Functionalization of Cellulose-Based Hydrogels with Bi-Functional Fusion Proteins Containing Carbohydrate-Binding Modules
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Cellulose-Based Hydrogels
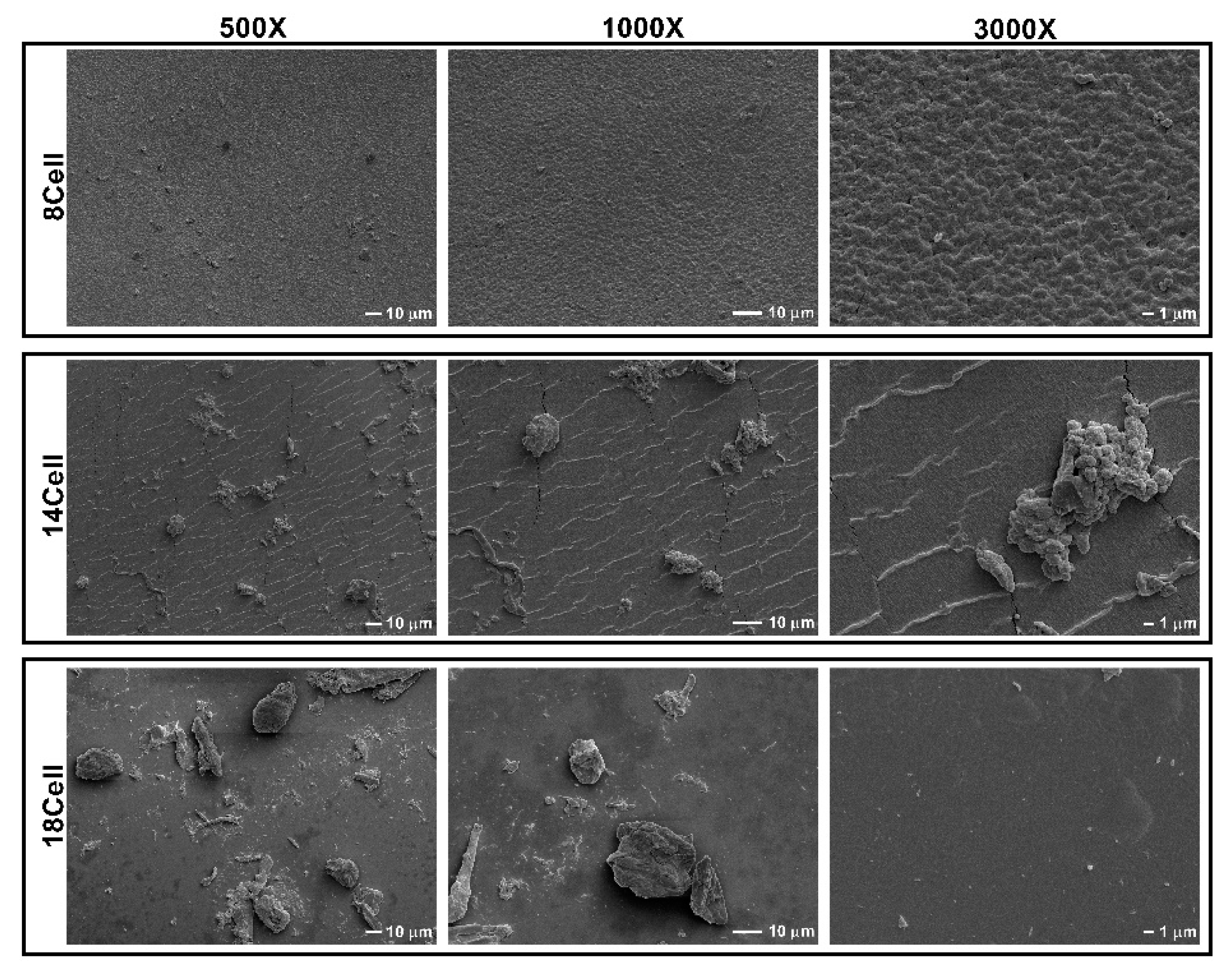
2.3. Surface Morphology Analysis of the Cellulose-Based Hydrogels
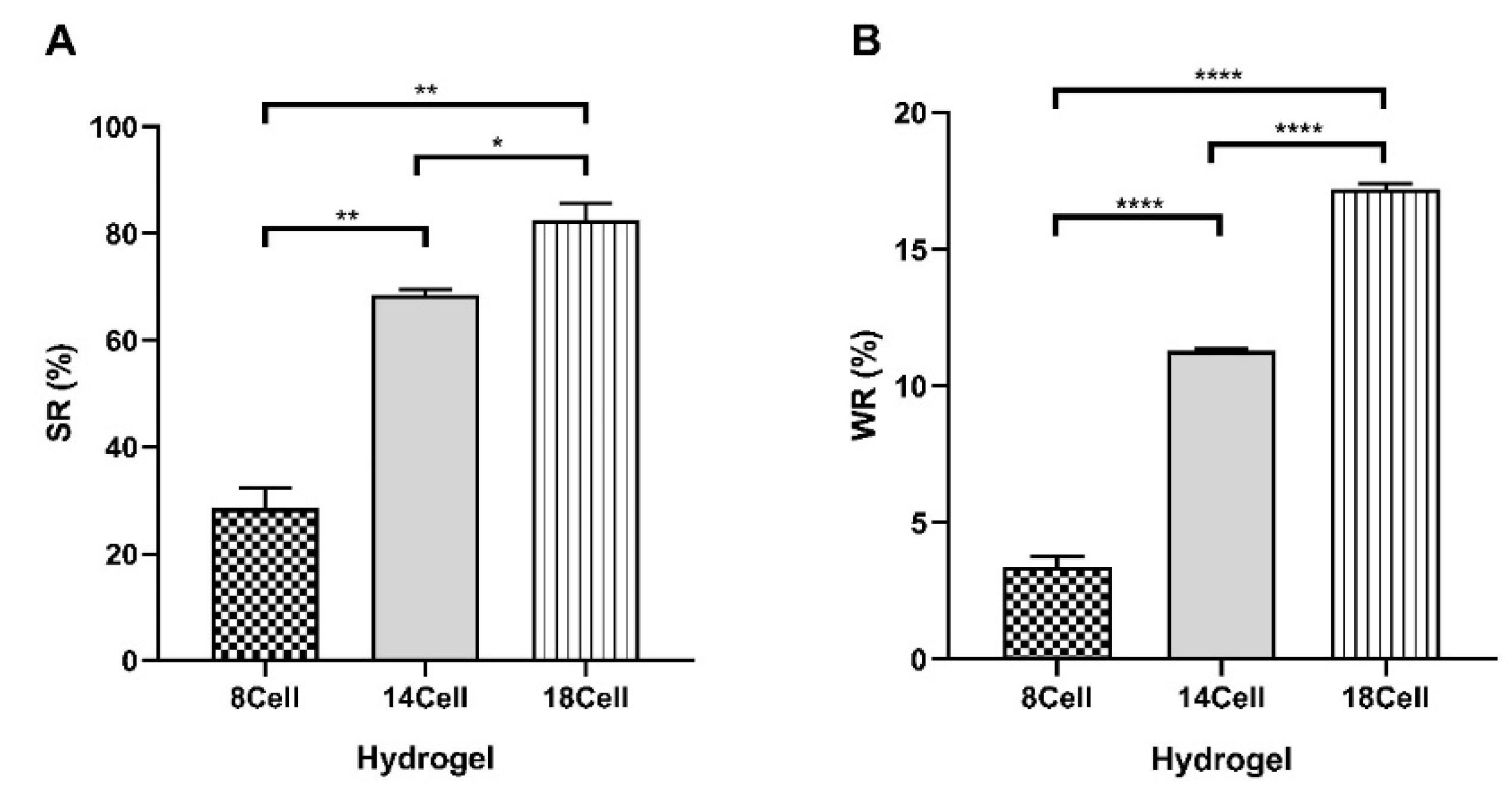
2.4. Swelling Ratio (SR) and Water Retention (WR) of Cellulose-Based Hydrogels
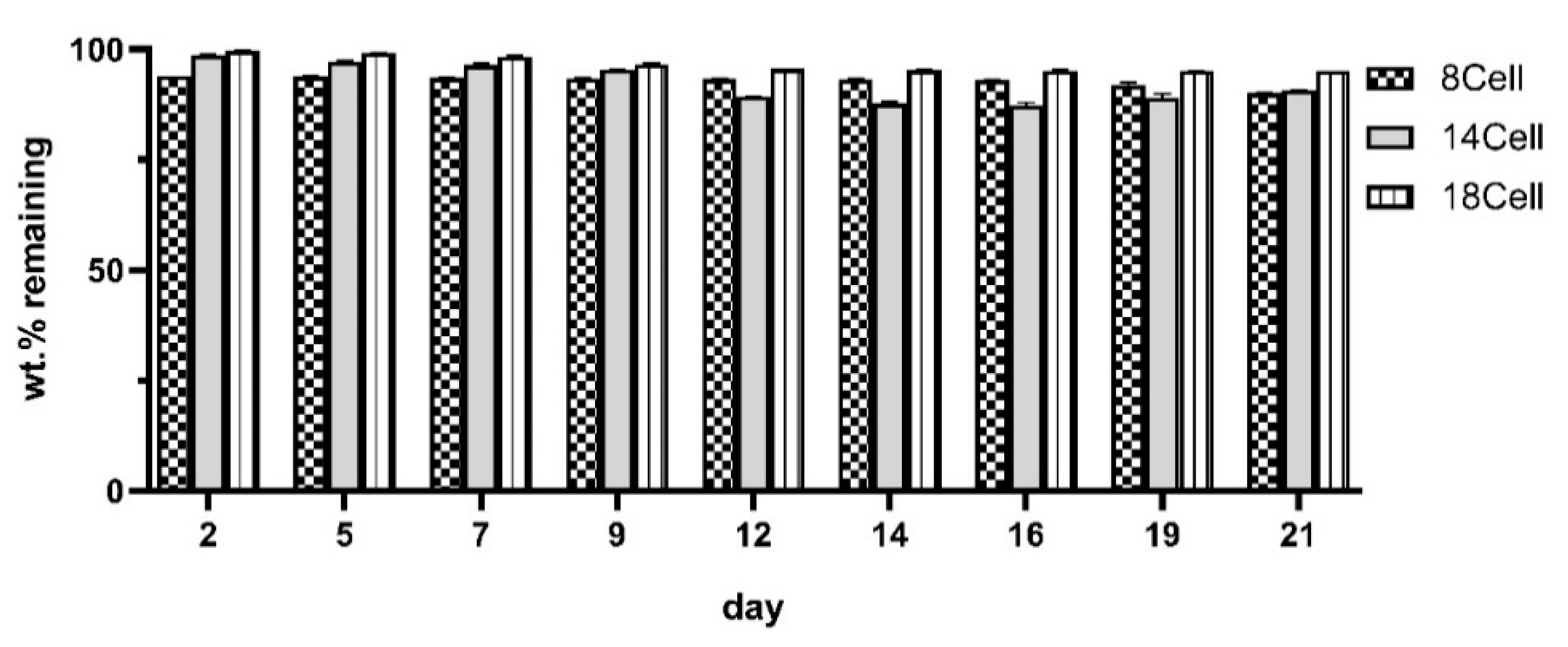
2.5. Analysis of the Degradation Profiles
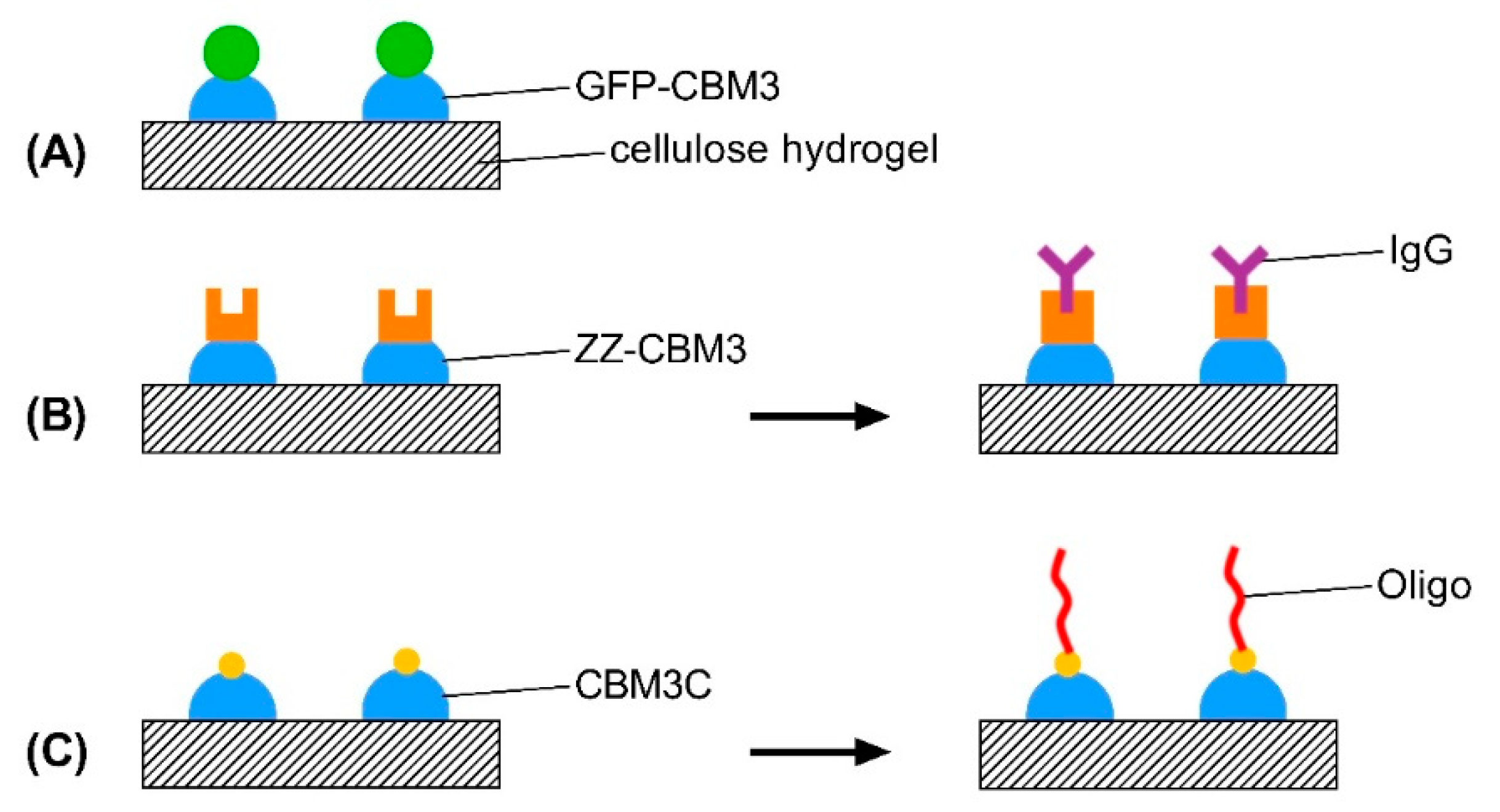
2.6. Design, Production and Purification of CBM-Recombinant Protein Fusions
2.7. Binding of CBM Fusions to Cellulose Hydrogels
2.8. Measuring the Binding of CBM-Based Fusions to the Hydrogels
2.9. Storage Stability of Immobilized Recombinant CBM Fusion Proteins
2.10. Testing of the Functionality of CBM-X Fusions
2.10.1. ZZ-CBM3
2.10.2. CBM3C
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Surface Morphology Analysis
3.2. Swelling and Water Retention Studies
3.3. Degradation Profile of the Hydrogels
3.4. Recombinant CBM Fusion Proteins
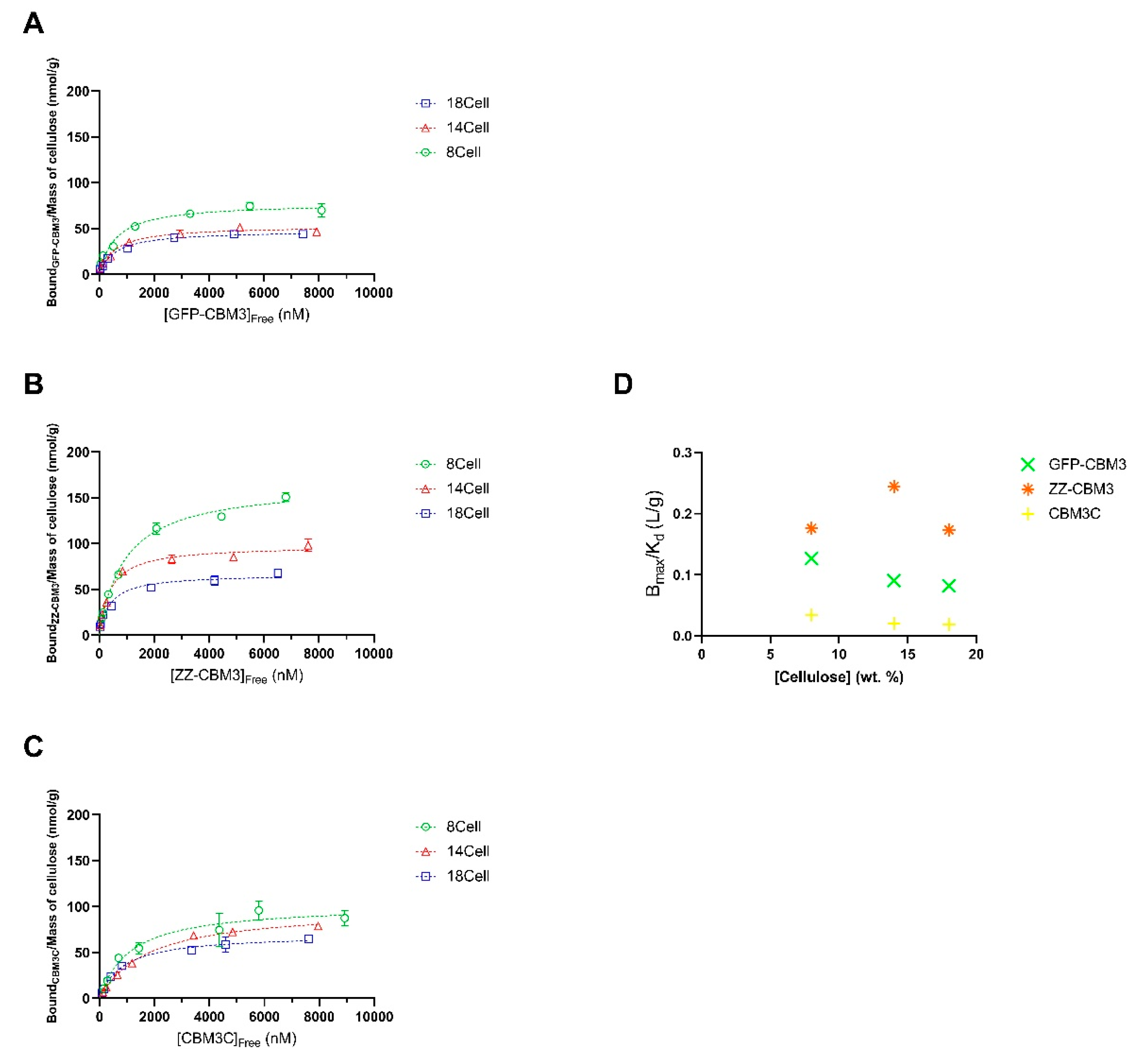
3.5. Binding of the CBM Fusions to the Hydrogels
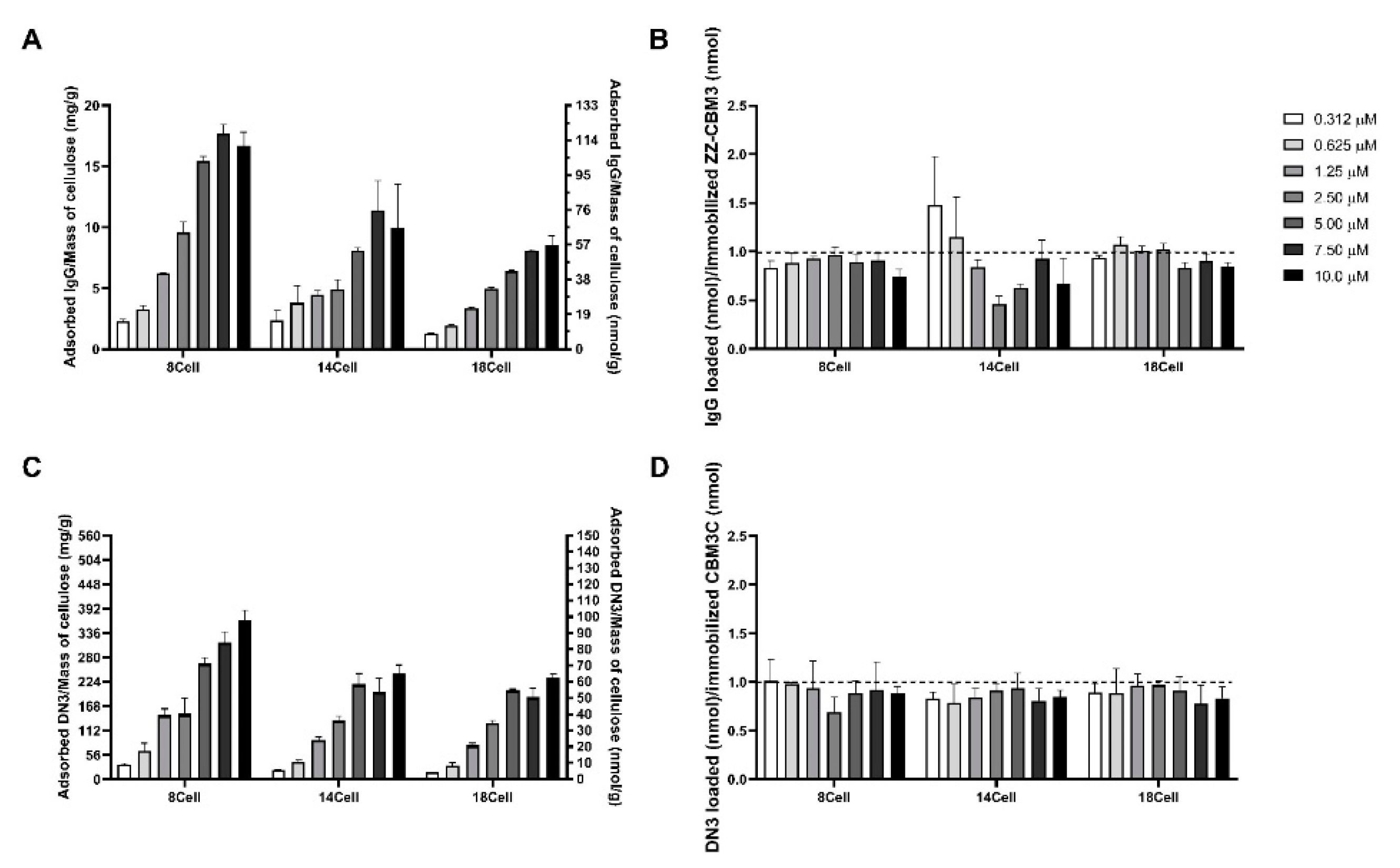
3.6. Storage Stability of Immobilized CBM Fusion Proteins
3.7. Testing of the Functionality of CBM-X Fusions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oprea, M.; Voicu, S.I. Recent advances in composites based on cellulose derivatives for biomedical applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 247, 116683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, N.A.; El-Gamal, A.R.; Gouda, M.; Mahrous, F. A new approach for natural dyeing and functional finishing of cotton cellulose. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 82, 1205–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavoine, N.; Guillard, V.; Desloges, I.; Gontard, N.; Bras, J. Active bio-based food-packaging: Diffusion and release of active substances through and from cellulose nanofiber coating toward food-packaging design. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 149, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.; Wei, X.; Zhang, Y.