Effect of Y Addition on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of ZM31 Alloy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
3. Results and Discussion
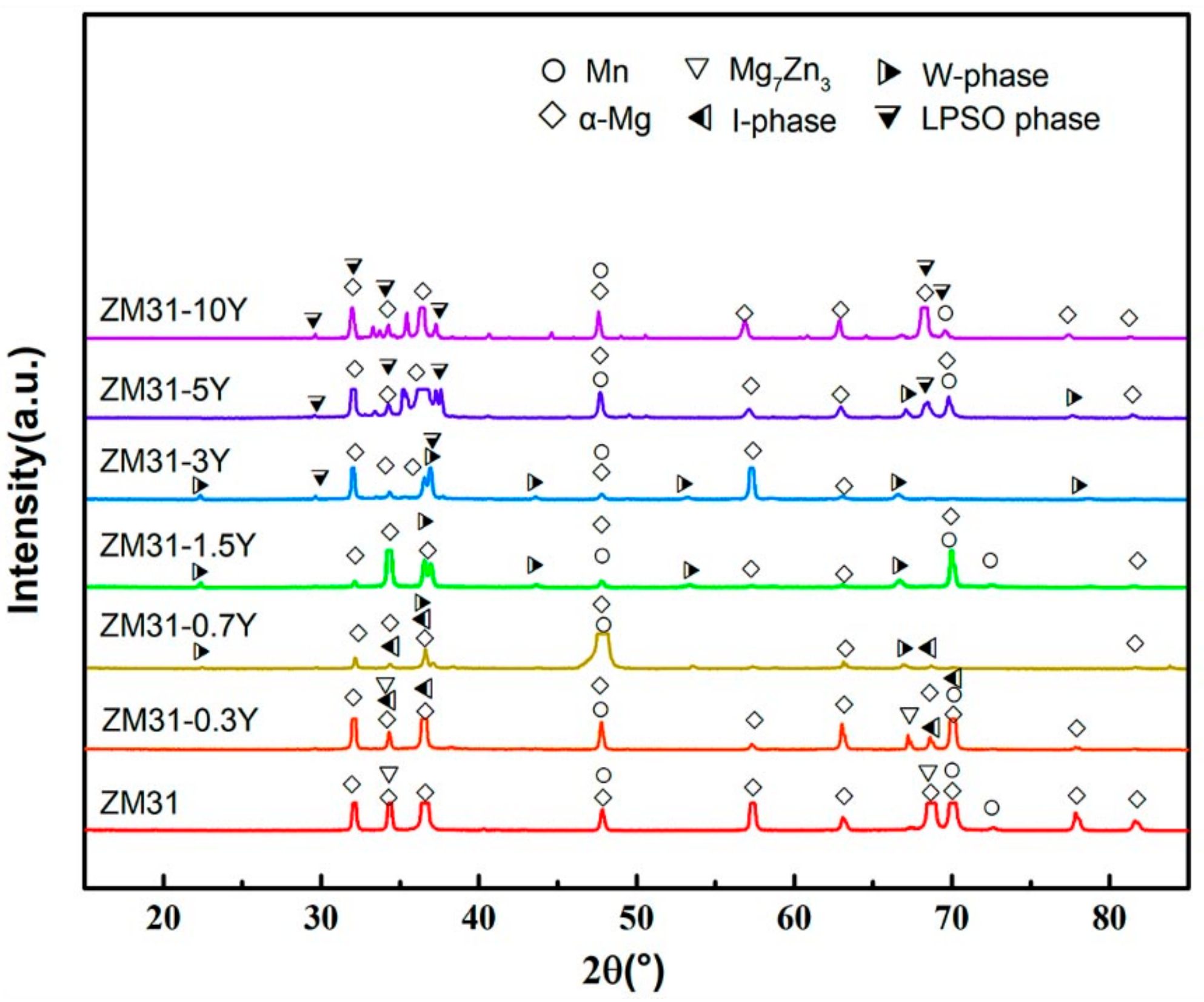
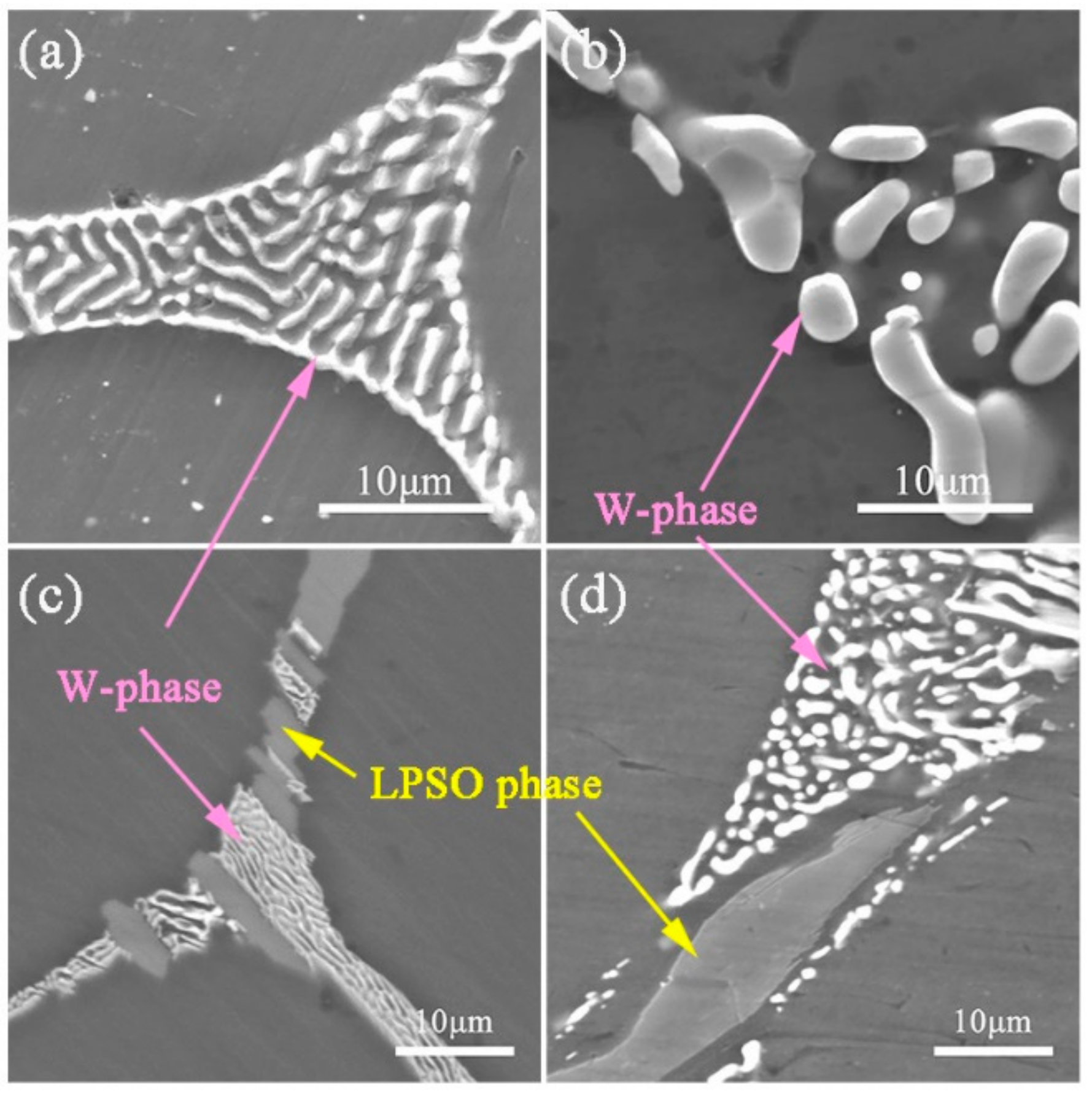
