Adsorption of Anionic Dye on the Acid-Functionalized Bentonite
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Acid-Functionalization of Bentonite
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Adsorption Experiments
2.5. Isothermal and Kinetic Studies
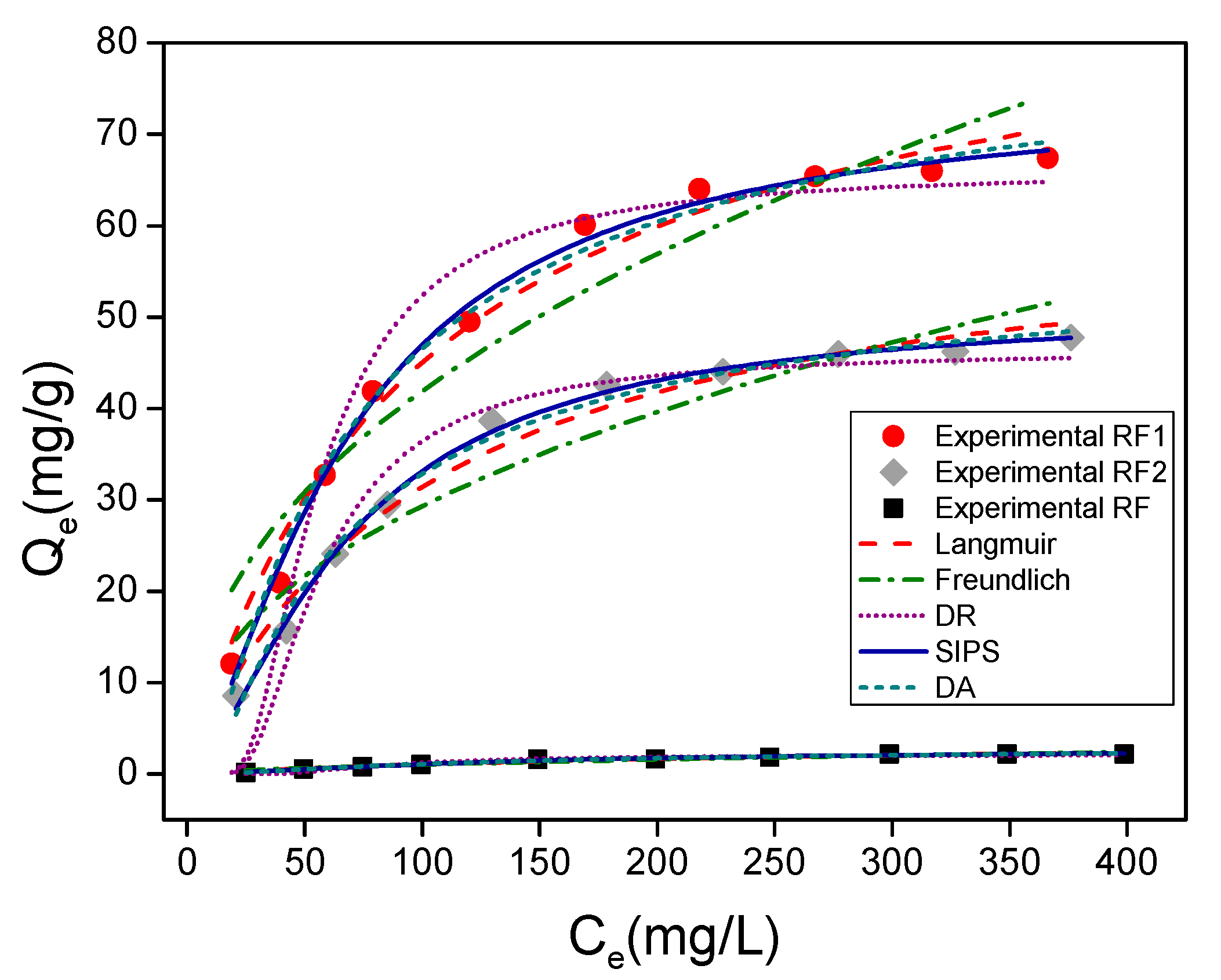
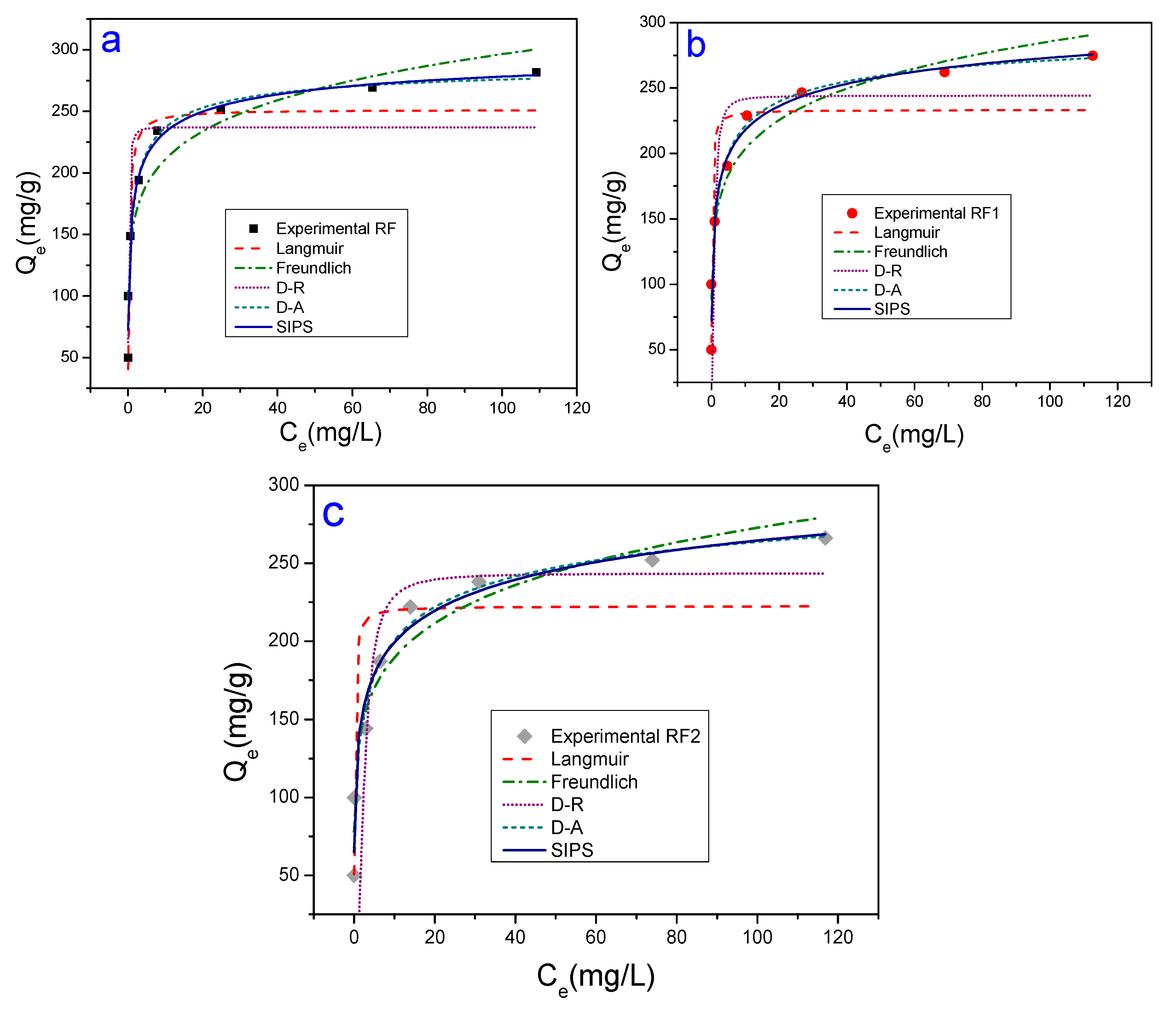
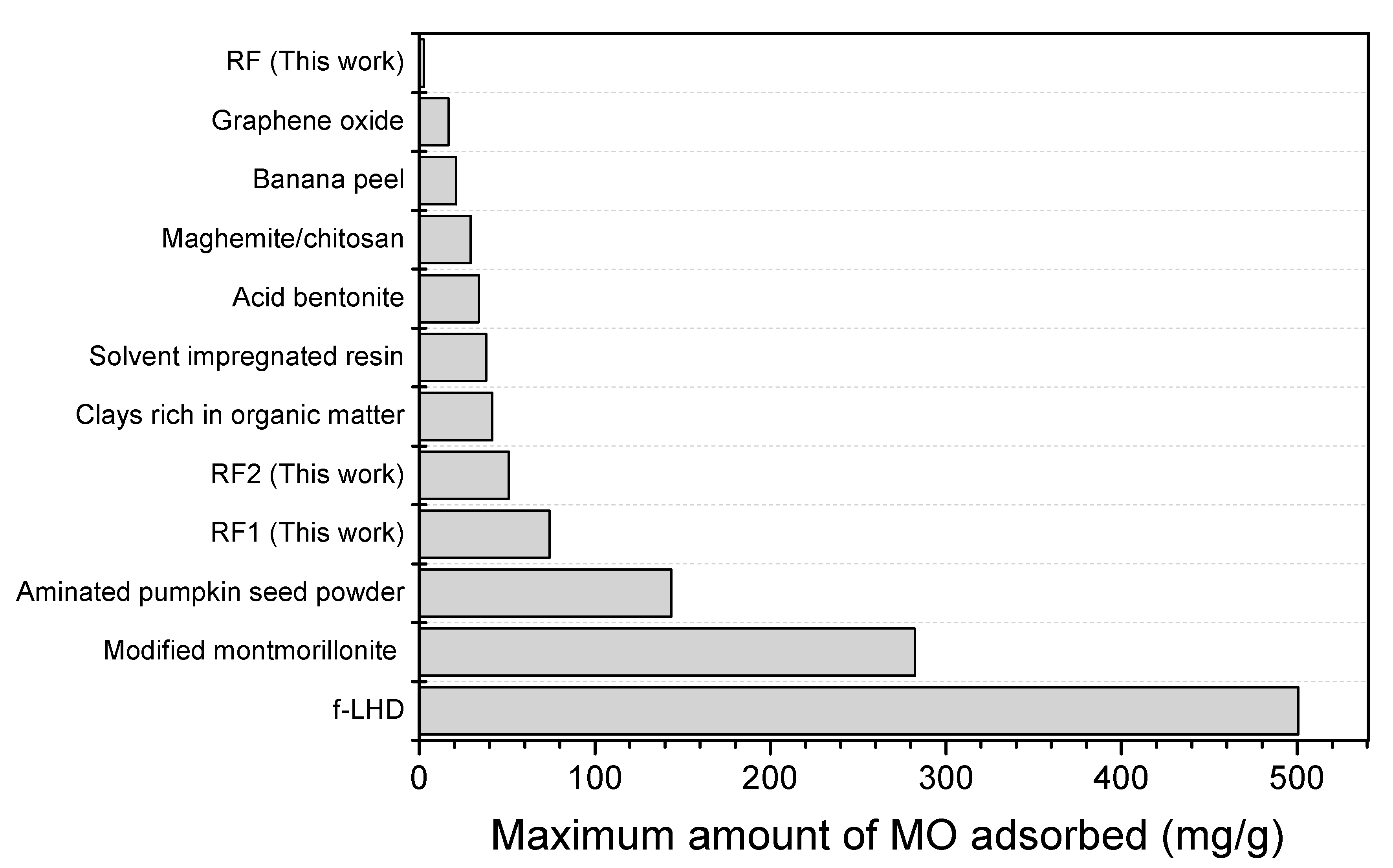
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Natural and Activated Clays
3.2. Adsorption Tests
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Djilani, C.; Zaghdoudi, R.; Djazi, F.; Bouchekima, B.; Lallam, A.; Modarressi, A.; Rogalski, M. Adsorption of dyes on activated carbon prepared from apricot stones and commercial activated carbon. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2015, 53, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagub, M.T.; Sen, T.K.; Afroze, S.; Ang, H.M. Dye and its removal from aqueous solution by adsorption: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 209, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errais, E.; Duplay, J.; Darragi, F.; M’Rabet, I.; Aubert, A.; Huber, F.; Morvan, G. Efficient anionic dye adsorption on natural untreated clay: Kinetic study and thermodynamic parameters. Desalination 2011, 275, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, M.A.; Shah, A.A.; Almani, K.F.; Tahira, A.; Chalangar, S.E.; Chandio, A.D.; Nur, O.; Willander, M.; Ibupoto, Z.H. Efficient photo catalysts based on silver doped ZnO nanorods for the photo degradation of methyl orange. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 23289–23297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Tang, G.; Yan, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, X.; Wang, H.; Feng, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wu, J.; Chen, W.; et al. The decolorization of methyl orange by persulfate activated with natural vanadium-titanium magnetite. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 509, 144886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calimli, M.H.; Nas, M.S.; Burhan, H.; Mustafov, S.D.; Demirbas, Ö.; Sen, F. Preparation, characterization and adsorption kinetics of methylene blue dye in reduced-graphene oxide supported nanoadsorbents. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 309, 113171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.; Feng, J.F.; Peng, Q.Y.; Zhao, H.F.; Miao, Y.C.; Pan, H. Super-fast degradation of high concentration methyl orange over bifunctional catalyst Fe/Fe3C@C with microwave irradiation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 392, 122279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Yan, S.; Huang, G.; Yang, Q.; Huang, S.; Cai, J. Fabrication of N-doped carbons from waste bamboo shoot shell with high removal efficiency of organic dyes from water. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 303, 122939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azari, A.; Nabizadeh, R.; Nasseri, S.; Mahvi, A.H.; Mesdaghinia, A.R. Comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis of dyes adsorption by carbon-based adsorbent materials: Classification and analysis of last decade studies. Chemosphere 2020, 250, 126238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holkar, C.R.; Jadhav, A.J.; Pinjari, D.V.; Mahamuni, N.M.; Pandit, A.B. A critical review on textile wastewater treatments: Possible approaches. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 182, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Q.Y.; Gao, B.Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Sun, X.; Wang, S.G.; Gu, R.R. Synthesis of polyamine flocculants and their potential use in treating dye wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhao, C.; Chen, D.; Ma, Y.; Yang, W. Ammonium-Functionalized Hollow Polymer Particles As a pH-Responsive Adsorbent for Selective Removal of Acid Dye. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 16690–16698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Sun, M.; Tang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Qi, J.; Rao, Y.; Zhang, Q. All-solid-state BiVO4/ZnIn2S4 Z-scheme composite with efficient charge separations for improved visible light photocatalytic organics degradation. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 547–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, A.; Iqbal, M.; Javed, A.; Aftab, K.; Nazli, Z.I.H.; Bhatti, H.N.; Nouren, S. Dyes adsorption using clay and modified clay: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 256, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, K.A.; Youssef, M.A.; Abd El-Rahiem, F.H.; Hassan, M.S. Dye removal using some surface modified silicate minerals. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2014, 24, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N.; You, S.J.; Chao, H.P. Fast and efficient adsorption of methylene green 5 on activated carbon prepared from new chemical activation method. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 188, 322–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal-Bernal, A.M.; Gómez-Granados, F.; Giraldo, L.; Moreno-Piraján, J.C.; Balsamo, M.; Erto, A. Kinetic and thermodynamic study of n-pentane adsorption on activated carbons modified by either carbonization or impregnation with ammonium hydroxide. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2020, 110196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameda, T.; Horikoshi, K.; Kumagai, S.; Saito, Y.; Yoshioka, T. Adsorption of urea, creatinine, and uric acid onto spherical activated carbon. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 237, 116367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partlan, E.; Ren, Y.; Apul, O.G.; Ladner, D.A.; Karanfil, T. Adsorption kinetics of synthetic organic contaminants onto superfine powdered activated carbon. Chemosphere 2020, 253, 126628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Gui, Y.; Liu, P.; Xue, Y.; Song, W. Functional fibrous materials-based adsorbents for uranium adsorption and environmental remediation. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 390, 124597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Yin, K.; Wu, J.; Wu, Z.; Chu, D.; He, J.; Duan, J.A. Ultrafast nano-structuring of superwetting Ti foam with robust antifouling and stability towards efficient oil-in-water emulsion separation. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 17607–17614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherifi, Z.; Boukoussa, B.; Mokhtar, A.; Hachemaoui, M.; Zeggai, F.Z.; Zaoui, A.; Bachari, K.; Meghabar, R. Preparation of new nanocomposite poly(GDMA)/mesoporous silica and its adsorption behavior towards cationic dye. React. Funct. Polym. 2020, 214, 104611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igberase, E.; Osifo, P.O. Mathematical modelling and simulation of packed bed column for the efficient adsorption of Cu(II) ions using modified bio-polymeric material. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandclément, C.; Seyssiecq, I.; Piram, A.; Wong-Wah-Chung, P.; Vanot, G.; Tiliacos, N.; Roche, N.; Doumenq, P. From the conventional biological wastewater treatment to hybrid processes, the evaluation of organic micropollutant removal: A review. Water Res. 2017, 111, 297–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nekouei Marnani, N.; Shahbazi, A. A novel environmental-friendly nanobiocomposite synthesis by EDTA and chitosan functionalized magnetic graphene oxide for high removal of Rhodamine B: Adsorption mechanism and separation property. Chemosphere 2019, 218, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Mishra, R.; Saha, P.; Kushwaha, P. Adsorption thermodynamics, kinetics and isosteric heat of adsorption of malachite green onto chemically modified rice husk. Desalination 2011, 265, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juchen, P.T.; Piffer, H.H.; Veit, M.T.; Da Cunha Gonçalves, G.; Palácio, S.M.; Zanette, J.C. Biosorption of reactive blue BF-5G dye by malt bagasse: Kinetic and equilibrium studies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 7111–7118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temesgen, F.; Gabbiye, N.; Sahu, O. Biosorption of reactive red dye (RRD) on activated surface of banana and orange peels: Economical alternative for textile effluent. Surf. Interfaces 2018, 12, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mattos, N.R.; de Oliveira, C.R.; Camargo, L.G.B.; da Silva, R.S.R.; Lavall, R.L. Azo dye adsorption on anthracite: A view of thermodynamics, kinetics and cosmotropic effects. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 209, 806–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, D.S.; Wu, C.W.; Adebajo, M.O.; Jin, G.C.; Yu, W.H.; Ji, S.F.; Zhou, C.H. Adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution onto porous cellulose-derived carbon/montmorillonite nanocomposites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 161, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robati, D.; Mirza, B.; Rajabi, M.; Moradi, O.; Tyagi, I.; Agarwal, S.; Gupta, V.K. Removal of hazardous dyes-BR 12 and methyl orange using graphene oxide as an adsorbent from aqueous phase. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 284, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Zhong, H.; Chen, P.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, G. Single and simultaneous adsorption of methyl orange and p-chlorophenol on organo-vermiculites modified by an asymmetric gemini surfactant. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 580, 123740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahin, Ö.; Kaya, M.; Saka, C. Plasma-surface modification on bentonite clay to improve the performance of adsorption of methylene blue. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 116–117, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellaoui, L.; Franco, D.; Ghalla, H.; Georgin, J.; Netto, M.S.; Luiz Dotto, G.; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A.; Belmabrouk, H.; Bajahzar, A. Insights of the adsorption mechanism of methylene blue on brazilian berries seeds: Experiments, phenomenological modelling and DFT calculations. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 394, 125011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teich-McGoldrick, S.L.; Greathouse, J.A.; Jové-Colón, C.F.; Cygan, R.T. Swelling Properties of Montmorillonite and Beidellite Clay Minerals from Molecular Simulation: Comparison of Temperature, Interlayer Cation, and Charge Location Effects. J. Phys. Chem. 2015, 119, 20880–20891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaari, I.; Moussi, B.; Jamoussi, F. Interactions of the dye, C.I. direct orange 34 with natural clay. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 647, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, W.; Dammak, N.; Hadjltaief, H.B.; Eloussaief, M.; Benzina, M. Sono-assisted adsorption of Cristal Violet dye onto Tunisian Smectite Clay: Characterization, kinetics and adsorption isotherms. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 163, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentahar, Y.; Hurel, C.; Draoui, K.; Khairoun, S.; Marmier, N. Adsorptive properties of Moroccan clays for the removal of arsenic(V) from aqueous solution. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 119, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentahar, Y.; Draoui, K.; Hurel, C.; Ajouyed, O.; Khairoun, S.; Marmier, N. Physico-chemical characterization and valorization of swelling and non-swelling Moroccan clays in basic dye removal from aqueous solutions. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2019, 154, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, H.; Hu, B.; Dang, Z.; Yang, C.; Li, L. Adsorption of arsenic on modified montmorillonite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 97–98, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chang, P.H.; Jiang, W.T.; Jean, J.S.; Hong, H. Mechanism of methylene blue removal from water by swelling clays. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 168, 1193–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, M.L.; Martins, J.L.; Ramos, M.M.; Bijani, R. Estimation of clay minerals from an empirical model for Cation Exchange Capacity: An example in Namorado oilfield, Campos Basin, Brazil. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 158, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooli, F.; Liu, Y.; Al-Faze, R.; Al Suhaimi, A. Effect of acid activation of Saudi local clay mineral on removal properties of basic blue 41 from an aqueous solution. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 116–117, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komadel, P. Acid activated clays: Materials in continuous demand. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 131, 84–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foletto, E.L.; Volzone, C.; Morgado, A.F.; Porto, L.M. Influência do tipo de ácido usado e da sua concentração na ativação de uma argila bentonítica. Cerâmica 2001, 47, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulton, B.J.A.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Sampaio, D.V.; Silva, L.D.; Cunha, T.R.; Zanotto, E.D.; Pizani, P.S. The origin of the unusual DSC peaks of supercooled barium disilicate liquid. CrystEngComm 2019, 21, 2768–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira da Costa, F.; Rodrigues da Silva Morais, C.; Rodrigues, A.M. Sustainable glass-ceramic foams manufactured from waste glass bottles and bentonite. Ceram. Int. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, V.O.; Rodrigues, A.M. Improvements on sintering and thermal expansion of lithium aluminum silicate glass-ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Medeiros, P.S.S.; Lira, H.D.L.; Rodriguez, M.A.; Menezes, R.R.; Neves, G.D.A.; Santana, L.N.D.L. Incorporation of quartzite waste in mixtures used to prepare sanitary ware. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 2148–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, L.N.L.; Gomes, J.; Menezes, R.R.; Neves, G.A.; Lira, H.L.; Segadães, A.M. Microstructure development in clays upon heat treatment: Kinetics and equilibrium. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 135, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, W.P.; Silva, V.J.; Gomes, J.; Menezes, R.R.; Neves, G.A.; Ferreira, H.C.; Santana, L.N.L. Avaliação da influência de diferentes tratamentos térmicos sobre as transformações de fases esmectitas. Cerâmica 2014, 60, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Putro, J.N.; Santoso, S.P.; Ismadji, S.; Ju, Y.H. Investigation of heavy metal adsorption in binary system by nanocrystalline cellulose—Bentonite nanocomposite: Improvement on extended Langmuir isotherm model. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 246, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Wang, L.; Ge, Y.; Su, H.; Li, Z. Lignin xanthate resin–bentonite clay composite as a highly effective and low-cost adsorbent for the removal of doxycycline hydrochloride antibiotic and mercury ions in water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 368, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bering, B.P.; Gordeeva, V.A.; Dubinin, M.M.; Efimova, L.I.; Serpinskii, V.V. Development of concepts of the volume filling of micropores in the adsorption of gases and vapors by microporous adsorbents - Communication 4. Differential heats and entropies of adsorption. Bull. Acad. Sci. USSR Div. Chem. Sci. 1971, 20, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Zhang, Z. Application of Dubinin–Radushkevich isotherm model at the solid/solution interface: A theoretical analysis. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 277, 646–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizian, S. Kinetic models of sorption: A theoretical analysis. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 276, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S. Review of second-order models for adsorption systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 136, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.Z.; Leong, Y.K. Ageing and collapse of bentonite gels—Effects of li, na, k and cs ions. Rheol. Acta 2014, 53, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooli, F.; Yan, L. Chemical and thermal properties of organoclays derived from highly stable bentonite in sulfuric acid. Appl. Clay Sci. 2013, 83–84, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pentrák, M.; Hronský, V.; Pálková, H.; Uhlík, P.; Komadel, P.; Madejová, J. Alteration of fine fraction of bentonite from Kopernica (Slovakia) under acid treatment: A combined XRD, FTIR, MAS NMR and AES study. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 163, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptiste, B.J.; Esther, N.; Mirela, P.; Richard, K. Adsorption isotherm and kinetics modeling of carotene and free fatty acids adsorption from palm oil onto montmorillonite. Int. J. Biosci. 2013, 6655, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezende, M.J.C.; Pinto, A.C. Esterification of fatty acids using acid-activated Brazilian smectite natural clay as a catalyst. Renew. Energy 2016, 92, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieseki, L.; Bertella, F.; Treichel, H.; Penha, F.G.; Pergher, S.B.C. Acid treatments of montmorillonite-rich clay for fe removal using a factorial design method. Mater. Res. 2013, 16, 1122–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellini, E.; Malferrari, D.; Bernini, F.; Brigatti, M.F.; Castro, G.R.; Medici, L.; Mucci, A.; Borsari, M. Baseline studies of the clay minerals society source clay montmorillonite stx-1b. Clays Clay Miner. 2017, 65, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, P.S. Ciência e Tecnologia de Argilas, 2nd ed.; Edgard Blücher: São Paulo, Brazil, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Morais, I.C.G.; Silva, I.A.; Buriti, B.M.A.B.; Fernandes, J.V.; Silva, D.S.; Neves, G.A.; Ferreira, H.S. Influence of the additivation process on cation exchange capacity and viscosity of bentonitic clay dispersions. Ceramica 2020, 66, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korichi, S.; Elias, A.; Mefti, A.; Bensmaili, A. The effect of microwave irradiation and conventional acid activation on the textural properties of smectite: Comparative study. Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 59–60, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pálková, H.; Hronský, V.; Jankovič, L.Š.; Madejová, J. The effect of acid treatment on the structure and surface acidity of tetraalkylammonium-montmorillonites. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 395, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupskaya, V.V.; Zakusin, S.V.; Tyupina, E.A.; Dorzhieva, O.V.; Zhukhlistov, A.P.; Belousov, P.E.; Timofeeva, M.N. Experimental study of montmorillonite structure and transformation of its properties under treatment with inorganic acid solutions. Minerals 2017, 7, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angaji, M.T.; Zinali, A.Z.; Qazvini, N.T. Study of Physical, Chemical and Morphological Alterations of Smectite Clay upon Activation and Functionalization via the Acid Treatment. World J. Nano Sci. Eng. 2013, 3, 41006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, A.K.; Mishra, B.G.; Mishra, D.K.; Singh, R.K. Effect of sulphuric acid treatment on the physico-chemical characteristics of kaolin clay. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2010, 363, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, A.M.; Shaikh, S.M.R.; Jalab, R.; Gulied, M.H.; Nasser, M.S.; Benamor, A.; Adham, S. Adsorption of organic pollutants by natural and modified clays: A comprehensive review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 228, 115719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salleh, M.A.M.; Mahmoud, D.K.; Karim, W.A.W.A.; Idris, A. Cationic and anionic dye adsorption by agricultural solid wastes: A comprehensive review. Desalination 2011, 280, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, S.H.; Zahir, A.; Khan, A.; Afzal, S.; Mansha, M. Adsorption of Mordant Red 73 dye on acid activated bentonite: Kinetics and thermodynamic study. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 254, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amari, A.; Gannouni, H.; Khan, M.I.; Almesfer, M.K.; Elkhaleefa, A.M.; Gannouni, A. Effect of structure and chemical activation on the adsorption properties of green clay minerals for the removal of cationic dye. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, B.; Chudasama, C.D.; Jasra, R.V. Determination of structural modification in acid activated montmorillonite clay by FT-IR spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2006, 64, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndé, H.S.; Tamfuh, P.A.; Clet, G.; Vieillard, J.; Mbognou, M.T.; Woumfo, E.D. Comparison of HCl and H2SO4 for the acid activation of a cameroonian smectite soil clay: Palm oil discolouration and landfill leachate treatment. Heliyon 2019, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salawuden, T.O.; Dada, E.O.; Alagbe, S.O. Performance evaluation of acid treated clays for palm oil bleaching. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2007, 2, 1677–1680. [Google Scholar]
- Elmoubarki, R.; Mahjoubi, F.Z.; Tounsadi, H.; Moustadraf, J.; Abdennouri, M.; Zouhri, A.; El Albani, A.; Barka, N. Adsorption of textile dyes on raw and decanted Moroccan clays: Kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamics. Water Resour. Ind. 2015, 9, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, R.R.; Lalhmunsiama; Gupta, P.; Sawant, S.Y.; Shahmoradi, B.; Lee, S.M. Porous synthetic hectorite clay-alginate composite beads for effective adsorption of methylene blue dye from aqueous solution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 114, 1315–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, K.Y.; Hameed, B.H. Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 156, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, S.K.; Katsaros, F.K.; Kouvelos, E.P.; Nolan, J.W.; Le Deit, H.; Kanellopoulos, N.K. Heavy metal sorption by calcium alginate beads from Laminaria digitata. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 1765–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastos Andrade, C.G.; Justo, V.F.; Matos, C.M.; Valenzuela, M.G.S.; Volzone, C.; Valenzuela-Diaz, F.R. Evaluation of acid treatment on brown bentonite. In Characterization of Minerals, Metals, and Materials 2015; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccari, A. Clays and catalysis: A promising future. Appl. Clay Sci. 1999, 14, 161–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Asheh, S.; Banat, F.; Al-Omari, R.; Duvnjak, Z. Predictions of binary sorption isotherms for the sorption of heavy metals by pine bark using single isotherm data. Chemosphere 2000, 41, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toor, M.; Jin, B. Adsorption characteristics, isotherm, kinetics, and diffusion of modified natural bentonite for removing diazo dye. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 187, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte Neto, J.F.; Pereira, I.D.S.; Da Silva, V.C.; Ferreira, H.C.; Neves, D.G.A.; Menezes, R.R. Study of equilibrium and kinetic adsorption of rhodamine B onto purified bentonite clays. Ceramica 2018, 64, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leodopoulos, C.; Doulia, D.; Gimouhopoulos, K.; Triantis, T.M. Single and simultaneous adsorption of methyl orange and humic acid onto bentonite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 70, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Su, M.; Chen, J.; Xu, Z.; Tang, J.; Chang, X.; Chen, D. Superior adsorption of methyl orange by h-MoS2 microspheres: Isotherm, kinetics, and thermodynamic studies. Dyes Pigments 2019, 170, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayed, A.M.; Abdel Wahed, M.S.M.; Mohamed, E.A.; Sillanpää, M. Insights on the role of organic matters of some Egyptian clays in methyl orange adsorption: Isotherm and kinetic studies. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 166, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annadurai, G.; Juang, R.S.; Lee, D.J. Use of cellulose-based wastes for adsorption of dyes from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2002, 92, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Fu, Y.-Q.; Zhu, H.-Y.; Yao, J.; Xiao, L. Removal of Methyl Orange from Aqueos Solutions by Magnetic Maghemite/Chitosan Nanocomposite Films: Adsorption Kinetics an Equilibrium. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 125, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbaiah, M.V.; Kim, D.S. Adsorption of methyl orange from aqueous solution by aminated pumpkin seed powder: Kinetics, isotherms, and thermodynamic studies. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 128, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.P.; Tian, S.P.; Zhu, M.; Zhao, Y.Z.; Li, K.X.; Ma, Q.; Ding, S.Y.; Gao, J.; Miao, Z. Modification of montmorillonite by Gemini surfactants with different chain lengths and its adsorption behavior for methyl orange. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 151, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hassani, K.; Beakou, B.H.; Kalnina, D.; Oukani, E.; Anouar, A. Effect of morphological properties of layered double hydroxides on adsorption of azo dye Methyl Orange: A comparative study. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 140, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafi, R.; Hafiane, A. Removal of methyl orange (MO) from aqueous solution using cationic surfactants modified coffee waste (MCWs). J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 58, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
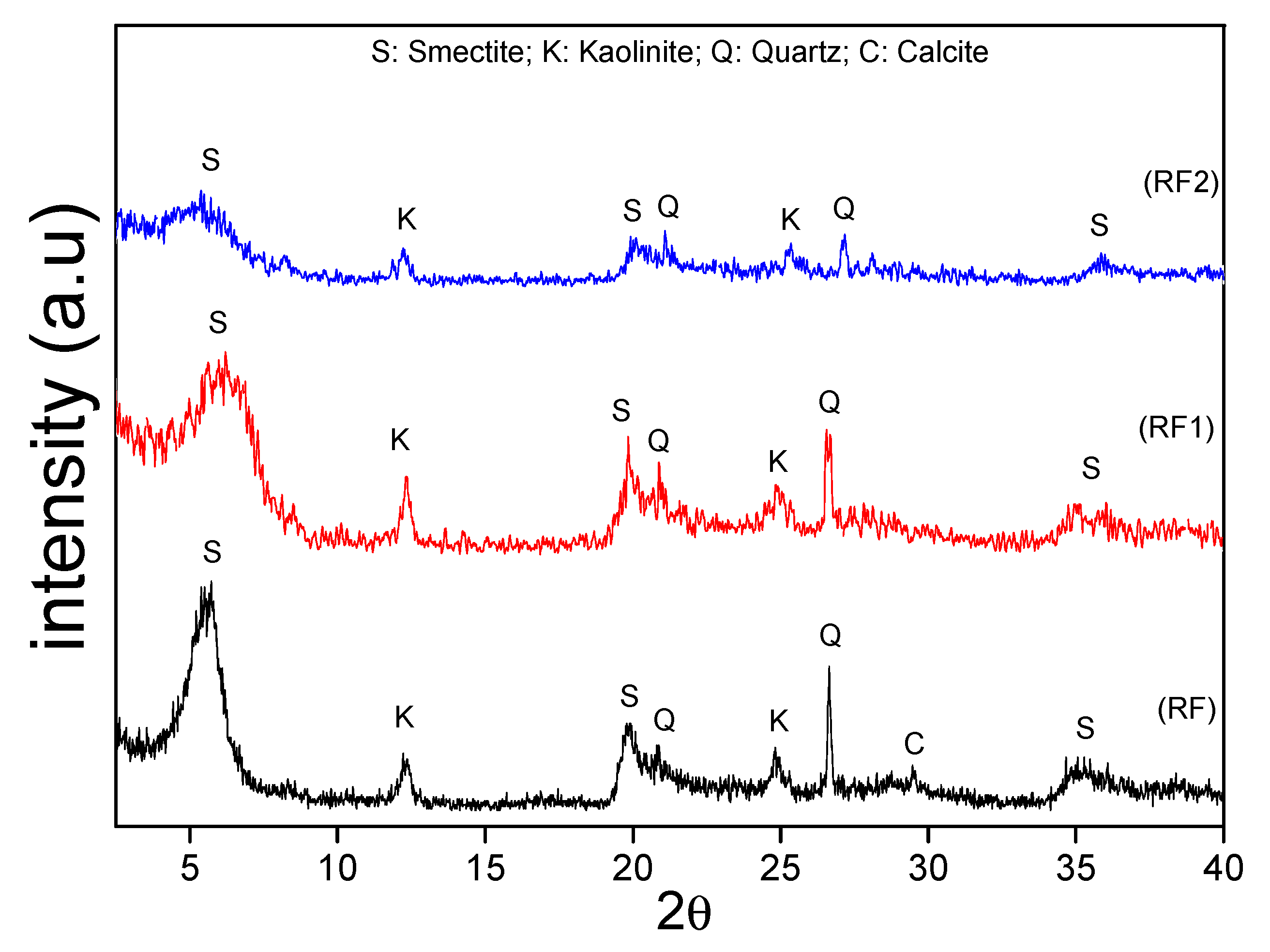
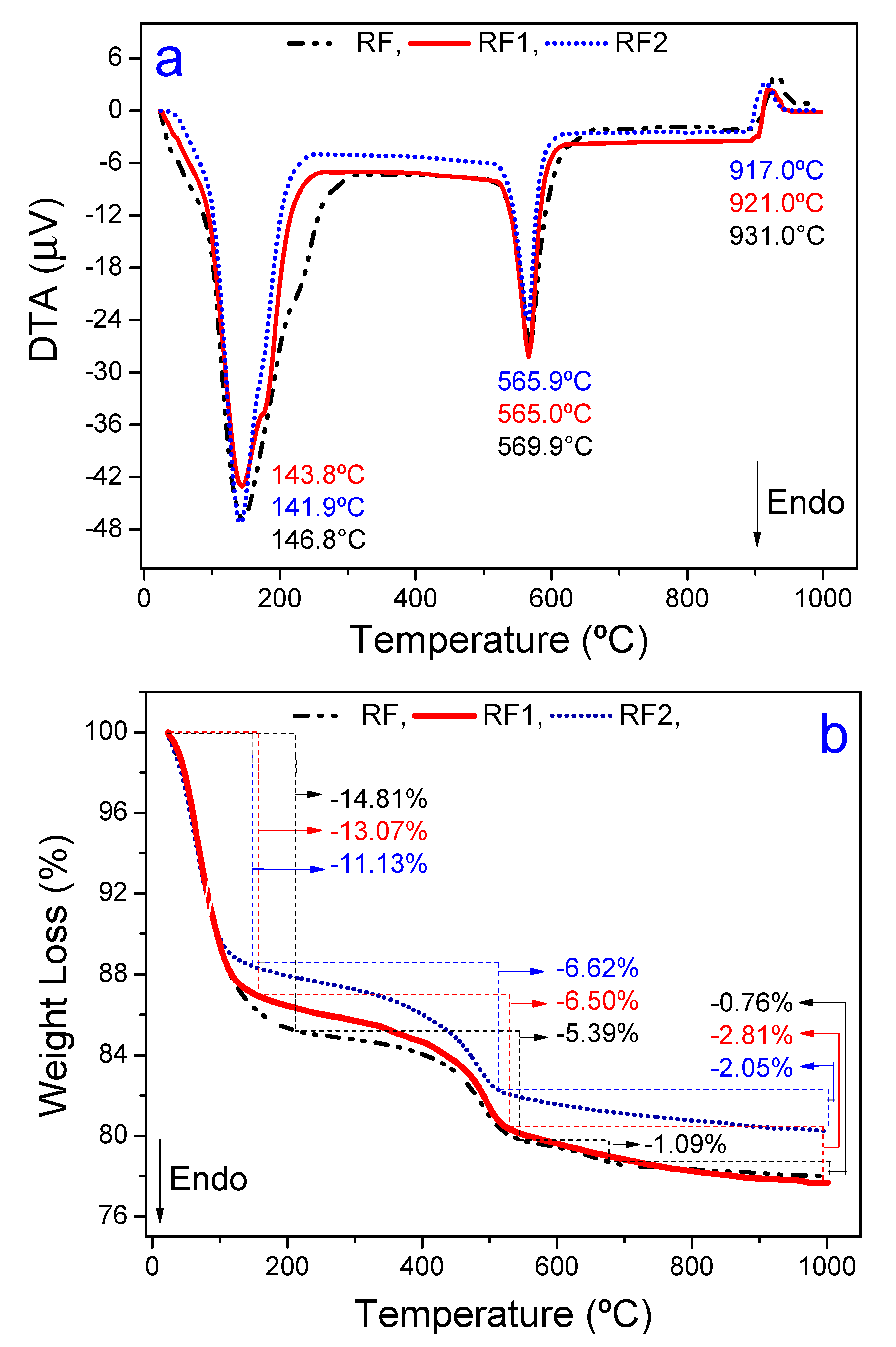
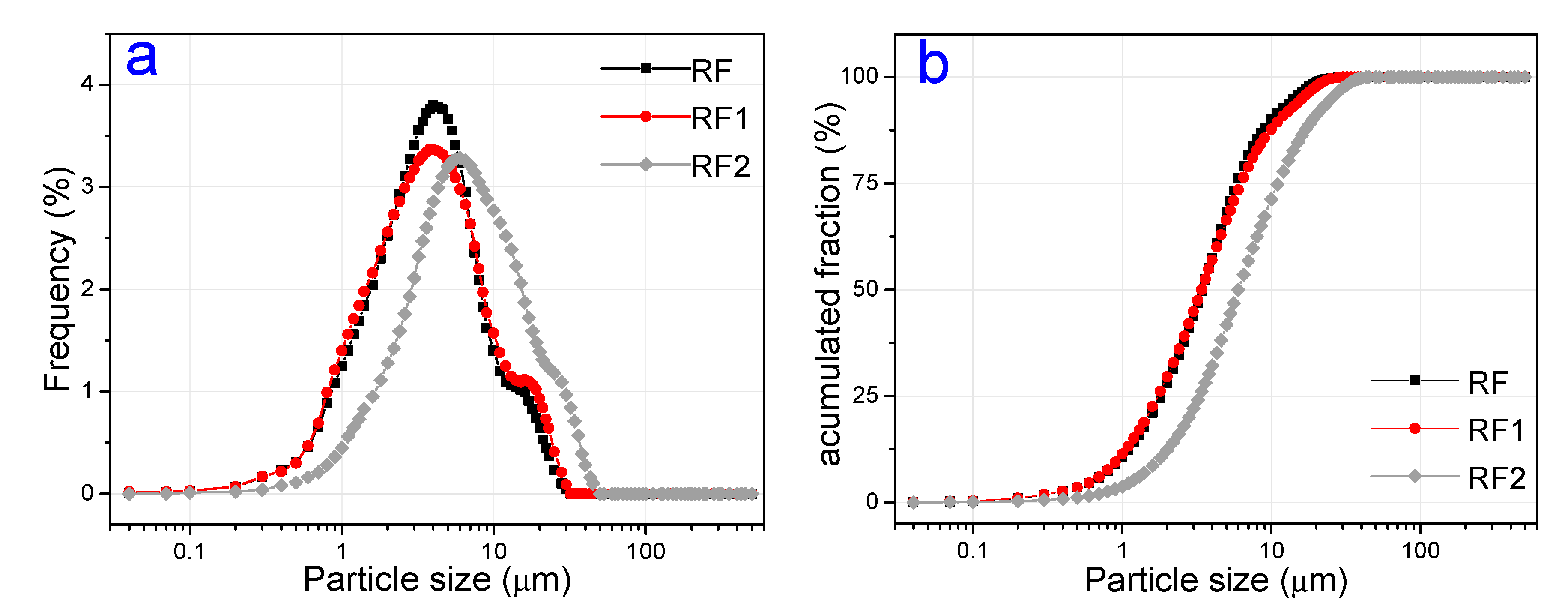

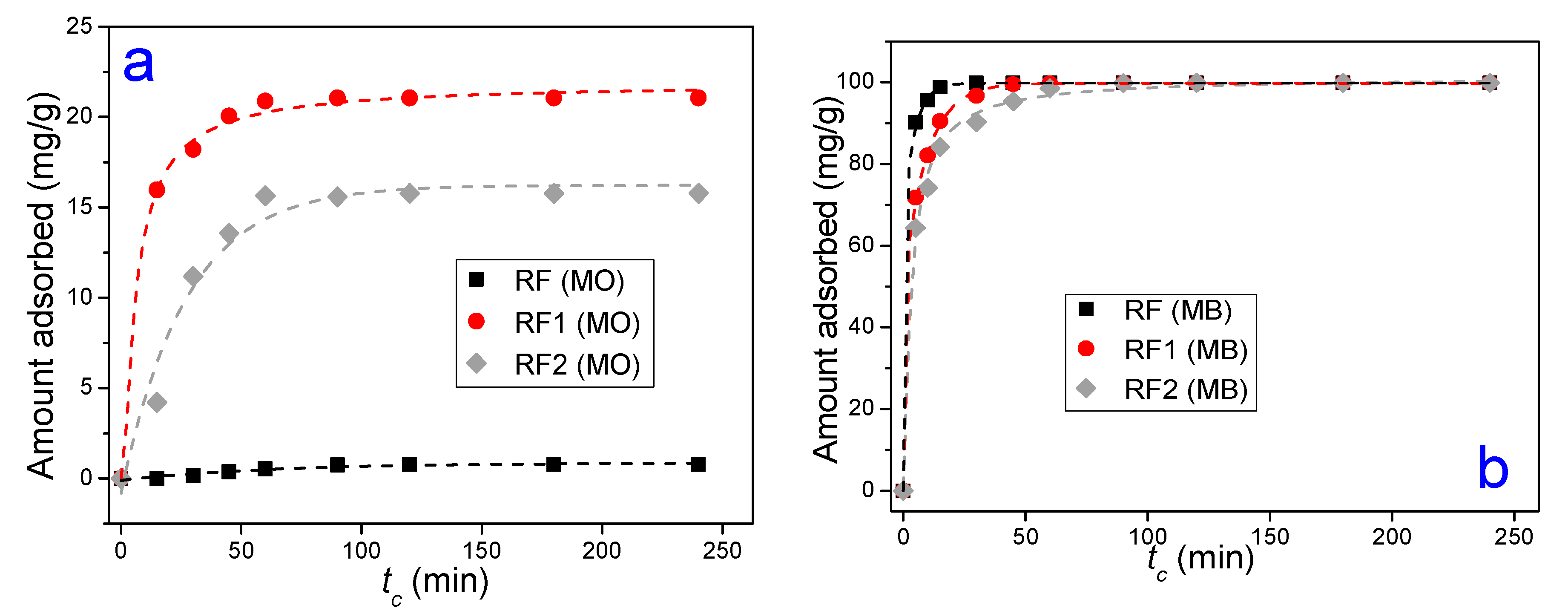


