Fabrication and Evaluation of Nano-TiO2 Superhydrophobic Coating on Asphalt Pavement
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
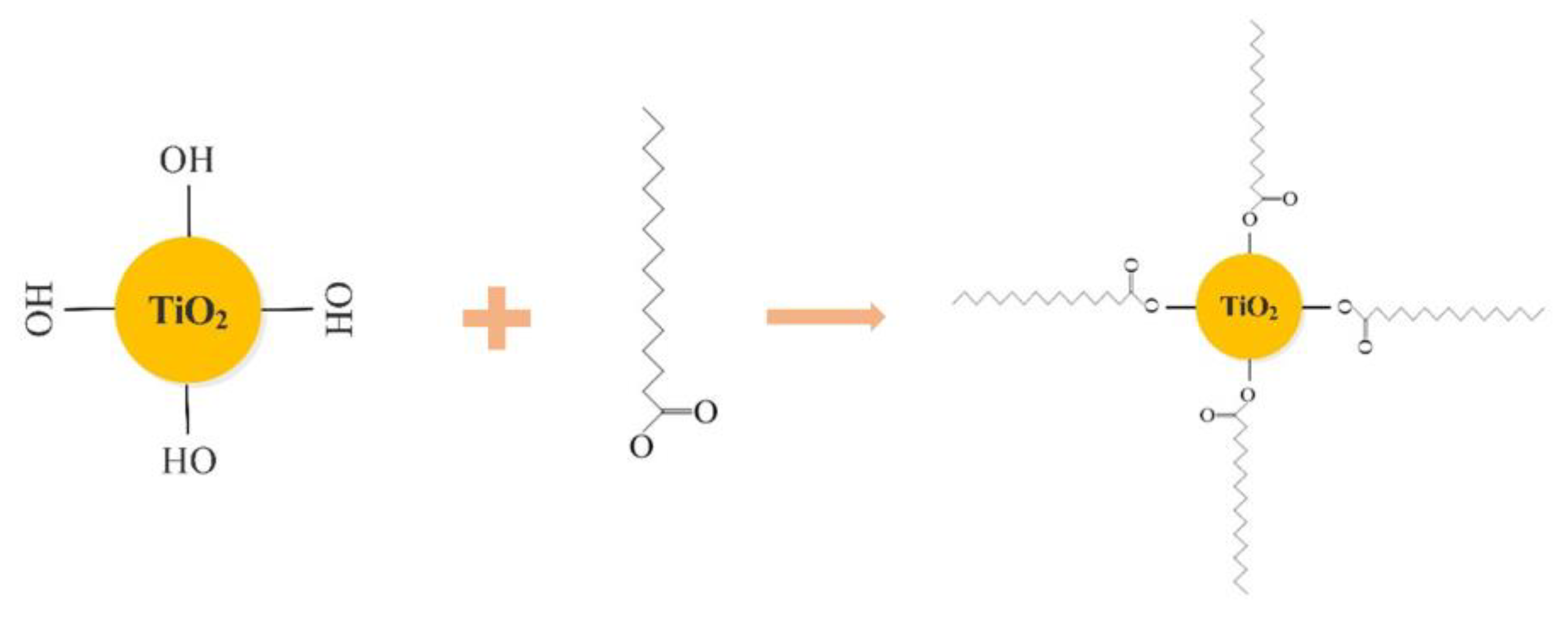
2.2. Preparation of Hydrophobic Nano-TiO2
2.3. Fabrication of Superhydrophobic Coating for Contact Angle Test
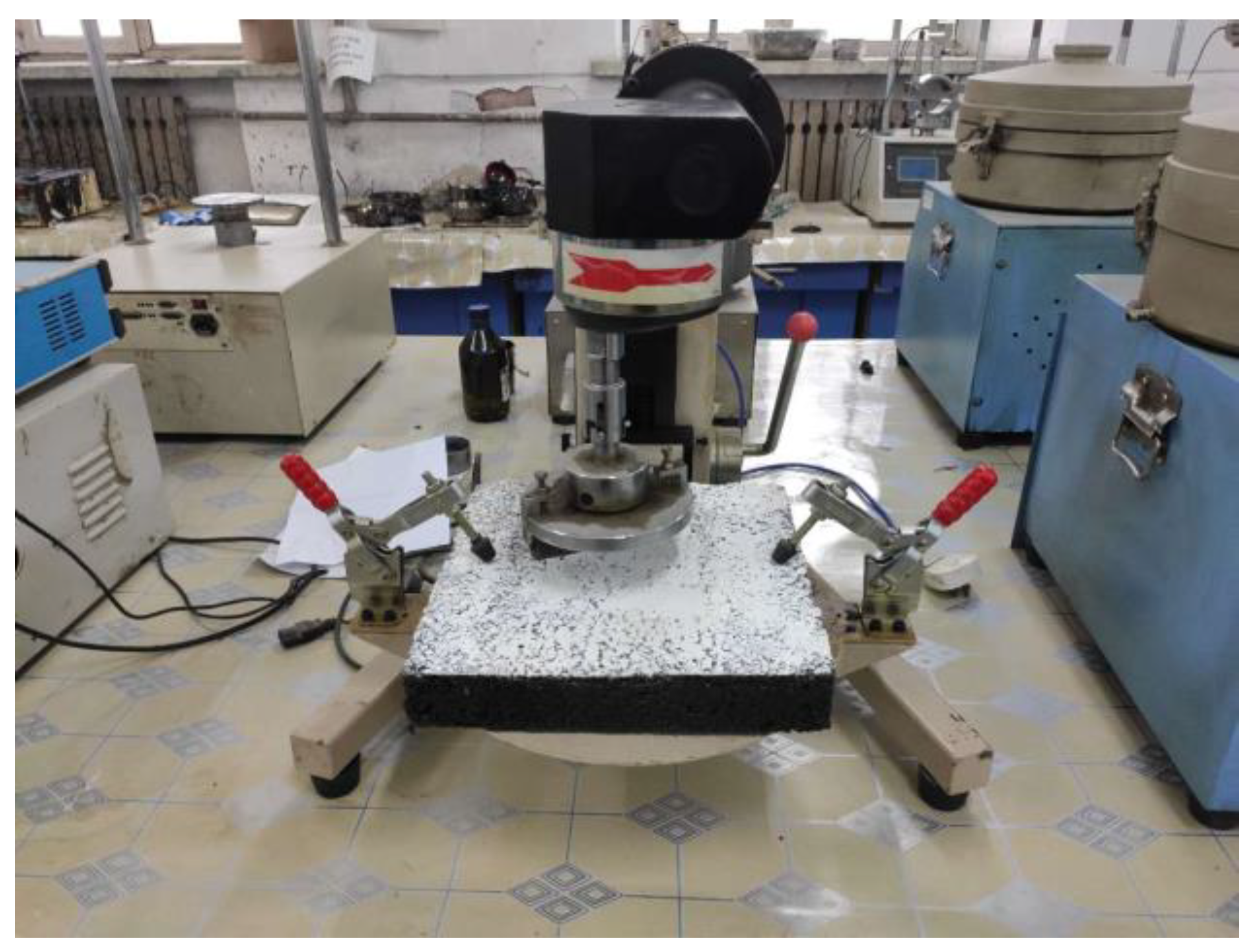
2.4. Preparation of Asphalt Mixture