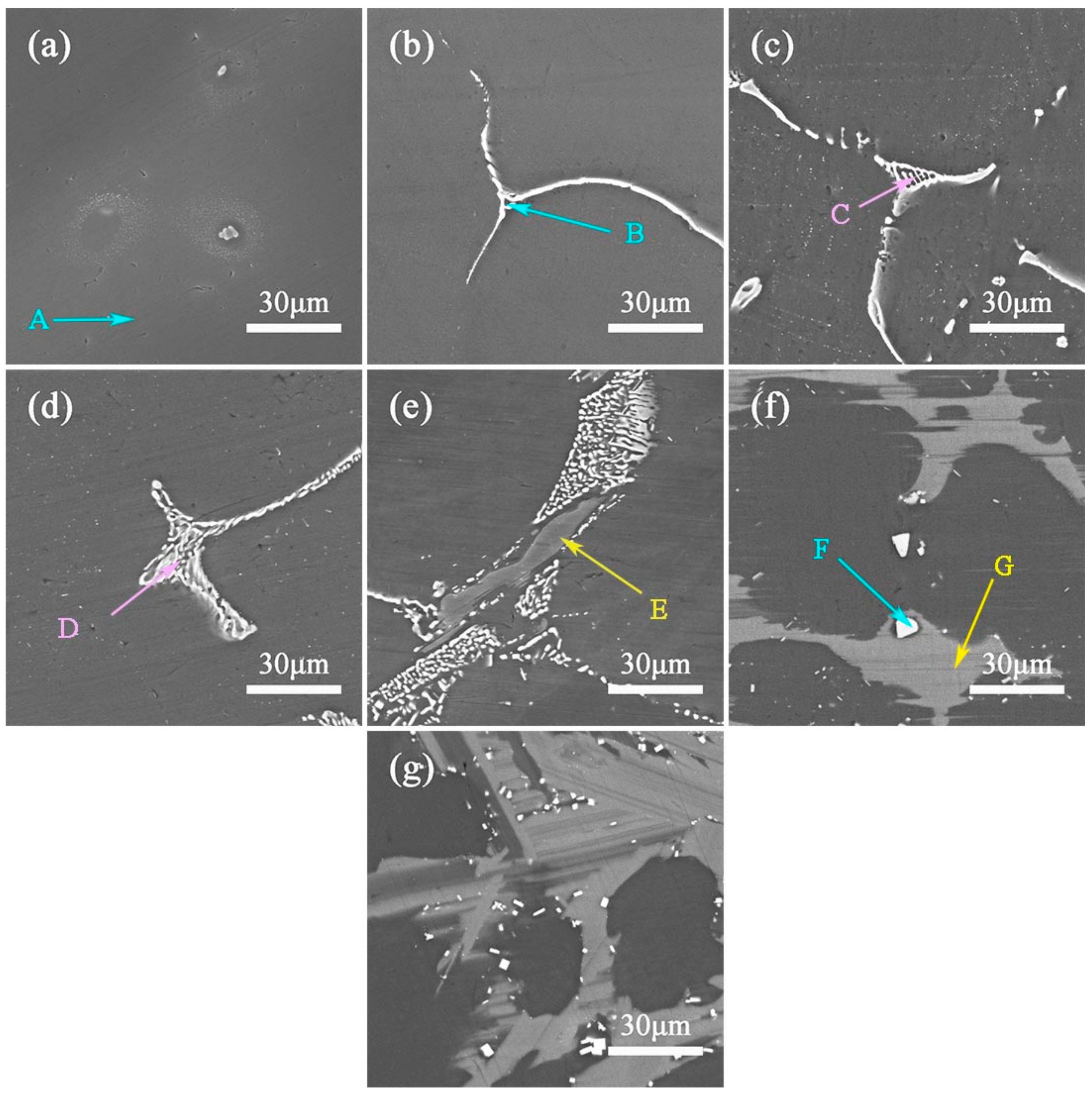
3.1. As-Cast and as-Homogenized Microstructures
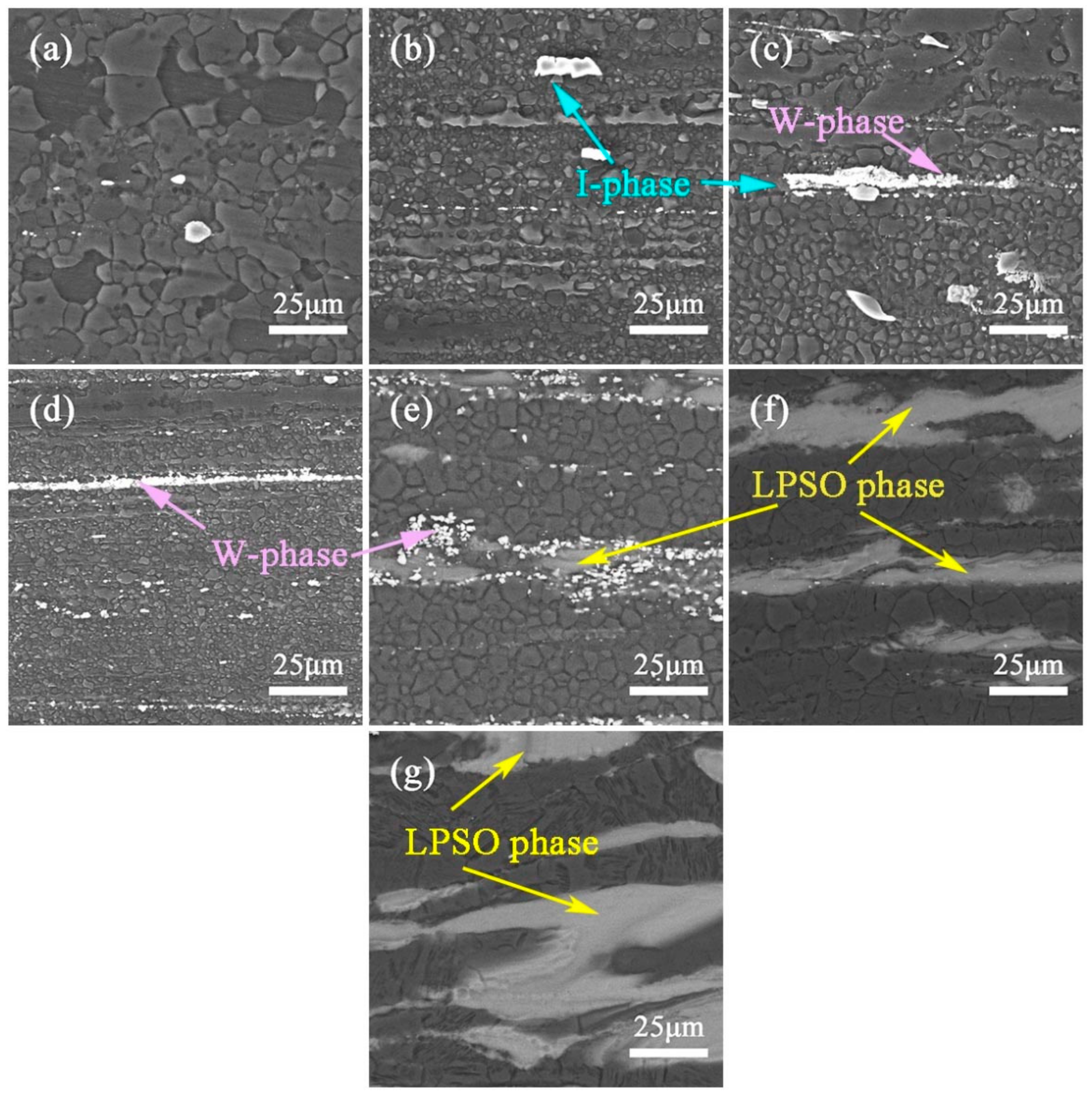
3.2. As-Extruded Microstructure
3.3. Mechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
- The Y addition has an obvious effect on the phase composition and microstructure of the ZM31 alloy. On one hand, the Y addition can significantly refine the dendrite size of the as-cast ZM31 alloy, and on the other hand, various phase compositions including Mg7Zn3, I-phase, W-phase, and LPSO phase can be obtained by adjusting the Zn/Y ratio. Based on the results of thermal analysis and microstructural observations, the phase stability follows the trend of LPSO phase> W-phase> I-phase> Mg7Zn3 phase.
