Mechanical Properties and Wear Resistance of Commercial Stainless Steel Used in Dental Instruments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Elemental Composition Analysis
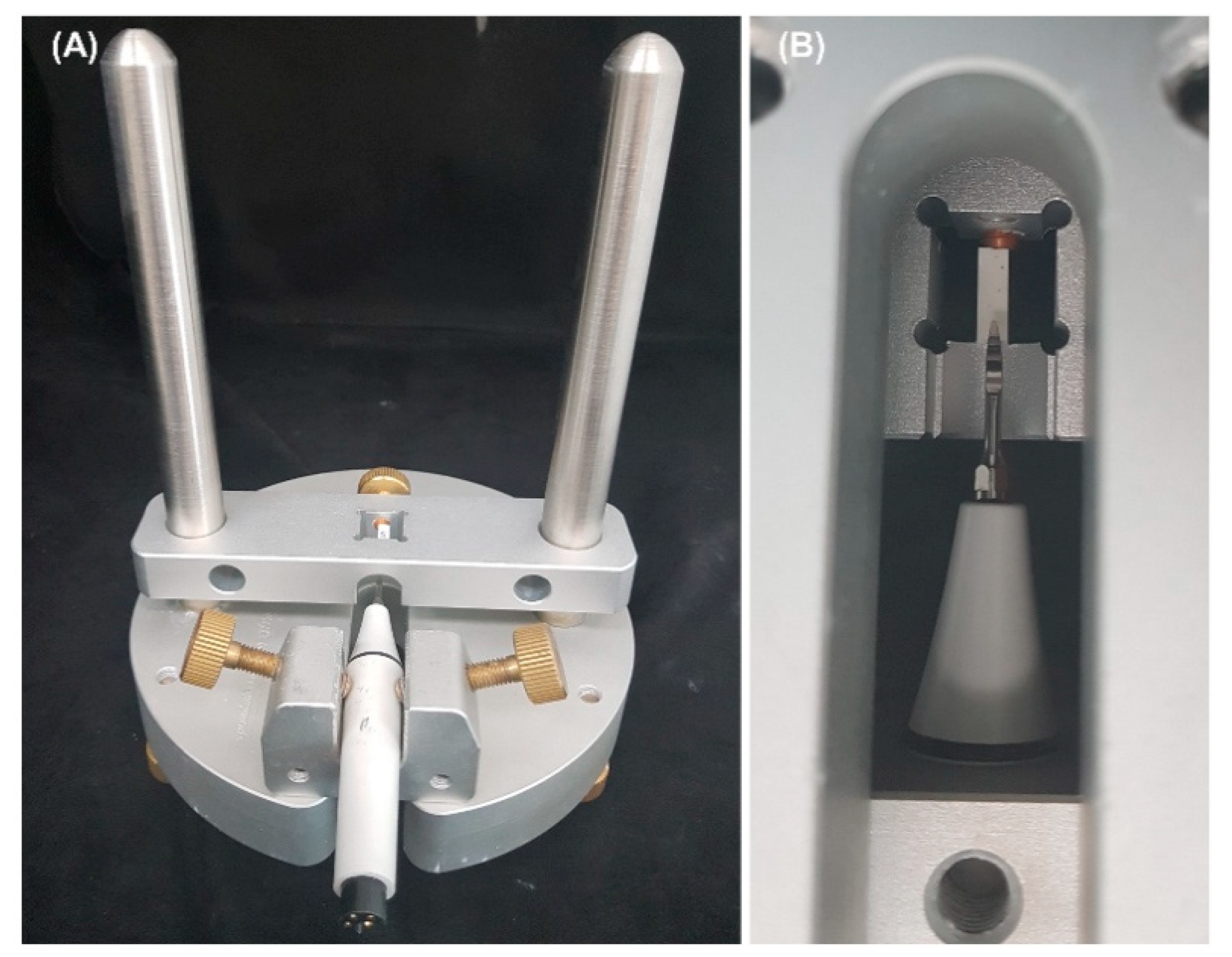
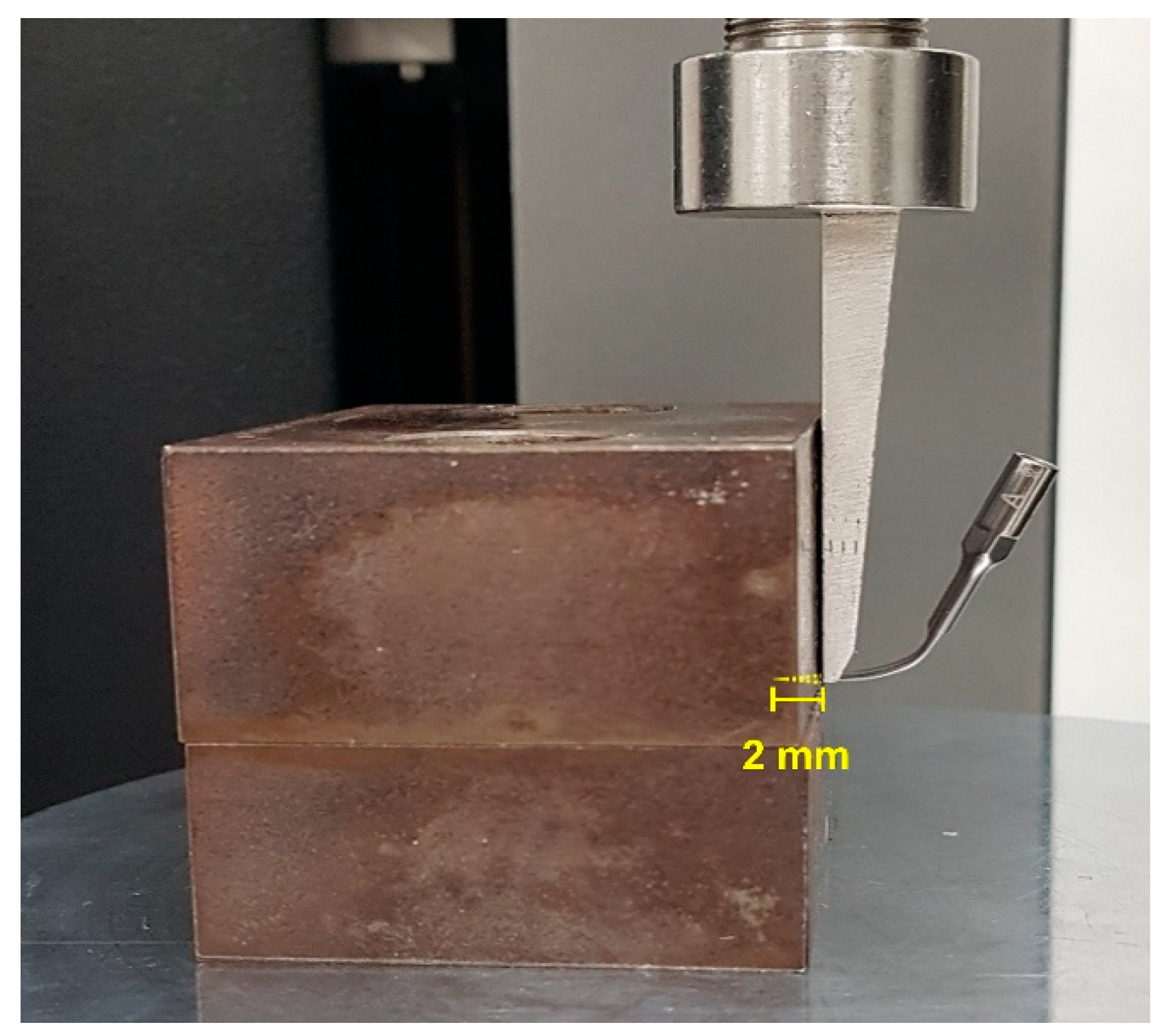
2.3. Shear Strength Test
2.4. Vickers Hardness Test
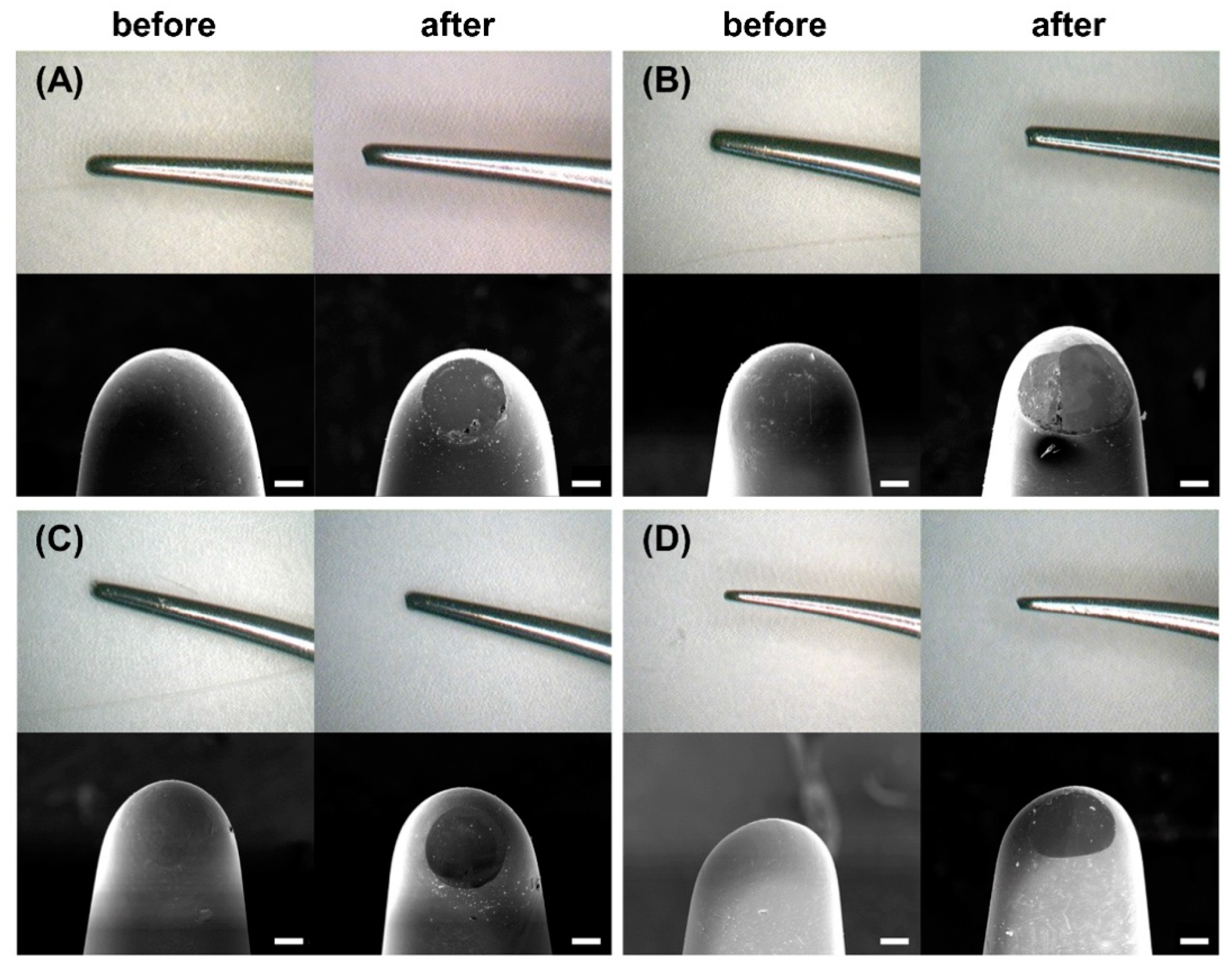
2.5. Wear Test
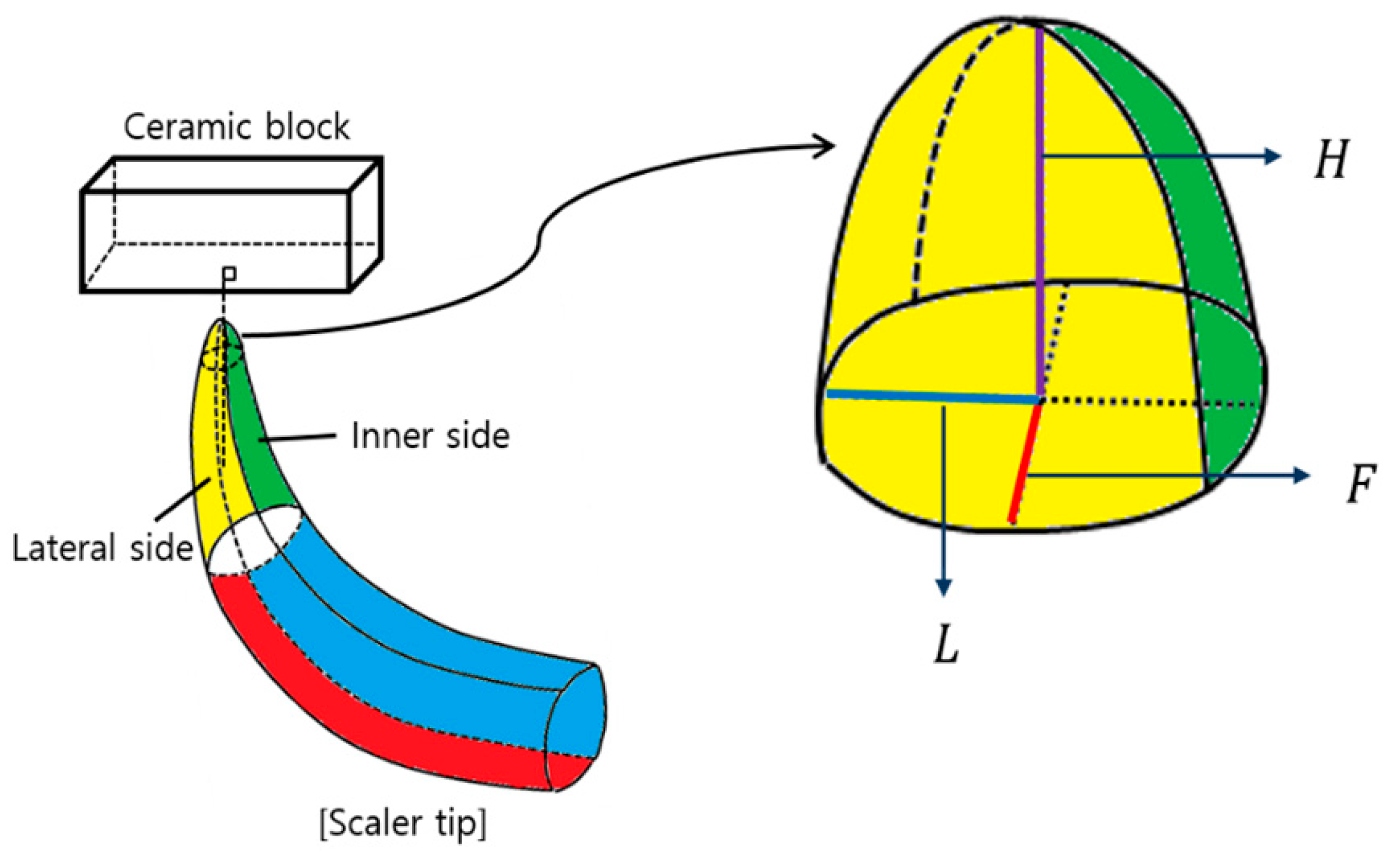
2.6. Wear Degree by Mass and Volume for Stainless-Steel Ultrasonic Scaler Tips
2.7. Grain Size
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
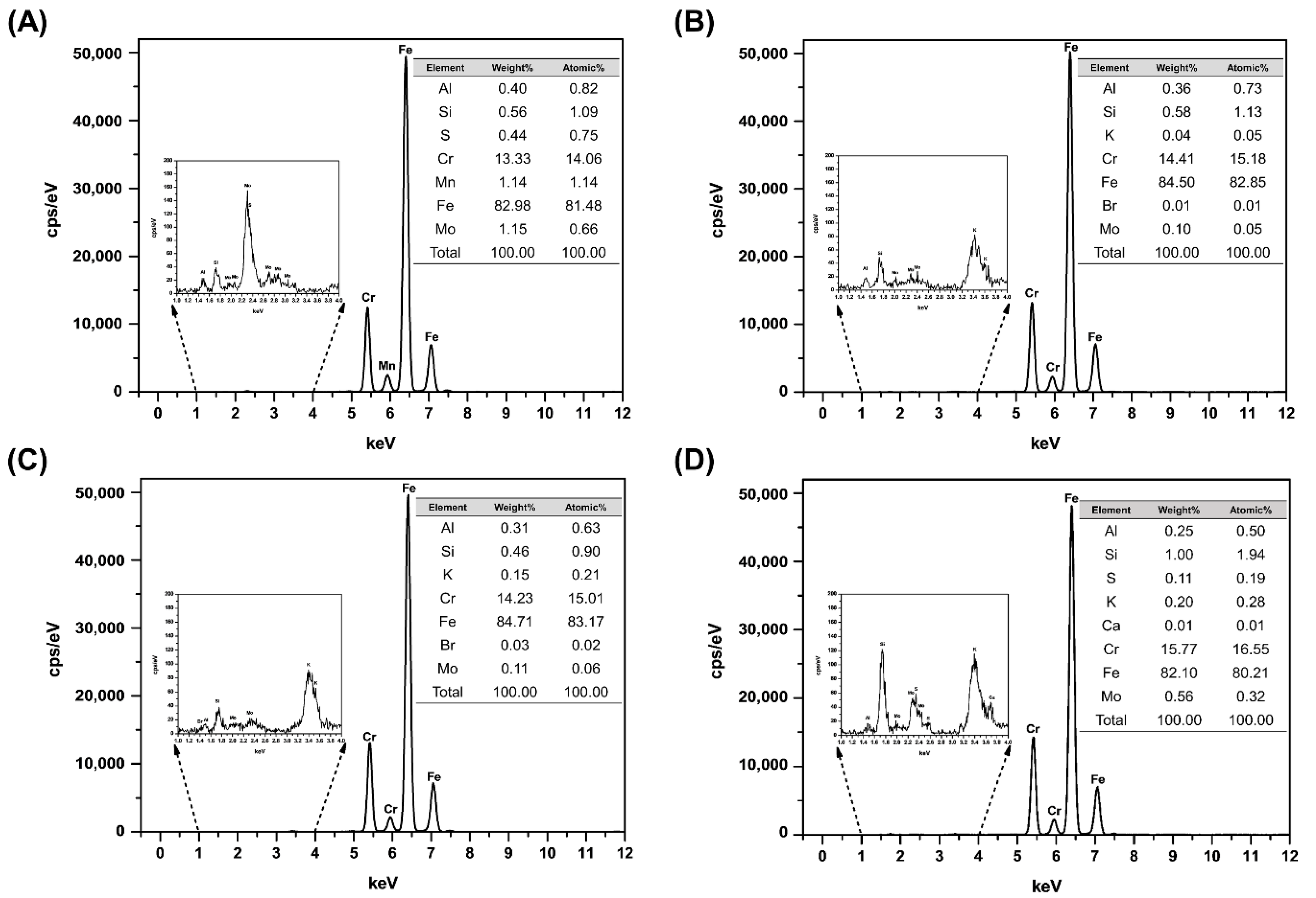
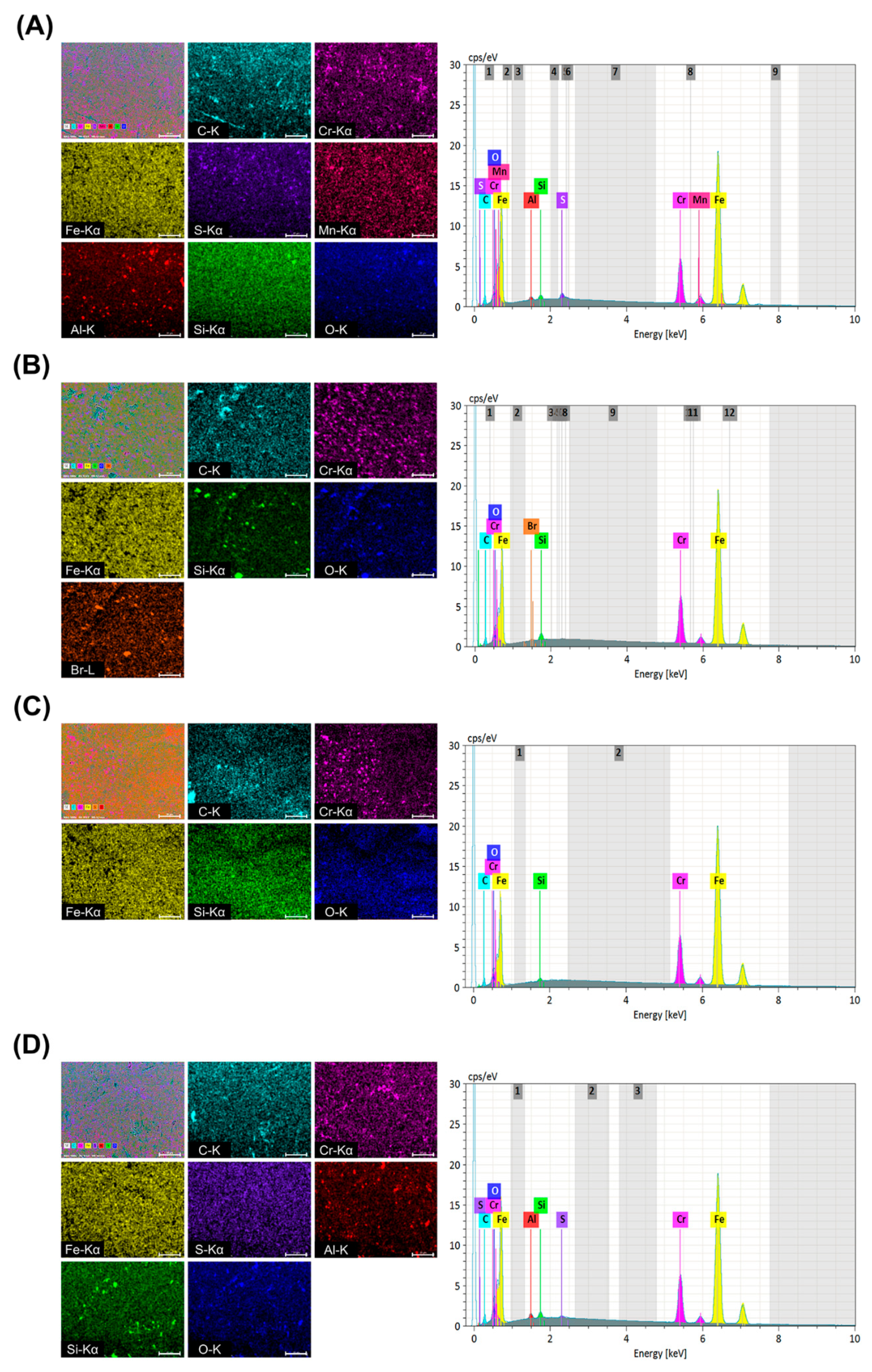
3.1. Elemental Composition Analysis
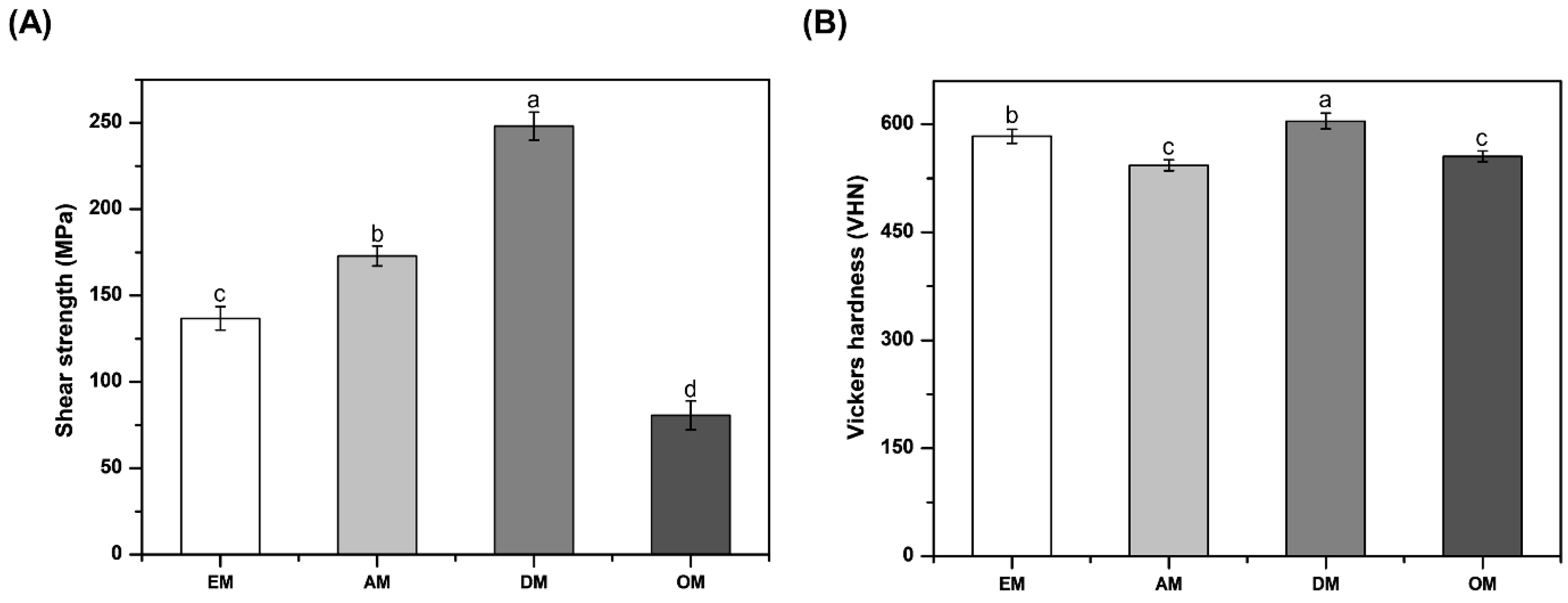
3.2. Shear Strength
3.3. Vickers Hardness
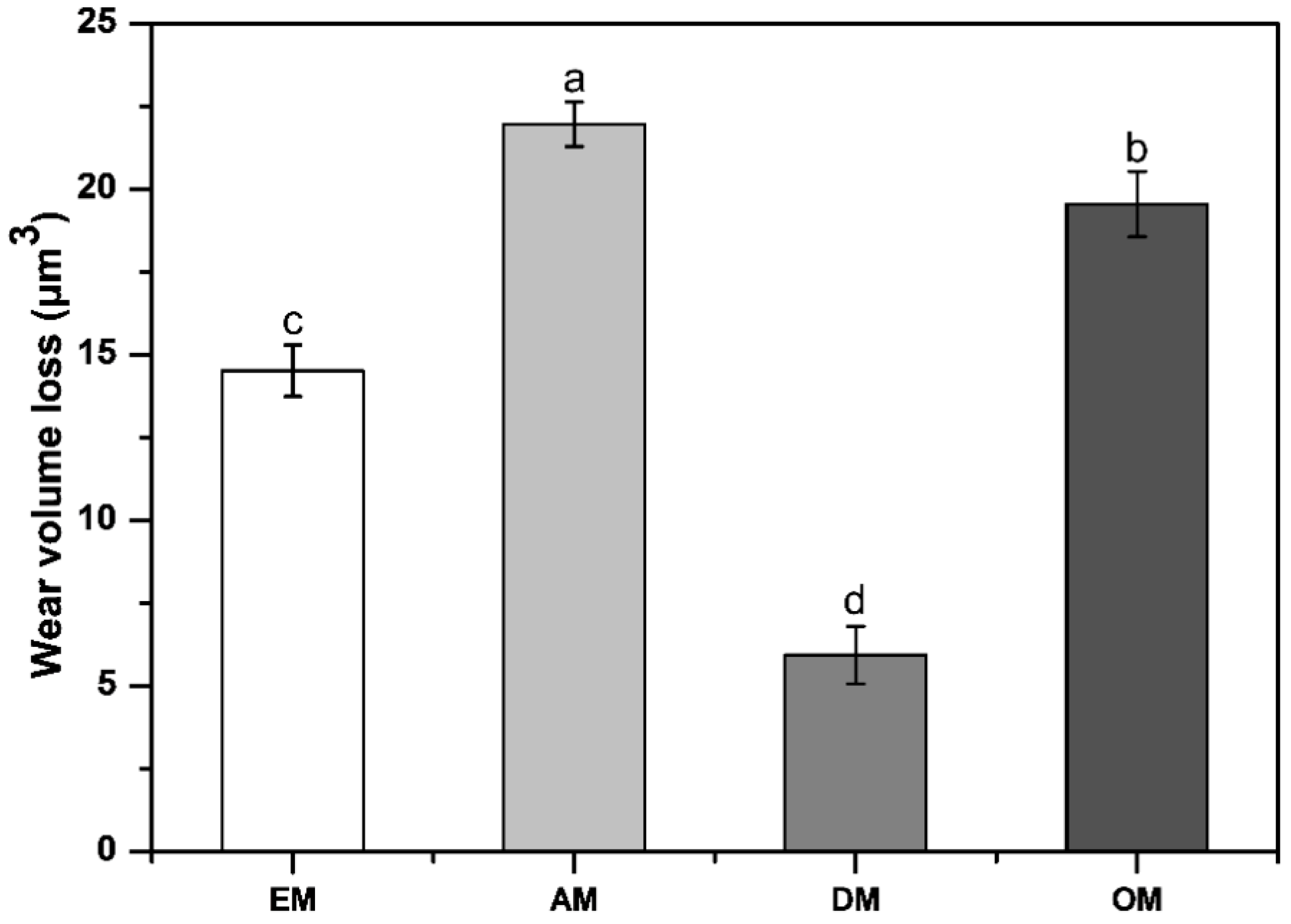
3.4. Wear Degree by Mass and Volume
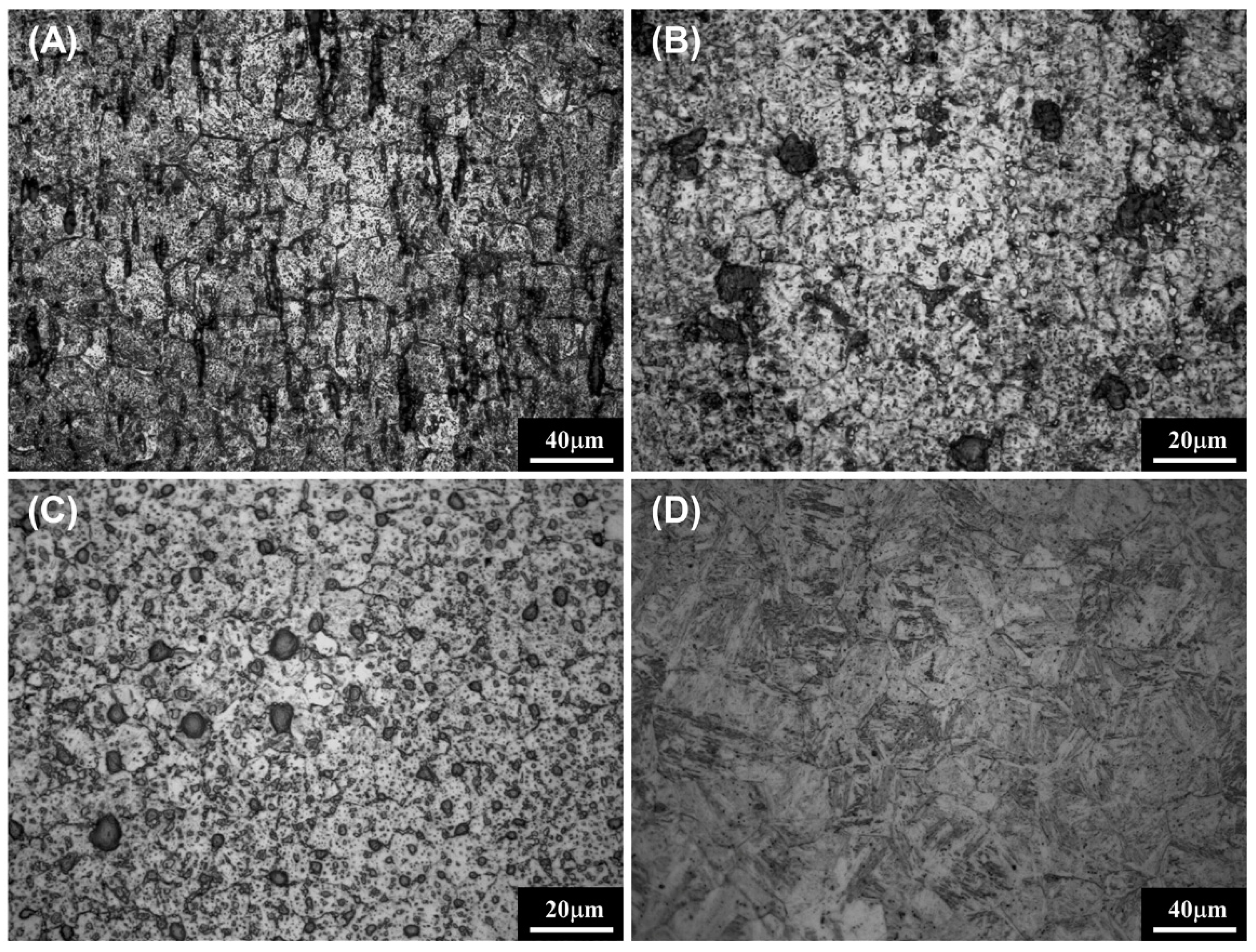
3.5. Grain Size
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huynh, H.T.; Verneau, J.; Levasseur, A.; Drancourt, M.; Aboudharam, G. Bacteria and archaea paleomicrobiology of the dental calculus: A review. Mol. Oral Microbiol. 2016, 31, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, R.C.; Brown, L.J.; Löe, H. Periodontal Diseases in the United States Population. J. Periodontol. 1998, 69, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, S.; Mealey, B.L.; Mariotti, A.; Chapple, I.L. Dental plaque-induced gingival conditions. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45, S17–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tecco, S.; Grusovin, M.; Sciara, S.; Bova, F.; Pantaleo, G.; Capparé, P. The association between three attitude-related indexes of oral hygiene and secondary implant failures: A retrospective longitudinal study. Int. J. Dent. Hyg. 2017, 16, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherlone, E.F.; Capparé, P.; Tecco, S.; Polizzi, E.; Pantaleo, G.; Gastaldi, G.; Grusovin, M.G. A Prospective Longitudinal Study on Implant Prosthetic Rehabilitation in Controlled HIV-Positive Patients with 1-Year Follow-Up: The Role of CD4+ Level, Smoking Habits, and Oral Hygiene. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2015, 18, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pihlstrom, B.L.; Michalowicz, B.S.; Johnson, N.W. Periodontal diseases. Lancet 2005, 366, 1809–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabaci, T.; Çanakçi, C.; Çiçek, Y. Sonic and ultrasonic scalers in periodontal treatment: A review. Int. J. Dent. Hyg. 2007, 5, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishida, M.; Sato, S.; Ito, K. Effects of a new ultrasonic scaler on fibroblast attachment to root surfaces: A scanning electron microscopy analysis. J. Periodontal Res. 2004, 39, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drisko, C.; Cochran, D.; Blieden, T.; Bouwsma, O.; Cohen, R.; Damoulis, P.; Fine, J.; Greenstein, G.; Hinrichs, J.; Somerman, M. Position paper: Sonic and ultrasonic scalers in periodontics. Research, Science and Therapy Committee of the American Academy of Periodontology. J. Periodontol. 2000, 71, 1792–1801. [Google Scholar]
- Busslinger, A.; Lampe, K.; Beuchat, M.; Lehmann, B. A comparative in vitro study of a magnetostrictive and a piezoelectric ultrasonic scaling instrument. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2001, 28, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lea, S.C.; Landini, G.; Walmsley, A. Vibration characteristics of ultrasonic scalers assessed with scanning laser vibrometry. J. Dent. 2002, 30, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.-H.; Shon, W.-J.; Bae, K.-S.; Kum, K.-Y.; Lee, W.-C.; Park, Y.-S. Evaluation of the safety and efficiency of novel metallic ultrasonic scaler tip on titanium surfaces. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2011, 23, 1269–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seol, H.W.; Heo, S.J.; Koak, J.Y.; Kim, S.K.; Baek, S.H.; Lee, S.Y. Surface alterations of several dental materials by a novel ultrasonic scaler tip. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants. 2012, 27, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lea, S.C.; Landini, G.; Walmsley, A.D. The effect of wear on ultrasonic scaler tip displacement amplitude. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2006, 33, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabaci, T.; Cicek, Y.; Dilsiz, A.; Erdogan, I.Y.; Kose, O.; Kizildağ, A. Influence of tip wear of piezoelectric ultrasonic scalers on root surface roughness at different working parameters. A profilometric and atomic force microscopy study. Int. J. Dent. Hyg. 2012, 11, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirunyapruk, C.; Sanponpute, T. Application of Using Standard Equipment for Dental Scaler Tip Testing according to ISO 18397. J. Mech. Eng. Autom. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinjari, B.; Addazio, G.D.; Bozzi, M.; Celletti, R.; Traini, T.; Mavriqi, L.; Caputi, S. Comparison of a Novel Ultrasonic Scaler Tip vs. Conventional Design on a Titanium Surface. Materials 2018, 11, 2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yao, Y.; A Warner, J.; Qu, J.; Yun, F.; Ye, Z.; Ringer, S.P.; Zheng, R. Grain size quantification by optical microscopy, electron backscatter diffraction, and magnetic force microscopy. Micron 2017, 101, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/ (accessed on 9 February 2021).
- Lea, S.C.; Walmsley, A.D. Mechano-physical and biophysical properties of power-driven scalers: Driving the future of powered instrument design and evaluation. Periodontol. 2000 2009, 51, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wear of ultrasonic scaler tips. Dent. Abstr. 2006, 51, 284–285. [CrossRef]
- Chun, K.A.; Kum, K.-Y.; Lee, W.-C.; Baek, S.-H.; Choi, H.-W.; Shon, W.-J. Evaluation of the safety and efficiency of novel metallic implant scaler tips manufactured by the powder injection molding technique. BMC Oral Health 2017, 17, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Kang, J.; Zhu, L.; Shu, D.; Peng, P.; She, D.; Meng, D.; Li, Y. Effects of grain size on tensile property and fracture morphology of 316L stainless steel. Mater. Lett. 2019, 254, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, E. The Deformation and Ageing of Mild Steel: III Discussion of Results. Proc. Phys. Soc. B 1951, 64, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petch, N. The cleavage strength of polycrystals. J. Iron Steel Inst. 1953, 174, 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Ngan, A. Specimen size and grain size effects on tensile strength of Ag microwires. Scr. Mater. 2011, 64, 717–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappalainen, R.; Yli-Urpo, A.; Seppä, L. Wear of dental restorative and prosthetic materials in vitro. Dent. Mater. 