Properties of Metallic and Oxide Thin Films Based on Ti and Co Prepared by Magnetron Sputtering from Sintered Targets with Different Co-Content
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Preparation of Targets and Thin Films
2.2. Methods of Targets and Thin Film Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Influence of Ti–Co Target Composition on Its Sputtering Conditions
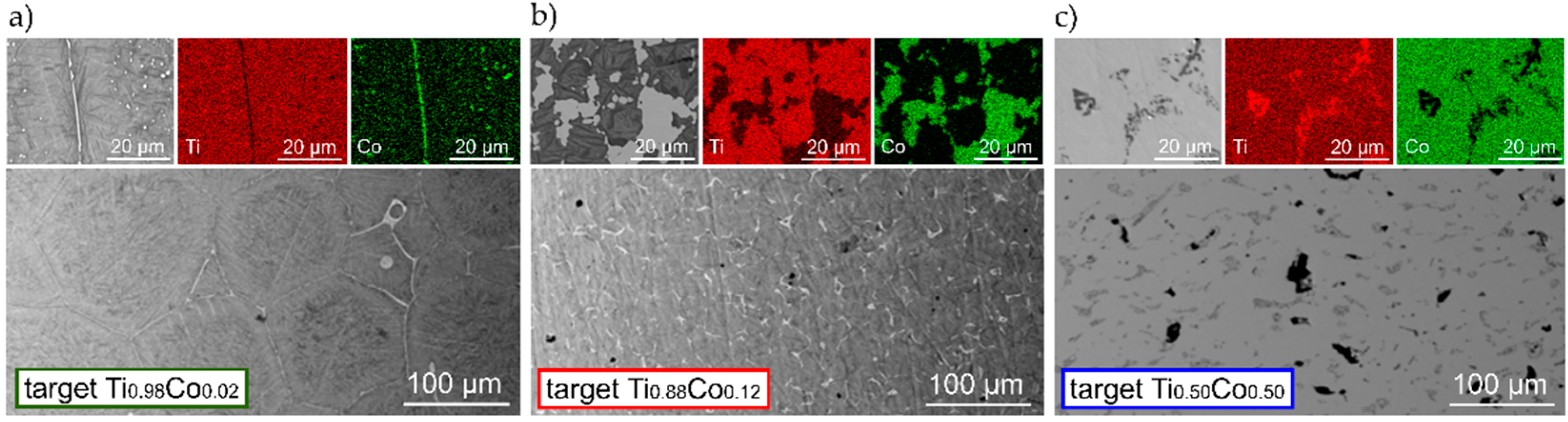
3.1.1. Material Composition of Sintered Ti–Co Targets
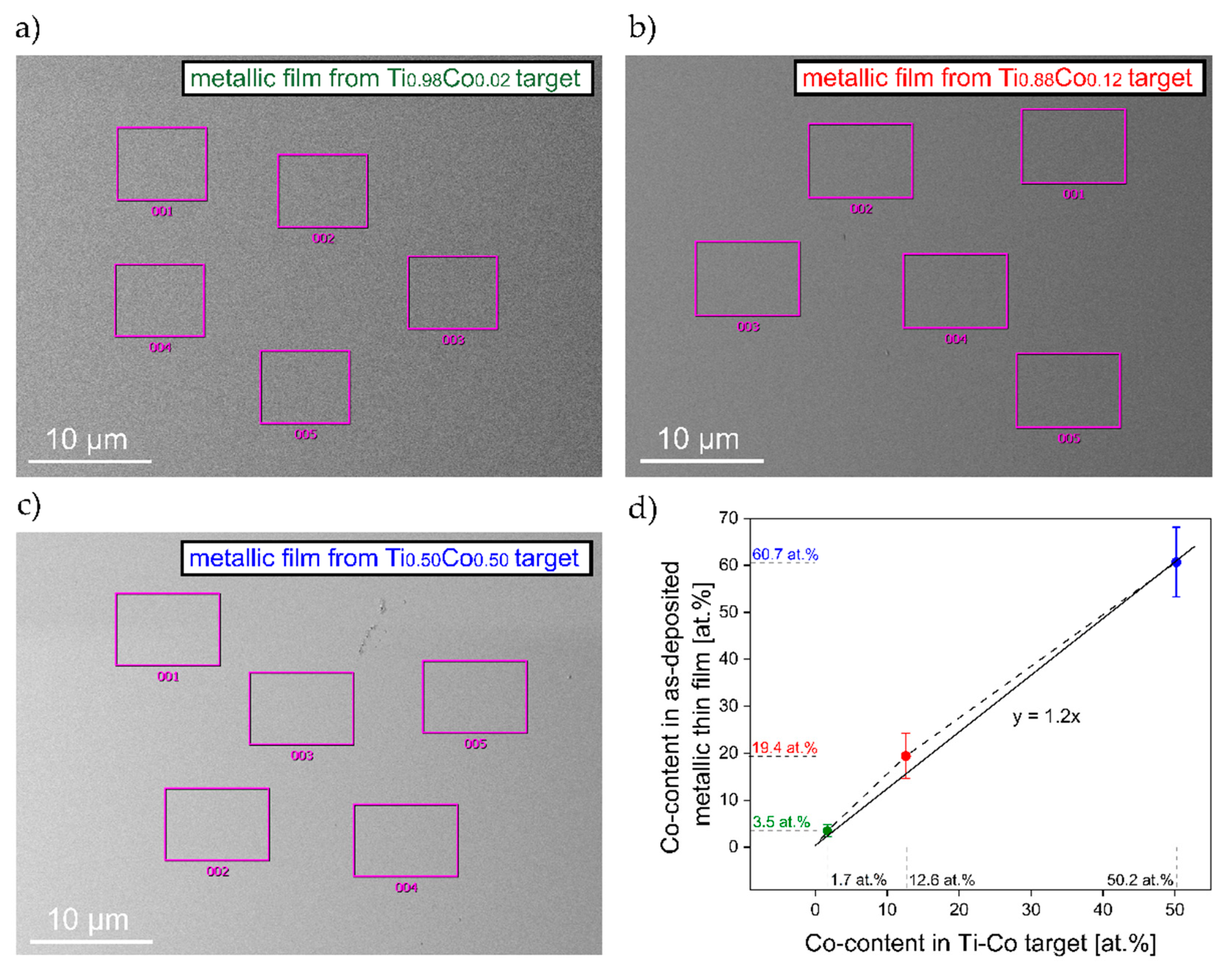
3.1.2. Material Composition of Metallic Ti–Co Thin Films
3.1.3. Material Composition of Oxide (Ti,Co)Ox Thin Films
3.1.4. Roughness of Metallic Ti–Co and Oxide (Ti,Co)Ox Thin Films
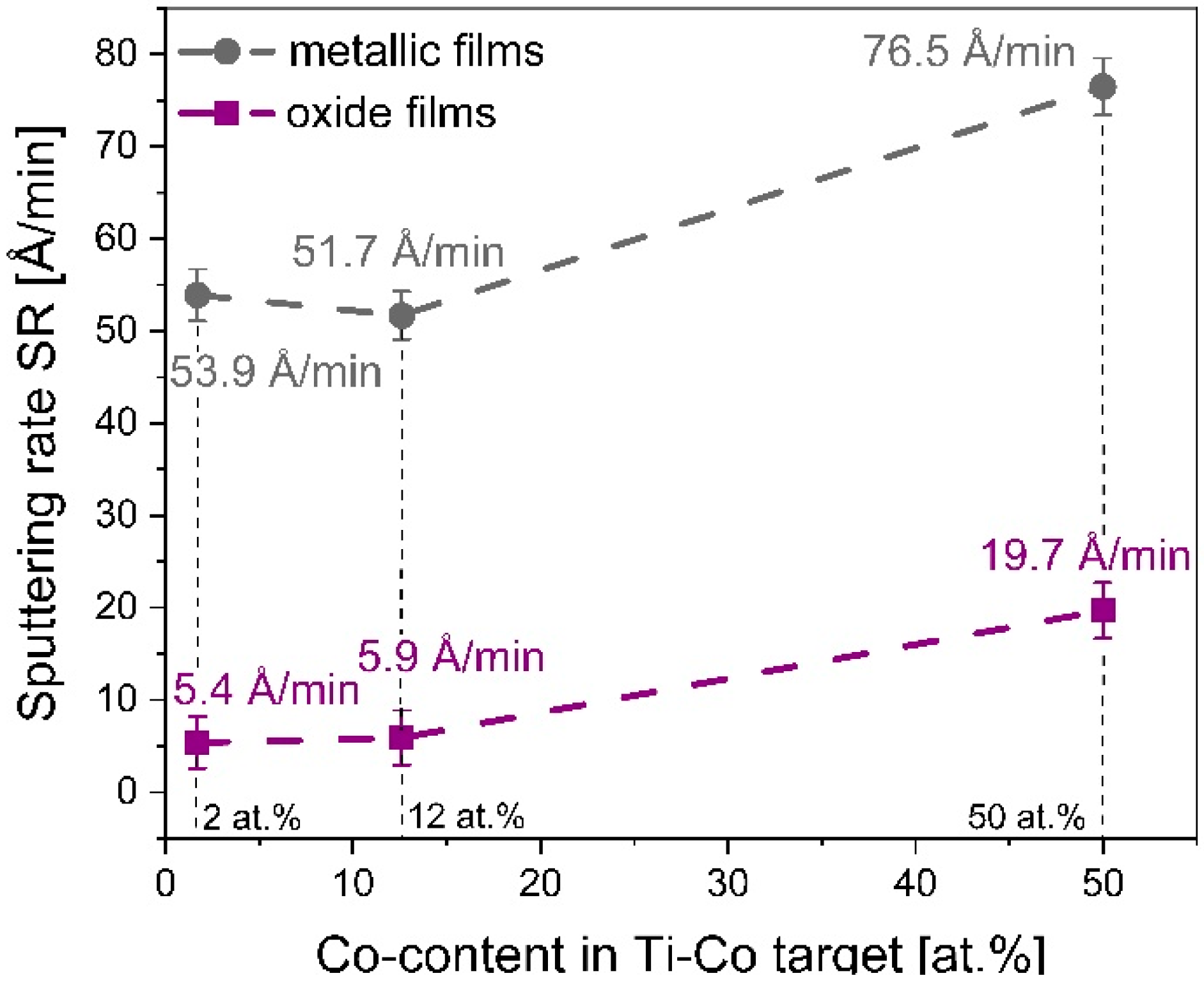
3.1.5. Sputtering Rate of T-Co Targets for Metallic and Oxide Films
3.2. Structural, Optical and Electrical Characterization of (Ti,Co)Ox Thin Films
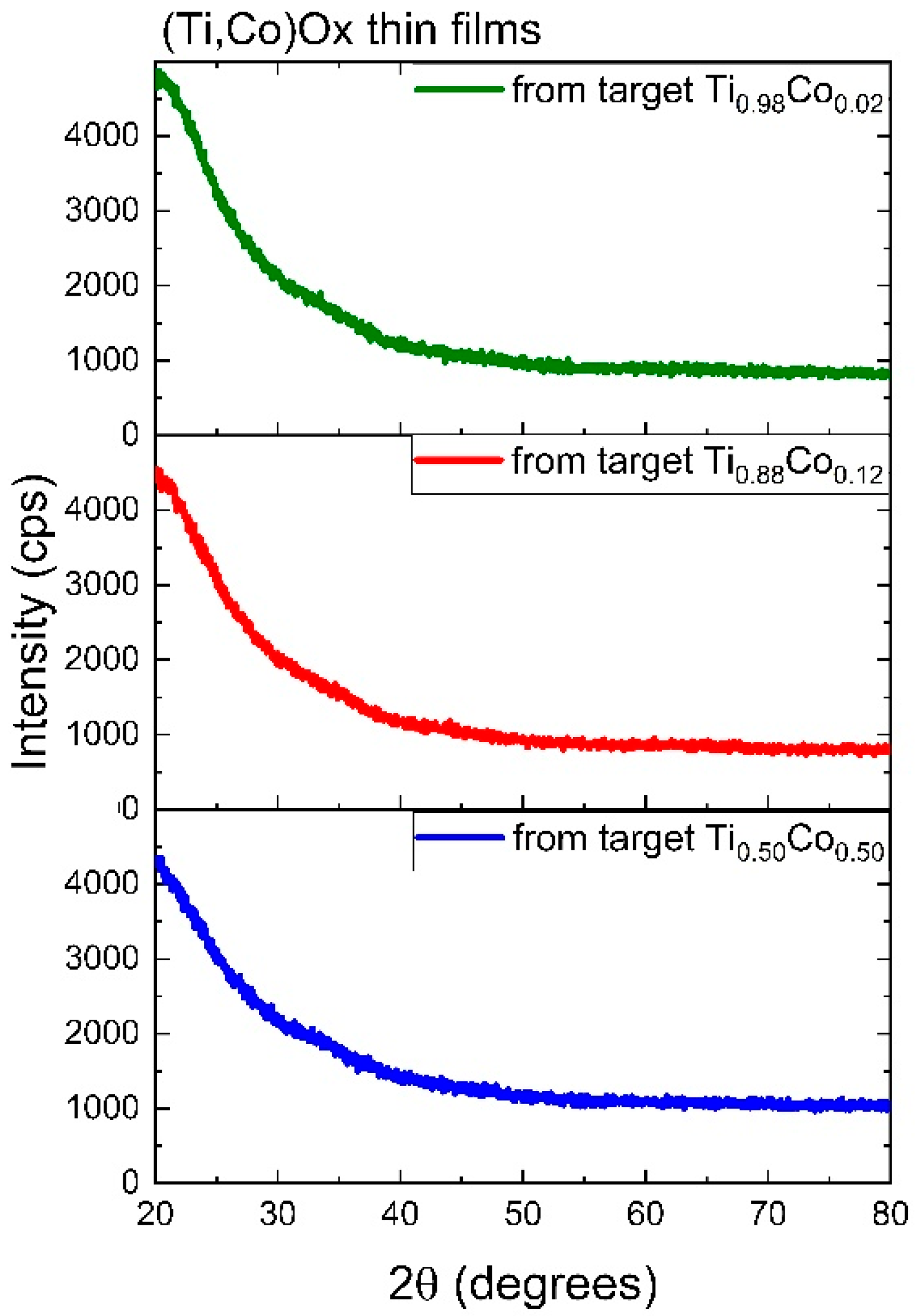
3.2.1. Structure of Oxide (Ti,Co)Ox Coatings
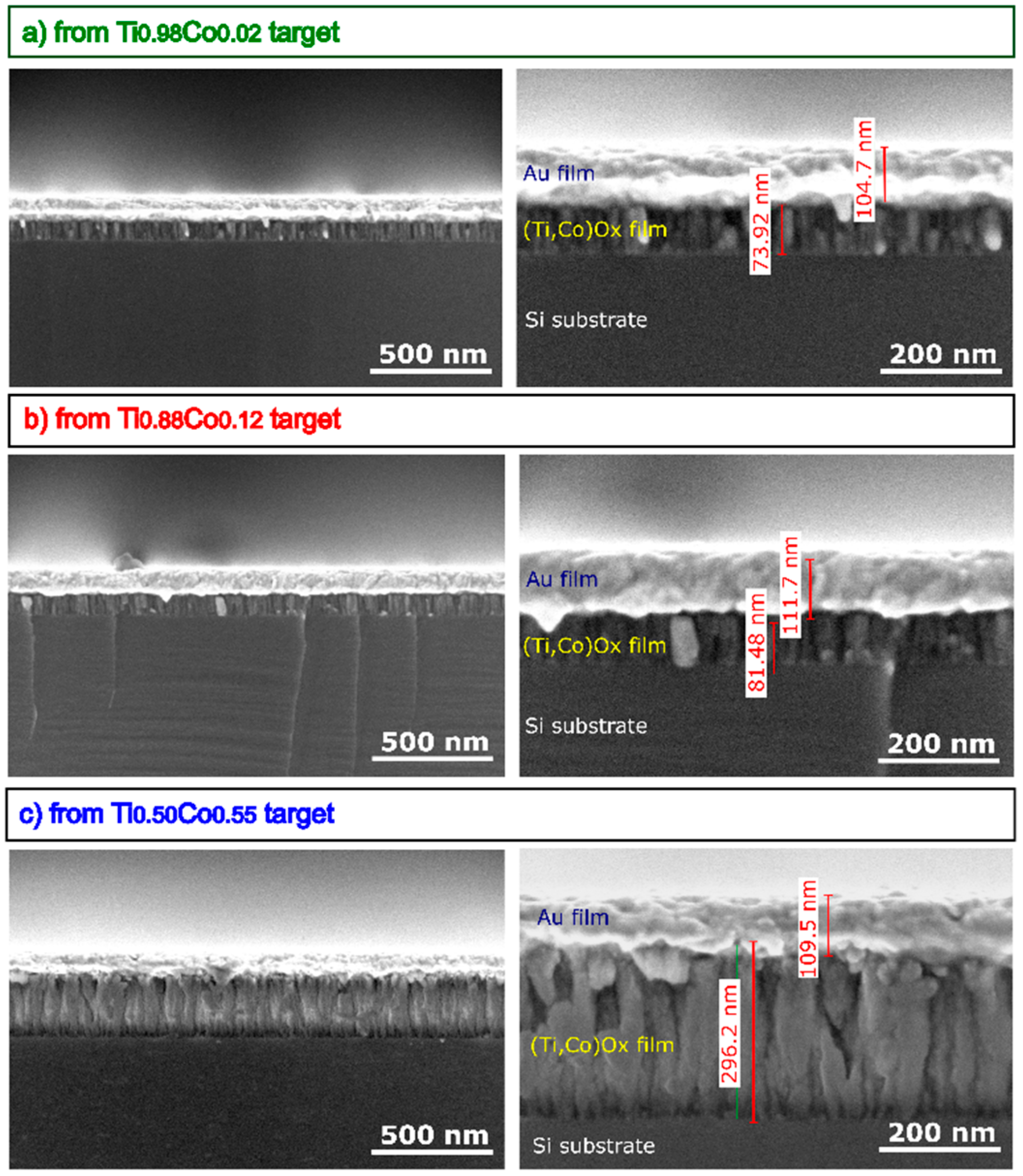
3.2.2. Microstructure and Morphology of Oxide (Ti,Co)Ox Coatings
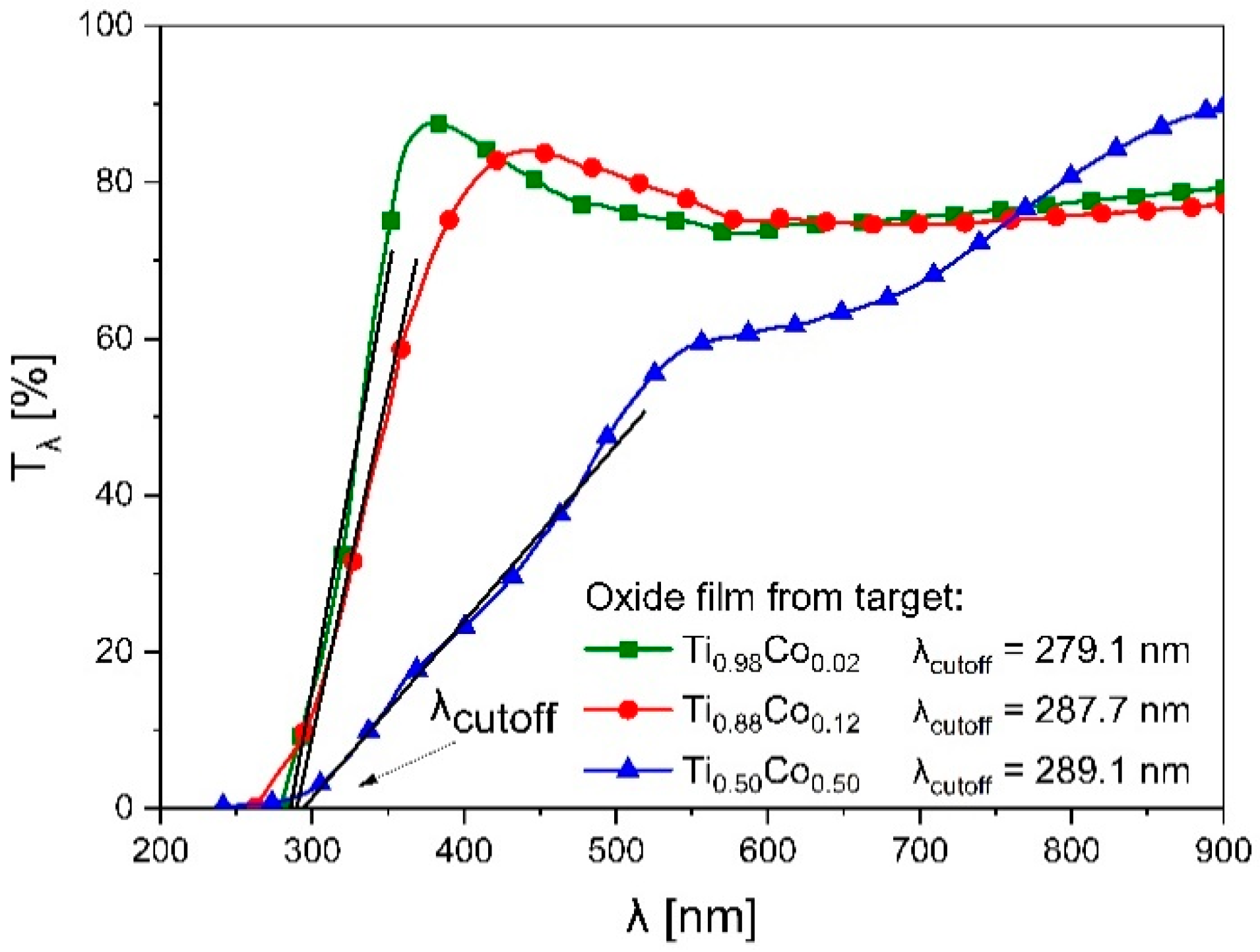
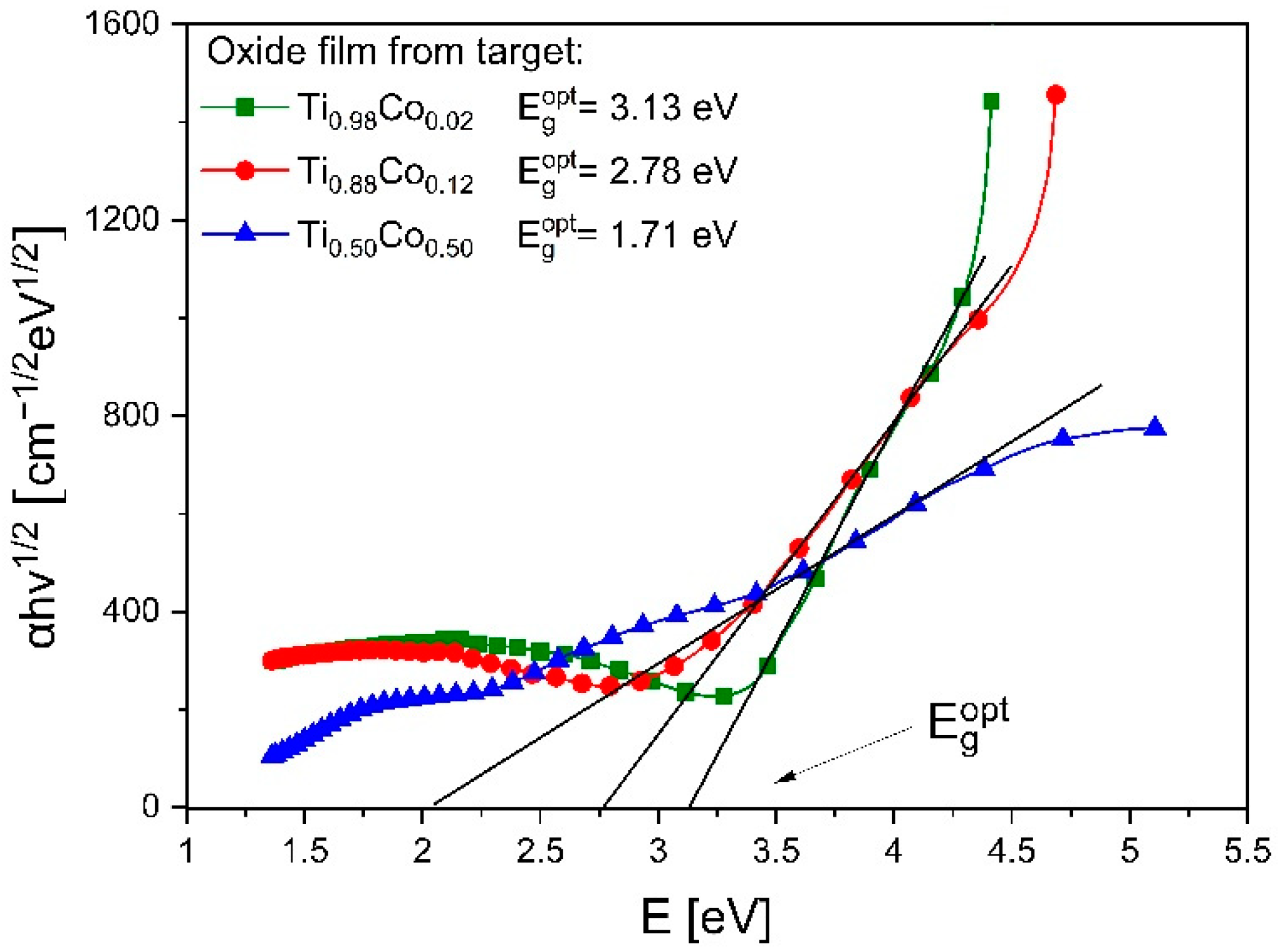
3.2.3. Optical Properties of Oxide (Ti,Co)Ox Coatings
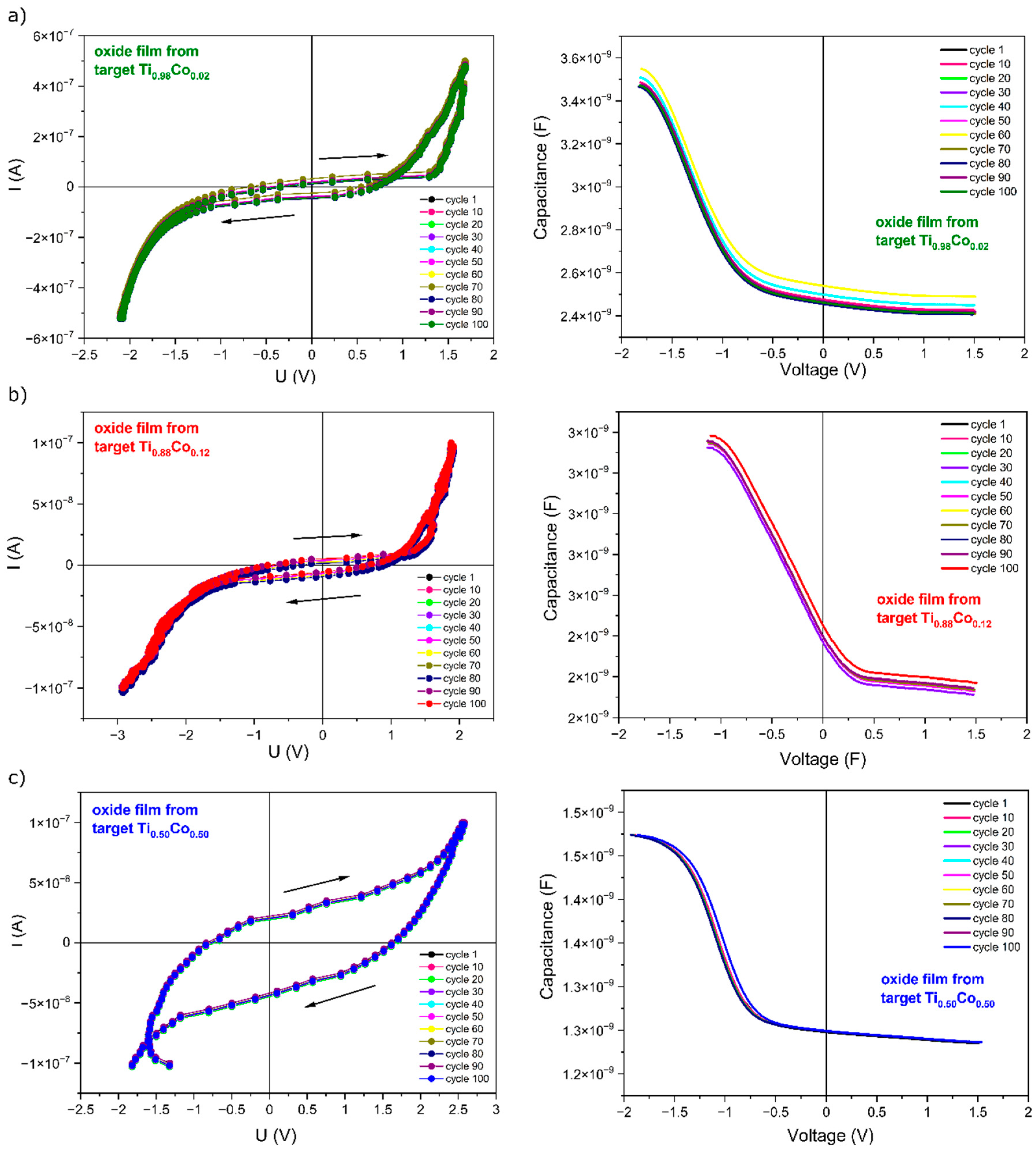
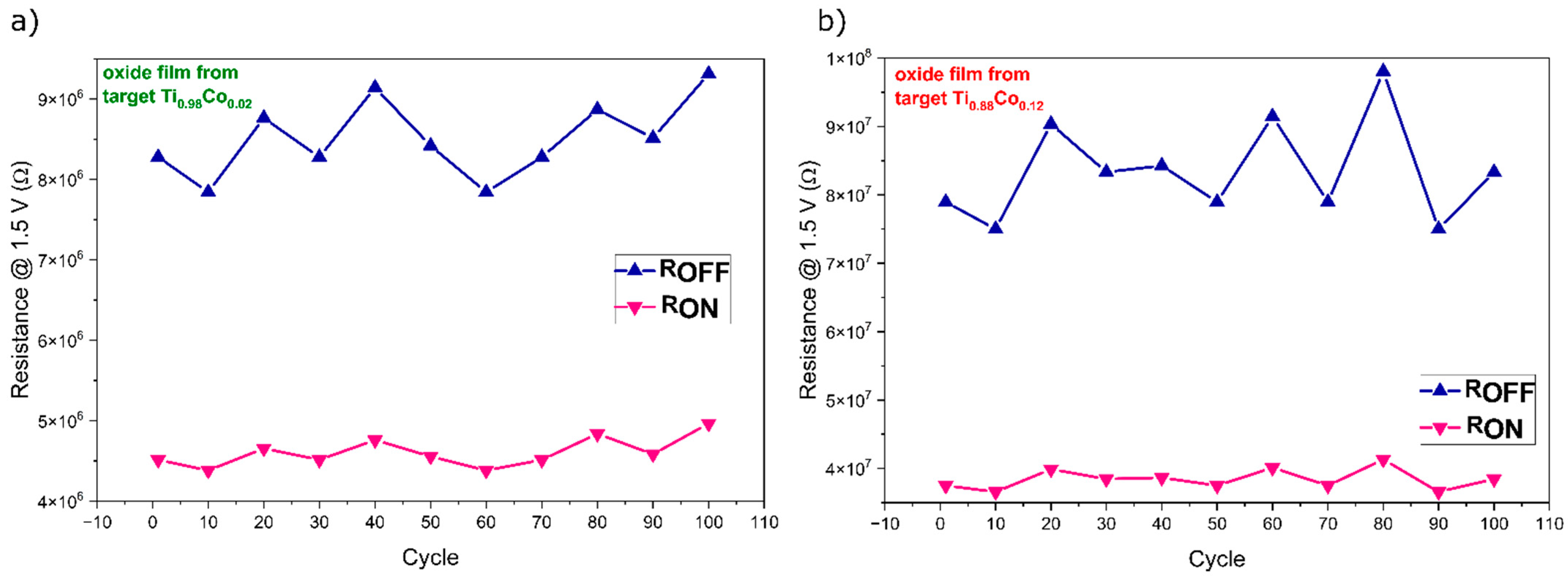
3.2.4. Electrical Properties of Oxide (Ti,Co)Ox Coatings
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, C.