Abstract
Nowadays, we consume very large amounts of medicinal substances. Medicines are used to cure, halt, or prevent disease, ease symptoms, or help in the diagnosis of illnesses. Some medications are used to treat pain. Ibuprofen is one of the most popular drugs in the world (it ranks third). This drug enters our water system through human pharmaceutical use. In this article, we describe and compare the biodegradation of ibuprofen and ibuprofen derivatives—salts of L-valine alkyl esters. Biodegradation studies of ibuprofen and its derivatives have been carried out with activated sludge. The structure modifications we received were aimed at increasing the biodegradation of the drug used. The influence of the alkyl chain length of the ester used in the biodegradation of the compound was also verified. The biodegradation results correlated with the lipophilic properties (log P).
1. Introduction
Due to their high effectiveness in pain management strategies, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are a widely used group of drugs in the world. Ibuprofen went to treatment over 50 years ago and has become one of the most popular non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the world. This compound is characterized by high lipophilicity. In 2000, ibuprofen consumption reached 300 tons in Germany, 162 tons in England, 58 tons in Poland, and 25 tons in Switzerland [1]. It is worth noting that ibuprofen consumption constantly increases. The global ibuprofen market was valued at US$294.4 million in 2020, and is expected to reach US$447.6 million by the end of 2026. As a result of increased production, consumption, and easy availability of NSAIDs, the pollution of the environment with these substances increases, which often end up in wastewater and then into waters in an unchanged composition [2,3,4]. The release of these drugs into the environment poses a real threat to animals, humans, and the ecosystem [5,6,7].
Few literature reports have described the degradation of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (including ibuprofen) using the active sludge. The most popular method of degradation is based on the decomposition of ibuprofen by ligninolytic species of mushrooms [8]. However, hydroxylated derivatives of ibuprofen (1-hydroxyibuprofen, 2-hydroxyibuprofen, 1,2-dihydroxyibuprofen) formed as a result of degradation may have higher toxicity than the parent compound [9]. Nonetheless, in the case of the biotransformation of ibuprofen (by the Nocardia sp. NRRL 5646 strain), metabolites of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs were ibuprophenyl and ibuprophenyl acetate, which were further mineralized [10]. An interesting solution that eliminates the formation of these derivatives of ibuprofen is the biodegradation of ibuprofen utilizing aerobic microorganisms (Sphingomonas strain) that treat the test compound as the only source of carbon and energy [11]. In the first stage, thioesterification of ibuprofen takes place in the presence of CoA ligase, resulting in ibuprophenyl-CoA. Then, as a result of the deoxygenation of the aromatic ring, 4-isobutyl catechol is formed. In the next stage of research, the catechol system was split, resulting in 2-hydroxy-5-isobutylhexa-2,4-diene acid [11,12].
Low solubility and bioavailability are factors that limit the effectiveness of many drugs. Various structural drug modifications are used to change these parameters. For example, antiviral nucleoside analogues derived from valine esters such as valine ester prodrugs of acyclovir, ganciclovir, cyclopropavir, and valganciclovir are known [13,14,15,16,17,18,19]. Moreover, it is well known that D-valine tert-butyl ester hydrochloride is used as an intermediate in pharmaceuticals and as an antitumor drug. L-valine alkyl ester hydrochlorides are also used in the synthesis of peptides [20,21]. However, no research has been undertaken on the biodegradation of these compounds.
In our previous publications, we described the synthesis, properties, skin penetration, and skin accumulation of new ibuprofen derivatives—L-valine alkyl ester ibuprofenates [22,23]. It has been shown that these compounds have a much higher solubility in water and body fluids and better skin permeability, therefore being an alternative to ibuprofen. Due to numerous advantages, it was decided to verify how these compounds can affect the environment, in order to investigate the effect of changing the form of a compound from acidic-ibuprofen to its organic salt-ibuprofenate amino acid alkyl ester on its biodegradation.
The stimulus to take up this topic was the lack of information on the biodegradation of ionic liquids. As was shown previously, the obtained compounds, due to their chemical structure and melting point below 100 °C, belong to the group of ionic liquids. The conversion of solid active pharmaceutical ingredients into liquid forms is very promising. The literature mentions a special group of ionic liquids called ionic liquid comprising active pharmaceutical ingredients (API-ILs). API-ILs can be used, among others, in synthesis (as a solvent, co-solvent, reagent, catalyst, or enantioselectivity enhancers), crystallization, solvents, co-solvents, or emulsifiers for API solubilization. Moreover, ionic liquids may display specific biological activities, therefore they are potential pharmaceutical substances [24,25,26]. Ionic liquids can also be used in drug delivery systems [27,28].
Ionic liquids used as active substances contained in pharmaceutical formulae should be characterized by low toxicity and high biodegradability. According to biodegradation tests recommended by the OECD, only paracetamol and salicylic acid derivatives are considered biodegradable by active sludge. Due to the low biodegradability of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, the research has been conducted for several years on the intensification of degradation processes involving active sludge [29].
The literature on the subject states that ionic liquids containing short, side alkyl chains in their structure are characterized by low toxicity and high resistance to biodegradation [30]. Other reports in the literature indicate that ionic liquids with substituents from one to five carbon atoms are relatively less toxic than liquids with substituents from seven and more carbon atoms. This relationship also applies to biodegradability as ionic liquids are more biodegradable with short-chain alkyl substituents [31,32]. However, apart from the length of the side alkyl chains, the susceptibility of ionic liquids to biodegradation can be increased by the appropriate choice of substituents present in the structure of ionic liquids [33,34]. Ester groups greatly increase the susceptibility of the compound to degradation, while amide groups reduce the susceptibility of the test compound to biodegradation [34,35]. The challenge, therefore, is to combine the low toxicity of the resulting compound with its high biodegradability. Biodegradation of active pharmaceutical amino acid alkyl ester derivatives has not been described so far.
The present study was carried out to determine the effect of the structure of the organic cation (Figure 1), in particular, the alkyl chain length, on the biodegradation process of these compounds. In this study, properties such as water solubility and partition coefficient were correlated with the biodegradability results.