1989, 5, 35–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, D.; Gonzalez, F.; Palumbo, G.; Aust, K.; Erb, U. The effect of grain size on the wear properties of electrodeposited nanocrystalline nickel coatings. Scr. Mater. 2001, 44, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.-K.; Tan, H.; Chen, J.; Martini, A.; Zhang, C. Effect of carbon content on microstructure, hardness and wear resistance of CoCrFeMnNiCx high-entropy alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 2020, 847, 156533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H. Tribological properties of titanium-based alloys. Surf. Eng. Light Alloy. 2010, 58–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Yao, J.H.; Zhang, Q.L.; Yao, M.X.; Collier, R. Microstructures and Hardness/Wear Performance of High-Carbon Stellite Alloys Containing Molybdenum. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2015, 46, 5504–5513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressan, J.; Daros, D.; Sokolowski, A.; Mesquita, R.; Barbosa, C. Influence of hardness on the wear resistance of 17-4 PH stainless steel evaluated by the pin-on-disc testing. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2008, 205, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, R.; Srinivas, S. Effect of heat treatment on hardness, tensile strength and microstructure of hot and cold forged Al6061 metal matrix composites reinforced with silicon carbide particles. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 1065g3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, S.S.d.; Adabo, G.L.; Henriques, G.E.P.; Nóbilo, M.A.d.A. Vickers hardness of cast commercially pure titanium and Ti-6Al-4V alloy submitted to heat treatments. Braz. Dent. J. 2006, 17, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baghjari, S.; Mousavi, S.A. Effects of pulsed Nd:YAG laser welding parameters and subsequent post-weld heat treatment on microstructure and hardness of AISI 420 stainless steel. Mater. Des. 2013, 43, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
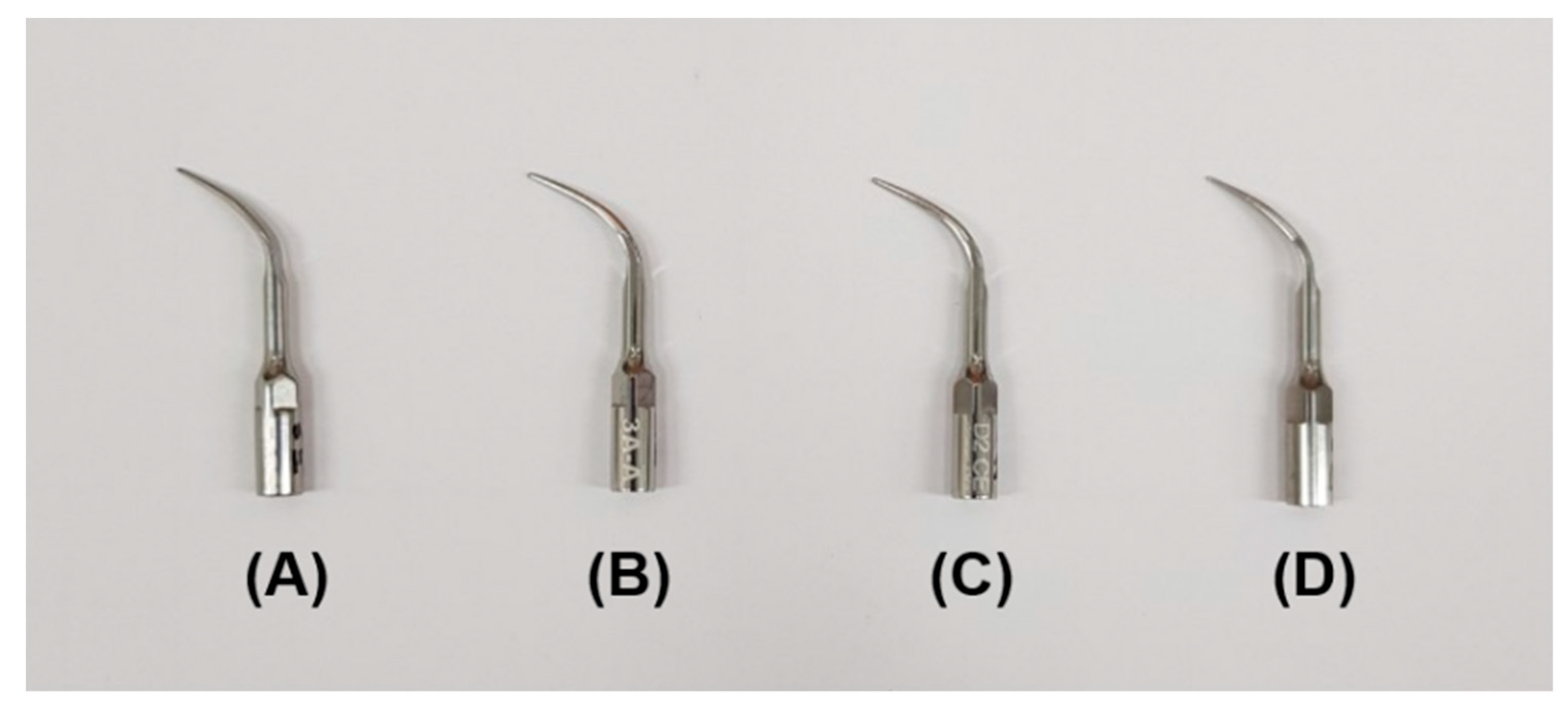

| Group | Manufacturer | Product Name | Location | Materials | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM | Electro Medical Systems | A Type | Nyon, Switzerland | Stainless steel | Full mouth/ Supragingival |
| AM | 3A MEDES | A Korea | Gyeonggi-do, Korea | Stainless steel | Full mouth/ Supragingival |
| DM | Dmetec | D2 | Gyeonggi-do, Korea | Stainless steel | Full mouth/ Supragingival |
| OM | OSUNG MND | USEA | Gyeonggi-do, Korea | Stainless steel | Full mouth/ Supragingival |