-P.; Chen, H.; Nakaruk, A.; Koshy, P.; Sorrell, C.C. Effect of annealing temperature on the photocatalytic activity of TiO2 thin films. Energy Procedia 2013, 34, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mergel, D.; Buschendorf, D.; Eggert, S.; Grammes, R.; Samset, B. Density and refractive index of TiO2 films prepared by reactive evaporation. Thin Solid Film. 2000, 371, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitui, M.; Mwamburi, M.M.; Gaitho, F.; Maghanga, M. Optical Properties of TiO2 based multilayer thin films: Application to optical filters. Int. J. Thin Film. Sci. Technol. 2015, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsaeedy, H.I.; Qasem, A.; Yakout, H.A.; Mahmoud, M. The pivotal role of TiO2 layer thickness in optimizing the performance of TiO2/P-Si solar cell. J. Alloy. Compd. 2021, 867, 159150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyson-Sypien, B.; Radecka, M.; Rekas, M.; Swierczek, K.; Michalow-Mauke, K.; Graule, T.; Zakrzewska, K. Grain-size-dependent gas-sensing properties of TiO2 nanomaterials. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 211, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, J.; Liao, T.; Ayoko, G.A.; Bell, J.; Sun, Z. Cobalt oxide-based nanoarchitectures for electrochemical energy applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 103, 596–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, M.; Mitan, M.; Kim, H.; Vaya, D. Efficient photocatalytic degradation of Malachite green dye using facilely synthesized cobalt oxide nanomaterials using citric acid and oleic acid. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2021, 155, 110125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajbhiye, M.M.; Sharma, S.; Nigam, A.K.; Ningthoujam, R.S. Tuning of single to multi-domain behavior for monodispersed ferromagnetic cobalt nanoparticles. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2008, 466, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaloyeros, A.E.; Pan, Y.; Goff, J.; Arkles, B. Cobalt thin films: Trends in processing technologies and emerging applications. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2019, 8, P119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirohata, A.; Yamada, K.; Nakatani, Y.; Prejbeanu, J.L.; Diényd, B.; Pirro, P.; Hillebrands, B. Review on spintronics: Principles and device applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 509, 166711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bewan, S.; Ndolomingo, N.J.; Meijboom, R.; Bingwa, N. Cobalt oxide promoted tin oxide catalysts for highly selective glycerol acetalization reaction. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2021, 128, 108578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Švegl, F.; Orel, B.; Hutchins, M.G.; Kalcher, K. Structural and spectroelectrochemical investigations of sol-gel derived electrochromic spinel Co3O4 films. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1996, 143, 1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahlawane, N.; Rivera, E.F.; Kohse-Höinghaus, K.; Brechling, A.; Kleineberg, U. Characterization and tests of planar Co3O4 model catalysts prepared by chemical vapor deposition. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2004, 53, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, S.; Alkhtaby, L.A.; Giorgetti, E.; Zoppi, A.; Maurizio Muniz, M. Influence of cobalt doping on the structural, optical and luminescence properties of sol-gel derived TiO2 nanoparticles. Philos. Mag. 