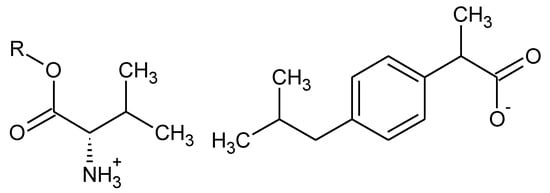
Figure 1.
The structures of ibuprofen salts with L-valine alkyl esters, R = C1–C8.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ionic Liquids Used
All ionic liquids used in the research were obtained in accordance with the methodology described in our previous publication [22,23]. The synthesis consisted of three steps. In the first step, the esterification and the chloro-hydrogenation reactions of amino acids with the use of alcohol and a chlorinating agent were run simultaneously, respectively. The obtained amino acid alkyl ester hydrochloride was then neutralized with a 25% ammonia solution. In the last step, the obtained ester was reacted with ibuprofen. The reactions were carried out in diethyl ether. All obtained compounds were fully characterized and described. Identity studies were confirmed based on the analysis of 1H NMR, 13C NMR, FTIR, UV–Vis spectra, and all the necessary spectroscopic data have been described previously [22,23].
2.2. Elemental Analysis
The elemental analysis CHNS/O was performed by using a Thermo Scientific™ FLASH 2000 CHNS/O Analyzer (Waltham, MA, USA). Compounds were weighed to an accuracy of ±0.000001 g in tin crucibles (2–3 mg) for analysis in CHNS mode, and in silver crucibles (1–2 mg) in oxygen mode, respectively. 2,5-(Bis(5-tert-butyl-2-benzo-oxazol-2-yl) thiophene (BBOT), sulfanilamide, L-cysteine, and L-methionine were used as standards to calibrate the device in CHNS mode. In oxygen mode, acetanilide and benzoic acid were used.
2.3. Chemicals and the Test Medium
For the determination of biodegradability and to assess the lipophilicity of L-valine alkyl ester ibuprofenates, KH2PO4, K2HPO4, Na2HPO4·2H2O, NH4Cl, MgSO4·7H2O, CaCl2·2H2O, KOH, NaOH, HCl, and FeCl3·6H2O were purchased from Chempur, Piekary Śląskie (Poland). All other chemicals were of the highest purity commercially available.
The test medium was prepared from the following solutions (per liter): 10 mL of solution a—adjusted to pH 7.4 (per liter): 8.5 g of KH2PO4, 21.75 g of K2HPO4, 33.4 g of Na2HPO4·2H2O, and 0.5 g of NH4Cl; 1 mL of solution b (per liter): 22.5 g of MgSO4·7H2O; 1 mL of solution c (per liter): 36.4 g of CaCl2·2H2O; 1 mL of solution d (per liter): 0.25 g of FeCl3·6H2O.
2.4. Origin of Active Sludge Samples
Active sludge samples were collected from the sewage treatment plant “Pomorzany” from the aeration chamber; later aerated, and stored until use. The concentration of active sludge suspensions was subjected to a microbiological test used for the designation of the total number of microorganisms (Schulke Mikrocount Duo, Norderstedt, Germany). A microbiological test with medium and TTC agar was immersed for 10 s in an active sludge. The test was secured at room temperature for four days, after which the number of bacteria was evaluated (by evaluating the appearance of the test against the appearance of a benchmark test)—Figure 2.
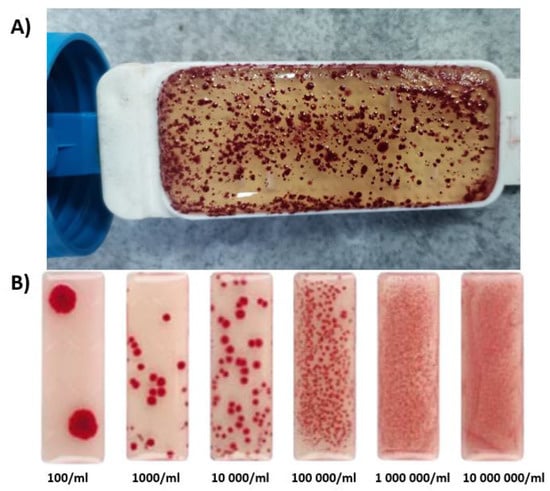
Figure 2.
(A) Appearance of the test obtained after immersion of the insert in the active sludge (the number of bacteria per 1 mL of active sludge after a 96-h observation). (B) Appearance of the reference test.
The organic compounds (IBU, [ValOMe][IBU], [ValOEt][IBU], [ValOPr][IBU], [ValOiPr][IBU], [ValOBu][IBU], [ValOAm][IBU], [ValOHex][IBU], [ValOHept][IBU], [ValOOct][IBU], SDS) were the only sources of carbon and energy (concentration—40 mg/L organic carbon) and were tested in duplicate.
Biodegradation in the mineral medium by CO2 production—General method for determining aerobic biodegradation potential [29,36,37,38,39].
First, the test vessels were set up in line (1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5), as shown in Figure 3, and a magnetic stirrer was also installed (1.6). Then, the vessels were connected with tubes. Compressed air (A) flowing through CO2 absorbers (B, C) aerated the test system. Air, whose speed was adjusted by a valve (I) was directed to a CO2 absorber (1.1), then to a CO2 indicator (1.2), aiming to indicate any CO2 in the air by turbidity.
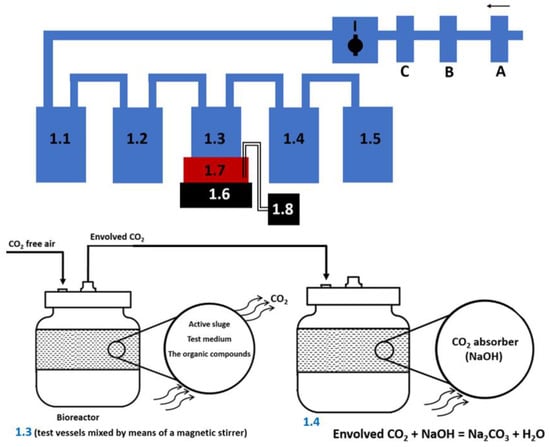
Figure 3.
The test system to measure carbon dioxide.
The test system to measure carbon dioxide is shown in Figure 3.