2.5. Water Contact Angle (WCA) Test
2.6. Characterization
2.7. Evaluation of Water Stability of Asphalt Mixture
2.7.1. Water Absorption Test
2.7.2. Water Permeability Test
2.8. Anti-Skid Performance Test of Asphalt Pavement
2.8.1. Surface Texture Depth Test
2.8.2. British Pendulum Number Test
2.9. Wet Track Abrasion Test
3. Results and Discussions
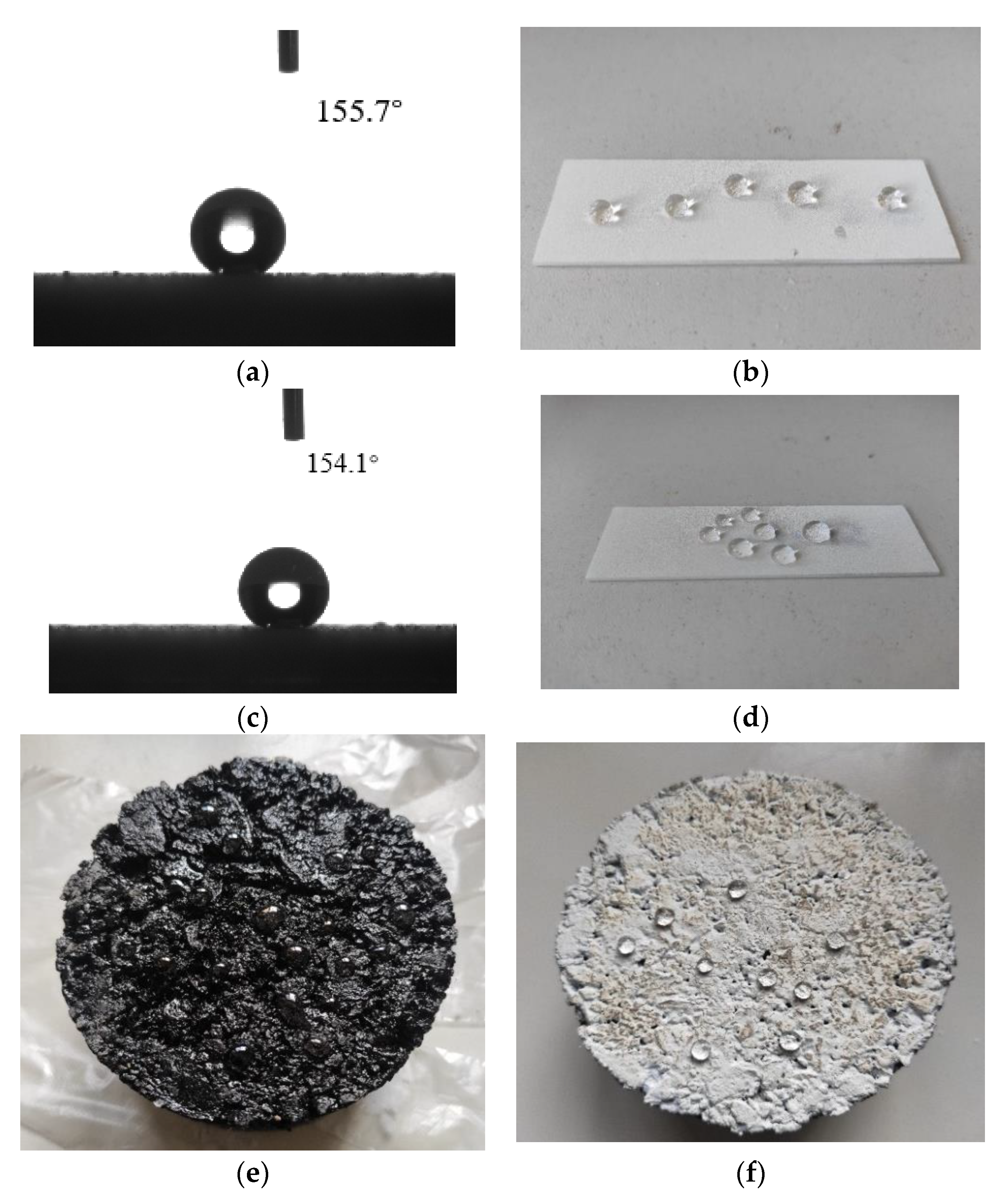
3.1. Water Contact Angle and Rolling Angle Test
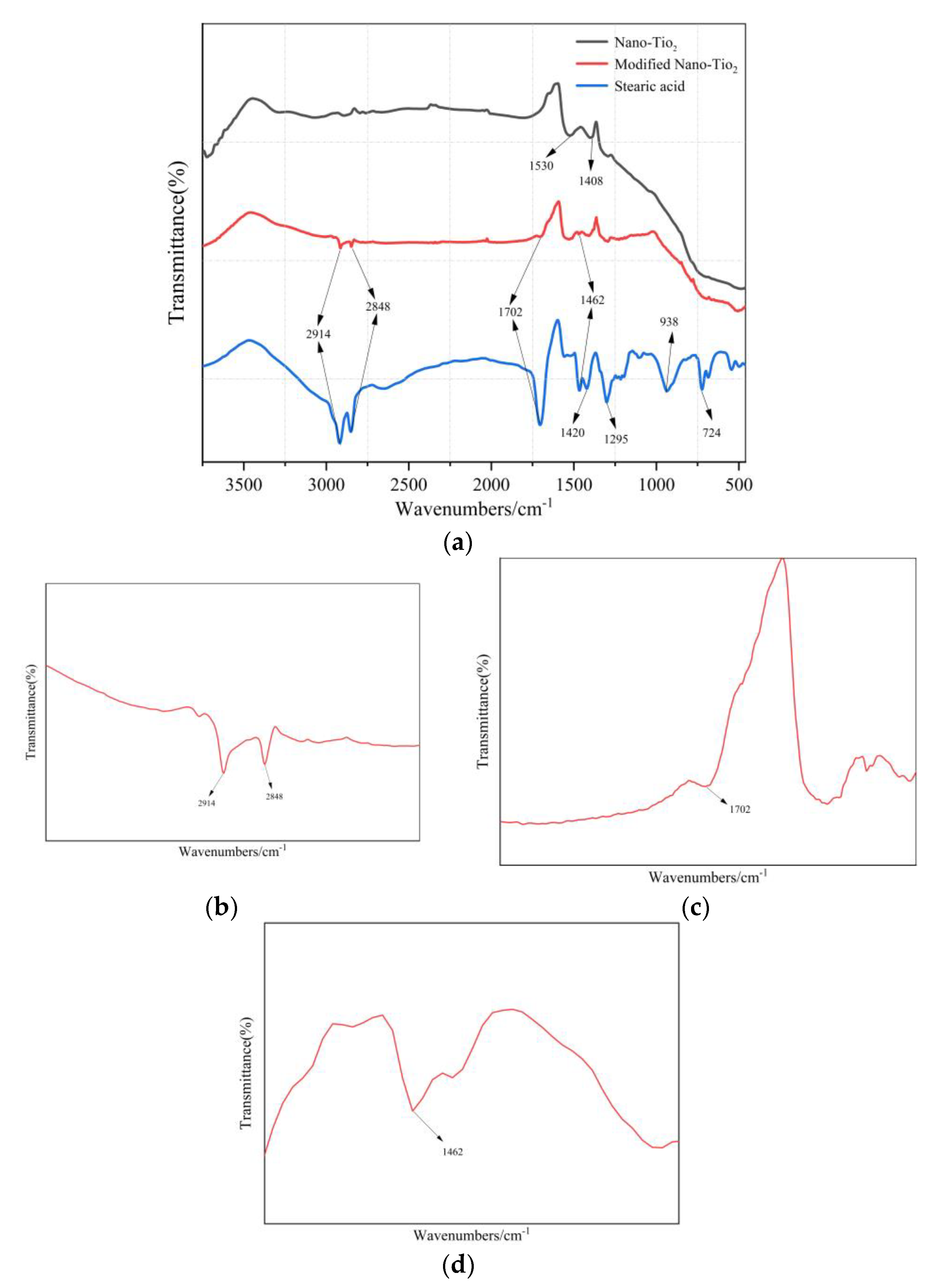
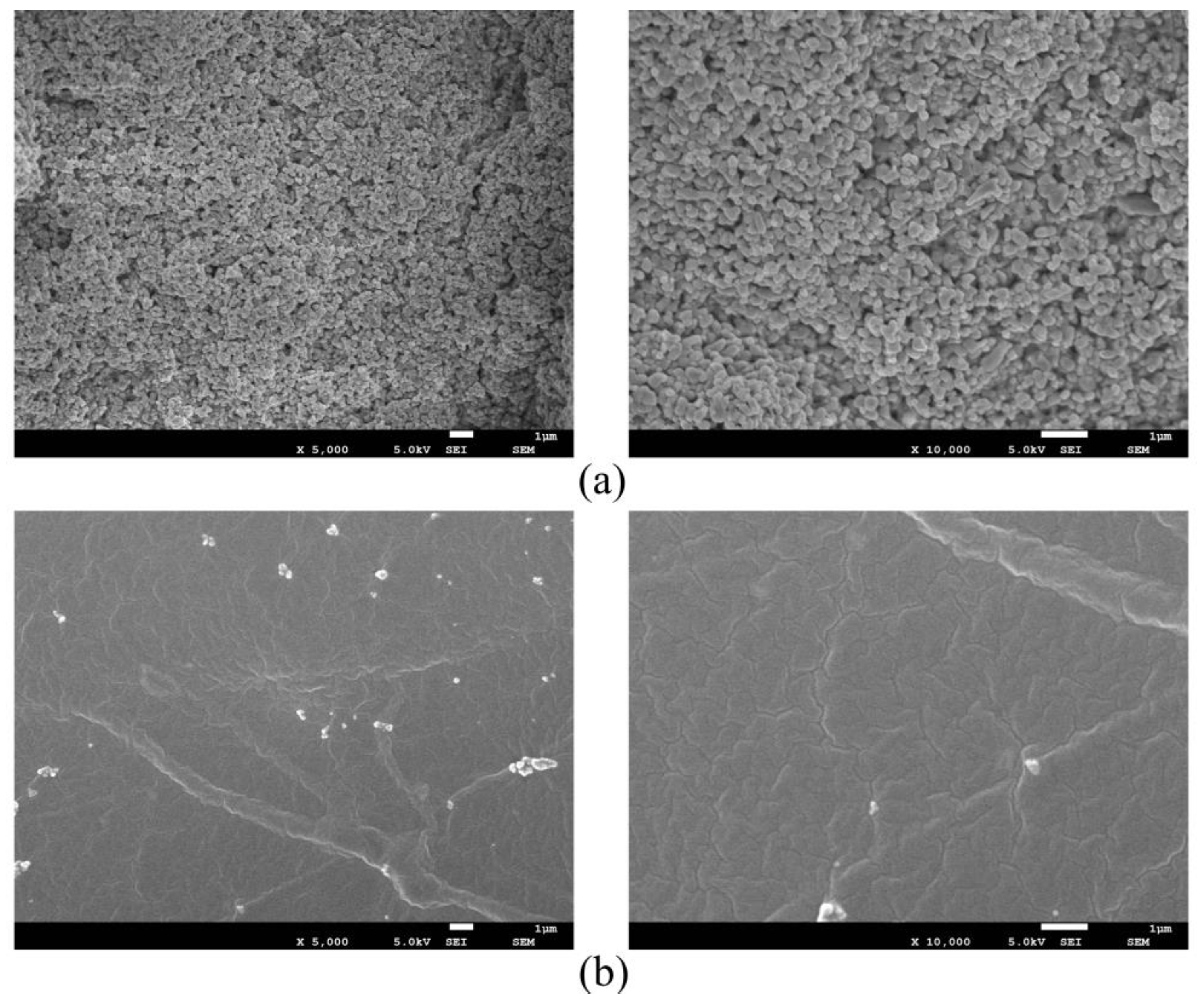
3.2. Characterization of As-Prepared Samples
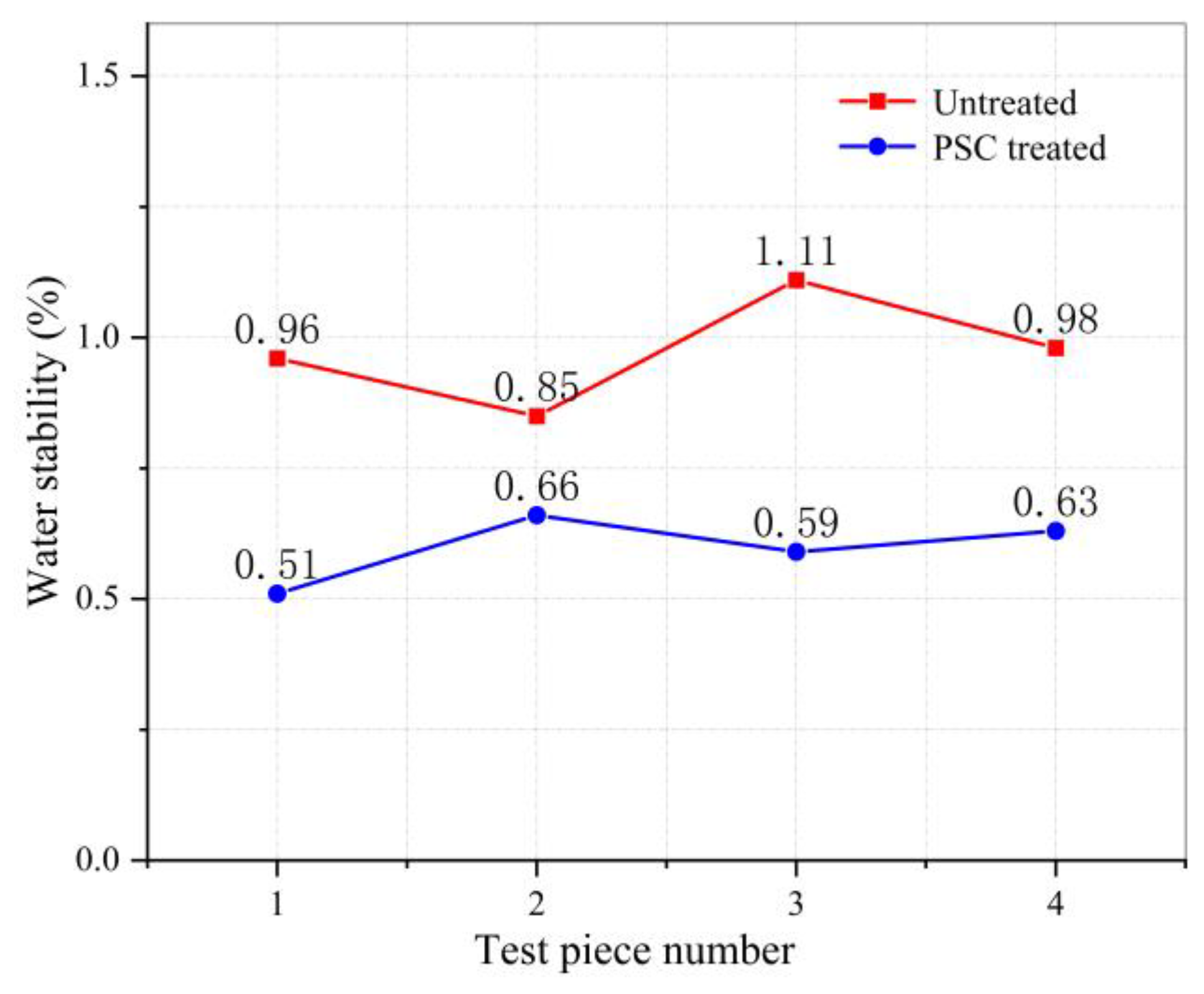
3.3. Water Stability Test Results
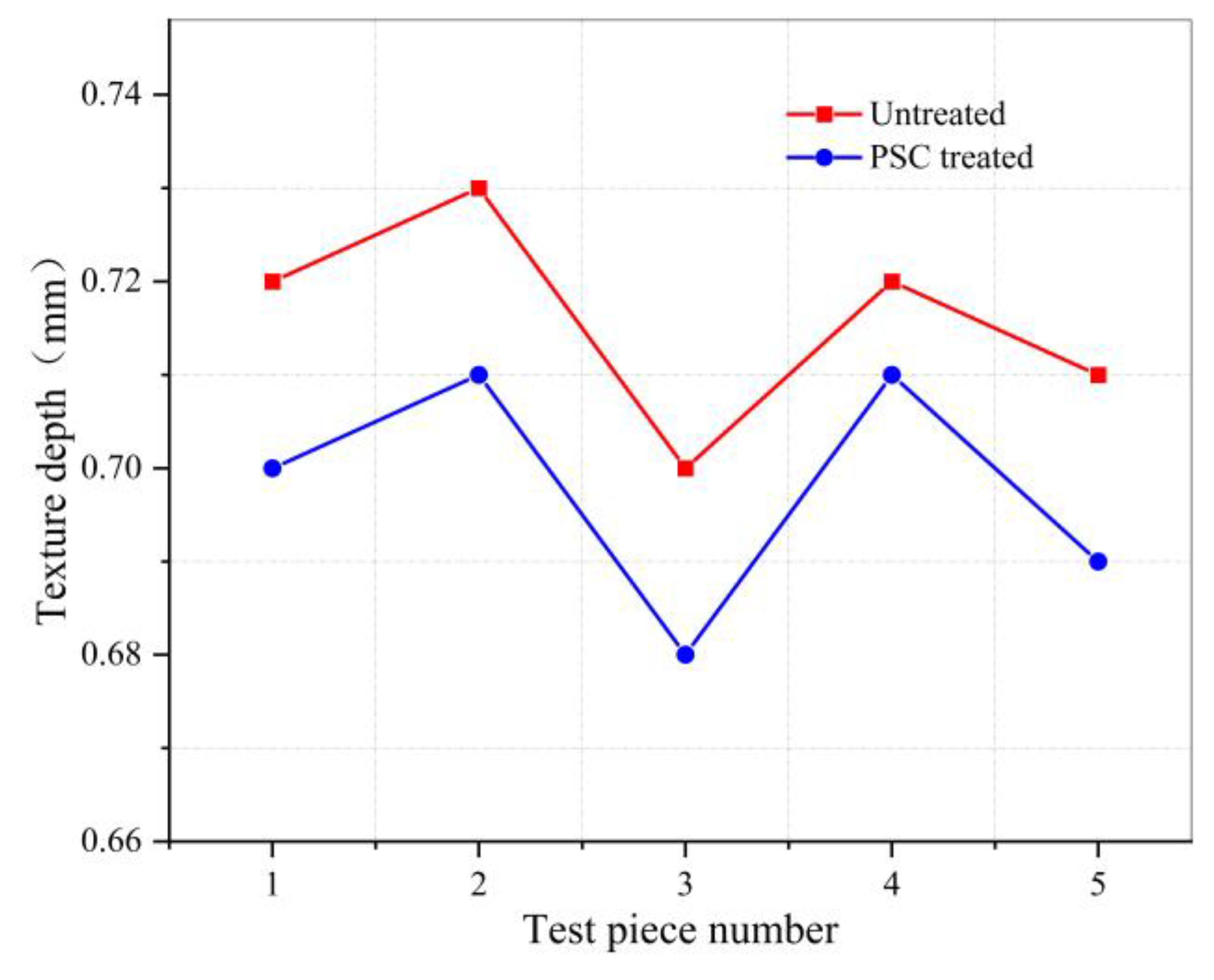
