Effect of Autoclaving Time on Corrosion Resistance of Sandblasted Ti G4 in Artificial Saliva
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
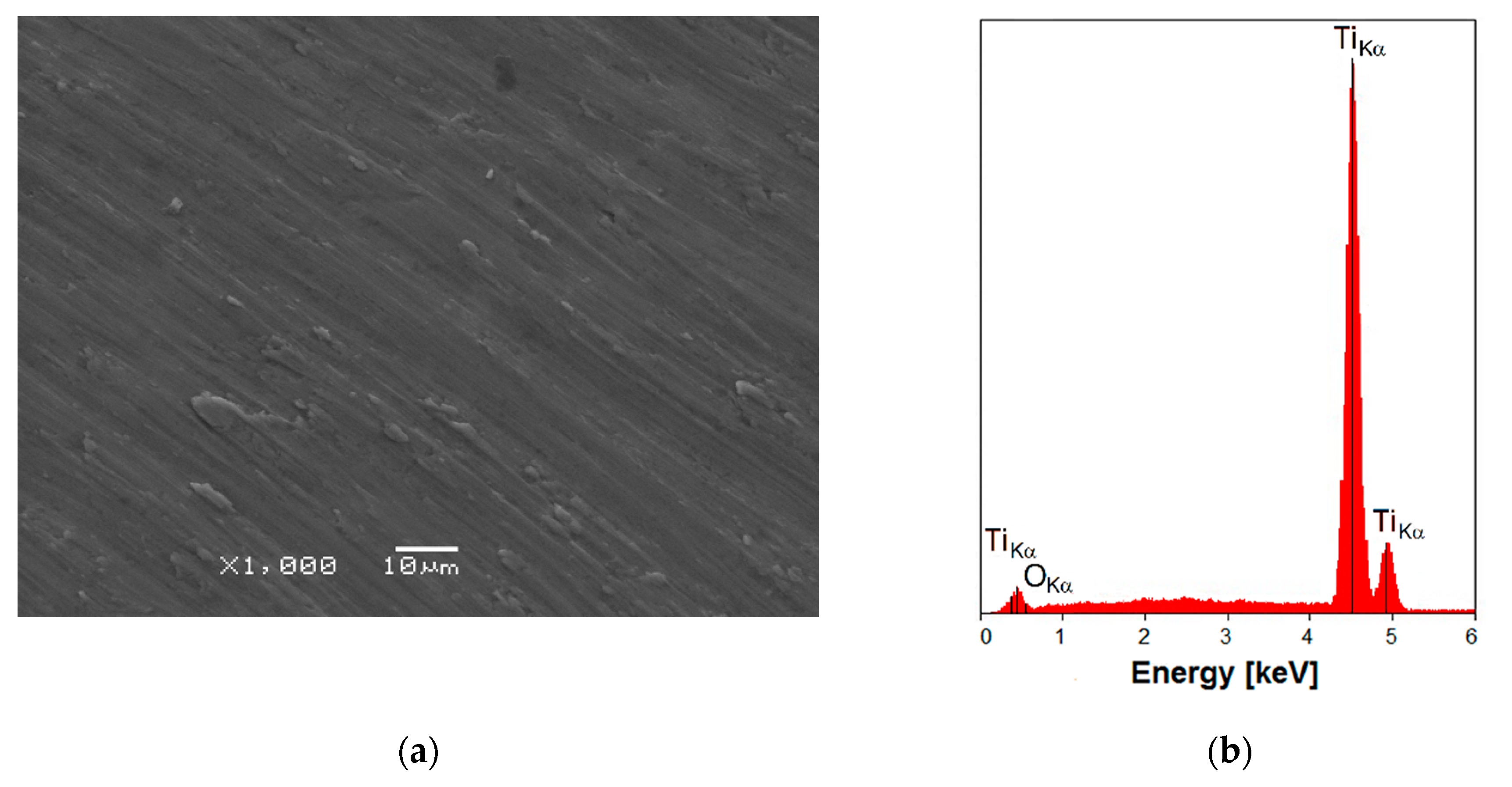
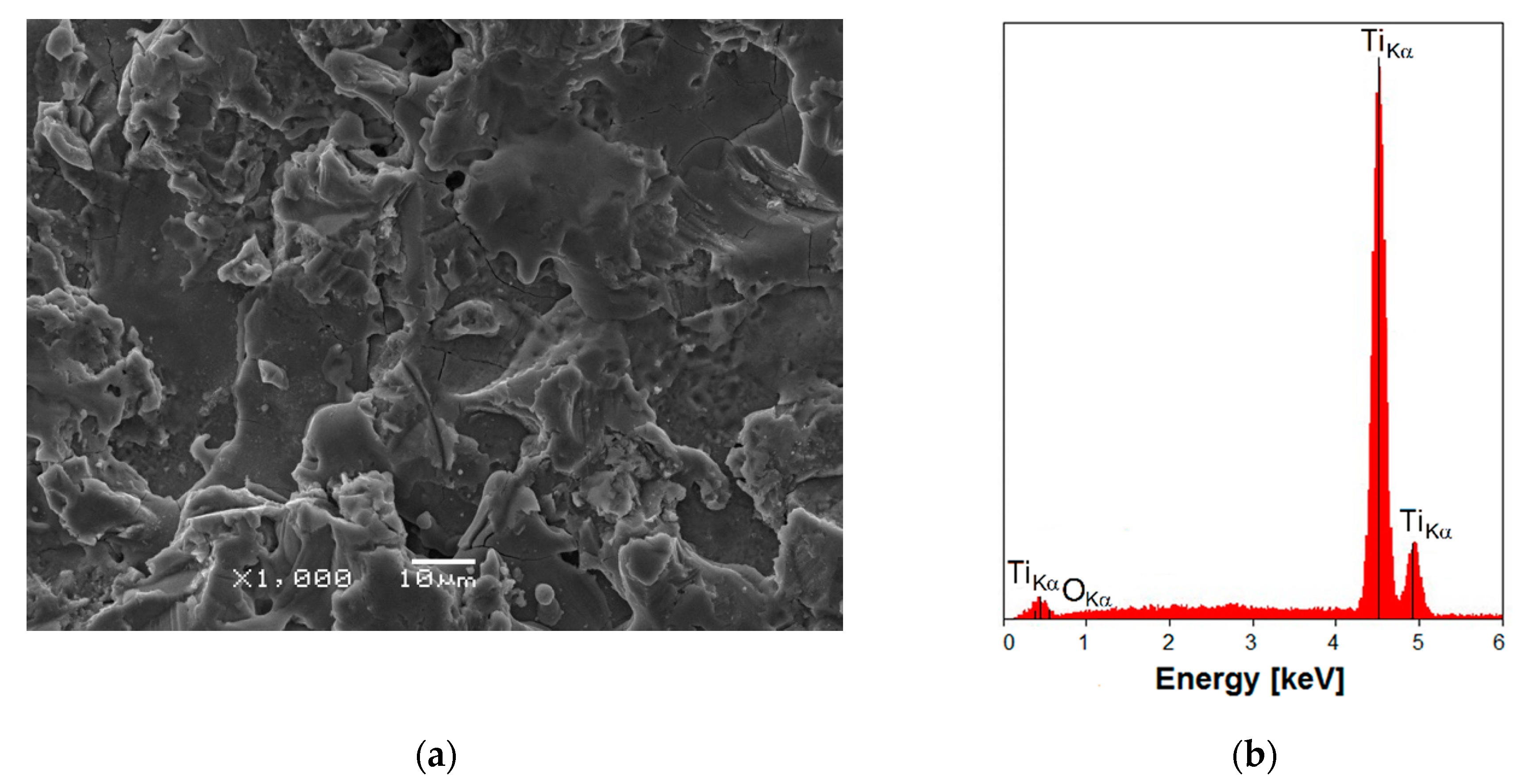
3.1. SEM/EDS Observations
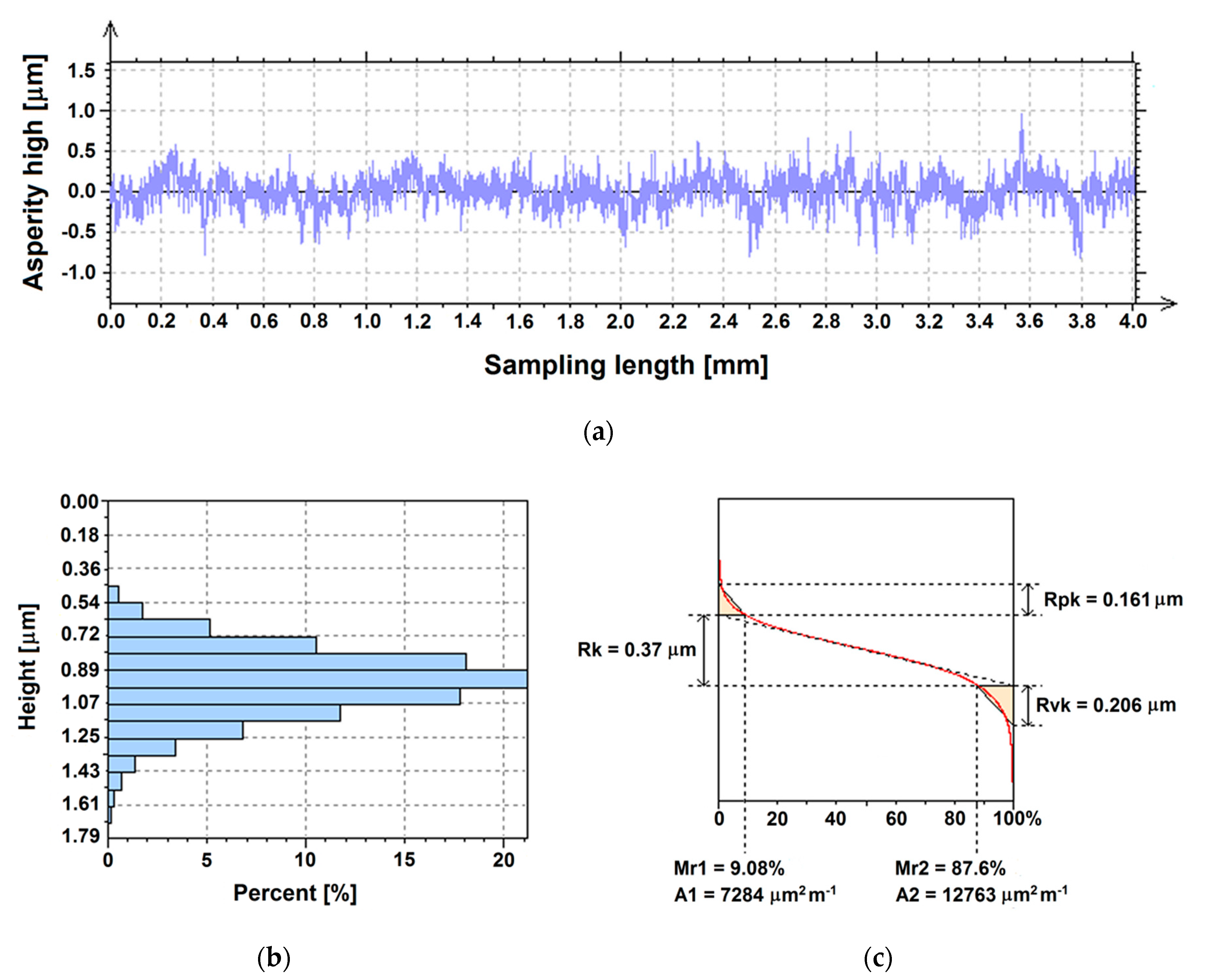
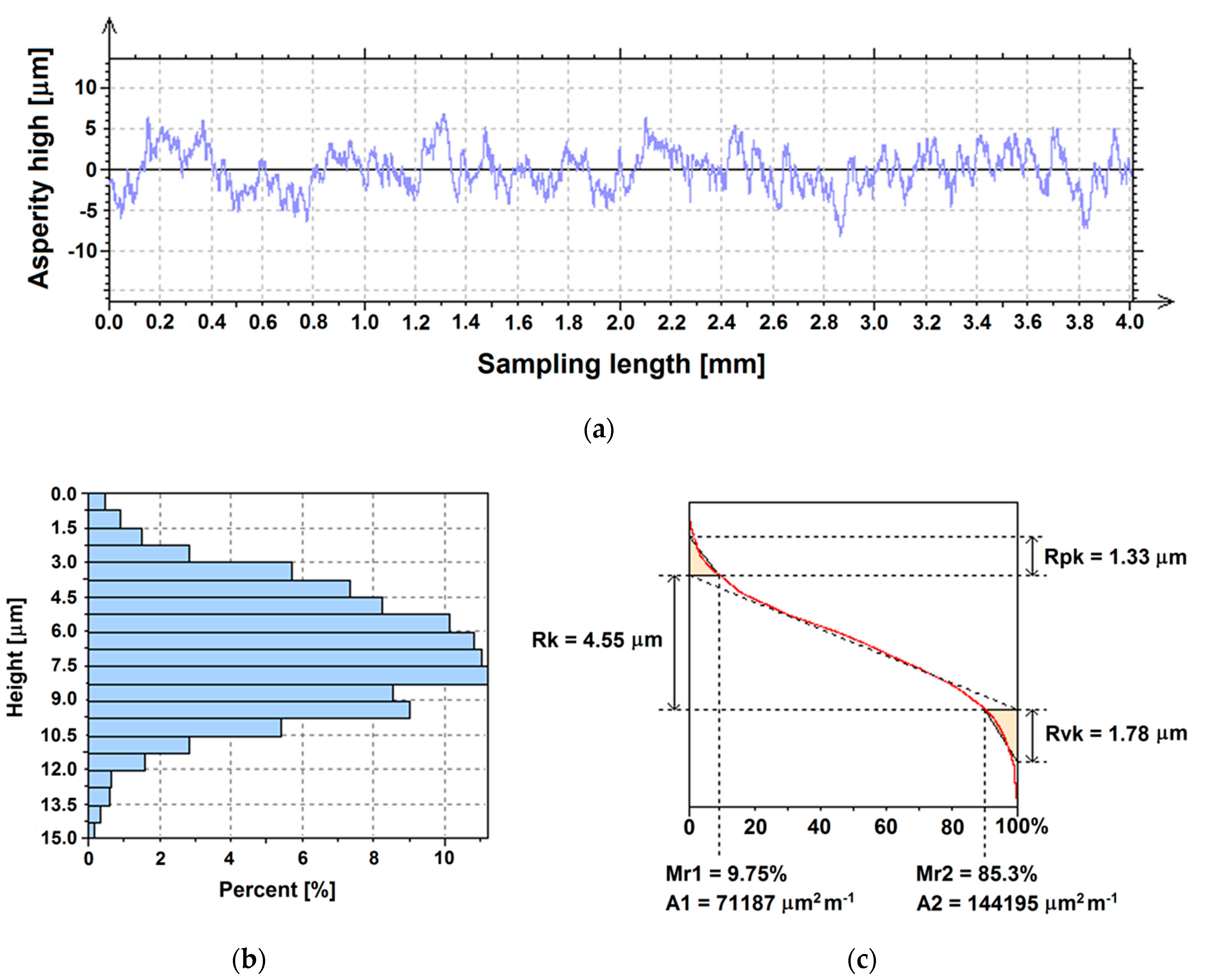
3.2. Surface Roughness
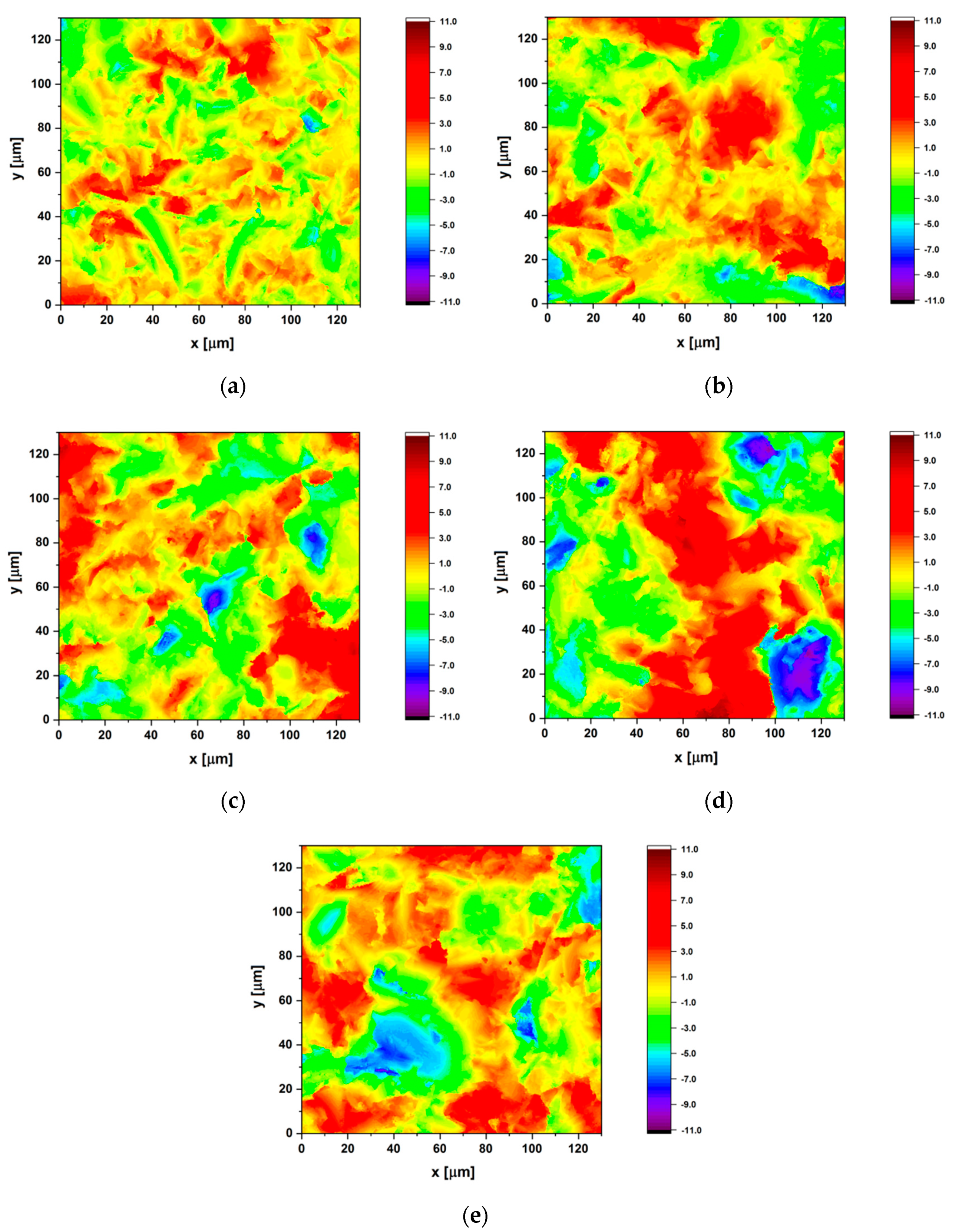
3.3. Surface Topography
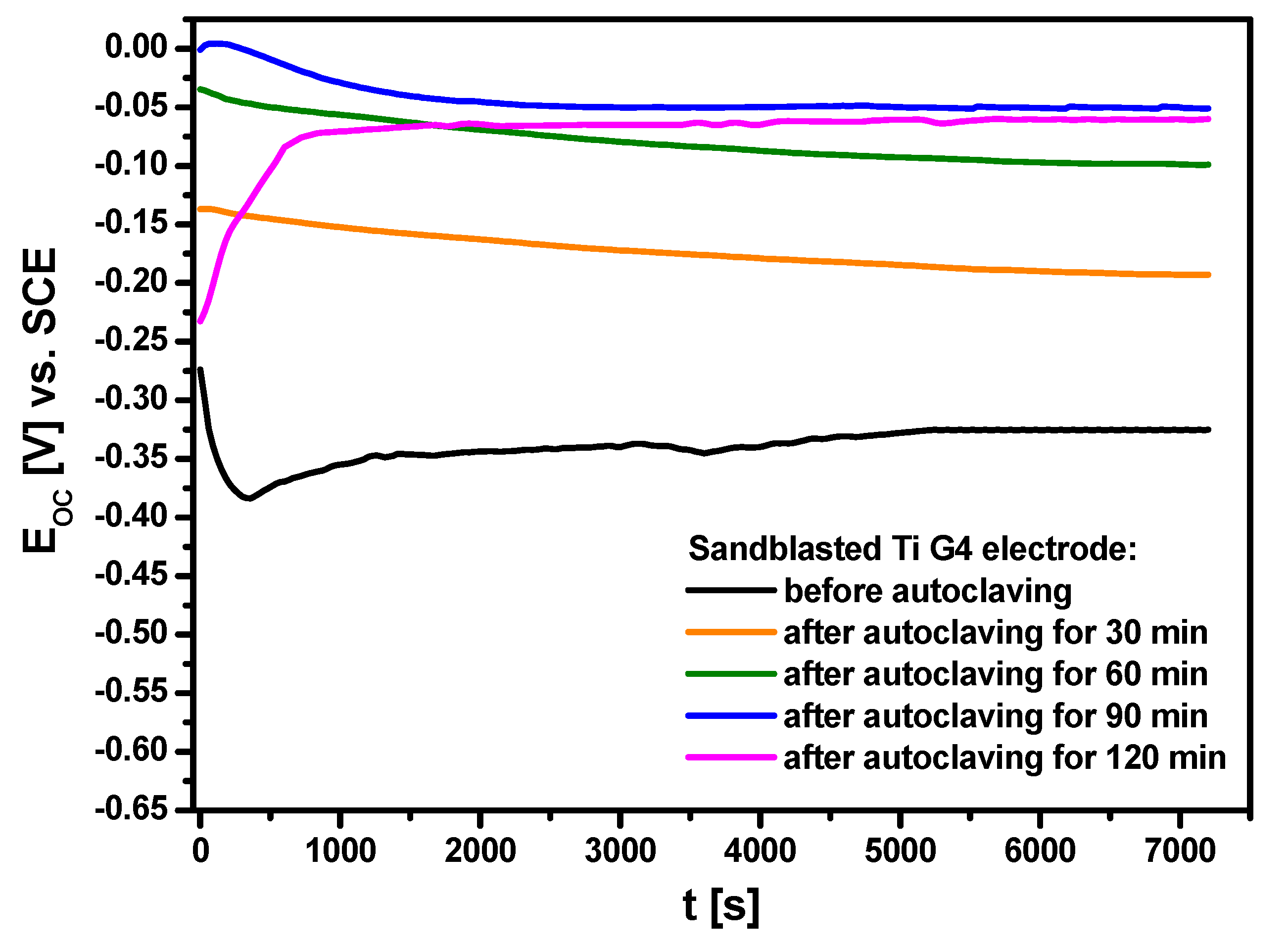
3.4. Open Circuit Potential Measurements
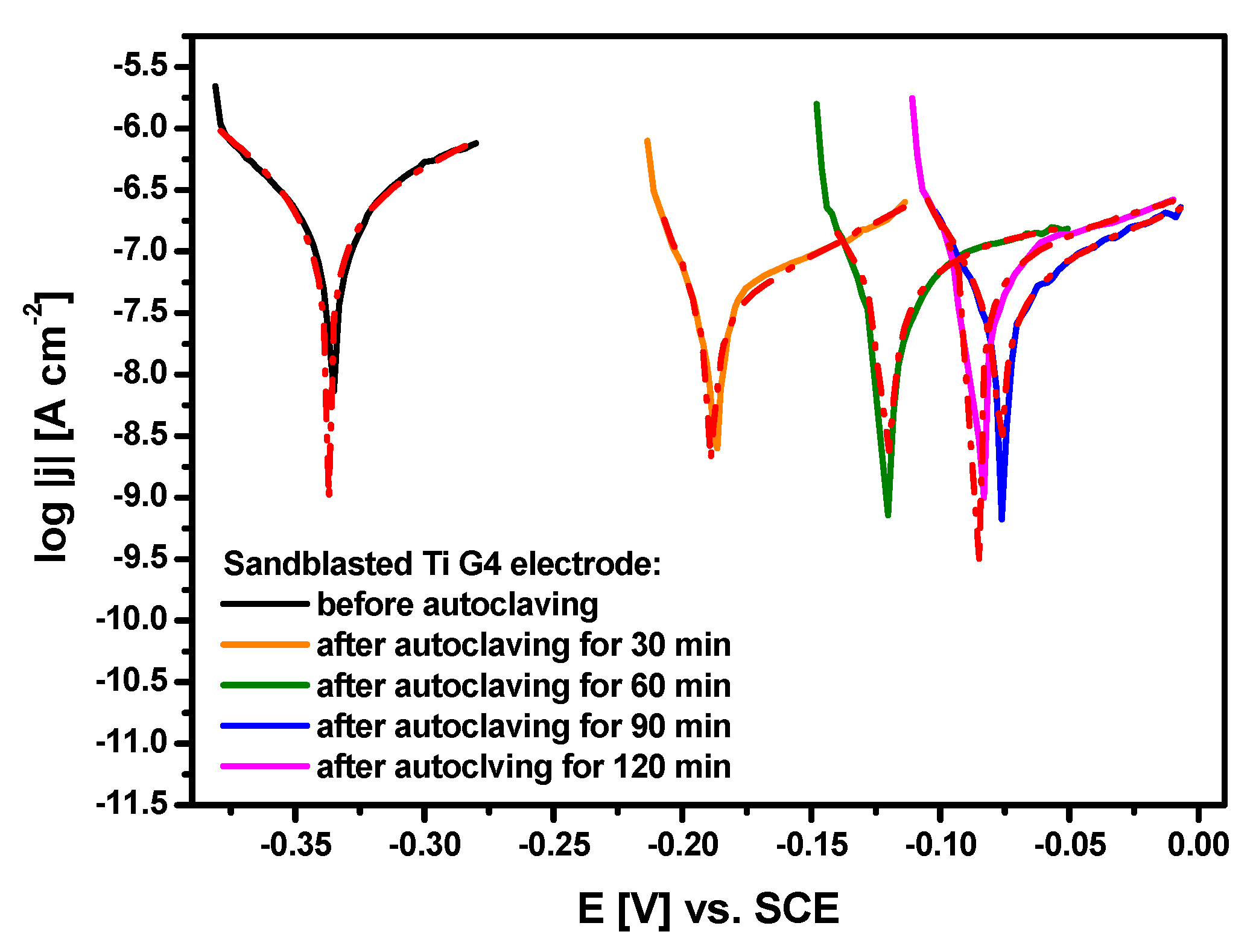
3.5. Polarization Curves Near the Open Circuit Potential
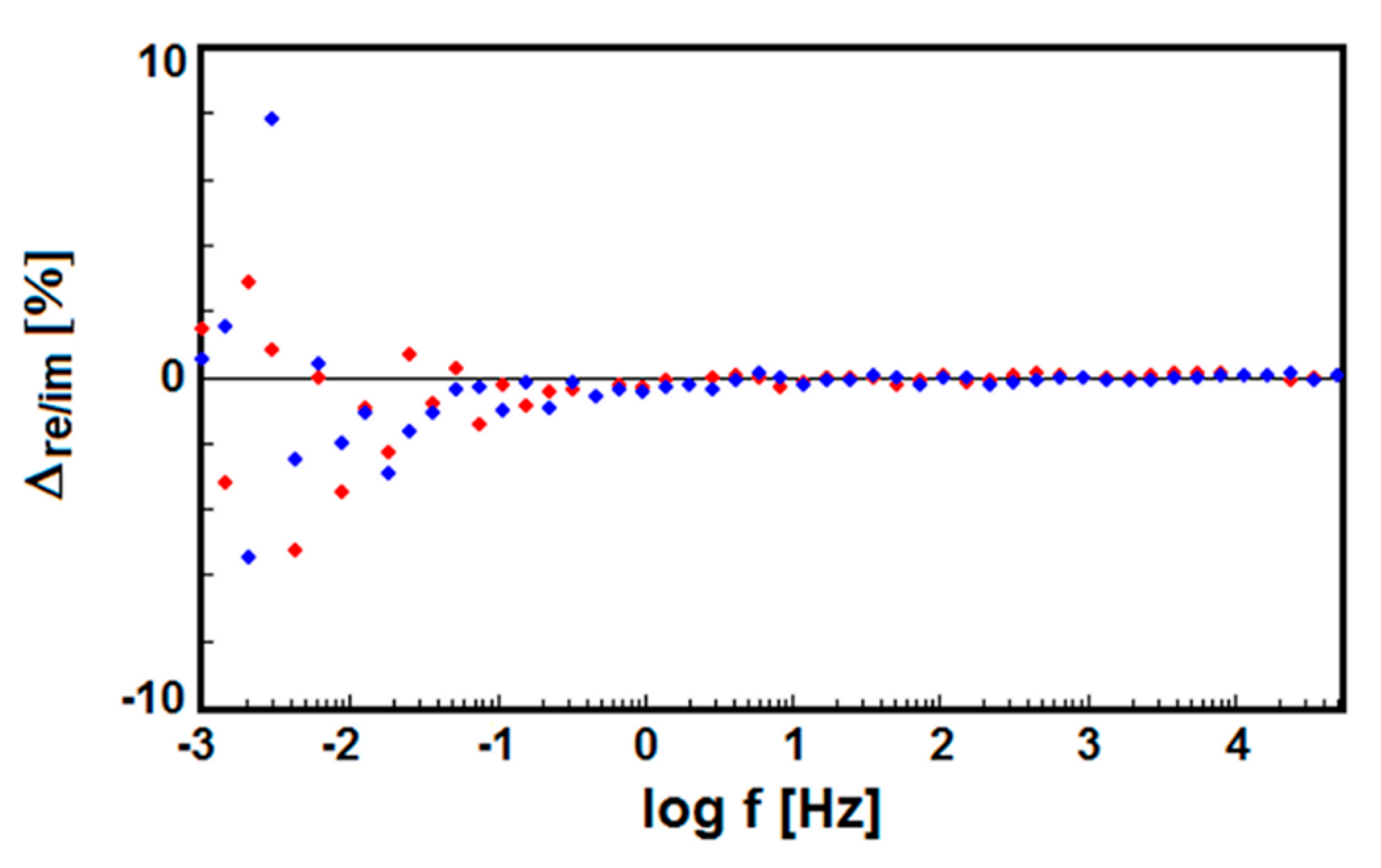
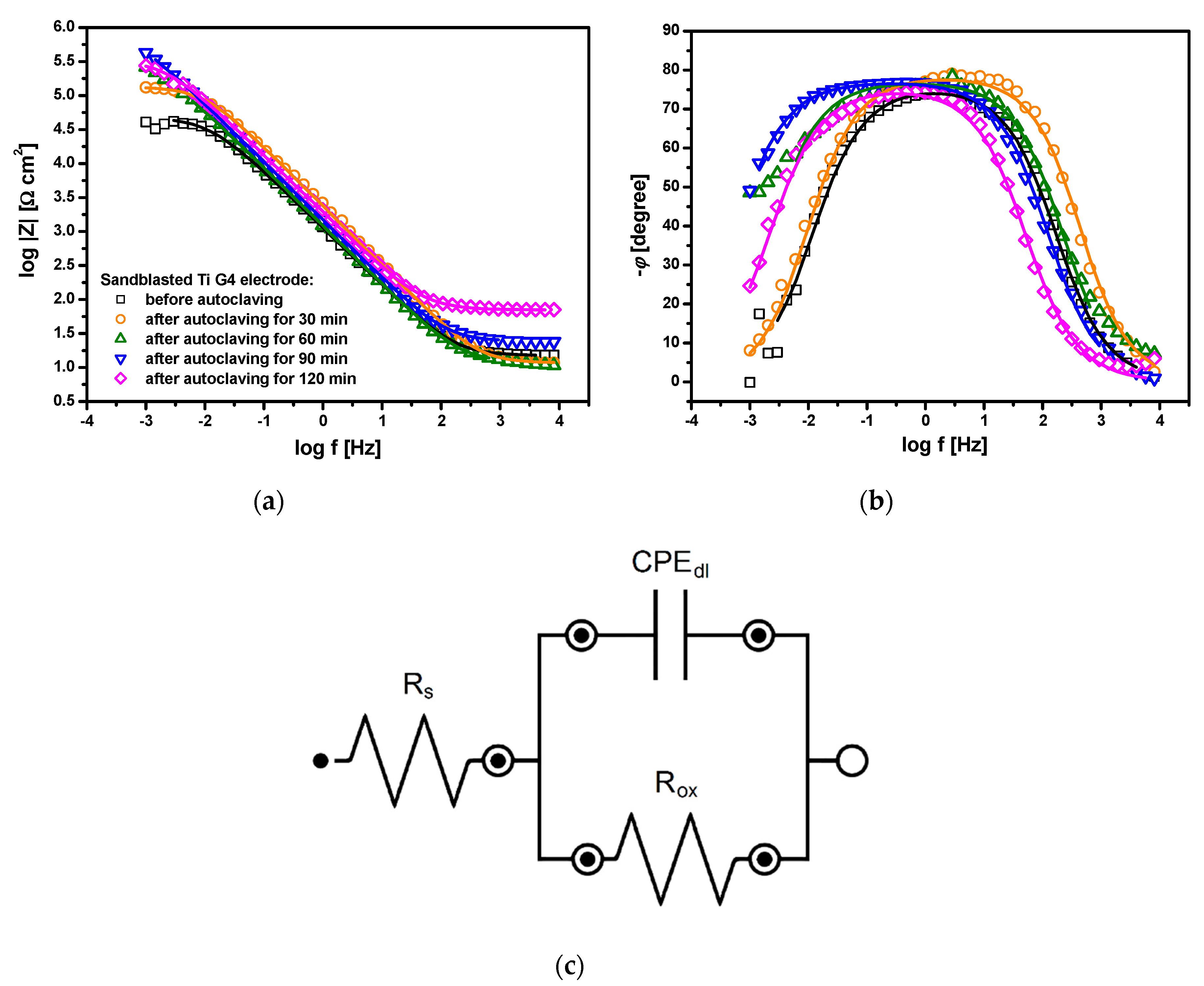
3.6. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Study
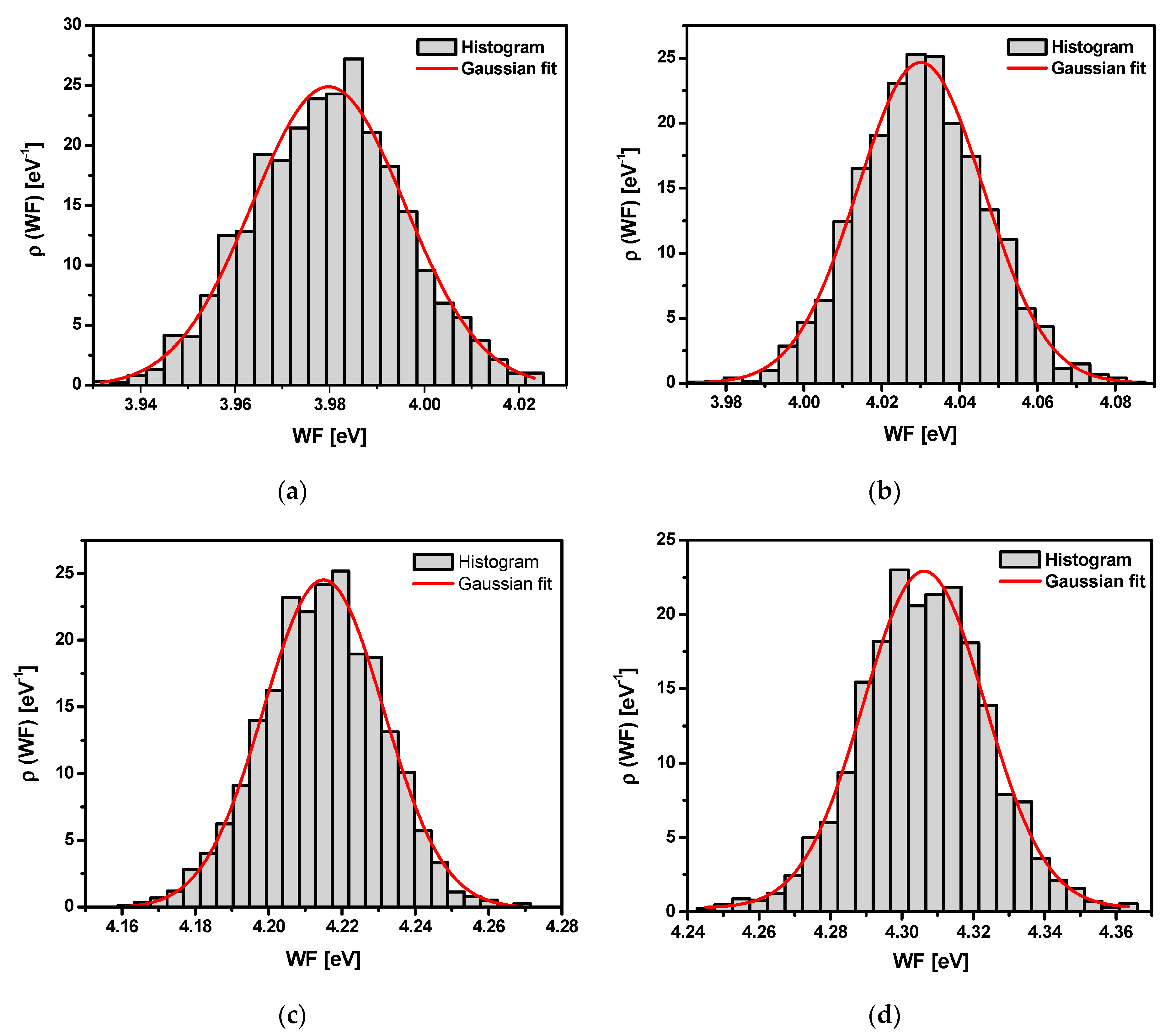
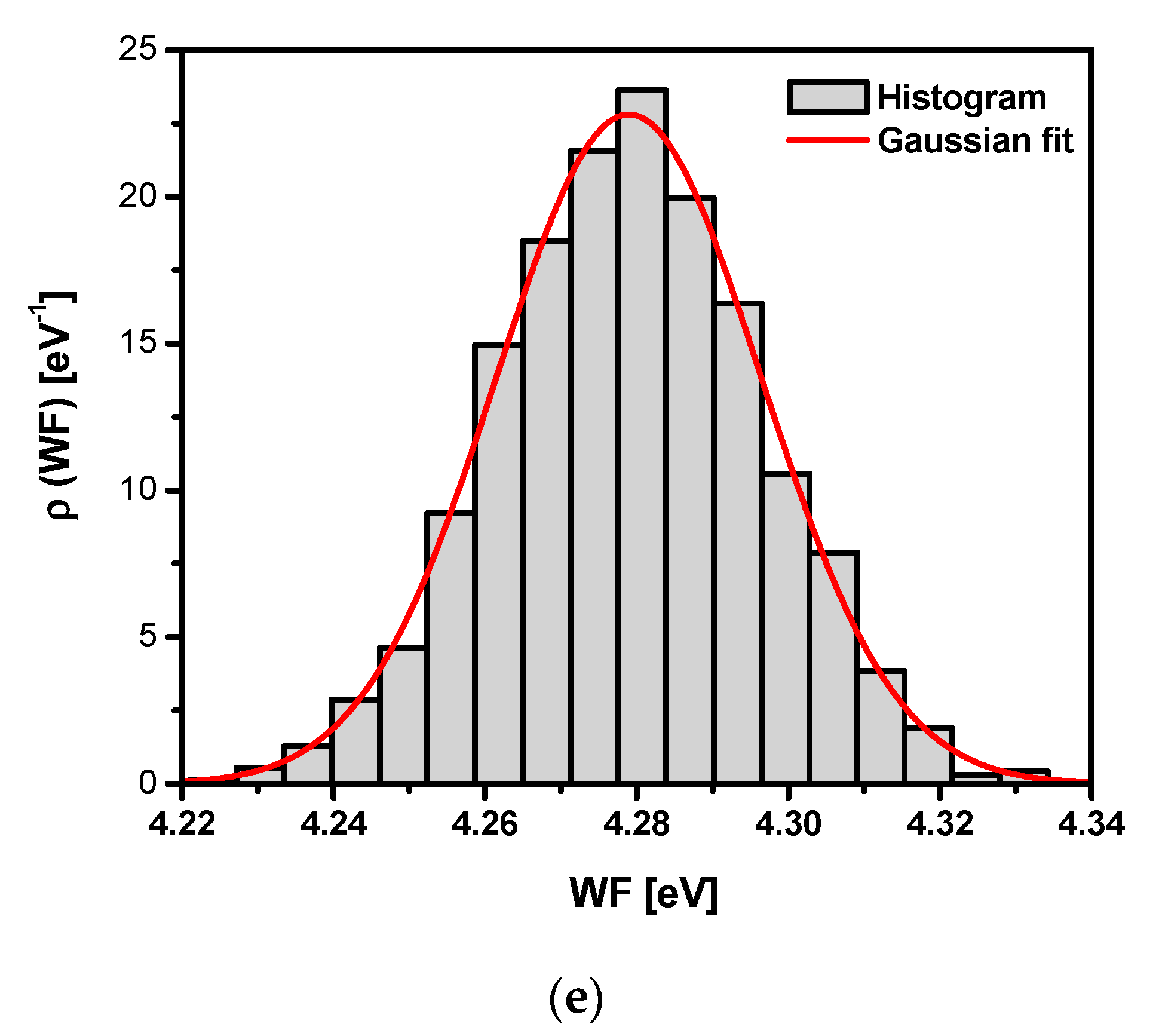
3.7. Scanning Kelvin Probe Measurements
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nicholson, J.W. Titanium alloys for dental implants: A review. Prosthesis 2020, 2, 100–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, J.L. Electrochemical Behavior of Metals in the Biological Milieu. In Comprehensive Biomaterials II, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 19–49. [Google Scholar]
- Lobat, T. Applications of Biomedical Engineering in Dentistry; Springer: Chem, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, R.P. Titanium based biomaterial for bone implants: A mini review. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 26, 3148–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budmir, J.; Mravak-Stipetić, M.; Bulat, V.; Ferček, I.; Japundžić, I.; Lugović-Mihić, L. Allergic reactions in oral and perioral diseases-What do allergy skin test results show. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2019, 127, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandu, G.S.; Hema, B.S.; Mahajan, H.; Mishra, S. Dental Metal Allergy: An Update. J. Res. Adv. Dent. 2014, 3, 156–163. [Google Scholar]
- Brånemark, P.I.; Zarb, G.A.; Albrektsson, T. Tissue-Integrated Prostheses: Osseointegration in Clinical Dentistry, 1st ed.; Quintessence Publishing Company: Batavia, IL, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Kapoor, N.; Nagpal, A.; Verma, R. Surface Treatment of Titanium Implant and Dental Implant Design: Titanium as Biomaterial and Method Used for Surface Treatment to Increase Bone and Soft Tissue Integration; LAP LAMBERT Academic Publishing: Beau-Bassin, Mauritius, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Le Guéhennec, L.; Soueidan, A.; Layrolle, P.; Amouriq, Y. Surface treatments of titanium dental implants for rapid osseointegration. Dent. Mater. 