Application of Magnetic Nanoparticles Coated with Crosslinked Zwitterionic Poly(ionic liquid)s for the Extraction of Oligonucleotides
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Apparatus and Conditions
2.2.1. Characterization of Polymerizable ILs and MNPs
2.2.2. Chromatographic Method
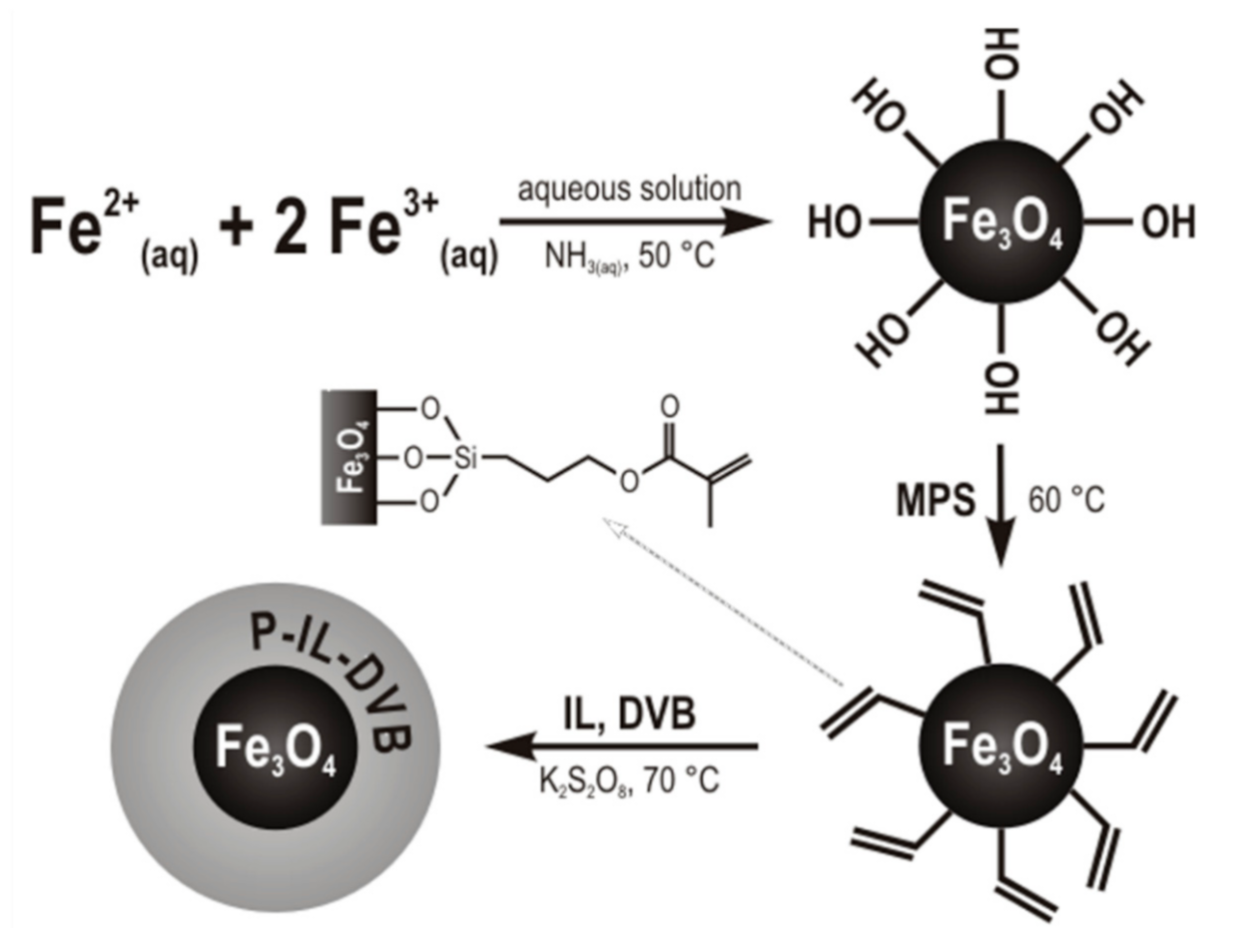
2.3. Synthesis of Polymerizable IL and MNPs
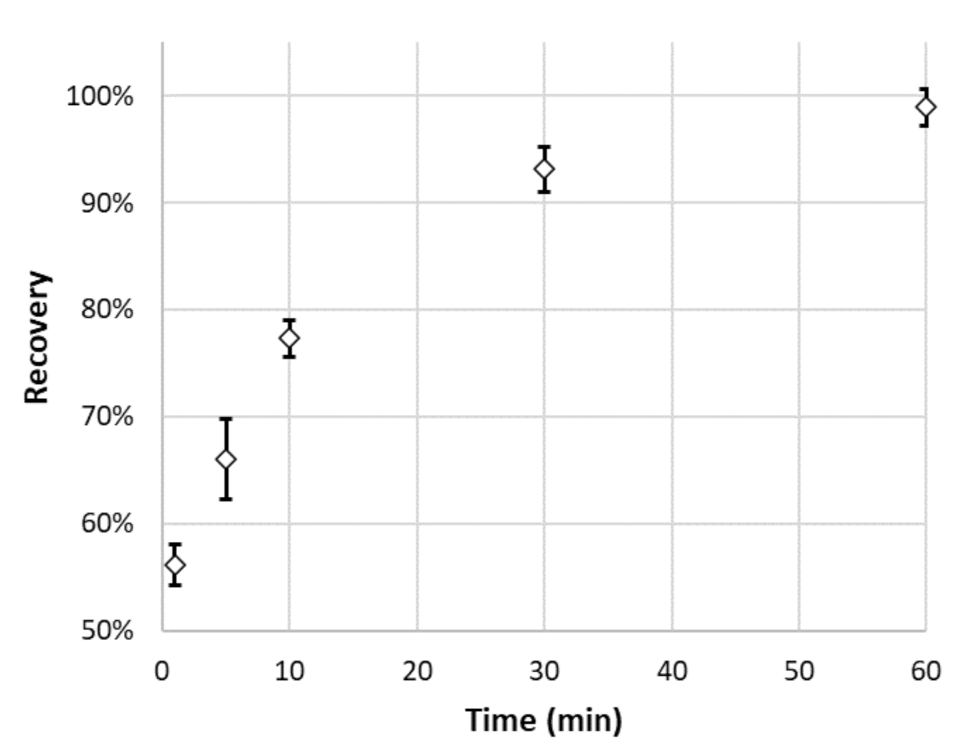
2.4. Adsorption and Desorption of OGN
2.5. Fortification and Preparation of Serum Samples
2.6. Chromatographic Method Validation
3. Results and Discussion
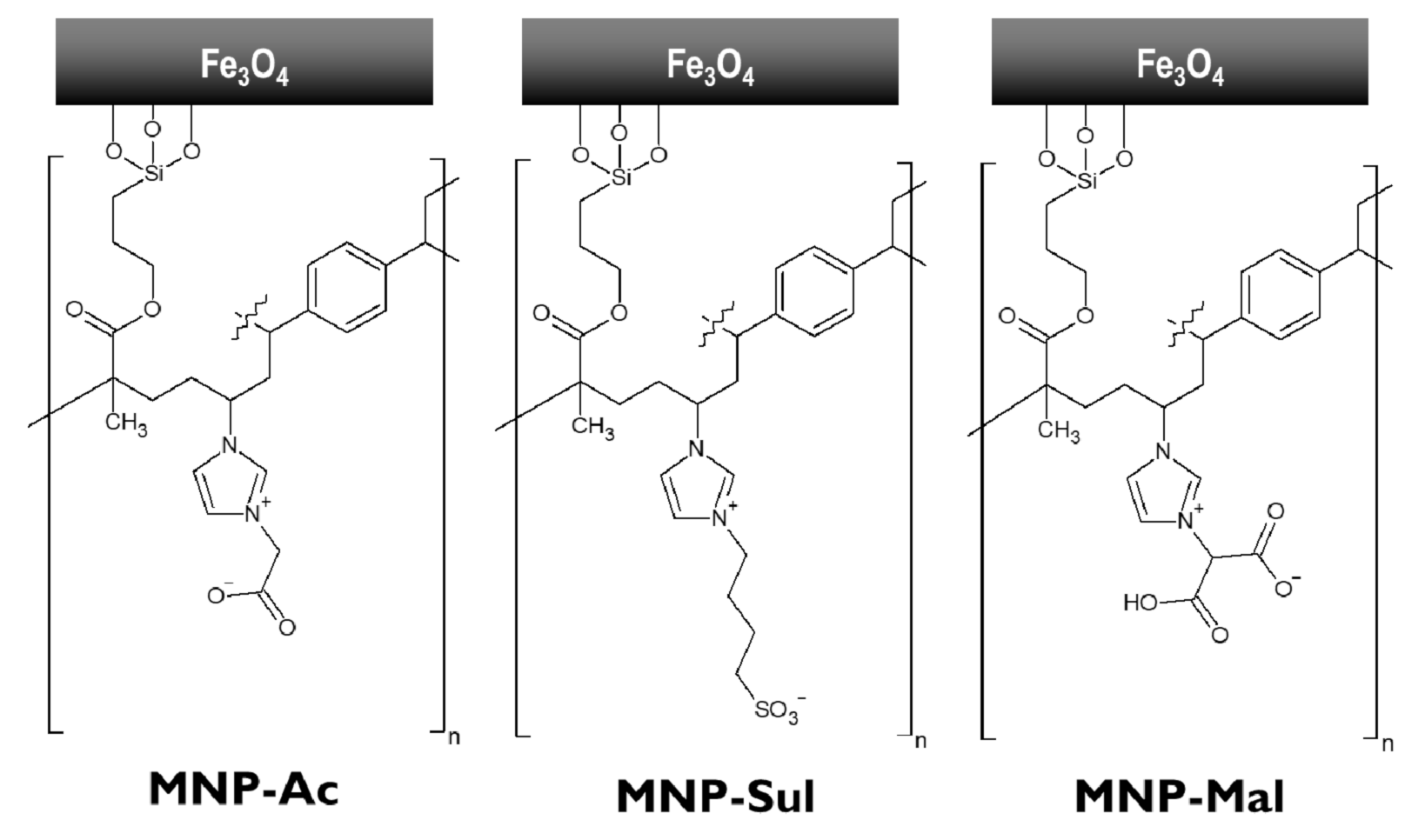
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of ILs and MNPs
3.1.1. Synthesis and Characterization of ILs
3.1.2. Synthesis and Characterization of MNP
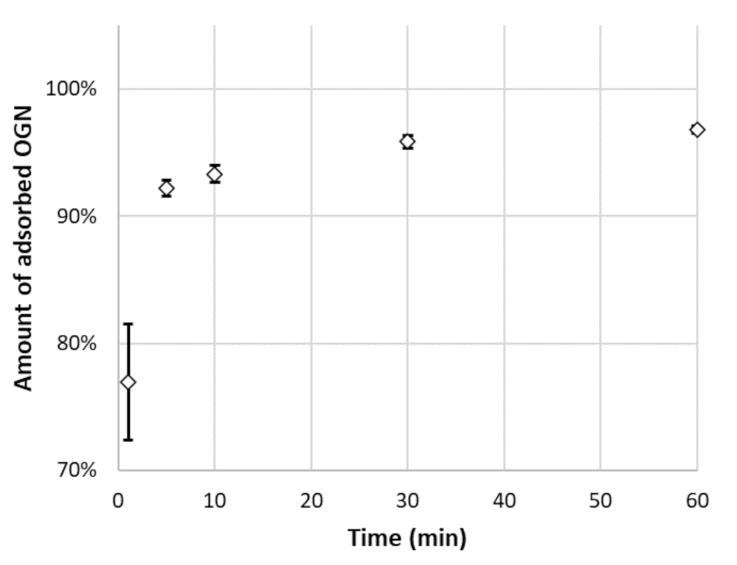
3.2. Adsorption of OGNs on the MNPs
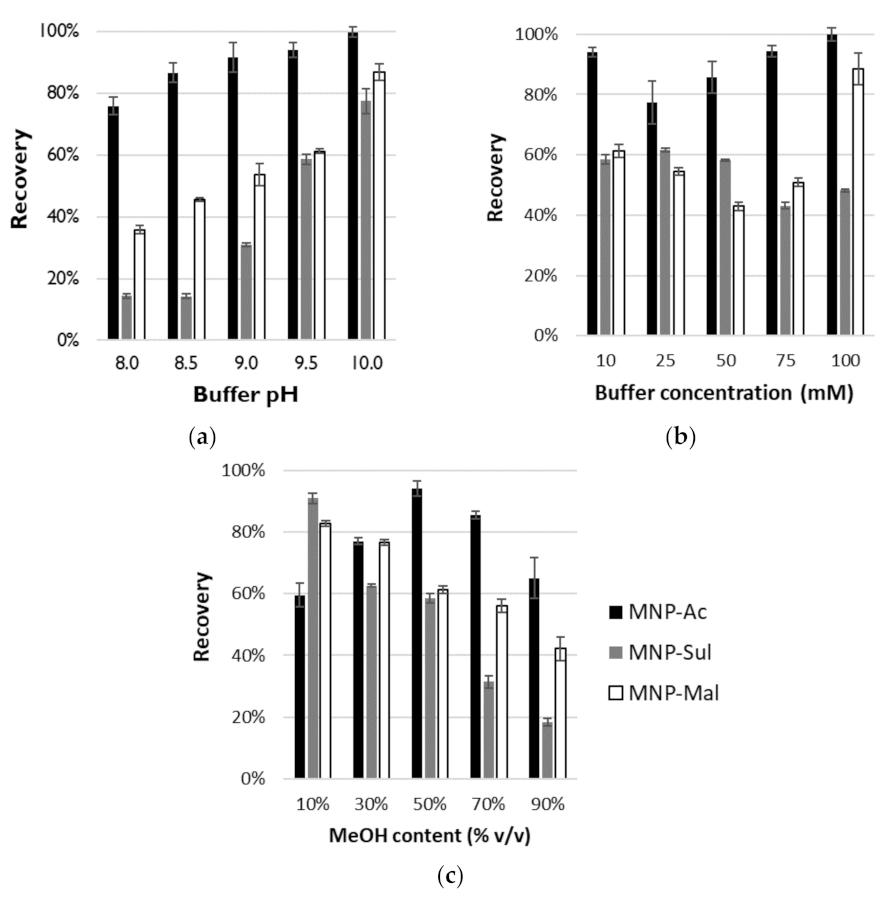
3.3. Studies on OGN Desorption
3.3.1. The IE Mode
3.3.2. The HI Mode
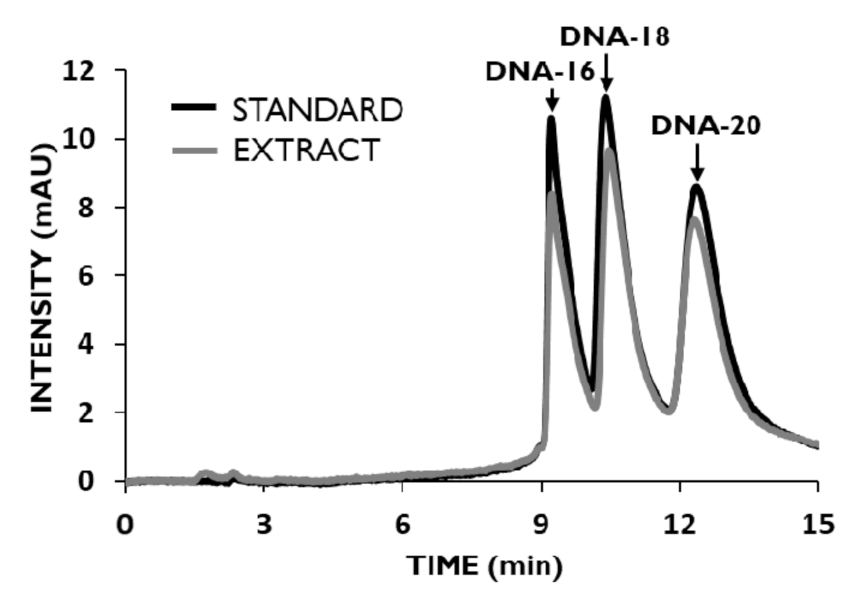
3.4. Extraction of OGNs with Different Lengths and Modifications
3.5. Chromatographic Method Validation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, W. MicroRNAs: Biomarkers, Diagnostics, and Therapeutics. In Bioinformatics in MicroRNA Research. Methods in Molecular Biology; Huang, J., Ed.; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 1617, pp. 154–196. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Sen, S. MicroRNA as Biomarkers and Diagnostics. J. Cell. Physiol. 2016, 231, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, L.T.; Gong, J.; Pham, T.T.; Kim, Y.; Le, M.T.N. microRNA exchange via extracellular vesicles in cancer. Cell Prolif. 