Cost-Effectively 3D-Printed Rigid and Versatile Interpenetrating Polymer Networks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
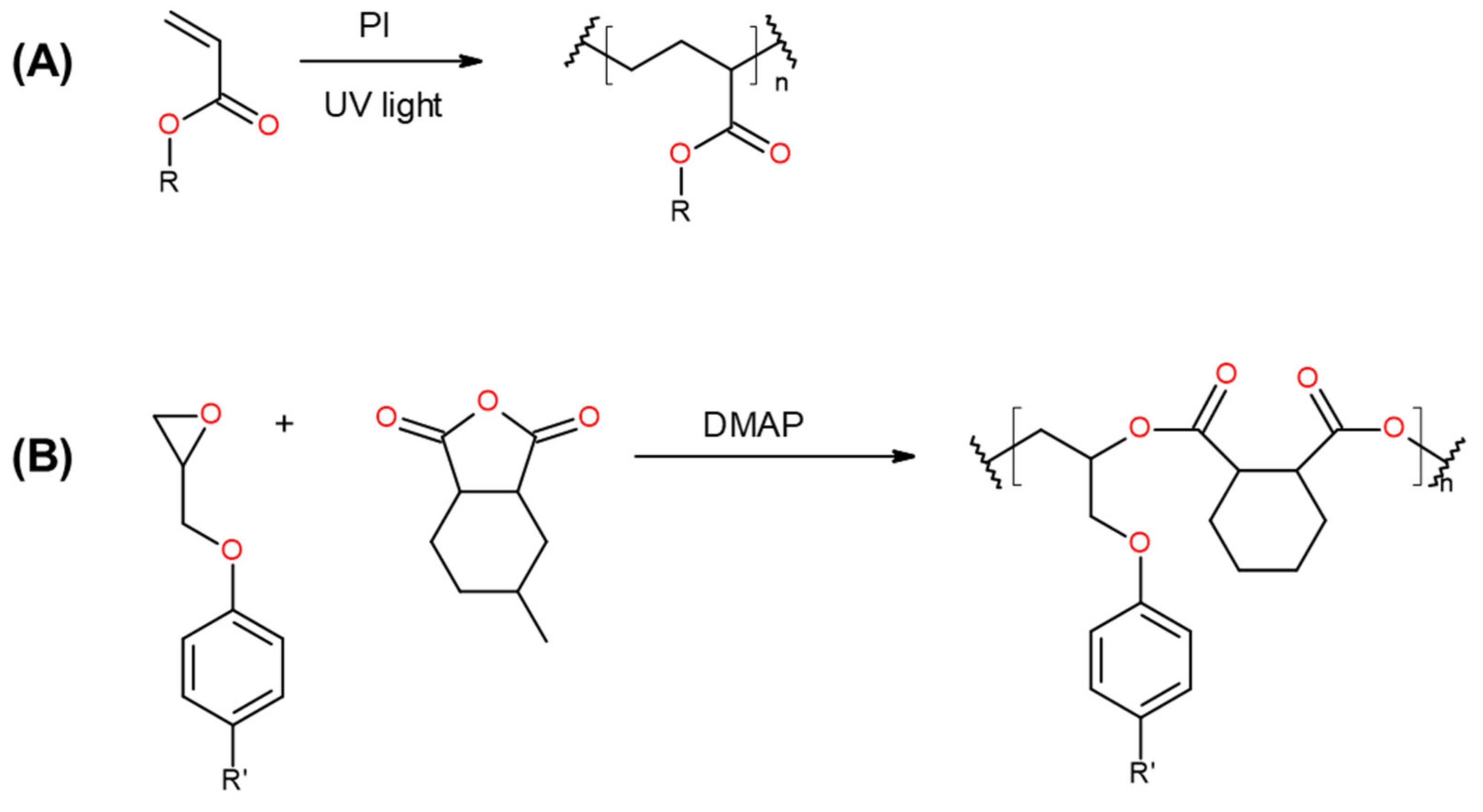
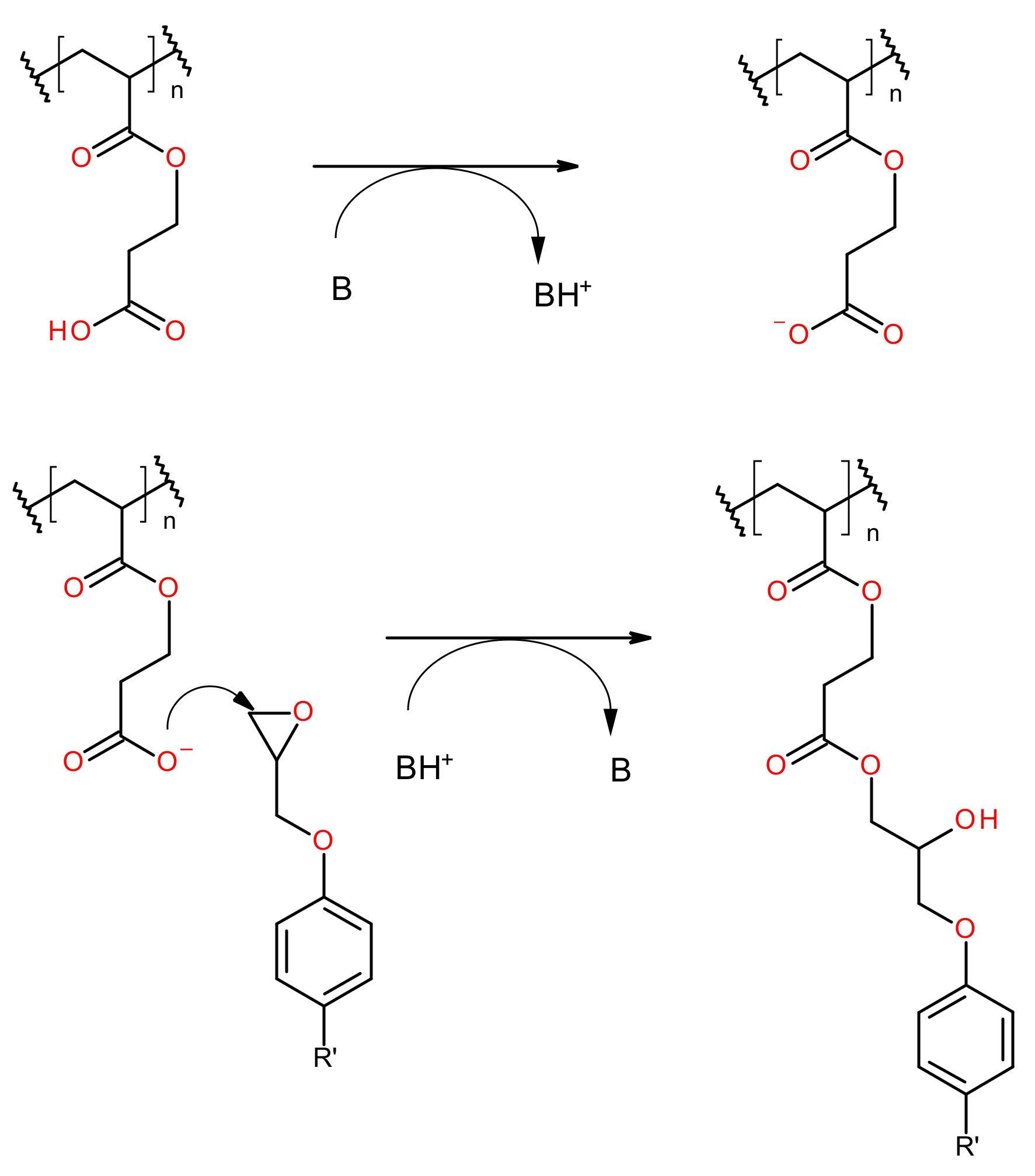
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
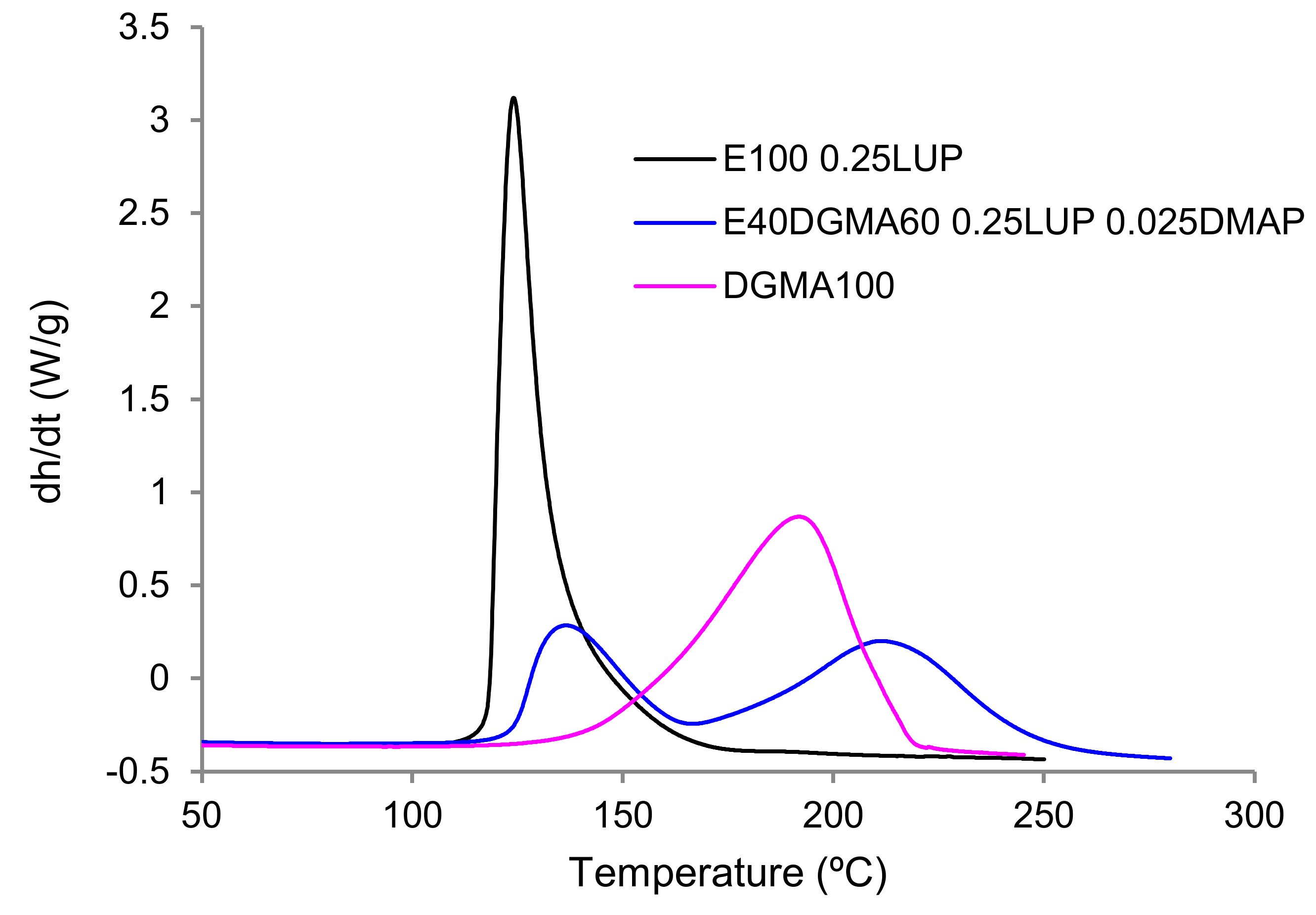
3.1. Curing Kinetics
3.2. Material Properties
3.2.1. Thermal and Viscoelastic Properties
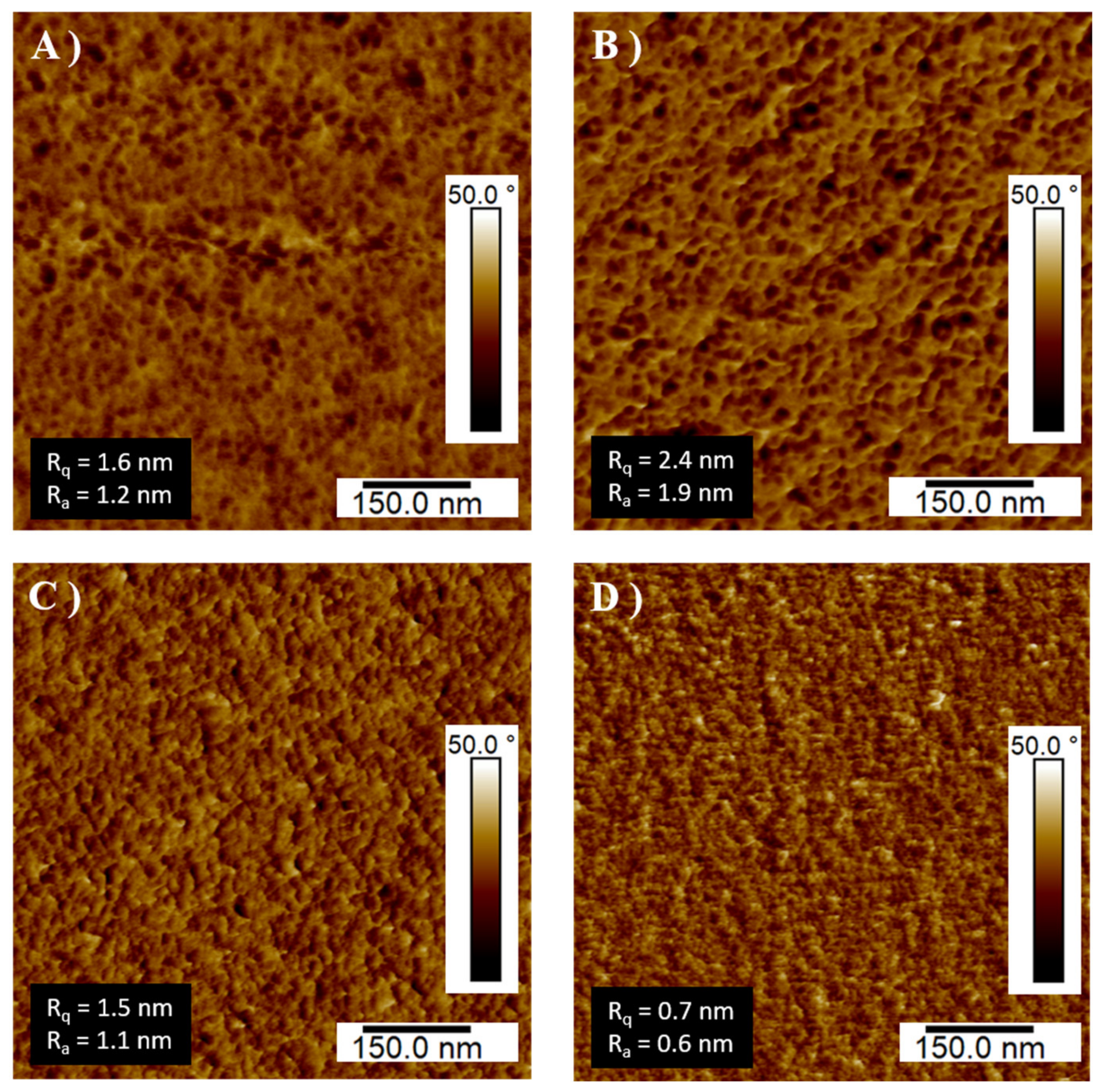
3.2.2. Network Topology and Phase Separation
3.2.3. Mechanical Properties
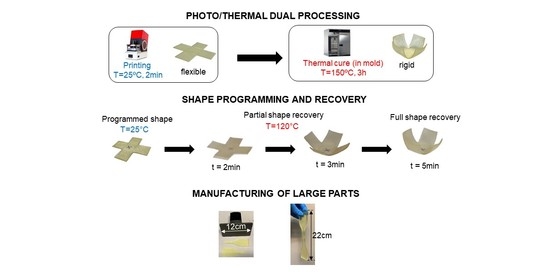
3.3. Prospective 3D Printing Applications
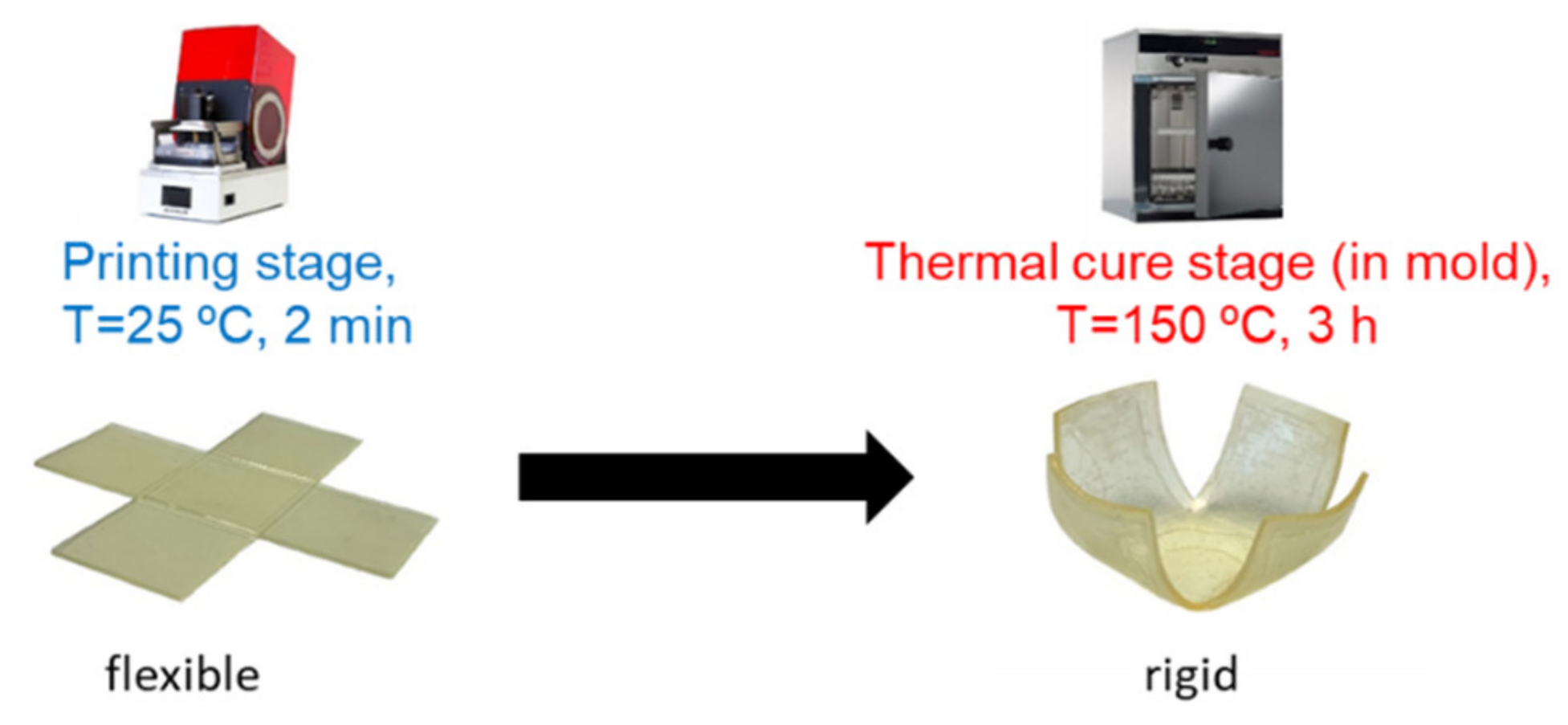
3.3.1. Shape Memory Cube Printed at Reduced Cost
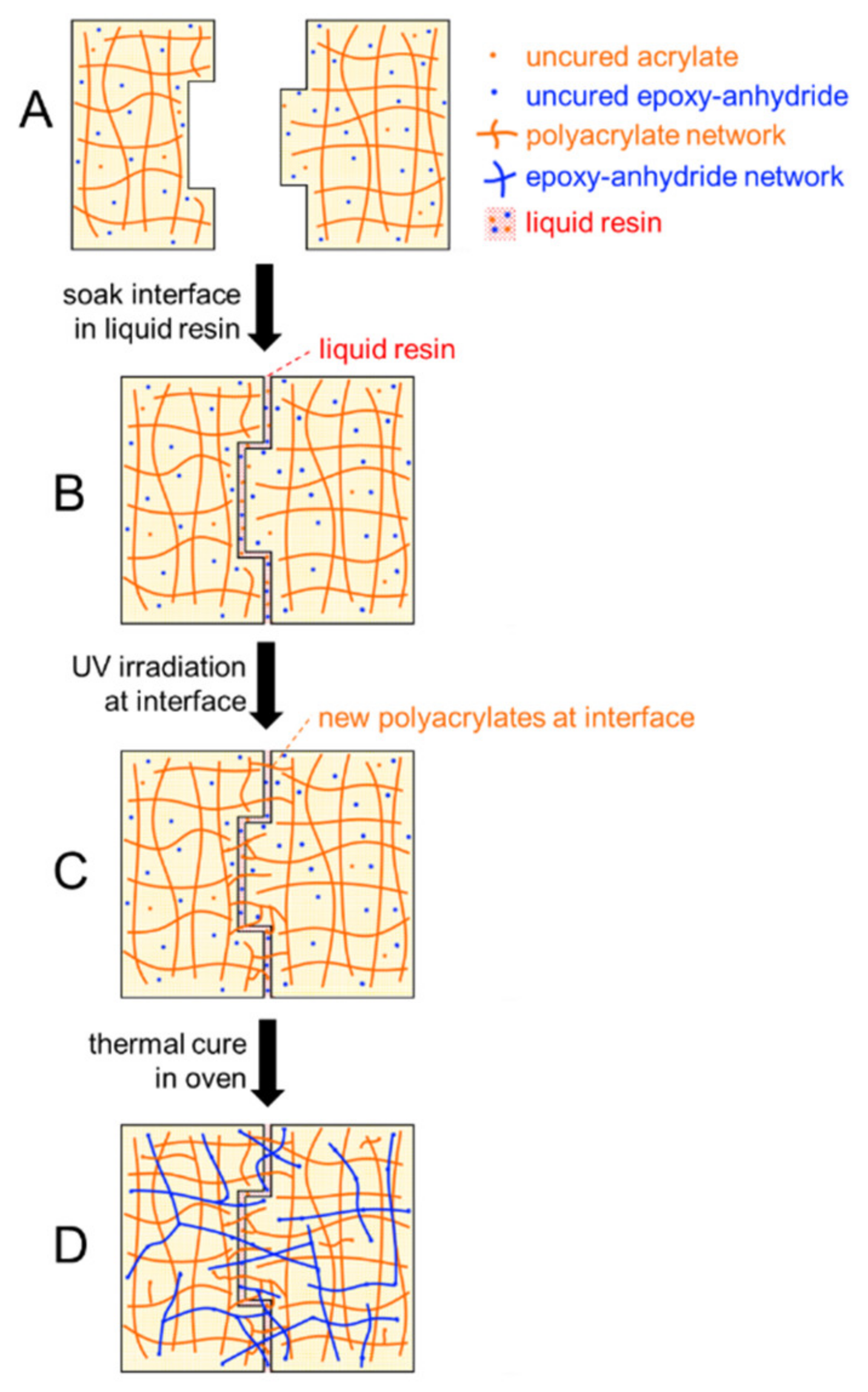
3.3.2. Production of Large Components by Parts
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ngo, T.D.; Kashani, A.; Imbalzano, G.; Nguyen, K.T.Q.; Hui, D. Additive manufacturing (3D printing): A review of materials, methods, applications and challenges. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 143, 172–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poelma, J.; Rolland, J. Rethinking digital manufacturing with polymers. Insights 2017, 358, 1384–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Przeradzka, M.A.; van Bochove, B.; Bor, T.C.; Grijpma, D.W. Phase-separated mixed-macromer hydrogel networks and scaffolds prepared by stereolithography. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2017, 28, 1212–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahmen, V.; Redmann, A.J.; Austermann, J.; Quintanilla, A.L.; Mecham, S.J.; Osswald, T.A. Fabrication of hybrid composite T-joints by co-curing with 3D printed dual cure epoxy. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 183, 107728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Bakhtiary Noodeh, M.; Delpouve, N.; Saiter, J.M.; Tan, L.; Negahban, M. Printing continuously graded interpenetrating polymer networks of acrylate/epoxy by manipulating cationic network formation during stereolithography. Express Polym. Lett. 2016, 10, 1003–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Yu, R.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhao, X.; Huang, W. A comparative study on 3D printed silicone-epoxy/acrylate hybrid polymers via pure photopolymerization and dual-curing mechanisms. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 5101–5111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolland, J.P. Functional materials for 3D manufacturing using Carbon’s CLIP technology. J. Photopolym. Sci. Technol. 2016, 29, 451–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, R.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wu, X.; Zhao, T.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, W. Three-dimensional printing of shape memory composites with epoxy-acrylate hybrid photopolymer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 1820–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Du, Z.; Yong, T.; Han, W. Preparation of a novel hybrid type photosensitive resin for stereolithography in 3D printing and testing on the accuracy of the fabricated parts. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mater. Sci. Ed. 2017, 32, 726–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcione, C.E.; Striani, R.; Montagna, F.; Cannoletta, D.; Esposito Corcione, C.; Striani, R.; Montagna, F.; Cannoletta, D.; Corcione, C.E.; Striani, R.; et al. Organically modified montmorillonite polymer nanocomposites for stereolithography building process. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2015, 2014, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hola, E.; Pilch, M.; Ortyl, J. Thioxanthone derivatives as a new class of organic photocatalysts for photopolymerisation processes and the 3D printing of photocurable resins under visible light. Catalysts 2020, 10, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Nie, J.; Zhu, X. A high performance phenyl-free LED photoinitiator for cationic or hybrid photopolymerization and its application in LED cationic 3D printing. Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 2855–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokbel, H.; Anderson, D.; Plenderleith, R.; Dietlin, C.; Morlet-Savary, F.; Dumur, F.; Gigmes, D.; Fouassier, J.P.; Lalevée, J. Simultaneous initiation of radical and cationic polymerization reactions using the “G1” copper complex as photoredox catalyst: Applications of free radical/cationic hybrid photopolymerization in the composites and 3D printing fields. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 132, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffini, G.; Invernizzi, M.; Levi, M.; Natale, G.; Postiglione, G.; Turri, S. 3D-printable CFR polymer composites with dual-cure sequential IPNs. Polymer 2016, 91, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Kuang, X.; Li, V.; Kang, G.; Qi, H.J. Fabrication of tough epoxy with shape memory effects by UV-assisted direct-ink write printing. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 1879–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, K.; Fang, D.; Kang, G.; Qi, H.J. High-speed 3D printing of high-performance thermosetting polymers via two-stage curing. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2018, 39, 1700809/1–1700809/8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konuray, O.; Altet, A.; Bonada, J.; Tercjak, A.; Fernández-Francos, X.; Ramis, X. Epoxy Doped, Nano-scale Phase-separated Poly-Acrylates with Potential in 3D Printing. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2021, 306, 2000558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Francos, X.; Konuray, O.; Ramis, X.; Serra, À.; De, S. Enhancement of 3D-printable materials by dual-curing procedures. Materials 2021, 14, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Uzcategui, A.C.; Muralidharan, A.; Ferguson, V.L.; Bryant, S.J.; McLeod, R.R. Understanding and Improving Mechanical Properties in 3D printed Parts Using a Dual-Cure Acrylate-Based Resin for Stereolithography. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2018, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konuray, O.; Di Donato, F.; Sangermano, M.; Bonada, J.; Tercjak, A.; Ramis, X. Dual-curable stereolithography resins for superior thermomechanical properties. Express Polym. Lett. 2020, 14, 881–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Kowsari, K.; Serjouei, A.; Dunn, M.L.; Ge, Q. Reprocessable thermosets for sustainable three-dimensional printing. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, Q.; Yu, K.; Kuang, X.; Mu, X.; Dunn, C.K.; Dunn, M.L.; Wang, T.; Jerry Qi, H. Recyclable 3D printing of vitrimer epoxy. Mater. Horizons 2017, 4, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yang, M.; Ji, M.; Kuang, X.; Qi, H.J.; Wang, T. Recyclable thermosetting polymers for digital light processing 3D printing. Mater. Des. 2021, 197, 109189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Wang, C.; Yu, J.; Wang, J.; Chu, F. Two-Step 3 D-Printing Approach toward Sustainable, Repairable, Fluorescent Shape-Memory Thermosets Derived from Cellulose and Rosin. ChemSusChem 2020, 13, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konuray, O.; Fernández-Francos, X.; Ramis, X.; Serra, À. Acetoacetate based thermosets prepared by dual-Michael addition reactions. Polymers 2019, 11, 1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Konuray, O.; Salla, J.M.; Morancho, J.M.; Fernández-Francos, X.; García-Alvarez, M.; Ramis, X. Curing kinetics of acrylate-based and 3D printable IPNs. Thermochim. Acta 2020, 692, 178754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Erba, I.E.; Williams, R.J.J. Homopolymerization of Epoxy Monomers Initiated by 4-(Dimethylamino)pyridine. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2006, 46, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocks, J.; Rintoul, L.; Vohwinkel, F.; George, G. The kinetics and mechanism of cure of an amino-glycidyl epoxy resin by a co-anhydride as studied by FT-Raman spectroscopy. Polymer 2004, 45, 6799–6811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernández-Francos, X.; Rybak, A.; Sekula, R.; Ramis, X.; Serra, A. Modification of epoxy-anhydride thermosets using a hyperbranched poly(ester-amide): I. Kinetic study. Polym. Int. 2012, 61, 1710–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morancho, M.; Fern, X.; Ramis, X. Curing kinetics of dually-processed acrylate-epoxy 3D printing resins. Thermochim. Acta 2021, 701, 178963/1–178963/10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, M.; Fernández-Francos, X.; Ferrando, F.; Ramis, X.; Serra, À. Efficient impact resistance improvement of epoxy/anhydride thermosets by adding hyperbranched polyesters partially modified with undecenoyl chains. Polymer 2012, 53, 5232–5241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, G.T. Influence of diluent and of copolymer composition on the glass temperature of a polymer system. Bull. Am. Phys. Soc. 1952, 1, 123. [Google Scholar]
- Cano, L.; Builes, D.H.; Carrasco-Hernandez, S.; Gutierrez, J.; Tercjak, A. Quantitative nanomechanical property mapping of epoxy thermosetting system modified with poly(ethylene oxide-b-propylene oxide-b-ethylene oxide) triblock copolymer. Polym. Test. 2017, 57, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lantean, S.; Roppolo, I.; Sangermano, M.; Fabrizio Pirri, C.; Chiappone, A. Development of new hybrid acrylic/epoxy DLP-3D printable materials. Inventions 2018, 3, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russo, C.; Fernández-Francos, X.; De la Flor, S. Rheological and Mechanical Characterization of Dual-Curing Thiol-Acrylate-Epoxy Thermosets for Advanced Applications. Polymers 2019, 11, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leng, J.; Lan, X.; Liu, Y.; Du, S. Shape-memory polymers and their composites: Stimulus methods and applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2011, 56, 1077–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Formulation | E (wt.%) | CA (wt.%) | DG (wt.%) | MA (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E100 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| E80DGMA20 | 80 | 0 | 10.48 | 9.52 |
| E60DGMA40 | 60 | 0 | 20.96 | 19.04 |
| E40DGMA60 | 40 | 0 | 31.44 | 28.56 |
| E20DGMA80 | 20 | 0 | 41.93 | 38.07 |
| DGMA100 | 0 | 0 | 52.38 | 47.56 |
| E37.5DGMA57.5DGCA5 | 37.5 | 2.39 | 32.73 | 27.37 |
| E35DGMA55DGCA10 | 35 | 4.79 | 34.02 | 26.18 |
| E32.5DGMA52.5DGCA15 | 32.5 | 7.18 | 35.32 | 24.99 |
| Formulation | Nanodomain Size (nm) |