2007, 23, 844–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Singh, S.; Prakash, C. Current trends in biomaterials and bio-manufacturing. In Biomanufacturing; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.W.; Chien, E.Y.; Chien, H.H. Dental implant bioactive surface modifications and their effects on osseointegration: A review. Biomark. Res. 2016, 4, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandal, S.; Ghalaut, P.; Shekhawat, H.; Nagar, P. Osseointegration in Dental Implants: A Literature Review. Med. Sci. 2014, 4, 411–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokabber, T.; Zhou, Q.; Vakis, A.I.; van Rijn, P.; Pei, Y.T. Mechanical and biological properties of electrodeposited calcium phosphate coatings. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 100, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alla, R.K.; Ginjupalli, K.; Upadhya, N.; Shammas, M.; Ravi, R.K.; Sekhar, R. Surface roughness of implants: A review. Trends Biomater. Artif. Organs 2011, 25, 112–118. [Google Scholar]
- Wennerberg, A. The importance of surface roughness for implant incorporation. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 1998, 38, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bruyn, H.; Christiaens, V.; Doornewaard, R.; Jacobsson, M.; Cosyn, J.; Jacquet, W.; Vervaeke, S. Implant surface roughness and patient factors on long-term peri-implant bone loss. Periodontol. 2000 2017, 73, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dank, A.; Aartman, I.H.A.; Wismeijer, D.; Tahmaseb, A. Effect of dental implant surface roughness in patients with a history of periodontal disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Implant Dent. 2019, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haimov, H.; Yosupov, N.; Pinchasov, G.; Juodzbalys, G. Bone Morphogenetic Protein Coating on Titanium Implant Surface: A Systematic Review. J. Oral Maxillofac. Res. 2017, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoli, I.R.; Filgueira, M.; Ferreira, L.M.; de Sousa, L.L.; Mariano, N.A.; Ramos, A.S.; Nunes, C.A.; dos Santos, C.; Ramos, E.C.T. Microstructure and corrosion behavior in SBF medium of spark plasma sintered Ti-xZr-20Si-10B (x = 5, 7, 10, 15, 20 at.-%) alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 797, 1157–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, C.A.; Valiquette, N.; Pilliar, R.M. Osseointegration of sintered porous-surfaced and plasma spray-coated implants: An animal model study of early postimplantation healing response and mechanical stability. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1999, 47, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asri, R.I.M.; Harun, W.S.W.; Hassan, M.A.; Ghani, S.A.C.; Buyong, Z. A review of hydroxyapatite-based coating techniques: Sol–gel and electrochemical depositions on biocompatible metals. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2016, 57, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usinskas, P.; Stankeviciute, Z.; Beganskiene, A.; Kareiva, A. Sol-gel derived porous and hydrophilic calcium hydroxyapatite coating on modified titanium substrate. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 307, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordioli, G.; Majzoub, Z.; Piatelli, A.; Scarano, A. Removal torque and histomorphometric investigation of 4 different titanium surfaces: An experimental study in the rabbit tibia. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Impants 2000, 15, 668–674. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.P.; Wang, X.Y.; Li, J.X.; Li, D.Y.; Man, C.-S.; Shepard, M.J.; Zhai, T. Enhancement of fatigue and corrosion properties of pure Ti by sandblasting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 429, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupp, F.; Scheideler, L.; Olshanska, N.; de Wild, M.; Wieland, M.; Geis-Gerstorfer, J. Enhancing surface free energy and hydrophilicity through chemical modification of microstructured titanium implant surfaces. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2006, 76, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellingsen, J.E.; Johansson, C.B.; Wennerberg, A.; Holmén, A. Improved retention and bone-tolmplant contact with fluoride-modified titanium implants. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Implant. 2004, 19, 659–666. [Google Scholar]
- London, R.M.; Roberts, F.A.; Baker, D.A.; Rohrer, M.D.; O’Neal, R.B. Histologic comparison of a thermal dualetched implant surface to machined, TPS, and HA surfaces: Bone contact in vivo in rabbits. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Impants. 2002, 17, 369–376. [Google Scholar]
- Albrektsson, T.; Wennerberg, A. Oral implant surfaces: Part 2—Review focusing on clinical knowledge of different surfaces. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2004, 17, 544–564. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Xiaoyu, Y.; Yuan, S.; Minhua, T.; Jian, L.; Aidi, N.; Xing, L. Morphology improvement of sandblasted and acid-etched titanium surface and osteoblast attachment promotion by hydroxyapatite coating. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2015, 44, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Guehennec, L.; Lopez-Heredia, M.-A.; Enkel, B.; Weiss, P.; Amouriq, Y.; Layrolle, P. Osteoblastic cell behaviour on different titanium implant surfaces. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, F.; Ferrari, D.; Herten, M.; Mihatovic, I.; Wieland, M.; Sager, M.; Becker, J. Effects of surface hydrophilicity and microtopography on early stages of soft and hard tissue integration at non-submerged titanium implants: An immunohistochemical study in dogs. J. Periodontol. 