In the test vessel, 1.3, we placed: 250 mL of the test medium, 2.5 mL of active sludge, and organic compound in a quantity corresponding to 40 mg/L of organic carbon. The concentrations of the starting compounds IBU, [ValOMe][IBU], [ValOEt][IBU], [ValOPr][IBU], [ValOiPr][IBU], [ValOBu][IBU], [ValOAm][IBU], [ValOHex][IBU], [ValOHept][IBU], [ValOOct][IBU], SDS, were respectively: 53.24, 59.16, 58.16, 57.96, 57.96, 57.44, 57.00, 56.56, 56.16, 55.80, and 84.12 mg/L.
As a result of the biodegradability of the compound, the vessel 1.3 produced carbon dioxide, which reacts with NaOH (1.4), to produce Na2CO3:
NaOH + CO2 = Na2CO3 + H2O,
To determine the amount of carbon dioxide in the vessel (1.3), 10 mL solution from 1.4 was collected in a 25 mL flask. The contents of the flask were replenished with deionized water to the established limit. The sample was then analyzed using a total organic carbon analyzer TOC-LCSH/CSN, Shimadzu Corporation:
Na2CO3 + 2 HCl = CO2 + 2 NaCl + H2O,
NaHCO3 + HCl = CO2 + NaCl + H2O,
NaHCO3 + HCl = CO2 + NaCl + H2O,
First, the test sample contains carbonates and acidic carbonates acidified with hydrochloric acid (to obtain pH < 3). Carbonates and acidic carbonates are converted into carbon dioxide. Thus, the amount of inorganic carbon in the test sample was obtained. The test system to measure carbon dioxide is shown in Figure 3 and it consisted of the following elements: A: compressed air, aeration of the test system (aeration rate from 50 to 100 mL/min), B, C: CO2 absorber (KOH), I: aeration rate control valve a test system, 1.1: CO2 absorber (KOH)—concentration 10 mol/L, 1.2: CO2 indication (Ba(OH)2)—concentration 0.01 mol/L, 1.3: test vessels with a capacity of 500 mL mixed through a magnetic stirrer 1.6, 1.4: CO2 absorber (NaOH)—concentration 0.05 mol/L, 1.5: O2 absorber (H2O), 1.7: plastic container with cryostat 1.8. Test vessel with a capacity of 500 mL placed in a plastic container. The vessels were equipped with a cryostat in order to accurately determine the temperature of the water bath. Incubation was carried out at a temperature of 23 °C. Test results obtained are shown in Table 1 and Table 2.

Table 1.
Half-life of ibuprofen and L-valine alkyl esters ibuprofenate by bacterial cultures.

Table 2.
Phase of degradation of ibuprofen and L-valine alkyl ester ibuprofenates by bacterial cultures.
2.5. HPLC Analysis
The content of the test compound in the test medium (test vessel 1.3, Figure 3), solubility determinations, and concentration in the water phase in the partition coefficient experiments were determined using a Shimadzu, model Nexera-i, LC-2040C 3D PLUS HPLC system (Kyoto, Japan), equipped with a UV–VIS/DAD detector and Kinetex®F5 column (2.6 μm; 150 × 4.6 mm; Phenomenex, Torrance, CA, USA).
Analyses were performed at 35 °C under isocratic conditions, with the mobile phase consisting of the water–acetonitrile mixture (50/50, v/v) and a flow rate of 1 cm3/min. The detection wavelength was 210 nm. Data acquisition and processing were performed using a LabSolutions/LC Solution System (LabSolutions Lite, 5.93, Shimadzu (Kyoto, Japan)). Injections were repeated at least three times for each sample and the results were averaged. The concentration of ibuprofen and its salts was calculated on peak area measurements using a calibration curve method.
2.6. Solubility Experiments
The solubility of ibuprofen and L-valine alkyl ester ibuprofenates in deionized water and phosphate buffer (7.4—corresponding to the concentration in test vessel 1.3, Figure 3) were determined. An excess of substance was added to 2 cm3 of water or buffer in a screwed vial and was stirred vigorously at 25.00 ± 0.05 °C or 32.00 ± 0.05 °C for 24 h. Then, the mixture was centrifuged at the respective temperature, and liquid above the solid was taken, diluted, and analyzed by the HPLC method to determine the concentration of the substance.
2.7. Determination of Partition Coefficient
To determine the partition coefficient for ibuprofen and L-valine alkyl ester ibuprofenates, 10 mg (with an accuracy of 0.01 mg) of the respective compound was weighed. Then, 5 cm3 water (or buffer) saturated with n-octanol and 5 cm3 of n-octanol saturated with water were added. The mixture was vigorously agitated at 25 °C for 3 h followed by centrifugation at 7500 rpm, at 25 °C for 10 min for better phase separation. After centrifugation, the aqueous layer was decanted and analyzed by HPLC to determine the concentration of the compound. The partition coefficient log Pow was calculated following the formula:
where cw and coct represent concentration (mg/dm3) of the substance dissolved in the aqueous layer (water or phosphate buffer) and octanol, respectively.
log Pow = log coct − log cw,
The concentration of the compound dissolved in octanol was calculated by the formula:
where c0 is a total concentration (mg/dm3), calculated based on the mass of compound used in the experiment.
Coct = c0 − cw (mg/dm3),
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Elemental Analysis
Before starting the biodegradation tests, the organic carbon content was confirmed by elemental analysis. The results of the content of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, sulfur, and oxygen in the tested compounds are presented below.
Elemental analysis (%) for IBU: C 75.69, H 8.80, N 0.00, O 15.51, for [ValOMe][IBU]: C (67.63), H (9.26), N (4.11), O (18.18), for [ValOEt][IBU]: C 68.25, H 9.47, N 3.92, O 18.18, for [ValOPr][IBU]: C 68.80, H 9.70, N 3.82, O 17.50, for [ValOiPr][IBU]: C 69.23, H 9.65, N 3.86, O 17.45, for [ValOBu][IBU]: C 69.64, H 9.82, N 3.67, O 16.77, for [ValOAm][IBU]: C 70.08, H 9.99, N 3.74, O 16.25, for [ValOHex][IBU]: C 70.39, H 10.10, N 3.44, O 15.64, for [ValOHept][IBU]: C (71.22), H (10.30), N (3.04), O (15.14), for [ValOOct][IBU]: C (71.64), H (10.43), N (3.08), O (14.63), for SDS: C 46.14, H 98.13, N 0.00, O 24.58, S 12.32.