-H.P.J.; Zhu, Z.; You, C.; Ma, Y. Stoichiometric conversion of cellulosic biomass by in vitro synthetic enzymatic biosystems for biomanufacturing. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 9550–9559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Lan, F.; Yan, M.; Yu, J. Nanomaterials-modified cellulose paper as a platform for biosensing applications. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 4366–4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, B.; Zhang, M.; Shen, J.; He, Z.; Fatehi, P.; Ni, Y. Applications of cellulose-based materials in sustained drug delivery systems. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 2485–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainal, S.H.; Mohd, N.H.; Suhaili, N.; Anuar, F.H.; Lazim, A.M.; Othaman, R. Preparation of cellulose-based hydrogel: A review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 10, 935–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poletto, M.; Ornaghi, H.L.; Zattera, A.J. Native cellulose: Structure, characterization and thermal properties. Materials 2014, 7, 6105–6119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtenay, J.C.; Sharma, R.I.; Scott, J.L. Recent advances in modified cellulose for tissue culture applications. Molecules 2018, 23, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazón, P.; Velazquez, G.; Vázquez, M. Novel composite films from regenerated cellulose-glycerol-polyvinyl alcohol: Mechanical and barrier properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 89, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H. A one-step approach to make cellulose-based hydrogels of various transparency and swelling degrees. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 186, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Zhang, L. Cellulose-based hydrogels: Present status and application prospects. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrícia Allue, D.; Vagner Roberto, B. Synthesis and characterization of a new cellulose acetate-propionate gel: Crosslinking density determination. Open J. Polym. Chem. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsioptsias, C.; Sakellariou, K.G.; Tsivintzelis, I.; Papadopoulou, L.; Panayiotou, C. Preparation and characterization of cellulose acetate–Fe2O3 composite nanofibrous materials. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 81, 925–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swatloski, R.P.; Spear, S.K.; Holbrey, J.D.; Rogers, R.D. Dissolution of cellulose with ionic liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 4974–4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, J.; Yu, J.; Zhang, X.; He, J.; Zhang, J. Application of ionic liquids for dissolving cellulose and fabricating cellulose-based materials: State of the art and future trends. Mater. Chem. Front. 2017, 1, 1273–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, C.; Mishra, A.; Chauhan, S.; Verma, P.; Srivastava, V.; Quraishi, M.A.; Ebenso, E.E. Dissolution of cellulose in ionic liquids and their mixed cosolvents: A review. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2019, 13, 100162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosan, B.; Michels, C.; Meister, F. Dissolution and forming of cellulose with ionic liquids. Cellulose 2008, 15, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durmaz, E.N.; Zeynep Çulfaz-Emecen, P. Cellulose-based membranes via phase inversion using [EMIM]OAc-DMSO mixtures as solvent. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2018, 178, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Lindbrathen, A.; Sandru, M.; Gutierrez, M.T.G.; Zhang, X.; Hillestad, M.; He, X. Spinning cellulose hollow fibers using 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate(-)dimethylsulfoxide co-solvent. Polymers 2018, 10, 972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satani, H.; Kuwata, M.; Shimizu, A. Simple and environmentally friendly preparation of cellulose hydrogels using an ionic liquid. Carbohydr. Res. 2020, 494, 108054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, F.K.; Moreira, S.M.G.; Domingues, L.; Gama, F.M.P. Improving the affinity of fibroblasts for bacterial cellulose using carbohydrate-binding modules fused to RGD. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2010, 92A, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarikaya, M.; Tamerler, C.; Jen, A.K.-Y.; Schulten, K.; Baneyx, F. Molecular biomimetics: Nanotechnology through biology. Nat. Mater. 