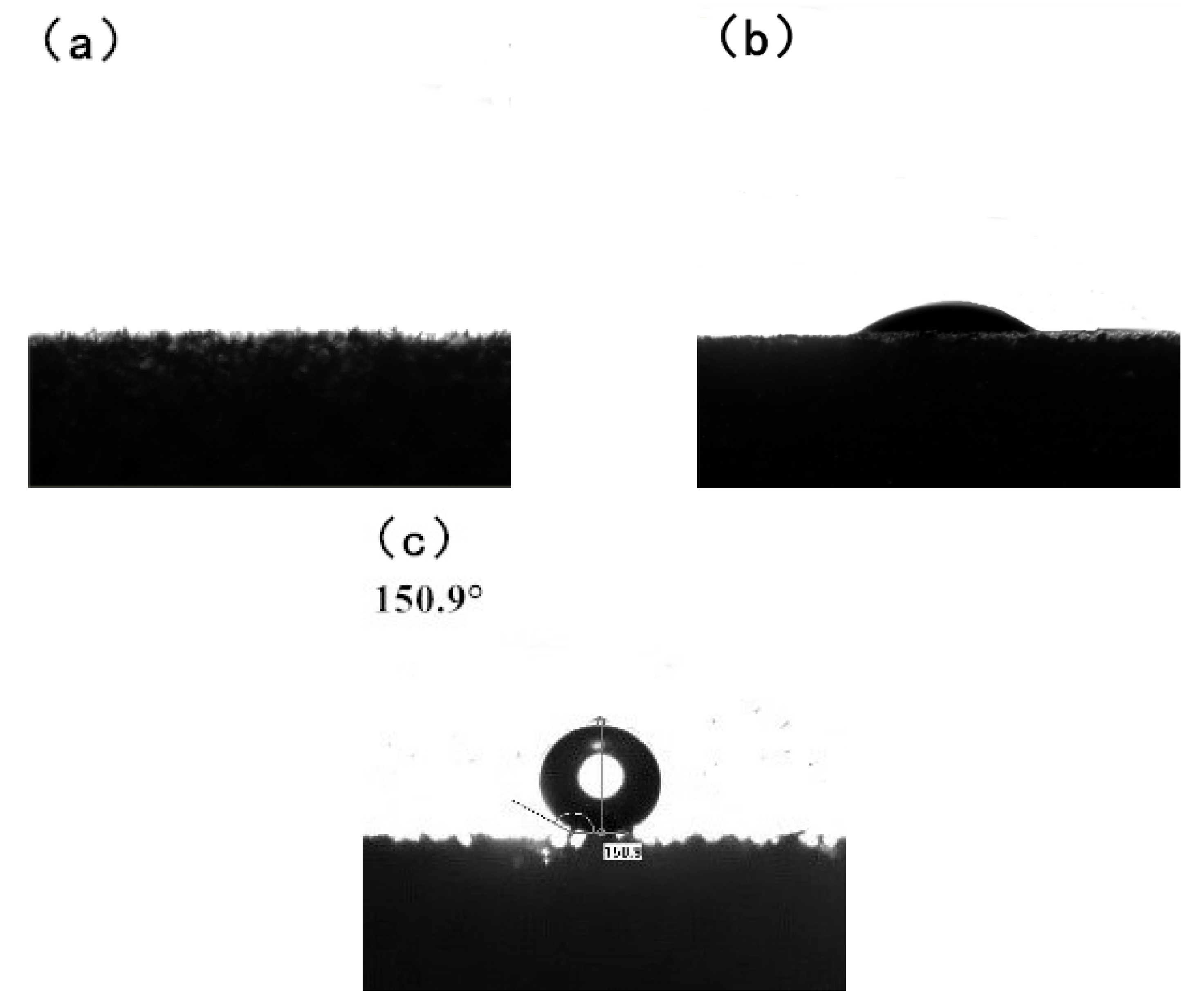
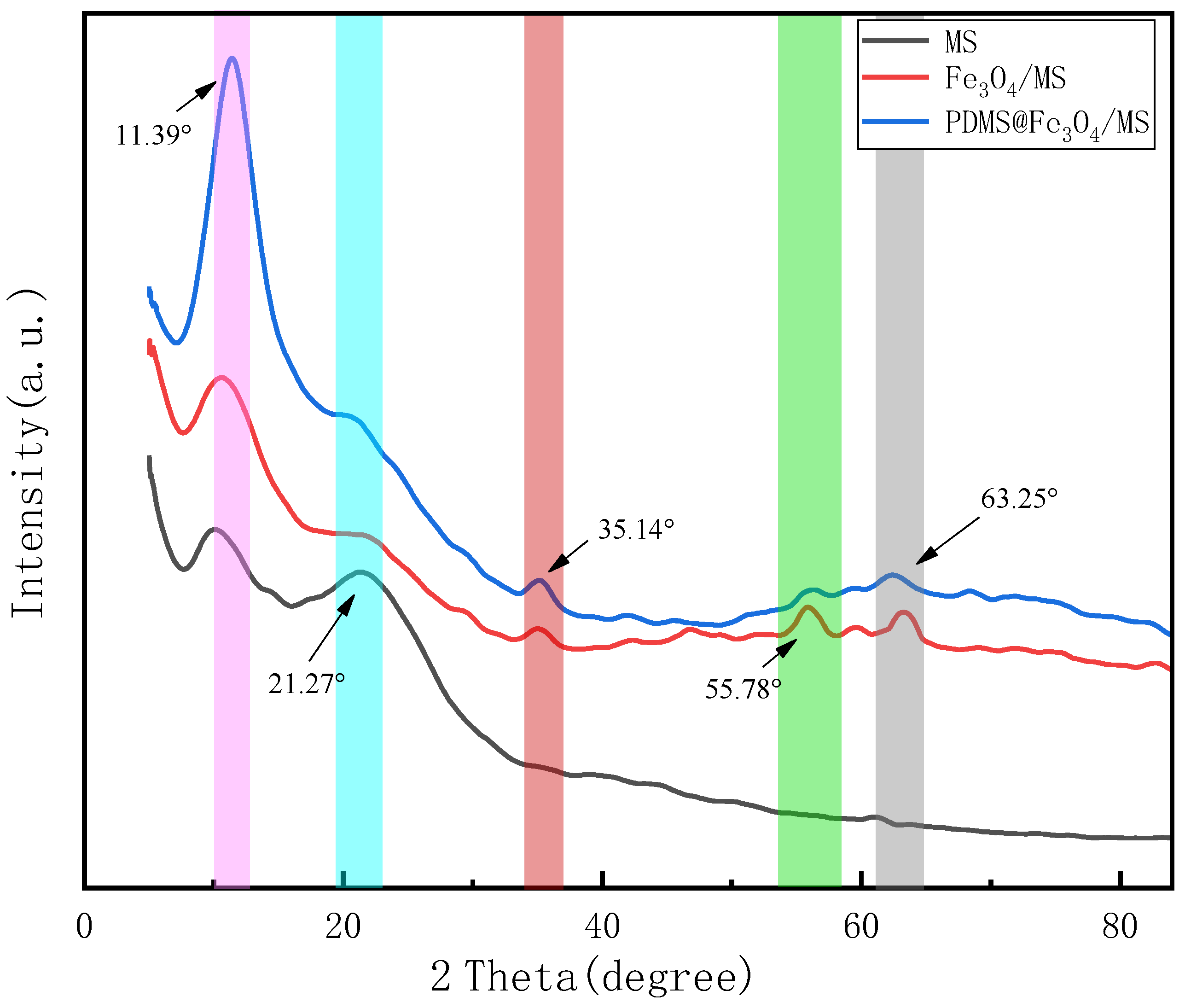
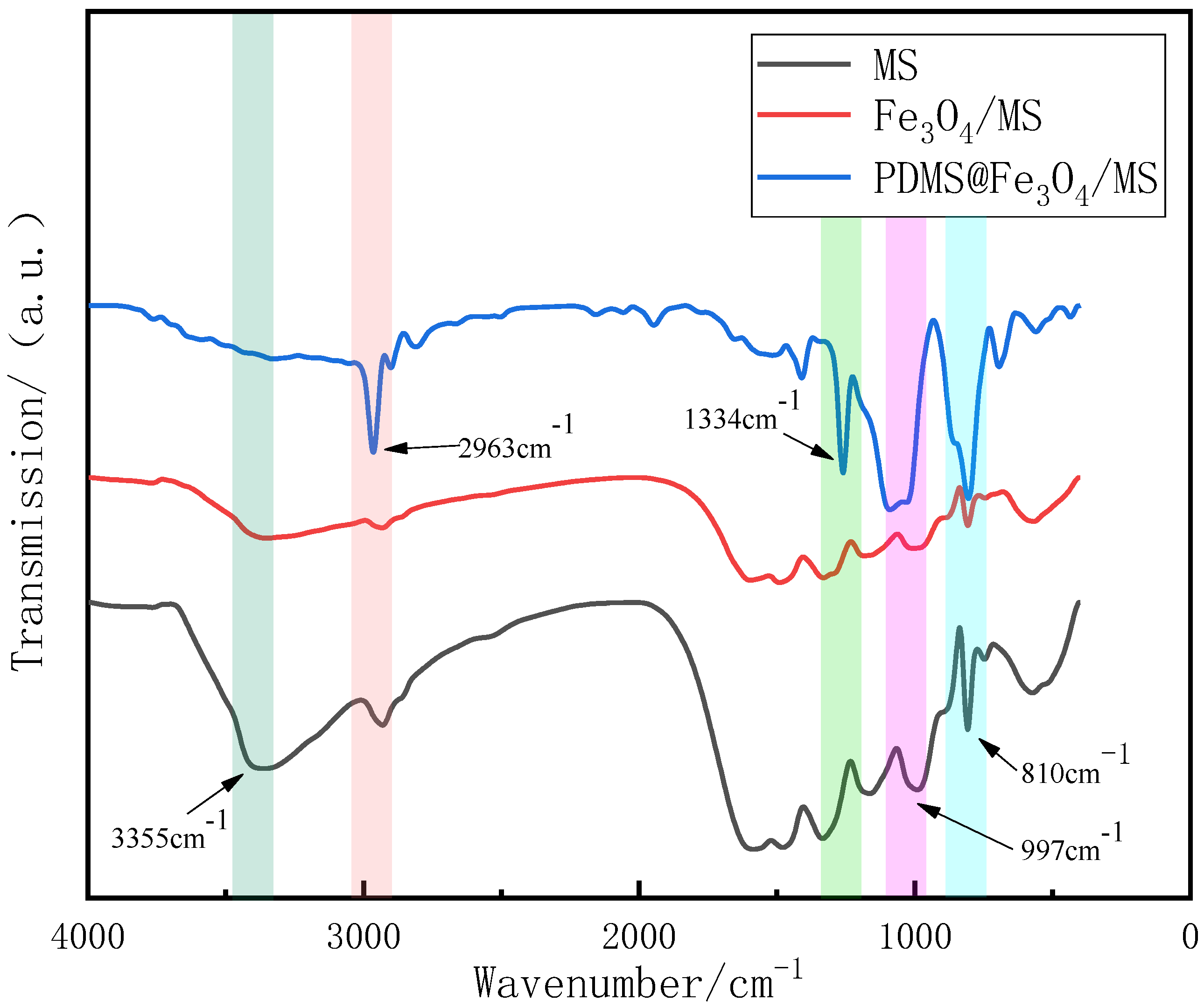
3.1. Characterization and Analysis of Original Sponge and Modified Sponge
3.2. Modified Sponge Oil Absorption Capacity and Oil-Water Separation Test
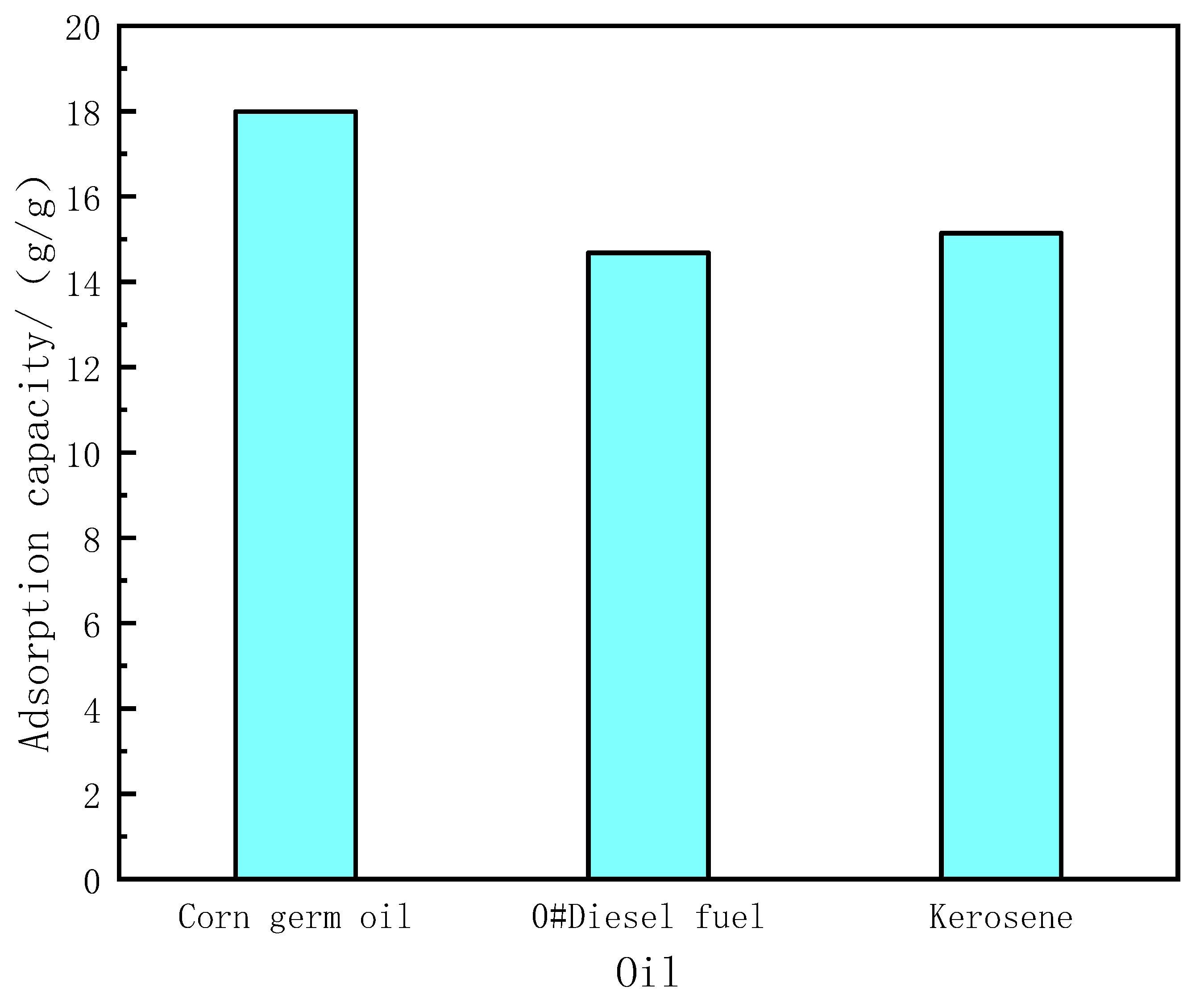
3.2.1. Oil Absorption Capacity of Modified Sponge
3.2.2. Modified Sponge Oil-Water Separation Test
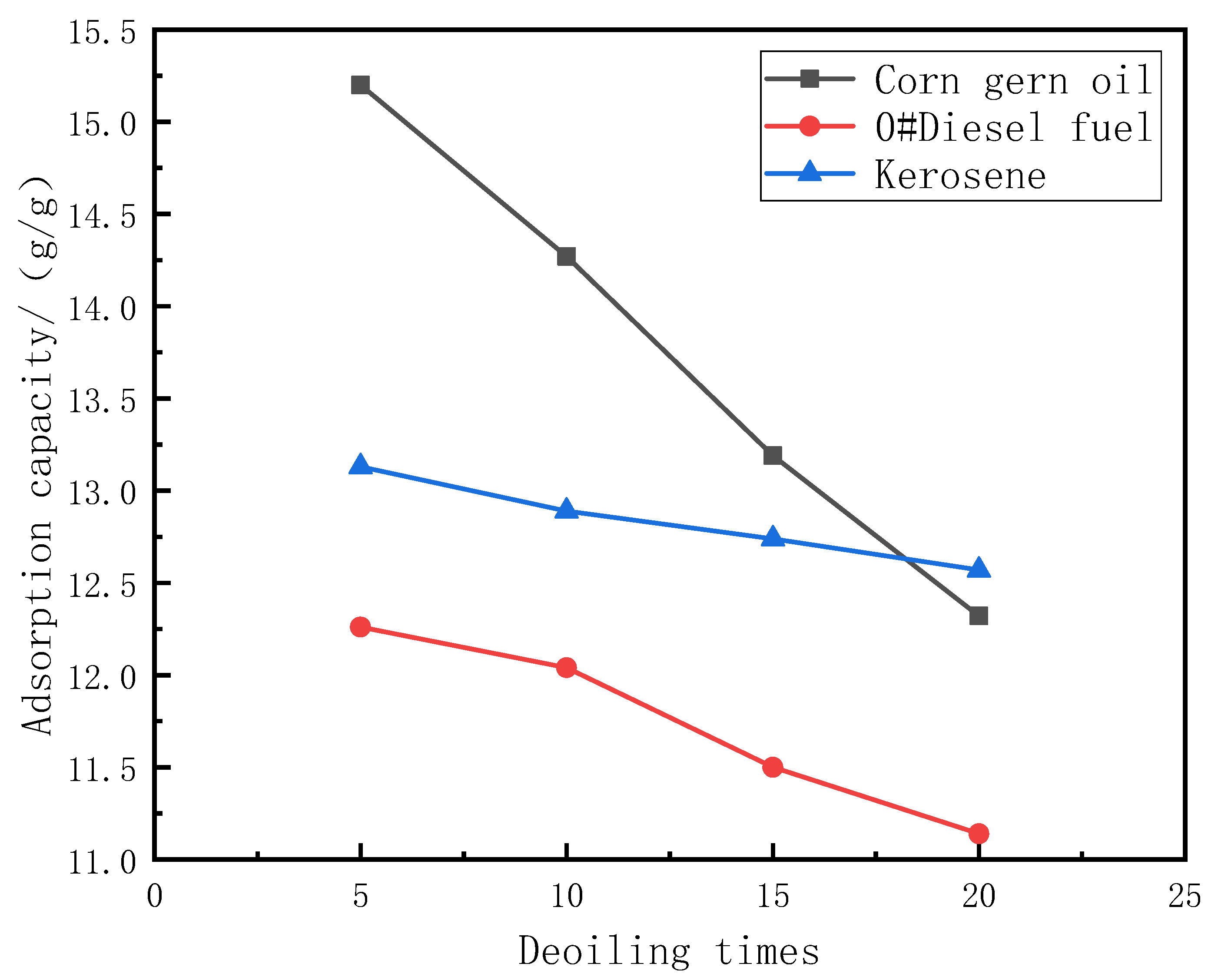
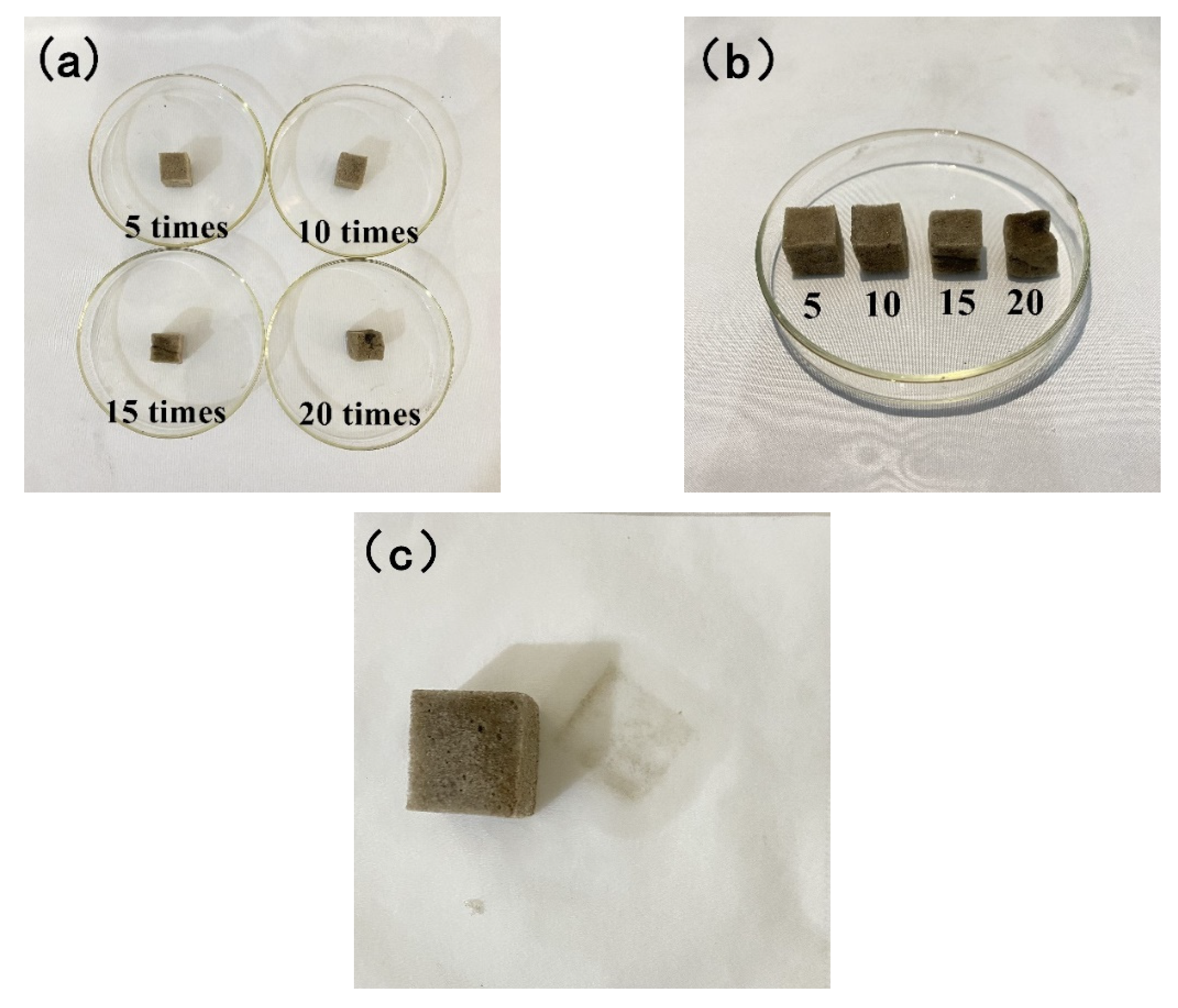
3.2.3. Modified Sponge Repeated Oil Absorption and Oil-Water Separation Performance Test
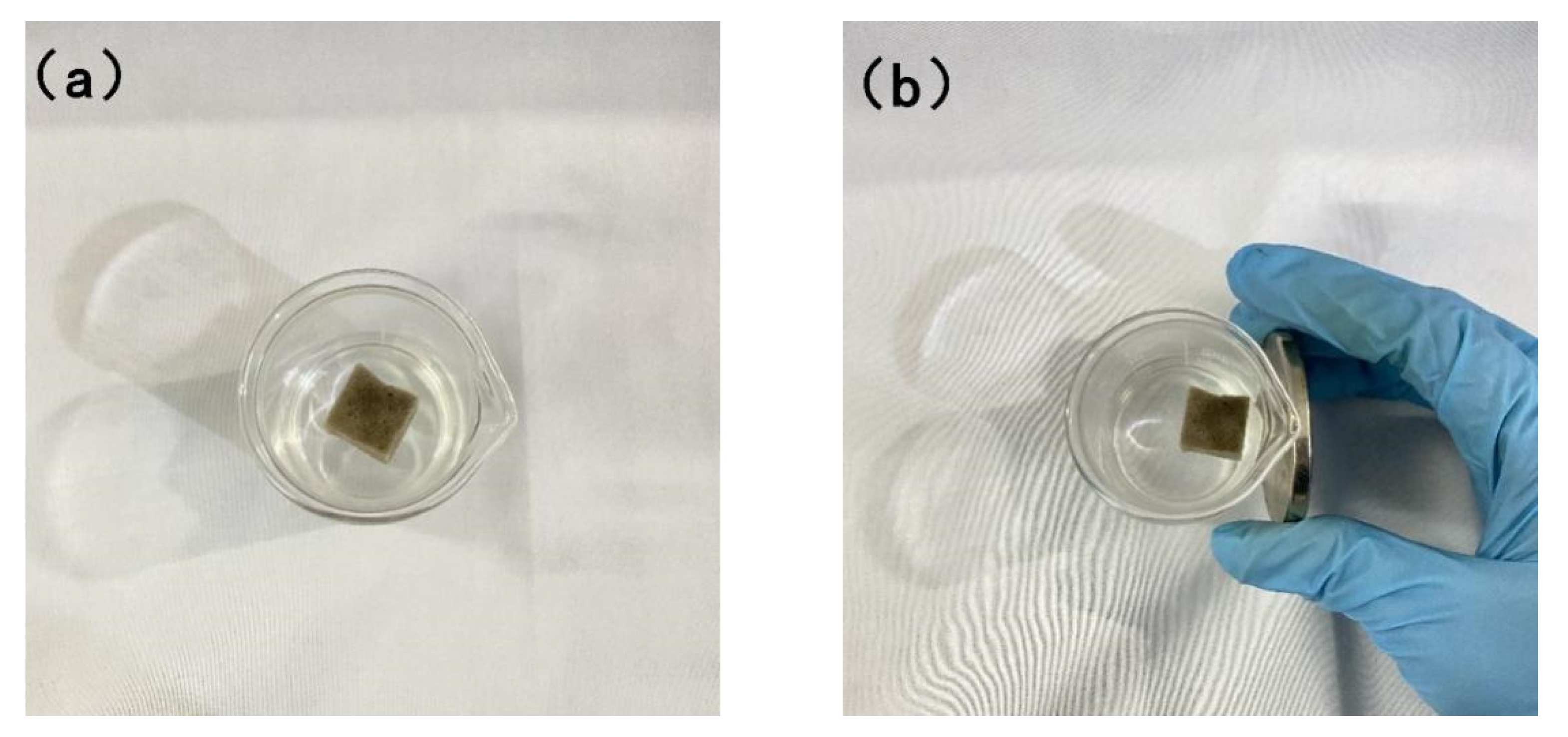
3.3. Test of Modified Sponge Affected by Magnetic Force
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chan, Y.J.; Chong, M.F.; Law, C.L.; Hassell, D.G. A review on anaerobic-aerobic treatment of industrial and municipal wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 155, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Xu, Z. Mineral-Coated Polymer Membranes with Superhydrophilicity and Underwater Superoleophobicity for Effective Oil/Water Separation. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, B.; Wu, L.; Li, L.; Seeger, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, A. Superwetting double-layer polyester materials for effective removal of both insoluble oils and soluble dyes in water. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 11581–11588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurell, J.; Gullett, B. Aerostat sampling of PCDD/PCDF emissions from the Gulf oil spill in situ burns. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 9431–9437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, T. It’s all caused by oil spills–The most serious series of offshore oil spills in history. Ocean. World 2010, 7, 28–31. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, M.; Wang, J.; Yao, X.; Liao, M.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, L. Underwater oil capture by a three-dimensional network architectured organosilane surface. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 2861–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besharati Fard, M.; Hamidi, D.; Alavi, J.; Jamshidian, R.; Pendashteh, A.; Mirbagheri, S.A. Saline oily wastewater treatment using Lallemantia mucilage as a natural coagulant: Kinetic study, process optimization, and modeling. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 163, 113326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aisien, F.; Hymore, F.; Ebewele, R. Potential application of recycled rubber in oil pollution control. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2003, 85, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.Y.; Yan, L.; Li, S.P.; Xu, X.R. Treatment of aging oily wastewater by demulsification/flocculation. Environ. Lett. 2016, 51, 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, J.; Shi, L.-A.; Wang, Y.-C.; Zhao, H.-Y.; Yao, H.-B.; Zhu, Y.-B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, H.-W.; Wu, H.-A.; Yu, S.-H. Joule-heated graphene-wrapped sponge enables fast clean-up of viscous crude-oil spill. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheryan, M.; Rajagopalan, N. Membrane processing of oily streams. Wastewater treatment and waste reduction. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 151, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubí, H.; Fall, C.; Ortega, R. Pollutant removal from oily wastewater discharged from car washes through sedimentation-coagulation. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 59, 2359–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Xiang, Q.; Ma, C.; Ren, Y.; Qiu, K. Continuous electrocoagulation degradation of oily wastewater with Fe78Si9B13 amorphous ribbons. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 40101–40108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salahi, A.; Mohammadi, T. Experimental investigation of oily wastewater treatment using combined membrane systems. Water Sci. Technol. A J. Int. Assoc. Water Pollut. Research. 