Hydraulic Activity and Microstructure Analysis of High-Titanium Slag
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Instruments
2.3. Test Method
2.3.1. Hydraulic Activity Test
2.3.2. Content of Glass Phase
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Hydraulic Activity Test
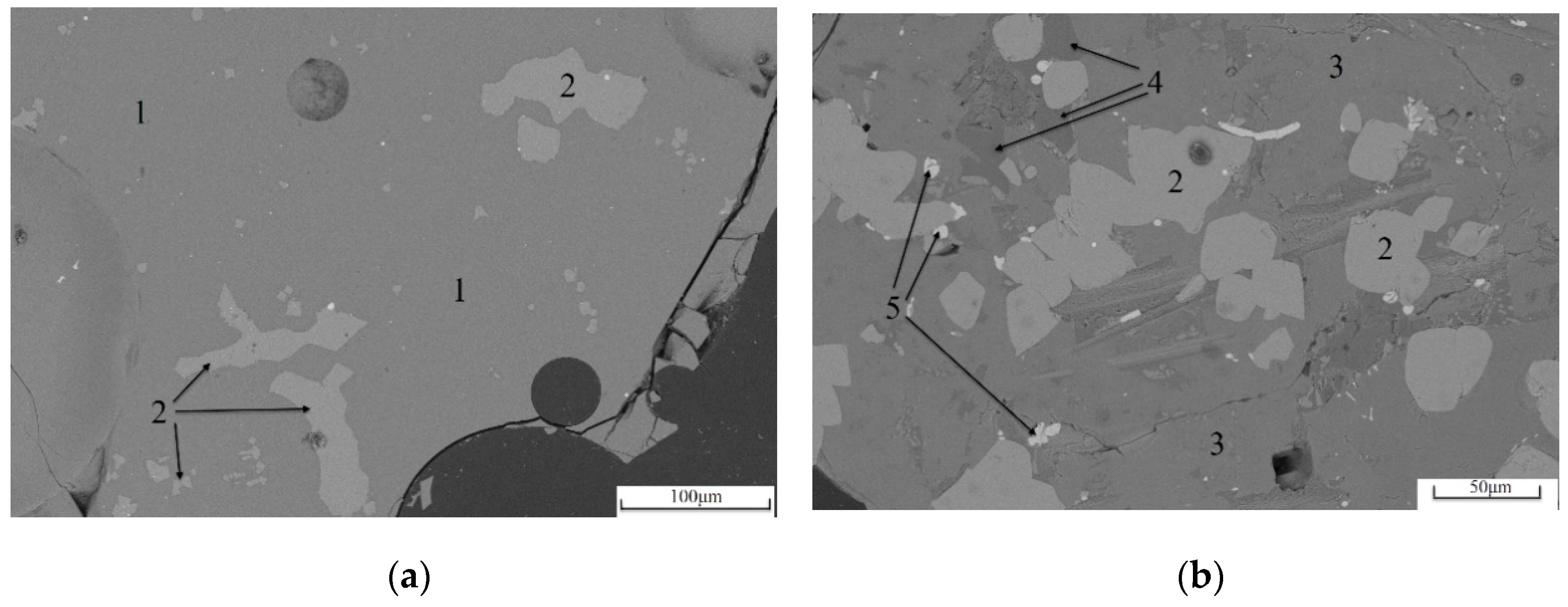
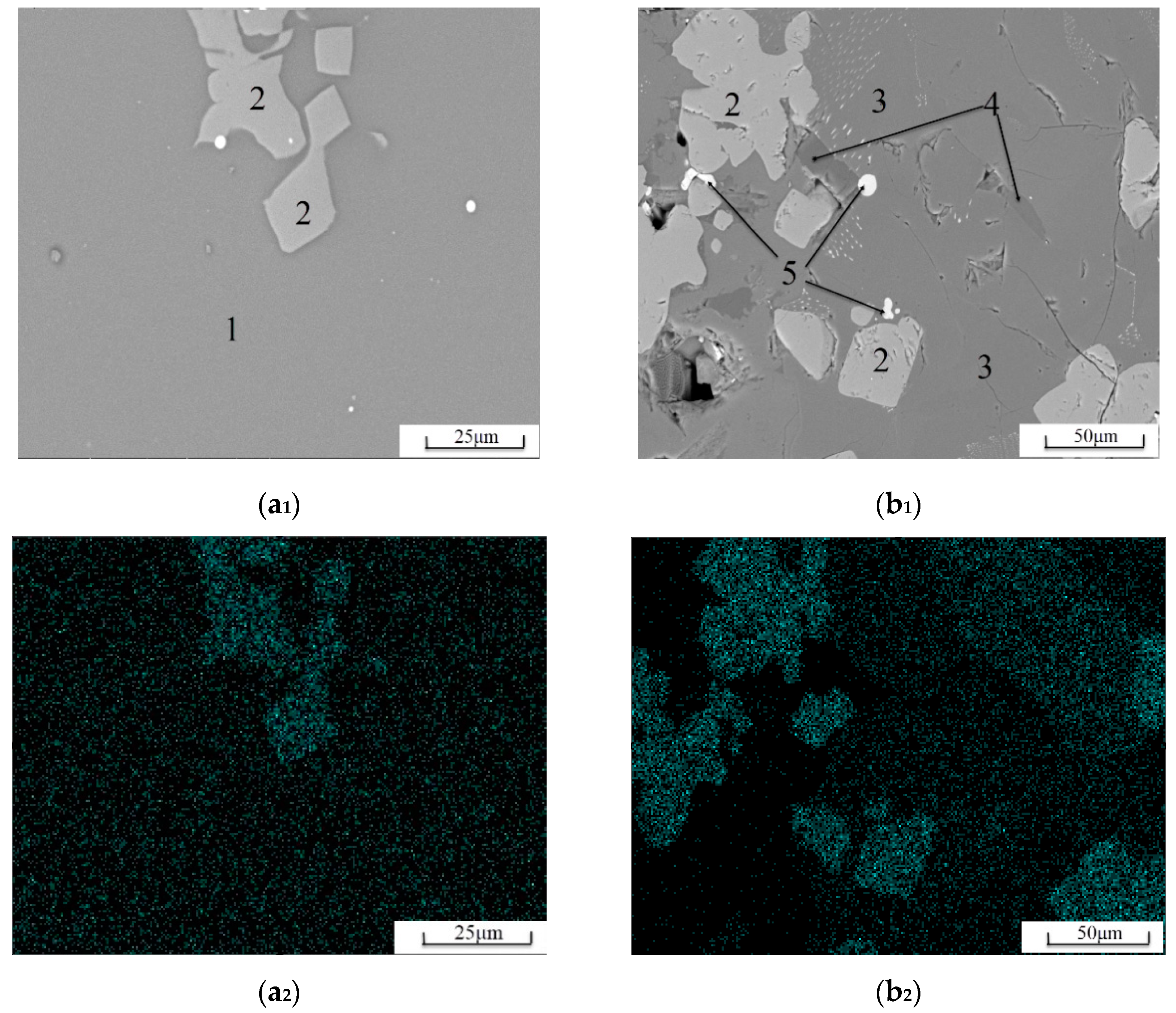
3.2. Mineral Phase Analysis
3.2.1. Mineral Phase Identification
3.2.2. Distribution Characteristics of Elemental Ti
3.2.3. Glass Phase Content
3.3. Analysis of Glass Phase Microstructure
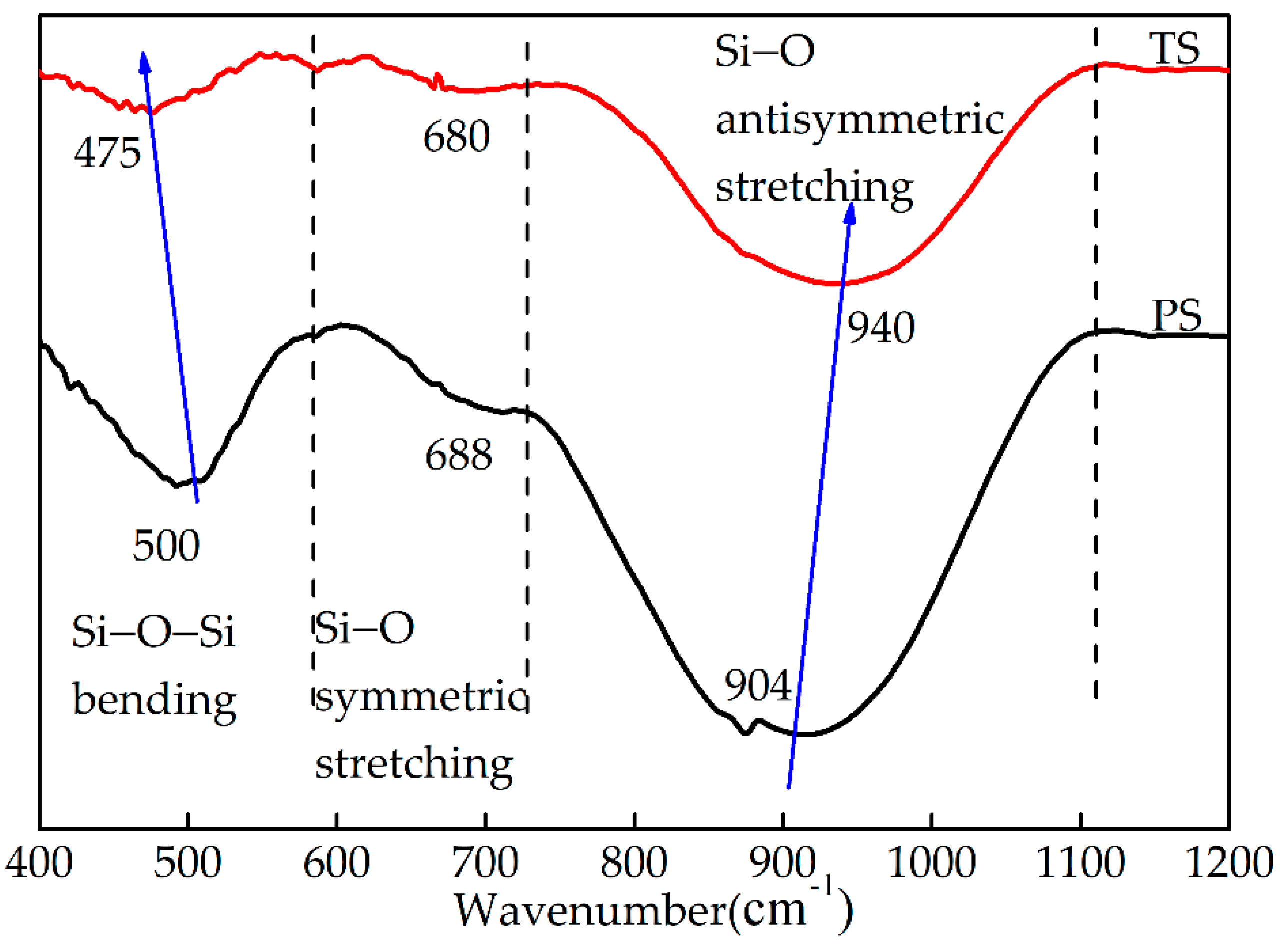
3.3.1. FTIR Spectroscopy Analysis
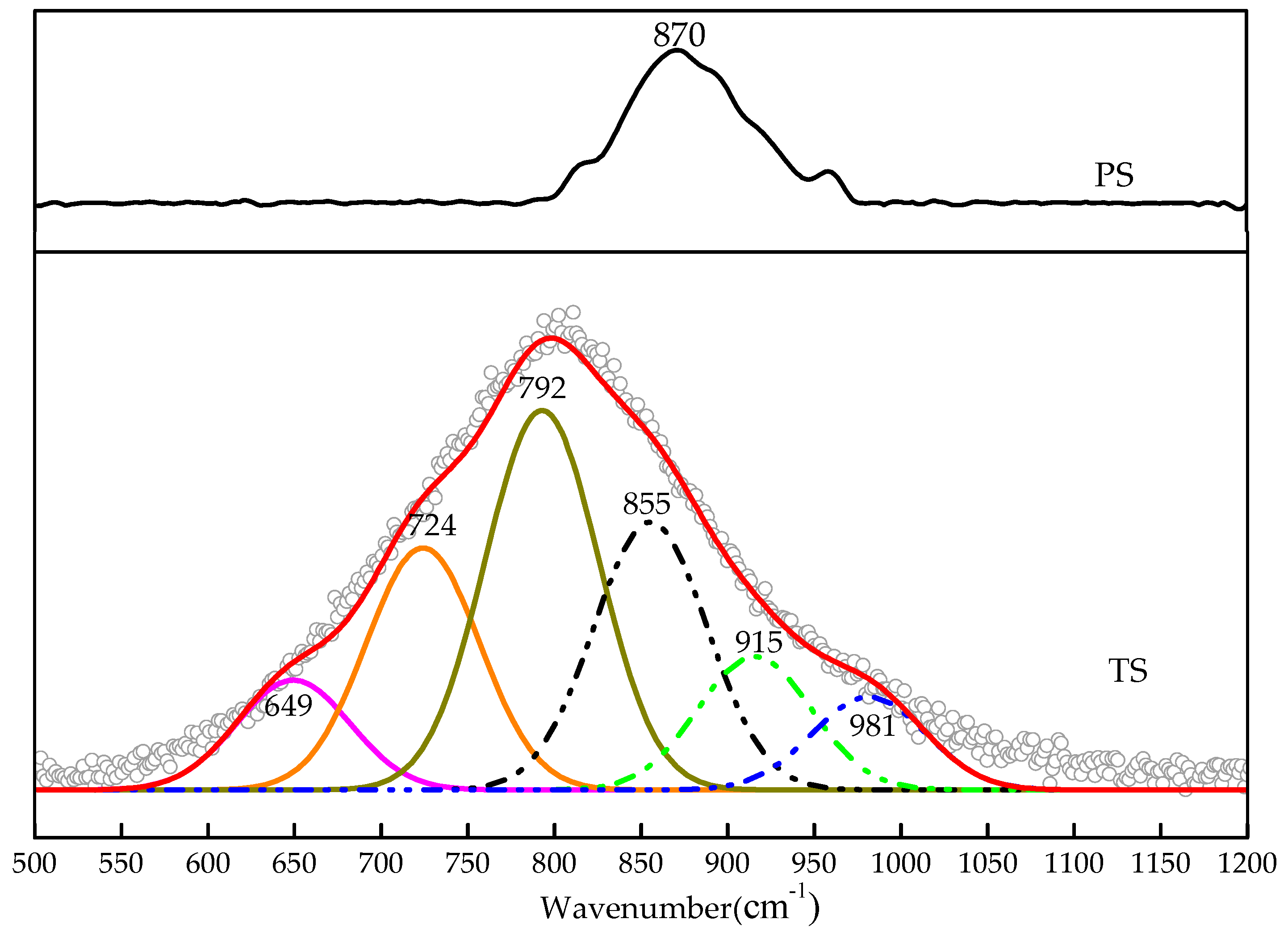
3.3.2. Raman Spectrum Analysis
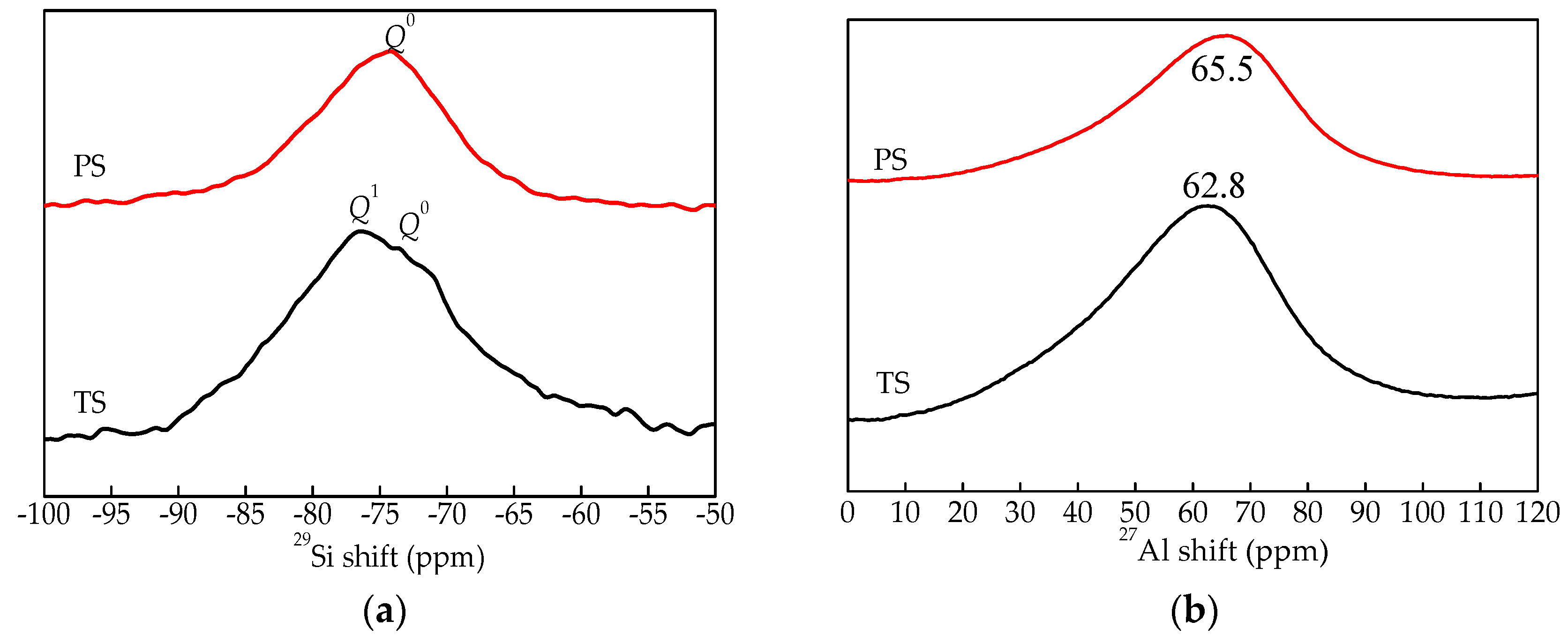
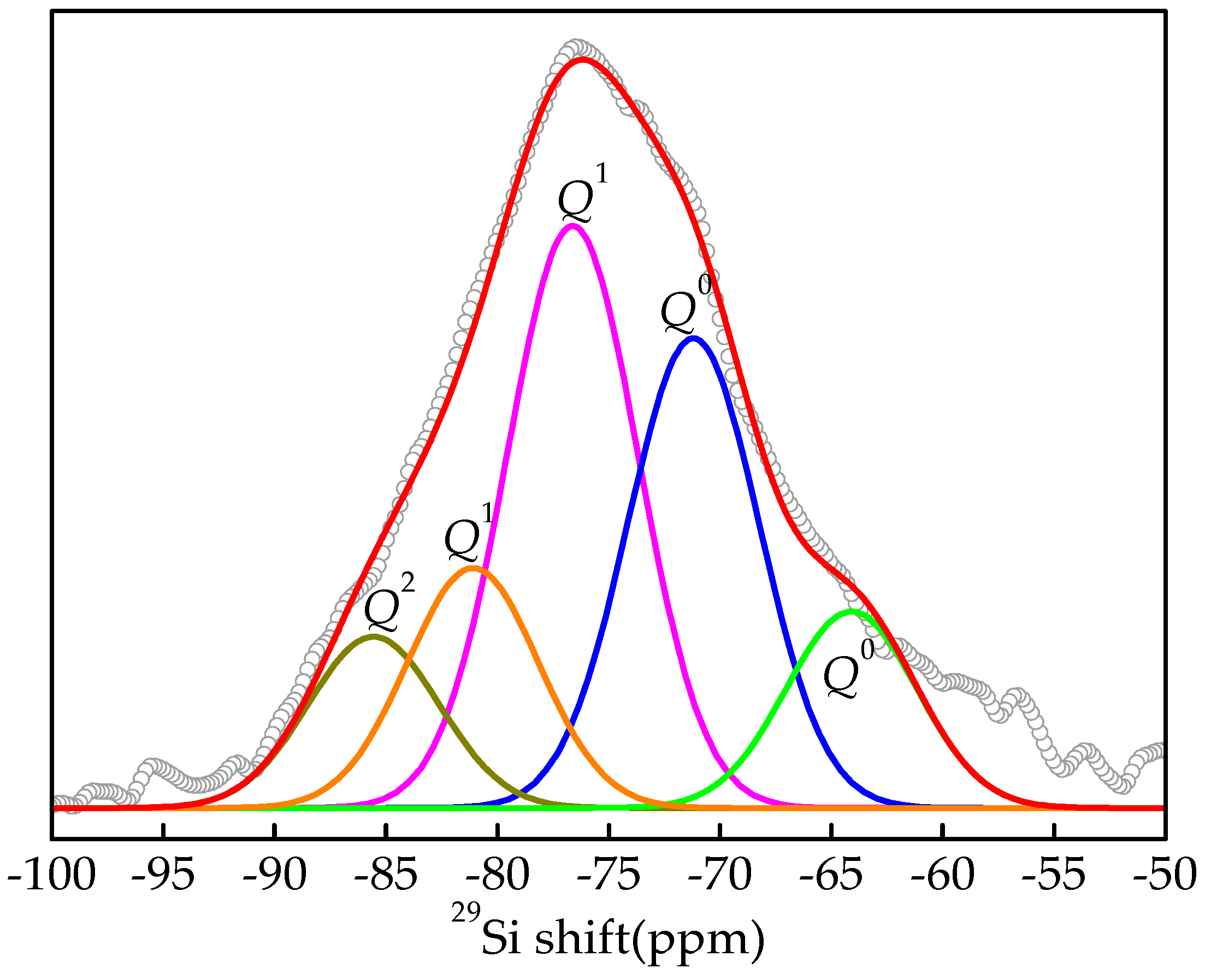
3.3.3. NMR Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| XRD | X-ray Diffraction |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscope |
| EDS | Energy Dispersive Spectrometer |
| BEI | Back Scattering Electron Image |
| FTIR | Fourier Transform Infrared spectroscopy |
| NMR | Nuclear Magnetic Resonance spectroscopy |
| TS | Water-quenched high-titanium slag |
| PS | Blast furnace slag |
| TM | Slow-cooling high-titanium slag |
