The Mechanical Properties of Kevlar Fabric/Epoxy Composites Containing Aluminosilicates Modified with Quaternary Ammonium and Phosphonium Salts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Part
2.1. Materials
2.2. Modification of Bentonite with Quaternary Ammonium and Phosphonium Salts
2.3. Preparation of Epoxy Compositions
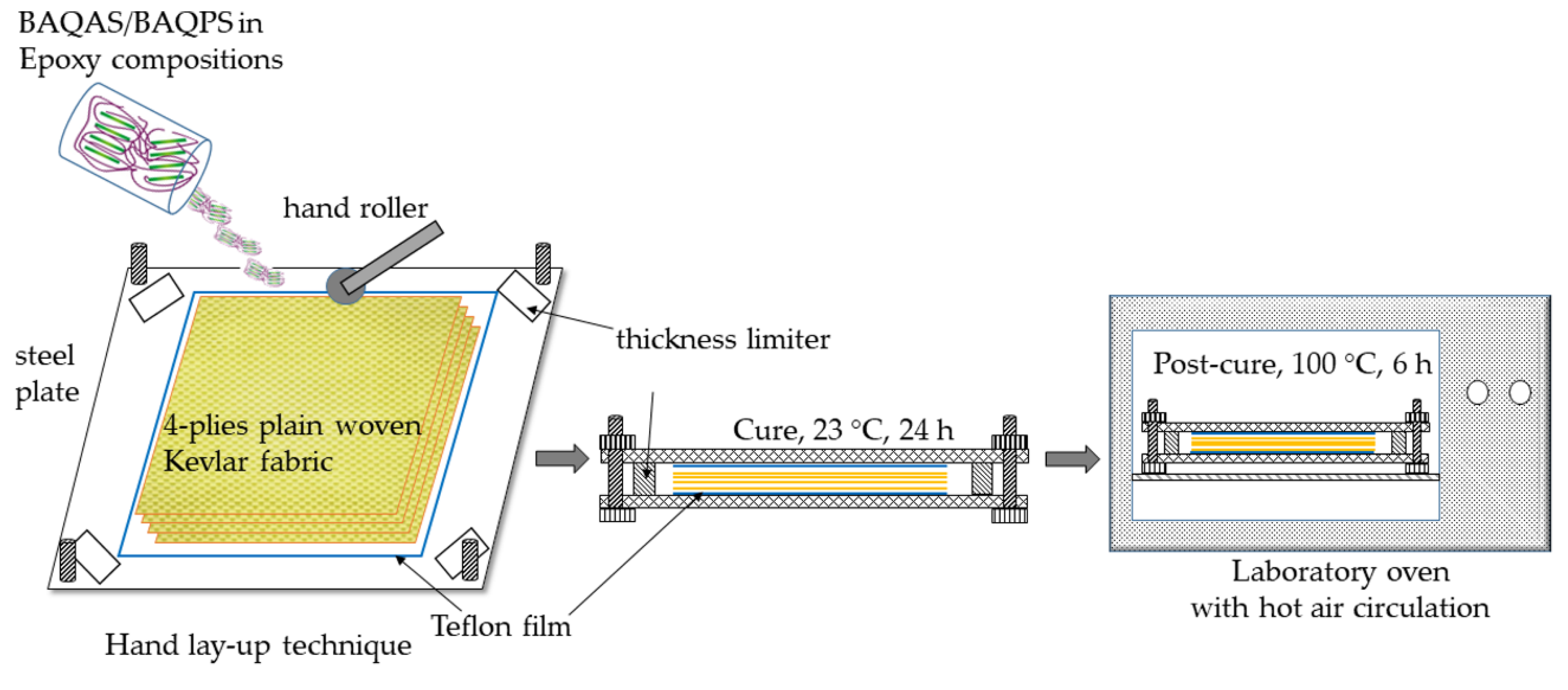
2.4. Preparation of Kevlar Fabric/Epoxy/Organoclay Composites
2.5. Morphology and Structure Analysis of Kevlar/Epoxy/Organoclay Composites
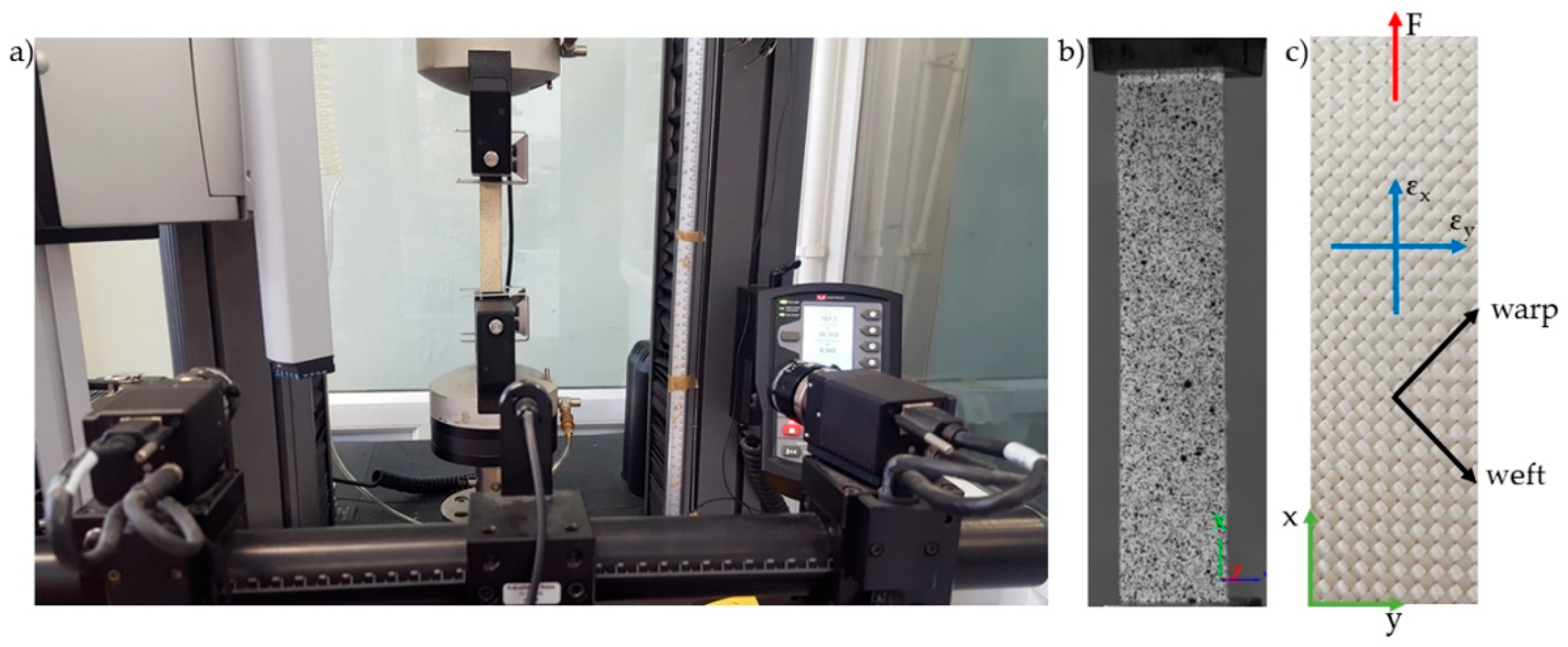
2.6. Study of Mechanical Properties
3. Results
3.1. Mechanical Properties of Kevlar/Epoxy/Organoclay Composites
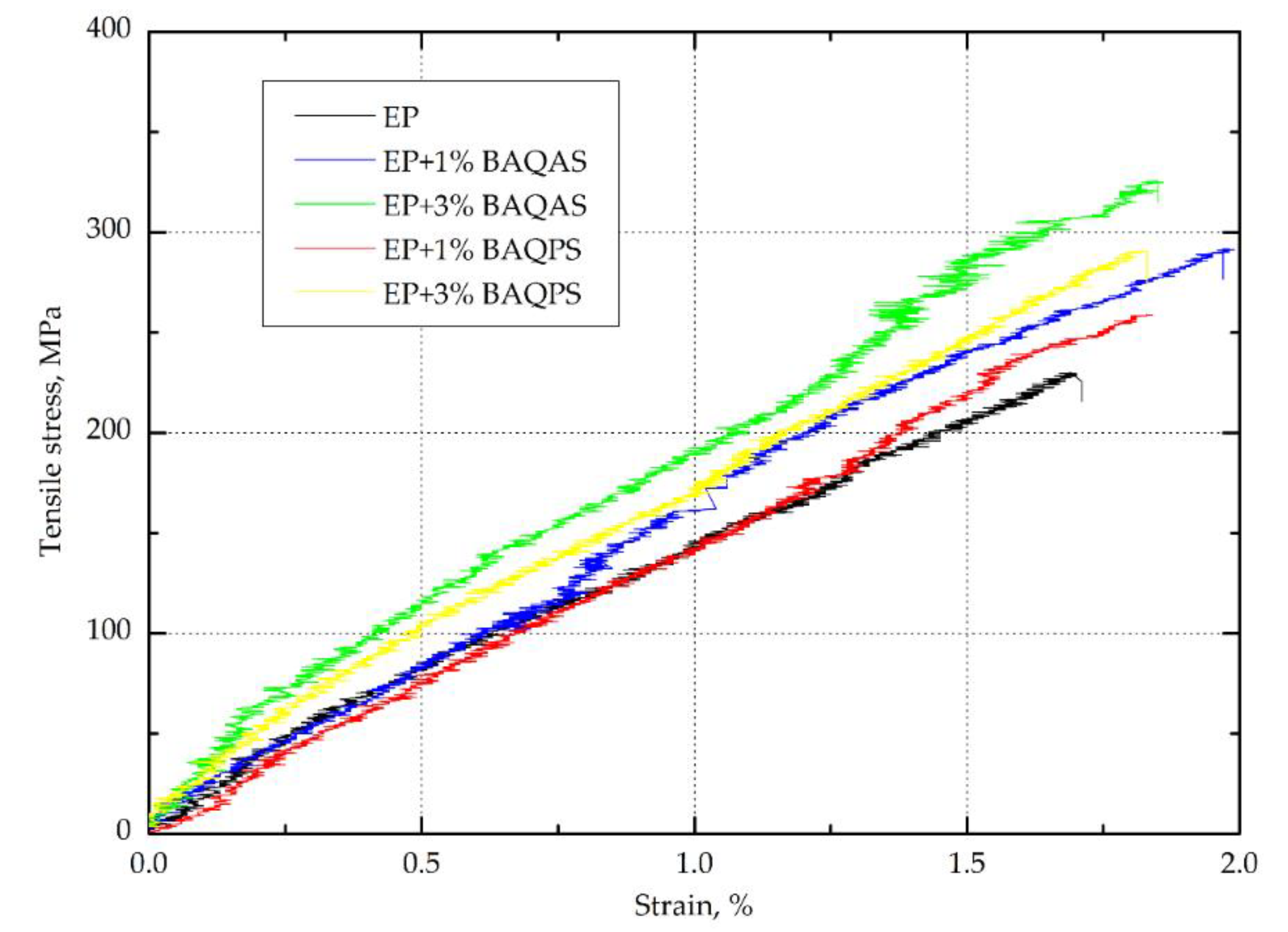
3.1.1. Tensile Strength
3.1.2. Flexural Strength
3.1.3. In-Plane Shear Strength
3.2. Morphology and Structure of Kevlar/Epoxy/Organoclay Composites
3.2.1. Analysis of Wide-Angle X-ray Diffraction
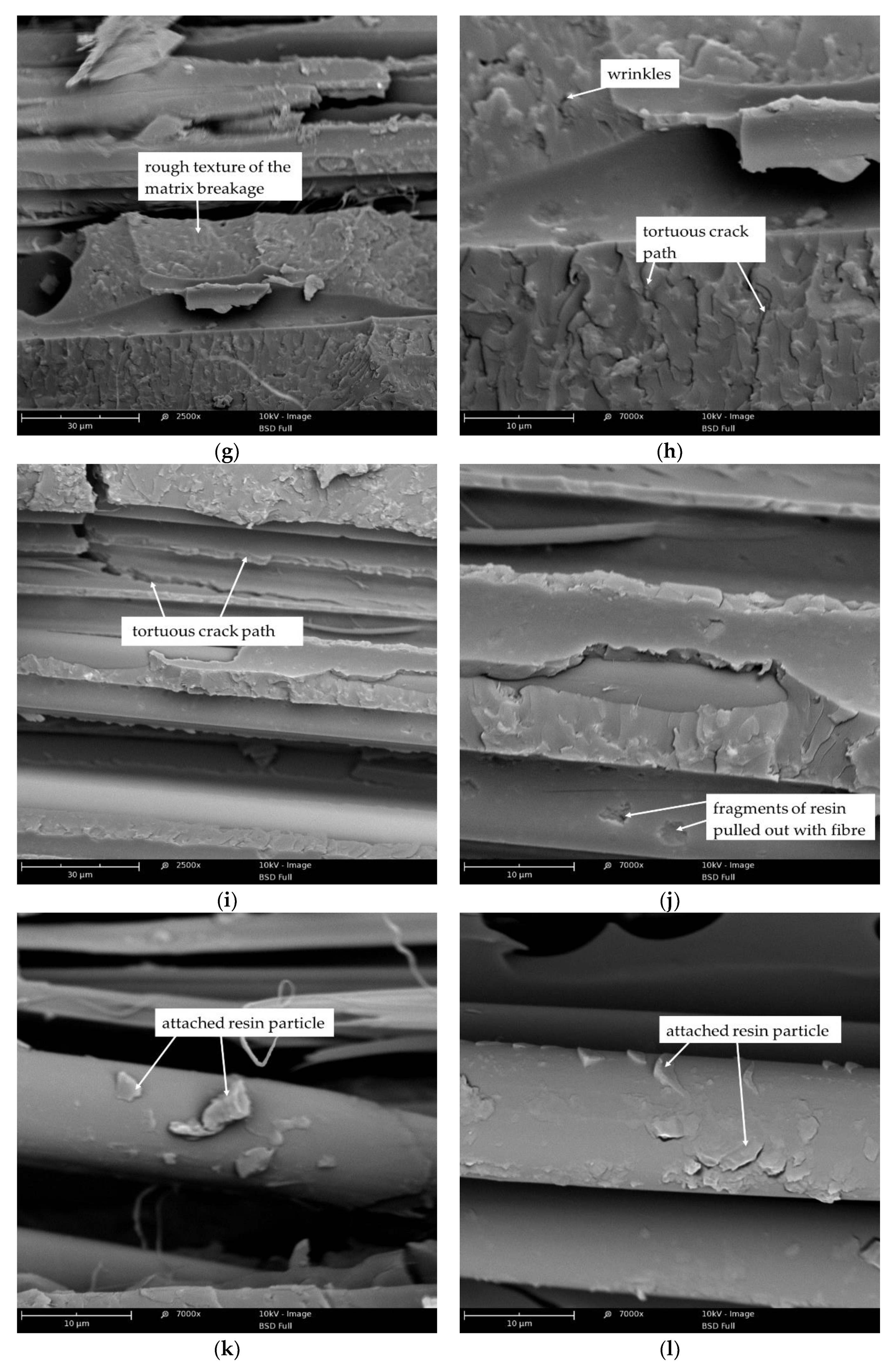
3.2.2. SEM Analysis of Brittle Fracture Surface of Kevlar/Epoxy/Organoclays Composites
3.2.3. Atomic Force Microscopy Analysis of Fiber Surface
4. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gore, P.M.; Kandasubramanian, B. Functionalized Aramid Fibers and Composites for Protective Applications: A Review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 16537–16563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, S.G.; de Amorim, W.F.; Manes, A.; Amico, S.C. The Effect of Thickness on Vacuum Infusion Processing of Aramid/Epoxy Composites for Ballistic Application. J. Compos. Mater. 2019, 53, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanen, C.; Solmaz, M.Y. Ballistic Tests of Lightweight Hybrid Composites for Body Armor. Mater. Test. 2019, 61, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, S.N.; Milanezi, T.L.; Louro, L.H.L.; Lima, É.P.; Braga, F.O.; Gomes, A.V.; Drelich, J.W. Novel Ballistic Ramie Fabric Composite Competing with KevlarTM Fabric in Multilayered Armor. Mater. Des. 2016, 96, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehlert, G.J.; Sodano, H.A. Zinc Oxide Nanowire Interphase for Enhanced Interfacial Strength in Lightweight Polymer Fiber Composites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2009, 1, 1827–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yuan, L.; Liang, G.; Gu, A. Effect and Origin of the Structure of Hyperbranched Polysiloxane on the Surface and Integrated Performances of Grafted Kevlar Fibers. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 320, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, T.; Wang, R.; Zhou, W. Effect of Grafting Alkoxysilane on the Surface Properties of Kevlar Fiber. Polym. Compos. 