The obtained results confirm that only pure compounds were used in the research.
3.2. Biodegradation Studies
The number of bacteria (per 1 mL of active sludge) was about 100,000 (after a 96-h observation)—Figure 2.
Degradation of ibuprofen, L-valine alkyl ester ibuprofenates, and SDS (Figure 4).
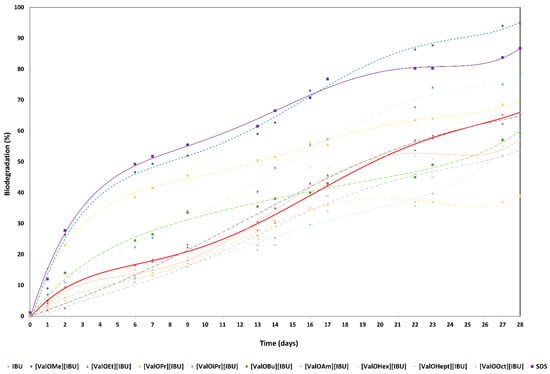
Figure 4.
Biodegradation curves for the ibuprofen (red line), L-valine alkyl ester ibuprofenates, and SDS (as the reference compound—purple line).
Tables S1 and S2 in the Supplementary Materials present the biodegradation of ionic liquids based on ibuprofen and SDS (as a reference compound) by bacterial cultures.
The maximum level of biodegradation after 28 days was 65.4% ± 3.1 of ibuprofen. The highest degree of biodegradability (94.7% ± 2.3) was assigned to [ValOMe][IBU], and slightly lower degrees of biodegradation (86.8% ± 8.5) were characterized by the reference compound—sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS). Furthermore, five modified compounds [ValOEt][IBU], [ValOPr][IBU], [ValOiPr][IBU], [ValOBu][IBU], and [ValOAm][IBU] were characterized readily by biodegradabilities of 65.7% ± 0.6, 69.5% ± 10.6, 77.0% ± 1.0, 59.5% ± 9.8, and 59.7% ± 10.6, respectively. While extending the side alkyl chain, poorly biodegradation susceptibility of tested compounds was observed: [ValOHex][IBU] (57.0% ± 3.4), [ValOHept][IBU] (54.0% ± 1.5), and [ValOOct][IBU] (39.0% ± 5.4) after 28 days of the experiment (Figure 4, Tables S1 and S2).
Half-life of ibuprofen and L-valine alkyl esters ibuprofenate by bacterial cultures (Table 1).
Table 2 presents the phase of degradation of ionic liquids based on ibuprofen and SDS.
The half-life of ibuprofen was 20.5 days (Table S1), whereas after 33 h of conducting tests involving IBU, a 10% degradation of the test compound was achieved (Table 2). It is therefore classified as easily degradable. Furthermore, four modified compounds [Va-lOMe][IBU], [ValOEt][IBU], [ValOPr][IBU], [ValOiPr][IBU] occurring as ionic liquids and SDS were characterized by a shorter half-life of 12.7, 19.3, 12.9, 14.5, and 6.8 days, respectively, than standard ibuprofen (Table 1). The compounds containing 4, 5, 6, 7, and 8 carbon atoms within the side chain [ValOBuIBU], [ValOAmIBU], [ValOHex][IBU], [ValOHept][IBU], and [ValOOct][IBU] were characterized by a longer half-life than the original ibuprofen. The half-life of these compounds was 23.7, 23.4, 22.5, 26.0, and 35.9 days, respectively (Table S1).
The compound containing the propyl group [ValOPr][IBU] in its structure and sodium dodecyl sulfate reached 10% degradation already after 15 h, however, [Va-lOMe][IBU] containing the shortest side alkyl chain in its structure reached 10% degradation after 17 h. In contrast, the [ValOiPr][IBU] containing the isopropyl group reached 10% degradation not until 34 h later (due to adaptations of the lag phase microorganisms). Longer adaptation times for microorganisms in the lag phase are required by the following compounds: [ValOEt][IBU] (118 h), [ValOAm][IBU] (48 h), [ValOHex][IBU] (46 h), [ValOHept][IBU] (65 h), [ValOOct][IBU] (37 h); see Table S2.
Degradation of the ibuprofen and its esters by active sludge was indicated by the consumption of the tested compounds after 68 days of conducting the process.
As shown in Figure 5, bacterial cultures are capable of degrading ibuprofen, L-valine alkyl ester ibuprofenates, and SDS. Almost 100% of IBU (52.71 mg/L), [ValOMe][IBU] (58.57 mg/L), [ValOEt][IBU] (57.58 mg/L), [ValOPr][IBU] (57.38 mg/L), [ValOiPr][IBU] (57.38 mg/L), [ValOBu][IBU] (56.87 mg/L), and SDS (84.11 mg/L) was degraded within 68 days.
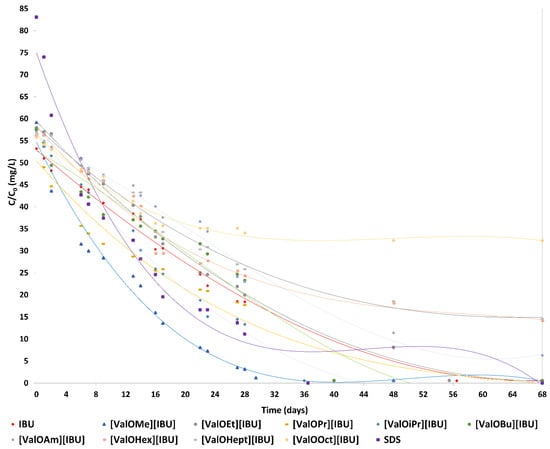
Figure 5.
Degradation profiles of ibuprofen, the alkyl esters of L-valine, and SDS by bacterial cultures. Experimental conditions: IBU= 53.24 mg/L, [ValOMe][IBU] = 59.16 mg/L, [ValOEt][IBU] = 58.16 mg/L, [ValOPr][IBU] = 58.00 mg/L, [ValOiPr][IBU] = 57.96 mg/L, [ValOBu][IBU] = 57.44 mg/L, [ValOAm][IBU] = 57.00 mg/L, [ValOHex][IBU] = 56.56 mg/L, [ValOHept][IBU] = 56.16 mg/L, [ValOOct][IBU] = 55.80 mg/L, SDS = 84.12 mg/L.