| A7 | Index of hydraulic activity for 7 d |
| A28 | Index of hydraulic activity for 28 d |
| Ka | The pozzolanic activity rate |
| Qn | Types of Si–O–X group, n is the bridge oxygen number of coordination around Si |
| RBO | Relative bridge oxygen number |
References
- Ma, J.W.; Sui, Z.T.; Chen, B.C. Separating titania from treated slag by gravity separation or flotation. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2000, 10, 520–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.Z.; Lü, H.H.; Liu, M.C.; Zhang, Z.L.; Wu, X.R.; Liu, W.M.; Wang, P.; Li, L.S. Direct extraction of perovskite CaTiO3 via efficient dissociation of silicates from synthetic Ti-bearing blast furnace slag. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 167, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Feng, K.Q.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, H.L. Effect of sintering temperature on the microstructure and properties of foamed glass-ceramics prepared from high-titanium blast furnace slag and waste glass. Int. J. Min. Met. Mater 2017, 24, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.R.; Zhang, Y.J.; Dong, P.; Hua, Y.X.; Zhang, Q.B.; Wang, D.; Duan, J.G.; Zhang, Z. Electrolytic synthesis of TiC/SiC nanocomposites from high titanium slag in molten salt. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 3596–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.L.; Chen, W.; Ruan, X.L.; Tang, X.Y. Experimental study on axial compression behavior and bearing capacity analysis of high titanium slag CFST columns. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middlemas, S.; Fang, Z.Z.; Fan, P. Life cycle assessment comparison of emerging and traditional Titanium dioxide manufacturing processes. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 89, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rytvin, V.; Perepelitsyn, V.; Ponomarenko, A. Titanium-Alumina Slag–Semifunctional Technogenic Resource of High-Alumina Composition. Part 2. Use of Ferrotitanium Slag for Producing Refractories in Metallurgy and Other Branches of Industry1. Refract. Ind. Ceram. 2018, 58, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Shi, Y.; Yang, H.Q. Study on hydration activity of alkali-activated cementitious composite of high-titanium slag and cement. Yangtze River 2011, 24, 55–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.M. Study on the Performance