2020, 53, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, T.C.; Langer, R.; Wood, M.J.A. Advances in oligonucleotide drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 673–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K.; Sharma, R.K.; Singh, S.K. Antisense oligonucleotides: Modifications and clinical trials. MedChemComm 2014, 5, 1454–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGinnis, A.C.; Chen, B.; Bartlett, M.G. Chromatographic methods for the determination of therapeutic oligonucleotides. J. Chromatogr. B 2012, 883, 76–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Studzińska, S. Review on investigations of antisense oligonucleotides with the use of mass spectrometry. Talanta 2018, 176, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vásconez, J.; Pero-Gascon, R.; Giménez, E.; Benavente, F. Comparison of capillary electrophoresis and zwitterionic-hydrophilic interaction capillary liquid chromatography with ultraviolet and mass spectrometry detection for the analysis of microRNA biomarkers. Talanta 2020, 219, 121263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuckowski, Ł.; Kaczmarkiewicz, A.; Studzińska, S. Review on sample preparation methods for oligonucleotides analysis by liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B 2018, 1090, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacNeill, R.; Hutchinson, T.; Acharya, V.; Stromeyer, R.; Ohorodnik, S. An oligonucleotide bioanalytical LC-SRM methodology entirely liberated from ion-pairing. Bioanalysis 2019, 11, 1157–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemsley, M.; Ewles, M.; Lee, G. Development of a bioanalytical method for quantification of a 15-mer oligonucleotide at sub-ng/ml concentrations using LC-MS/MS. Bioanalysis 2012, 4, 