Abstract
Lubrication for extreme conditions, such as high temperature, cryogenic temperature, vacuum pressure, high load, high speed, and corrosive environments, is a continuing challenge among tribologists and space engineers due to the inadequate friction and wear properties of liquid lubricants. As a result, tremendous research effort has been put forward to study lubrication mechanisms for various machine elements under challenging conditions over the past two decades. Self-lubricating materials have been most widely used for adequate lubrication in extreme conditions in recent years. This review paper presents state-of-the-art of materials for lubrication in extreme condition applications in aerospace, automotive, and power generation areas. More specifically, solid lubricants dispersed in various matrices for lubrication application were analyzed in-depth under challenging conditions. This study also reports the self-lubricating materials and their lubrication mechanisms. Finally, various applications and challenges of self-lubricating materials were explored.
1. Introduction
The energy loss associated with moving mechanical assemblies (MMA) is a potential problem in industrial applications. Friction and wear account for almost 30% of primary energy loss, and the corresponding financial loss has been estimated to be in billions [1]. Therefore, scholars focused on novel lubricating materials to enhance the performance and reduce the frequent replacement of mechanical components due to wear failure resulting from inadequate lubrication. The concept of lubrication can be traced back to prehistoric times when people used lubricants derived from plants and animals fat to reduce friction during relative motion [2]. The stable and effective operation of a lubricant is essential to augment the efficiency and lifetime of machinery. The demand for lubrication arises when friction and wear are hard to regulate in designated applications. Unfortunately, liquid lubricants have inferior tribological properties and cannot perform their intended tasks in challenging environments [2,3,4]. In addition, equipment working under these conditions demands stable and superior tribological properties, such as excellent anti-friction properties and remarkable wear resistance for improving the reliability and service life [5]. The demand for developing novel lubricants generally arises in conditions typically encountered in aerospace [6,7,8], automotive, power generation, and machining [9,10,11] applications. The challenging conditions include high temperature (HT), cryogenic temperature, vacuum pressure, high load, high speed, and corrosive environments [12,13,14,15,16].
The inferior tribological properties of liquid lubricants can be mitigated by designing a new type of lubricant that can provide superior tribological properties. Therefore, scholars have relentlessly explored novel lubricant technologies and searched for potential lubricating materials as a global cure for inadequate friction and wear [17]. The advent of industrialization and escalating demands for efficient lubrication in diverse applications has made researchers focus more on self-lubricating materials [18,19]. These classes of materials are widely perceived to provide excellent tribological properties in extreme conditions. Moreover, they can adapt themselves based on external conditions by changing their states, and provide the required tribological properties. The challenges in the diverse fields of application have tempted researchers to develop self-lubricating materials in recent years, increasing the number of research papers related to this field. This trend has mainly been observed from the year 2011, which is represented in Figure 1.

Figure 1.
A bar graph shows journal articles published between 2000 and 2021 on “self-lubricating materials” from the Web of Science.
Furthermore, developing self-lubricating materials that provide superior lubricity for severe conditions is demanding for scholars working in tribology. Dispersing solid lubricants into various matrices, such as metal matrix, polymer matrix, ceramic matrix, and intermetallic matrix, is a commonly employed method to develop potential self-lubricating materials [18,20]. The solid lubricants that are predominantly used in self-lubricating materials include soft metals [21,22,23,24], transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) [25,26,27,28], metal oxides [29,30,31,32], fluorides [33,34,35,36], hexagonal boron nitride (h–BN) [37,38,39,40], and polymers [41,42,43]. The solid lubricant phase associated with the self-lubricating material forms a lubricious phase due to the tribo-chemical reaction and ultimately leads to a constant lubricant supply to the interfaces. In addition to the superior lubricity, self-lubricating materials must possess properties, such as high thermal conductivity, oxidation resistance, chemical stability, and low shear strength over the entire working regime. Solid lubricants can be applied on the machine component surface by simple methods, such as painting and burnishing. Self-lubricating coatings can be prepared using magnetron sputtering [44,45], laser cladding [46,47,48], thermal spraying [49], and vapor deposition techniques [50,51,52]. In addition, powder metallurgy is a widely used technique to introduce solid lubricants into various matrices to obtain self-lubricating materials [53,54,55].
There are a significant number of reviews on various lubricants for diverse industrial applications. However, very few reviews explore the use of self-lubricating materials exclusively dedicated to extreme condition applications. This review provides a comprehensive discussion on the friction and wear behavior of self-lubricating materials for challenging environments. Section 2 addresses the dispersing of solid lubricants in various matrices, such as metal, polymer, ceramic, and intermetallic matrices. In addition, the lubrication mechanisms of self-lubricating materials under various challenging conditions were explored in detail. Finally, the applications and challenges of self-lubricating materials are elucidated in Section 3.
2. Tribology of Solid Lubricants
Liquid lubricants are not capable of providing superior tribological properties in severe environments. Therefore, solid lubricants were introduced to different matrices to enhance the reliability and self-adaptability of the lubricating material, and are expected to provide adequate lubrication. The primary reason for the superior lubrication properties of solid lubricants is their ability to shear through the mating surface, and their lubricious behavior can be correlated to their layered structure. For example, solid lubricants, such as TMDs, h–BN, and graphite, possess unique lamellar structures. Therefore, these solid lubricants are widely employed as a potential reinforcement phase in self-lubricating composites, and as a coating in MMA working in challenging conditions [56]. Under the action of external force, these layers align parallel to the direction of force and slide over each other, reducing the friction between surfaces during relative motion. The following section explains the tribological behavior and properties of solid lubricants dispersed in various matrices to provide superior lubricity in extreme environments. Figure 2 represents the typical solid lubricants used for self-lubricating materials in challenging environments. Table 1 indicates the applied ranges we considered in this study based on the available literature.
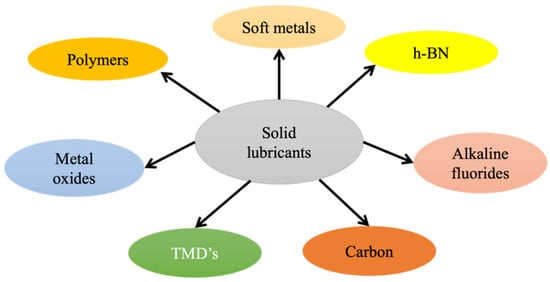
Figure 2.
Typical solid lubricants.

Table 1.
The applied range of extreme conditions.
2.1. Soft Metals
Soft metals contain multiple slip planes and exhibit unique characteristics of low CoF over broad working temperatures [63]. These characteristics are due to the inherent properties possessed by soft metals, such as low surface roughness and high viscosity. For example, Ag, Sn, Au, Pb, In, Pt, etc., are considered soft metals. In soft metals, the frictional heat developed during sliding destroys lattice defects, such as dislocations and vacancies [12]. The destruction of lattice defects leads to improper work hardening, and this mechanism is responsible for providing superior lubricity in extreme conditions. Silver is the most commonly used solid lubricant among soft metals as a reinforcement in the matrix, and silver has a high diffusion coefficient. The high diffusion coefficient helps the easy formation of the lubrication film. Thus, it provides remarkable tribological properties. Scholars conducted tribological testing under different testing conditions with silver as the reinforcement in intermetallic matrix, ceramic matrix, and polymer matrix self-lubricating materials. They observed that different compounds at various temperatures give superior lubricity and low wear rate. Figure 3 shows the stable operating temperature range of various solid lubricants.
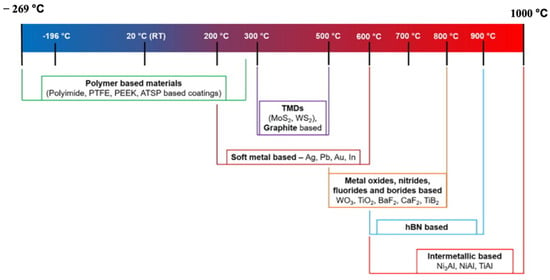
Figure 3.
Stable working temperature for different solid lubricants. Reproduced with permission from [57]. Copyright Elsevier, 2021.
Wang et al. [24] performed tribological studies on three different samples named NA (90Ni3Al–10Ag), MA10 (71.57Ni–7.29Al–4.71Cr–6.32Mo–0.12Zr–0.005B–10Ag) and MA20 (63.62Ni–6.48Al–4.18Cr–5.62Mo–0.10Zr–0.005B–20Ag) from room temperature (RT) to 900 °C. The authors revealed that between RT and 400 °C, the presence of silver in the matrix provided the lubricating effect. In addition, the authors reported that an MA20 alloy showed superior self-lubricating performance over a broad temperature regime. The usage of 20 wt. % Ag in the Ni3Al matrix provided a CoF of 0.2 and wear rate of 1 × 10−5 mm3/Nm to 2 × 10−5 mm3/Nm between 800 °C and 900 °C. The lubrication mechanism and CoF variation over a broad temperature regime for MA and NA alloy is shown in Figure 4. The Ag2MoO4 and NiO film formed at HT prevented the direct contact of tribo pairs and provided improved tribological properties in MA alloys. On the other hand, the Ag2O and NiO glaze film formed on the NA alloy has inferior HT tribological properties compared to the Ag2MoO4 and NiO film formed in MA alloys. Scholars reported that Ag2MoO4 possesses a lamellar structure with weak bonding between oxygen and silver, which can shear easily at HT and provide enhanced tribological properties [64].
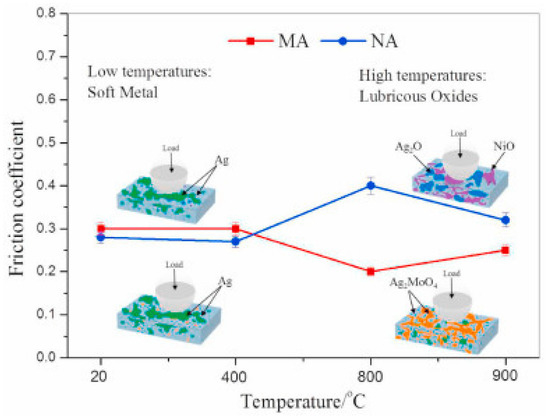
Figure 4.
The variation in CoF with temperature and lubrication mechanism for MA and NA alloy. Reproduced with permission from [24]. Copyright Elsevier, 2021.
Liu et al. [65] studied the self-lubricating mechanism of M50 bearings used in aviation industries under high load and HT conditions. In this analysis, the researchers developed a micro-dimple structure on M50 steel dispersed with multiple lubricants. The authors considered two sets of samples, MM-S (M50–50Sn40Ag10Cu) and MM-ST (M50–50Sn40Ag10Cu–TiO2). The authors revealed that micro-dimple structures filled with M50 steel have a self-adaptive lubrication ability. Furthermore, the titanium dioxide nanoparticles played a significant role above 12 N. In contrast, Sn, Ag, and Cu played a pivotal role below 12 N. The addition of TiO2 nanoparticles imparted enhanced wear resistance and low friction properties. The self-lubricating mechanism of the M50 steel matrix dispersed with multiple solid lubricants is represented in Figure 5.
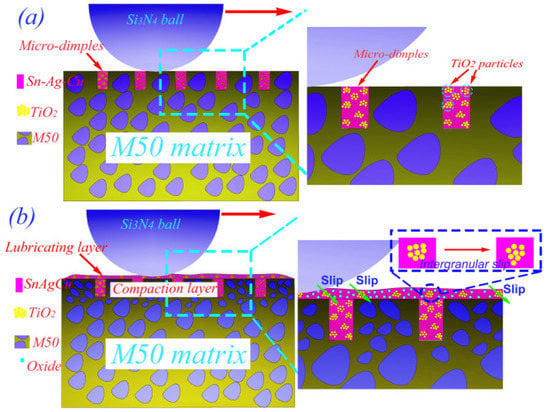
Figure 5.
The self-lubrication mechanism of the M50 bearing dispersed with multiple lubricants (a) Sn, Ag, Cu/TiO2 removed from micro-dimples, (b) Slip behavior of TiO2 particles. Reproduced with permission from [65]. Copyright Elsevier, 2021.
With increases in temperature, the Sn, Ag, Cu, and TiO2 come out of the micro-dimples, and the wear debris that forms leads to the formation of a lubrication structure due to friction. This lubrication structure is made of a lubrication layer and a compaction layer. The compaction layer formed on the subsurface supports the lubrication layer. The lubricating layer is formed on the surface rich in Sn, Ag, and Cu, shown in Figure 5a. Under heavy loads, the lubrication layer breaks down in MM-S, and the tribological properties deteriorate. When the sample is subjected to more than 12 N load, the effect of TiO2 particles in the micro-dimples is prominent. TiO2 nanoparticles are enriched in the lubrication layer, and the high strength of these nanoparticles prevents the rupture of the lubrication layer on the worn surface, as is represented in Figure 5b.