2007, 78, 2171–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Lam, W.M.; Lin, C.J.; Qiu, G.X.; Wu, Z.H.; Luk, K.D.K.; Lu, W.W. Biocompatibility of electrophoretical deposition of nanostructured hydroxyapatite coating on roughen titanium surface: In vitro evaluation using mesenchymal stem cells. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2007, 82, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buser, D.; Broggini, N.; Wieland, M.; Schenk, R.K.; Denzer, A.J.; Cochran, D.L.; Hoffmann, B.; Lussi, A.; Steinemann, S.G. Enhanced bone apposition to a chemically modified SLA titanium surface. J. Dent. Res. 2004, 83, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokstad, A.; Braegger, U.; Brunski, J.B.; Carr, A.B.; Naert, I.; Wennerberg, A. Quality of dental implants. Int. Dent. J. 2003, 53, 409–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.; Bose, S.; Bandyopadhyay, A. Surface modifications and cell-materials interactions with anodized Ti. Acta Biomater. 2007, 3, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İzmir, M.; Ercan, B. Anodization of titanium alloys for orthopedic applications. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2019, 13, 28–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simka, W.; Sadkowski, A.; Warczak, M.; Iwaniak, A.; Dercz, G.; Michalska, J.; Maciej, A. Characterization of passive films formed on titanium during anodic oxidation. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 8962–8968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.W.; Lee, S.G.; Choi, B.J.; Suh, J.Y. Effects of a cell adhesion molecule coating on the blasted surface of titanium implants on bone healing in the rabbit femur. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2007, 22, 533–541. [Google Scholar]
- Özcan, M.; Hämmerle, C. Titanium as a reconstruction and implant material in dentistry: Advantages and pitfalls. Materials 2012, 5, 1528–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osak, P.; Łosiewicz, B. EIS study on interfacial properties of passivated Nitinol orthodontic wire in saliva modified with Eludril® mouthwash. Prot. Met. Phys. Chem. Surf. 2018, 54, 680–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitag, M.; Łosiewicz, B.; Goryczka, T.; Lelątko, J. Application of EIS to study the corrosion resistance of passivated NiTi shape memory alloy in simulated body fluid. Solid State Phenom. 2012, 183, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serro, A.P.; Saramago, B. Influence of sterilization on the mineralization of titanium implants induced by incubation in various biological model fluids. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 4749–4760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basiaga, M.; Walke, W.; Paszenda, Z.; Kajzer, A. The effect of EO and steam sterilization on the mechanical and electrochemical properties of titanium grade 4. Mater. Tehnol. 2016, 50, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Olivares-Navarrete, R.; Baier, R.E.; Meyer, A.E.; Tannenbaum, R.; Boyan, B.D.; Schwartz, Z. Effect of cleaning and sterilization on titanium implant surface properties and cellular response. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 1966–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanzi, M.C.; Farè, S.; Candiani, G. Sterilization and Degradation. In Foundations of Biomaterials Engineering, 1st ed.; Elsevier Science & Technology: London, UK, 2019; pp. 289–328. [Google Scholar]
- Mabboux, F.; Ponsonnet, L.; Morrier, J.J.; Benay, G.; Jaffrezic, N.; Barsotti, O. Effect of multiple desinfection/sterilization on surface characteristics of titanium based implants and in vitro bacterial adherence. Eur. Cells Mater. 2005, 9, 21–22. [Google Scholar]
- Stróż, A.; Łosiewicz, B.; Zubko, M.; Chmiela, B.; Balin, K.; Dercz, G.; Gawlikowski, M.; Goryczka, T. Production, structure and biocompatible properties of oxide nanotubes on Ti13Nb13Zr alloy for medical applications. Mater. Charact. 2017, 132, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smołka, A.; Dercz, G.; Rodak, K.; Łosiewicz, B. Evaluation of corrosion resistance of nanotubular oxide layers on the Ti13Zr13Nb alloy in physiological saline solution. Arch. Met. Mater. 2015, 60, 2681–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO. ISO 10271: Dentistry-Corrosion Test Methods for Metallic Materials; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- ISO. ISO 5832–2: Implants for Surgery-Metallic Materials-Part 2: Unalloyed Titanium; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM. ASTM F67–13: Standard Specification for Unalloyed Titanium, for Surgical Implant Applications (UNS R50250, UNS R50400, UNS R50550, UNS R50700); ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- FEPA. FEPA standard 42–1: Macrogrits F4~F220 for Grains of Fused Aluminium Oxide, Silicon Carbide and Other Abrasive Materials for Bonded Abrasives; FEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- AUTOLAB. Electrochemical Instruments, Description of the Instrument; Eco Chemie, B.V., Ed.; Kanaalweg: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Eco Chemie, B.V. Kanaalweg. In User Manual for Frequency Response Analysis (FRA) for Windows Version 4.9; Eco Chemie, B.V. Kanaalweg: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Łosiewicz, B.; Popczyk, M.; Szklarska, M.; Smołka, A.; Osak, P.; Budniok, A. Application of the scanning Kelivin probe technique for characterization of corrosion interfaces. Solid State Phenom. 2015, 228, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilghman, B.G. Improvement in Cutting and Engraving Stone, Metal, Glass, &c. US Patent No. 108408, 18 October 1870. [Google Scholar]
