Application of BP Artificial Neural Network in Preparation of Ni–W Graded Coatings
Abstract
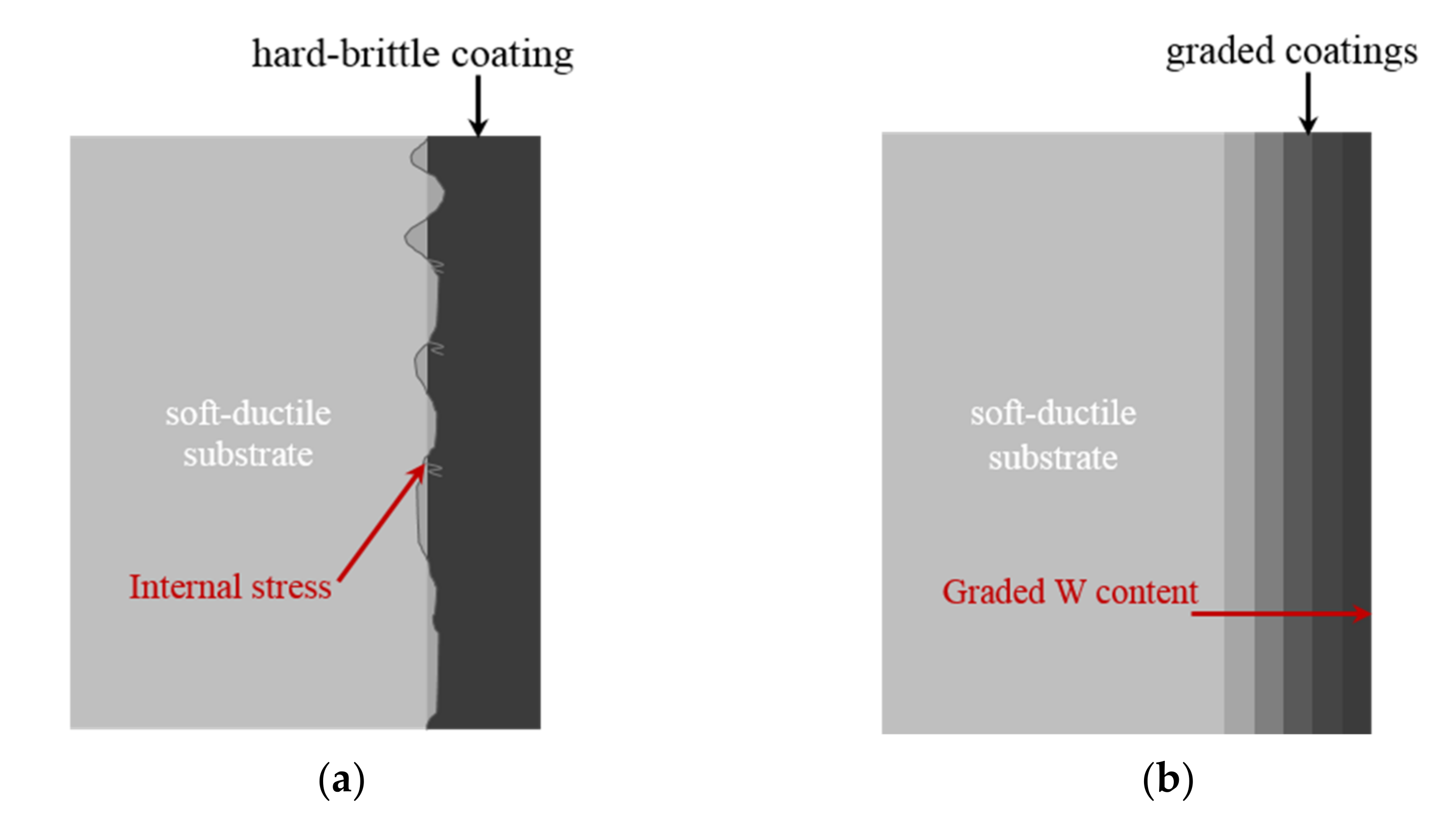
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
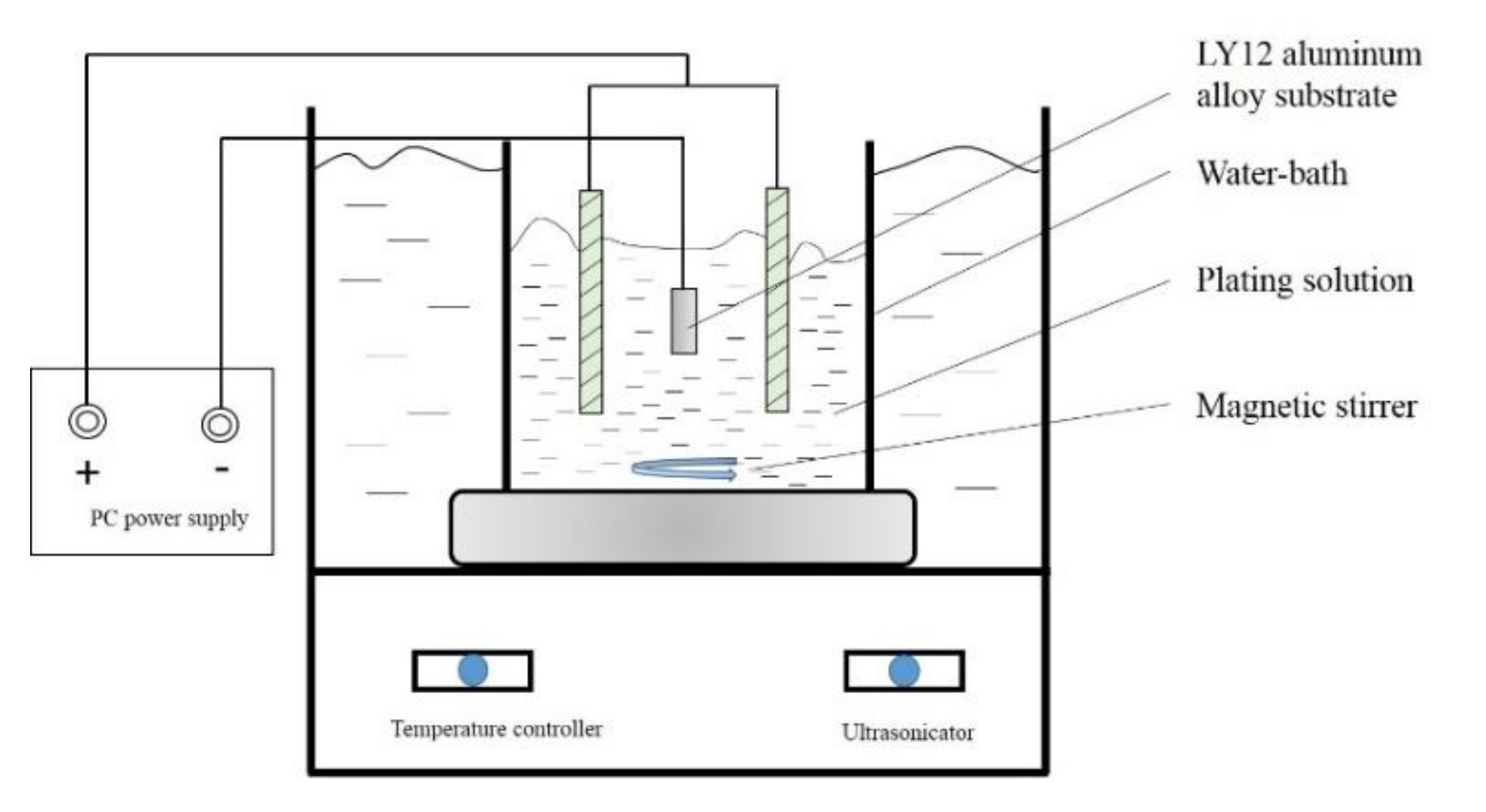
2.2. Bath Composition and Plating Parameters
2.3. Composite Coating Characterization
3. Design of Test
4. BP Neural Network Structure
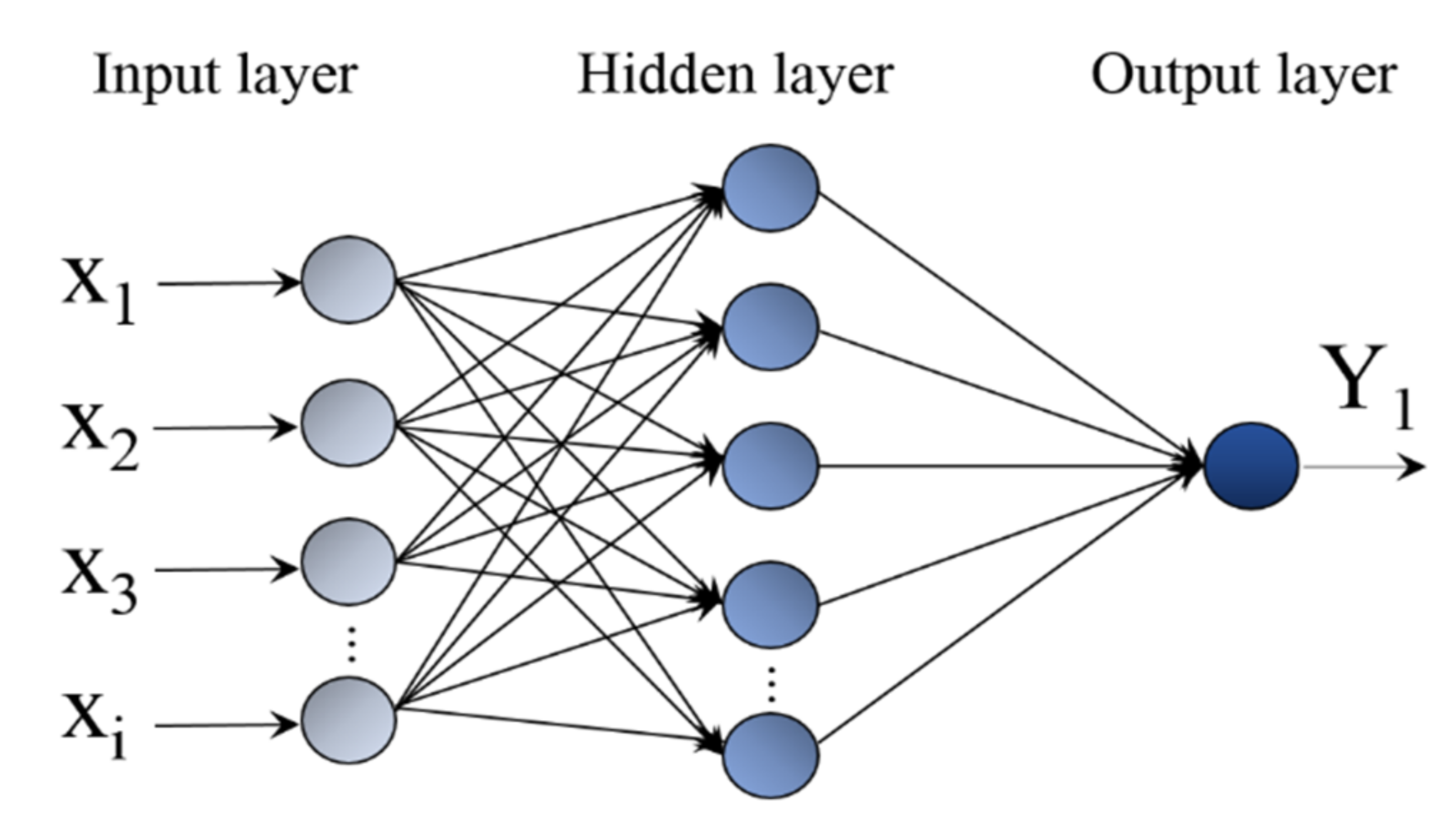
4.1. Design of BP Neural Network
4.2. Network Training and Prediction
4.2.1. Data Processing
4.2.2. Network Training and Prediction
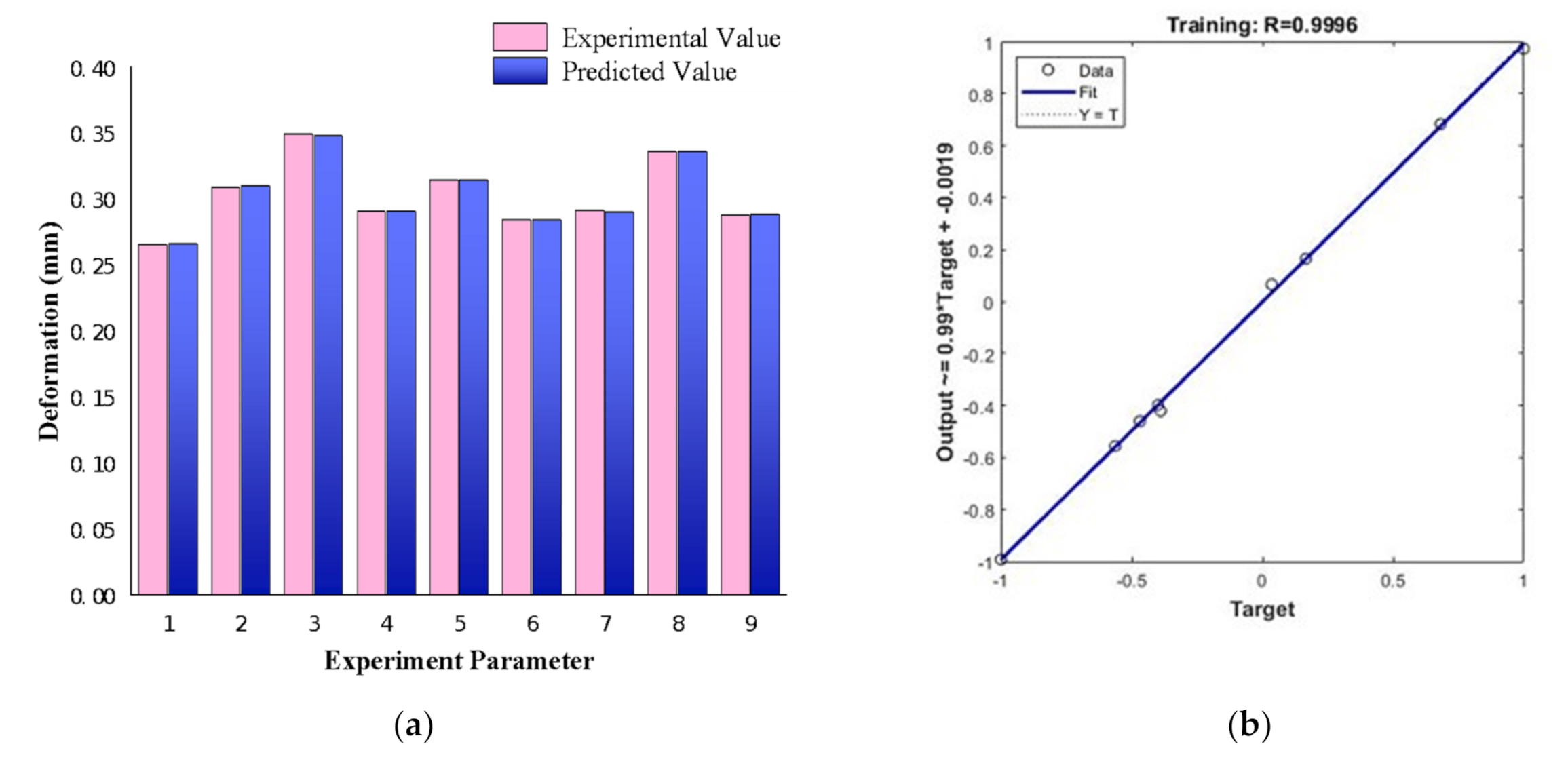
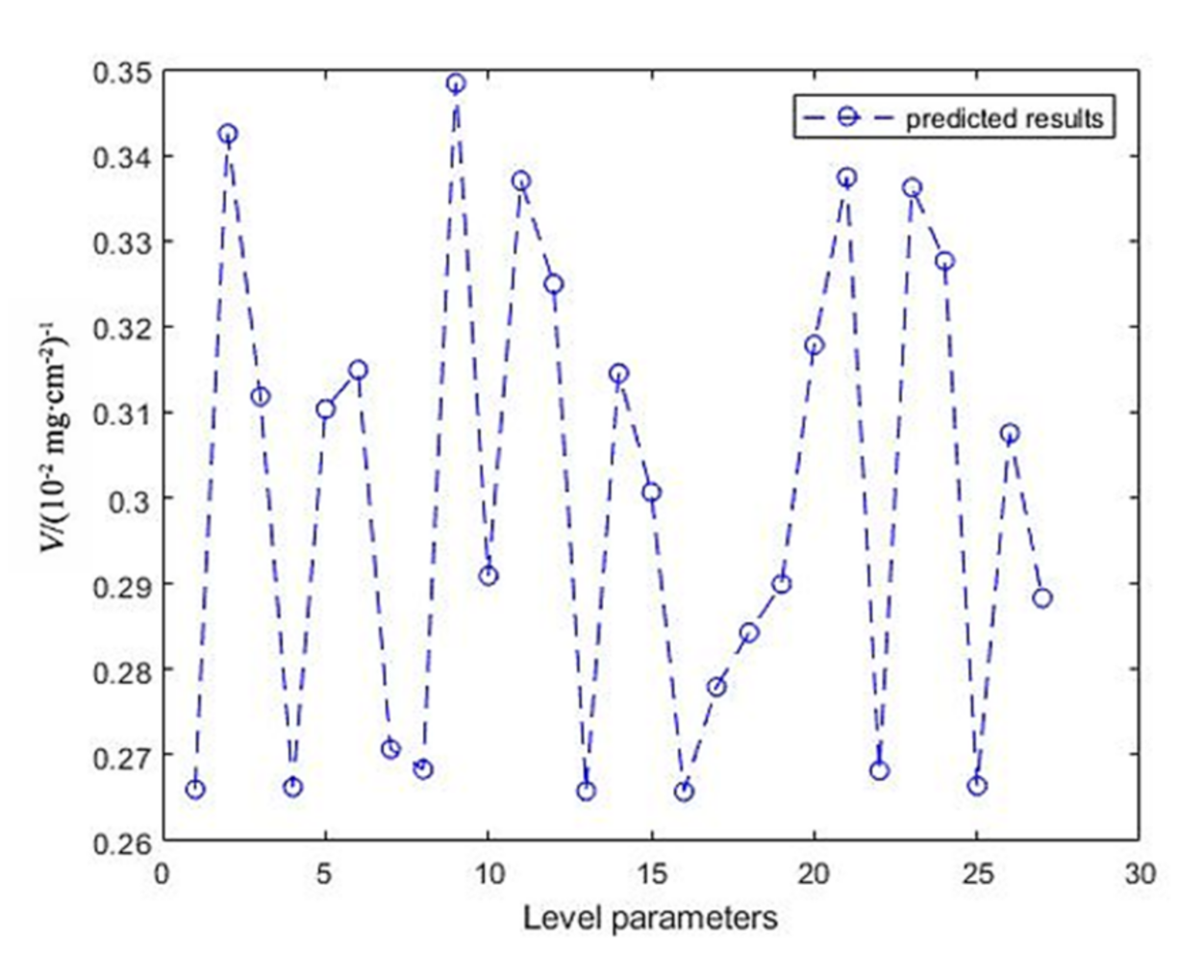
4.3. Prediction of BP Neural Network
5. Results and Discussion
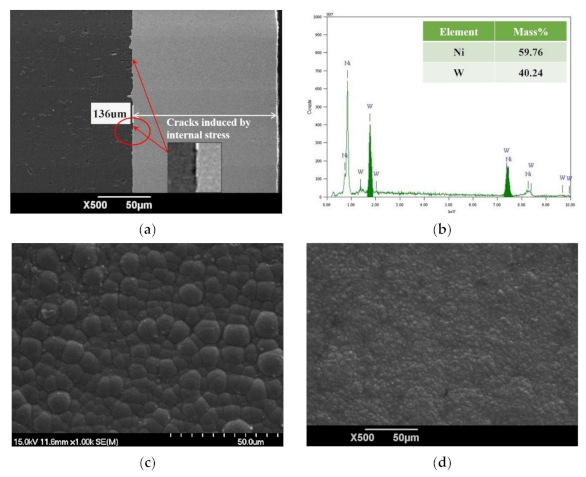
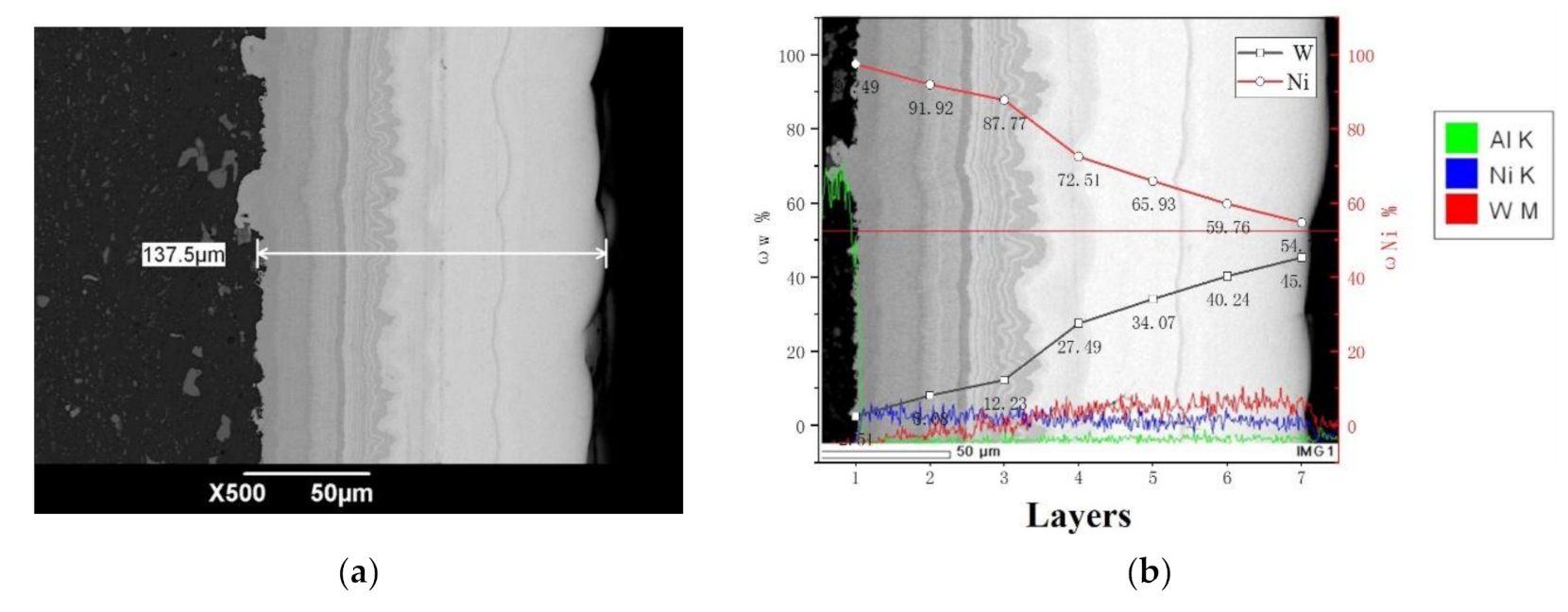
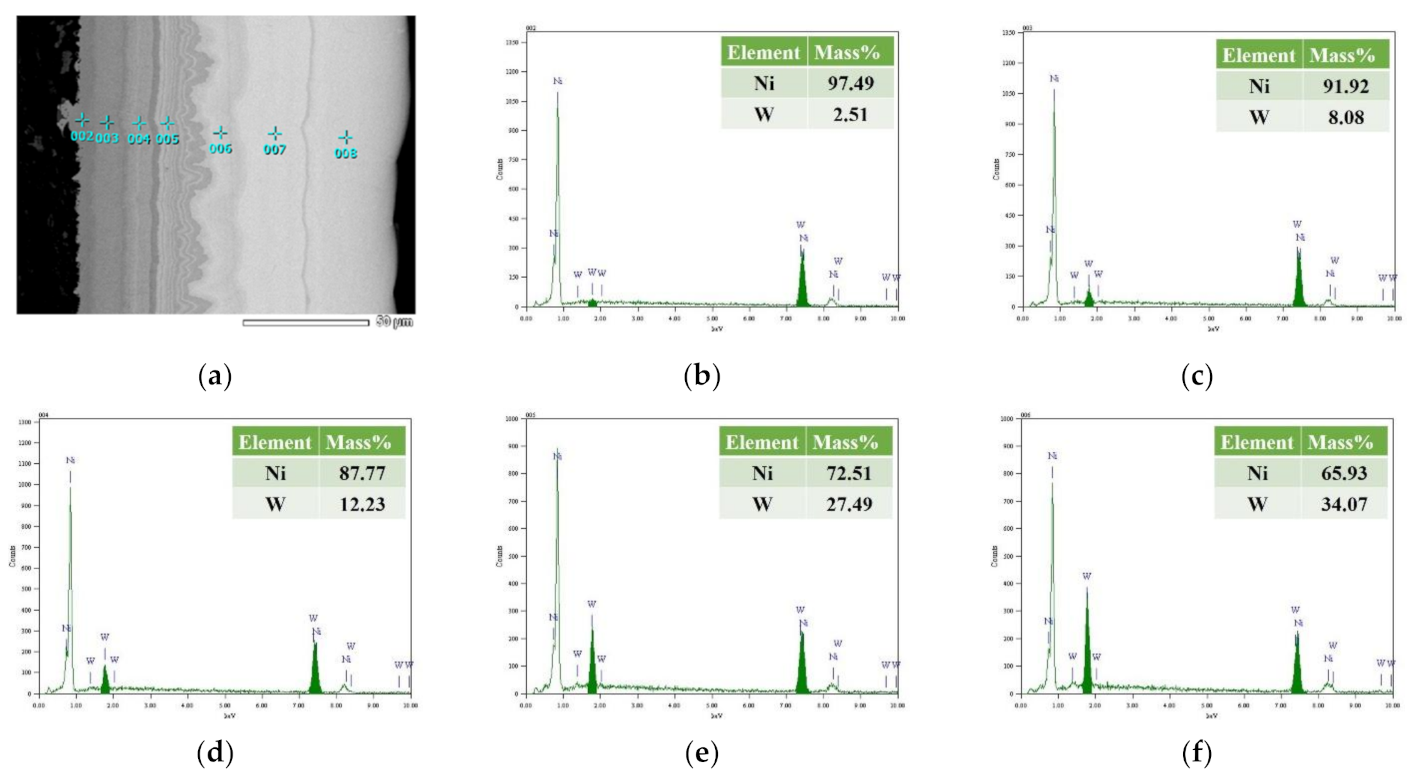
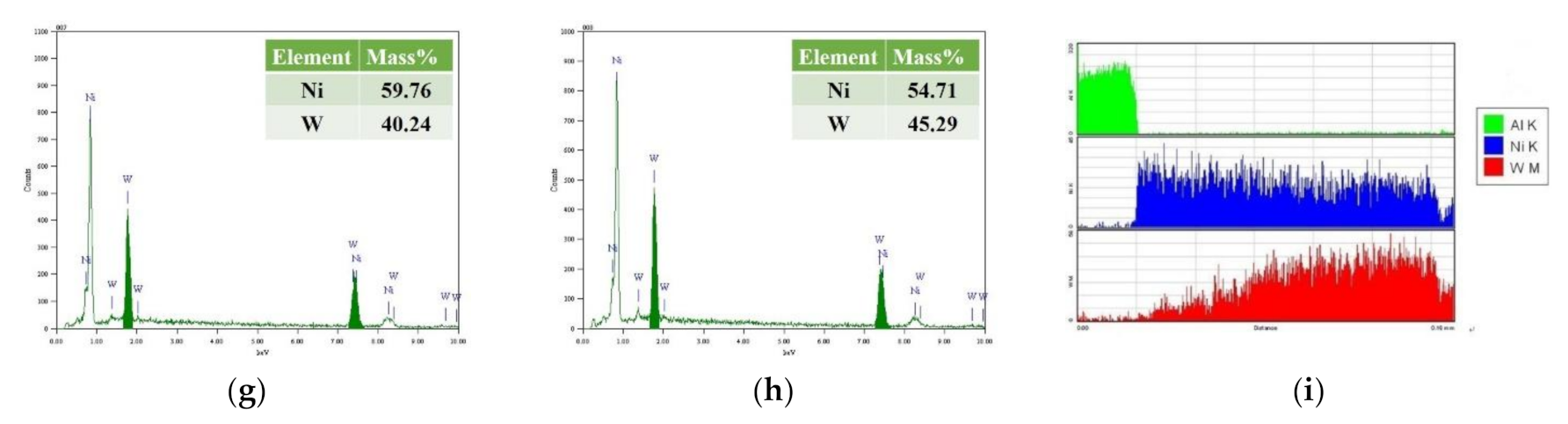
5.1. The Cross-Sectional Morphology and EDS Spectra Analysis of the Prepared Ni–W Coatings
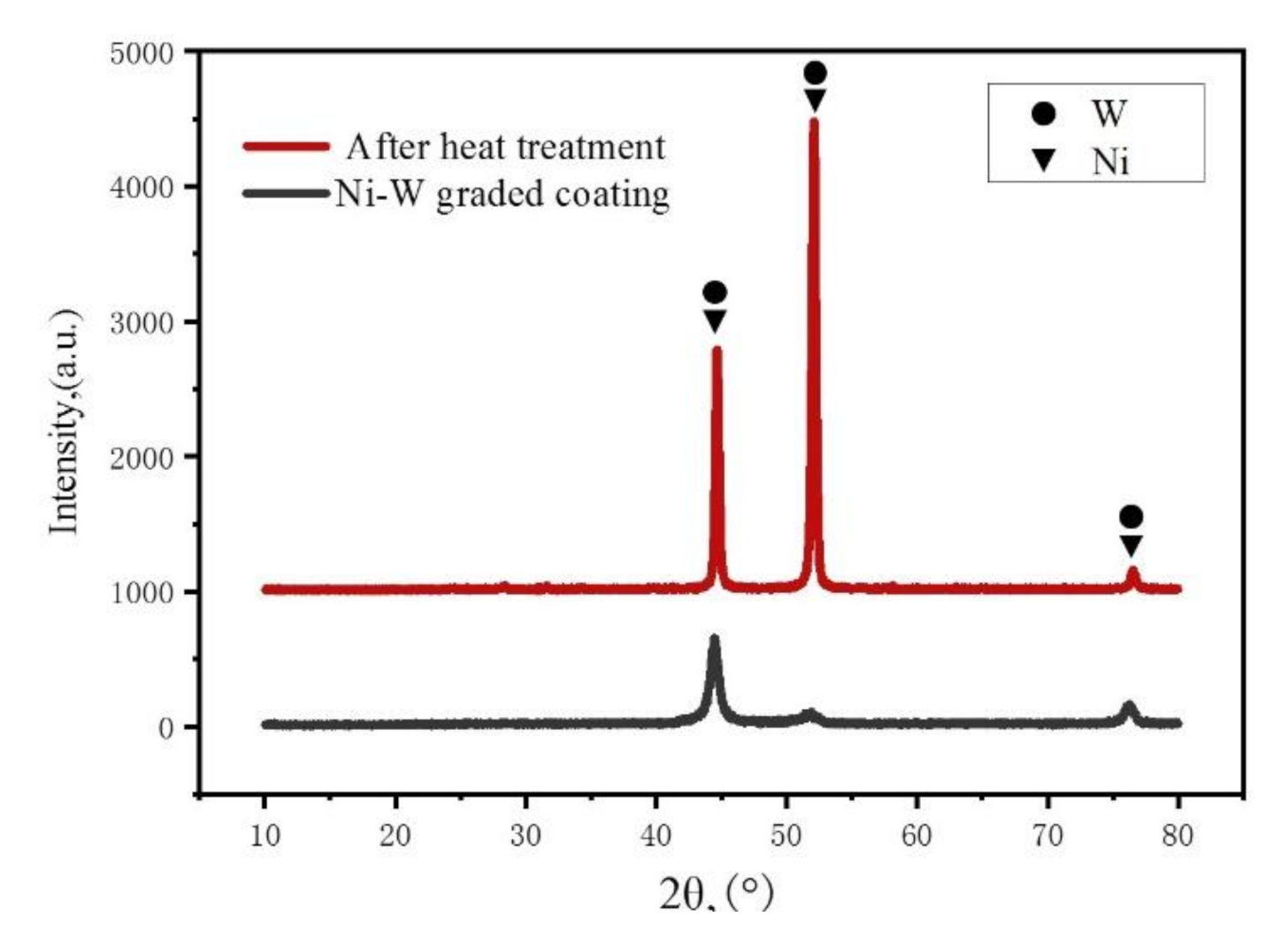
5.2. The XRD of Ni–W Graded Coatings
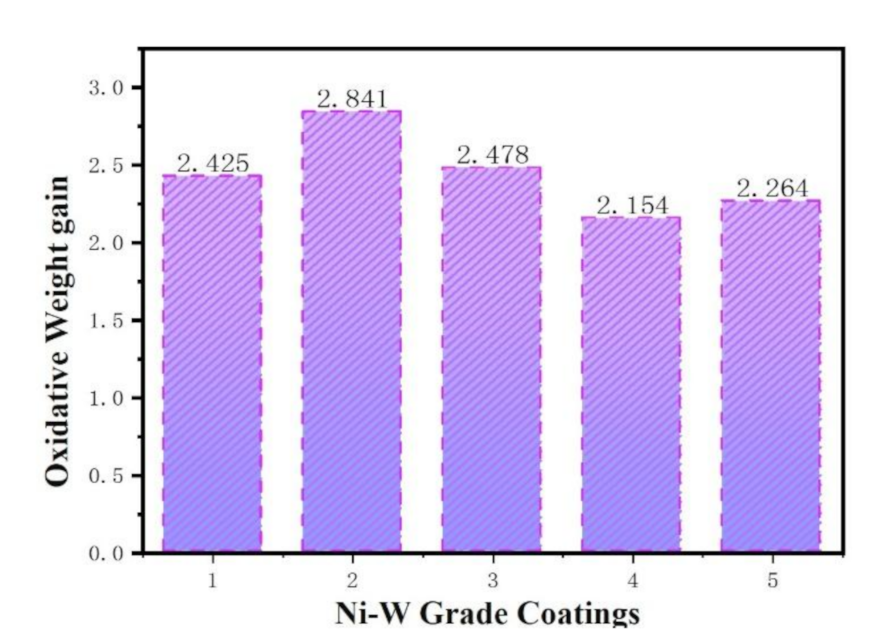
5.3. The High Temperature Oxidation Resistance of Ni–W Graded Coatings
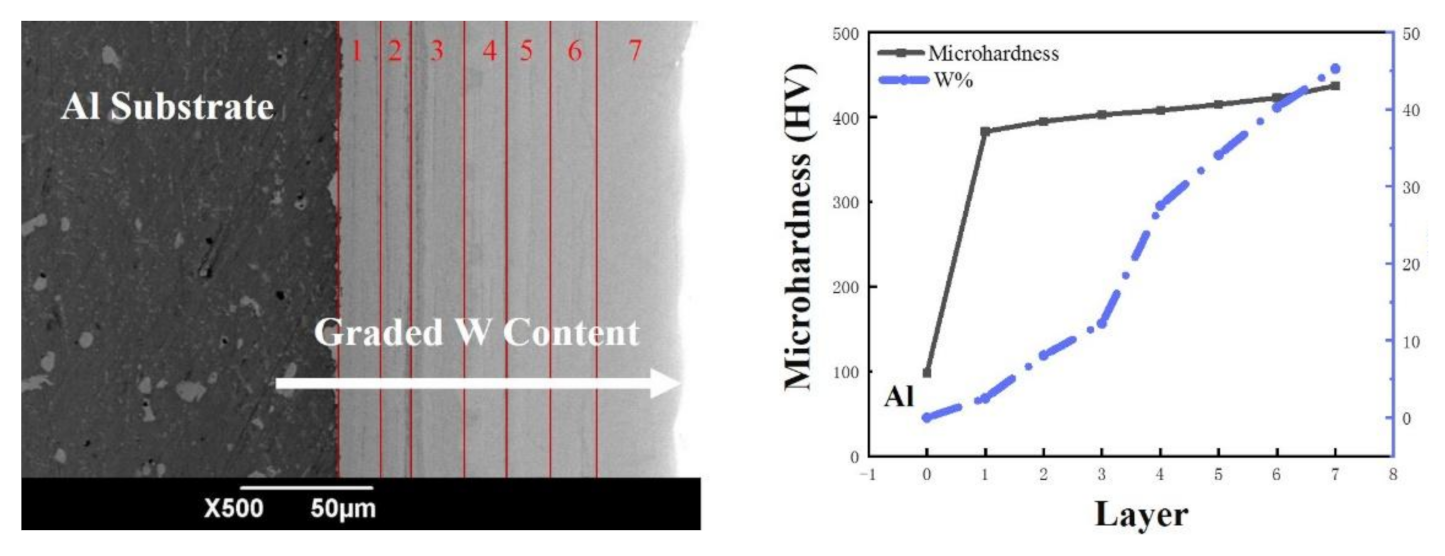
5.4. The Micro-Hardness of Ni–W Graded Coatings
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Symbols | Definition | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| ΔM | The oxidation weight gain of the coating | mg/cm2 |
| M1 | The mass of the sample before high-temperature oxidation | g |
| M2 | The mass of the sample after high-temperature oxidation | g |
| S | The surface area of the sample | cm2 |
| mx | The oxidative weight gain | g |
| V | The reciprocal of the oxidative weight gain | 1/g |
| Symbols | Definition |
|---|---|
| BP | Backward propagation |
| ANN | Artificial neural network |
| Ni–W | Nickel and tungsten |
| HVOF | High velocity oxygen fuel |
| LY-12 | A high strength duralumin |
| KSY | A muffle furnace model |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscope |
| EDX | Energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy |
| EDS | Energy disperse spectroscopy |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| VH | Vickers hardness |
References
- Pan, C.-Q.; Zhong, Q.-D.; Yang, J.; Cheng, Y.F.; Li, Y.-L. Investigating crevice corrosion behavior of 6061 Al alloy using wire beam electrode. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 14, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Liu, S.; Luo, L.; Peng, Z.; Liang, J.; Wang, P. Plasma electrolytic fluorination on Al alloys: Coating growth and plasma discharge behavior. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 29758–29770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapliyal, S.; Shukla, S.; Zhou, L.; Hyer, H.; Agrawal, P.; Agrawal, P.; Komarasamy, M.; Sohn, Y.; Mishra, R.S. Design of heterogeneous structured Al alloys with wide processing window for laser-powder bed fusion additive manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 42, 1002002. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, G.; Wu, C.; Liu, W.; Rong, Y.; Huang, Y. Anti-corrosion superhydrophobic surfaces of Al alloy based on micro-protrusion array structure fabricated by laser direct writing. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 881, 160649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, D.; Mei, T.; Xia, W.; Zhang, W. Fabrication and characterization of boron nitride reinforced Ni–W nanocomposite coating by electrodeposition. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 777, 1234–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neethu, R.M.; Hegde, A.C. Development of Ni–W alloy coatings and their electrocatalytic activity for water splitting reaction. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2020, 597, 412359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shajahan, S.; Basu, A. Corrosion, oxidation and wear study of electro-co-deposited ZrO2-TiO2 reinforced Ni–W coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 393, 125729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasekar, N.P.; Bathini, L.; Ramakrishna, L.; Rao, D.S.; Padmanabham, G. Pulsed electrodeposition, mechanical properties and wear mechanism in Ni–W/SiC nanocomposite coatings used for automotive applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 527, 146896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.-F.; Zhu, C.-F.; Yang, C.-P.; Lv, Y.-N. Preparation of amorphous Ni–W coating for the current collector of Na/S battery by electrodeposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 346, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasekar, N.P.; Hebalkar, N.; Jyothirmayi, A.; Lavakumar, B.; Ramakrishna, M.; Sundararajan, G. Influence of pulse parameters on the mechanical properties and electrochemical corrosion behavior of electrodeposited Ni–W alloy coatings with high tungsten content. Corros. Sci. 2020, 165, 108409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, B.; Ji, C. Synthesis and characterization of Ni–W/TiN nanocomposite coating with enhanced wear and corrosion resistance deposited by pulse electrodeposition. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 14015–14028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Hossain Bhuiyan, M.E.; Moreno, S.; Minary-Jolandan, M. Direct-Write Printing Copper-Nickel (Cu/Ni) Alloy with Controlled Composition from a Single Electrolyte Using Co-Electrodeposition. ACS Appl Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 18683–18691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behroozfar, A.; Hossain Bhuiyan, M.E.; Daryadel, S.; Edwards, D.; Rodriguez, B.J.; Minary-Jolandan, M. Additive printing of pure nanocrystalline nickel thin films using room environment electroplating. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 55301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panchal, S.; Mathew, M.; Dincer, I.; Agelin-Chaab, M.; Fraser, R.; Fowler, M. Thermal and electrical performance assessments of lithium-ion battery modules for an electric vehicle under actual drive cycles. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2018, 163, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchal, S.; Dincer, I.; Agelin-Chaab, M.; Fraser, R.; Fowler, M. Design and simulation of a lithium-ion battery at large C-rates and varying boundary conditions through heat flux distributions. Measurement 2018, 116, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panchal, S.; Dincer, I.; Agelin-Chaab, M.; Fraser, R.; Fowler, M. Experimental and theoretical investigation of temperature distributions in a prismatic lithium-ion battery. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2016, 99, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchal, S.; Dincer, I.; Agelin-Chaab, M.; Fraser, R.; Fowler, M. Experimental investigation and simulation of temperature distributions in a 16Ah-LiMnNiCoO2 battery during rapid discharge rates. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 53, 937–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allahyarzadeh, M.H.; Aliofkhazraei, M.; Rouhaghdam, A.R.S.; Torabinejad, V. Gradient electrodeposition of Ni-Cu-W(alumina) nanocomposite coating. Mater. Des. 2016, 107, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, M.; Chi, J.; Wang, S.; Yang, S.; Yang, J.; Wei, Y. Effect of Ti on microstructure characteristics, carbide precipitation mechanism and tribological behavior of different WC types reinforced Ni-based gradient coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 374, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Zhang, W.; Luo, Z.; Sun, X.; Li, Z.; Lin, L. Ultrasonic characterization of thermal barrier coatings porosity through BP neural network optimizing Gaussian