of Hydraulic Concrete Using High Titanium Slag as Additive and Aggregate. Master’s Thesis, Changjiang River Scientific Research Institute, Wuhan China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ao, J.Q. Study on hydration characteristics of grounded high titanium slag. Gang Tie Fan Tai 2004, 25, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Yang, H.M.; Wang, Y.C.; Yang, H.Q.; Li, J.Z. Impact of high-titanium slag on performance of cement-based composites. New Buildding Mater. 2009, 9, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.X.; Xu, Z.Z.; Luo, Z.M.; Pan, Z.H.; Cheng, L. The activation and hydration of glassy cementitious materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2002, 32, 1145–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, N.; El-Hemaly, S.; Al-Wakeel, E.; El-Korashy, S.; Brown, P. Characterization and evaluation of the hydraulic activity of water-cooled slag and air-cooled slag. Cem. Concr. Res. 2001, 31, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.Q.; Wang, P.; Ke, C.M.; Yan, W.; Wei, Y.W.; Li, N. Hydration behavior of spinel containing high alumina cement from high titania blast furnace slag. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 79, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, H.Z.; Zhang, Z.L.; Wang, Y.H. Rapid evaluation on activity of pozzolanic materials. Jianzhu Cailiao Xuebao 2001, 4, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.K.; Liang, S.; Liu, Z.S. Chemical phase analysis of glass content in fly ash. Guisuanyan Tongbao 2017, 36, 3588–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.Q.; Zhang, Z.T.; Liu, L.L.; Wang, X.D. FTIR, Raman and NMR investigation of CaO–SiO2–P2O5 and CaO–SiO2–TiO2–P2O5 glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2015, 420, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Sun, H.H.; Li, L.T. Glass phase structure of blast furnace slag. Adv. Mater. Res. 2010, 168, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuville, D.R.; Ligny, D.; Henderson, G.S. Advances in Raman spectroscopy applied to earth and material sciences. Rev. Miner. Geochem. 2014, 78, 509–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.L.; Jiang, G.C.; Xu, K.D. High temperature Raman spectra of sodium disilicate crystal, glass and its liquid. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2001, 282, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuville, D.R.; Mysen, B.O. Role of aluminium in the silicate network: In situ, high-temperature study of glasses and melts on the join SiO2-NaAlO2. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1996, 60, 1727–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Q.F.; Wang, Z.; Chou, K.C. Viscosity Estimations of Multi-Component Slags. Steel Res. Int. 2011, 82, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Liao, J.L.; Wang, X.D.; Zhang, Z.T. Raman spectroscopic study of the structural properties of CaO–MgO–SiO2–TiO2 slags. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2013, 376, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mysen, B. Phosphorus speciation changes across the glass transition in highly polymerized alkali silicate glasses and melts. Am. Miner. 1996, 81, 1531–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mysen, B.O. Role of Al in depolymerized, peralkaline aluminosilicate melts in the systems Li2O-Al2O3-SiO2, Na2O-Al2O3-SiO2, and K2O-Al2O3-SiO2. Am. Miner. 1990, 75, 120–134. [Google Scholar]
- McMillan, P. Structural studies of silicate glasses and melts—applications and limitations of Raman spectroscopy. Am. Miner. 1984, 69, 622–644. [Google Scholar]
- Cong, X.D.; Kirkpatrick, R.J. Hydration of Calcium Aluminate Cements: A Solid-State 27 Al NMR Study. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1993, 76, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippmaa, E.; Maegi, M.; Samoson, A. Structural studies of silicates by solid-state high-resolution silicon-29 NMR. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1980, 102, 4889–4893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, Z.J. Research on Activated Coal Gangue and Corrosion Behavior of Steel Rebar in Gangue Based Mortars. Doctor’s Thesis, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]

| Sample | CaO | SiO2 | Al2O3 | TiO2 | MgO | Fe2O3 | Na2O | LOI | Sum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TM | 26.64 | 24.76 | 13.22 | 20.39 | 8.37 | 1.20 | 0.95 | 1.64 | 97.17 |
| TS | 28.36 | 26.36 | 13.33 | 17.18 | 8.39 | 1.31 | 0.16 | 1.30 | 96.39 |
| PS | 35.92 | 33.65 | 16.90 | 0.07 | 10.13 | 0.13 | 0.33 | 1.55 | 98.67 |
| Sample | A7 | A28 | Ka |
|---|---|---|---|
| PS | 125.6 | 95.6 | 99.3 |
| TS | 35.1 | 35.8 | 56.8 |
| TM | 21.2 | 23.5 | 35.7 |
| Method | PS | TS | TM |
|---|---|---|---|
| XRD | 98.03 | 97.34 | 1.82 |
| alkali-acid two stage dissolution | 99.49 | 98.35 | 1.91 |
| Types of Si-O-X group | Symbol | Chemical Shift/ppm |
|---|---|---|
| Monosilicate | Q0 | −68–−76 |
| Disilicates and chain end groups | Q1 | −76–−82 |
| Chain middle groups | Q2 | −82–−88 |
| Layers and chain branching sites | Q3 | −88–−98 |
| Three-dimensional networks | Q4 | −98–−129 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hou, X.; Wang, D.; Shi, Y.; Guo, H.; He, Y. Hydraulic Activity and Microstructure Analysis of High-Titanium Slag. Materials 2020, 13, 1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13051239
Hou X, Wang D, Shi Y, Guo H, He Y. Hydraulic Activity and Microstructure Analysis of High-Titanium Slag. Materials. 2020; 13(5):1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13051239
Chicago/Turabian StyleHou, Xinkai, Dan Wang, Yiming Shi, Haitao Guo, and Yingying He. 2020. "Hydraulic Activity and Microstructure Analysis of High-Titanium Slag" Materials 13, no. 5: 1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13051239
APA StyleHou, X., Wang, D., Shi, Y., Guo, H., & He, Y. (2020). Hydraulic Activity and Microstructure Analysis of High-Titanium Slag. Materials, 13(5), 1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13051239