1457–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, L.; Shen, H. LC-TOF-MS methods to quantify siRNAs and major metabolite in plasma, urine and tissues. Bioanalysis 2019, 11, 1983–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, J.; Enders, J.; Arciprete, M.; Tran, C.; Aluri, K.; Guan, L.-H.; O’Shea, J.; Bisbe, A.; Charissé, K.; et al. Discovery of a novel deaminated metabolite of a single-stranded oligonucleotide in vivo by mass spectrometry. Bioanalysis 2019, 11, 1955–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Li, J.; Tran, C.; Aluri, K.; Zhang, X.; Clausen, V.; Zlatev, I.; Guan, L.; Chong, S.; Charisse, K.; et al. Oligonucleotide quantification and metabolite profiling by high-resolution and accurate mass spectrometry. Bioanalysis 2019, 11, 1967–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sips, L.; Ediage, E.N.; Ingelse, B.; Verhaeghe, T.; Dillen, L. LC-MS quantification of oligonucleotides in biological matrices with SPE or hybridization extraction. Bioanalysis 2019, 11, 1941–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, G.; Beverly, M. The use of strong anion-exchange (SAX) magnetic particles for the extraction of therapeutic siRNA and their analysis by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 25, 3207–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, A.; Locatelli, M.; Ulusoy, H. Recent Trends in Microextraction Techniques Employed in Analytical and Bioanalytical Sample Preparation. Separations 2017, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rehim, M.; Pedersen-Bjergaard, S.; Abdel-Rehim, A.; Lucena, R.; Moein, M.M.; Cárdenas, S.; Miró, M. Microextraction approaches for bioanalytical applications: An overview. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1616, 460790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, I.; Fernandes, C. Magnetic solid phase extraction for determination of drugs in biological matrices. Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berensmeier, S. Magnetic particles for the separation and purification of nucleic acids. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 73, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Li, R.; Chen, Y.; Pan, P.; Tong, W.; Dong, X.; Chen, Y.; Yu, D. Integrated DNA and RNA extraction using magnetic beads from viral pathogens causing acute respiratory infections. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuckowski, Ł.; Zalesińska, E.; Dzieszkowski, K.; Rafiński, Z.; Studzińska, S. Poly(ionic liquid)s as new adsorbents in dispersive micro-solid-phase extraction of unmodified and modified oligonucleotides. Talanta 2021, 221, 121662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Leng, Y.; Wang, J. Heteropolyanion-paired cross-linked ionic copolymer: An efficient heterogeneous catalyst for hydroxylation of benzene with hydrogen peroxide. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 204, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Peng, K.; Mi, Y. Preparation and properties of magnetic polystyrene microspheres. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 103, 3660–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Li, J.; Fu, R.; Lu, Z.; Yang, W. Facile preparation of superparamagnetic Fe3O4/poly(St-co-MPS)/SiO2 composite particles with high magnetization by introduction of silanol groups. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2009, 9, 5874–5879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Yang, S.; Wang, P.G. Matrix effects and application of matrix effect factor. Bioanalysis 2017, 9, 1839–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpert, A.J. Effect of salts on retention in hydrophilic interaction chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1538, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studzińska, S.; Nuckowski, Ł.; Kilanowska, A. Ultra-High-Performance Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography Hyphenated with ESI-Q-TOF-MS for the Analysis of Unmodified and Antisense Oligonucleotides. Chromatographia 2020, 83, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Abbreviation | Type of Modification | Molecular Mass (g mol−1) | Sequence 5′-3′ |
|---|---|---|---|
| DNA-20 | unmodified DNA | 6063 | GCCCAAGCTGGCATCCGTCA |
| DNA-18 | unmodified DNA | 5461 | GCCCAAGCTGGCATCCGT |
| DNA-16 | unmodified DNA | 4827 | GCCCAAGCTGGCATCC |
| DNA-11 | unmodified DNA | 3342 | GCCCAAGCTGG |
| miRNA372 | unmodified RNA | 7609 | AAAGUGCUGCGACAUUUGAGCGU |
| miRNA222 | unmodified RNA | 6910 | AGCUACAUCUGGCUACUGGGU |
| PS-20 | phosphorothioate | 6368 | GCCCAAGCTGGCATCCGTCA |
| PS-11 | phosphorothioate | 3503 | GCCCAAGCTGG |
| ME-20 | 2’-O-methyl | 6621 | GCCCAAGCTGGCATCCGTCA |
| MOE-20 | 2’-O-(2-methoxyethyl) | 7657 | GCCCAAGCTGGCATCCGTCA |
| LNA-11 | locked nucleic acid | 3706 | GCCCAAGCTGG |
| Extraction Mode | Conditions | Amount of Adsorbed OGN | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MNP-Ac | MNP-Sul | MNP-Mal | ||
| Ion-exchange | 50 µL DNA-20 5 µM + 50 µL H2O | 63.2 ± 3.5% | 0 | 0 |
| 50 µL DNA-20 5 µM + 50 µL NH4OAc pH = 6.5 | 36.5 ± 1.3% | 0 | 0 | |
| 50 µL DNA-20 5 µM + 50 µL NH4OAc pH = 5.5 | 33.8 ± 1.0% | 0 | 0 | |
| 50 µL DNA-20 5 µM + 50 µL NH4OAc pH = 4.5 | 94.5 ± 3.8% | 0 | 27.2 ± 3.6% | |
