Peening Techniques for Surface Modification: Processes, Properties, and Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Peening Techniques
2.1. Shot Peening
2.1.1. Effect of Shot Peening on Engineering Materials
2.1.2. Advanced Shot Peening
2.2. Ultrasonic Impact Peening
2.2.1. Effect of Ultrasonic Impact Peening on Engineering Materials
2.3. Laser Shock Peening
2.3.1. Effect of Laser Shock Peening on Engineering Materials
2.3.2. Recent Developments in LSP
3. Applications and Future Directions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SP | Shot Peening |
| UIP | Ultrasonic Impact Peening |
| LSP | Laser Shock Peening |
| SMAT | Surface Mechanical Attrition Treatment |
| RCS | Residual Compressive Stress |
| SPD | Severe Plastic Deformation |
| SSP | Severe Shot Peeing |
| LBW | Laser Beam Welding |
| WSP | Warm Shot Peening |
| DSA | Dynamic Strain Aging |
| TIG | Tungsten Inert Gas Welding |
| FSW | Friction Stir Welding |
| FEM | Finite Element Model |
| RSM | Response Surface Methodology |
| SS | Stainless Steel |
| MSP | Microshot Peening |
| RSSP | Re-Peened Severe Shot Peening |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| TEM | Transmission Electron Microscopy |
| CMT | Cold Metal Transfer |
| AM | Additive Manufactured |
| LPwC | Laser Peening Without Coating |
| WLSP | Warm Laser Shock Peening |
| DP | Dynamic Precipitation |
| DC | Disloaction Cell |
| DT | Disloaction Tangle |
| MT | Mechanial Twin |
| DSP | Dual Shot Peening |
| SAED | Selected Area Electron Diffraction |
| BF | Bright Field |
| DF | Dark Field |
| BM | Base Material |
| CLSP | Cryogenic Laser Shock Peening |
| SLM | Selective Laser Melting |
| FS-LSP | Femtosecond Laser Shock Peening |
| LPF | Laser Peen Forming |
| LSSP | Laser Shock Surface Patterning |
| EP-LSP | Electro Pulsing-Assisted Laser Shock Peening |
| CC-LSP | Continuous Current Assisted Laser Shock Peening |
| SCC | Stress Corrosion Cracking |
| WAAM | Wire Arc Additively Manufactured |
| UNSM | Ultrasonic Nanocrystal Surface Modification |
| PEO | Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation |
| PC | Plasma-Carburizing |
References
- Azhari, A.; Sulaiman, S.; Rao, A.K.P. A review on the application of peening processes for surface treatment. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, B.; Kumar, D.; Fan, Z.; Castagne, S. Effect of deep cold rolling on mechanical properties and microstructure of nickel-based superalloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 728, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, N.R.; Wang, Z.B.; Tong, W.P.; Sui, M.L.; Lu, J.; Lu, K. An investigation of surface nanocrystallization mechanism in Fe induced by surface mechanical attrition treatment. Acta Mater. 2002, 50, 4603–4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacı, H.; Yetim, A.F.; Baran, Ö.; Çelik, A. Tribological behavior of DLC films and duplex ceramic coatings under different sliding conditions. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 7151–7158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, T.C.; Valiev, R.Z. The use of severe plastic deformation techniques in grain refinement. JOM 2004, 56, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Obaid, Y.F. Shot peening mechanics: Experimental and theoretical analysis. Mech. Mater. 1995, 19, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, G.S.; Xu, J.H. Surface Integrity and Fatigue Property of a High Speed Milled Titanium Alloy. Adv. Mater. Res. 2008, 53-54, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Yao, M.; Wang, R. Compressive residual stress introduced by shot peening. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 1998, 73, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.-K.; Yin, Y.-F.; Yao, M. Effects of shot peening on fatigue properties of 0Cr13Ni8Mo2Al steel. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2003, 19, 372–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.K.; Wu, X.R.; Lu, F.; Yao, M.; Yan, Q. Influence of Shot Peening on Fatigue Properties in Ultra-High Strength Steels. Mater. Sci. Forum 2005, 490–491, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, Z. Microstructure evolution and strengthening mechanisms of pure titanium with nano-structured surface obtained by high energy shot peening. Vacuum 2016, 125, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherifard, S.; Fernandez-Pariente, I.; Ghelichi, R.; Guagliano, M. Fatigue behavior of notched steel specimens with nanocrystallized surface obtained by severe shot peening. Mater. Des. 2013, 45, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherifard, S.; Fernndez Pariente, I.; Ghelichi, R.; Guagliano, M. Fatigue properties of nanocrystallized surfaces obtained by high energy shot peening. Procedia Eng. 2010, 2, 1683–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Harada, Y.; Fukauara, K.; Kohamada, S. Effects of microshot peening on surface characteristics of high-speed tool steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2008, 201, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, Y.; Fukaura, K.; Haga, S. Influence of microshot peening on surface layer characteristics of structural steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2007, 191, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.C.; Zhang, Y.K.; Lu, J.Z.; Xuan, F.Z.; Wang, Z.D.; Tu, S.T. Improvement of fatigue life of Ti6Al4V alloy by laser shock peening. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 3411–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.B.; Caslaru, R. Fabrication and characterization of micro dent arrays produced by laser shock peening on titanium Ti6Al4V surfaces. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2011, 211, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gujba, A.K.; Medraj, M. Laser peening process and its impact on materials properties in comparison with shot peening and ultrasonic impact peening. Materials 2014, 7, 7925–7974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Yang, W.; Huang, Z.; Lu, Z. Effects of residual stress and surface roughness on the fatigue life of nickel aluminium bronze alloy under laser shock peening. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2021, 244, 107524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, M.; Amini, S.; Mahdavi, S.M. The investigation of laser shock peening effects on corrosion and hardness properties of ANSI 316L stainless steel. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 88, 1557–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ning, C.; Huang, Y.; Cao, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W. Improvement of abrasion resistance in artificial seawater and corrosion resistance in NaCl solution of 7075 aluminum alloy processed by laser shock peening. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2017, 90, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.; Kim, P.; Jeong, H.; Jeong, S. Enhancement of abrasion and corrosion resistance of duplex stainless steel by laser shock peening. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2012, 212, 1347–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.K. Improvement of fatigue property in 7050-T7451 aluminum alloy by laser peening and shot peening. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 3823–3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadhim, A.; Salim, E.T.; Fayadh, S.M.; Al-Amiery, A.A.; Kadhum, A.A.H.; Mohamad, A.B. Effect of multipath laser shock processing on microhardness, surface roughness, and wear resistance of 2024-T3 Al alloy. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongchao, Q. Experimental investigation of laser peening on Ti17 titanium alloy for rotor blade applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 351, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand Kumar, S.; Sundar, R.; Ganesh Sundara Raman, S.; Gnanamoorthy, R.; Kaul, R.; Ranganathan, K.; Bindra, K.S. Effects of laser peening on fretting wear behaviour of alloy 718 fretted against two different counterbody materials. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2017, 231, 1276–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.Y.; Lu, J.Z.; Zhang, Y.K.; Zhou, J.Z.; Zhang, L.F.; Dai, F.Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhong, J.W.; Cui, C.Y. Effects of laser shock processing on mechanical properties and micro-structure of ANSI 304 austenitic stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 4783–4788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Hou, X.; Zhou, X.; Gao, H.; Mankoci, S.; Qin, H.; Ren, Z.; Doll, G.L.; Martini, A.; Dong, Y.; et al. Effects of laser shock peening on the wear and degradation behaviors of magnesium alloys. In Proceedings of the International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference, Blacksburg, VA, USA, 27 June–1 July 2016; Volume 2, pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, C.; Lu, Y.; Nastasi, M.; Cui, B. Laser shock processing of polycrystalline alumina ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 100, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundar, R.; Sudha, C.; Rai, A.K.; Ganesh, P.; Kolhatkar, A.; Murugesan, S.; Karthik, V.; Biswal, R.; Raju, S.; Ranganathan, K.; et al. Effect of laser shock peening on the microstructure, tensile and heat transport properties of Alloy D9. Lasers Manuf. Mater. Process. 2020, 7, 259–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yao, Z.; Deng, Q. Experimental study on laser shock processing of brass. J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing Miner. Metall. Mater. 2007, 14, 529–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.K.; Sunil Kumar, B.; Sundar, R.; Ram Sankar, P.; Ganesh, P.; Kaul, R.; Kain, V.; Ranganathan, K.; Bindra, K.S.; Singh, B. Enhancement of intergranular corrosion resistance of type 304 stainless steel through laser shock peening. Corros. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadge, P.; Gupta, P.K.; Sasikumar, C. Surface Nano-crystallizationof AISI 304 Stainless Steel through Shot Peening Technique. Mater. Today Proc. 2015, 2, 3245–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Song, G.; Niu, W.; Xu, Z.; Huang, C. Effect of shot peening on fatigue crack propagation of Ti6Al4V. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 25, 101430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasikumar, K.S.K.; Dineshkumar, K.; Deeban, K.; Sambathkumar, M.; Saravanan, N. Effect of shot peening on surface properties of Al7075 hybrid aluminum metal matrix composites. In Proceedings of the Materials Today: Proceedings; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 33, pp. 2792–2794. [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer, W.; Frey, T. Strengthening of ceramics by shot peening. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2006, 26, 2639–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Guan, Y.; Zhu, L.; Li, Y.; Zhai, J.; Lin, J. Effects of ultrasonic shot peening process parameters on nanocrystalline and mechanical properties of pure copper surface. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 259, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Tao, N.; Hong, Y.; Xu, B.; Lu, J.; Lu, K. Microstructure and evolution of mechanically-induced ultrafine grain in surface layer of AL-alloy subjected to USSP. Acta Mater. 2002, 50, 2075–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A.; Malaki, M.; Eskandari, A. Strength enhancement of the welded structures by ultrasonic peening. Mater. Des. 2012, 38, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, X.; Ma, G. Effect of ultrasonic impact treatment on the stress corrosion cracking of 304 stainless steel welded joints. J. Press. Vessel Technol. Trans. ASME 2009, 131, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Shukla, P.; Subramaniyan, A.K.; Zammit, A.; Swanson, P.; Lawrence, J.; Fitzpatrick, M.E. Residual stresses induced by laser shock peening in orthopaedic Ti6Al7Nb alloy. Opt. Laser Technol. 2020, 131, 106446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sealy, M.P.; Guo, Y.B. Surface integrity and process mechanics of laser shock peening of novel biodegradable magnesium-calcium (Mg-Ca) alloy. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2010, 3, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakimets, I.; Richard, C.; Béranger, G.; Peyre, P. Laser peening processing effect on mechanical and tribological properties of rolling steel 100Cr6. Wear 2004, 256, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, E.; Unal, O.; Guagliano, M.; Bagherifard, S. The effects of shot peening, laser shock peening and ultrasonic nanocrystal surface modification on the fatigue strength of Inconel 718. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 810, 141029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathallah, R.; Sidhom, H.; Braham, C.; Castex, L. Effect of surface properties on high cycle fatigue behaviour of shot peened ductile steel. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2003, 19, 1050–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guagliano, M. Relating Almen intensity to residual stresses induced by shot peening: A numerical approach. J. Mater. Proc. Technol. 2001, 110, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liu, H.; Wei, P.; Zhu, C.; Lin, Q. Effect of shot peening coverage on hardness, residual stress and surface morphology of carburized rollers. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 384, 125273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M.; Matsui, T.; Murakami, Y. Mechanism of creation of compressive residual stress by shot peening. Int. J. Fatigue 1998, 20, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umemoto, M.; Todaka, Y.; Tsuchiya, K. Formation of Nanocrystalline Structure in Steels by Air Blast Shot Peening. Mater. Trans. 2003, 44, 1488–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llaneza, V.; Belzunce, F.J. Study of the effects produced by shot peening on the surface of quenched and tempered steels: Roughness, residual stresses and work hardening. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 356, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemenz, M.; Schulze, V.; Rohr, I.; Löhe, D. Application of the FEM for the prediction of the surface layer characteristics after shot peening. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2009, 209, 4093–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unal, O. Optimization of shot peening parameters by response surface methodology. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 305, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, Y.; Jeon, U.; Yoon, H. Use of response surface methodology for shot peening process optimization of an aircraft structural part. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 87, 2967–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, R.; Verma, C.S.; Rana, R.S.; Dwivedi, R.K.; Dwivedi, R.; Banoriya, D. Optimization of Process Parameters of Shot Peening Using ABQUS. Mater. Today Proc. 2017, 4, 2119–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Liu, H.; Zhu, C.; Chen, D.; Zhou, S. Effects of different shot peening parameters on residual stress, surface roughness and cell size. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 398, 126054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Wu, G.; Gan, J.; Yang, Y.; Huang, H.; He, J.; Zhong, H. Combining the finite element method and response surface methodology for optimization of shot peening parameters. Int. J. Fatigue 2019, 129, 105231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacı, H.; Bozkurt, Y.B.; Yetim, A.F.; Aslan, M.; Çelik, A. The effect of surface plastic deformation produced by shot peening on corrosion behavior of a low-alloy steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 360, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C. Plasma nitriding of AISI 304 austenitic stainless steel with pre-shot peening. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 204, 3222–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asquith, D.T.; Yerokhin, A.L.; Yates, J.R.; Matthews, A. The effect of combined shot-peening and PEO treatment on the corrosion performance of 2024 Al alloy. Thin Solid Films 2007, 516, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, S.; Guagliano, M. Review of shot peening processes to obtain nanocrystalline surfaces in metal alloys. Surf. Eng. 2009, 25, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani-Gangaraj, S.M.; Cho, K.S.; Voigt, H.J.L.; Guagliano, M.; Schuh, C.A. Experimental assessment and simulation of surface nanocrystallization by severe shot peening. Acta Mater. 2015, 97, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherifard, S.; Guagliano, M. Fatigue behavior of a low-alloy steel with nanostructured surface obtained by severe shot peening. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2012, 81, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherifard, S.; Ghelichi, R.; Guagliano, M. A numerical model of severe shot peening (SSP) to predict the generation of a nanostructured surface layer of material. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 204, 4081–4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Xing, S.; Li, J.; He, J.; Lu, Y.; Jiang, C.; Ji, V. Surface residual stress and microstructure evolutions of Hastelloy X alloy after severe shot peening. Vacuum 2021, 187, 110136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miková, K.; Bagherifard, S.; Bokuvka, O.; Guagliano, M.; Trško, L. Fatigue behavior of X70 microalloyed steel after severe shot peening. Int. J. Fatigue 2013, 55, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zheng, H.; Gu, X.; Jiang, B.; Liang, J. Effect of severe shot peening on corrosion behavior of AZ31 and AZ91 magnesium alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 770, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unal, O.; Cahit Karaoglanli, A.; Varol, R.; Kobayashi, A. Microstructure evolution and mechanical behavior of severe shot peened commercially pure titanium. Vacuum 2014, 110, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Yang, B.; Zhang, J.; Wu, M.; Lu, L. Effect of micro-shot peening, conventional shot peening and their combination on fatigue property of EA4T axle steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2020, 275, 116320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fern, I. TEM evaluation of steel nanocrystalline surfaces obtained by severe shot peening. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 418, 127238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhu, W.; Jiang, C.; Guagliano, M.; Xing, S.; Wang, L. Microstructure evolution and residual stress distribution of nanostructured Mg-8Gd-3Y alloy induced by severe shot peening. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 404, 126465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherifard, S.; Fernandez-Pariente, I.; Ghelichi, R.; Guagliano, M. Effect of severe shot peening on microstructure and fatigue strength of cast iron. Int. J. Fatigue 2014, 65, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Zhang, Z.; Hou, J.; Barber, G.C.; Qiu, F. Tribological behavior of shot peened/austempered AISI 5160 steel. Tribol. Int. 2020, 145, 106197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, M.; Kakishima, H. Improvement of tribological performance of steel by solid lubricant shot-peening in dry rolling/sliding contact wear tests. Wear 2006, 260, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundar, R.; Ganesh, P.; Gupta, R.K.; Ragvendra, G.; Pant, B.K.; Kain, V.; Ranganathan, K.; Kaul, R.; Bindra, K.S. Laser Shock Peening and its Applications: A Review. Lasers Manuf. Mater. Process. 2019, 6, 424–463. [Google Scholar]
- Montross, C.S.; Wei, T.; Ye, L.; Clark, G.; Mai, Y.W. Laser shock processing and its effects on microstructure and properties of metal alloys: A review. Int. J. Fatigue 2002, 24, 1021–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.; Wang, D.; Jing, H.; Huo, L. The effects of ultrasonic peening treatment on the ultra-long life fatigue behavior of welded joints. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 3299–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, D.; Xia, L.; Lei, Z.; Li, Y. Effects of ultrasonic impact treatment on pre-fatigue loaded high-strength steel welded joints. Int. J. Fatigue 2015, 80, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deguchi, T.; Mouri, M.; Hara, J. Fatigue strength improvement for ship structures by Ultrasonic Peening. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2012, 17, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daavari, M.; Sadough Vanini, S.A. Corrosion fatigue enhancement of welded steel pipes by ultrasonic impact treatment. Mater. Lett. 2015, 139, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaki, M.; Ding, H. A review of ultrasonic peening treatment. Mater. Des. 2015, 87, 1072–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statnikov, E.S.; Vityazev, V.N. Physics and mechanism of ultrasonic impact. Ultrasonics 2006, 44, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.D.; Sun, G.F.; Lu, Y.; Chen, M.Z.; Bi, K.D.; Ni, Z.H. Microstructural characterization and mechanical behavior of ultrasonic impact peened and laser shock peened AISI 316L stainless steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 385, 125403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Xie, J.; Chen, D.; Ma, Y.; Guo, D.; Shao, B.; Li, C.; Dong, J.; Cao, P.; Yoon, J.H. Observation of magnetic properties and microstructural evolution of 301 stainless steel upon ultrasonic shot peening. Materialia 2020, 10, 100651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Guan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xie, Z.; Lin, J. Influence of process parameters of ultrasonic shot peening on surface nanocrystallization and hardness of pure titanium. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 89, 1451–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Shen, J.; Hu, S.; Liang, Y.; Bai, P. Effects of ultrasonic peening treatment on surface quality of CMT-welds of Al alloys. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2018, 254, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Chattopadhyay, V.P.K.; Singh, V. Surface Nanocrystallization Induced by Ultrasonic Shot Peening and Its Effect on Corrosion Resistance of Ti–6Al–4V Alloy. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2019, 72, 789–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, C.S.; Chattopadhyay, K.; Singh, V.; Mahobia, G.S. Enhancement of low-cycle fatigue life of high-nitrogen austenitic stainless steel at low strain amplitude through ultrasonic shot peening. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 25, 101576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Jian, Y.; Zhao, X.; Meng, D.; Pan, F.; Han, Q. The tribological behavior of a surface-nanocrystallized magnesium alloy AZ31 sheet after ultrasonic shot peening treatment. J. Magnes. Alloys 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, V.; Singh, J.K.; Chattopadhyay, K.; Srinivas, N.C.S.; Singh, V. Influence of ultrasonic shot peening on corrosion behavior of 7075 aluminum alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 723, 826–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Han, Q.; Wang, S.; Xu, R. Microstructure, corrosion behaviour and thermal stability of AA 7150 after ultrasonic shot peening. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 398, 126127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Mahobia, G.S.; Chattopadhyay, K. Surface nanocrystallization of β-titanium alloy by ultrasonic shot peening. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 28, 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Tian, L.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J. Properties and formation mechanism of cladding layer on high-strength low-alloy steel subjected to ultrasonic impact treatment with titanium alloy pin. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 418, 127256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, Q.; Han, B.; Song, L.; Li, J.; Yang, J. Investigation on microstructure and properties of AlxCoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloys by ultrasonic impact treatment. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 816, 152626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Han, B.; Li, M.; Hu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y. Investigation on microstructure and properties of laser cladded AlCoCrCuFeNi high entropy alloy coating by ultrasonic impact treatment. Intermetallics 2021, 128, 107017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyre, P.; Berthe, L.; Fabbro, R.; Bartnicki, E. Experimental study of laser-driven shock waves in stainless steels. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 84, 5985–5992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatamleh, O. A comprehensive investigation on the effects of laser and shot peening on fatigue crack growth in friction stir welded AA 2195 joints. Int. J. Fatigue 2009, 31, 974–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montross, C.S.; Florea, V. The influence of coatings on subsurface mechanical properties of laser peened 2011-T3 aluminum. J. Mater. Sci. 2011, 6, 1801–1807. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, G.J.; Shehadeh, M.A. Dislocation behavior in silicon crystal induced by laser shock peening: A multiscale simulation approach. Scr. Mater. 2005, 53, 1013–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.; Wang, S.; Guo, D.; Wu, H.; Wang, J.; Dai, Y.; Xia, X.; Xie, Y. Confining Medium and Absorptive Overlay: Their Effects on a Laser-induced Shock Wave. Opt. Lasers Eng. 1998, 29, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Jin, H.; Gu, Y.; Ren, A.; Huang, L.; Qian, X. Optics & Laser Technology Research on precision control of sheet metal forming by laser shock waves with semi-die. Opt. Laser Technol. 2013, 45, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Bhamare, S.; Ramakrishnan, G.; Mannava, S.R.; Langer, K.; Wen, Y.; Qian, D.; Vasudevan, V.K. Thermal relaxation of residual stress in laser shock peened Ti–6Al–4V alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2012, 206, 4619–4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thareja, R.K.; Shukla, S. Synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles by laser ablation of zinc in liquid. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 253, 8889–8895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, X.; Peng, W.; Ma, G. Influence of Laser Peening Parameters on Residual Stress Field of 304 Stainless Steel. J. Press. Vessel Technol. 2008, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddaiah, A.; Mao, B.; Liao, Y.; Menezes, P.L. Surface characterization and tribological performance of laser shock peened steel surfaces. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 351, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, B.; Swaroop, S. Review: Laser shock peening as post welding treatment technique. J. Manuf. Process. 2018, 32, 721–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercelis, P.; Kruth, J.P. Residual stresses in selective laser sintering and selective laser melting. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2006, 12, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.K.; Lu, J.Z.; Dai, F.Z.; Feng, A.X.; Luo, K.Y.; Zhong, J.S.; Wang, Q.W.; Luo, M.; Qi, H. Effects of laser shock processing on electrochemical corrosion resistance of ANSI 304 stainless steel weldments after cavitation erosion. Corros. Sci. 2013, 66, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Fang, Y.; Madigan, B.; Xu, G.; Zhou, J. Investigation of microstructures and residual stresses in laser peened Incoloy 800H weldments. Opt. Laser Technol. 2014, 57, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, A.; Muvvala, G.; Sarkar, S.; Racherla, V.; Nath, A.K. Effect of laser shock peening on microstructural, mechanical and corrosion properties of laser beam welded commercially pure titanium. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 133, 106527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.T.; Zhang, Y.K.; Chen, J.F.; Zhou, J.Y.; Ge, M.Z.; Lu, Y.L.; Li, X.L. Effects of laser shock peening on stress corrosion behavior of 7075 aluminum alloy laser welded joints. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 647, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Guo, W.; Jia, Q.; Chen, G.; Chi, J.; Zhang, H.; Wu, S.; Peng, C.; Peng, P. Effects of laser shock peening on microstructure and mechanical properties of TIG welded alloy 600 joints. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 808, 140914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Feng, X.; Teng, J.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, L. Effect of laser shock peening on microstructure and fatigue properties of thin-wall welded Ti-6A1-4V alloy. Vacuum 2021, 184, 109986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekar, G.; Kailasanathan, C.; Verma, D.K. Investigation on un-peened and laser shock peened weldment of Inconel 600 fabricated by ATIG welding process. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 690, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Sun, S.; Xu, S.; Li, Y.; Ren, G. Microstructure and properties in the weld surface of friction stir welded 7050-T7451 aluminium alloys by laser shock peening. Vacuum 2018, 152, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyre, P.; Scherpereel, X.; Berthe, L.; Carboni, C.; Fabbro, R.; Béranger, G.; Lemaitre, C. Surface modifications induced in 316L steel by laser peening and shot-peening. Influence on pitting corrosion resistance. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2000, 280, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruschau, J.J.; John, R.; Thompson, S.R.; Nicholas, T. Fatigue crack nucleation and growth rate behavior of laser shock peened titanium. Int. J. Fatigue 1999, 21, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, P.; Sundar, R.; Kumar, H.; Kaul, R.; Ranganathan, K.; Hedaoo, P.; Tiwari, P.; Kukreja, L.M.; Oak, S.M.; Dasari, S.; et al. Studies on laser peening of spring steel for automotive applications. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2012, 50, 678–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackel, L.; Rankin, J.R.; Rubenchik, A.; King, W.E.; Matthews, M. Laser peening: A tool for additive manufacturing post-processing. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 24, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juijerm, P.; Altenberger, I. Residual stress relaxation of deep-rolled Al-Mg-Si-Cu alloy during cyclic loading at elevated temperatures. Scr. Mater. 2006, 55, 1111–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Wang, Z.; Cai, J.; Xu, X.; Luo, K.; Wu, L.; Lu, J. Effects of laser shock peening on the hot corrosion behaviour of the selective laser melted Ti6Al4V titanium alloy. Corros. Sci. 2021, 188, 109558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Luo, P.; Yue, G.; Hu, Y. Analysis of microstructure and high-temperature tensile properties of 2060 Al-Li alloy strengthened by laser shock peening. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 860, 158539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Chen, H.; Huang, W.; Chen, J.; Zuo, L.; Li, C.; He, J.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, S. Effect of laser shock peening on high cycle fatigue properties of aluminized AISI 321 stainless steel. Int. J. Fatigue 2021, 147, 106180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