2017, 97, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, S.; Sandeep, K.M.; Kumar, P.; Dharmaprakash, S.M.; Byrappa, K. Characterization of transparent semiconducting cobalt doped titanium dioxide thin films prepared by sol–gel process. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 1098–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Xiang, W.; Kuang, J.; Liu, W.; Cao, W. Effect of cobalt doping on the electronic, optical and photocatalytic properties of TiO2. Solid State Sci. 2015, 46, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.R.; Kim, K.J. Structural and optical properties of rutile and anatase TiO2 thin films: Effects of Co doping. Thin Solid Film. 2005, 484, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, M.; Vijayalakshmi, S.; Venkataraj, S.; Jayavel, R. Effect of cobalt doping on the structural and optical properties of TiO2 films prepared by sol-gel process. Thin Solid Film. 2008, 516, 3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Zhai, Z.; Jiang, L.; Shi, Y.; Yana, Y.; Duan, D.; Zhen, K.; Wang, J. Facile and new synthesis of cobalt doped mesoporous TiO2 with high visible-light performance. Powder Technol. 2014, 266, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, M.Z.; Ameran, Z.F.; Mamat, M.H.; Malek, M.F.; Rasheid, N.A.; Noor, U.M.; Rusop, M. Effects of cobalt doping concentration on the structural, electrical, and optical properties of titanium dioxide thin films. In Proceedings of the Institute of Electronics Engineers, 2011 International Conference on Electronic Devices, Systems and Applications (ICEDSA), Mid Valley City, Malaysia, 25–27 April 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, N.M.; Podder, J. The role of Al and Co co-doping on the band gap tuning of TiO2 thin films for applications in photovoltaic and optoelectronic devices. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2021, 121, 105419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo-ping, Z.; Nan-nan, X.; Gong-ping, L.; Tian-jing, L.; Xing-xin, G.; Jing-sheng, C. The magnetic properties and microscopic structural of a ferromagnetic semiconductor: Rutile TIO2 single crystals implanted with cobalt ions. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 229, 109–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganshina, E.A.; Granovsky, A.B.; Orlov, A.F.; Perov, N.S.; Vashuk, M.V. Magneto-optical spectroscopy of diluted magnetic oxides TiO2−δ: Co. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2009, 321, 723–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroz, H.P.; Galíndez, E.F.; Dussan, A. Ferromagnetic-like behavior of Co doped TiO2 flexible thin films fabricated via co-sputtering for spintronic applications. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, H.; Ni, L.; Wang, Y. Non-Volatile In-Memory Computing by Spintronics; Morgan & Claypool Publishers: Williston, VT, USA, 2017; pp. 13–14. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, C.; Du, Y.; Zhu, M.; Huo, W.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Y. Microstructure and mechanical properties of in situ TiC/Ti composites with a laminated structure synthesized by spark plasma sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 812, 141136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimler, D.; Lindemann, J.; Gammer, C.; Spoerk-Erdely, P.; Stark, A.; Clemens, H.; Mayer, S. Novel intermetallic-reinforced near-α Ti alloys manufactured by spark plasma sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 792, 139798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depla, D.; De Gryse, R. Target poisoning during reactive magnetron sputtering: Part I: The influence of ion implantation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2004, 183, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waite, M.M.; Ismat Shah, S.I. Target poisoning during reactive sputtering of silicon with oxygen and nitrogen. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2007, 140, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, M.; Eisenmenger-Sittner, C. In situ assessment of target poisoning evolution in magnetron sputtering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 324, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiatrowski, A.; Mazur, M.; Obstarczyk, A.; Kaczmarek, D.; Pastuszek, R.; Wojcieszak, D.; Grobelny, M.; Kalisz, M. Influence of magnetron powering mode on various properties of TiO2 thin films. Mater. Sci. Pol. 2018, 36, 748–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiatrowski, A.; Mazur, M.; Obstarczyk, A.; Wojcieszak, D.; Kaczmarek, D.; Morgiel, J.; Gibson, D. Comparison of the physicochemical properties of TiO2 thin films obtained by magnetron sputtering with continuous and pulsed gas flow. Coatings 2018, 8, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bohórquez, A.J.; Quiroz, H.P.; Dussan, A. Growth and crystallization of Cobalt-doped TiO2 alloys: Effect of substrate and annealing temperature. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 474, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.N.R.; Subba Rao, G.V. Transition Metal Oxides—Crystal Chemistry, Phase Transition and Related Aspects; 1974 U.S. Department of Commerce, Michigan, National Bureau of Standards. Available online: http://refhub.elsevier.com/S2405-8440(20)30183-3/sref26 (accessed on 1 March 2021).
- NIST Laboratory. Co Oxides Structure; 2019. Available online: https://srdata.nist.gov/xps/main_search_menu.aspx (accessed on 15 February 2021).
- Thornton, J.A. Structure-zone models of thin films. Model. Opt. Thin Film. 1988, 0821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroz, H.P.; Dussan, A. Synthesis temperature dependence on magnetic properties of cobalt doped TiO2 thin films for spintronic applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 484, 688–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domaradzki, J.; Wojcieszak, D.; Kotwica, T.; Mańkowska, E. Memristors: A short review on fundamentals, structures, materials and applications. Int. J. Electron. Telecommun. 2020, 66, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domaradzki, J.; Kotwica, T.; Mazur, M.; Kaczmarek, D.; Wojcieszak, D. Memristive properties of transparent oxide semiconducting (Ti,Cu)Ox-gradient thin film. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2018, 33, 015002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Target | Co-Content [at.%] | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| In the Target | In the Film | ||
| Metallic (Ti–Co) | Oxide (Ti,Co)Ox | ||