Shi et al. [22] conducted tribological testing on a TiAl matrix reinforced with 0 wt. %, 5 wt. %, 10 wt. %, and 15 wt. % silver, respectively named T1, T2, T3, and T4. The tribological testing was performed at RT and temperatures ranging from 200 °C to 800 °C. They summarized that silver provides lubrication in the moderate temperature range. Ti2AlC, silver oxides, titanium oxides, and silicon oxides provide a superior lubricating effect at HT, and Al2O3 acts as the wear-resistant phase. T1 and T3 samples showed higher CoF and wear rates with the rise in temperature due to the existing tribo-film thickness. The increased thickness of the tribo-film eventually leads to fragmentation and further clogging between the surfaces. Among all the tested samples, T3 exhibited better self-lubrication characteristics. The observed CoF and wear rate with the rise in temperature from RT to 800 °C for T3 samples were 0.26–0.43 and 1.56 × 10−4 mm3/Nm–3.26 × 10−4 mm3/Nm, respectively. The authors summarized that the CoF and wear rate for a TiAl matrix containing silver is less than that of the base alloy. Shen et al. [66] conducted HT tribological studies on TiAl composites containing Ag and V2O5 nanowires. The authors showed that the TiAl matrix dispersed with 5 wt. % Ag and 1.5 wt. % V2O5 nanowires have excellent tribological properties at HT due to continuity in the lubrication film and the synergic effect of Ag and V2O5. The wear mechanism of TiAl–5Ag–1.5V2O5 from 300 °C to 600 °C tested against Si3N4 is represented in Figure 6.
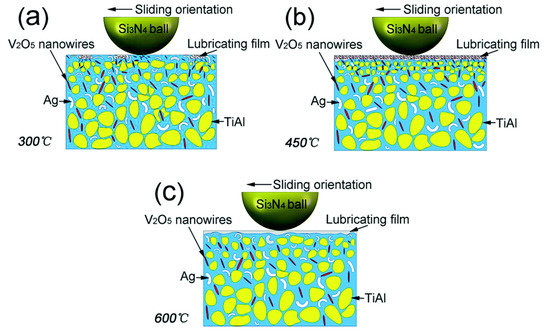
Figure 6.
Wear mechanism of TiAl–5 Ag–1.5 V2O5 (a) 300 °C, (b) 450 °C, (c) 600 °C. Reproduced with permission from [66]. Copyright RCS advances, 2016.
At 300 °C, less Ag and V2O5 is squeezed from the matrix, leading to the formation of a very minute film on the worn surface, represented in Figure 6a. When the temperature rises to 450 °C, a thick and continuous lubricating film is observed on the worn surface. In this case, the greater amount of V2O5 homogenously distributed over the film provides the shear strength and prevents the plastic flow of Ag, as shown in Figure 6b. The lowest CoF and wear rate was reported at 450 °C. When the temperature rises to 650 °C, V2O5 gets softened, and quickly forms wear debris, and it can easily detach from the worn surface. It is observed that there was no V2O5 present in the worn track. A significant amount of Ag squeezed from the wear track helps form the lubricating film at this temperature. The formed lubricating film consists of Ag and a high amount of V2O5, providing low friction and low wear, as shown in Figure 6c. Table 2 represents the various solid lubricants in intermetallic matrixes and their corresponding behaviors under various extreme conditions.

Table 2.
Solid lubricants in the intermetallic matrix and their extreme condition behaviors.
In summary, soft metals contain multiple slip planes, which prevent work hardening during relative motion. Among soft metals, silver is most widely adopted for use with self-lubricating materials for challenging environments. This is attributed to its better oxidation resistance and high thermal conductivity, which helps the easy dissipation of frictional heat during relative motion. The primary mechanism of self-lubrication for silver is the high diffusion and easy formation of the tribo layer at the interface. As a result, silver is capable of providing superior lubrication properties below 500 °C. In addition, 5 wt. % to 25 wt. % silver additions are beneficial to obtain superior tribological properties. On the other hand, a silver addition beyond 30 wt. % in the matrix leads to inferior tribological properties.
2.2. Transition Metal Dichalcogenides (TMD)
The general representation of these classes of compounds is MX2. The M can be Mo or W, and X can be S, Se, or Te. The most commonly used TMDs are molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) and WS2. In MoS2, the Mo atom is at the center, sandwiched between two S atom layers. MoS2 consists of a lamellar structure with thin atomic planes and is anisotropic [73]. The weak van der Waals forces between the interlayers help easy shearing in the <0001> crystallographic direction and in parallel basal planes [26,74,75]. The easy sliding in the <0001> direction leads to reduced CoF and improved wear resistance. In addition, the strong ionic bond exit between sulfur and molybdenum offers significant resistance against penetration of asperities. As a result, TMDs can quickly move in the direction of the applied load, thereby resulting inS minimum friction. Researchers reported that MoS2 is highly susceptible in a moist environment. Therefore, researchers adopted different strategies for enhancing the tribological performance of MoS2 in a humid environment. The adopted strategies include multilayer films and various doping elements [76,77,78]. Scholars observed that MoS2–Ti film and MoS2–Pb film possess enhanced friction and wear properties [79]. However, when the MoS2–Ti film was tested under a strong vacuum, it showed inferior tribological properties. Zhao et al. [27] studied the self-adaptive behavior of the MoS2–Pb–Ti film used for space applications. The authors summarized that the introduction of Pb and Ti improved the tribological properties of a MoS2–Pb–Ti film tested in vacuum and air at different relative humidity values (RH). The variations in CoF and wear rate for MoS2 and different films coated on MoS2 tested in a vacuum are shown in Figure 7.
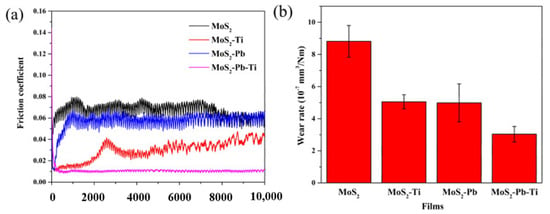
Figure 7.
Variation in (a) friction coefficient and (b) wear rates tested in vacuum. Reproduced with permission [27]. Copyright, 2018.
The MoS2–Pb–Ti film tested in vacuum showed low friction and low wear properties because of the improvement in elastic modulus, transfer layer, and dominant contact interfaces of MoS2, whereas in humid air, the sacrificial effect of Pb and Ti hindered the attack of O2 and H2O. The MoS2–Pb–Ti film showed a lower and more stable CoF compared to other films on MoS2. The reported wear rate for MoS2 is 8.8 × 10−7 mm3/Nm, which is the highest among all the other films. However, MoS2–Pb–Ti showed a reduced wear rate compared to other films. The CoF and wear rates for MoS2 and various films of Ti, Pb, and Pb–Ti on MoS2 at various RH values are represented in Figure 8. Upon deeper examination, it is clear that the CoF for MoS2 film increases to a higher value with heavy fluctuation when RH increases from 10% to 70% (Figure 8a). The MoS2–Ti film did not show much variation in CoF with an increase in RH, as shown in Figure 8b. However, the MoS2–Pb film showed a CoF of 0.03 at RH 10%, which jumped to 0.19 at RH 70% (Figure 8c). The MoS2–Pb–Ti showed fluctuations at high humidity values but similar CoF values to the MoS2–Ti film (Figure 8d).
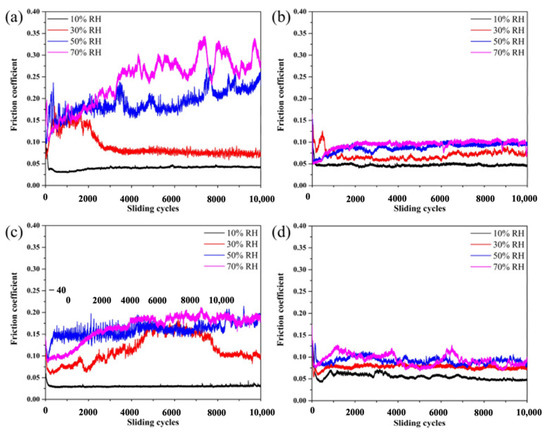
Figure 8.
Tribological testing in the air at different RH and corresponding variation in CoF for (a) MoS2, (b) MoS2–Ti, (c) MoS2–Pb, and (d) MoS2–Pb–Ti films. Reproduced with permission [27]. Copyright, 2018.
The combination of MoS2, Pb, and Ti gives the best tribological performance compared to stand-alone MoS2 and a combination of MoS2 with Ti or Pb when tested in a vacuum and in the air in the humidity range 10–70%.
Dunckle et al. [14] conducted friction studies on MoS2 + Ti films under cryogenic vacuum conditions. They summarized that MoS2 + Ti films could retain their tribological performance with low wear when subjected to thermal cycling from RT to cryogenic temperature under ultra-high vacuum conditions. They also revealed that MoS2-based coatings are an effective lubrication provider in a vacuum in the cryogenic environment. Liu et al. [80] studied the friction and wear properties of M50 steel-based self-lubricating composites containing 5 wt. % MoS2 tested from 150 °C to 450 °C. The tribological test conditions included a ball-on-disk HT tribometer with a load of 20 N and a sliding speed of 0.2 m/s against Si3N4. They summarized the excellent lubrication performance at higher temperatures because of the enriched presence of MoS2 and FeS in the film, and they reported that above 250 °C, the regeneration of FeS provided significant stability to the film up to 450 °C. The wear mechanism of M50 steel with 5 wt. % MoS2 from 150 °C to 450 °C is represented in Figure 9. The authors revealed that a lubricating structure is absent at low temperatures, and on the worn surface, they observed small amounts of MoS2 and FeS, as shown in Figure 9a.
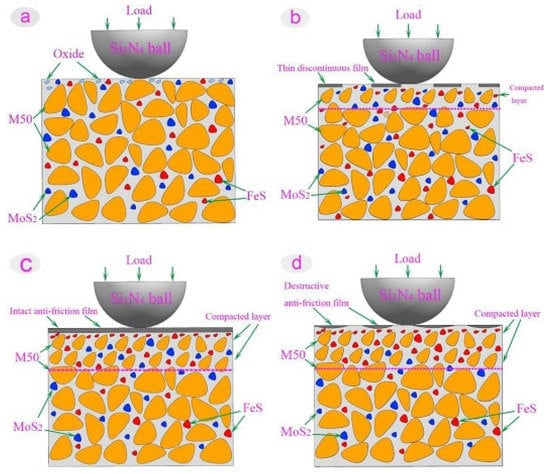
Figure 9.
Wear mechanisms of M50 steel with 5 wt. % MoS2 at (a) 150 °C, (b) 250 °C, (c) 350 °C, and (d) 450 °C. Reproduced with permission from [80]. Copyright, 2017.
Under the external load from a Si3N4 counter material, the subsurface of the M50 steel dispersed with 5 wt. % MoS2 when subjected to compaction, and the compacted layer formed at 250 °C. At the same time, the MoS2 and FeS from this layer were squeezed out slowly to form a lubricating film. The formed film was not adequate to cover the whole friction surface, and hence at 250 °C, inferior tribological properties were observed as represented in Figure 9b. At 350 °C, enhanced lubrication properties were observed because of the presence of continuous lubrication film. The lubricating film possesses the synergistic effects of the lubrication properties of MoS2 and the plastic flow of FeS, as shown in Figure 9c. At 450 °C, the authors observed partial damage of the lubrication structure, the oxidation of MoS2 to MoO3, and the reduced strength of the compaction layer, as shown in Figure 9d, which eventually led to the deterioration of the superior tribological properties. The decomposition of FeS explains the partial existence of the lubricating film. The author’s design reduces friction and wear properties for M50 steels dispersed with 5 wt. % MoS2 bearing steels compared to pure M50 at 450 °C. WS2 is another popular TMD with a layered structure that prevents the friction derived from the contact of surfaces, which it converts into a relative slip of the molecular layer under external load. Wu et al. [81] studied the dry sliding characteristics of a Ag–Cu-based composite containing 8 wt. % to 24 wt. % WS2 tested at three different conditions: vacuum, dry nitrogen, and humid air. The tribological test was conducted on a pin-on-disc tester with a sliding velocity of 1 m/s and a load of 5 N, and the counter body was silver, having a hardness of 120 on the Brinnel scale. The authors observed high CoF and low wear rates in the humid air, but low CoF and low wear rates for dry N2. Cao et al. [82] replaced graphite with WS2 in the copper matrix composite and observed significant improvements in the mechanical properties and wear resistance when graphite was returned, along with WS2, into the copper matrix. These superior properties are due to interfacial chemical bonding between WS2 and the copper matrix. On the other hand, the authors reported excess solid lubricant on the worn surfaces, a thicker film, and a low depth of the plastic deformation zone in the subsurface.