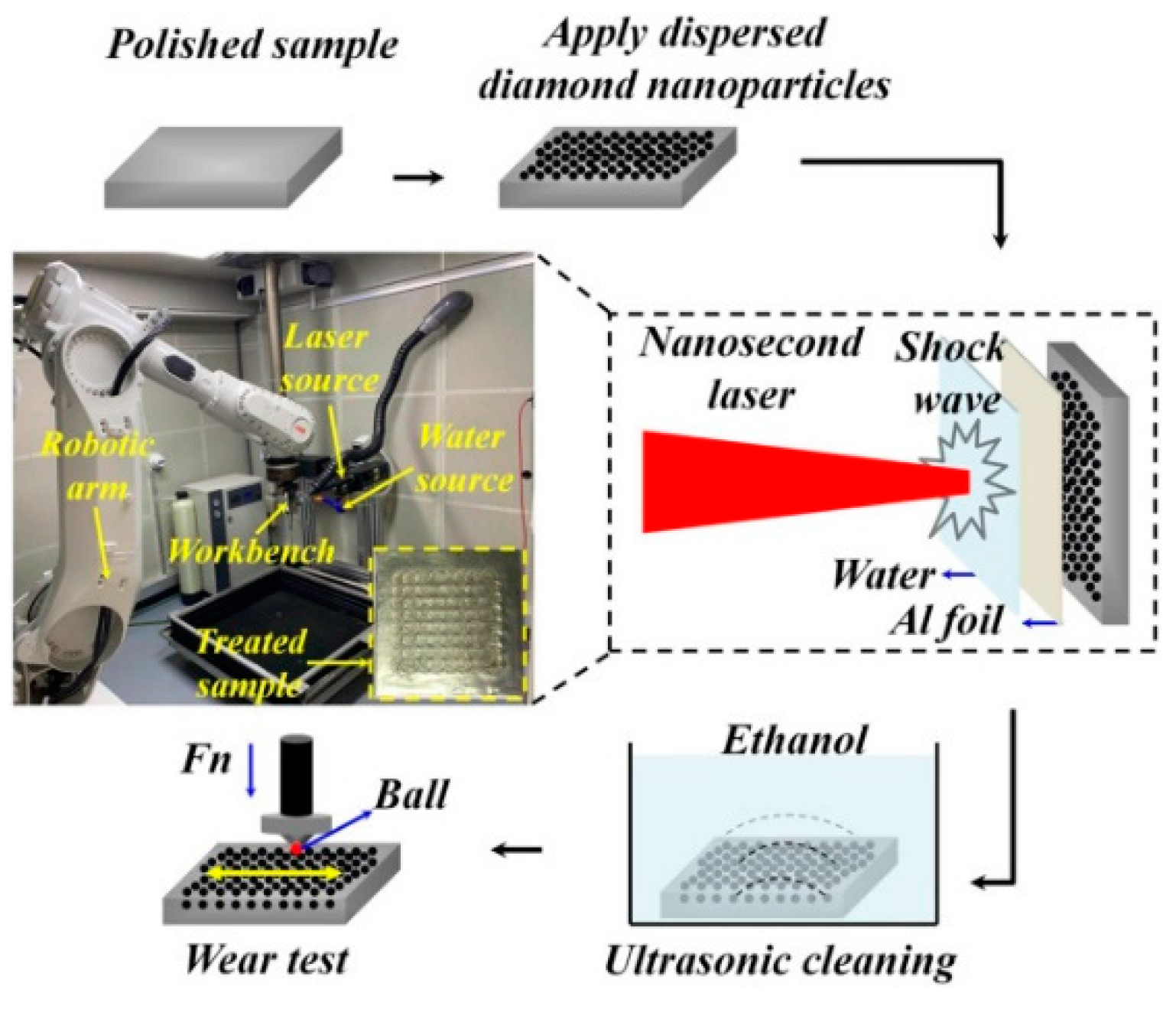
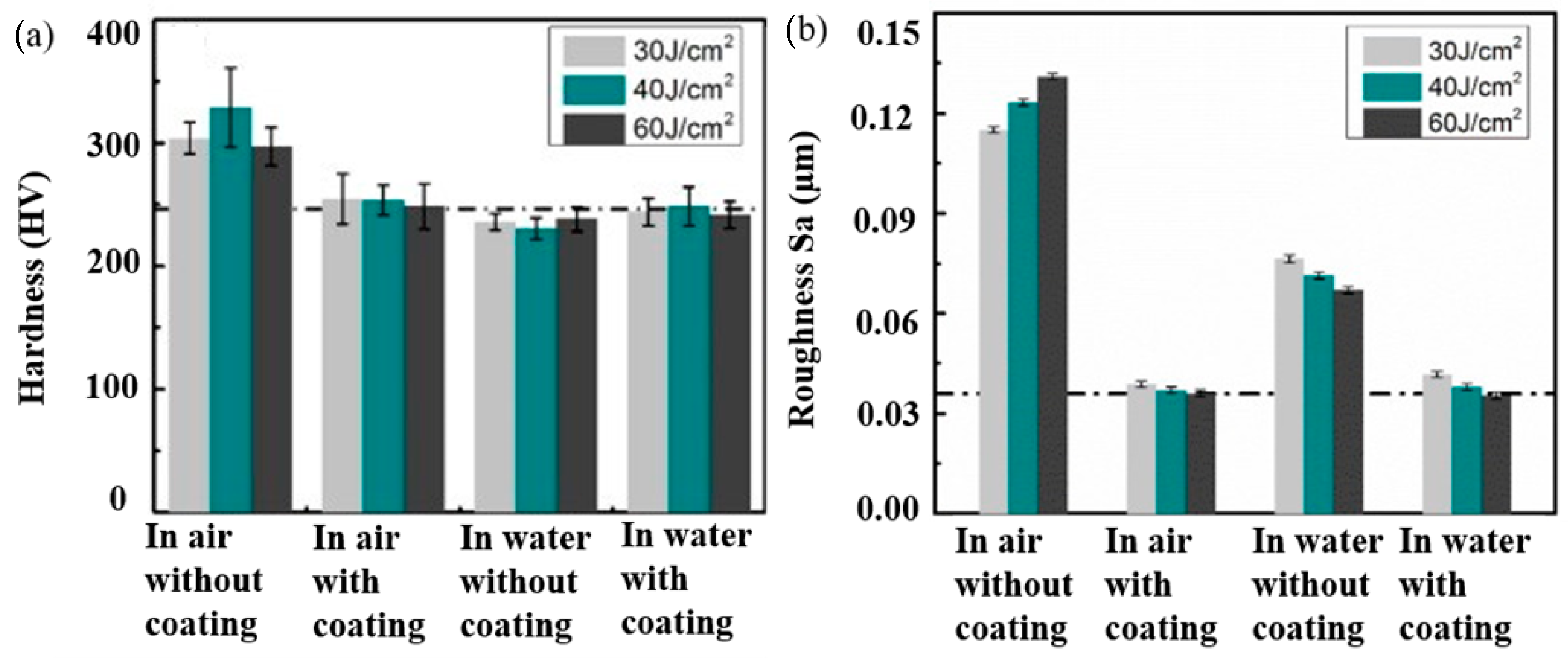
- Lu, H.; Ren, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, H.; Xin, Z.; Wan, H.; Li, Z.; Tu, X.; Cheng, L.; He, K.; et al. Wear resistance of 20Cr2Ni4A alloy steel treated by laser shock peening and implantation of diamond nanoparticles. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 412, 127070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maawad, E.; Sano, Y.; Wagner, L.; Brokmeier, H.G.; Genzel, C. Investigation of laser shock peening effects on residual stress state and fatigue performance of titanium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 536, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakino, Y.; Sano, Y.; Kim, Y. Application of laser peening without coating on steel welded joints. Int. J. Struct. Integr. 2011, 2, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, Y.; Masaki, K.; Gushi, T.; Sano, T. Improvement in fatigue performance of friction stir welded A6061-T6 aluminum alloy by laser peening without coating. Mater. Des. 2012, 36, 809–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Xu, H.; Zou, S.; Che, Z. Investigation of surface integrity on TC17 titanium alloy treated by square-spot laser shock peening. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2012, 25, 650–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altenberger, I.; Stach, E.A.; Liu, G.; Nalla, R.K.; Ritchie, R.O. An in situ transmission electron microscope study of the thermal stability of near-surface microstructures induced by deep rolling and laser-shock peening. Scr. Mater. 2003, 48, 1593–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
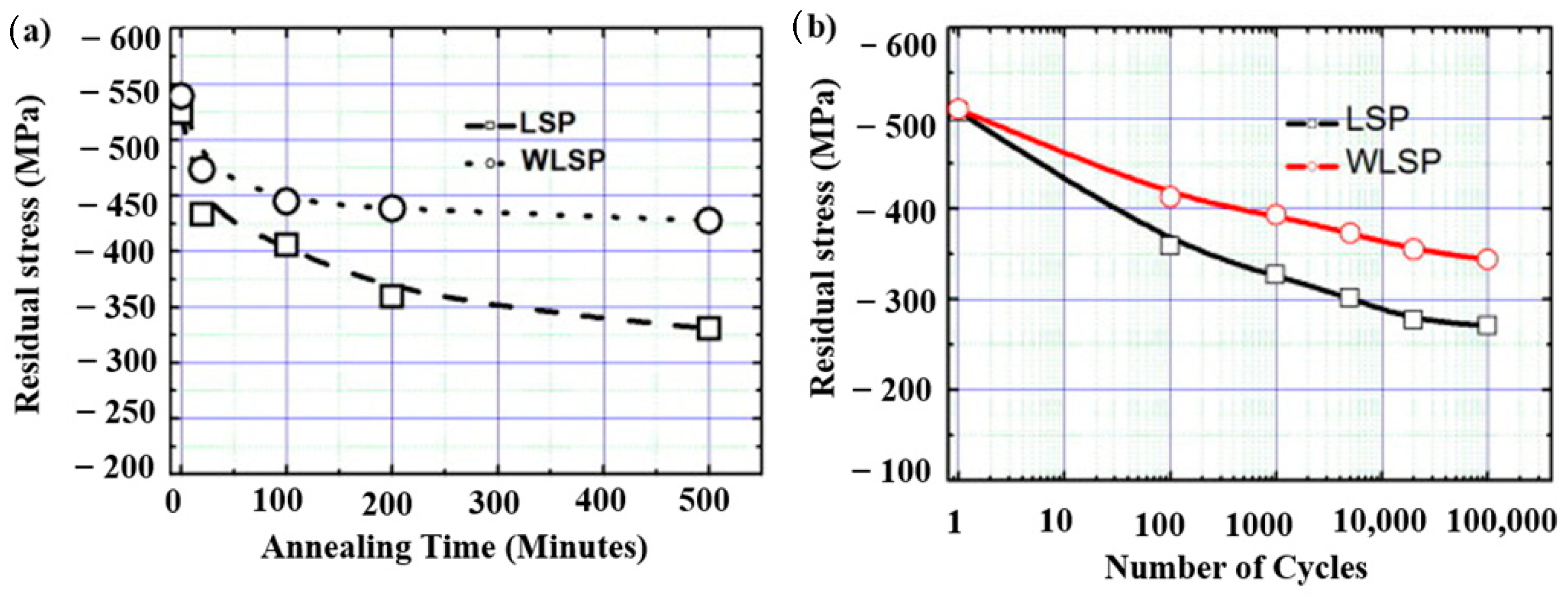
- Tani, G.; Orazi, L.; Fortunato, A.; Ascari, A.; Campana, G. Warm Laser Shock Peening: New developments and process optimization. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2011, 60, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Suslov, S.; Ye, C.; Cheng, G.J. The mechanisms of thermal engineered laser shock peening for enhanced fatigue performance. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 4997–5009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Suslov, S.; Kim, B.J.; Stach, E.A.; Cheng, G.J. Fatigue performance improvement in AISI 4140 steel by dynamic strain aging and dynamic precipitation during warm laser shock peening. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 1014–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, J.; Huang, S.; Zhou, J. Improvement of Damping Property and Its E ff ects on the Vibration Fatigue in Ti6Al4V Titanium Alloy Treated by Warm Laser Shock Peening. Metals 2019, 9, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, J.; Liu, L.; Feng, A.; Huang, S.; Meng, X. High-cycle bending fatigue behavior of TC6 titanium alloy subjected to laser shock peening assisted by cryogenic temperature. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 409, 126848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
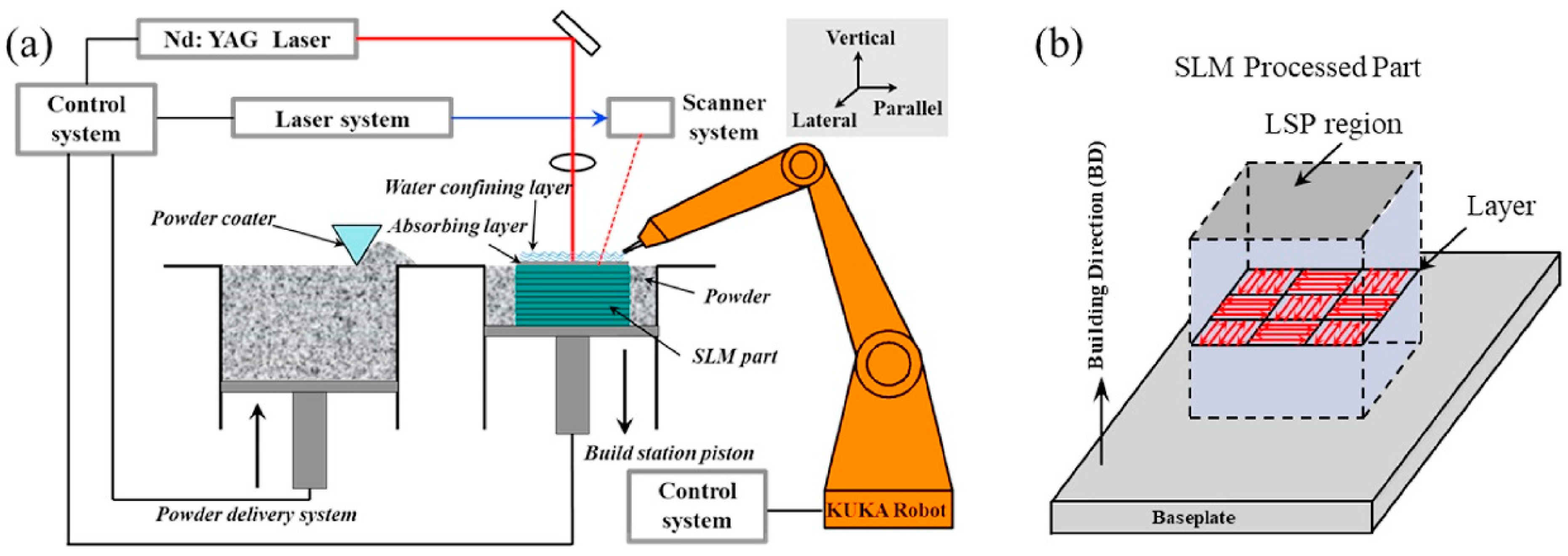
- Kalentics, N.; de Seijas, M.O.V.; Griffiths, S.; Leinenbach, C.; Logé, R.E. 3D laser shock peening—A new method for improving fatigue properties of selective laser melted parts. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 33, 101112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaeh, M.F.; Branner, G. Investigations on residual stresses and deformations in selective laser melting. Prod. Eng. 2010, 4, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Lu, H.; Xu, X.; Yao, J.; Cai, J.; Luo, K. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture High-performance integrated additive manufacturing with laser shock peening—Induced microstructural evolution and improvement in mechanical properties of Ti6Al4V alloy components. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2020, 148, 103475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalentics, N.; Sohrabi, N.; Tabasi, H.G.; Griffiths, S.; Jhabvala, J.; Leinenbach, C.; Burn, A.; Logé, R.E. Healing cracks in selective laser melting by 3D laser shock peening. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 30, 100881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, H.; Tsuyama, M.; Miyauti, S.; Shibayanagi, T.; Tsukamoto, M.; Abe, N. Femtosecond and nanosecond laser peening of stainless steel. J. Laser Micro Nanoeng. 2010, 5, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, H. Femtosecond Laser Peening of Stainless Steel. J. Laser Micro Nanoeng. 2009, 4, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ren, Z.; Jia, X.; Yang, W.; Nassreddin, N.; Dong, Y.; Ye, C.; Fortunato, A.; Zhao, X. The effects of the confining medium and protective layer during femtosecond laser shock peening. Manuf. Lett. 2021, 27, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yocom, C.J.; Zhang, X.; Liao, Y. Research and development status of laser peen forming: A review. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 108, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagisaka, Y.; Kamiya, M.; Matsuda, M.; Ohta, Y. Application of femtosecond laser peen forming to sheet metal bending. J. Laser Micro Nanoeng. 2012, 7, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagisaka, Y.; Kamiya, M.; Matsuda, M.; Ohta, Y. Thin-sheet-metal bending by laser peen forming with femtosecond laser. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2010, 210, 2304–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Xu, X.; Yao, Z.; Hu, J. Laser peen forming induced two way bending of thin sheet metals and its mechanisms Laser peen forming induced two way bending of thin sheet metals. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, B.; Siddaiah, A.; Liao, Y.; Menezes, P.L. Laser surface texturing and related techniques for enhancing tribological performance of engineering materials: A review. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 53, 153–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, B.; Siddaiah, A.; Menezes, P.L.; Liao, Y. Surface texturing by indirect laser shock surface patterning for manipulated friction coefficient. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2018, 257, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Mao, B.; Siddaiah, A.; Menezes, P.L.; Liao, Y. Direct laser shock surface patterning of an AZ31B magnesium alloy: Microstructure evolution and friction performance. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2020, 275, 116333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ren, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Z.; Lin, D.; Zhang, R.; Graber, M.J.; Thomas, N.K.; Kerek, Z.D.; et al. Microstructure evolution and electroplasticity in Ti64 subjected to electropulsing-assisted laser shock peening. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 802, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yan, X.; Zhang, C.; Deng, L.; Lu, Y.; Nastasi, M. Materialia Localized plasticity in silicon carbide ceramics induced by laser shock processing. Materialia 2019, 6, 100265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanrad, S.; Tong, J. Procedia Engineering Characterization of foreign object damage (FOD) and early fatigue crack growth in laser shock peened Ti6AL4V aerofoil specimens. Procedia Eng. 2010, 2, 1751–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Vukelic, S.; Yao, Y.L. Numerical Investigation of Opposing Dual Sided Microscale Laser Shock Peening. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2006, 129, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cellard, C.; Retraint, D.; François, M.; Rouhaud, E.; Le Saunier, D. Laser shock peening of Ti-17 titanium alloy: Influence of process parameters. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 532, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, B.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Zhong, Q. Very high cycle fatigue behavior of shot-peened 3Cr13 high strength spring steel. Mater. Des. 2013, 50, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, A.; Schulze, V.; Vo, O. Effects of warm peening on fatigue life and relaxation behaviour of residual stresses in AISI 4140 steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2000, 293, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peral, L.B.; Zafra, A.; Bagherifard, S.; Guagliano, M.; Fernández-Pariente, I. Effect of warm shot peening treatments on surface properties and corrosion behavior of AZ31 magnesium alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 401, 126285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Shen, J.; Hu, S.; Han, J.; Wang, Q.; Cai, Y. Effects of ultrasonic peening treatment layer by layer on microstructure of components fabricated by wire and arc additive manufacturing. Mater. Lett. 2021, 284, 128917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Duan, B.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Si, C. Effect of ultrasonic shot peening on microstructure evolution and corrosion resistance of selective laser melted Ti6Al4V alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 11, 1090–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lago, J.; Trško, L.; Jambor, M.; Nový, F.; Bokůvka, O.; Mičian, M.; Pastorek, F. Fatigue Life Improvement of the High Strength Steel Welded Joints by Ultrasonic Impact Peening. Metals 2019, 9, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammersley, G.; Hackel, L.A.; Harris, F. Surface prestressing to improve fatigue strength of components by laser shot peening. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2000, 34, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhao, J.; Qiao, H.; Hu, X.; Yang, Y. The new technologies developed from laser shock processing. Materials 2020, 13, 1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Ling, X.; Zhang, M. Influence of surface modifications by laser shock processing on the acid chloride stress corrosion cracking susceptibility of AISI 304 stainless steel. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2018, 91, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.Z.; Luo, K.Y.; Yang, D.K.; Cheng, X.N.; Hu, J.L.; Dai, F.Z.; Qi, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhong, J.S.; Wang, Q.W.; et al. Effects of laser peening on stress corrosion cracking (SCC) of ANSI 304 austenitic stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 2012, 60, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Liu, X.; Yeung, K.W.K.; Guo, H.; Li, P.; Hu, T.; Chung, C.Y.; Chu, P.K. Surface nano-architectures and their effects on the mechanical properties and corrosion behavior of Ti-based orthopedic implants. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 233, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavarz, M.; Tan, B.; Venkatakrishnan, K. Functionalized Stress Component onto Bio-template as a Pathway of Cytocompatibility. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanov, A.; Karimbaev, R.; Maleki, E.; Unal, O.; Pyun, Y.S.; Amanov, T. Effect of combined shot peening and ultrasonic nanocrystal surface modification processes on the fatigue performance of AISI 304. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 358, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, N.; Tanaka, S.; Takasugi, T. Effects of combined plasma-carburizing and shot-peening on fatigue and wear properties of Ti6Al4V alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2009, 203, 1400–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
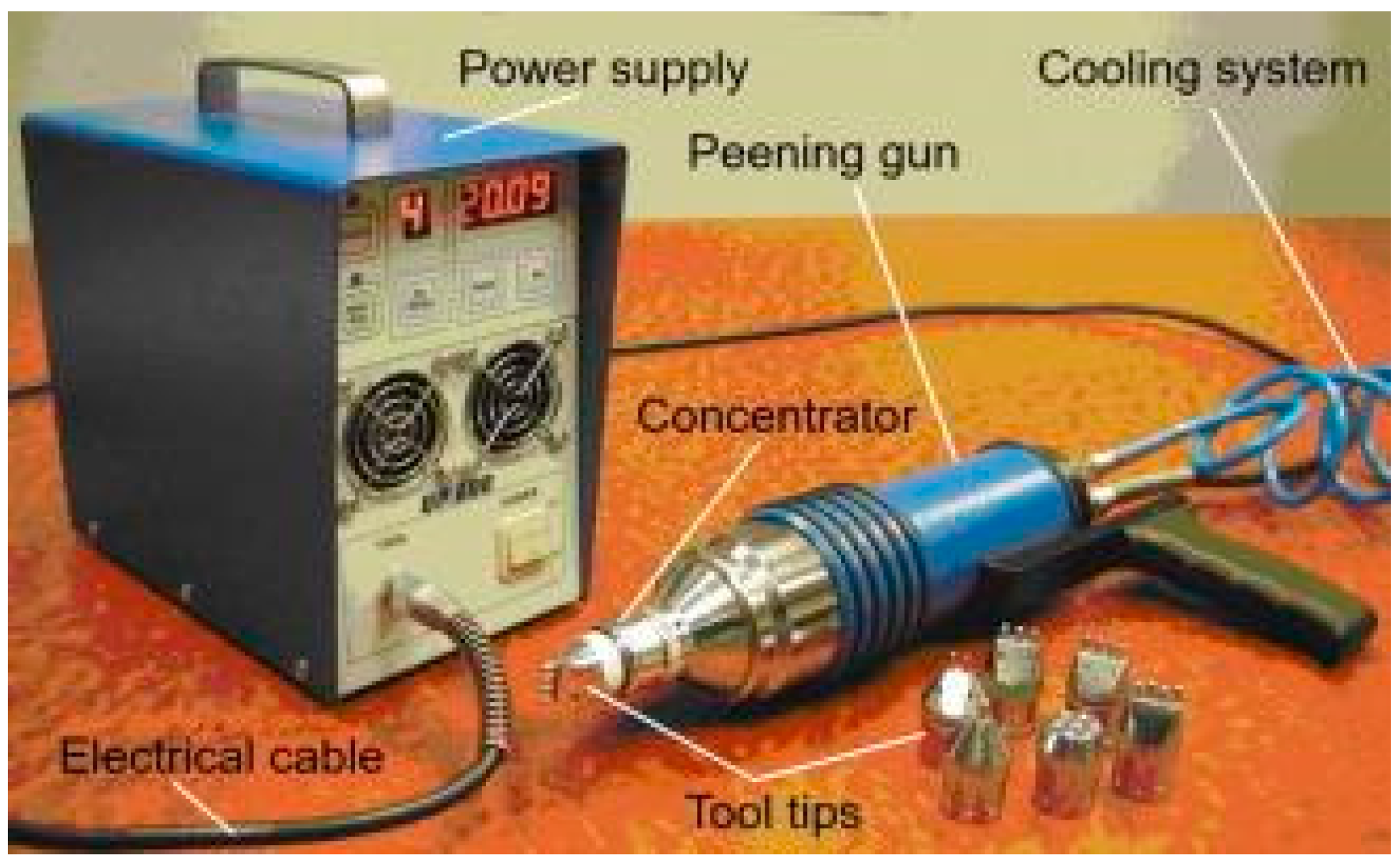
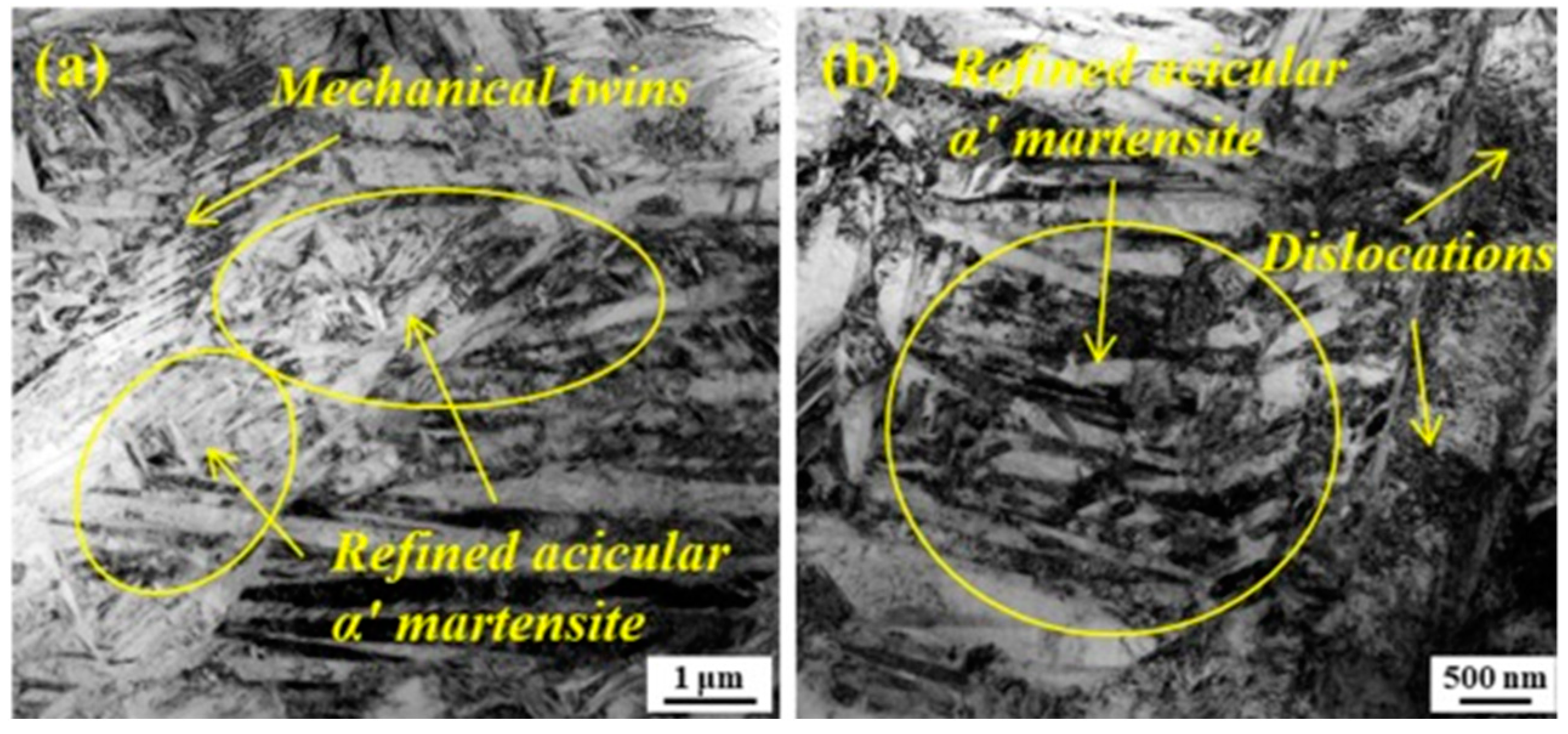

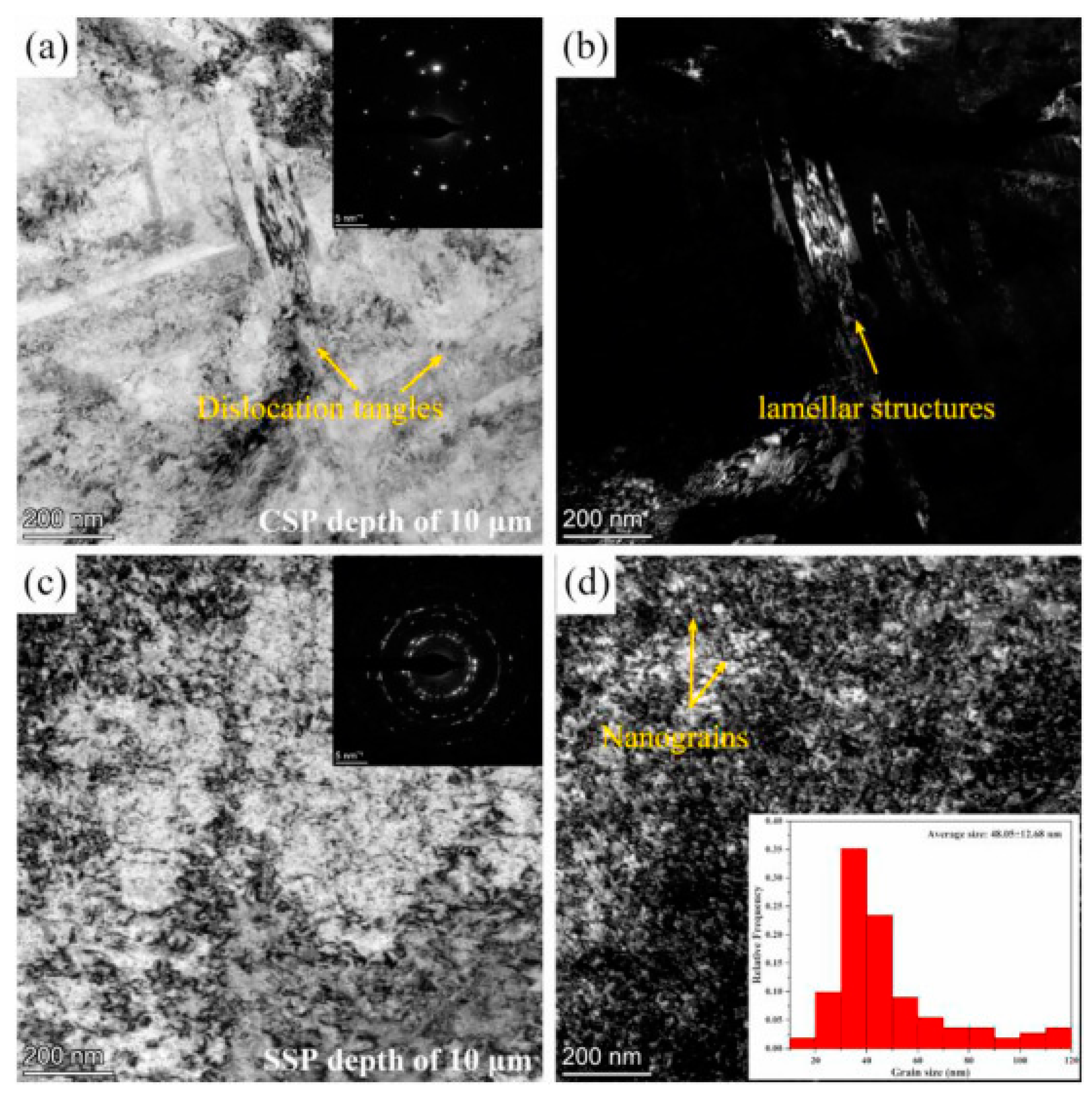
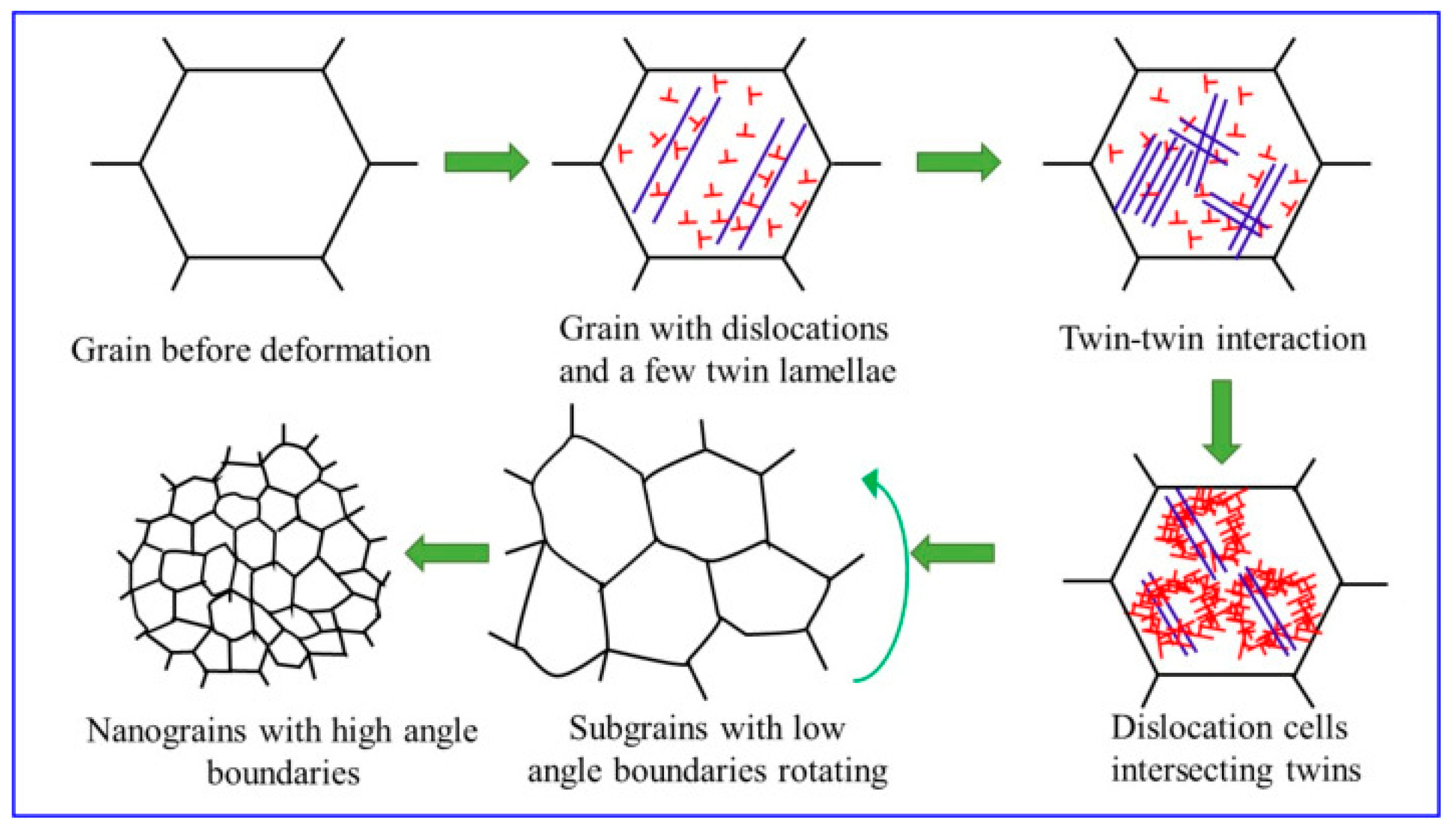

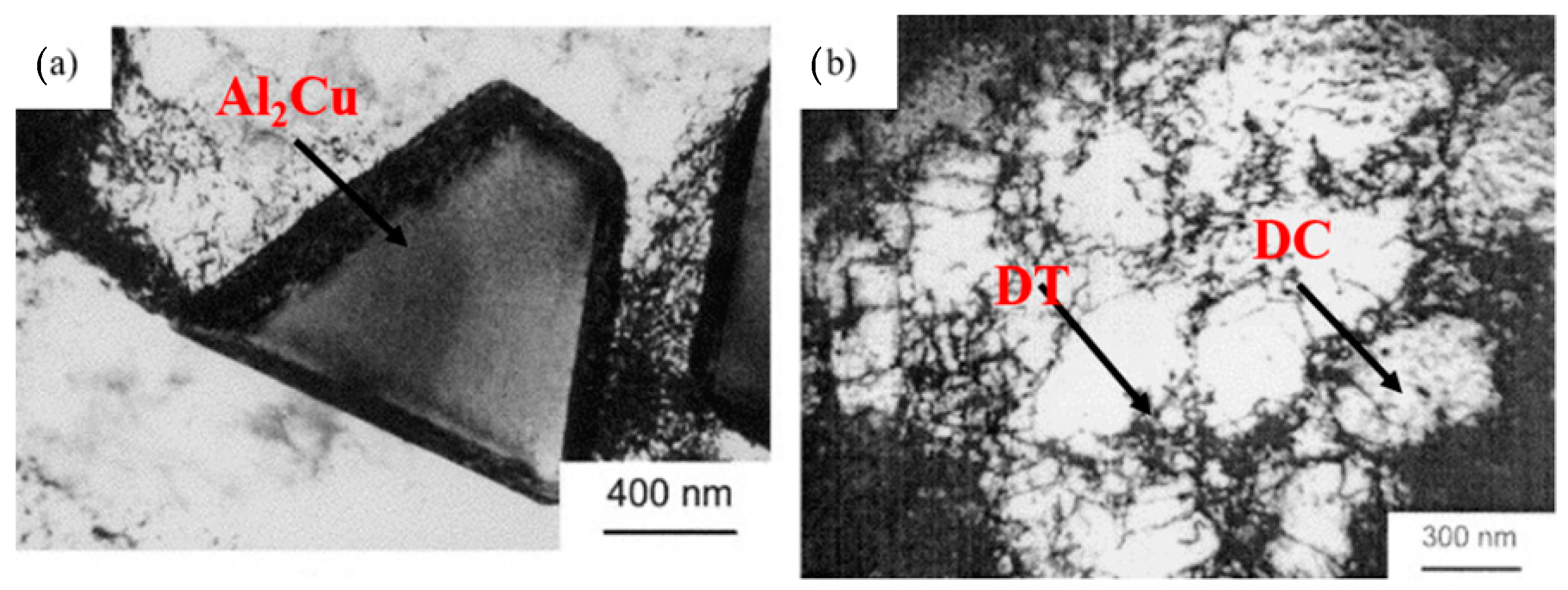
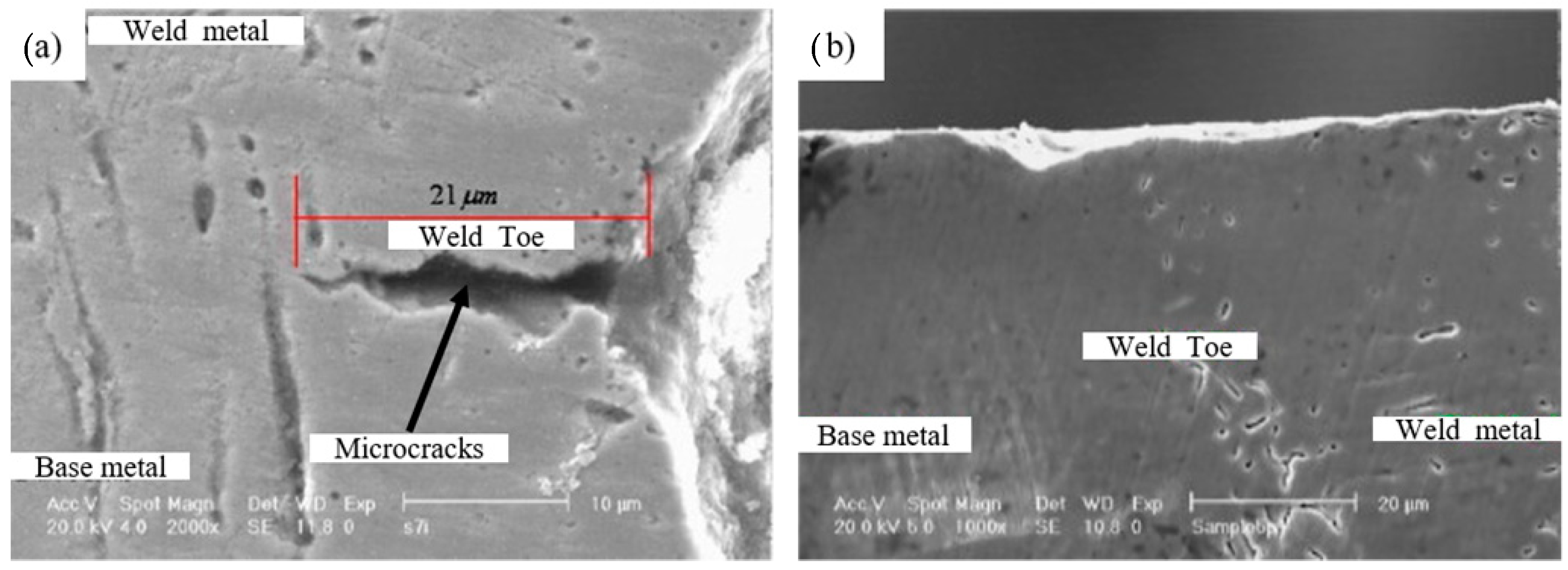

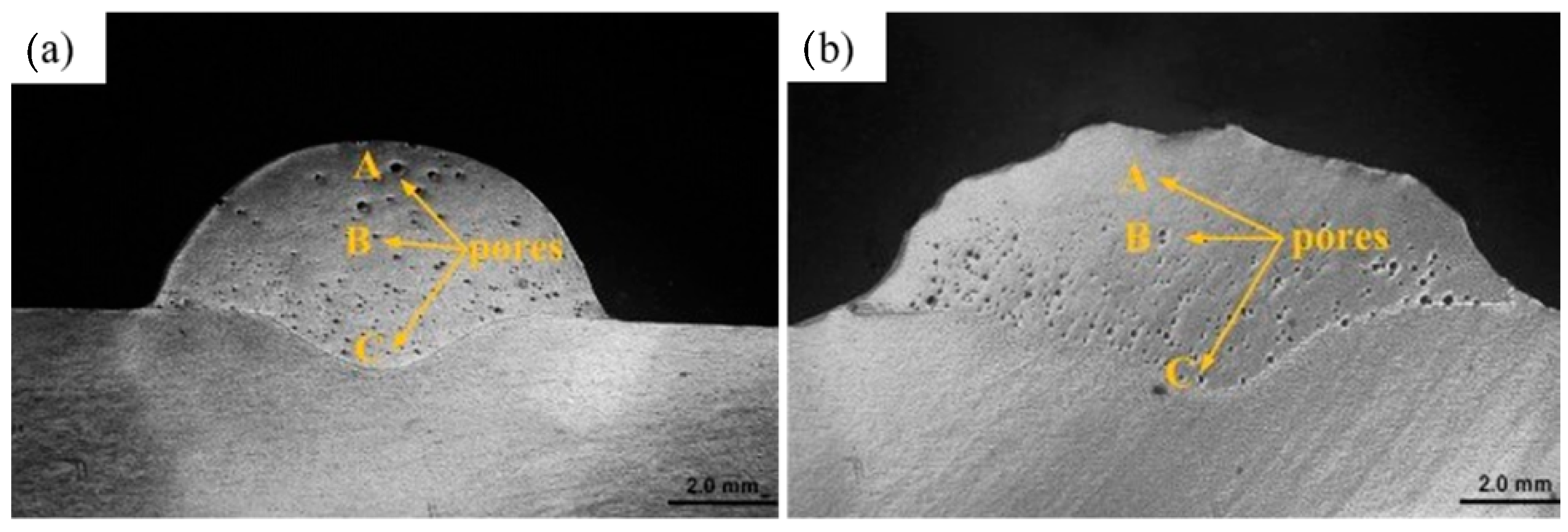
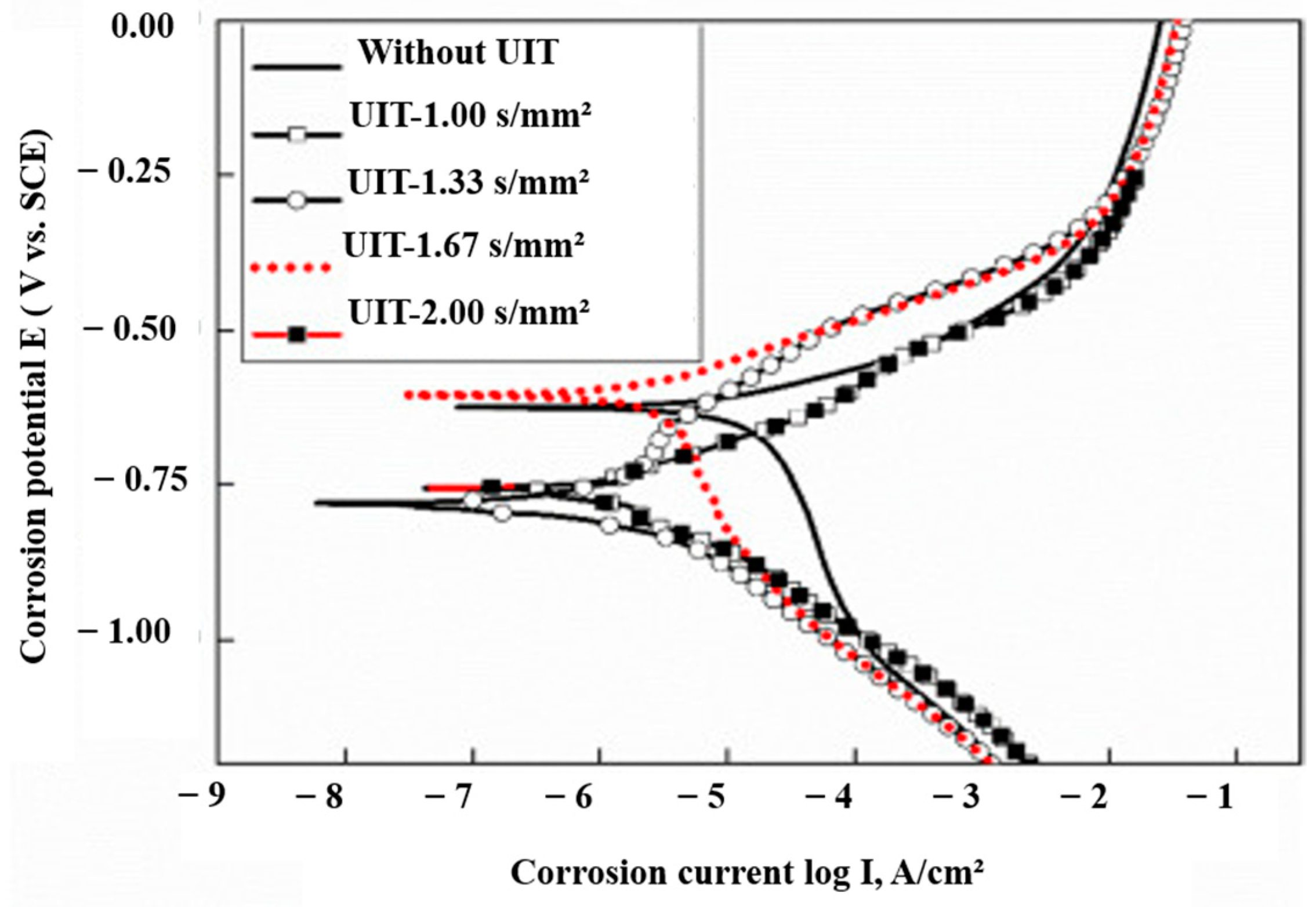
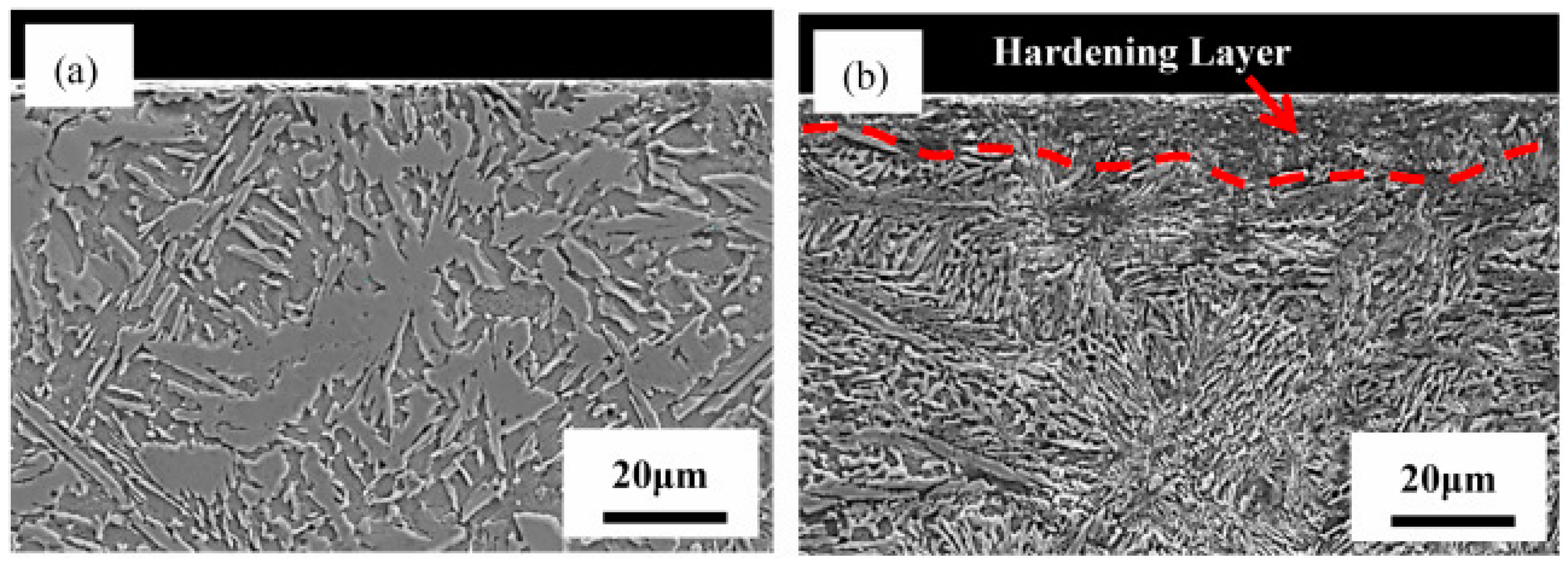
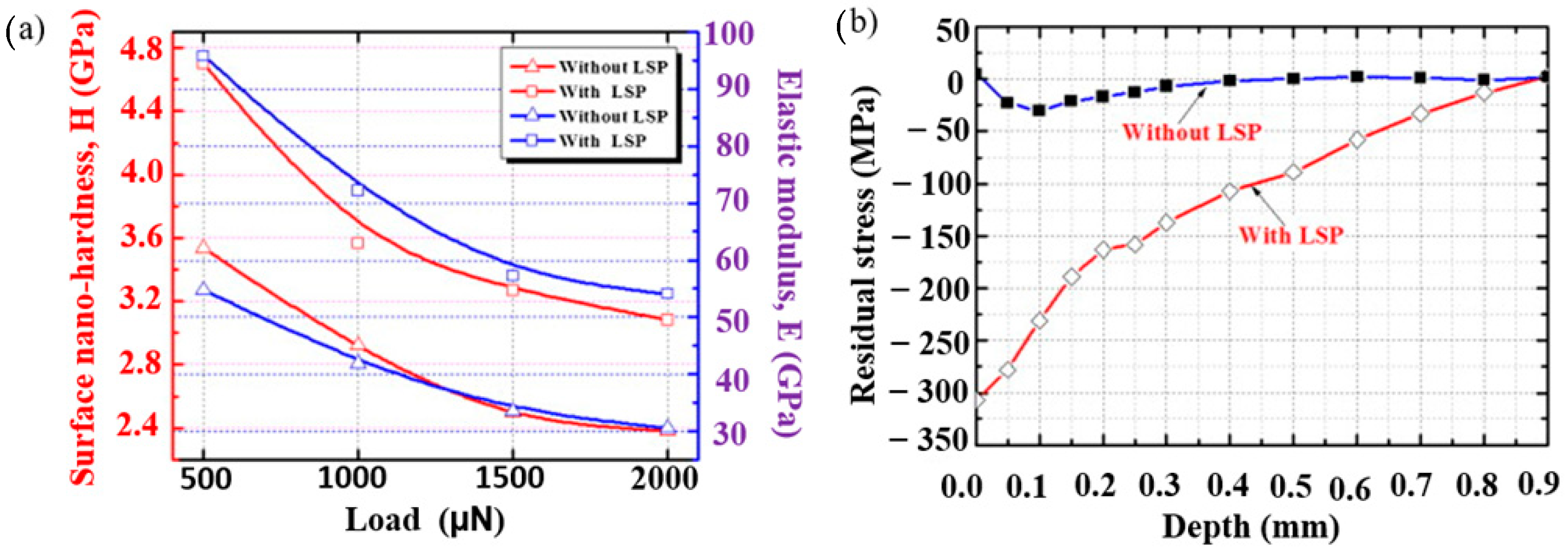
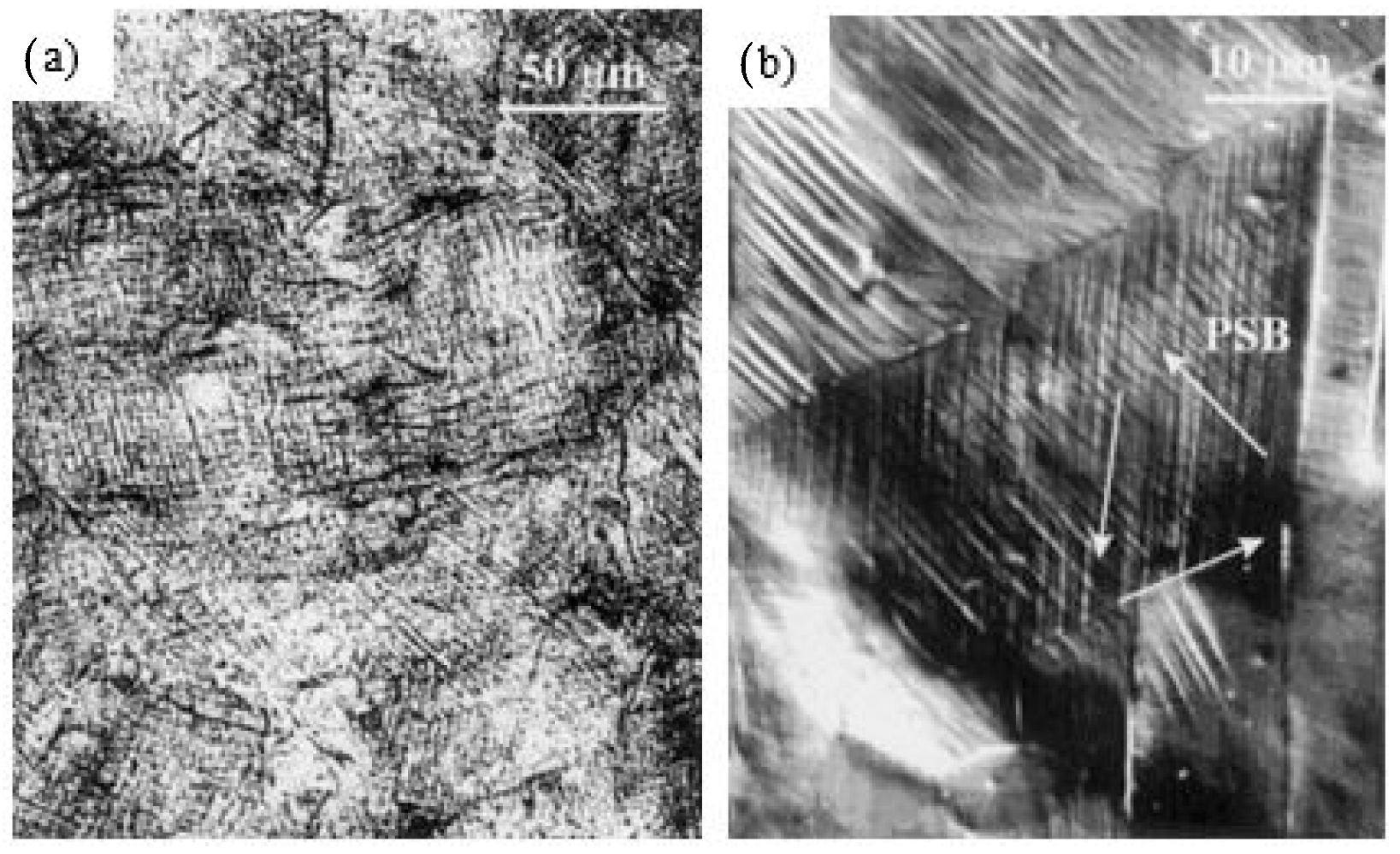