- Y can significantly improve the room temperature mechanical properties of the as-extruded ZM31 alloy. Under the same extrusion conditions, as the Y content increases, the mechanical properties show an increasing trend. Among them, the ZM31-10Y alloy with LPSO phase has the best mechanical properties, that is, the UTS and YTS reach 403 MPa and 342 MPa, respectively.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, Q.; Jiang, B.; Pan, H.; Song, B.; Jiang, Z.; Dai, J.; Wang, L.; Pan, F. Influence of different extrusion processes on mechanical properties of magnesium alloy. J. Magnes. Alloy. 2014, 2, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Ren, Y.; Fu, H.; Zhao, H.; Wang, L.; Meng, X.; Qin, G. Recent developments in rare-earth free wrought magnesium alloys having high strength: A review. J. Alloy. Compd. 2016, 663, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, A.A. Magnesium casting technology for structural applications. J. Magnes. Alloy. 2013, 1, 2–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahreen, N.; Zhang, D.F.; Pan, F.S.; Jiang, X.Q.; Li, D.Y.; Chen, D.L. Hot Deformation and Work Hardening Behavior of an Extruded Mg–Zn–Mn–Y Alloy. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 31, 1161–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschab, J. Superior light metals by texture engineering: Optimized aluminum and magnesium alloys for automotive applications. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 818–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, W.; Pan, F.; Chen, X.; Wei, G.; Mao, J. Microstructure and mechanical properties of as-extruded and as-aged Mg–Zn–Al–Sn alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 656, 165–173. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, S.; Lei, T.; Li, N.; Feng, F. Effects of Zn on microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion behavior of Mg–Zn alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2012, 32, 2570–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, Z.; Pan, H.; Guo, C.; Wang, Z.; Zou, G.; Jiang, F. Asymmetry of tensile-compressive mechanical behaviors of Mg-RE-Zn alloy strengthened by long period stacking ordered phase. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 667, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Bo, X.; Huang, F.; Zhong, M.; Zhang, D. Effect of Y addition on the microstructures and mechanical properties of as-aged Mg-6Zn-1Mn-4Sn (wt%) alloy. J. Alloy. Compd. 2016, 689, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Chen, J.B.; Liu, T.; Liu, J.X.; Wang, W.Y.; Liu, Z.K.; Hui, X.D. High strength Mg94Zn2.4Y3.6 alloy with long period stacking ordered structure prepared by near-rapid solidification technology. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 679, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosalie, J.M.; Somekawa, H.; Singh, A.; Mukai, T. Effect of precipitation on strength and ductility in a Mg–Zn–Y alloy. J. Alloy. Compd. 2013, 550, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.; Scudino, S.; Anwar, M.S.; Shahid, R.N.; Srivastava, V.C.; Uhlenwinkel, V.; Stoica, M.; Vaughan, G.; Eckert, J. Al-based metal matrix composites reinforced with Al–Cu–Fe quasicrystalline particles: Strengthening by interfacial reaction. J. Alloy. Compd. 2014, 607, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Chen, X.H.; Wang, L.; Wang, W.Y.; Liu, Z.K.; Liu, J.X.; Hui, X.D. High strength Mg-Zn-Y alloys reinforced synergistically by Mg 12 ZnY phase and Mg 3 Zn 3 Y 2 particle. J. Alloy. Compd. 2017, 703, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Sandlöbes, S.; Raabe, D. On the room temperature deformation mechanisms of a Mg–Y–Zn alloy with long-period-stacking-ordered structures. Acta Mater. 