In summary, the most widely used TMDs for self-lubrication purposes in challenging environments are MoS2 and WS2. The lamellar structure helps to provide easy shearing during relative motion and can provide superior lubrication characteristics up to 400 °C. MoS2 cannot be used for self-lubrication in humid or moist environments because of the oxidation reaction. The oxide formed possesses higher shear strength and gives rise to inferior tribological properties. WS2 can withstand temperatures up to 800 °C and provide superior lubrication properties even at cryogenic temperatures (−190 °C).
2.3. Metal Oxides
Lubricious oxides (binary and ternary) are thermally stable at HT and are considered effective lubricants. However, they are not capable of providing lubrication at RT. It is mentioned that with temperature increases, a change in tribological behavior is observed for many oxides. These changes in tribological properties can be related to the brittle to ductile transition when the temperature rises above a critical temperature. Therefore, temperature plays a predominant role in oxide lubrication. Researchers have proposed several theories regarding the lubricating mechanism of oxides. The crystal–chemical model centered around the crystal chemistry of oxides has received wide attention [83]. This model primarily correlates the CoF and the ionic potential of lubricious oxides. The author postulated that the higher the ionic potential of oxides, the lower the CoF. At higher ionic potential, the cations are screened effectively by oxygen, and here, they did not come across other cations during sliding, which helps with easy shearing. However, there are controversies regarding the crystal–chemical model. Scholars have reported that oxide lubrication is complicated because some oxides can plastically deform and protect the interacting surfaces. Apart from that, many oxides break up during sliding and lead to abrasive wear. The introduction of the polarizability approach solves the issues associated with the crystal–chemical model. Under the polarizability approach, scholars have correlated the binding energy and polarizability of ions [84].
Zhu et al. [29] studied the friction and wear properties at HT of NiAl alloy and two different NiAl matrix-based composites containing metallic oxides, such as ZnO and CuO, and metallic powders of Mo and Cr. The authors observed that the NiAl alloy had significant wear and CoF at elevated temperatures. However, the NiAl composite containing solid lubricant CuO showed a reduction in CoF when tested from RT to HT. The reported value of CoF was about 1.0 at RT and 0.53 at 600 °C, with a low CoF of about 0.28 at 800 °C which rose to 0.3 at 1000 °C. The authors observed a smooth lubricating layer composed of CuO and MoO3 at 800 °C, responsible for the self-lubricating behavior. The wear rate increased when the test temperature increased from RT to 600 °C, and showed a reduced wear rate of 2.3 × 10−6 mm3/Nm at 800 °C.
The worn surface of the composite NiAl + 25.47 Cr + 10.07 Mo + 15.00 CuO is shown in Figure 10. The authors observed that delaminated layers at RT and grooves were visible at 600 °C, as represented in Figure 10a,b, respectively. A smooth lubricating glaze layer was observed at 800 °C, indicated in Figure 10c. At 1000 °C, the formed lubricating glaze layer was broken down, and grooves were observed, as in Figure 10d. Similar CoF and wear rates were reported for the composite containing ZnO. The superior tribological properties at 800 °C for ZnO-based composite are due to MoO3 and Cr2O3. At 1000 °C, the ZnO-based composite showed enhanced wear resistance due to the ZnO layer on the wear track. Essa et al. [85] studied the effect of WS2 and ZnO as solid lubricant additives on the friction and wear behavior of M50 steel matrix composites from RT to 800 °C. The authors considered four different composites named M (M50), MZ (M50 + 10%ZnO), MW (M50 + 10%WS2), and MZW (M50 + 10%ZnO + 10%WS2).
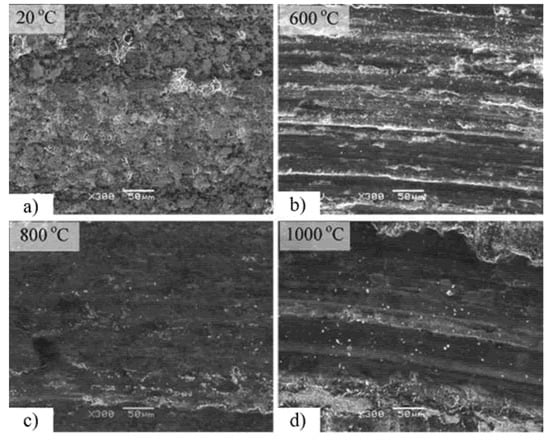
Figure 10.
Worn surface of the composite at different temperatures (a) RT, (b) 600 °C, (c) 800 °C, (d) 1000 °C for CuO-based composite. Reproduced with permission from [29]. Copyright Elsevier, 2012.
The tribological test was conducted on a pin-on-disc at HT with a sliding velocity of 0.2 m/s and applied load of 12 N, and the counter surface used was Si3N4. The authors revealed that the individual addition of solid lubricants does not enhance tribological properties. The authors summarized that WS2 helps to enhance lubricating properties from RT to 400 °C, except at 200 °C. On the contrary, ZnO imparted superior tribological properties in the temperature range of 600 to 800 °C. ZnO and WS2 synergistically reduced CoF and wear rate over a broad range of temperatures. The CoF was reduced by 43.64% for MZW compared to M at 800 °C. EDS analysis confirmed that ZnO and ZnWO4 were responsible for reducing CoF at HT for the MZW composite. Wang et al. [86] studied the friction and wear behavior of a NiAl composite coating containing nanostructured TiO2 and Bi2O3 from RT to 800 °C. The authors considered three composite coatings with a 3:2 ratio of TiO2 and Bi2O3. The authors observed a significant reduction in friction and wear properties at 800 °C. The reduced CoF and wear rate are due to the combined effect of Bi4Ti3O12 and NiTiO3. The composite coating with 30 wt. % TiO2 and Bi2O3 showed better low-friction and low-wear properties for the whole test temperature. Li et al. [87] studied the tribological behavior of a Ni–Cr–Mo-based composite containing TiO2 and Bi2O3 as solid lubricants. The authors considered four different composites (NC1, NC2, NC3, and NC4) having different wt. % TiO2: Bi2O3 and NiCr (NC) alloy. In the experiment, they used 0 wt. %, 10 wt. %, 20 wt. %, and 30 wt. % metal oxides (TiO2/Bi2O3). The authors observed lower CoF for NC3 and lower wear rate for NC4 containing 20 wt. % and 30 wt. % metallic oxides. The friction and wear studies were conducted using a ball-on-disk at HT with a load of 10 N and sliding speed of 200 r/min, against Al2O3 at 800 °C. The variations in CoF and wear rate for different samples are indicated in Figure 11. Among the five samples, NC showed the highest CoF and wear rate. However, NC1 showed a CoF of 0.36 and a reduced wear rate compared to NC. This is because of the formation of the MoO3 layer at HT. Increased additions of TiO2 and Bi2O3 directly affect the CoF and wear rate of NC2, NC3, and NC4. The increased wt. % of metal oxide in the matrix for these specimens reduced the CoF and wear rate, as shown in Figure 11a,b. NC4 showed a low CoF of 0.18. NC4 has a higher wear rate than NC3, due to the shredding of oxide particles because of friction. The remarkable tribological properties at HT are due to the formation of Bi4Ti3O12 on the worn surface. The authors observed a lower CoF for NC3 and a lower wear rate for NC4 containing 20 wt. % and 30 wt. % metallic oxides. Table 3 represents a self-lubricating composite based on ceramic matrix and its HT behavior.

Figure 11.
The variation of (a) friction coefficient, (b) wear rate for Ni–Cr–Mo-based composite containing TiO2/Bi2O3. Reproduced with permission from [87]. Copyright Elsevier, 2021.

Table 3.
Ceramic matrix-based self-lubricating composites and their HT behavior.
In summary, both binary and ternary oxides can provide superior tribological properties at high temperatures. Among binary oxides, V2O5 provides a low CoF and wear rate because of the low shear strength. A combination of metallic oxides can provide superior tribological properties at extremely HT.
2.4. Fluorides
Fluorides exhibit significantly superior tribological properties above 500 °C, and inferior properties at low temperatures and RT [92]. The primary reason for providing potent lubricity at HT is the change in wear mechanism from brittle-to-ductile, while the higher CoF and enhanced wear rate are due to the three-body abrasion. LiF, CaF2 BaF2, CeF3 LaF3, etc., are some of the examples of commonly used fluorides. CaF2 is soft, poorly soluble in water and thermally stable over a wide temperature, and its thermal expansion closely matches that of many alloys [93,94]. These properties lead to the extensive use of CaF2 in ferrous-based self-lubricating composites [95]. Han et al. [93] conducted friction and wear studies on Fe–Mo composites containing different wt. % of CaF2 content. The authors divulged that 8 wt. % of CaF2 in the Fe–10Mo matrix provides a superior reduction in wear and CoF at RT and at 600 °C. The reported self-lubricating characteristics for Fe–Mo–CaF2 at HT are due to the lubricious film consisting of CaMoO4 and CaF2. Similar results were observed when 8 wt. % BaF2 was added as a solid lubricant Fe–Mo-based self-lubricating composite [96]. Liu et al. [97] conducted friction and wear studies on self-lubricating cemented carbides based on WC–12Co with 0 wt. % to 20 wt. % CaF2 as the solid lubricant. The authors reported that the introduction of CaF2 caused a reduction in CoF, reduced wear loss, and refined grains of WC. A lubricating film based on CaF2 was formed at the interfaces during tribological testing, which remarkably increased the tribological properties. The authors reported that 20 wt. % CaF2 reduces the CoF by 22% and wear loss by 93%, compared to the friction and wear behavior of WC-12Co. However, they also revealed that a greater addition of CaF2 leads to increased porosity, which subsequently causes degradation in the mechanical properties. Figure 12 shows the volume loss and CoF at different volume percents of CaF2 during tribological testing. It is evident that the addition of a higher volume percent CaF2 enhances the tribological properties and plays a prominent role in the lubrication of cemented carbides.
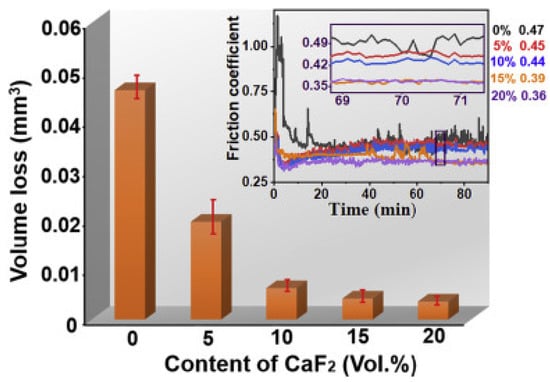
Figure 12.
The variation in CoF and wear volume loss with different wt. % of CaF2 during dry sliding conditions. Reproduced with permission from [97]. Copyright Elsevier, 2021.
Zhen et al. [98] investigated the tribological characteristics of a Ni-based solid lubricating composite containing Ag, CaF2, and graphite and studied the effect of temperature on these composites from 25 °C to 800 °C in vacuum conditions. The authors revealed that the composite exhibited enhanced tribological properties over the broad temperature regime. They reported that 2 wt. % of graphite content is optimum for enhanced tribological properties in the temperature range of 25–400 °C, due to the formation of high-strength carbides. Below 600 °C, the diffusion of Ag into the worn surface helps to reduce friction and wear. Kong et al. [90] studied the HT tribological characteristics of ZrO2 matrix-based self-lubricating composite containing MoS2 and CaF2 as solid lubricant additives. In this experiment, they considered 10 wt. % MoS2 and 0–30 wt. % CaF2. The tribological testing was performed from RT to 1000 °C. The authors revealed that the addition of 10 wt. % MoS2 and CaF2 to the ZrO2 matrix manifested low friction and low wear characteristics over the broad temperature range. The reported CoF and wear rate at 1000 °C for ZrO2 (Y2O3)–10 MoS2–10 CaF2 was 0.27 and 1.54 × 10−5 mm3/Nm. The superior lubricating effect from RT to 400 °C was provided by MoS2, whereas the combined effect of CaMoO4 and CaF2 provides remarkable tribological properties from 800 °C to 1000 °C. Cui et al. [99] studied the HT self-lubricating characteristics of the CoCrW matrix with LaF3 and Ag as solid lubricant additives. The test parameters include a load of 10 N, a sliding speed of 0.20 m/s, Si3N4 as the counterpart, and a temperature from RT to 1000 °C using a ball-on-disk HT tribometer. The authors reported enhanced tribological properties at HT because of the combined effect of metal oxides, chromates, and LaF3. The reported wear mechanism at HT was abrasive and oxidative wear.