2010, 62, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, H.; Xiong, S.; Chen, R.; Wang, Y. Extremely efficient and recyclable absorbents for oily pollutants enabled by ultrathin-layered functionalization. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 18816–18823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Li, J.; Wang, J. Synthesis strategy of modified sponge and its oil-water separation application research progress. New Chem. Mater. 2020, 48, 18–21. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, J.; Sun, G.; Wu, G.; Guo, L.; Zhong, Y.; Wnag, M.; You, B. An innovative study on low surface energy micronano coatings with multilevel structures for laminar flow design. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2019, 32, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirhosseinian, N.; Anbia, M.; Salehi, S. Preparation and characterization of superhydrophobic melamine and melamine-derived carbon sponges modified with reduced graphene oxide–TiO2 nanocomposite as oil absorbent materials. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 1536–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Li, C.; Wang, H.; Li, L.; Ye, H.; Chen, J. Preparation of superhydrophobic and lipophilic sponge material and separation of oil and water. Ship Ocean. Eng. 2021, 37, 59–62. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Shuai, Q.; Luo, Y.; Dong, Y.; Tan, M.; Chen, B. Preparation and application of polydimethylsiloxane/micronanosilver/polydopamine modified superhydrophobic sponge. Appl. Chem. 2015, 32, 726–732. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Liu, C.; Ma, J.; Li, X. Preparation of superhydrophobic and super lipophilic melamine sponge and its oil-water separation performance. Chin. J. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 39, 686–691. [Google Scholar]
- Oribayo, O.; Feng, X.; Rempel, G.L.; Pan, Q. Modification of formaldehyde-melamine-sodium bisulfite copolymer foam and its application as effective sorbents for clean-up of oil spills. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2017, 160, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Song, S.; Zhao, Z. Graphene oxide (GO)/polyacrylamide (PAM) composite hydrogels as efficient cationic dye adsorbents. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 2017, 513, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S. Mussel-Inspired One-Step Copolymerization to Engineer Hierarchically Structured Surface with Superhydrophobic Properties for Removing Oil from Water. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 17144–17150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, E.; Liu, Z.; Gao, D.; Yuan, R.; Sun, L.; Zhu, Y. A novel carbon nanotubes reinforced superhydrophobic and superoleophilic polyurethane sponge for selective oil-water separation through a chemical fabrication. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, C.; Bai, Y.; Barras, A.; Szunerits, S. Polyurethane sponge functionalized with superhydrophobic nanodiamond particles for efficient oil/water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 307, 319–325. [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko, Y.; Iyi, N.; Matsumoto, T.; Kitamura, K. Preparation of higher-ordered inorganic-organic nanocomposite composed of rodlike cationic PDMS and polyacrylate. J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 1572–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Moya, S.; Lichtenfeld, H.; Casoli, A.; Fiedler, H.; Donath, E.; Möhwald, H. The decomposition process of melamine formaldehyde cores: The key step in the fabrication of ultrathin polyelectrolyte multilayer capsules. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2001, 286, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolz, A.; Le Floch, S.; Reinert, L.; Ramos, S.M.M.; Tuaillon-Combes, J.; Soneda, Y.; Chaudet, P.; Baillis, D.; Blanchard, N.; Duclaux, L.; et al. Melamine-derived carbon sponges for oil-water separation. Carbon 2016, 107, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Han, M.; Hao, H.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y. Preparation and application of nano-ferric oxide. Low Carbon World 2021, 11, 231–232. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Liang, X.; Pi, N.; Yang, H.; Liu, X.; Yang, Y. Effects of pretreatment for micron glass on its nano-Fe3O4 coating layer. Glas. Phys. Chem. 2015, 41, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sponge | Initial Mass/g | Mass after Adsorption/g | The Mass of Adsorbed Oil/g | Adsorption Capacity g/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MS | 0.03 | 2.81 | 2.79 | 93 |
| PDMS@Fe3O4/MS | 0.19 | 2.94 | 2.75 | 14.49 |
| Oil | 5 Times (g/g) | 10 Times (g/g) | 15 Times (g/g) | 20 Times (g/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corn gern oil | 15.20 ± 0.21 | 14.27 ± 0.25 | 13.19 ± 0.19 | 12.32 ± 0.23 |
| 0#Diesel fuel | 12.26 ± 0.21 | 12.04 ± 0.24 | 11.50 ± 0.23 | 11.14 ± 0.22 |
| Kerosene | 13.13 ± 0.34 | 12.89 ± 0.31 | 12.74 ± 0.37 | 12.57 ± 0.35 |
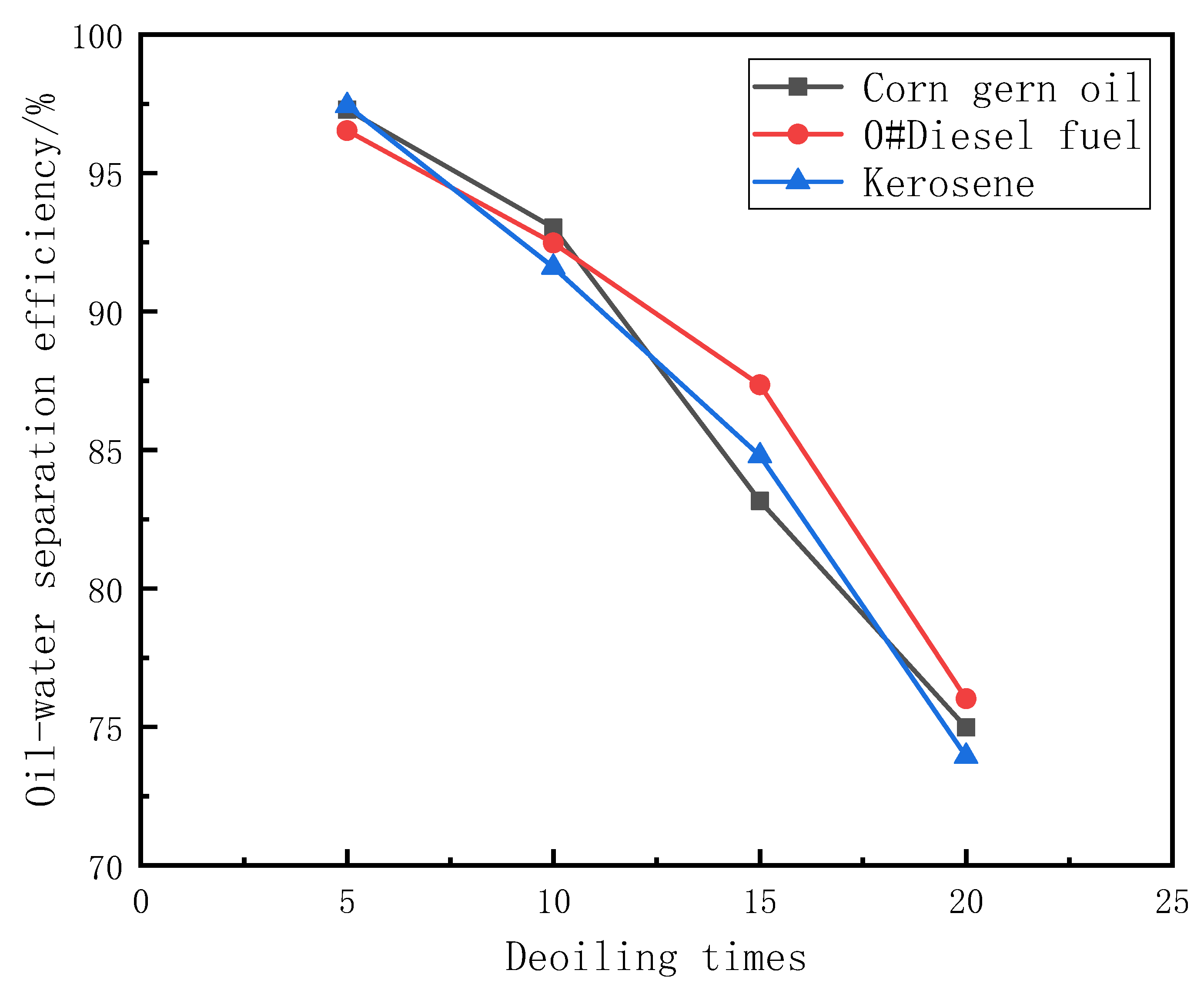