A total of 89.0% [ValOAm][IBU], 75.0% [ValOHex][IBU], and 74.0% [ValOHept][IBU] degradation was observed after 68 days, in contrast, only 42.0% [ValOOct][IBU] degradation was observed after 68 days. These results indicate the bacterial cultures are active for both ibuprofen, the alkyl esters of L-valine, and SDS.
Between 1–28 days of conducting the degradation rate of the tested compounds was the highest and was respectively: 2.3% for IBU and for [ValOEt][IBU], 3.4% for [ValOMe][IBU], 2.5% for [ValOPr][IBU], 2.8% for [ValOiPr][IBU], 2.1% [ValOBu][IBU] and for [ValOAm][IBU], 2.0% for [ValOHex][IBU], 1.9% for [ValOHept][IBU], 1.4% [ValOOct][IBU], and 3.1% for the reference compound.
At 29–68 days, the degradation rate of [ValOBu][IBU], [ValOAm][IBU], [ValOHex][IBU], [ValOHept][IBU] and [ValOOct][IBU] by active sludge decreased (amounted to ≤1%/day). In the case of IBU, [ValOMe][IBU], [ValOEt][IBU], [ValOPr][IBU], and [ValOiPr][IBU], the degradation rate by active sludge amounted to ≥1%/day.
3.3. Solubility Experiments
Dependence of half-life of the alkyl esters of L-valine on its solubility.
It can be further noted that half-lives for these compounds depend on the solubility of these compounds. In biodegradation studies, poor solubility may result in low bioavailability and thus lower biodegradation rates, as shown in Figure 6.
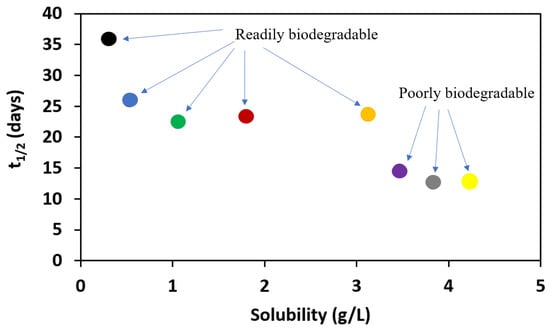
Figure 6.
Dependence of half-life of the alkyl esters of L-valine on its solubility: [ValOMe][IBU]—black dot, [ValOEt][IBU]—blue dot, [ValOPr][IBU]—green dot, [ValOBu][IBU]—red dot, [ValOAm][IBU]—orange dot, [ValOHex][IBU]—violet dot, [ValOHept][IBU]—grey dot, [ValOOct][IBU]—yellow dot.
3.4. Determination of Partition Coefficient
Dependence of biodegradability on the alkyl chain length and the lipophilicity in the alkyl esters of L-valine (Figure 7).
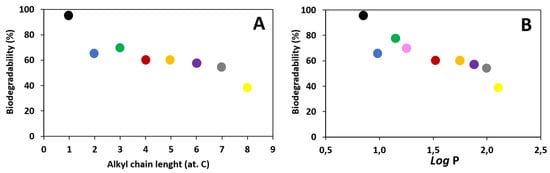
Figure 7.
Dependence of biodegradability (A) on the alkyl chain length, (B) on the lipophilicity (expressed as log P): [ValOMe][IBU]—black dot, [ValOEt][IBU]—blue dot, [ValOPr][IBU]—green dot, [ValOiPr][IBU]—pink dot, [ValOBu][IBU]—red dot, [ValOAm][IBU]—orange dot, [ValOHex][IBU]—violet dot, [ValOHept][IBU]—grey dot, [ValOOct][IBU]—yellow dot.
It has been shown that the length of the alkyl chain in the cationic part of the ionic liquid (in the alkyl ester of L-valine) affects biodegradability. A significant decrease in biodegradability was noticed with an increase in the length of the carbon chain, as shown in Figure 8A. Moreover, a relationship was observed between the lipophilicity of the analyzed compounds, expressed as the partition coefficient (log P) and biodegradability (Figure 8B). The obtained results indicate that the less lipophilic the compound, the higher the biodegradation. The reason for this phenomenon is probably the higher toxicity against bacteria from activated sludge of these compounds [40,41].
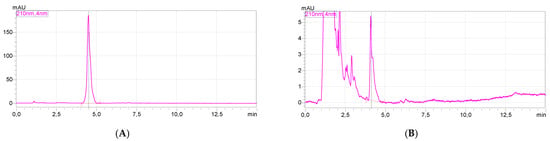
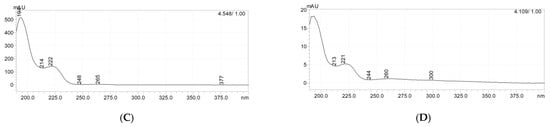
Figure 8.
HPLC chromatograms (A,B) and UV–Vis spectra (C,D) of [ValOAm][IBU] (reference, at (A,C)) and in the test ves-sel after 28 days of biodegradation at (B,D).
3.5. HPLC Analysis
HPLC analysis of the solutions in the test vessel after 28 days of biodegradation showed that the test compound could still be detected in the test vessel after the test time. For confirmation, the chromatogram and the UV–Vis spectrum of the test compound are shown (Figure 8, at left). The right side of Figure 6 shows the chromatogram and the UV–Vis spectrum for the signal with a retention time of 4.109 min; the remaining peaks visible in this chromatogram come from the test mixture and are also detected in the blank. As can be seen, the obtained UV–Vis spectra are identical, therefore the analyzed compound was [ValOAm][IBU]. A similar situation was observed for the remaining compounds.
The presence of intermediates (hydroxylated derivatives) in the test vessel may be responsible for the decreased degradation rate of ibuprofen and its esters [29,36,37,38,39]. The major metabolites of ibuprofen are 1-hydroxyibuprofen, 2-hydroxyibuprofen, and 1,2-dihydroxyibuprofen. There are not many literature reports on the degradation of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in aqueous media. Mostly, only the initial stages of biotransformation of these compounds are known [29,41,42,43].