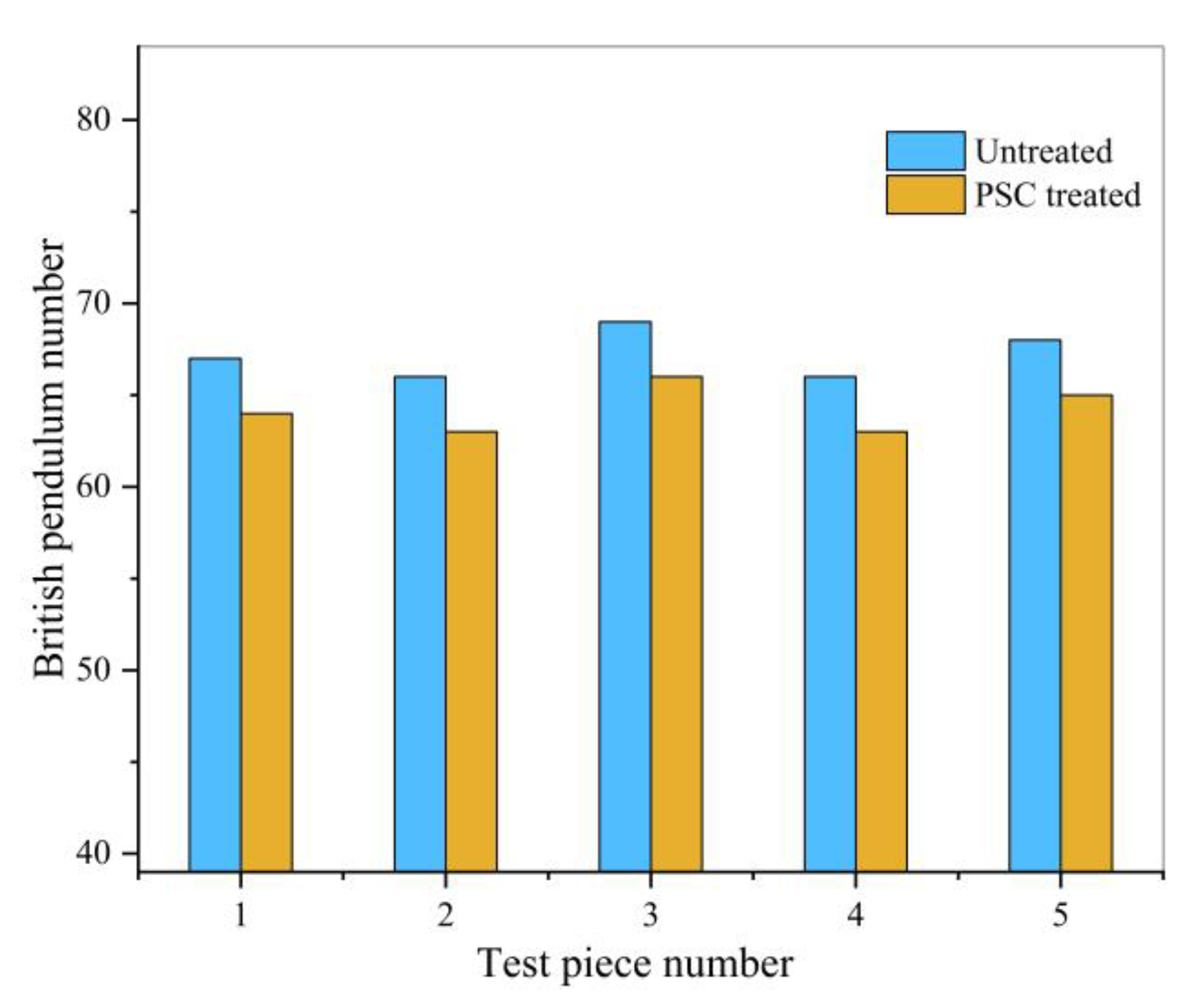
3.4. Anti-Skid Test Results
3.5. Coating the Abrasion Resistance Test
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The water contact angle and rolling angle of PSC are 153.5° and 4.7°, respectively. It can make the surface of the asphalt pavement obtain superhydrophobic ability, so that the water could be discharged from the surface of the pavement quickly.
- (2)
- Based on FT-IR and SEM. It could be seen that the low surface energy modification of stearic acid transforms nano-TiO2 from hydrophilic to super-hydrophobic, and PSC has successfully constructed a micro-nano rough structure on the surface of the asphalt mixture specimen.
- (3)
- The water absorption and water permeability test results show PSC can improve the water stability of the asphalt mixture and form an impervious layer on the surface of the road to prevent early water damage.
- (4)
- Although PSC will have a certain negative impact on the anti-skid performance of asphalt pavement, the impact is small—all meet the requirements of use.