| 50 µL DNA-20 5 µM + 50 µL NH4OAc pH = 3.5 | 93.3 ± 2.1% | 93.1 ± 0.8% | 93.1 ± 2.3% | |
| Hydrophilic interactions | 50 µL DNA-20 5 µM + 50 µL ACN | 89.3 ± 2.3% | 45.1 ± 1.3% | 68.9 ± 2.1% |
| 50 µL DNA-20 5 µM + 450 µL ACN | 59.5 ± 3.4% | 64.1 ± 2.7% | 50,5 ± 1.9% | |
| 50 µL DNA-20 5 µM + 50 µL ACE | 83.6 ± 0.7% | 43.3 ± 1.7% | 37.4 ± 2.5% | |
| 50 µL DNA-20 5 µM + 450 µL ACE | 65.2 ± 1.5% | 62.7 ± 1.1% | 80.1 ± 2.9% | |
| MNP | Conditioning | Adsorption | Desorption | Recovery |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MNP-Ac | 50 µL H2O/ACN 50/50 v/v | 50 µL DNA20 5 µM + 50 µL ACN | 50 µL H2O | 23.4 ± 0.6% |
| 50 µL NH3(aq) pH = 9.5 | 34.7 ± 1.1% | |||
| MNP-Sul | 50 µL H2O/ACN 50/450 v/v | 50 µL DNA20 5 µM + 450 µL ACN | 50 µL H2O | 13.2 ± 0.3% |
| 50 µL NH3(aq) pH = 9.5 | 16.9 ± 0.3% | |||
| MNP-Mal | 50 µL H2O/ACE 50/450 v/v | 50 µL DNA20 5 µM + 450 µL ACE | 50 µL H2O | 13.7 ± 0.5% |
| 50 µL NH3(aq) pH = 9.5 | 16.8 ± 0.2% |
| Adsorbent | 2.0 mg of MNP-Ac |
|---|---|
| Conditioning | 100 µL MeOH, mixing, magnetic separation, supernatant remove |
| 100 µL 10 mM NH4OAc pH = 4.5, mixing, magnetic separation, supernatant remove | |
| Sample load | 50 µL sample + 50 µL 10 mM NH4OAc pH = 4.5, 15 min of mixing, magnetic separation, supernatant remove |
| Washing | 100 µL 10 mM NH4OAc pH = 4.5, mixing, magnetic separation, supernatant remove |
| Elution | 50 µL 10 mM NH4OAc pH = 9.5/MeOH 50/50 v/v, 30 min of mixing, magnetic separation, supernatant remove, centrifugation (14,000 rpm, 10 min), analysis |
| OGN | DNA-16 | DNA-18 | DNA-20 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration range | 1.25–20.0 μM | |||