2007, 28, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Qian, X.-M.; He, X.-Q.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Liu, J.-P. Surface Modification of Kevlar by Grafting Carbon Nanotubes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 123, 1983–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazarika, A.; Deka, B.K.; Kim, D.; Park, Y.-B.; Park, H.W. Microwave-Induced Hierarchical Iron-Carbon Nanotubes Nanostructures Anchored on Polypyrrole/Graphene Oxide-Grafted Woven Kevlar® Fiber. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2016, 129, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahaya, R.; Sapuan, S.M.; Jawaid, M.; Leman, Z.; Zainudin, E.S. Effect of Layering Sequence and Chemical Treatment on the Mechanical Properties of Woven Kenaf–Aramid Hybrid Laminated Composites. Mater. Des. 2015, 67, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahaya, R.; Sapuan, S.; Jawaid, M.; Leman, Z.; Zainudin, E. Mechanical Performance of Woven Kenaf-Kevlar Hybrid Composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2014, 33, 2242–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.H. Pairing Effect and Tensile Properties of Laminated High-Performance Hybrid Composites Prepared Using Carbon/Glass and Carbon/Aramid Fibers. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 79, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi-Khojin, A.; Bashirzadeh, R.; Mahinfalah, M.; Nakhaei-Jazar, R. The Role of Temperature on Impact Properties of Kevlar/Fiberglass Composite Laminates. Compos. Part B Eng. 2006, 37, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valença, S.L.; Griza, S.; de Oliveira, V.G.; Sussuchi, E.M.; de Cunha, F.G.C. Evaluation of the Mechanical Behavior of Epoxy Composite Reinforced with Kevlar Plain Fabric and Glass/Kevlar Hybrid Fabric. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 70, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangana, S.; Epaarachchi, J.; Ferdous, W.; Leng, J. A Novel Hybridised Composite Sandwich Core with Glass, Kevlar and Zylon Fibres—Investigation under Low-Velocity Impact. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2020, 137, 103430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, A.F.; de Oliveira, A.M.; Leao, S.G.; Martins, M.G. Aramid Fabric/Nano-Size Dual Phase Shear Thickening Fluid Composites Response to Ballistic Impact. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2018, 112, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-J.; Zhang, Z.