- Kasemo, B.; Lausmaa, J. Surface science aspects on inorganic biomaterials. Crit. Rev. Biocompat. 1986, 2, 335–380. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz, I.; Pacha-Olivenza, M.Á.; Tejero, R.; Anitua, E.; González-Martín, M.L.; Escudero, M.L.; Garcıía-Alonso, M.C. Corrosion behavior of surface modifications on titanium dental implant. In situ bacteria monitoring by electrochemical techniques. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2018, 106, 997–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO. ISO 4287: Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS)-Surface Texture: Profile Method-Terms, Definitions and Surface Texture Parameters; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- ISO. ISO 13565–2: Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS)-Surface Texture: Profile Method; Surfaces Having Stratified Functional Properties-Part 2: Height Characterization Using the Linear Material Ratio Curve; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Pawlus, P.; Reizer, R.; Wieczorowski, M. A review of methods of random surface topography modeling. Tribol. Int. 2020, 152, 106530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawley, J.B. Handbook of Biological Confocal Microscopy, 3rd ed.; Springer Science+Business Media LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO. ISO 25178-2: Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS)-Surface Texture: Areal-Part 2: Terms, Definitions and Surface Texture Parameters; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R. Electrochemical Methods. In Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Brunette, D.M.; Tengvall, P.; Textor, M.; Thomsen, P. Titanium in Medicine. In Material Science, Surface Science, Engineering, Biological Responses and Medical Applications; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2001; pp. 145–162. [Google Scholar]
- Pourbaix, M. Atlas of Electrochemical Equilibria in Aqueous Solutions, 2nd ed.; NACE International, National Association of Corrosion Engineers: Houston, TX, USA, 1974; ISBN 10-0915567989. [Google Scholar]