- (5)
- The coating abrasion resistance test shows that PSC has a certain degree of abrasion resistance on asphalt pavement, and it is not easy to cause loss under wheel friction.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bazzaz, M.; Darabi, M.K.; Little, D.N.; Garg, N. Effect of Evotherm-M1 on Properties of Asphaltic Materials Used at NAPMRC Testing Facility. J. Test. Eval. 2019, 48, 2256–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzaz, M.; Darabi, M.K.; Little, D.N.; Garg, N. A Straightforward Procedure to Characterize Nonlinear Viscoelastic Response of Asphalt Concrete at High Temperatures. Transp. Res. Rec. 2018, 2672, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darabi, M.K.; Huang, C.-W.; Bazzaz, M.; Masad, E.A.; Little, D.N. Characterization and validation of the nonlinear viscoelastic-viscoplastic with hardening-relaxation constitutive relationship for asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 216, 648–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, Q.L. Water damage and prevention measures of asphalt pavement of expressway (Part 1). J. China Foreign Highw. 2000, 3, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.A. Technical Ways to Solve the Early Damage of Asphalt Pavement by Water. Highway 2000, 5, 71–76. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L. Nanostructured Materials with Superhydrophobic Surface—From Nature to Biomimesis. Chem. Ind. Eng. Prog. 2003, 22, 1258–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latthe, S.S.; Terashima, C.; Nakata, K.; Fujishima, A. Superhydrophobic surfaces developed by mimicking hierarchical surface morphology of lotus leaf. Molecules 2014, 19, 4256–4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Liu, K.; Yao, X.; Jiang, L. Bioinspired Surfaces with Superwettability: New Insight on Theory, Design, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 8230–8293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthlott, W.; Neinhuis, C. Purity of the sacred lotus, or escape from contamination in biological surfaces. Planta 1997, 202, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Cheng, F.; Zhao, B. Bio-inspired polymeric structures with special wettability and their applications: An overview. Polymers 2017, 9, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arabzadeh, A.; Ceylan, H.; Kim, S.; Gopalakrishnan, K.; Sassani, A.; Sundararajan, S.; Taylor, P.C. Superhydrophobic coatings on Portland cement concrete surfaces. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 141, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Vivian, I.; Hejazi, V.; Kozhukhova, M.I.; Nosonovsky, M.; Sobolev, K. Self-Assembling Particle-Siloxane Coatings for Superhydrophobic Concrete. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 13284–13294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakerzadeh, M.; Abtahi, S.M.; Allafchian, A.; Chamani, M.R. Examining the effect of different super hydrophobic nanomaterials on asphalt pavements. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 180, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manca, M.; Cannavale, A.; De Marco, L.; Aricò, A.S.; Cingolani, R.; Gigli, G. Durable Superhydrophobic and Antireflective Surfaces by Trimethylsilanized Silica Nanoparticles-Based Sol−Gel Processing. Langmuir 2009, 25, 6357–6362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.; Mao, Y.; Gupta, M.; Gleason, K.K.; Rutledge, G.C. Superhydrophobic Fabrics Produced byElectrospinning and Chemical Vapor Deposition. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 9742–9748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Song, J.; Liu, X.; Xu, W.; Xing, Y.; Wei, Z. Preparation of Superoleophobic and Superhydrophobic Titanium Surfaces via an Environmentally Friendly Electrochemical Etching Method. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Zhou, S.; Gu, G.; Wu, L. A facile and large-area fabrication method of superhydrophobic self-cleaning fluorinated polysiloxane/TiO2 nanocomposite coatings with long-term durability. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 6161–6164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Gurney, R.S.; Liu, D. Superhydrophobic and photocatalytic PDMS/TiO2 coatings with environmental stability and multifunctionality. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 561, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-D.; Seo, H.O.; Sim, C.W.; Jeong, M.-G.; Kim, Y.D.; Lim, D.C. Preparation of highly stable superhydrophobic TiO2 surfaces with completely suppressed photocatalytic activity. Prog. Org. Coat. 2013, 76, 596–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Liu, T.; Xu, C.; Ge, Z. Controllable fabrication of superhydrophobic TiO2 coating with improved transparency and thermostability. Colloids and Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 441, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, Y.; Yang, C.; Hu, C.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, C. A facile method to prepare superhydrophobic fluorinated polysiloxane/ZnO nanocomposite coatings with corrosion resistance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 326, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, W.; Kar, P.; Roy, P.; Bu, L.; Shoute, L.C.T.; Kumar, P.; Shankar, K. Resistance of Superhydrophobic Surface-Functionalized TiO2 Nanotubes to Corrosion and Intense Cavitation. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, S.; Ding, X.; Wu, L. Fabrication of ambient-curable superhydrophobic fluoropolysiloxane/TiO2 nanocomposite coatings with good mechanical properties and durability. Prog. Org. Coat. 2013, 76, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Yang, J.; Yin, L.; Chen, B.; Tang, H.; Liu, C.; Li, C. Fabrication of superhydrophobic polyurethane/MoS2 nanocomposite coatings with wear-resistance. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 459, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabzadeh, A.; Ceylan, H.; Kim, S.; Gopalakrishnan, K.; Sassani, A. Superhydrophobic Coatings on Asphalt Concrete Surfaces: Toward Smart Solutions for Winter Pavement Maintenance. Transp. Res. Rec. 2016, 2551, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Chen, P.; You, Z.; Lv, S.; Xu, F.; Zhang, W.; Yu, J.; Zhang, H. The anti-icing and mechanical properties of a superhydrophobic coating on asphalt pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 190, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Hu, X.; You, Z.; Xu, F.; Jiang, G.; Ouyang, H.; Guo, C.; Ma, H.; Lu, L.; Dai, J. Investigation of anti-icing, anti-skid, and water impermeability performances of an acrylic superhydrophobic coating on asphalt pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 264, 120702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha Segundo, I.; Ferreira, C.; Freitas, E.F.; Carneiro, J.O.; Fernandes, F.; Júnior, S.L.; Costa, M.F. Assessment of photocatalytic, superhydrophobic and self-cleaning properties on hot mix asphalts coated with TiO2 and/or ZnO aqueous solutions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 166, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China. Standard Test Methods of Bitumen and Bituminous Mixtures for Highway Engineering; Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2011.
