Magnetic Properties and Morphology Copper-Substituted Barium Hexaferrites from Sol-Gel Auto-Combustion Synthesis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
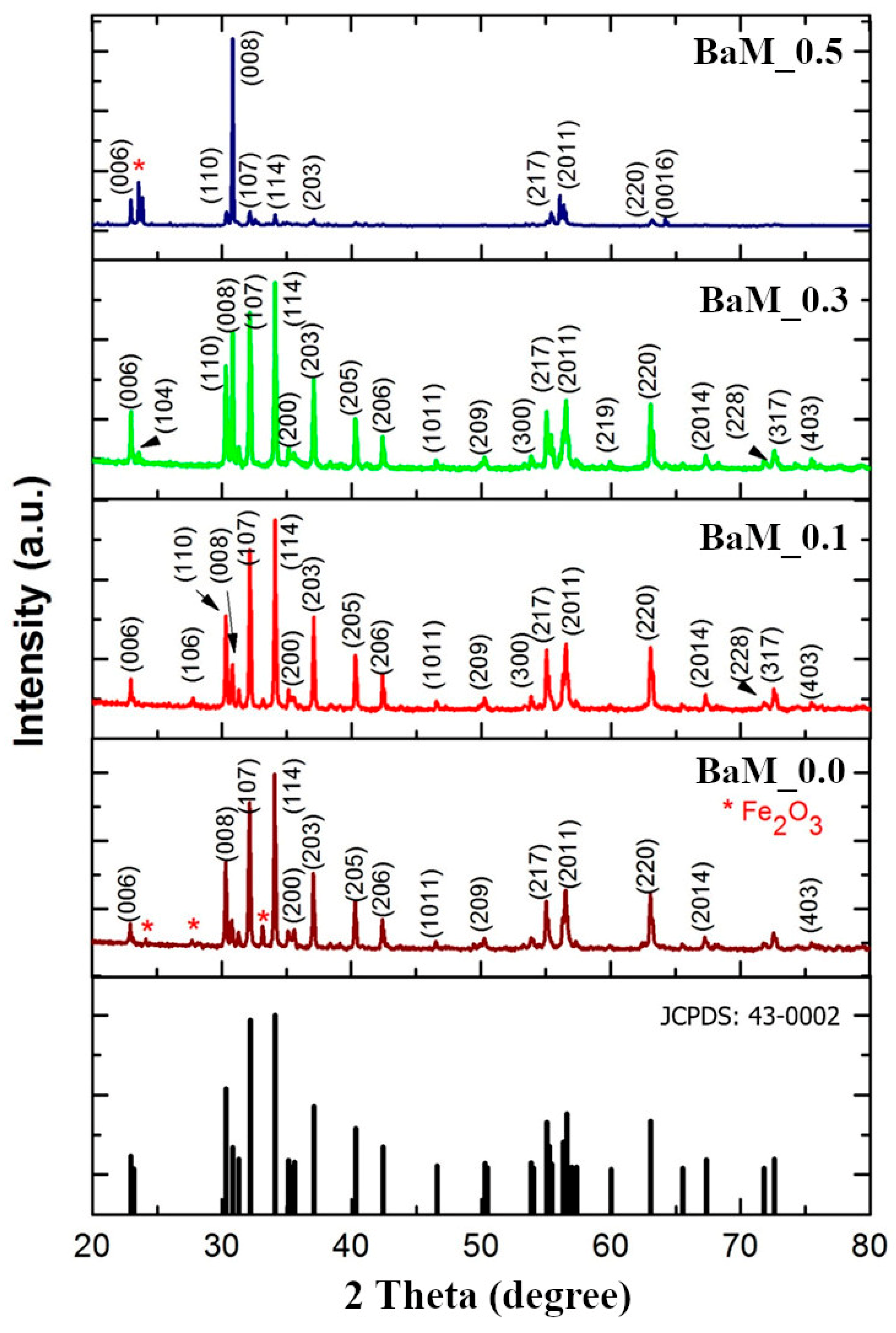
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pullar, R. Hexagonal ferrites: A review of the synthesis, properties and applications of hexaferrite ceramics. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2012, 57, 1191–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalegani, Z.; Nemati, A. Effect of Ce-Co substitution on structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of M-type barium hex-aferrite nanoparticles synthetized by sol-gel auto-combustion route. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2015, 26, 2134–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikmanesh, H.; Hoghoghifard, S.; Hadi-Sichani, B. Study of the structural, magnetic, and microwave absorption properties of the simultaneous substitution of several cations in the barium hexaferrite structure. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 775, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanida, A.; Stavropoulos, S.; Speliotis, T.; Psarras, G.C. Magneto-dielectric behaviour of M-type hexaferrite/polymer nano-composites. Materials 2018, 11, 2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Charoensuk, T.; Thongsamrit, W.; Ruttanapun, C.; Jantaratana, P.; Sirisathitkul, C. Loading effect of sol-gel derived barium hexaferrite on magnetic polymer composites. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shater, R.E. Exploring the annealing temperature impacting on the magnetic coupling of nanometer soft grain and micro-structure hard grain nanocomposites. Chin. J. Phys. 2019, 57, 403–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makled, M.H.; Sheha, E. An attempt to utilize hard magnetic BaFe12O19 phase as a cathode for magnesium batteries. J. Electron. Mater. 2019, 48, 1612–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borin, D.; Müller, R.; Odenbach, S. Magnetoviscosity of a magnetic fluid based on barium hexaferrite nanoplates. Materials 2021, 14, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asiri, S.; Güner, S.; Demir, A.; Yildiz, A.; Manikandan, A.; Baykal, A. Synthesis and magnetic characterization of cu substituted barium hexaferrites. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2017, 28, 1065–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slimani, Y.; Almessiere, M.; Baykal, A. AC susceptibility study of Cu substituted BaFe12O19 nanohexaferrites. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 13097–13105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Guha, S.; Supriya, S.; Pradhan, L.K.; Kar, M. Correlation between crystal structure parameters with magnetic and dielectric parameters of Cu-doped barium hexaferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 499, 166213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiq, M.A.; Waqar, M.; Muhammad, Q.K.; Waleed, M.; Saleem, M.; Anwar, M.S. Conduction mechanism and magnetic be-havior of Cu doped barium hexaferrite ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 5134–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadivelan, S.; Jaya, N.V. Investigation of magnetic and structural properties of copper substituted barium ferrite powder particles via co-precipitation method. Results Phys. 2016, 6, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rekaby, M.; Shehabi, H.; Awad, R. Influence of cobalt addition and calcination temperature on the physical properties of BaFe12O19 hexaferrites nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 7, 015057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, N.; Song, J. XAFS and XPS studies on site occupation of Sm3+ ions in Sm doped M-type BaFe12O19. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 377, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bsoul, I.; Mahmood, S. Magnetic and structural properties of BaFe12−xGaxO19 nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 489, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhage, V.N.; Mane, M.; Babrekar, M.; Kale, C.; Jadhav, K. Influence of chromium substitution on structural and magnetic properties of BaFe12O19 powder prepared by sol–gel auto combustion method. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 4394–4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, R.; Desai, S.; Tamboli, Q.; Shirsath, S.E.; Patange, S. Ce3+ incorporated structural and magnetic properties of M type barium hexaferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 378, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, G.; Asri, S.; Khusro, S.N.; Tariq, G.H.; Awan, M.S.; Irshad, M.; Safeen, A.; Iqbal, Y.; Shah, W.H.; Anis-Ur-Rehman, M. Enhanced Magnetic Properties of Barium Hexaferrite. J. Electron. Mater. 2020, 49, 4318–4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veisi, S.S.; Yousefi, M.; Amini, M.; Shakeri, A.; Bagherzadeh, M. Magnetic and microwave absorption properties of Cu/Zr doped M-type Ba/Sr hexaferrites prepared via sol-gel auto-combustion method. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 773, 1187–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudsainiyan, R.K.; Chawla, S.K.; Meena, S.S. Correlation between site preference and magnetic properties of Co–Zr doped BaCoxZrxFe(12–2x)O19 prepared under sol–gel and citrate precursor sol–gel conditions. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 615, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzaid, M. Enhancement in optical properties of lanthanum-doped manganese barium hexaferrites under different substitutions. Adv. Cond. Matter Phys. 2021, 2021, 8849595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawar, N.; Chitkara, M.; Sandhu, I.S.; Jolly, J.S.; Malhotra, S. Structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of pure and nickel-doped barium nanohexaferrites synthesized using chemical co-precipitation technique. Cogent Phys. 2016, 3, 1208450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.-H.; Shen, S.-Y.; Zheng, H.; Zheng, P.; Wu, Q.; Zheng, L. Effect of powder grain size on microstructure and magnetic properties of hexagonal barium ferrite ceramic. J. Electron. Mater. 2018, 47, 4085–4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azis, R.A.S.; Che Muda, N.N.; Hassan, J.; Shaari, A.H.; Ibrahim, I.R.; Mustaffa, M.S.; Sulaiman, S.; Matori, K.A.; Fen, Y.W. Effect of ratio in ammonium nitrate on the structural, microstructural, magnetic, and AC conductivity properties of BaFe12O19. Materials 2018, 11, 2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mohammed, H.; Albarody, T.; Susilawati, S.; Gohari, S.; Doyan, A.; Prayogi, S.; Bilad, M.; Alebrahim, R.; Saeed, A. Process Optimization of