- Lasia, A. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy and its Applications; Springer Science+Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brug, G.J.; Van den Eeden, A.L.G.; Sluyters-Rehbach, M.; Sluyters, J.H. The analysis of electrode impedances complicated by the presence of a constant phase element. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1984, 176, 275–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, J.R.; Burleigh, T.D. Oxides formed on titanium by polishing, etching, anodizing, or thermal oxidizing. Corrosion 2000, 56, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubisztal, J.; Kubisztal, M.; Haneczok, G. Quantitative characterization of material surface-Application to Ni + Mo electrolytic composite coatings. Mater. Charact. 2016, 122, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubisztal, J.; Kubisztal, M.; Stach, S.; Haneczok, G. Corrosion resistance of anodic coatings studied by scanning microscopy and electrochemical methods. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2018, 350, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Kaushik, B.K.; Negi, Y.S. Perspectives and challenges for organic thin film transistors: Materials, devices, processes and applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2014, 25, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hölzl, J.; Schulte, F.K. Work Functions of Metals. In Solid Surface Physics; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1979. [Google Scholar]


| C | Fe | O | H | N | Ti |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <0.080% | <0.500% | <0.400% | <0.008% | <0.050% | 98.962% |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | Yield Point (MPa) 0.2% | HV5 Hardness | Elongation |
|---|---|---|---|
| >800 | >700 | >280 | >10% |
| Melting Temperature | Density | Modulus of Elasticity |
|---|---|---|
| 1610 °C | 4.5 g cm−3 | 114 GPa |
| Component | Content (%) |
|---|---|
| Al2O3 | 99.702 |
| SiO2 | 0.035 |
| Fe2O3 | 0.045 |
| TiO2 | 0.008 |
| CaO | 0.02 |
| Na2O | 0.19 |
| Component | Content (g dm−3) |
|---|---|
| NaCl | 0.70 |
| KCl | 1.20 |
| Na2HPO4 | 0.26 |
| NaHCO3 | 1.50 |
| KSCN | 0.33 |
| Parameter | Ti G4 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Machine Surface | Sandblasted Surface | |||
| Value | Standard Deviation | Value | Standard Deviation | |
| Pa(µm2 m−1) | 0.13 | 0.01 | 1.89 | 0.11 |
| Pq(µm) | 0.17 | 0.01 | 2.33 | 0.12 |
| Pp(µm] | 0.87 | 0.28 | 7.23 | 1.02 |
| Pv(µm) | 0.78 | 0.03 | 7.55 | 0.96 |
| Pt(µm] | 1.65 | 0.25 | 14.80 | 1.94 |
| Psk | −0.07 | 0.35 | −0.08 | 0.10 |
| Pku | 4.34 | 1.35 | 2.79 | 0.39 |
| Ra(µm) | 0.12 | 0.01 | 1.65 | 0.07 |
| Rz(µm] | 1.23 | 0.11 | 11.20 | 0.83 |
| Rp(µm) | 0.69 | 0.17 | 5.37 | 0.51 |
| Type of Sample | Sa (μm) | SD |
|---|---|---|
| Ti G4 sandblasted | 1.34 | 0.07 |
| Ti G4 sandblasted and autoclaved for 30 min | 1.84 | 0.09 |
| Ti G4 sandblasted and autoclaved for 60 min | 2.16 | 0.11 |
| Ti G4 sandblasted and autoclaved for 90 min | 3.14 | 0.16 |
| Ti G4 sandblasted and autoclaved for 120 min | 2.21 | 0.11 |