- Zhang, X.; Shi, F.; Niu, J.; Jiang, Y.G.; Wang, Z.Q. Superhydrophobic surfaces: From structural control to functional application. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 621–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China. Field Test Regulations for Highway Subgrade and Pavement; Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Yao, X.; Xu, L.; Jiang, L. Fabrication and Characterization of Superhydrophobic Surfaces with Dynamic Stability. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 3343–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Yin, X.; Wang, N.; Liu, L.; Xing, J. Preparation and tribological properties of stearic acid-modified hierarchical anatase TiO2 microcrystals. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 2778–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Tao, F.; Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Cui, Y. A novel TiO2@stearic acid/chitosan coating with reversible wettability for controllable oil/water and emulsions separation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 232, 115807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Yu, S.; Jiao, S.; Lv, Z.; Liu, E.; Zhao, Y.; Cao, N. Fabrication of superhydrophobic TiO2 quadrangular nanorod film with self-cleaning, anti-icing properties. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 11508–11516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoumi, H.; Haghighi khoshkhoo, R.; Mirfendereski, S.M. Modification of physical and thermal characteristics of stearic acid as a phase change materials using TiO2-nanoparticles. Thermochim. Acta 2019, 675, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzadeh, M.; Dehghani, K.; Rezaei, M.; Mahidashti, Z. Effect of stearic acid as a low cost and green material on the self-cleaning and anti-corrosion behavior of anodized titanium. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 583, 123971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Wang, H.; Yuan, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lin, D.; Chen, L.; Zhu, Y. Durable and anti-corrosion superhydrophobic coating with bistratal structure prepared by ambient curing. Prog. Org. Coat. 2020, 149, 105922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xie, T.; Lei, S.; Ou, J.; Li, W.; Xue, M.; Huang, D. Preparation and properties of foundry dust/Portland cement based composites and superhydrophobic coatings. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 246, 118466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Groups of Nano-TiO2 Sample | Stearic Acid Content (g) | Whether Ultrasonic Dispersion | Final Stirring Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 3 | Yes | 70 |
| S2 | 3 | Yes | 50 |
| S3 | 1 | Yes | 70 |
| S4 | 4 | Yes | 70 |
| S5 | 3 | No | 50 |
| S6 | 3 | No | 70 |
| Sample Serial Number | Measured Contact Angle (°) | Average Value of Measured Contact Angle (°) | Maximum Angle (°) | Variance | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test Point 1 | Test Point 2 | Test Point 3 | ||||
| S1 | 154.6 | 154.1 | 155.7 | 154.8 | 155.7 | 0.45 |
| S2 | 153.9 | 148.7 | 153.7 | 152.1 | 153.9 | 5.79 |
| S3 | 151.8 | 154.5 | 152.3 | 152.9 | 154.5 | 1.38 |
| S4 | 150.1 | 149.3 | 150.4 | 149.9 | 150.4 | 0.22 |
| S5 | 152.9 | 150.1 | 153.2 | 152.1 | 153.2 | 1.95 |
| S6 | 149.8 | 154.3 | 152.7 | 152.3 | 154.3 | 3.47 |
| PU | 107.8 | 109.9 | 106.2 | 108.0 | 109.9 | 2.30 |
| PSC | 153.8 | 154.1 | 152.7 | 153.5 | 154.1 | 0.36 |
| Measured rolling angle (°) | ||||||
| S1 | 2.7 | 2.5 | 3.5 | 2.9 | 3.5 | 0.19 |
| PU | >10 | >10 | >10 | >10 | -- | -- |
| PSC | 4.3 | 4.7 | 5.0 | 4.7 | 5 | 0.08 |
| Sample Group | ma (g) | mw (g) | mf (g) | Sa (%) | Average Value (%) | Reduced Ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSC treated | 1183.3 | 695.5 | 1185.8 | 0.51 | 0.60 | 60.5 |
| 1179.7 | 699.5 | 1182.9 | 0.66 | |||
| 1181.9 | 692.9 | 1184.8 | 0.59 | |||
| 1184.8 | 694.3 | 1187.9 | 0.63 | |||
| Untreated | 1184.5 | 700.6 | 1189.2 | 0.96 | 0.98 | |
| 1181.0 | 700.8 | 1185.1 | 0.85 | |||
| 1183.0 | 702.3 | 1188.4 | 1.11 | |||
| 1176.7 | 700.7 | 1181.4 | 0.98 |
| Sample | Water Permeability Coefficient (mL/min) | Average Value (mL/min) |
|---|---|---|
| Untreated | 26.6 | 27.5 |
| 28.1 | ||
| 27.9 | ||
| PSC treated | impermeable | impermeable |
| impermeable | ||
| impermeable |
| MTD of Untreated Samples (mm) | MTD of PSC Treated Samples (mm) | Reduced Ratio (%) | Average Reduced Ratio (%) | Standard Requirement (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.72 | 0.70 | 2.8 | 2.5 | ≥0.55 |
| 0.73 | 0.71 | 2.7 | ||
| 0.70 | 0.68 | 2.9 | ||
| 0.72 | 0.71 | 1.4 | ||
| 0.71 | 0.69 | 2.8 |
| Sample | British Pendulum Number | Average Number | Reduce the Magnitude (%) | Standard Requirement | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Untreated | 67 | 66 | 69 | 66 | 68 | 67.2 | 4.4 | ≥45 |
| PSC Treated | 64 | 63 | 66 | 63 | 65 | 64.2 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Lin, X.; Wang, H. Fabrication and Evaluation of Nano-TiO2 Superhydrophobic Coating on Asphalt Pavement. Materials 2021, 14, 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14010211
Li H, Lin X, Wang H. Fabrication and Evaluation of Nano-TiO2 Superhydrophobic Coating on Asphalt Pavement. Materials. 2021; 14(1):211. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14010211
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Hongfeng, Xiangwen Lin, and Hongguang Wang. 2021. "Fabrication and Evaluation of Nano-TiO2 Superhydrophobic Coating on Asphalt Pavement" Materials 14, no. 1: 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14010211
APA StyleLi, H., Lin, X., & Wang, H. (2021). Fabrication and Evaluation of Nano-TiO2 Superhydrophobic Coating on Asphalt Pavement. Materials, 14(1), 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14010211