in situ magnetic-anisotropy spark plasma sintering of M-type-based barium hexaferrite BaFe12O19. Materials 2021, 14, 2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godara, S.K.; Dhaka, R.K.; Kaur, N.; Malhi, P.S.; Kaur, V.; Sood, A.K.; Bahel, S.; Bhadu, G.R.; Chaudhari, J.C.; Pushkarna, I.; et al. Synthesis and characterization of Jamun pulp based M-type barium hexaferrite via sol–gel auto-combustion. Results Phys. 2021, 22, 103903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaranarayanan, V.; Khan, D. Mechanism of the formation of nanoscale M-type barium hexaferrite in the citrate precursor method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1996, 153, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, P.; Ravi, S. Influence of Ti-Substitution on structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of M-type barium hexaferrite. J. Electron. Mater. 2019, 48, 5062–5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wu, W.; Zhou, C.; Zhou, S.; Li, M.; Ning, Y. Structural and magnetic properties evolution of Co-Nd substituted M-type hexagonal strontium ferrites synthesized by ball-milling-assisted ceramic process. J. Electron. Mater. 2017, 47, 2110–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | c/a Ratio | Vcell (Å3) | Crystallite Size (nm) | Remanent Magnetization (emu/g) | Magnetic Squareness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BaM_0.0 (x = 0.0) | 3.94 | 699 | 71 | 35.8 ± 0.8 | 0.479 |
| BaM_0.1 (x = 0.1) | 3.94 | 699 | 68 | 22.5 ± 1.9 | 0.402 |
| BaM_0.3 (x = 0.3) | 3.94 | 699 | 72 | 25.0 ± 1.1 | 0.379 |
| BaM_0.5 (x = 0.5) | 3.94 | 697 | 96 | 7.2 ± 3.5 | 0.132 |
| X | Ba1−xCuxFe12O19 Sol-gel Combustion [9] | BaFe12−xCuxO19 Solid-State Reaction [12] | BaFe12−xCuxO19 Sol-gel Combustion [This Work] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MS (emu/g) | HC (Oe) | MS (emu/g) | HC (Oe) | MS (emu/g) | HC (Oe) | |
| 0.0 | 48.27 | 2853 | 89.0 | 2263.1 | 74.8 | 2626 |
| 0.1 | 54.36 | 1726 | 115.0 | 932.5 | 56.0 | 1246 |
| 0.2 | 49.93 | 2121 | - | - | - | - |
| 0.3 | 53.61 | 2344 | 115.1 | 262.1 | 65.9 | 1241 |
| 0.4 | 45.75 | 2460 | - | - | - | - |
| 0.5 | 40.49 | 2415 | 88.5 | 1911.0 | 54.4 | 343 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lohmaah, A.; Chokprasombat, K.; Pinitsoontorn, S.; Sirisathitkul, C. Magnetic Properties and Morphology Copper-Substituted Barium Hexaferrites from Sol-Gel Auto-Combustion Synthesis. Materials 2021, 14, 5873. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14195873
Lohmaah A, Chokprasombat K, Pinitsoontorn S, Sirisathitkul C. Magnetic Properties and Morphology Copper-Substituted Barium Hexaferrites from Sol-Gel Auto-Combustion Synthesis. Materials. 2021; 14(19):5873. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14195873
Chicago/Turabian StyleLohmaah, Abdulmumeen, Komkrich Chokprasombat, Supree Pinitsoontorn, and Chitnarong Sirisathitkul. 2021. "Magnetic Properties and Morphology Copper-Substituted Barium Hexaferrites from Sol-Gel Auto-Combustion Synthesis" Materials 14, no. 19: 5873. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14195873
APA StyleLohmaah, A., Chokprasombat, K., Pinitsoontorn, S., & Sirisathitkul, C. (2021). Magnetic Properties and Morphology Copper-Substituted Barium Hexaferrites from Sol-Gel Auto-Combustion Synthesis. Materials, 14(19), 5873. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14195873