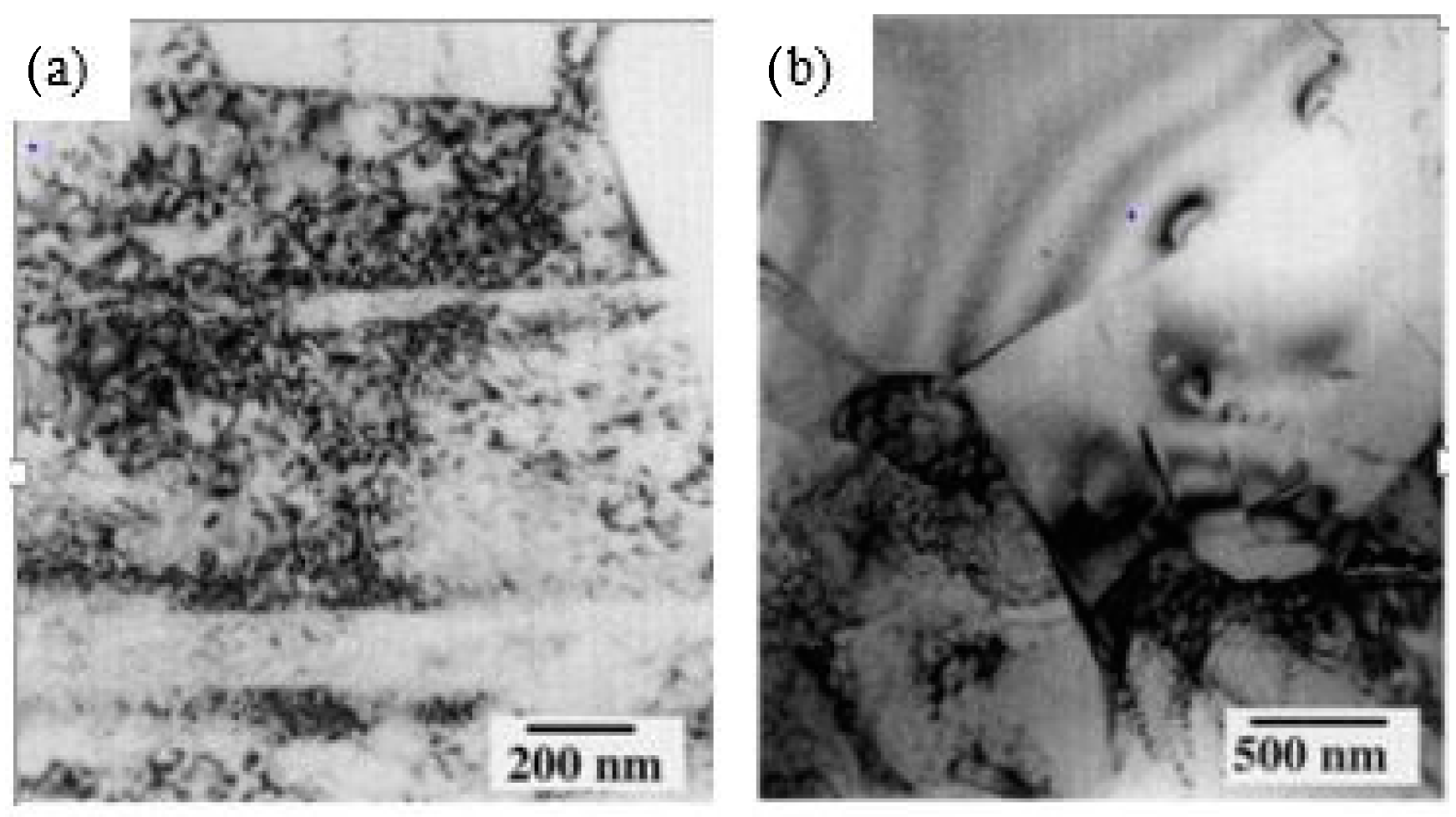
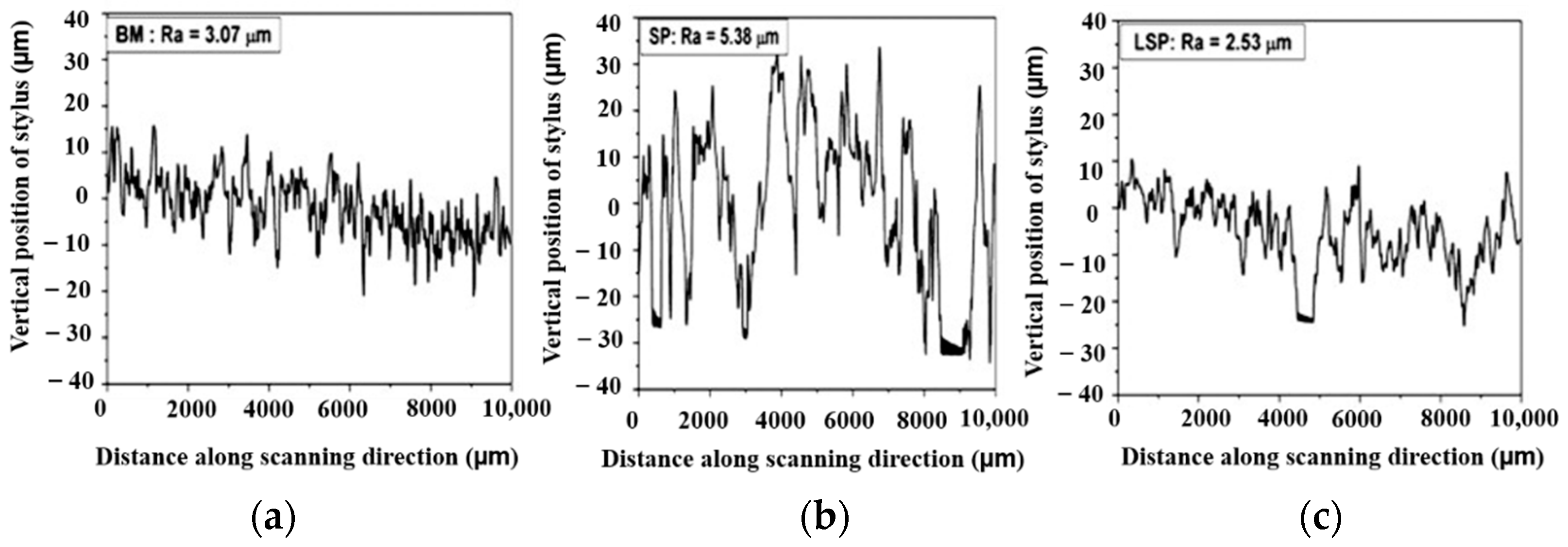

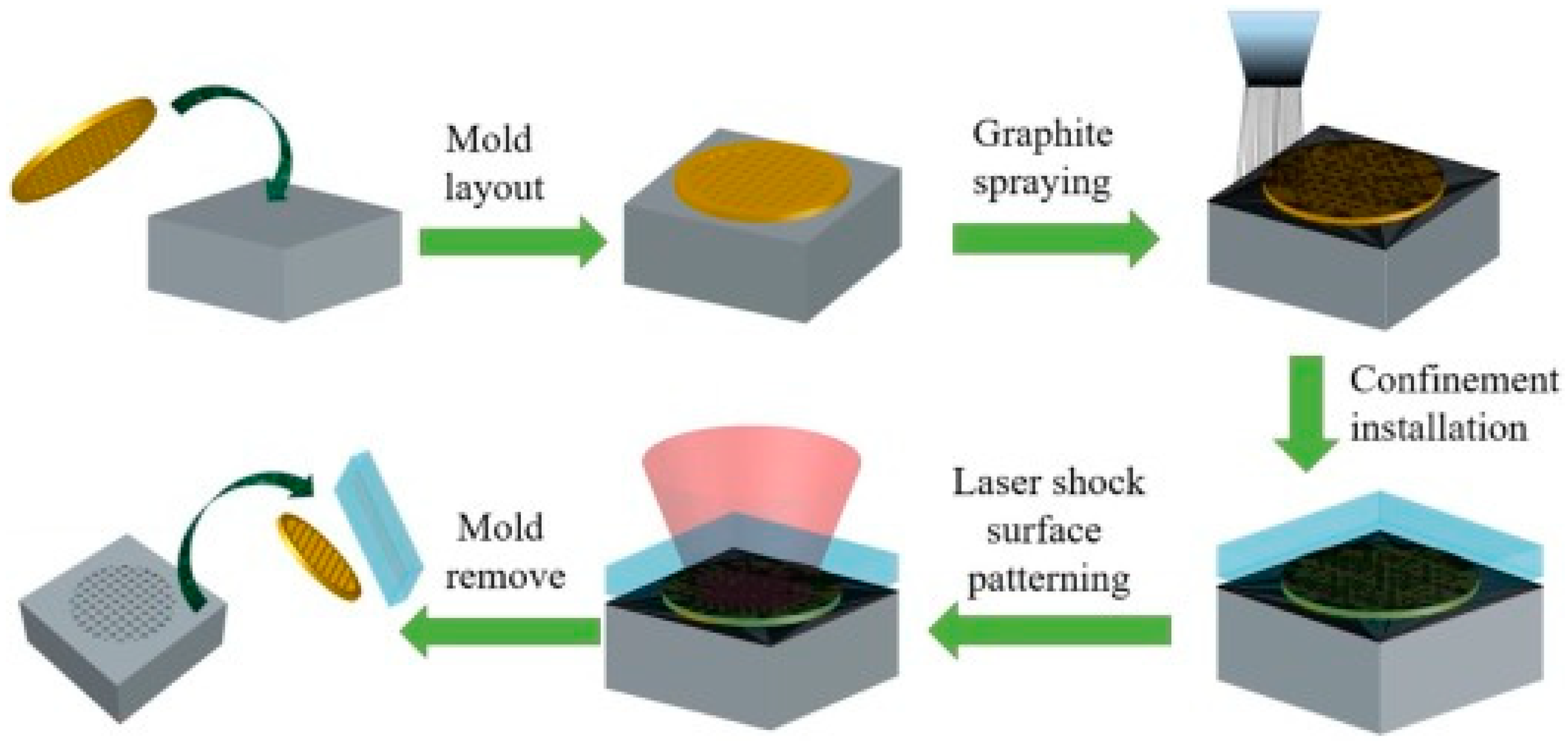
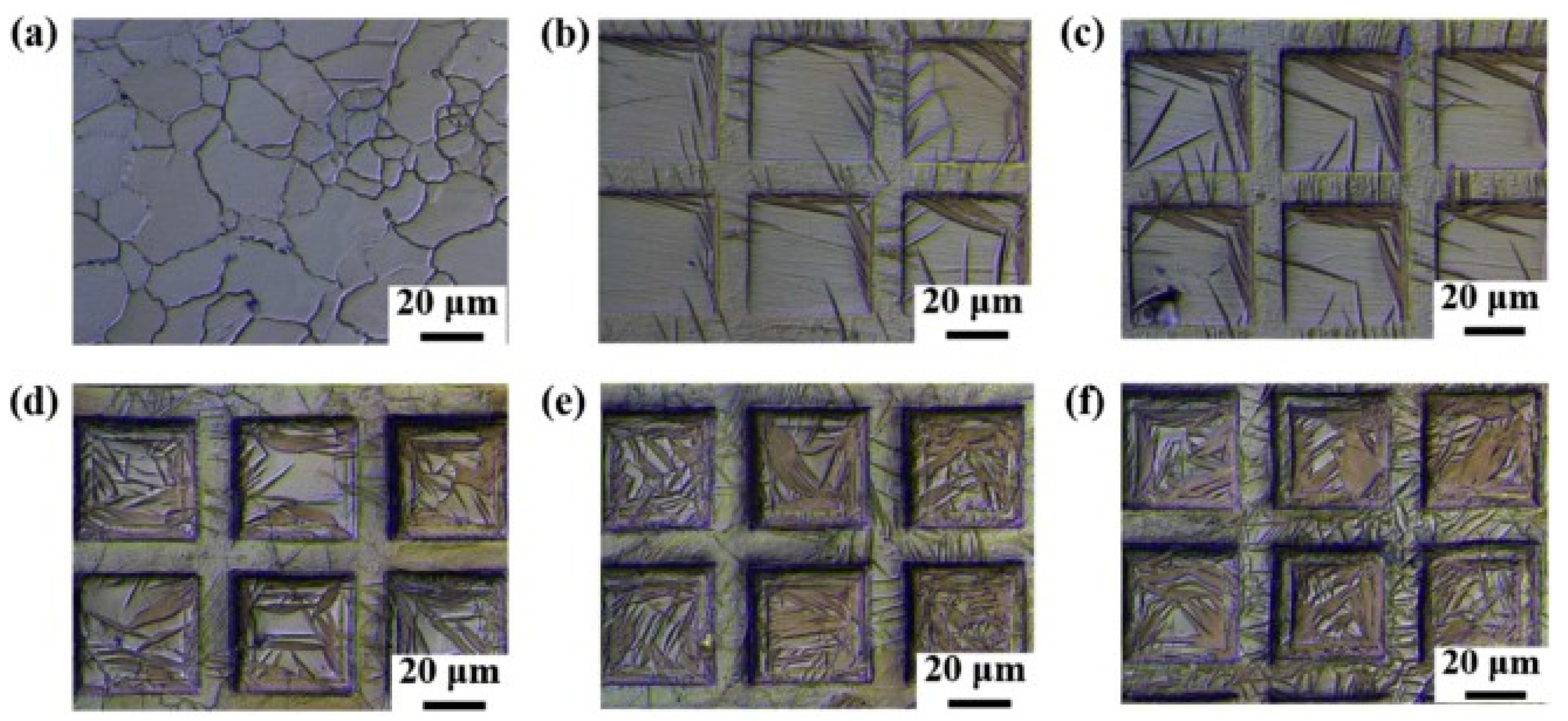
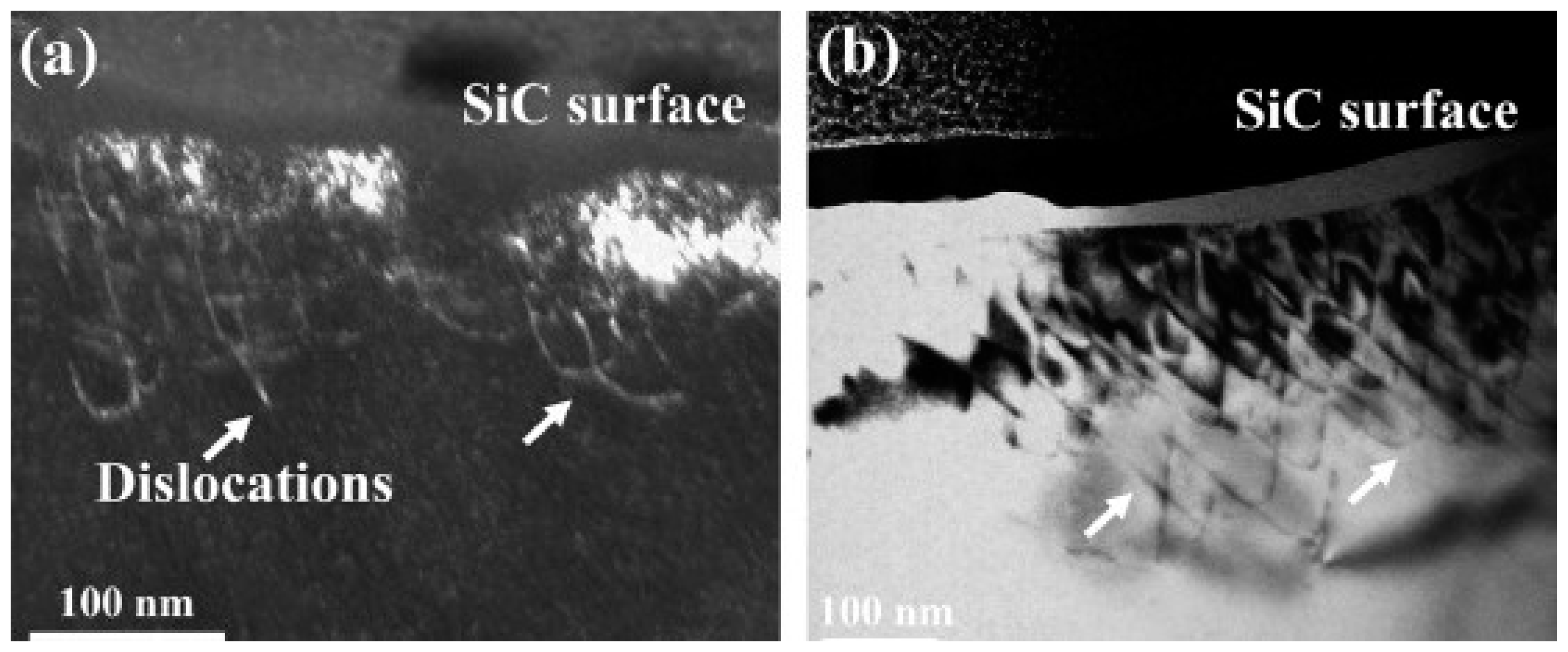
| Substrate | Technique | Findings | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| AISI 304 SS | SP | Microhardness increased by 52%, strength by 14% and fracture toughness by 18%. | [33] |
| Ti6Al4V | SP | Improved the fatigue life by 34% and reduced the short crack propagation rate by 34–60% compared to unpeened specimen. | [34] |
| AISI 4140 low alloy steel | SP | Increased corrosion resistance, surface roughness, promoted grain refinement and subgrain formation. The corrosion mechanism changed from uniform corrosion to crevice corrosion | [57] |
| hastelloy X alloy | SSP | After SSP, residual stress at depth 125 μm is 1200 MPa, average grain size on the surface ~50 nm, depth of compressed layer was 700 μm and hardness on the surface 2.2 times compared to SP | [64] |
| X70 steel | SSP | Increased fatigue performance Improved work hardening and surface roughness | [65] |
| AZ31 and AZ91 magnesium alloys | SSP | Nano grains on deformed layer Microhardness of both alloys increased The corrosion resistance of AZ31 alloy improved | [66] |
| Pure Ti | SSP | Ultra-fine grained surface with grain size 100 nm Microhardness and elastic moduli increased | [67] |
| Cast iron | SSP & RSSP | High work hardening, deeper RCS, nano crystallization RP reduced surface roughness and improved fatigue performance. | [71] |
| High speed tool steel | MSP | Residual stress was higher on the surface with low surface roughness Improved peening effect | [14] |
| Structural steel | MSP | Improve fatigue performance and wear resistance Enhanced peening effect | [15] |
| Substrate | Findings | References |
|---|---|---|
| High-nitrogen austenitic SS | Fatigue life enhanced at low strain amplitude by 18% Grain size of 15 and 12 nm observed for peening duration of 3 and 18 min The thickness of the refined region is approximately 260 μm and 345 μm for 3 and 18 min peening | [87] |
| AZ31 Magnesium alloy | The grain size on the surface is 37 nm Microhardness at the surface increased by 141% Coefficient of friction reduced Improved wear resistance Delamination wear mechanism retarded after UIP | [88] |
| 7075 Aluminum alloy | Observed surface nanocrystalization Refined grains Improved corrosion resistance | [89] |
| 7150 Aluminum alloy | Observed surface nanocrystalization Exfoliation susceptibility decreased Corrosion resistance increased | [90] |
| β-titanium alloy | A nanocrystalline layer of 100 μm thickness on the surface Improved microhardness No new phase formed, decreased β phase because of stress-induced martensite | [91] |
| Material | Findings | References |
|---|---|---|
| ANSI 316L SS | Surface hardness improved by 35% Improvement in corrosion resistance | [20] |
| 7075 Aluminium alloy | Hardness increased Abrasion resistance improved | [21] |
| Duplex SS | Wear volume reduced by 39% Corrosion rate reduced by 74.2% Corrosion pit size reduced by 50% | [22] |
| Ti-17 | Fatigue life increased Microhardness increased Grain refinement | [25] |
| Alloy 718 | Observed nanocrystallites and grain refinement at the surface Surface hardness increased Fretting wear resistance increased | [26] |
| ANSI 304 austenitic SS | Nano hardness improved Elastic modulus increased High RCS observed Mechanical twin formation observed | [27] |
| AZ31B magnesium alloy | Hardness increased by 20% Yield strength increased by 18.75% Refined grains Improved wear resistance | [28] |
| Polycrystalline α-Al2O3 Ceramics | Improved resistance to indentation cracking. Plastic deformation occurred at the grain boundary and elastic deformation in α-Al₂O₃ grains | [29] |
| Alloy D9 | Microhardness increased by 32% Yield strength increased by 63% Improved thermal stability | [30] |
| Brass H62 | Surface roughness increased by 28.3% Wear mass loss decreased by 31.78% | [31] |
| Materials | Type of Welding | Remarks | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| ANSI 304 SS | LBW | Surface roughness in weld zone (WZ) and heat affected zone (HAZ) reduced Significant residual compressive stress in weldment Refined grains in WZ and HAZ | [107] |
| Alloy 600 | TIG | Tensile strength of joint increased by 9% Yield of joint increased by 25% Improvement in microhardness, dislocation density Improved fatigue resistance of joint | [111] |
| Inconel 600 | ATIG | Tensile fracture location changed from weld to base material side Weldment tensile strength and hardness value increased | [113] |
| 7050-T7451 aluminum alloys | FSW | Hardness in TMAZ and HAZ increased Fatigue life increased by 30%, 27%, and 5% under different loading conditions | [114] |
| LSP Techniques | Applications | References |
|---|---|---|
| LPwC | Used where sacrificial coating is difficult to apply | [124,125] |
| WLSP | Precipitate hardenable materials | [129,130] |
| CLSP | Metals that form deformation twins | [133] |
| fs-LSP | Circumstances where confining medium and sacrificial coating is difficult to apply | [140] |
| LPF | For shaping and forming components with complex shapes | [141,142,143] |
| EP-LSP | Low plasticity materials | [148] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
John, M.; Kalvala, P.R.; Misra, M.; Menezes, P.L. Peening Techniques for Surface Modification: Processes, Properties, and Applications. Materials 2021, 14, 3841. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14143841
John M, Kalvala PR, Misra M, Menezes PL. Peening Techniques for Surface Modification: Processes, Properties, and Applications. Materials. 2021; 14(14):3841. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14143841
Chicago/Turabian StyleJohn, Merbin, Prasad Rao Kalvala, Manoranjan Misra, and Pradeep L. Menezes. 2021. "Peening Techniques for Surface Modification: Processes, Properties, and Applications" Materials 14, no. 14: 3841. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14143841
APA StyleJohn, M., Kalvala, P. R., Misra, M., & Menezes, P. L. (2021). Peening Techniques for Surface Modification: Processes, Properties, and Applications. Materials, 14(14), 3841. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14143841