2015, 82, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Teng, X.; Lou, G.; Zhou, G.; Leng, J. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg–Zn–Y alloy containing LPSO phase and I-phase. Mater. Res. Express 2017, 4, 086502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.H.; Liang, S.M.; Chen, R.S.; Han, E.H. Solidification pathways and constituent phases of Mg–Zn–Y–Zr alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 2009, 468, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Le, Q.; Hu, W.; Bao, L.; Cui, J. Effects of phase composition and content on the microstructures and mechanical properties of high strength Mg–Y–Zn–Zr alloys. Mater. Des. 2015, 88, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, F.g.; Zhang, D.F.; Zhang, X.H.; Pan, F.S. Effect of Y addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg–Zn–Mn alloy. T. Nonferr. Metal. Soc. China 2014, 24, 1352–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, F.g.; Zhang, D.F.; Zhang, X.H.; Xu, X.X. Effects of Mn addition and X-phase on the microstructure and mechanical properties of high-strength Mg-Zn-Y-Mn alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 593, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhang, J.; Que, Z.; Xu, C.; Niu, X. Effects of Mn on the microstructure and mechanical properties of long period stacking ordered Mg95Zn2.5Y2.5 alloy. Mater. Lett. 2013, 109, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honma, T.; Ohkubo, T.; Hono, K.; Kamado, S. Chemistry of nanoscale precipitates in Mg–2.1Gd–0.6Y–0.2Zr (at.%) alloy investigated by the atom probe technique. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 395, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nodooshan, H.R.J.; Liu, W.; Wu, G.; Rao, Y.; Zhou, C.; He, S.; Ding, W.; Mahmudi, R. Effect of Gd content on microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg–Gd–Y–Zr alloys under peak-aged condition. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 615, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiuchi, T.; Ikee, H.; Hamaya, A.; Minamoto, S.; Miura, S. Experimental Study on Phase Diagram in the Vicinity of X or W Phase in the Mg-Zn-Y Ternary System. Mater. Sci. Forum 2012, 706–709, 1170–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.C.; Peng, Q.M.; Fang, D.Q. In Phase Compositions of a Mg-Dy-Zn Alloy Containing LPSO Structures. Mater. Sci. Forum 2015, 815, 470–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.K.; Tang, W.N.; Liu, L.; Xu, Y.B.; Han, E.H. Effect of W-phase on the mechanical properties of as-cast Mg–Zn–Y–Zr alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 2008, 461, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagihara, K.; Kinoshita, A.; Sugino, Y.; Yamasaki, M.; Kawamura, Y.; Yasuda, H.Y.; Umakoshi, Y. Effect of long-period stacking ordered phase on mechanical properties of Mg97Zn1Y2 extruded alloy. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 6282–6293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagihara, K.; Kinoshita, A.; Fukusumi, Y.; Yamasaki, M.; Kawamura, Y. High-temperature compressive deformation behavior of Mg97Zn1Y2 extruded alloy containing a long-period stacking ordered (LPSO) phase. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 560, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoi, T.; Takahashi, K.; Moriyama, H.; Hirohashi, M. A high-strength Mg–Ni–Y alloy sheet with a long-period ordered phase prepared by hot-rolling. Scr. Mater. 2008, 59, 1155–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimoto, S.; Yamasaki, M.; Kawamura, Y. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Extruded Mg-Zn-Y Alloys with 14H Long Period Ordered Structure. Metall. Trans. 2006, 47, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Nominal Alloys | Actual Composition (wt.%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg | Zn | Mn | Y | |