| Ti0.98Co0.02 | 1.7 | 3.5 | 1.8 |
| Ti0.88Co0.12 | 12.6 | 19.4 | 17.6 |
| Ti0.50Co0.50 | 50.2 | 60.7 | 57.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wojcieszak, D.; Mazur, M.; Pokora, P.; Wrona, A.; Bilewska, K.; Kijaszek, W.; Kotwica, T.; Posadowski, W.; Domaradzki, J. Properties of Metallic and Oxide Thin Films Based on Ti and Co Prepared by Magnetron Sputtering from Sintered Targets with Different Co-Content. Materials 2021, 14, 3797. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14143797
Wojcieszak D, Mazur M, Pokora P, Wrona A, Bilewska K, Kijaszek W, Kotwica T, Posadowski W, Domaradzki J. Properties of Metallic and Oxide Thin Films Based on Ti and Co Prepared by Magnetron Sputtering from Sintered Targets with Different Co-Content. Materials. 2021; 14(14):3797. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14143797
Chicago/Turabian StyleWojcieszak, Damian, Michał Mazur, Patrycja Pokora, Adriana Wrona, Katarzyna Bilewska, Wojciech Kijaszek, Tomasz Kotwica, Witold Posadowski, and Jarosław Domaradzki. 2021. "Properties of Metallic and Oxide Thin Films Based on Ti and Co Prepared by Magnetron Sputtering from Sintered Targets with Different Co-Content" Materials 14, no. 14: 3797. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14143797
APA StyleWojcieszak, D., Mazur, M., Pokora, P., Wrona, A., Bilewska, K., Kijaszek, W., Kotwica, T., Posadowski, W., & Domaradzki, J. (2021). Properties of Metallic and Oxide Thin Films Based on Ti and Co Prepared by Magnetron Sputtering from Sintered Targets with Different Co-Content. Materials, 14(14), 3797. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14143797