In summary, fluorides can provide superior tribological properties above 500 °C because of the brittle to ductile transition. However, at RT and temperatures below 500 °C, fluorides are brittle and cannot perform the intended task of self-lubrication. The most widely used fluorides for self-lubrication purposes are CaF2 and BaF2.
2.5. Hexagonal Boron Nitride (h–BN)
h–BN possesses a layered structure similar to TMDs, in which a strong covalent bond holds each layer, whereas the bonding between interlayers is the Van der Walls bond. These materials shear very quickly along the basal plane during external loading because of the lamella structure, and provide superior lubricity and enhanced tribological properties [40,100,101]. The crystal structure of h–BN consists of hexagonal rings with boron and nitrogen bonded at 120°. Lamella slip along the basal plane is considered as the prominent mechanism favoring superior lubricity [102,103]. Scholars have reported that h–BN could enhance the tribological properties of ceramics and metals [38,104,105,106]. Chen et al. [100] conducted tribological experiments on the h–BN matrix-based composites containing SiC with Al2O3 and Y2O3 as sintering additives on a rotating ball-on-disk HT tribometer from RT to 900 °C. The following paramesters were selected for the tribological study: sliding velocity of 0.094 m/s, a load of 10 N, a sliding radius of 5 mm, and a Si3N4 ball as the counterpart. They made three composites with 75, 70, and 50 vol. % of h–BN named 75BSAY, 70BSAY, and 50BSAY, respectively. Figure 13 represents the CoF of the three composites tested at different temperatures. Both 75BSAY and 70BSAY composites showed an increase in CoF with temperature rise, and the maximum values of reported CoF were 0.43 and 0.44, respectively, at 400 °C. The 70BSAY composite showed higher CoF than 75BSAY at RT and 900 °C. However, the 50BSAY composite showed higher CoF at RT, and with a rise in temperature, the CoF dropped down and reached 0.33 at 900 °C, which is 38% less than CoF at RT. The authors mentioned that adding more h–BN in the matrix can enhance the anti-friction behavior of the composites.
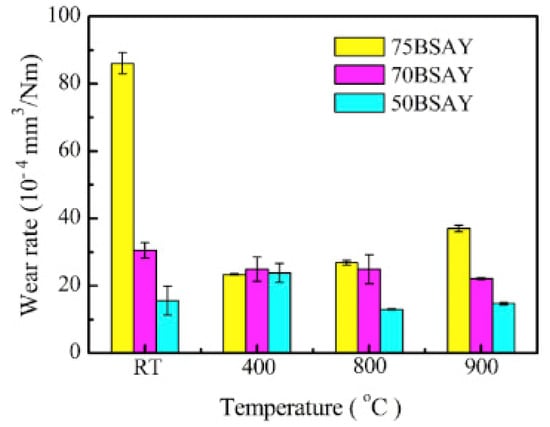
Figure 13.
The variation in CoF for different test temperatures for the three composites. Reproduced with permission from [100]. Copyright Elsevier, 2020.
Cao et al. [61] conducted friction and wear tests on pure h–BN and h–BN sintered with CaB2O4 additive in atmospheric and water vapor environments from RT to 800 °C. They made two sets of composites: one with pure h–BN and the other containing 10 wt. % CaB2O4. The tribological testing was conducted on a ball-on-disk HT tribometer with the following test parameters: a load of 1.5 N, a speed of 0.188 m/s for 10 min, and Si3N4 as the counterpart. The authors observed almost similar CoF at RT for both pure h–BN and h–BN containing 10 wt. % CaB2O4 (0.18 and 0.19) tested in atmospheric conditions. Both composites showed increased CoF with temperature increases, and at 400 °C, both reported their highest CoF values of 0.58 and 0.51, respectively. The composite with 10 wt. % CaB2O4 showed a 14% reduction in CoF at 400 °C compared to pure h–BW. With a further increase in test temperature to 800 °C, the pure h–BN and the h–BN containing 10 wt. % CaB2O4 showed reduced CoF values of 0.38 and 0.35, respectively. The increased CoF with the rise in temperature from RT to 400 °C is attributed to the adhesion of h–BN on the counter ball surface, whereas the reduced CoF at HT is due to the formation of molten B2O3. However, the friction test conducted in the water vapor environment showed a reduced CoF at RT. The reported CoF values for pure h–BN and h–BN containing 10 wt. % CaB2O4 are 0.08 and 0.07, respectively. The reduced CoF is due to the formation of a water film at the interfaces under relative motion. An increase in test temperature to 400 °C for both composites led to increase in CoF (0.25 and 0.23). However, these values are lower compared to those of the composite tested under atmospheric conditions. The reduced CoF was due to the reaction of water vapor with h–BN to form B2O3 and the further reaction of B2O3 with water vapor to form H3BO3. The formed H3BO3 possessed a lamellar structure that can shear very easily under external force, which reduced the CoF. At 800 °C, the reported CoF values for pure h–BN and h–BN containing 10 wt. % CaB2O4 were 0.22 and 0.21, which are less than the CoF values observed when tribological testing was performed under atmospheric conditions. Zhao et al. [107] studied the friction and wear behavior of a nickel-based composite coating tested from 25 °C to 600 °C. The authors made three different powder compositions, which were Ni60, Ni60 with h–BN coating, and Ni60 with nano-Cu encapsulated with h–BN, represented as C1, C2, and C3. The friction and wear studies were conducted on a high-temperature pin-on-disk setup with a load of 30 N and speed of 50 rpm for 30 min using Al2O3 as the counter surface. The wear process during the tribological testing is represented in Figure 14. The common wear mechanisms reported for these coatings tested at different temperatures are abrasive and adhesive wear. The process (Figure 14, 1–4) represents the abrasive wear mechanism, which occurred under low-temperature tribological testing (25–200 °C). The strength of the coating was very high at this temperature. Under the action of external load from the Al2O3 counter body, hard particles detached from the coating. At this testing temperature, the detachment of the wear debris from the worn surface is difficult, and thus the wear rate was low.
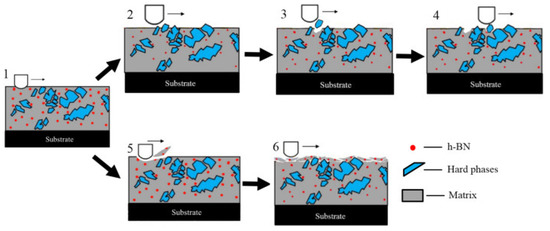
Figure 14.
The wear process: adhesive wear observed at low temperature (1–4), abrasive wear observed at HT (1,5,6). Reproduced with permission from [107]. Copyright Elsevier, 2019.
Process 1,5,6 (Figure 14, sections 1, 5, 6) represents the mechanism of adhesive wear, which occurs at high testing temperatures, and at these temperatures, the coating has low strength. The Al2O3 counter body forcefully detaches the solid lubricant and matrix from the coating and leads to wear debris formation. The formed wear debris gets attached to the worn surface, and a glaze layer is formed. C1 underwent abrasive wear, and with the addition of Cu and h–BN, C2 and C3 underwent micro-plowing wear. At 400 °C, a combined lubricating effect from h–BN, Cr2O3, and NiO was observed on C1 and C2, and the reported wear mechanism was a mixture of adhesive and abrasive wear. However, C3 showed adhesive wear because of CuO’s lubrication and the synergistic effects of other lubricants. Delamination was observed on the worn surfaces C1, C2, and C3 at 600 °C because of adhesive wear. Among all the coatings tested from 25 °C to 500 °C, C3 showed low CoF and wear properties. The authors revealed that nano-Cu encapsulated with h–BN increased the h–BN content in the coating, leading to enhanced wear resistance in the temperature range of 25–600 °C. Among all the coatings tested from 25 °C to 500 °C, C3 showed low CoF and wear properties. This was predominantly due to the higher h–BN content in the coating and the oxidation of copper to CuO.
In summary, h–BN possesses a layered structure, and these materials can shear very quickly along the basal plane during relative motion. h–BN possesses high thermal conductivity and oxidation resistance and is commonly used with metal matrix and ceramic matrix for self-lubricating applications because it can provide excellent tribological properties at HT conditions.
2.6. Polymers
Polymers are widely used in cryogenic environments because of their excellent tribological properties. For example, the mechanical components present in satellites are subjected to thermal cycling when the spacecraft is moving out of the Earth’s shadow in low-earth orbit, where the temperature is in the cryogenic range [108]. Therefore, scholars have investigated the use of polymers and self-lubricating polymer composites, especially for cryogenic temperature applications [109,110,111]. Wang et al. [109] performed tribological studies on polyimide (PI), polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), and polyetheretherketone (PEEK) at cryogenic temperatures in a vacuum. They observed high hardness in all the polymers in the cryogenic environment, which reduced the mating surface’s contact area. This reduction in contact area leads to reduced CoF at cryogenic temperatures. In addition, they reported a reduction in wear volume with the reduction in temperature, which is attributed to reduced mobility. Figure 15 represents the CoF and wear rate for three different polymers at −50 °C in a vacuum. The figure shows that the CoF and wear rates of polymers were lower for the 5 N than the 0.5 N load.

Figure 15.
The variation in (a) CoF, (b) wear rates of three different polymer matrix-based composite tested in a vacuum at −50 °C. Reproduced with permission from [109]. Copyright Elsevier, 2016.
Theiler et al. [111] conducted tribological studies on a PEEK composite made of carbon fibers, MoS2, and graphite between −80 °C and 20 °C in a vacuum environment. The authors revealed that MoS2-filled PEEK composite developed a smooth transfer film with high MoS2 concentration in the surface at −80 °C. They also revealed that sliding velocity significantly affects the tribological properties of PEEK-containing MoS2 solid lubricants.
Chang et al. [112] described the tribological properties of epoxy nanocomposite filled with short carbon fiber (SCF), graphite, PTFE, and nano TiO2 particles. The authors performed tribological testing using a pin-on-disk setup at different contact pressures and sliding velocities. A fixed contact pressure of 1 MPa and different sliding velocities, such as 0.5 m/s, 1 m/s, 1.5 m/s, and 2 m/s, were used for the first set of experiments. Tribological testing with these parameters on epoxy nanocomposites without nano TiO2 particles showed a CoF of 0.45 at 0.5 m/s that rose to 1 when tested at 2 m/s. However, the addition of 5 wt. % nano TiO2 led to a CoF of 0.3 at 0.5 m/s that rose to 0.4 at 2 m/s. In the second case, the authors used a fixed sliding velocity of 1 m/s and different contact pressures, such as 1 MPa, 2 MPa, 3 MPa, and 4 MPa. The authors observed a CoF of 0.35 at 1 MPa, which reduced to 0.25 at 4 MPa for the epoxy nanocomposite without nano TiO2. The authors revealed that the highest wear resistance was observed at an extreme pressure velocity (PV) factor of 12 MPa m/s, corresponding to 5 wt. % of nano TiO2 in the nanocomposite. Scholars also conducted tribological studies on PEEK and PEI composites containing different additives, such as SCF, graphite, PTFE, nano TiO2 particles, and ZnS. They performed friction and wear studies at RT and HT using different PV conditions [58,59]. The tribological test results are summarized in Table 4.

Table 4.
Tribological properties of polymer composites under different PV conditions.
In summary, polymers are ideal solid lubricant additives for self-lubrication characteristics in a cryogenic environment, and offer excellent tribological properties. Furthermore, among polymers, PTFE provides lower CoF because of its specific structure.