| Calibration curve equation | y = 1.3675x − 1.2946 | y = 2.0206x − 1.6838 | y = 1.8008x − 1.6348 | |
| R2 | 0.9996 | 0.9996 | 0.9995 | |
| LOD (µM) | 0.29 | 0.28 | 0.32 | |
| LOQ (µM) | 0.95 | 0.92 | 1.08 | |
| RSD (%) intra-day | 1.25 µM | 2.90 | 3.59 | 4.93 |
| 7.5 µM | 2.12 | 2.40 | 3.59 | |
| 15.0 µM | 1.52 | 1.60 | 1.49 | |
| RSD (%) inter-day | 1.25 µM | 7.45 | 6.67 | 7.26 |
| 7.5 µM | 5.55 | 5.68 | 4.95 | |
| 15.0 µM | 3.75 | 3.54 | 3.18 | |
| Recovery (%) | 82.1 ± 2.1 | 82.5 ± 3.3 | 85.0 ± 3.6 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nuckowski, Ł.; Dzieszkowski, K.; Rafiński, Z.; Studzińska, S. Application of Magnetic Nanoparticles Coated with Crosslinked Zwitterionic Poly(ionic liquid)s for the Extraction of Oligonucleotides. Materials 2021, 14, 3146. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14123146
Nuckowski Ł, Dzieszkowski K, Rafiński Z, Studzińska S. Application of Magnetic Nanoparticles Coated with Crosslinked Zwitterionic Poly(ionic liquid)s for the Extraction of Oligonucleotides. Materials. 2021; 14(12):3146. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14123146
Chicago/Turabian StyleNuckowski, Łukasz, Krzysztof Dzieszkowski, Zbigniew Rafiński, and Sylwia Studzińska. 2021. "Application of Magnetic Nanoparticles Coated with Crosslinked Zwitterionic Poly(ionic liquid)s for the Extraction of Oligonucleotides" Materials 14, no. 12: 3146. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14123146
APA StyleNuckowski, Ł., Dzieszkowski, K., Rafiński, Z., & Studzińska, S. (2021). Application of Magnetic Nanoparticles Coated with Crosslinked Zwitterionic Poly(ionic liquid)s for the Extraction of Oligonucleotides. Materials, 14(12), 3146. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14123146