| Sandblasted Ti G4 | Ecor (V) | jcor (A cm−2) | bc (V dec−1) | ba (V dec−1) | Rp (Ω cm2) | CR at Ecor (mm yr−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before autoclaving | −0.337(5) | 2.88(30) × 10−7 | 0.073(5) | 0.124(12) | 6.92 × 104 | 2.51 × 10−3 |
| After autoclaving for 30 min | −0.189(5) | 3.55(3) × 10−8 | 0.025(2) | 0.093(5) | 2.39 × 105 | 3.09 × 10−4 |
| After autoclaving for 60 min | −0.120(4) | 1.01(12) × 10−7 | 0.058(6) | 0.324(77) | 2.10 × 105 | 8.77 × 10−4 |
| After autoclaving for 90 min | −0.077(4) | 5.67(3) × 10−8 | 0.040(2) | 0.117(5) | 2.30 × 105 | 4.93 × 10−4 |
| After autoclaving for 120 min | −0.085(5) | 8.57(5) × 10−8 | 0.034(2) | 0.158(10) | 1.42 × 105 | 7.46 × 10−4 |
| Sandblasted Ti G4 | Rs (Ω·cm2) | Tdl (F cm−2 s ϕ−1) | ϕdl | Rox (Ω cm2) | (F cm−2) | dox (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before autoclaving | 14.90(11) | 1.88(1) × 10−4 | 0.844(2) | 4.81(7) × 104 | 6.30 × 10−5 | 1.2 |
| After autoclaving for 30 min | 11.64(14) | 8.49(7) × 10−5 | 0.872(2) | 1.34(2) × 105 | 3.08 × 10−5 | 1.3 |
| After autoclaving for 60 min | 12.03(37) | 1.71(2) × 10−4 | 0.858(3) | 2.30(23) × 105 | 6.13 × 10−5 | 1.4 |
| After autoclaving for 90 min | 24.24(13) | 1.41(1) × 10−4 | 0.856(1) | 8.80(28) × 105 | 5.43 × 10−5 | 2.0 |
| After autoclaving for 120 min | 70.20(67) | 1.11(1) × 10−4 | 0.840(2) | 3.36(8) × 105 | 4.39 × 10−5 | 3.0 |
| Sandblasted Ti G4 | σ2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Before autoclaving | 3.98 | (0.02)2 |
| After autoclaving for 30 min | 4.03 | (0.02)2 |
| After autoclaving for 60 min | 4.22 | (0.02)2 |
| After autoclaving for 90 min | 4.31 | (0.02)2 |
| After autoclaving for 120 min | 4.28 | (0.02)2 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Łosiewicz, B.; Osak, P.; Maszybrocka, J.; Kubisztal, J.; Stach, S. Effect of Autoclaving Time on Corrosion Resistance of Sandblasted Ti G4 in Artificial Saliva. Materials 2020, 13, 4154. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13184154
Łosiewicz B, Osak P, Maszybrocka J, Kubisztal J, Stach S. Effect of Autoclaving Time on Corrosion Resistance of Sandblasted Ti G4 in Artificial Saliva. Materials. 2020; 13(18):4154. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13184154
Chicago/Turabian StyleŁosiewicz, Bożena, Patrycja Osak, Joanna Maszybrocka, Julian Kubisztal, and Sebastian Stach. 2020. "Effect of Autoclaving Time on Corrosion Resistance of Sandblasted Ti G4 in Artificial Saliva" Materials 13, no. 18: 4154. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13184154
APA StyleŁosiewicz, B., Osak, P., Maszybrocka, J., Kubisztal, J., & Stach, S. (2020). Effect of Autoclaving Time on Corrosion Resistance of Sandblasted Ti G4 in Artificial Saliva. Materials, 13(18), 4154. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13184154