-Z.; Guo, F. A Study on the Sliding Wear of Hybrid PTFE/Kevlar Fabric/Phenolic Composites Filled with Nanoparticles of TiO2 and SiO2. Tribol. Trans. 2010, 53, 678–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, W. Tribological Behavior of Kevlar Fabric Composites Filled with Nanoparticles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 111, 2419–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Dang, W.; Lu, Z.; Deng, J.; Hao, Y.; Su, Z.; Zhang, M. Fabrication of Mechanically Robust and UV-Resistant Aramid Fiber-Based Composite Paper by Adding Nano-TiO2 and Nanofibrillated Cellulose. Cellulose 2018, 25, 3913–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyin, S.O.; Brantseva, T.V.; Kotomin, S.V.; Antonov, S.V. Epoxy Nanocomposites as Matrices for Aramid Fiber-Reinforced Plastics. Polym. Compos. 2018, 39, E2167–E2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haro, E.E.; Odeshi, A.G.; Szpunar, J.A. The Energy Absorption Behavior of Hybrid Composite Laminates Containing Nano-Fillers under Ballistic Impact. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2016, 96, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodadadi, A.; Liaghat, G.; Vahid, S.; Sabet, A.R.; Hadavinia, H. Ballistic Performance of Kevlar Fabric Impregnated with Nanosilica/PEG Shear Thickening Fluid. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 162, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taraghi, I.; Fereidoon, A.; Taheri-Behrooz, F. Low-Velocity Impact Response of Woven Kevlar/Epoxy Laminated Composites Reinforced with Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes at Ambient and Low Temperatures. Mater. Des. 2014, 53, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taraghi, I.; Fereidoon, A.; Mohyeddin, A. The Effect of MWCNTs on the Mechanical Properties of Woven Kevlar/Epoxy Composites. Steel Compos. Struct. 2014, 17, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassyouni, M.I.; Abdel-Hamid, S.M.-S.; Abdel-Aziz, M.H.; Zoromba, M.S. Mechanical and Viscoelastic Study of Functionalized MWCNTs/Epoxy/Kevlar Composites. Polym. Compos. 2018, 39, E2064–E2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, P.N.B.; Ferreira, J.A.M.; Santos, P.; Richardson, M.O.W.; Santos, J.B. Impact Response of Kevlar Composites with Filled Epoxy Matrix. Compos. Struct. 2012, 94, 3520–3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, P.N.B.; Ferreira, J.A.M.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Benameur, T.; Richardson, M.O.W. Impact Response of Kevlar Composites with Nanoclay Enhanced Epoxy Matrix. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 46, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, P.N.B.; Ferreira, J.A.M.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Benameur, T.; Richardson, M.O.W. Impact Strength of Composites with Nano-Enhanced Resin after Fire Exposure. Compos. Part B Eng. 2014, 56, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Karippal, J.J.; Murthy, H.N.N.; Rai, K.S.; Sreejith, M.; Krishna, M. Study of Mechanical Properties of Epoxy/Glass/Nanoclay Hybrid Composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2011, 45, 1893–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.U.; Iqbal, K.; Munir, A.; Kim, J.-K. Quasi-Static and Impact Fracture Behaviors of CFRPs with Nanoclay-Filled Epoxy Matrix. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2011, 42, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleksy, M.; Szwarc-Rzepka, K.; Heneczkowski, M.; Oliwa, R.; Jesionowski, T. Epoxy Resin Composite Based on Functional Hybrid Fillers. Materials 2014, 7, 6064–6091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliwa, R.; Heneczkowski, M.; Oleksy, M. Epoxy composites for aviation industry. Polimery 2015, 60, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PL Pat 216 081. Available online: http://pl.espacenet.com/publicationDetails/originalDocument?FT=D&date=20140228&DB=&locale=pl_PL&CC=PL&NR=216081B1&KC=B1&ND=4# (accessed on 28 February 2014).
- PL Pat 217 487. Available online: https://pl.espacenet.com/publicationDetails/originalDocument?FT=D&date=20140731&DB=&locale=pl_PL&CC=PL&NR=217487B1&KC=B1&ND=4# (accessed on 31 July 2014).
- Plastics—Determination of Tensile Properties—Part 4: Test Conditions for Isotropic and Orthotropic Fibre-Reinforced Plastic Composites; Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2000.
- Fibre-Reinforced Plastic Composites—Determination of Flexural Properties; Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2001.
- Fibre-Reinforced Plastic Composites—Determination of the In-Plane Shear Stress/Shear Strain Response, Including the In-Plane Shear Modulus and Strength, by the Plus or Minus 45 Degree Tension Test Method; Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2000.
- Bozkurt, Ö.Y. Hybridization Effects on Tensile and Bending Behavior of Aramid/Basalt Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Composites. Polym. Compos. 2017, 38, 1144–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.; Reis, P.; Costa, J.; Richardson, M. Fatigue Behaviour of Kevlar Composites with Nanoclay-Filled Epoxy Resin. J. Compos. Mater. 