| Group | Before Mass (mg) | After Mass (mg) | Amount of Wear (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| EM | 813.69 ± 3.98 | 813.59 ± 4.01 | 0.10 ± 0.09 * |
| AM | 822.43 ± 6.93 | 822.39 ± 6.90 | 0.04 ± 0.07 * |
| DM | 807.75 ± 2.91 | 807.70 ± 2.88 | 0.05 ± 0.08 * |
| OM | 815.50 ± 2.92 | 815.38 ± 2.95 | 0.13 ± 0.12 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Go, H.-B.; Bang, J.-Y.; Kim, K.-N.; Kim, K.-M.; Kwon, J.-S. Mechanical Properties and Wear Resistance of Commercial Stainless Steel Used in Dental Instruments. Materials 2021, 14, 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14040827
Go H-B, Bang J-Y, Kim K-N, Kim K-M, Kwon J-S. Mechanical Properties and Wear Resistance of Commercial Stainless Steel Used in Dental Instruments. Materials. 2021; 14(4):827. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14040827
Chicago/Turabian StyleGo, Hye-Bin, Jae-Yun Bang, Kyoung-Nam Kim, Kwang-Mahn Kim, and Jae-Sung Kwon. 2021. "Mechanical Properties and Wear Resistance of Commercial Stainless Steel Used in Dental Instruments" Materials 14, no. 4: 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14040827
APA StyleGo, H.-B., Bang, J.-Y., Kim, K.-N., Kim, K.-M., & Kwon, J.-S. (2021). Mechanical Properties and Wear Resistance of Commercial Stainless Steel Used in Dental Instruments. Materials, 14(4), 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14040827