process regression algorithm. Ultrasonics 2020, 100, 105981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, A.; Fals, H.D.C.; Roca, A.S.; Siqueira, I.B.A.F.; Caliari, F.R.; da Cruz, J.R.; Vaz, R.F.; de Sousa, M.J.; Pukasiewicz, A.G.M. Artificial neural networks applied to the analysis of performance and wear resistance of binary coatings Cr3C237WC18M and WC20Cr3C27Ni. Wear 2021, 477, 203797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Xiao, G.; Ma, C. Application of artificial neural networks to predict corrosion behavior of Ni–SiC composite coatings deposited by ultrasonic electrodeposition. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 5425–5430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhu, Y.; Xiao, G. Application of artificial neural networks to predict sliding wear resistance of Ni–TiN nanocomposite coatings deposited by pulse electrodeposition. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40 Pt A, 11767–11772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paturi, U.M.R.; Cheruku, S.; Geereddy, S.R. Process modeling and parameter optimization of surface coatings using artificial neural networks (ANNs): State-of-the-art review. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 38, 2764–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Ma, C.; Xia, F.; Zhang, Y. Application of artificial neural networks to predict the hardness of Ni–TiN nanocoatings fabricated by pulse electrodeposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 286, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, H.; Liao, H.; Deng, S. Prediction and analysis of high velocity oxy fuel (HVOF) sprayed coating using artificial neural network. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 378, 124988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, L.; Chitharanjan Hegde, A. A comparative study on the electrocatalytic activity of electrodeposited Ni–W and Ni-P alloy coatings. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 21156–21161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, L.; Hegde, A.C. Effect of magnetic field on corrosion protection efficacy of Ni–W alloy coatings. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 712, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shreeram, D.D.; Li, S.; Bedekar, V.; Cong, H.; Doll, G.L. Effect of reverse pulse time on electrodeposited Ni–W coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 325, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, L.; Chitharanjan Hegde, A. Electrodeposition of laminar coatings of Ni–W alloy and their corrosion behaviour. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 283, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.B.; Ko, J.H.; Kwon, S.C. High temperature oxidation of Ni–W coatings electroplated on steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 380, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lima-Neto, P.; Correia, A.N.; Santana, R.A.C.; Colares, R.P.; Barros, E.B.; Casciano, P.N.S.; Vaz, G.L. Morphological, structural, microhardness and electrochemical characterisations of electrodeposited Cr and Ni–W coatings. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 2078–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagopoulos, C.N.; Plainakis, G.D.; Lagaris, D.A. Nanocrystalline Ni–W coatings on copper. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2011, 176, 477–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argañaraz, M.P.Q.; Ribotta, S.B.; Folquer, M.E.; Gassa, L.M.; Benítez, G.; Vela, M.E.; Salvarezza, R.C. Ni–W coatings electrodeposited on carbon steel: Chemical composition, mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 5898–5903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allahyarzadeh, M.H.; Aliofkhazraei, M.; Rezvanian, A.R.; Torabinejad, V.; Sabour Rouhaghdam, A.R. Ni–W electrodeposited coatings: Characterization, properties and applications. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 307, 978–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunwang, N.; Wangyao, P.; Boonyongmaneerat, Y. The effects of heat treatments on hardness and wear resistance in Ni–W alloy coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 206, 1096–1101. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.B.; Ko, J.H.; Kwon, S.C. Oxidation of Ni–W coatings at 700 and 800 °C in air. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 193, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orrillo, P.A.; Ribotta, S.B.; Gassa, L.M.; Benítez, G.; Salvarezza, R.C.; Vela, M.E. Phosphonic acid functionalization of nanostructured Ni–W coatings on steel. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 433, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, K.-H.; Chang, Y.-F.; Chang, S.-M.; Chang, C.-H. The heat treatment effect on the structure and mechanical properties of electrodeposited nano grain size Ni–W alloy coatings. Thin Solid Film. 2010, 518, 7535–7540. [Google Scholar]
| Chemical Composition | Content (g/L) | Plating Conditions | Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
| NiSO4·7H2O | 30 g/L | Pulse current density | 5–15 mA/cm2 |
| Na2WO4·2H2O | 7.5 g/L-180 g/L | Duty cycle | 10–30% |
| C6H5O7(NH4)3 | 100 g/L | PH | 5 |
| NaBr | 5.4 g/L | Stirring rate | 100 (r/min) |
| CH4N2S | 2 drops | Temperature | 30–50 °C |
| C12H25SO4Na | 2 drops |
| mx/10−2 mg/cm2 | 3.763 | 3.235 | 2.861 | 3.437 | 3.179 | 3.521 | 3.433 | 2.974 | 3.472 |
| V/(10−2 mg/cm2)−1 | 0.2657 | 0.3091 | 0.3495 | 0.2909 | 0.3146 | 0.2840 | 0.2913 | 0.3362 | 0.2880 |
| Level | T/°C (T) | Current Density/mA/cm2 (C) | Duty Cycle (D) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 30 | 5 | 0.1 |
| 2 | 40 | 10 | 0.2 |
| 3 | 50 | 15 | 0.3 |