2012, 47, 1885–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isik, I.; Yilmazer, U.; Bayram, G. Impact Modified Epoxy/Montmorillonite Nanocomposites: Synthesis and Characterization. Polymer 2003, 44, 6371–6377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J. Characterization and Modeling of Mechanical Behavior of Polymer/Clay Nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 1607–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Hoa, S.V. Mechanical Properties of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Epoxy/Clay Nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2008, 68, 854–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, N.; Arumugam, V.; Rajkumar, S. Surface Modification of Kevlar Fibre Fabric and Its Influence on the Properties of Kevlar/Epoxy Composites. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2019, 42, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sockalingam, S.; Bremble, R.; Gillespie, J.W.; Keefe, M. Transverse Compression Behavior of Kevlar KM2 Single Fiber. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 81, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanitkar, Y.M.; Kulkarni, A.P.; Wangikar, K.S. Investigation of Flexural Properties of Glass-Kevlar Hybrid Composite. Eur. J. Eng. Res. Sci. 2016, 1, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Ekşı, S.; Genel, K. Comparison of Mechanical Properties of Unidirectional and Woven Carbon, Glass and Aramid Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Composites. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2017, 132, 879–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBaron, P.C.; Wang, Z.; Pinnavaia, T.J. Polymer-Layered Silicate Nanocomposites: An Overview. Appl. Clay Sci. 1999, 15, 11–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Hoa, S.V.; Pugh, M. Morphology and Performance of Epoxy Nanocomposites Modified with Organoclay and Rubber. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2004, 44, 1178–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainuddin, S.; Hosur, M.V.; Barua, R.; Kumar, A.; Jeelani, S. Effects of Ultraviolet Radiation and Condensation on Static and Dynamic Compression Behavior of Neat and Nanoclay Infused Epoxy/Glass Composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2011, 45, 1901–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.-L.; Kuo, J.-C.; Hsu, S.-M. Organoclay Effect on Transverse Compressive Strength of Glass/Epoxy Nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 7406–7412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Wang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Meng, C.