In contrast, biodegradability tests of enantiomers of ibuprofen carried out in accordance with OECD and using active sludge showed that the degradation of (R,S)-ibuprofen started only after five days of incubation. In addition, the results showed that the enantiomers of ibuprofen were recognized by the microorganisms present in the sludge because the biodegradation of (R)-ibuprofen was higher than for (S)-ibuprofen. The maximum level of biodegradation after 28 days of the experiment and the half-lives for these compounds were 68% in 18 days and 50% in 25 days, respectively [44]. In contrast, mineralization of ibuprofen performed in accordance with OECD due to adaptations of the lag phase microorganisms was less than 10% on the sixth day of experimentation. Ibuprofen thus did not inhibit the microbial activity at the applied concentration. Results clearly show that ibuprofen is readily biodegradable in aqueous systems, and, based on these data, apparently does not pose a risk for the environment [9,45,46,47,48,49]. Other reports in the literature also indicate that when carrying out anaerobic degradation of ibuprofen for 112 days and at a temperature of 37 °C (by methanogenic bacteria), there was no significant degradation of the test compound [50].
The research conducted by Coleman et al. [34] showed that the values of the degree of biodegradability of SDS were also high at about 95% after 28 days of the experiment. In the case of the compounds containing the propyl group [PrOCH2CH2OCOCH2min][OctOSO3] and butyl group [BuOCH2CH2OCOCH2min][OctOSO3], the degree of biodegradability (determined by CO2 released and during 0 to 28 days) was more than 60% [34]. The ionic liquid [EtOCH2CH2OCOCH2min][OctOSO3] containing the ethyl group had a slightly lower biodegradability value of 59% [34].
Functionalizing of long alkyl chains could be susceptibility to the degradation of ionic liquids. The introduction of ether, ester, ester, and ether groups (simultaneously), into long had alkyl chains improved the ecotoxicity of the ionic liquids as well as nitrile, hydroxyl, and ether groups on the alkyl chain and the double bond [34,51,52,53,54,55].
In 2014, Steudte et al. reported that the use of dicationic ionic liquids with higher hydrophilic moieties (thus replacing monovalent ions) are still less toxic than the monovalent cationic ILs [56,57].
4. Conclusions
In this study, microorganism activity was used to assess the ibuprofen and L-valine alkyl ester ibuprofenates’ biodegradability (under aerobic conditions) to determine whether they are persistent in the environment. A method to measure the biodegradability of these compounds, recommended by the OECD, was proposed as well as the aerobic biodegradability of 11 organic compounds, and assessed by measuring the CO2 released. The degree of biodegradability was calculated. The results were presented as the average value (with standard deviations) obtained from three series of tests. According to the degree of biodegradability value, ibuprofen and L-valine alkyl ester ibuprofenates were classified as readily and poorly biodegradable. As expected, a correlation between increasing chain length and increasing lipophilicity was found. It has also been shown that biodegradation decreases with increasing lipophilicity.
Our research on the assessment of the biodegradation of ibuprofen and L-valine alkyl ester ibuprofenates by bacterial cultures showed that eight of the 11 compounds tested (IBU, [ValOMe][IBU], [ValOEt][IBU], [ValOPr][IBU], [ValOiPr][IBU], [ValOBu][IBU], [ValOAm][IBU], and SDS) constitute an attractive source of carbon and energy for the microorganisms used and were easily biodegradable.
The biodegradability of these new, potentially very interesting, alternative compounds to the currently used ibuprofen has been shown to be dependent on the length of the ester chain of the amino acid cation. The most biodegradable compounds had a short alkyl chain. Considering our previous results, the permeability of these compounds through the skin, and the biodegradability results obtained now, the most promising modification is the use of isopropyl and propyl esters of amino acids.
The presented work is the basis for future research on the influence of the structure of amino acid ionic liquids including the type of amino acid used and the influence of alkyl chain branching on the biodegradation process.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ma14123180/s1, Table S1: Biodegradation of ibuprofen and L-valine alkyl ester ibuprofenates by bacterial cultures, Table S2: Biodegradation of ibuprofen and L-valine alkyl ester ibuprofenates by bacterial cultures.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.M., P.O.-R. and E.J.; Formal analysis, P.O.-R. and E.M.; Funding acquisition, P.O.-R.; Investigation, E.M.; Methodology, E.M., P.O.-R., J.K. and E.J.; Supervision, P.O.-R. and E.J.; Writing—original draft, E.M. and P.O.-R.; Writing—review & editing, E.M. and P.O.-R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by National Center for Research and Development (project no. LIDER/53/0225/L-11/19/NCBR/2020).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Any data related to the study can be provided on reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wieczerzak, M.; Kudłak, B.; Namieśnik, J. Study of the Effect of Residues of Pharmaceuticals on the Environment on the Example of Bioassay Microtox®. Mon. Chem. 2016, 147, 1455–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelic, A.; Gros, M.; Ginebreda, A.; Cespedes-Sánchez, R.; Ventura, F.; Petrovic, M.; Barcelo, D. Occurrence, Partition and Removal of Pharmaceuticals in Sewage Water and Sludge during Wastewater Treatment. Water Res. 2011, 45, 1165–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, E.; Rabayah, A.; Jönsson, J.Å. Sludge Removal of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs during Wastewater Treatment Studied by Direct Hollow Fiber Liquid Phase Microextraction. J. Environ. Prot. 2013, 4, 946–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, W.; Price, G.W.; Jamieson, R.; Lake, C. Biodegradation Kinetics of Individual and Mixture Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs in an Agricultural Soil Receiving Alkaline Treated Biosolids. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrie, B.; Barden, R.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B. A Review on Emerging Contaminants in Wastewaters and the Environment: Current Knowledge, Understudied Areas and Recommendations for Future Monitoring. Water Res. 2015, 72, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klampfl, C.W. Metabolization of Pharmaceuticals by Plants after Uptake from Water and Soil: A Review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 111, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Adeel, M.; Rasheed, T.; Zhao, Y.