| Sample | T | C | D | V/(10−2 mg/cm2)−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 (30) | 1 (5) | 1 (0.1) | 0.2657 |
| 2 | 1 (30) | 2 (10) | 2 (0.2) | 0.3091 |
| 3 | 1 (30) | 3 (15) | 3 (0.3) | 0.3495 |
| 4 | 2 (40) | 1 (5) | 1 (0.1) | 0.2909 |
| 5 | 2 (40) | 2 (10) | 2 (0.2) | 0.3146 |
| 6 | 2 (40) | 3 (15) | 3 (0.3) | 0.2840 |
| 7 | 3 (50) | 1 (5) | 1 (0.1) | 0.2913 |
| 8 | 3 (50) | 2 (10) | 2 (0.2) | 0.3362 |
| 9 | 3 (50) | 3 (15) | 3 (0.3) | 0.2880 |
| Sample | Experimental Value/% | Predicted Value/% | Relative Error/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.2657 | 0.2660 | 0.11 |
| 2 | 0.3091 | 0.3104 | 0.42 |
| 3 | 0.3495 | 0.3484 | 0.31 |
| 4 | 0.2909 | 0.2909 | 0 |
| 5 | 0.3146 | 0.3145 | 0.03 |
| 6 | 0.2840 | 0.2843 | 0.11 |
| 7 | 0.2913 | 0.2900 | 0.45 |
| 8 | 0.3362 | 0.3362 | 0 |
| 9 | 0.2880 | 0.2883 | 0.10 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, P.; Shi, Y.; Shang, P.; Wei, H.; Peng, T.; Pang, L.; Feng, R.; Zhang, W. Application of BP Artificial Neural Network in Preparation of Ni–W Graded Coatings. Materials 2021, 14, 6781. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14226781
Feng P, Shi Y, Shang P, Wei H, Peng T, Pang L, Feng R, Zhang W. Application of BP Artificial Neural Network in Preparation of Ni–W Graded Coatings. Materials. 2021; 14(22):6781. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14226781
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Pei, Yuhua Shi, Peng Shang, Hanjun Wei, Tongtong Peng, Lisha Pang, Rongrong Feng, and Wenyuan Zhang. 2021. "Application of BP Artificial Neural Network in Preparation of Ni–W Graded Coatings" Materials 14, no. 22: 6781. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14226781
APA StyleFeng, P., Shi, Y., Shang, P., Wei, H., Peng, T., Pang, L., Feng, R., & Zhang, W. (2021). Application of BP Artificial Neural Network in Preparation of Ni–W Graded Coatings. Materials, 14(22), 6781. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14226781