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, X. The Introduction of Asymmetric Heterocyclic Units into Poly(p-Phenylene Terephthalamide) and Its Effect on Microstructure, Interactions and Properties. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 13291–13303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andres Leal, A.; Deitzel, J.M.; McKnight, S.H.; Gillespie, J.W. Interfacial Behavior of High Performance Organic Fibers. Polymer 2009, 50, 1228–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Qin, W.; Wu, X. Improvement of the Atomic Oxygen Resistance of Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Cyanate Ester Composites Modified by POSS-Graphene-TiO2. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2016, 133, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.-Z.; Yu, B.; Hansen, R.V.; Chen, X.; Hu, X.; Yang, J. Grafting Low Contents of Branched Polyethylenimine onto Carbon Fibers to Effectively Improve Their Interfacial Shear Strength with an Epoxy Matrix. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 2, 1500122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Meng, C.; Dai, Y.; Luo, L.; Liu, X. Constructing a Weaving Structure for Aramid Fiber by Carbon Nanotube-Based Network to Simultaneously Improve Composites Interfacial Properties and Compressive Properties. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2019, 182, 107721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, J.H.S.; Angrizani, C.C.; Botelho, E.C.; Amico, S.C. Effect of Fiber Orientation on the Shear Behavior of Glass Fiber/Epoxy Composites. Mater. Des. (1980-2015) 2015, 65, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.-L.; Wu, M.-D. Organoclay Effect on Mechanical Responses of Glass/Epoxy Nanocomposites. J. Compos. Mater. 2008, 42, 553–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boufaida, Z.; Farge, L.; André, S.; Meshaka, Y. Influence of the Fiber/Matrix Strength on the Mechanical Properties of a Glass Fiber/Thermoplastic-Matrix Plain Weave Fabric Composite. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2015, 75, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilisik, K.; Erdogan, G.; Sapanci, E.; Gungor, S. Three-Dimensional Nanoprepreg and Nanostitched Aramid/Phenolic Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes Composites: Experimental Determination of in-Plane Shear. J. Compos. Mater. 