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Emerging Contaminants of High Concern and Their Enzyme-Assisted Biodegradation—A Review. Environ. Int. 2019, 124, 336–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodarte-Morales, A.I.; Feijoo, G.; Moreira, M.T.; Lema, J.M. Degradation of Selected Pharmaceutical and Personal Care Products (PPCPs) by White-Rot Fungi. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 27, 1839–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Hu, J.; Zhu, R.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, J. Degradation of Paracetamol by Pure Bacterial Cultures and Their Microbial Consortium. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 3687–3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Rosazza, J.P.N. Microbial Transformation of Ibuprofen by a Nocardia Species. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1994, 60, 1292–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdoch, R.W.; Hay, A.G. The Biotransformation of Ibuprofen to Trihydroxyibuprofen in Activated Sludge and by Variovorax Ibu-1. Biodegradation 2015, 26, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagle, J.; Porter, A.W.; Murdoch, R.W.; Rivera-Cancel, G.; Hay, A.G. Chapter 3 Biodegradation of Pharmaceutical and Personal Care Products. In Advances in Applied Microbiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; Volume 67, pp. 65–108. ISBN 978-0-12-374802-7. [Google Scholar]
- Mackman, R.L.; Cihlar, T. Prodrug Strategies in the Design of Nucleoside and Nucleotide Antiviral Therapeutics. In Annual Reports in Medicinal Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; Volume 39, pp. 305–321. ISBN 978-0-12-040539-8. [Google Scholar]
- Beauchamp, L.M.; Orr, G.F.; de Miranda, P.; Bumette, T.; Krenitsky, T.A. Amino Acid Ester Prodrugs of Acyclovir. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 1992, 3, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, C.M.; Faulds, D. Valaciclovir: A Review of Its Antiviral Activity, Pharmacokinetic Properties and Therapeutic Efficacy in Herpesvirus Infections. Drugs 1996, 52, 754–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormrod, D.; Scott, L.J.; Perry, C.M. Valaciclovir: A Review of Its Long Term Utility in the Management of Genital Herpes Simplex Virus and Cytomegalovirus Infections. Drugs 2000, 59, 839–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Drach, J.C.; Prichard, M.N.; Yanachkova, M.; Yanachkov, I.; Bowlin, T.L.; Zemlicka, J. L-Valine Ester of Cyclopropavir: A New Antiviral Prodrug. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 2009, 20, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanidis, D.; Brandl, M. Reactivity of Valganciclovir in Aqueous Solution. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2005, 31, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curran, M.; Noble, S. Valganciclovir. Drugs 2001, 61, 1145–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunami, K.-I.; Suzuki, M.; Matsumoto, K.; Yoneda, N.; Takiguchi, K. Syntheses and Biological Activities of Isonitrile Dipeptides. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1984, 48, 1073–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitta, S.; Komatsu, A.; Ishii, T.; Iwamoto, H.; Numata, K. Synthesis of Peptides with Narrow Molecular Weight Distributions via Exopeptidase-Catalyzed Aminolysis of Hydrophobic Amino-Acid Alkyl Esters. Polym. J. 2016, 48, 955–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ossowicz, P.; Klebeko, J.; Janus, E.; Nowak, A.; Duchnik, W.; Kucharski, Ł.; Klimowicz, A. The Effect of Alcohols as Vehicles on the Percutaneous Absorption and Skin Retention of Ibuprofen Modified with l-Valine Alkyl Esters. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 41727–41740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janus, E.; Ossowicz, P.; Klebeko, J.; Nowak, A.; Duchnik, W.; Kucharski, Ł.; Klimowicz, A. Enhancement of Ibuprofen Solubility and Skin Permeation by Conjugation with l-Valine Alkyl Esters. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 7570–7584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hough, W.L.; Rogers, R.D. Ionic Liquids Then and Now: From Solvents to Materials to Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2007, 80, 2262–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedro, S.N.; Freire, C.S.R.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Freire, M.G. The Role of Ionic Liquids in the Pharmaceutical Field: An Overview of Relevant Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraz, R.; Branco, L.C.; Prudêncio, C.; Noronha, J.P.; Petrovski, Ž. Ionic Liquids as Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients. ChemMedChem 2011, 6, 975–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adawiyah, N.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Hawatulaila, S.; Goto, M. Ionic Liquids as a Potential Tool for Drug Delivery Systems. Med. Chem. Commun. 2016, 7, 1881–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamshina, J.L.; Barber, P.S.; Rogers, R.D. Ionic Liquids in Drug Delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 1367–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, J.; Weiss, S.; Reemtsma, T. Pathways and Metabolites of Microbial Degradation of Selected Acidic Pharmaceutical and Their Occurrence in Municipal Wastewater Treated by a Membrane Bioreactor. Water Res. 2005, 39, 2654–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jastorff, B.; Mölter, K.; Behrend, P.; Bottin-Weber, U.; Filser, J.; Heimers, A.; Ondruschka, B.; Ranke, J.; Schaefer, M.; Schröder, H.; et al. Progress in Evaluation of Risk Potential of Ionic Liquids—Basis for an Eco-Design of Sustainable Products. Green Chem. 2005, 7, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jodynis-Liebert, J.; Nowicki, M.; Adamska, T.; Ewertowska, M.; Kujawska, M.; Petzke, E.; Konwerska, A.; Ostalska-Nowicka, D.; Pernak, J. Acute and Subacute (28-Day) Toxicity Studies of Ionic Liquid, Didecyldimethyl Ammonium Acesulfamate, in Rats. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 32, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jodynis-Liebert, J.; Nowicki, M.; Murias, M.; Adamska, T.; Ewertowska, M.; Kujawska, M.; Piotrowska, H.; Konwerska, A.; Ostalska-Nowicka, D.; Pernak, J. Cytotoxicity, Acute and Subchronic Toxicity of Ionic Liquid, Didecyldimethylammonium Saccharinate, in Rats. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2010, 57, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gathergood, N.; Scammells, P.J.; Garcia, M.T. Biodegradable Ionic Liquids: Part III. The First Readily Biodegradable Ionic Liquids. Green Chem. 2006, 8, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, D.; Gathergood, N. Biodegradation Studies of Ionic Liquids. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studzińska, S.; Buszewski, B. Study of Toxicity of Imidazolium Ionic Liquids to Watercress (Lepidium sativum L.). Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 393, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaf, S.; Al-Rimawi, F.; Khamis, M.; Zimmerman, D.; Shuali, U.; Nir, S.; Scrano, L.; Bufo, S.A.; Karaman, R. Efficiency of Advanced Wastewater Treatment Plant System and Laboratory-Scale Micelle-Clay Filtration for the Removal of Ibuprofen Residues. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2013, 48, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiedenbeck, E.; Kovermann, M.; Gebauer, D.; Cölfen, H. Liquid Metastable Precursors of Ibuprofen as Aqueous Nucleation Intermediates. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 19103–19109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arthur, R.B.; Bonin, J.L.; Ardill, L.P.; Rourk, E.J.; Patterson, H.H.; Stemmler, E.A. Photocatalytic Degradation of Ibuprofen over BiOCl Nanosheets with Identification of Intermediates. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 358, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanavas, S.; Priyadharsan, A.; Gkanas, E.I.; Acevedo, R.; Anbarasan, P.M. High Efficient Catalytic Degradation of Tetracycline and Ibuprofen Using Visible Light Driven Novel Cu/Bi2Ti2O7/RGO Nanocomposite: Kinetics, Intermediates and Mechanism. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 72, 512–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valkó, K.L. Lipophilicity and Biomimetic Properties Measured by HPLC to Support Drug Discovery. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 130, 35–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chmiel, T.; Mieszkowska, A.; Kempińska-Kupczyk, D.; Kot-Wasik, A.; Namieśnik, J.; Mazerska, Z. The Impact of Lipophilicity on Environmental Processes, Drug Delivery and Bioavailability of Food Components. Microchem. J. 2019, 146, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, B.; Kjeldal, H.; Lolas, I.; Knudsen, A.D.; Carvalho, G.; Nielsen, K.L.; Barreto Crespo, M.T.; Stensballe, A.; Nielsen, J.L. Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of Ibuprofen-Degrading Patulibacter sp. Strain I11. Biodegradation 2013, 24, 615–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco-Urrea, E.; Pérez-Trujillo, M.; Vicent, T.; Caminal, G. Ability of White-Rot Fungi to Remove Selected Pharmaceuticals and Identification of Degradation Products of Ibuprofen by Trametes Versicolor. Chemosphere 2009, 74, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escuder-Gilabert, L.; Martín-Biosca, Y.; Perez-Baeza, M.; Sagrado, S.; Medina-Hernández, M.J. Direct Chromatographic Study of the Enantioselective Biodegradation of Ibuprofen and Ketoprofen by an Activated Sludge. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1568, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girardi, C.; Nowak, K.M.; Carranza-Diaz, O.; Lewkow, B.; Miltner, A.; Gehre, M.; Schäffer, A.; Kästner, M. Microbial Degradation of the Pharmaceutical Ibuprofen and the Herbicide 2,4-D in Water and Soil—Use and Limits of Data Obtained from Aqueous Systems for Predicting Their Fate in Soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 444, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajibola, A.S.; Adebiyi, A.O.; Nwaeke, D.O.; Ajibola, F.O.; Adewuyi, G.O. Analysis, Occurrence and Ecological Risk Assessment of Diclofenac and Ibuprofen Residues in Wastewater from Three Wastewater Treatment Plants in South-Western Nigeria. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manag. 2021, 25, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.D.; Town, R.M.; Owen, S.F.; Hogstrand, C.; Bury, N.R. Effect of Water PH on the Uptake of Acidic (Ibuprofen) and Basic (Propranolol) Drugs in a Fish Gill Cell Culture Model. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 6848–6856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, H.; Chu, W.; Huang, Y.; Xu, L.; Chen, M.; Yan, M. Solar Photocatalytic Degradation of Ibuprofen with a Magnetic Catalyst: Effects of Parameters, Efficiency in Effluent, Mechanism and Toxicity Evolution. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 276, 116691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnusamy, G.; Farzaneh, H.; Tong, Y.; Lawler, J.; Liu, Z.; Saththasivam, J. Enhanced Catalytic Ozonation of Ibuprofen Using a 3D Structured Catalyst with MnO2 Nanosheets on Carbon Microfibers. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musson, S.E.; Campo, P.; Tolaymat, T.; Suidan, M.; Townsend, T.G. Assessment of the Anaerobic Degradation of Six Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 2068–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trush, M.; Metelytsia, L.; Semenyuta, I.; Kalashnikova, L.; Papeykin, O.; Venger, I.; Tarasyuk, O.; Bodachivska, L.; Blagodatnyi, V.; Rogalsky, S. Reduced Ecotoxicity and Improved Biodegradability of Cationic Biocides Based on Ester-Functionalized Pyridinium Ionic Liquids. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 4878–4889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trush, M.M.; Semenyuta, I.V.; Hodyna, D.; Ocheretniuk, A.D.; Vdovenko, S.I.; Rogalsky, S.P.; Kalashnikova, L.E.; Blagodatnyi, V.; Kobzar, O.L.; Metelytsia, L.O. Functionalized Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids: Biological Activity Evaluation, Toxicity Screening, Spectroscopic, and Molecular Docking Studies. Med. Chem. Res. 2020, 29, 2181–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, S.P.M.; Marques, C.S.; Rosatella, A.A.; Afonso, C.A.M.; Gonçalves, F.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Toxicity Assessment of Various Ionic Liquid Families towards Vibrio Fischeri Marine Bacteria. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 76, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viboud, S.; Papaiconomou, N.; Cortesi, A.; Chatel, G.; Draye, M.; Fontvieille, D. Correlating the Structure and Composition of Ionic Liquids with Their Toxicity on Vibrio Fischeri: A Systematic Study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 215–216, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalbán, M.G.; Víllora, G.; Licence, P. Ecotoxicity Assessment of Dicationic versus Monocationic Ionic Liquids as a More Environmentally Friendly Alternative. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 150, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steudte, S.; Stepnowski, P.; Cho, C.-W.; Thöming, J.; Stolte, S. (Eco)Toxicity of Fluoro-Organic and Cyano-Based Ionic Liquid Anions. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 9382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steudte, S.; Bemowsky, S.; Mahrova, M.; Bottin-Weber, U.; Tojo-Suarez, E.; Stepnowski, P.; Stolte, S. Toxicity and Biodegradability of Dicationic Ionic Liquids. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 5198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).