| ZM31 | Bal. | 3.00 | 1.08 | - |
| ZM31-0.3Y | Bal. | 2.74 | 0.91 | 0.34 |
| ZM31-0.7Y | Bal. | 3.15 | 0.92 | 0.64 |
| ZM31-1.5Y | Bal. | 2.56 | 0.79 | 1.47 |
| ZM31-3Y | Bal. | 2.61 | 0.76 | 2.83 |
| ZM31-5Y | Bal. | 2.93 | 0.79 | 4.83 |
| ZM31-10Y | Bal. | 3.24 | 0.83 | 10.93 |
| Test Materials | Billet Temperature (°C) | Extrusion Chamber Temperature (°C) | Mold Hole Diameter (mm) | Extrusion Ratio | Cooling Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZM31-xY (x = 0, 0.3, 0.7 and 1.5) | 350 | 350 | 16 | 25 | Air cooling |
| ZM31-xY (x = 3, 5 and 10) | 480 | 480 | 16 | 25 | Air cooling |
| Nominal Alloys | Mole (Zn)/(Y) | Main Phases |
|---|---|---|
| ZM31-0Y | - | α-Mg, Mn and Mg7Zn3 |
| ZM31-0.3Y | 14.37 | α-Mg, Mn, I-phase and Mg7Zn3 |
| ZM31-0.7Y | 5.70 | α-Mg, Mn, I-phase and W-phase |
| ZM31-1.5Y | 2.69 | α-Mg, Mn, W-phase |
| ZM31-3Y | 1.36 | α-Mg, Mn, W-phase and LPSO phase |
| ZM31-5Y | 0.82 | α-Mg, Mn, W-phase and LPSO phase |
| ZM31-10Y | 0.40 | α-Mg, Mn and LPSO phase |
| No. | Mg (at.%) | Mn (at.%) | Zn (at.%) | Y (at.%) | Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 97.9 (±0.11) | 0.4(±0.15) | 1.7 (±0.13) | 0 | α-Mg |
| B | 72.4 (±0.13) | 0 | 27.6(±0.21) | 0 | Mg7Zn3 |
| C | 47.5 (±0.09) | 1.8 (±0.14) | 42.4 (±0.44) | 8.3 (±0.71) | I-phase |
| D | 87.3 (±0.12) | 0.4 (±0.13) | 11.0 (±0.14) | 1.7 (±0.28) | I-phase and Mg7Zn3 |
| E | 72.3 (±0.08) | 0 | 16.4 (±0.83) | 11.3 (±0.75) | W-phase |
| F | 88.1 (±0.18) | 0.7 (±0.32) | 4.3 (±0.57) | 6.9 (±0.23) | LPSO phase |
| Nominal Alloys | Peak 1 | Peak 2 | Peak 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tp/°C | Tp/°C | Tp/°C | |
| ZM31 | - | - | 646.24 |
| ZM31-0.3Y | - | - | 645.93 |
| ZM31-0.7Y | 517.31 | - | 643.54 |
| ZM31-1.5Y | 528.89 | - | 642.38 |
| ZM31-3Y | 529.07 | - | 638.33 |
| ZM31-5Y | - | 546.67 | 626.71 |
| ZM31-10Y | - | 547.81 | 609.55 |
| No. | Mg (at.%) | Mn (at.%) | Y (at.%) | Zn (at.%) | phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 98.2 (±0.12) | 0.5 (± 0.23) | - | 1.3 (±0.13) | α-Mg |
| B | 47.5 (±0.23) | 1.9 (± 0.52) | 8.2 (±0.63) | 42.4 (±0.38) | I-phase |
| C | 51.8 (±0.19) | 0 | 20.3 (±0.43) | 28.9 (±0.26) | W-phase |
| D | 81.4 (±0.15) | 0.4 (±0.15) | 7.5 (±0.44) | 11.7 (±0.27) | W-phase |
| E | 88.1 (±0.23) | 0.3 (±0.12) | 6.7 (±0.45) | 5.9 (±0.43) | LPSO phase |
| F | 4.6 (±0.31) | - | 93.2 (±0.16) | 2.2 (±0.12) | Y |
| G | 88.1 (±0.21) | - | 6.8 (±0.44) | 5.1 (±0.32) | LPSO phase |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, X.; Cao, H.; Qi, F.; Ouyang, X.; Ye, Z.; Hou, C.; Li, L.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, N. Effect of Y Addition on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of ZM31 Alloy. Materials 2020, 13, 583. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13030583
Ye X, Cao H, Qi F, Ouyang X, Ye Z, Hou C, Li L, Zhang D, Zhao N. Effect of Y Addition on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of ZM31 Alloy. Materials. 2020; 13(3):583. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13030583
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Xue, Hongshuai Cao, Fugang Qi, Xiaoping Ouyang, Zhisong Ye, Caihong Hou, Lianhui Li, Dingfei Zhang, and Nie Zhao. 2020. "Effect of Y Addition on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of ZM31 Alloy" Materials 13, no. 3: 583. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13030583
APA StyleYe, X., Cao, H., Qi, F., Ouyang, X., Ye, Z., Hou, C., Li, L., Zhang, D., & Zhao, N. (2020). Effect of Y Addition on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of ZM31 Alloy. Materials, 13(3), 583. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13030583