2.7. Carbon
Carbon and carbon-based materials, such as graphite, graphene, diamond-like carbon (DLC), single-walled carbon nanotubes, multi-walled carbon nanotubes, multi-layered graphene, and graphene nanoplatelets (GNP), are used as solid lubricant additives in self-lubricating materials for challenging environments [113,114,115,116,117,118]. Among these carbon-based materials, graphene has gained tremendous attention due to its unique properties, such as high chemical inertness, high thermal conductivity, low shear strength, and enhanced mechanical and thermal properties [119]. Graphene is a two-dimensional material capable of providing low friction and wear properties, and is the fundamental building block of graphite [120]. The superior tribological properties possessed by graphite can be correlated to its layered structure, similar to MoS2, MoSe2, and WS2, which provides easy shearing and reduces the friction between contact surfaces in relative motion [120]. Scholars have demonstrated that graphene could be used in nano-scale or micro-scale systems to reduce friction and wear properties [121,122]. Berman et al. [120] revealed the unique behavior of graphene deposited on a steel surface when tested in dry and humid environments, and the authors observed low friction and wear. Kasar et al. [123] mentioned that graphene’s unique properties attract scholars to synthesize graphene-based self-lubricating nanocomposites for diverse applications in the automobile, aerospace, and chemical industries. Kasar et al. [124] revealed that single-layer, multilayer, and functionalized graphene could lead to reduced friction and wear rates when used as a solid lubricant additive in metal and polymer matrix composites. They summarized that graphene-based metal matrix and polymer matrix composites could be used for self-lubricating bearings. Zhai et al. [125] conducted tribological studies on Ni3Al matrix self-lubricating composites (NMSC) and Ni3Al matrix self-lubricating composites containing graphene nanoplatelets (NMSC-GNP), and explained the wear mechanism. The friction and wear studies were conducted using a ball-on-disk at HT with a load of 10 N and sliding speed of 0.2 m/s, from RT to 600 °C, with Si3N4 as the counterpart. Figure 16 represents the CoF and wear rate of NMSC and NMSC-GNP. The authors observed a CoF of 0.76 at RT for NMSC, which was reduced to 0.39 at 600 °C. NMSC−GNP exhibited a reduced CoF of 0.21–0.26 in the temperature range of RT to 400 °C, without any fluctuation, as shown in Figure 16a. However, the authors reported that at 600 °C, the CoF of NMSC−GNP increased to 0.36, close to NMSC (0.39).
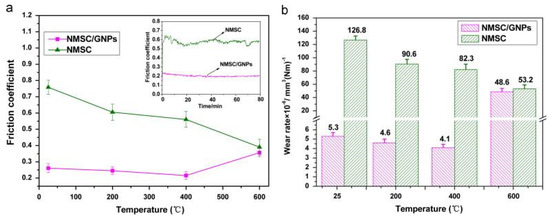
Figure 16.
Variation in CoF of (a) NMSC and NMSC−GNP and wear rates of (b) NMSC and NMSC−GNP. Reproduced with permission from [125]. Copyright Elsevier, 2014.
The observed wear rate for NMSC was 126.8 × 10−6 mm3/N/m at RT, which reduced to 82.3 × 10−6 mm3/N/m at 400 °C. However, the reported wear rate for NMSCGNP was 5.3 × 10−6 mm3/N/m at RT, which reduced to 4.1 × 10−6 mm3/N/m at 400 °C, as shown in Figure 16b. Thus, the observed wear rate at 400 °C for NMSC-GNP is 20 times less than the corresponding wear rate for NMSC 400 °C. The wear mechanism of NMSC−GNP is shown in Figure 17. GNPs were originally distributed uniformly in the Ni3Al matrix, which is represented in Figure 17a. However, during the tribological testing, formation of an ultrafine-grained region on the surface was observed. This is due to the simultaneous effect of the grain refinement of GNPs and the form of wear debris containing brittle particles of Si3N4 and friable particles of NMSC, as illustrated in Figure 17b. In addition to that, slippage of the laminated sheets of GNP was observed on the worn surface, which eventually led to the formation of GNP protective layer in Figure 17c. This protective layer can reduce friction and wear rates.
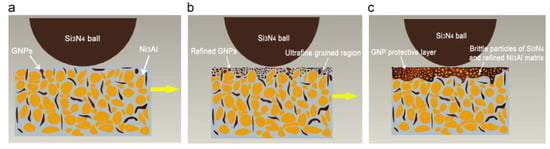
Figure 17.
The schematic of the wear mechanism of NMSC−GNP. Reproduced with permission from [125]. Copyright Elsevier, 2014.
Wan et al. [126] conducted tribological testing on a high−entropy alloy (HEA)-based composite and demonstrated the effects of the in situ formation of graphene on tribological properties. The composite (HEA-G) was prepared using the SPS method with graphite nanoplate (GP) as a reinforcement in the HEA matrix. The friction and wear studies were conducted using a ball-on-plate tribometer in a reciprocating mode for 1800 cycles, with a load ranging from 5 N to 100 N, a stroke length of 5 mm with various velocities, and GCr15 steel ball as the counter material. Figure 18 shows the schematic of the self-lubrication mechanism of the HEA-G composite and the formation of graphene. During tribological testing, the frictional heat caused the exfoliation of GP and the further formation of graphene. The formed graphene acts as a protective coating on the worn surface, leading to less friction and a lower wear rate. In addition to that, the tribo induced fine particles, graphene, and the fine oxide scale formed a non-continuous oxide on the worn surface. As a result, the authors observed a significant reduction in CoF and wear rate below 30 N. The superior tribological properties are attributed to the compound effect of the graphene and oxide layer formed on the worn surface.
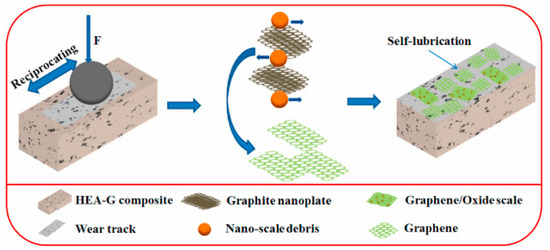
Figure 18.
Self-lubrication mechanism of HEA-G composite. Reproduced with permission from [126]. Copyright Elsevier, 2021.
Scholars have also adopted graphite as a reinforcement phase in metal, polymer, and ceramic matrices to develop self-lubricating materials. Graphite has also received attention for its self-lubricating and dry lubricating properties, which are attributed to the layered structure [127,128,129]. The layered structure promotes easy sliding due to the weak Van der Walls force between layers. It also possesses high thermal conductivity, which provides superior tribological properties at HT [130]. Scholars reported that the effectiveness of graphite is more pronounced in humid and air environments. Shirazi et al. [131] studied the tribological behavior of aluminum, silicon carbide, and graphite hybrid nanocomposites in atmospheric conditions and acidic solutions. They revealed that the addition of 2 wt. % graphite provided the lowest wear and CoF. Huai et al. [62] developed a graphite-based solid lubricant coating that significantly reduced CoF and wear rates tested in HT atmospheric conditions. The authors used unmodified graphite as a lubricant, amorphous SiO2 as the filler, and aluminum dihydrogen phosphate as a binder. The friction and wear studies were conducted using a ball-on-disk at HT with a load of 100 N and sliding speeds of 60 mm/s, 90 mm/s, and 120 mm/s, with Si3N4 as the counterpart. The tribological test was performed at 700 °C, 800 °C, and 900 °C. The authors revealed that they observed ultra-low CoF of 0.05 at 700 °C, 0.04 at 800 °C, and 0.07 at 900 °C. The authors reported that even after tribological studies, they had not observed wear scarring on the substrate surface because of the uniform coverage of the coating on the substrate. In addition to that, SiO2 and aluminum dihydrogen phosphate protected the graphite coating at HT, which is responsible for the superior lubricity.
In summary, carbon and carbon-based materials are promising materials for future self-lubricating applications in extreme conditions. These materials show superior lubricity, particularly under humid conditions. Hence these materials are ideal for humid environments.
3. Applications and Challenges
Self-lubricating materials are an advanced class of materials with diverse compositions, making them capable of performing the intended task with potential lubricating effects, especially in challenging conditions. Extreme condition lubrication is one of the potential issues faced by tribologists over the past two decades. Self-lubricants were initially introduced to enhance the efficiency and lifetime of bearings. During the early 1990s, these materials were extensively used with various mechanical components exclusively designed to operate under severe conditions to provide low friction and low wear [132]. Scholars incorporated soft metals into various matrices to give rise to self-lubricating characteristics in challenging conditions. The self-lubricating characteristics of soft metals can be attributed to the multiple slip planes, which prevent work hardening during relative motion. Usually, silver-based self-lubricating materials can provide superior friction and wear properties below 500 °C. The low shear stress and high diffusion coefficient of Ag at its interfaces provide excellent lubricity over a broad temperature range. Scholars have reported that introducing Ag and multiple solid lubricants can enhance tribological characteristics above 500 °C [64,133]. TiAl alloys are widely used for aerospace and automotive applications because of their excellent mechanical properties; however, they have inferior tribological properties. Scholars have reported that Ag addition to the TiAl intermetallic matrix enhances the tribological properties at elevated temperatures [22]. Soft metals are used in various mechanical components, such as mechanical seals, fasteners, rolling contact bearings, and sliding contact bearings, to provide superior lubricating properties. Among TMDs, MoS2 is considered a prospective solid lubricant capable of providing adequate lubrication over a broad temperature regime, making it specifically attractive in the aerospace, automobile, and forming industries [134]. MoS2 possesses outstanding friction and wear properties, which makes it a global solution for space applications. MoS2-based self-lubricating composites are widely used for high-vacuum and high-temperature applications. These self-lubricating composites can provide superior tribological properties, especially in the aerospace (vacuum and at HT), automotive, and forming industries (extreme pressure and temperature). The low friction and low wear properties offered by MoS2 depend on the external environment. The potential lubrication characteristics of MoS2 exist only in oxygen-free environments, and it loses its lubricating characteristics in humid and atmospheric conditions. The reported CoF for MoS2 in a dry or inert atmosphere is 0.002–0.05, escalating in a humid environment to 0.2 [57,135]. An exponential growth of the use of MoS2-based self-lubricating materials in electronic industries and battery applications has been observed in the last decade. Scholars have reported that MoS2 could be used for adaptive lubrication in M50 steel for aircraft bearing applications [80]. WS2 can function over a broad range of temperatures, including cryogenic (−190 °C) to 450 °C in air, and in extreme temperatures up to 800 °C [136]. Metallic oxide-based self-lubricants can provide remarkable tribological properties above 500 °C [137,138]. Researchers used a combination of metallic oxides and revealed that they could provide low friction and low wear characteristics at HT [139,140].
Fluoride-based solid lubricants, such as BaF2 and CaF2 dispersed in various matrices using powder metallurgy or as a coating in composites, are extensively employed in HT applications. Fluorides subjected to softening and with a smooth layer are formed at the interfaces when exposed to a temperature higher than 1000 °C. Some tri-fluorides also exhibit similar HT lubrication properties because of their chemical stability. Fluoride-based solid lubricants can be used with various matrices to provide potent lubrication properties in challenging environments. In addition, fluoride lubricants can be used in industrial applications that require self-lubrication, such as cutting tools [141], wire drawing dies [142], casting molds [143], sealing materials, and bearings [144]. They can also be used as anti-friction additives in greases and oils. h–BN can provide superior lubrication in dry and vacuum conditions [25]. It is predominantly used as a sealing coating in aircraft engines [145] PTFE-based piston rings are widely employed in reciprocating gas compressors because of their excellent self-lubrication capability and ability to form good sealing conditions [146]. PTFE-based thermoplastics are used for marine applications because of their excellent self-lubricating ability [147].