|---|---|
| E100 | 9 ± 2 |
| E40DGMA60 | 17 ± 4 |
| E32.5DGMA52.5DGCA15 | 10 ± 2 |
| DGMA100 | 7 ± 2 |
| Formulation | wsoft | whard | wacrylate,soft | wacrylate,hard |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E20DGMA80 | 0.336 | 0.664 | 0.467 | 0.065 |
| E40DGMA60 | 0.566 | 0.434 | 0.604 | 0.134 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Konuray, O.; Sola, A.; Bonada, J.; Tercjak, A.; Fabregat-Sanjuan, A.; Fernández-Francos, X.; Ramis, X. Cost-Effectively 3D-Printed Rigid and Versatile Interpenetrating Polymer Networks. Materials 2021, 14, 4544. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14164544
Konuray O, Sola A, Bonada J, Tercjak A, Fabregat-Sanjuan A, Fernández-Francos X, Ramis X. Cost-Effectively 3D-Printed Rigid and Versatile Interpenetrating Polymer Networks. Materials. 2021; 14(16):4544. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14164544
Chicago/Turabian StyleKonuray, Osman, Arnau Sola, Jordi Bonada, Agnieszka Tercjak, Albert Fabregat-Sanjuan, Xavier Fernández-Francos, and Xavier Ramis. 2021. "Cost-Effectively 3D-Printed Rigid and Versatile Interpenetrating Polymer Networks" Materials 14, no. 16: 4544. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14164544
APA StyleKonuray, O., Sola, A., Bonada, J., Tercjak, A., Fabregat-Sanjuan, A., Fernández-Francos, X., & Ramis, X. (2021). Cost-Effectively 3D-Printed Rigid and Versatile Interpenetrating Polymer Networks. Materials, 14(16), 4544. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14164544