2019, 53, 4077–4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilisik, K.; Karaduman, N.; Erdogan, G.; Sapanci, E.; Gungor, S. In-Plane Shear of Nanoprepreg/Nanostitched Three-Dimensional Carbon/Epoxy Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes Composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2019, 53, 3413–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, T.; Heimbs, S.; Maier, M. Mechanical Properties and Energy Absorption Capability of Woven Fabric Composites under ±45° Off-Axis Tension. Compos. Struct. 2015, 125, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, G.C.; Fellers, J.F.; Simunovic, S.; Starbuck, J.M. Energy Absorption in Polymer Composites for Automotive Crashworthiness. J. Compos. Mater. 2002, 36, 813–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, M.; Fan, J.; Shi, Z.; Li, H.; Yin, J. Kevlar®-Functionalized Graphene Nanoribbon for Polymer Reinforcement. Polymer 2014, 55, 2578–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmerman, J.F.; Hayes, B.S.; Seferis, J.C. Nanoclay Reinforcement Effects on the Cryogenic Microcracking of Carbon Fiber/Epoxy Composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2002, 62, 1249–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, N.A.; Woo, R.S.C.; Kim, J.-K.; Leung, C.C.K.; Munir, A. Mode I Interlaminar Fracture Behavior and Mechanical Properties of CFRPs with Nanoclay-Filled Epoxy Matrix. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2007, 38, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, B.; Li, W.; Lei, Q. Effects of Oxygen Plasma Treatment Power on Surface Properties of Poly(p-Phenylene Benzobisoxazole) Fibers. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 255, 3153–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymańska, J.; Bakar, M.; Białkowska, A.; Kostrzewa, M. Study on the Adhesive Properties of Reactive Liquid Rubber Toughened Epoxy-Clay Hybrid Nanocomposites. J. Polym. Eng. 2018, 38, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliwa, R.; Heneczkowski, M.; Oliwa, J.; Oleksy, M. Mechanical Strength of Epoxy/Organoclay/Carbon Fiber Hybrid Composites. Polimery 2017, 62, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasser, J.; Lin, J.; Steinke, K.; Sodano, H.A. Enhanced Interfacial Strength of Aramid Fiber Reinforced Composites through Adsorbed Aramid Nanofiber Coatings. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2019, 174, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zhang, J.; Teng, C. Covalent Functionalization of Aramid Fibers with Zinc Oxide Nano-Interphase for Improved UV Resistance and Interfacial Strength in Composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 188, 107996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Material | Ultimate Tensile Strength, MPa | Young’s Modulus, GPa | Elongation at Break, % |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP/Kevlar | 233.9 ± 12.5 | 13.9 ± 1.2 | 1.6 ± 0.2 |