Jianxin et al. [148] developed a sintered ceramic cutting tool containing CaF2 for dry cutting and explained the self-lubrication behavior. They performed dry cutting on hardened steel and cast iron with Al2O3/TiC, and Al2O3/TiC with CaF2, at different cutting speeds. The reported CoF at the tool–chip interface for dry cutting with hardened steel was 0.65 at 60 mm/min, which rose linearly to approximately 0.75 at 80 mm/min. When CaF2 was added into the ceramic matrix, the CoF was reduced to 0.58 at 60 mm/min, and then declined linearly to 0.45 at 80 mm/min. When Al2O3/TiC was used for the dry cutting of cast iron, the reported CoF was approximately 0.62 at 60 mm/min, which rose linearly to approximately 0.7 at 80 mm/min. However, when the authors used CaF2, they observed a reduced CoF of approximately 0.64 at 60 mm/min, which declined linearly to approximately 0.56 at 80 mm/min. Thus, the enhanced tribological properties are attributed to the presence of CaF2 in the ceramic matrix, forming a self-lubrication film at the tool and chip interface. Niste et al. [149] studied the self-lubricating behavior of aluminum reinforced with WS2 composite used as a piston in automotive engines, and explained the mechanism of self-lubrication. They adopted engine operating test conditions. They used two different types of WS2: a flat sheet (2H–WS2) and an inorganic fullerene (IF–WS2). An aluminum composite based on IF–WS2 showed a CoF of 0.15, and an aluminum composite based on 2H–WS2 showed a CoF of 0.13, compared to the 0.29 for pure aluminum tested at 25 °C. When the tribological test was performed at 100 °C, the observed CoF values were 0.16 and 0.12 for aluminum composites based on IF–WS2 and 2H–WS2, respectively, for the first twenty minutes. The reduced CoF for 2H–WS2 and IF–WS2 in the aluminum-based composite is because of the exfoliation of the layered structure. The authors observed significant wear resistance at HT attributed to the chemical reaction of WS2 with the aluminum matrix to form a chemical tribo-film. Yanar et al. [150] studied the tribological behavior of low-steel composite materials containing h–BN, used as a brake pad material for railway applications. In this study, the authors used an organic brake pad with 1 wt. %, 1.5 wt. %, and 2 wt. % of h–BN. The authors observed a significant reduction in CoF when the disk surface temperature was more than 250 °C. The authors recommended 1.5 wt. % of h–BN for a stable CoF under extreme brake conditions. Yan et al. [143] conducted tribological studies on self-lubricating composite coatings containing CaF2 in the Co-based alloy used for casting mold applications. The scholars considered four different coatings, out of which two were dispersed with 10 wt. % and 20 wt. % of CaF2. The authors observed CoF values of 0.31 and 0.24 for the coating that did not contain CaF2. However, the coatings containing 10 wt. % and 20 wt. % of CaF2 possessed low CoF values of 0.19 and 0.22, respectively. The authors revealed that coatings containing 10 wt. % and 20 wt. % of CaF2 showed better wear resistance than other coatings. The enhanced tribological properties were due to the easy shearing of CaF2 along the basal plane during tribological testing. Researchers from the NASA Glenn research center developed different coatings, such as PS100, PS200, PS300, and PS400, for extreme condition applications. PS100 is a nickel–chromium-based plasma coating containing glass as a binder, and silver and fluorides are the solid lubricants. This coating has very low CoF over a broad range of temperatures and has low wear resistance. However, these coatings can be effectively applied to compressor/turbine shaft seal applications. PS200 is nickel–cobalt-based plasma coating, containing chromium carbide as a binder, and silver and fluorides are the solid lubricants. This coating has applications in the cylinder walls of Stirling engines [151]. The scholars showed that PS212 (a coating in the 200 series) could be used for foil gas bearing applications [144]. PS300 is a nickel–chromium-based plasma coating containing chromium oxide as a binder, and silver and fluorides are the solid lubricants. Researchers showed that PS304 (a coating in the 300 series) could provide low friction and a low wear rate at HT up to 650 °C [152]. PS304 is an 80% nickel/20% chromium matrix that contains solid lubricants Ag and CaF2/BaF2. Nickel and chromium offer HT oxidation resistance. For strength enhancement, chromium oxide particles were used. In addition, Ag and CaF2/BaF2 were used to provide lubrication properties at different temperature ranges. Wang et al. [153] mentioned the wearing and galling damage of lift rods of a steam turbine governor subjected to metal–metal interaction at 540 °C. The researchers applied a PS304 coating on the lift rods, and they observed that the coating on the rods was intact even after 8500 h of operation. Upon a closer examination of the coated lift rods, the authors observed the formation of a lubricious glaze film that contained Cr2O3, Ag, and CaF2/BaF2. This lubricious film prevented the galling damage of the lift rods. PS400 is a nickel–molybdenum aluminum matrix containing chromium oxide as a binder, while Ag and CaF2/BaF2 are the solid lubricants. This coating is excellent for HT wear applications, and it is used for hot foil gas bearing applications [154]. Radil et al. [155] performed tribological testing on PS400 from 260 °C to 927 °C. They observed a low CoF of 0.37 to 0.84 when tested below 927 °C, and reported that the coating was dimensionally unstable at 927 °C.
Self-lubrication is the predominant method for providing superior tribological properties in extreme condition applications. However, there are certain circumstances in which solid lubricants cannot perform their intended self-lubricating functions in certain conditions. Among the listed solid lubricants, soft metals showed softening at HT, and they became extruded from the interfaces during relative motion, limiting their self-lubricating properties. Scholars have reported that a thicker silver coating on the substrate could lead to excessive plastic deformation, resulting in increased friction. Silver diffusion at HT is another issue, and Torres et al. [156] revealed a reduction in silver at HT in self-lubricating claddings composed of silver and MoS2. Gao et al. [157] reported the diffusion of silver to the interface at a temperature higher than 300 °C, leading to an increased wear rate and the subsequent collapse of the coating. The diffusion can be mitigated by using a barrier against the silver migration or multilayer coating [158]. Oxidation experiments conducted at 600 °C for 100 h showed no diffusion of silver at the interface. It has been observed that with over 30 wt. % Ag addition in the coating or in the matrix, the significant Ag content in wear debris causes instability in the lubricating film [7,12]. Researchers have reported that MoS2 is highly susceptible to moist environments. The MoS2-based composite or coating gets oxidized in a humid or moist atmosphere, leading to inferior tribological properties [57]. The unsaturated bonds of MoS2 get exposed to H2O, leading to inferior tribological properties. Scholars have reported the oxidation of graphite to carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide at 400 °C and 500 °C. Significant degradation of carbon to carbon dioxide is observed beyond 700 °C [159]. The deterioration of graphite finally leads to increased pore volume, which acts as a catalyst for the oxidation reaction. These factors limit the use of graphite to moderate temperature applications. The deposition of anti-oxidant coatings and plasma deposition techniques can prevent the oxidation of graphite at HT, which is not viable from an economic point of view [160,161].
The potential issues associated with individual solid lubricants can be avoided by introducing multiple lubricants into the matrix. The introduction of multiple solid lubricants to metal, polymer, and ceramic matrix materials can have the intended effects beyond the individual self-lubrication limit. For example, Niu et al. [53] incorporated Ag and CaF2/BaF2 into the Ni3Al matrix self-lubricating composite, and they studied the tribological properties from 25 °C to 1000 °C. Their study revealed that from 25 °C to 400 °C, Ag provided superior lubrication characteristics. Above 400 °C, CaF2/BaF2 acts as the lubricant and provides low CoF and wear properties. At 800 °C, the molybdates that formed, such as, NiMoO4, BaMoO4 and CaMoO4, acted as potential lubricants and provided low CoF and wear rates.
4. Conclusions
In this review article, a comprehensive discussion of self-lubricating materials for extreme condition applications is provided. This review focuses explicitly on the state-of-the-art of self-lubricating materials for various challenging conditions, such as HT, cryogenic temperature, vacuum pressure, high load, high speed, and corrosive environments. Liquid lubricants do not perform well in these challenging environments and can lose their tribological properties. On the other hand, self-lubricating materials can adjust themselves based on the surroundings and provide superior tribological properties. The superior tribological behavior of these materials under extreme conditions makes these materials very popular among scientists and space engineers. The friction, wear, and lubrication mechanisms of a broad spectrum of solid lubricants dispersed in metal, polymer, ceramic, and intermetallics matrices, in various challenging environments, are explained in detail via tribological testing. In addition, recent advances and the application of self-lubricating materials have been explored. This review paper can provide deeper insights for selection of self-lubricating materials for extreme condition applications.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.J.; methodology, M.J. and P.L.M.; writing—original draft preparation, M.J.; writing—review and editing M.J. and P.L.M.; supervision, P.L.M.; funding acquisition, P.L.M. Both authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors acknowledge the financial support from NASA CAN, grant number NV-80NSSC20M0221.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Nevada, Reno, for providing all research facilities.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
| CoF | Coefficient of friction |
| MoS2 | Molybdenum disulfide |
| WS2 | Tungsten disulfide |
| TMD | Transition metal dichalcogenide |
| h–BN | Hexagonal boron nitride |
| HT | High temperature |
| RT | Room temperature |
| SCF | Short carbon fibers |
| PI | Polyimide |
| PEEK | Polytheretherketone |
| PTFE | Polytetrafluoroethylene |
References
- Holmberg, K.; Andersson, P.; Erdemir, A. Global energy consumption due to friction in passenger cars. Tribol. Int. 2012, 47, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Yu, C.; Zhang, L.; Xie, G.; Guo, D.; Luo, J. Intelligent lubricating materials: A review. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 202, 108450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusaro, R.L. Evaluation of several polymer materials for use as solid lubricants in space. Tribol. Trans. 1988, 31, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aouadi, S.; Gao, H.; Martini, A.; Scharf, T.; Muratore, C. Lubricious oxide coatings for extreme temperature applications: A review. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 257, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DellaCorte, C. The effect of counterface on the tribological performance of a high temperature solid lubricant composite from 25 to 650 °C. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1996, 86-87, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, C.; Chromik, R.; Wahl, K.; Hu, J.; Voevodin, A. Preparation of chameleon coatings for space and ambient environments. Thin Solid Films 2007, 515, 6737–6743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, H.; Ripoll, M.R.; Prakash, B. Tribological behaviour of self-lubricating materials at high temperatures. Int. Mater. Rev. 2017, 63, 309–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, J.; Cheng, J.; Li, M.; Zhu, S.; Long, Z.; Yang, B.; Yang, J. Lubricating behavior of adaptive nickel alloy matrix composites with multiple solid lubricants from 25 °C to 700 °C. Tribol. Int. 2017, 109, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zailani, Z.A.; Zaibi, N.M.; Hamidon, R.; Harun, A.; Bahari, M.S.; Zakaria, S. Improvement on the surface quality in machining of aluminum alloy involving boron nitride nanoparticles. In Intelligent Manufacturing and Mechatronics; Bahari, M.S., Harun, A., Abidin, Z., Hamidon, R., Zakaria, S., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, S.; Hardell, J.; Courbon, C.; Winkelmann, H.; Prakash, B. High temperature friction and wear mechanism map for tool steel and boron steel tribopair. Tribol.-Mater. Surf. Interfaces 2014, 8, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, T.U.; Singh, S.K. Design, fabrication and characterization of a self-lubricated textured tool in dry machining. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 41, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Cheng, J.; Qiao, Z.; Yang, J. High temperature solid-lubricating materials: A review. Tribol. Int. 2018, 133, 206–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, J.; Cheng, J.; Zhu, S.; Hao, J.; Qiao, Z.; Yang, J.; Liu, W. High-temperature tribological behavior of a nickel alloy matrix solid-lubricating composite under vacuum. Tribol. Int. 2017, 110, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunckle, C.; Aggleton, M.; Glassman, J.; Taborek, P. Friction of molybdenum disulfide–titanium films under cryogenic vacuum conditions. Tribol. Int. 2011, 44, 1819–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunez, E.E.; Gheisari, R.; Polycarpou, A.A. Tribology review of blended bulk polymers and their coatings for high-load bearing applications. Tribol. Int. 2018, 129, 92–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burris, D.L. Investigation of the tribological behavior of polytetrafluoroethylene at cryogenic temperatures. Tribol. Trans. 2008, 51, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, P.L.; Nosonovsky, M.; Kailas, S.V.; Lovell, M.R. Friction and wear. In Tribology for Scientists and Engineers: From Basics to Advanced Concepts; Menezes, P.L., Nosonovsky, M., Ingole, S.P., Kailas, S.V., Lovell, M.R., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 43–91. ISBN 978-1-4614-1945-7. [Google Scholar]
- Omrani, E.; Rohatgi, P.K.; Menezes, P.L. Tribology and Applications of Self-Lubricating Materials; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; ISBN 1498768490. [Google Scholar]