| Oil | 5 Times (%) | 10 Times (%) | 15 Times (%) | 20 Times (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corn gern oil | 97.28 ± 0.023 | 93.02 ± 0.021 | 83.16 ± 0.029 | 74.98 ± 0.027 |
| 0#Diesel fuel | 96.53 ± 0.041 | 92.47 ± 0.039 | 87.35 ± 0.041 | 76.02 ± 0.037 |
| Kerosene | 97.43 ± 0.020 | 91.60 ± 0.022 | 84.79 ± 0.018 | 73.94 ± 0.024 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Fan, Z.; Liu, Q.; Tong, Q.; Wang, B. Fabrication of PDMS@Fe3O4/MS Composite Materials and Its Application for Oil-Water Separation. Materials 2022, 15, 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15010115
Wang J, Fan Z, Liu Q, Tong Q, Wang B. Fabrication of PDMS@Fe3O4/MS Composite Materials and Its Application for Oil-Water Separation. Materials. 2022; 15(1):115. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15010115
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jiaqi, Zhenzhong Fan, Qingwang Liu, Qilei Tong, and Biao Wang. 2022. "Fabrication of PDMS@Fe3O4/MS Composite Materials and Its Application for Oil-Water Separation" Materials 15, no. 1: 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15010115
APA StyleWang, J., Fan, Z., Liu, Q., Tong, Q., & Wang, B. (2022). Fabrication of PDMS@Fe3O4/MS Composite Materials and Its Application for Oil-Water Separation. Materials, 15(1), 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15010115