| EP+1%BAQAS/Kevlar | 303.1 ± 11.8 | 13.1 ± 0.9 | 1.9 ± 0.4 |
| EP+3%BAQAS/Kevlar | 302.9 ± 17.7 | 16.3 ± 3.0 | 1.6 ± 0.5 |
| EP+1%BAQPS/Kevlar | 260.3 ± 9.0 | 12.8 ± 1.0 | 1.8 ± 0.3 |
| EP+3%BAQPS/Kevlar | 285.7 ± 19.6 | 15.5 ± 0.2 | 1.7 ± 0.3 |
| Material | Ultimate Flexural Strength, MPa | Flexural Modulus, GPa | Elongation at Break, % |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP/Kevlar | 389.9 ± 22.0 | 20.8 ± 0.8 | 6.3 ± 0.3 |
| EP+1%BAQAS/Kevlar | 381.0 ± 19.3 | 20.3 ± 0.6 | 6.1 ± 0.4 |
| EP+3%BAQAS/Kevlar | 401.5 ± 20.6 | 23.4 ± 0.9 | 6.6 ± 0.5 |
| EP+1%BAQPS/Kevlar | 379.8 ± 19.9 | 20.2 ± 1.0 | 6.0 ± 0.6 |
| EP+3%BAQPS/Kevlar | 394.9 ± 23.3 | 21.7 ± 0.9 | 6.6 ± 0.5 |
| Material | Shear Strength at 5% Shear Strain, MPa | Shear Displacement at 5% Shear Strain, mm | Shear Modulus, MPa | Max Shear Strength, MPa | Max Shear Displacement, mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP/Kevlar | 18.3 ± 1.0 | 3.53 | 474.7 ± 24.0 | 23.3 ± 1.1 | 12.5 ± 2.1 |
| EP+1%BAQAS/Kevlar | 20.6 ± 0.9 | 4.10 | 609.1 ± 26.6 | 30.7 ± 4.4 | 23.1 ± 2.4 |
| EP+3%BAQAS/Kevlar | 22.8 ± 0.8 | 4.18 | 674.0 ± 27.1 | 34.7 ± 3.1 | 25.9 ± 2.6 |
| EP+1%BAQPS/Kevlar | 20.2 ± 1.2 | 4.13 | 591.0 ± 19.6 | 28.1 ± 2.1 | 19.5 ± 2.3 |
| EP+3%BAQPS/Kevlar | 21.9 ± 0.6 | 4.23 | 677.0 ± 17.3 | 29.4 ± 3.3 | 17.4 ± 3.5 |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oliwa, R. The Mechanical Properties of Kevlar Fabric/Epoxy Composites Containing Aluminosilicates Modified with Quaternary Ammonium and Phosphonium Salts. Materials 2020, 13, 3726. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13173726
Oliwa R. The Mechanical Properties of Kevlar Fabric/Epoxy Composites Containing Aluminosilicates Modified with Quaternary Ammonium and Phosphonium Salts. Materials. 2020; 13(17):3726. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13173726
Chicago/Turabian StyleOliwa, Rafał. 2020. "The Mechanical Properties of Kevlar Fabric/Epoxy Composites Containing Aluminosilicates Modified with Quaternary Ammonium and Phosphonium Salts" Materials 13, no. 17: 3726. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13173726
APA StyleOliwa, R. (2020). The Mechanical Properties of Kevlar Fabric/Epoxy Composites Containing Aluminosilicates Modified with Quaternary Ammonium and Phosphonium Salts. Materials, 13(17), 3726. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13173726