2003, 2, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, C.; Carvalho, V.; Domingues, L.; Gama, F.M. Recombinant CBM-fusion technology-Applications overview. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, V.M.R.; Pereira, P.M.M.; Brás, J.L.A.; Correia, M.; Cardoso, V.; Bule, P.; Alves, V.D.; Najmudin, S.; Venditto, I.; Ferreira, L.M.A.; et al. Stability and ligand promiscuity of type A carbohydrate-binding modules are illustrated by the structure of Spirochaeta thermophila StCBM64C. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 4847–4860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Einhauer, A.; Jungbauer, A. The FLAG™ peptide, a versatile fusion tag for the purification of recombinant proteins. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2001, 49, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukunaga, K.; Watanabe, T.; Novitasari, D.; Ohashi, H.; Abe, R.; Hohsaka, T. Antigen-responsive fluorescent antibody probes generated by selective N-terminal modification of IgGs. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 12734–12737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guesdon, J.-L.; Ternynck, T.; Avrameas, S. The use of avidin-biotin interaction in immunoenzymatic techniques. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1979, 27, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesch, H.P.; Kaikkonen, M.U.; Pikkarainen, J.T.; Ylä-Herttuala, S. Avidin-biotin technology in targeted therapy. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2010, 7, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.R.; Chang, B.H.; Allen, J.E.; Stiffler, M.A.; MacBeath, G. Predicting PDZ domain–peptide interactions from primary sequences. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 1041–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccaro, P.; Brannetti, B.; Montecchi-Palazzi, L.; Philipp, S.; Citterich, M.H.; Cesareni, G.; Dente, L. Distinct binding specificity of the multiple PDZ domains of INADL, a human protein with homology to INAD from Drosophila melanogaster. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 42122–42130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, B.; Moks, T.; Jansson, B.; Abrahmsen, L.; Elmblad, A.; Holmgren, E.; Henrichson, C.; Jones, T.A.; Uhlen, M. A synthetic IgG-binding domain based on staphylococcal protein A. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 1987, 1, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, A.M.M.; Prazeres, D.M.F.; Paulo, P.M.R. Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy study of the complexation of DNA hybrids, IgG antibody, and a chimeric protein of IgG-binding ZZ domains fused with a carbohydrate binding module. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 16606–16614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaniv, O.; Morag, E.; Borovok, I.; Bayer, E.A.; Lamed, R.; Frolow, F.; Shimon, L.J. Structure of a family 3a carbohydrate-binding module from the cellulosomal scaffoldin CipA of Clostridium thermocellum with flanking linkers: Implications for cellulosome structure. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun. 2013, 69, 733–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tormo, J.; Lamed, R.; Chirino, A.J.; Morag, E.; Bayer, E.A.; Shoham, Y.; Steitz, T.A. Crystal structure of a bacterial family-III cellulose-binding domain: A general mechanism for attachment to cellulose. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 5739–5751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouhmad, A.; Mamo, G.; Dishisha, T.; Amin, M.A.; Hatti-Kaul, R. T4 lysozyme fused with cellulose-binding module for antimicrobial cellulosic wound dressing materials. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 121, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, A.M.; Louro, A.F.; Martins, S.A.; Inacio, J.; Azevedo, A.M.; Prazeres, D.M. Capture and detection of DNA hybrids on paper via the anchoring of antibodies with fusions of carbohydrate binding modules and ZZ-domains. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 4340–4347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, A.; Rosa, A.M.M.; Azevedo, A.M.; Prazeres, D.M.F. A biomolecular recognition approach for the functionalization of cellulose with gold nanoparticles. J. Mol. Recognit. 2017, 30, e2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolba, M.; Minikh, O.; Brovko, L.Y.; Evoy, S.; Griffiths, M.W. Oriented Immobilization of Bacteriophages for Biosensor Applications. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S. Towards a molecular understanding of cellulose dissolution in ionic liquids: Anion/cation effect, synergistic mechanism and physicochemical aspects. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 4027–4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomimatsu, Y.; Suetsugu, H.; Yoshimura, Y.; Shimizu, A. The solubility of cellulose in binary mixtures of ionic liquids and dimethyl sulfoxide: Influence of the anion. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 279, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Zhou, Q.; Du, A.; van Kasteren, J.; Wang, Y. Preparation of nanoporous cellulose foams from cellulose-ionic liquid solutions. Mater. Lett. 2009, 63, 1851–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharekhani, H.; Olad, A.; Mirmohseni, A.; Bybordi, A. Superabsorbent hydrogel made of NaAlg-g-poly (AA-co-AAm) and rice husk ash: Synthesis, characterization, and swelling kinetic studies. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 168, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiller, K.L.; Laurencin, S.J.; Lowman, A.M. Characterization of the behavior of porous hydrogels in model osmotically-conditioned articular cartilage systems. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2009, 90, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantha, S.; Pillai, S.; Khayambashi, P.; Upadhyay, A.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, O.; Pham, H.M.; Tran, S.D. Smart Hydrogels in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. Materials 2019, 12, 3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, H.; Chu, C.R.; Payne, K.A.; Marra, K.G. Injectable in situ forming biodegradable chitosan–hyaluronic acid-based hydrogels for cartilage tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 2499–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, S.D.; Abueva, C.; Kim, B.; Lee, B.T. Chitosan–hyaluronic acid polyelectrolyte complex scaffold crosslinked with genipin for immobilization and controlled release of BMP-2. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 115, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, J.; Araújo, A.; Pinto, R.; Gama, F.M. Studies on the interaction of the carbohydrate binding module 3 from the Clostridium thermocellum CipA scaffolding protein with cellulose and paper fibres. Cellulose 2009, 16, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Kang, L.; Wei, H.; Arora, R.; Lee, Y. Study on the decreased sugar yield in enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulosic substrate at high solid loading. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2011, 164, 1139–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruys-Bagger, N.; Tatsumi, H.; Ren, G.R.; Borch, K.; Westh, P. Transient kinetics and rate-limiting steps for the processive cellobiohydrolase Cel7A: Effects of substrate structure and carbohydrate binding domain. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 8938–8948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuijk, A.; Koppert, R.; Versluis, P.; van Dalen, G.; Remijn, C.; Hazekamp, J.; Nijsse, J.; Velikov, K.P. Dispersions of attractive semiflexible fiberlike colloidal particles from bacterial cellulose microfibrils. Langmuir 2013, 29, 14356–14360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishizawa, C.I.; Jeoh, T.; Adney, W.S.; Himmel, M.E.; Johnson, D.K.; Davis, M.F. Can delignification decrease cellulose digestibility in acid pretreated corn stover? Cellulose 2009, 16, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljungquist, C.; Jansson, B.; Moks, T.; Uhlén, M. Thiol-directed immobilization of recombinant IgG-binding receptors. Eur. J. Biochem. 1989, 186, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madan, B.; Chaudhary, G.; Cramer, S.M.; Chen, W. ELP-z and ELP-zz capturing scaffolds for the purification of immunoglobulins by affinity precipitation. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 163, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, R.-M.; Yang, H.-M.; Yu, C.-M.; Tang, J.-B. Oriented covalent immobilization of engineered ZZ-Cys onto maleimide-Sepharose: An affinity platform for IgG purification. Chromatographia 2016, 79, 1271–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-M.; Bao, R.-M.; Cheng, Y.-Z.; Tang, J.-B. Site-specific covalent attachment of an engineered Z-domain onto a solid matrix: An efficient platform for 3D IgG immobilization. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 872, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