- Kasar, A.K.; Menezes, P.L. Friction and wear behavior of alumina composites with in-situ formation of aluminum borate and boron nitride. Materials 2020, 13, 4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, P.L.; Rohatgi, P.K.; Omrani, E. Self-Lubricating Composites; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; ISBN 9783662565285. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Chen, W.; Sun, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhu, S.; Cheng, J.; Yang, J. Tribological properties of Ni3Al-Ni3Nb-Ag self-lubricating alloys at a wide temperature range. Wear 2021, 480–481, 203933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Xu, Z.; Wang, M.; Zhai, W.; Yao, J.; Song, S.; Din, A.Q.U.; Zhang, Q. Tribological behavior of TiAl matrix self-lubricating composites containing silver from 25 to 800 °C. Wear 2013, 303, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, M.; Singh, V.; Gupta, A.K.; Regalla, S.P.; Bera, T.C.; Simhachalam, B.; Srinivas, K. Tin layer as a solid lubricant for cold tube drawing processes. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Technol. 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Tan, H.; Chen, W.; Zhu, S.; Cheng, J.; Yang, J. Tribological behavior of Ni3Al–Ag based self-lubricating alloy with Ag2MoO4 formed by high temperature tribo-chemical reaction. Tribol. Int. 2020, 153, 106659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S. Self-lubricating composites with 2D materials as reinforcement: A new perspective. Reinf. Plast. 2020, 65, 101–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlan, K.P.; de Mello, J.D.B.; Klein, A.N. Self-lubricating composites containing MoS2: A review. Tribol. Int. 2018, 120, 280–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, G.; Wang, L.; Xue, Q. Self-adaptive MoS2-Pb-Ti film for vacuum and humid air. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 345, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muratore, C.; Voevodin, A. Molybdenum disulfide as a lubricant and catalyst in adaptive nanocomposite coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 201, 4125–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Bi, Q.; Niu, M.; Yang, J.; Liu, W. Tribological behavior of NiAl matrix composites with addition of oxides at high temperatures. Wear 2012, 274–275, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Cheng, J.; Qiao, Z.; Tian, Y.; Yang, J. High temperature lubricating behavior of NiAl matrix composites with addition of CuO. J. Tribol. 2016, 138, 031607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, D.; Liu, J.; Singh, D.; Muratore, C.; Voevodin, A.; Mishra, S.; Rebholz, C.; Ge, Q.; Aouadi, S. Layered atomic structures of double oxides for low shear strength at high temperatures. Scr. Mater. 2010, 62, 735–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suszko, T.; Gulbiński, W.; Jagielski, J. The role of surface oxidation in friction processes on molybdenum nitride thin films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 194, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.-F.; Liu, X.-B.; Ren, J.; Luo, J.; Shi, S.-H.; Chen, Y.; Shi, G.-L.; Wu, S.-H. Investigation of laser cladding high temperature anti-wear composite coatings on Ti6Al4V alloy with the addition of self-lubricant CaF2. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 313, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumder, S.; Metselaar, H.S.C.; Sukiman, N.L.; Zulkifli, N.W.M. An overview of fluoride-based solid lubricants in sliding contacts. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 40, 4974–4996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Zhu, Y.; Ji, H.; Zheng, X.; Ruan, Q.; Niu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zeng, Y. Microstructures and tribological properties of plasma sprayed WC–Co–Cu–BaF2/CaF2 self-lubricating wear resistant coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 4938–4944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Bi, Q.; Zhu, S.; Yang, J.; Liu, W. Tribological properties of ZrO2 (Y2O3)–Mo–BaF2/CaF2 composites at high temperatures. Tribol. Int. 2012, 45, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemenz, M.; Schulze, V.; Rohr, I.; Löhe, D. Application of the FEM for the prediction of the surface layer characteristics after shot peening. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2009, 209, 4093–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zishan, C.; Hejun, L.; Qiangang, F.; Xinfa, Q. Tribological behaviors of SiC/h-BN composite coating at elevated temperatures. Tribol. Int. 2012, 56, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podgornik, B.; Kosec, T.; Kocijan, A.; Donik, Č. Tribological behaviour and lubrication performance of hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) as a replacement for graphite in aluminium forming. Tribol. Int. 2015, 81, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Bi, Q.; Yang, J.; Xia, Y.; Hao, J. Tribological properties of solid lubricants (graphite, h-BN) for Cu-based P/M friction composites. Tribol. Int. 2008, 41, 1145–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, K. Polymer composites for tribological applications. Adv. Ind. Eng. Polym. Res. 2018, 1, 3–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burris, D.L.; Sawyer, W.G. Tribological behavior of PEEK components with compositionally graded PEEK/PTFE surfaces. Wear 2007, 262, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, W.; Freudenberg, K.D.; Bhimaraj, P.; Schadler, L.S. A study on the friction and wear behavior of PTFE filled with alumina nanoparticles. Wear 2003, 254, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlan, K.P.; Gonçalves, P.D.C.; Consoni, D.R.; Dias, M.V.G.; De Lima, G.A.; de Mello, J.D.B.; Klein, A.N. Metallurgical Aspects of Self-lubricating Composites Containing Graphite and MoS2. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2017, 26, 1135–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, P.; Arnell, R. Magnetron sputtering: A review of recent developments and applications. Vacuum 2000, 56, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quazi, M.M.; Fazal, M.A.; Haseeb, A.S.M.A.; Yusof, F.; Masjuki, H.H.; Arslan, A. A Review to the Laser Cladding of Self-Lubricating Composite Coatings. Lasers Manuf. Mater. Process. 2016, 3, 67–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhou, J.; Guo, B.; Zhou, H.; Pu, Y.; Chen, J. Friction and wear behavior of laser cladding Ni/hBN self-lubricating composite coating. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 491, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.M.; Yu, R.L.; Li, S.Q. Microstructure and tribological properties of laser clad NiO/Al2O3 self-lubrication wear-resistant ceramic matrix composite coatings. Mocaxue Xuebao/Tribol. 2002, 22, 157–160. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, B.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, G.; Liao, H. Wear and corrosion resistant performance of thermal-sprayed Fe-based amorphous coatings: A review. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Peng, Z.; Yu, X.; Fu, Z.; Yue, W.; Wang, C. Microstructure and tribological performance of self-lubricating diamond/tetrahedral amorphous carbon composite film. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 3180–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalss, W.; Reiter, A.; Derflinger, V.; Gey, C.; Endrino, J. Modern coatings in high performance cutting applications. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2006, 24, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, Y.; Sur, G. The effect of Al2O3, TiN and Ti (C,N) based CVD coatings on tool wear in machining metal matrix composites. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2004, 179, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, M.; Bi, Q.; Yang, J.; Liu, W. Tribological performance of a Ni3Al matrix self-lubricating composite coating tested from 25 to 1000 °C. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2012, 206, 3938–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Song, S.; Zhai, W.; Wang, M.; Xu, Z.; Yao, J.; Din, A.Q.U.; Zhang, Q. Tribological behavior of Ni3Al matrix self-lubricating composites containing WS2, Ag and hBN tested from room temperature to 800 °C. Mater. Des. 2014, 55, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Bi, Q.; Yang, J.; Liu, W.; Xue, Q. Ni3Al matrix high temperature self-lubricating composites. Tribol. Int. 2011, 44, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, K. Solid Lubricants and Coatings for Extreme Environments: State-of-the-Art Survey; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 2007.
- Kumar, R.; Antonov, M. Self-lubricating materials for extreme temperature tribo-applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 44, 4583–4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Ye, L.; Friedrich, K. Tribological properties of high temperature resistant polymer composites with fine particles. Tribol. Int. 2007, 40, 1170–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Friedrich, K. Effect of nanoparticles on the tribological behaviour of short carbon fibre reinforced poly(etherimide) composites. Tribol. Int. 2005, 38, 966–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhu, S.; Cheng, J.; Qiao, Z.; Yang, J. Tribological properties of Mo and CaF2 added SiC matrix composites at elevated temperatures. Tribol. Int. 2017, 111, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Du, L.; Huang, C.; Liu, W.; Zhang, W. Wear behavior of sintered hexagonal boron nitride under atmosphere and water vapor ambiences. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 10195–10200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huai, W.; Zhang, C.; Wen, S. Graphite-based solid lubricant for high-temperature lubrication. Friction 2020, 9, 1660–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, C.J.; Menezes, P.L.; Lovell, M.R.; Jen, T.-C. Tribology of solid lubricants. In Tribology for Scientists and Engineers; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 447–494. [Google Scholar]
- Aouadi, S.; Paudel, Y.; Simonson, W.; Ge, Q.; Kohli, P.; Muratore, C.; Voevodin, A. Tribological investigation of adaptive Mo2N/MoS2/Ag coatings with high sulfur content. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2009, 203, 1304–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lu, Z.; Dong, H.; Cao, Y.; Yang, H. Study on self-adaptive lubrication mechanism of surface micro-dimple structure filled with multiple lubricants. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 861, 158479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Shi, X.; Yang, K.; Zou, J.; Zhai, W.; Huang, Y. Tribological performance of TiAl matrix composites containing silver and V2O5 nanowires at elevated temperatures. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 56294–56302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Bi, Q.; Yang, J.; Liu, W. Influence of Cr content on tribological properties of Ni3Al matrix high temperature self-lubricating composites. Tribol. Int. 2011, 44, 1182–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Li, F.; Ma, J.; Cheng, J.; Yin, B.; Yang, J.; Qiao, Z.; Liu, W. Tribological properties of Ni3Al matrix composites with addition of silver and barium salt. Tribol. Int. 2015, 84, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Shi, X.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, Q. The research on the sliding friction and wear behaviors of TiAl-10 wt%Ag at elevated temperatures. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2017, 186, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Shi, X.; Wang, M.; Zhai, W.; Yao, J.; Song, S.; Zhang, Q. Effect of Ag and Ti3SiC2 on tribological properties of TiAl Matrix self-lubricating composites at room and increased temperatures. Tribol. Lett. 2014, 53, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Shi, X.; Zhai, W.; Ibrahim, A.M.M.; Xu, Z.; Song, S.; Chen, L.; Zhu, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, Q. Effect of TiB2 on tribological properties of TiAl self-lubricating composites containing Ag at elevated temperature. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2014, 24, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Zhai, W.; Wang, M.; Xu, Z.; Yao, J.; Song, S.; Wang, Y. Tribological behaviors of NiAl based self-lubricating composites containing different solid lubricants at elevated temperatures. Wear 2014, 310, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, I.; Park, C.; Choi, H.C. Synthesis and properties of molybdenum disulphide: From bulk to atomic layers. RSC Adv. 2014, 5, 7495–7514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharf, T.W.; Prasad, S.V. Solid lubricants: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 48, 511–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spalvins, T. Lubrication with sputtered MoS2 films: Principles, operation, and limitations. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 1992, 1, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-F.; Parakash, B.; Hardell, J.; Fang, Q.-F. Tribological properties of transition metal di-chalcogenide based lubricant coatings. Front. Mater. Sci. 2012, 6, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, G.; Wang, L. Low humidity-sensitivity of MoS2/Pb nanocomposite coatings. Wear 2016, 350–351, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Lu, Z.; Wu, G.; Zhang, G.; Wang, L.; Xue, Q. Preparation and properties of DLC/MoS2 multilayer coatings for high humidity tribology. Mater. Res. Express 2016, 3, 066401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorak, S.D.; Wahl, K.J.; Singer, I.L. In situ analysis of third body contributions to sliding friction of a Pb–Mo–S coating in dry and humid air. Tribol. Lett. 2007, 28, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Shi, X.; Wu, C.; Yang, K.; Huang, Y.; Deng, X.; Yan, Z.; Xue, B. Tribological behavior of M50-MoS2 self-lubricating composites from 150 to 450 °C. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2017, 198, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-S.; Li, J.-F.; Zhang, L.; Qian, Z.-Y. Effects of environment on dry sliding wear behavior of silver–copper based composites containing tungsten disulfide. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2017, 27, 2202–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Qian, Z.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, J.; Zhou, K. Tribological behavior of Cu matrix composites containing graphite and tungsten disulfide. Tribol. Trans. 2014, 57, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdemir, A. A crystal chemical approach to the formulation of self-lubricating nanocomposite coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 200, 1792–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, V.; Komatsu, T. Classification of Simple Oxides: A polarizability approach. J. Solid State Chem. 2002, 163, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essa, F.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, X. Investigation of the effects of mixtures of WS2 and ZnO solid lubricants on the sliding friction and wear of M50 steel against silicon nitride at elevated temperatures. Wear 2017, 374-375, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Feng, X.; Lu, C.; Yi, G.; Jia, J.; Li, H. Mechanical and tribological properties of plasma sprayed NiAl composite coatings with addition of nanostructured TiO2/Bi2O3. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 349, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Gao, Y.; Li, C.; Kang, Y.; Hou, X.; Liu, F.; Zhao, S. Improved tribological performance of nickel based high temperature lubricating composites with addition of metallic oxides. Wear 2021, 480–481, 203938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Kato, K.; Umehara, N. Tribological properties of self-lubricating CMC/Al2O3 pairs at high temperature in air. Tribol. Lett. 1998, 4, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Hu, L.; Qin, B.; Fan, H.; Zhang, Y. Fabrication and tribological behavior of Al2O3/MoS2–BaSO4 laminated composites doped with in situ formed BaMoO4. Tribol. Int. 2018, 118, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Bi, Q.; Niu, M.; Zhu, S.; Yang, J.; Liu, W. High-temperature tribological behavior of ZrO2–MoS2–CaF2 self-lubricating composites. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2013, 33, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Sasaki, S.; Murakami, T.; Umeda, K. Spark-plasma-sintered ZrO2(Y2O3)-BaCrO4 self-lubricating composites for high temperature tribological applications. Ceram. Int. 2005, 31, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Corte, C.; Sliney, H.E. Composition optimization of self-lubricating chromium-carbide-based composite coatings for use to 760 °C. ASLE Trans. 1987, 30, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Jia, J.; Lu, J.; Wang, J. High temperature tribological characteristics of Fe–Mo-based self-lubricating composites. Tribol. Lett. 2009, 34, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konopka, K.; Roik, T.A.; Gavrish, A.P.; Vitsuk, Y.Y.; Mazan, T. Effect of CaF2 surface layers on the friction behavior of copper-based composite. Powder Met. Met. Ceram. 2012, 51, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, A.; Sharma, S.M. High temperature friction and wear characteristics of Fe–Cu–C based self-lubricating material. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2017, 70, 2641–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivyas, P.D.; Charoo, M.S. Tribological characterization of iron-based self-lubricating composite under dry sliding conditions. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. D 2021, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Lu, H.; Liu, C.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Song, X. Tribological behavior of WC-Co-CaF2 self-lubricating cemented carbides. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2021, 96, 105492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, J.; Cheng, J.; Tan, H.; Sun, Q.; Zhu, S.; Yang, J.; Liu, W. Investigation of tribological characteristics of nickel alloy-based solid-lubricating composites at elevated temperatures under vacuum. Friction 2020, 9, 990–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Liu, H.; Li, S.; Gao, G.; Kou, Z. Design and high-temperature tribological properties of CoCrW with rare earth fluoride composites. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 2402–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, S.; Sun, Q.; Cheng, J.; Yu, Y.; Yang, J. Tribological properties of h-BN matrix solid-lubricating composites under elevated temperatures. Tribol. Int. 2020, 148, 106333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, Y.; Wakabayashi, T.; Okada, K.; Wada, T.; Nishikawa, H. Boron nitride as a lubricant additive. Wear 1999, 232, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Honda, F. Chemical contribution to friction behavior of sintered hexagonal boron nitride in water. Wear 2000, 237, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, W.; Zhao, B.; Yang, C.; Ding, W. Effects of h-BN particles on the microstructure and tribological property of self-lubrication CBN abrasive composites. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 2457–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; He, G.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y. Tribological behavior of boron nitride nanoplatelet reinforced Ni3Al intermetallic matrix composite fabricated by selective laser melting. Mater. Des. 2019, 165, 107579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-I.; Hou, K.-H.; Ger, M.-D.; Wang, G.-L. The effect of incorporated self-lubricated BN(h) particles on the tribological properties of Ni–P/BN(h) composite coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 357, 1727–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Planche, M.-P.; Peyraut, F.; Liao, H.; Lasalle, A.; Allimant, A.; Montavon, G. Microstructural, mechanical and tribological properties of suspension plasma sprayed YSZ/h-BN composite coating. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2018, 38, 4512–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Feng, K.; Yao, C.; Nie, P.; Huang, J.; Li, Z. Microstructure and tribological properties of laser cladded self-lubricating nickel-base composite coatings containing nano-Cu and h-BN solid lubricants. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 359, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Choi, H.S.; Choi, W.J.; Kwon, H. Effect of vacuum thermal cyclic exposures on unidirectional carbon fiber/epoxy composites for low earth orbit space applications. Compos. Part B Eng. 2011, 43, 726–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zheng, F.; Wang, T. Tribological properties of polymers PI, PTFE and PEEK at cryogenic temperature in vacuum. Cryogenics 2016, 75, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theiler, G.; Hübner, W.; Gradt, T.; Klein, P.; Friedrich, K. Friction and wear of PTFE composites at cryogenic temperatures. Tribol. Int. 2002, 35, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theiler, G.; Gradt, T. Friction and wear of PEEK composites in vacuum environment. Wear 2010, 269, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Breidt, C.; Friedrich, K. Tribological properties of epoxy nanocomposites: I. Enhancement of the wear resistance by nano-TiO2 particles. Wear 2005, 258, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, P.L.; Rohatgi, P.K.; Lovell, M.R. Self-lubricating behavior of graphite reinforced metal matrix composites. In Green Tribology: Biomimetics, Energy Conservation and Sustainability; Nosonovsky, M., Bhushan, B., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 445–480. ISBN 978-3-642-23681-5. [Google Scholar]
- Rajak, D.; Kumar, A.; Behera, A.; Menezes, P. Diamond-like carbon (DLC) coatings: Classification, properties, and applications. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, A.D.; Omrani, E.; Menezes, P.L.; Rohatgi, P.K. Mechanical and tribological properties of self-lubricating metal matrix nanocomposites reinforced by carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and graphene—A review. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 77, 402–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabandeh-Khorshid, M.; Omrani, E.; Menezes, P.L.; Rohatgi, P.K. Tribological performance of self-lubricating aluminum matrix nanocomposites: Role of graphene nanoplatelets. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2016, 19, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omrani, E.; Moghadam, A.D.; Menezes, P.L.; Rohatgi, P.K. Influences of graphite reinforcement on the tribological properties of self-lubricating aluminum matrix composites for green tribology, sustainability, and energy efficiency—A review. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 83, 325–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddaiah, A.; Kumar, P.; Henderson, A.; Misra, M.; Menezes, P.L. Surface energy and tribology of electrodeposited Ni and Ni–graphene coatings on steel. Lubricants 2019, 7, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, D.; Erdemir, A.; Sumant, A.V. Reduced wear and friction enabled by graphene layers on sliding steel surfaces in dry nitrogen. Carbon 2013, 59, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, D.; Erdemir, A.; Sumant, A.V. Graphene: A new emerging lubricant. Mater. Today 2014, 17, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Peng, Y.; Lang, H. A novel approach to decrease friction of graphene. Carbon 2017, 118, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zou, K. Friction and wear properties of different types of graphene nanosheets as effective solid lubricants. Langmuir 2015, 31, 7782–7791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasar, A.; Menezes, P.L. Synthesis and recent advances in tribological applications of graphene. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 97, 3999–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasar, A.K.; Xiong, G.; Menezes, P.L. Graphene-reinforced metal and polymer matrix composites. JOM 2018, 70, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, W.; Shi, X.; Wang, M.; Xu, Z.; Yao, J.; Song, S.; Wang, Y. Grain refinement: A mechanism for graphene nanoplatelets to reduce friction and wear of Ni3Al matrix self-lubricating composites. Wear 2014, 310, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Geng, Y.; Tieu, A.K.; Hai, G.; Tan, H.; Chen, J.; Cheng, J.; Yang, J. In-situ formed graphene providing lubricity for the FeCoCrNiAl based composite containing graphite nanoplate. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 221, 109032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliney, H. Solid lubricant materials for high temperatures—A review. Tribol. Int. 1982, 15, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omrani, E.; Moghadam, A.; Kasar, A.; Rohatgi, P.; Menezes, P. Tribological performance of graphite nanoplatelets reinforced Al and Al/Al2O3 self-lubricating composites. Materials 2021, 14, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Tian, S.; Menezes, P.L.; Xiong, G. Carbon solid lubricants: Role of different dimensions. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 107, 3875–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Guo, Q.; Shi, J.; Zhai, G.; Liu, L. Graphite blocks with high thermal conductivity derived from natural graphite flake. Carbon 2008, 46, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosleh-Shirazi, S.; Akhlaghi, F.; Li, D. Effect of graphite content on the wear behavior of Al/2SiC/Gr hybrid nano-composites respectively in the ambient environment and an acidic solution. Tribol. Int. 2016, 103, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusaro, R. Self-lubricating polymer composites and polymer transfer film lubrication for space applications. Tribol. Int. 1990, 23, 105–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muratore, C.; Voevodin, A.; Hu, J.; Zabinski, J. Tribology of adaptive nanocomposite yttria-stabilized zirconia coatings containing silver and molybdenum from 25 to 700 °C. Wear 2006, 261, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazirisereshk, M.R.; Martini, A.; Strubbe, D.A.; Baykara, M.Z. Solid Lubrication with MoS2: A Review. Lubricants 2019, 7, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polcar, T.; Cavaleiro, A. Review on self-lubricant transition metal dichalcogenide nanocomposite coatings alloyed with carbon. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 206, 686–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvi, E.; Ma, Y.; Aksoy, R.; Ertas, A.; White, A. High pressure X-ray diffraction study of tungsten disulfide. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2006, 67, 2183–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolelli, G.; Candeli, A.; Lusvarghi, L.; Ravaux, A.; Cazes, K.; Denoirjean, A.; Valette, S.; Chazelas, C.; Meillot, E.; Bianchi, L. Tribology of NiCrAlY+Al2O3 composite coatings by plasma spraying with hybrid feeding of dry powder + suspension. Wear 2015, 344-345, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Yi, G.; Wang, W.; Shan, Y.; Jia, J. Tribological properties of NiCr–Al2O3 cermet-based composites with addition of multiple-lubricants at elevated temperatures. Tribol. Int. 2013, 67, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagde, P.; Sapate, S.; Khatirkar, R.; Vashishtha, N. Friction and abrasive wear behaviour of Al2O3-13TiO2 and Al2O3-13TiO2 + Ni graphite coatings. Tribol. Int. 2018, 121, 353–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulbiński, W.; Suszko, T. Thin films of MoO3–Ag2O binary oxides—The high temperature lubricants. Wear 2006, 261, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Cao, T.; Yang, X.; Liu, J.; Sun, J.; Zhao, J. Wear behavior and self tribofilm formation of hot-pressed Al2O3/TiC/CaF2 ceramic composites sliding against cemented carbide. Ceram. Int. 2007, 33, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, Z.; Song, P.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Mao, K. Laminated structure optimization and drawing performance of Al2O3–TiC/Al2O3–TiC–CaF2 self-lubricating laminated ceramic conical die. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 12480–12489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, P.; Yu, Z.; Li, C.; Xu, P.; Lu, Y. Laser cladding of Co-based alloy/TiC/CaF2 self-lubricating composite coatings on copper for continuous casting mold. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 232, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DellaCorte, C.; Zaldana, A.R.; Radil, K.C. A systems approach to the solid lubrication of foil air bearings for oil-free turbomachinery. J. Tribol. 2004, 126, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraoun, H.; Grosdidier, T.; Seichepine, J.-L.; Goran, D.; Aourag, H.; Coddet, C.; Zwick, J.; Hopkins, N. Improvement of thermally sprayed abradable coating by microstructure control. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 201, 2303–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radcliffe, C. Sealing material developments for reciprocating gas compressors. Seal. Technol. 2005, 2005, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodiouchkina, M.; Lind, J.; Pelcastre, L.; Berglund, K.; Rudolphi, K.; Hardell, J. Tribological behaviour and transfer layer development of self-lubricating polymer composite bearing materials under long duration dry sliding against stainless steel. Wear 2021, 484–485, 204027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jianxin, D.; Tongkun, C.; Xuefeng, Y.; Jianhua, L. Self-lubrication of sintered ceramic tools with CaF2 additions in dry cutting. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2006, 46, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niste, V.B.; Ratoi, M.; Tanaka, H.; Xu, F.; Zhu, Y.; Sugimura, J. Self-lubricating Al-WS2 composites for efficient and greener tribological parts. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanar, H.; Purcek, G.; Demirtas, M.; Ayar, H.H. Effect of hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) addition on friction behavior of low-steel composite brake pad material for railway applications. Tribol. Int. 2021, 107274, in preproof. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliney, E. Tribological Properties of PM212: Composite 1990 Annual Meeting of the Society; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 1990.
- DellaCorte, C.; Laskowski, J.A. Tribological evaluation of PS300: A new chrome oxide-based solid lubricant coating sliding against Al2O3 from 25° to 650 °C. Tribol. Trans. 1997, 40, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W. Application of a high temperature self-lubricating composite coating on steam turbine components. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2004, 177–178, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DellaCorte, C.; Edmonds, B.J. NASA PS400: A New High Temperature Solid Lubricant Coating for High Temperature Wear Applications; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 2009; pp. 1–15.
- Radil, K.; DellaCorte, C. The performance of PS400 subjected to sliding contact at temperatures from 260 to 927 °C. Tribol. Trans. 2016, 60, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, H.; Slawik, S.; Gachot, C.; Prakash, B.; Ripoll, M.R. Microstructural design of self-lubricating laser claddings for use in high temperature sliding applications. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 337, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Otero-De-La-Roza, A.; Gu, J.; Stone, D.; Aouadi, S.M.; Johnson, E.R.; Martini, A. (Ag,Cu)–Ta–O ternaries as high-temperature solid-lubricant coatings. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 15422–15429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muratore, C.; Hu, J.; Voevodin, A. Tribological coatings for lubrication over multiple thermal cycles. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2009, 203, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaowei, L.; Jean-Charles, R.; Suyuan, Y. Effect of temperature on graphite oxidation behavior. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2004, 227, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechepurenko, A.; Samuni, S. Oxidation protection of graphite by BN coatings. J. Solid State Chem. 2000, 154, 162–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Singh, D.; Singh, M. Enhancement of oxidation resistance of graphite foams by polymer derived-silicon carbide coating for concentrated solar power applications. Energy Procedia 2015, 69, 900–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).