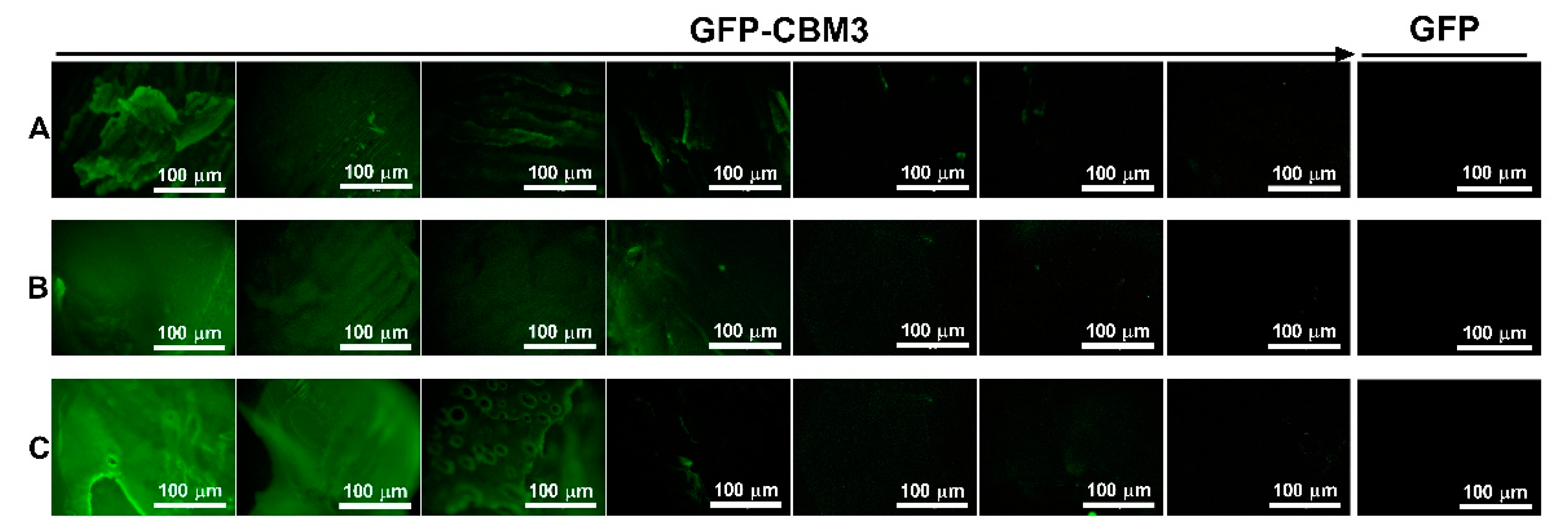
| Entry | Cellulose (g) | [EMIM][Ac] (g) | DMSO (g) | [Cellulose] (wt.%) 1 | Sample |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.4 | 3 | 2 | 8 | 8Cell |
| 2 | 0.7 | 14 | 14Cell | ||
| 3 | 0.9 | 18 | 18Cell |
| Fusion Protein | Number of Amino Acids | MW (KDa) | Extinction Coefficient, ε (M−1·cm−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CBM3 | 159 | 17.6 | 35,410 |
| CBM3 derivatives | |||
| GFP-CBM3 | 574 | 63.2 | 73,020 |
| ZZ-CBM3 | 286 | 31.9 | 38,390 |
| CBM3C | 184 | 20.2 | 35,535 |
| Parameters | 8Cell | 14Cell | 18Cell | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GFP-CBM3 | ZZ-CBM3 | CBM3C | GFP-CBM3 | ZZ-CBM3 | CBM3C | GFP-CBM3 | ZZ-CBM3 | CBM3C | |
| Bmax (nmol/g) | 77.81 | 165.3 | 102.1 | 52.77 | 97.71 | 98.55 | 47.80 | 66.59 | 69.88 |
| Kd (nM) | 599.7 | 940.4 | 1113 | 566.0 | 400 | 1769 | 586.3 | 383.9 | 853.6 |
| Bmax/Kd (L/g) | 0.1297 | 0.1758 | 0.09173 | 0.09323 | 0.2443 | 0.05571 | 0.08153 | 0.1735 | 0.08187 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barbosa, M.; Simões, H.; Prazeres, D.M.F. Functionalization of Cellulose-Based Hydrogels with Bi-Functional Fusion Proteins Containing Carbohydrate-Binding Modules. Materials 2021, 14, 3175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14123175
Barbosa M, Simões H, Prazeres DMF. Functionalization of Cellulose-Based Hydrogels with Bi-Functional Fusion Proteins Containing Carbohydrate-Binding Modules. Materials. 2021; 14(12):3175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14123175
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarbosa, Mariana, Hélvio Simões, and Duarte Miguel F. Prazeres. 2021. "Functionalization of Cellulose-Based Hydrogels with Bi-Functional Fusion Proteins Containing Carbohydrate-Binding Modules" Materials 14, no. 12: 3175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14123175
APA StyleBarbosa, M., Simões, H., & Prazeres, D. M. F. (2021). Functionalization of Cellulose-Based Hydrogels with Bi-Functional Fusion Proteins Containing Carbohydrate-Binding Modules. Materials, 14(12), 3175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14123175