| Clays | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MgO | CaO | TiO2 | RuO2 | K2O | Cr2O3 | SO3 | Others | LF * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RF | 45.3 | 20.7 | 5.9 | 2.7 | 1.6 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.04 | 0.1 | 0.05 | 22.1 |
| RF1 | 47.8 | 20.5 | 5.7 | 2.2 | 0.2 | 0.8 | - | - | 0.03 | 0.1 | 0.03 | 22.3 |
| RF2 | 54.2 | 19.1 | 3.3 | 1.7 | - | 0.5 | - | - | - | 1.1 | 0.42 | 19.7 |
| Samples | D < 2 μm | (2 μm < D < 20 μm) | D > 20 μm | Average Diameter (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RF | 27.98% | 70.77% | 1.25% | 4.66% |
| RF1 | 29.55% | 68.31% | 2.14% | 4.96% |
| RF2 | 12.31% | 75.37% | 8.92% | 8.46% |
| Models | Parameters | Methyl Orange | Methylene Blue | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RF | RF1 | RF2 | RF | RF1 | RF2 | ||
| Langmuir | (mg/g) Error | 3.84 | 89.48 | 62.34 | 251.4 | 233.3 | 222.5 |
| 0.41 | 4.54 | 3.01 | 16.57 | 17.31 | 16.46 | ||
| KL(L/mg) | 3.8 × 10−3 | 1.0 × 10−2 | 1.0 × 10−2 | 3.62 | 8.89 | 7.98 | |
| Error | 7.9 × 10−4 | 1.4 × 10−3 | 1.3 × 10−2 | 1.86 | 5.64 | 4.86 | |
| R2 | 0.975 | 0.976 | 0.977 | 0.840 | 0.761 | 0.753 | |
| Freundlich | KF (mg1−(1/n)g−1L1/n) | 5.9 × 10−2 | 5.49 | 3.97 | 150.23 | 145.05 | 131.73 |
| Error | 2.2 × 10−2 | 1.74 | 1.26 | 11.78 | 9.85 | 9.11 | |
| nF | 1.61 | 2.26 | 2.30 | 6.77 | 6.80 | 6.32 | |
| Error | 0.07 | 0.30 | 0.32 | 1.01 | 0.87 | 0.76 | |
| R2 | 0.945 | 0.908 | 0.904 | 0.904 | 0.933 | 0.950 | |
| D-R | (mg/g) | 2.15 | 65.92 | 46.31 | 237.03 | 244.11 | 243.47 |
| Error | 0.11 | 2.61 | 1.71 | 17.22 | 23.71 | 23.78 | |
| KDR (KJ/mol) | 9.2 × 10−4 | 3.8 × 10−4 | 3.9 × 10−4 | 2.4 × 10−8 | 1.8 × 10−−7 | 1.1 × 10−6 | |
| Error | 1.7 × 10−4 | 6.5 × 10−5 | 6.6 × 10−5 | 8.4 × 10−9 | 1.3 × 10−7 | 6.9 × 10−7 | |
| R2 | 0.928 | 0.926 | 0.932 | 0.768 | 0.602 | 0.617 | |
| D-A | (mg/g) | 3.51 | 86.40 | 58.14 | 294.24 | 311.19 | 347.67 |
| Error | 0.70 | 7.86 | 4.09 | 22.64 | 38.56 | 74.33 | |
| KDA (KJ/mol) | 6.78 | 4.45 | 4.92 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.10 | |
| Error | 1.66 | 0.73 | 0.82 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.10 | |
| nDA | 0.71 | 0.80 | 0.86 | 0.53 | 0.40 | 0.30 | |
| Error | 0.17 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.10 | |
| R2 | 0.985 | 0.986 | 0.988 | 0.964 | 0.962 | 0.961 | |
| Sips | (mg/g) | 2.68 | 74.23 | 51.10 | 314.02 | 353.42 | 403.37 |
| Error | 0.25 | 2.58 | 1.23 | 33.19 | 72.73 | 139.19 | |
| KS(L/mmol) | 7.7 × 10−4 | 2.1 × 10−3 | 1.5 × 10−3 | 1.07 | 0.76 | 0.50 | |
| Error | 6.8 × 10−4 | 1.0 × 10−3 | 6.1 × 10−4 | 0.32 | 0.33 | 0.28 | |
| nS | 1.47 | 1.45 | 1.54 | 0.43 | 0.33 | 0.29 | |
| Error | 0.22 | 0.13 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.08 | |
| R2 | 0.987 | 0.993 | 0.995 | 0.985 | 0.981 | 0.987 | |
| Models | Parameters | Methyl Orange | Methylene Blue | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RF | RF1 | RF2 | RF | RF1 | RF2 | ||
| Pseudo-first-order | Q1 (mg/g) | 0.88 | 20.85 | 16.25 | 99.50 | 98.51 | 97.03 |
| Error | 0.11 | 0.23 | 0.63 | 0.36 | 1.21 | 1.79 | |
| K1 (min−1) | 0.01 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.46 | 0.23 | 0.17 | |
| Error | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | |
| R2 | 0.94 | 0.99 | 0.94 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.97 | |
| Pseudo-second-order | Q2 (mg/g) | 1.23 | 22.02 | 18.76 | 100.80 | 102.28 | 102.03 |
| Error | 0.27 | 0.26 | 1.53 | 0.30 | 0.59 | 0.76 | |
| K2(gmin−1min−1) | 8.3 × 10−3 | 8.3 × 10−3 | 2.3 × 10−3 | 18.4 × 10−3 | 9.6 × 10−3 | 9.0 × 10−3 | |
| Error | 5.8 × 10−3 | 1.0 × 10−3 | 9.2 × 10−4 | 1.61 × 10−3 | 2.8 × 10−4 | 1.9 × 10−4 | |
| R2 | 0.96 | 0.99 | 0.96 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernandes, J.V.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Menezes, R.R.; Neves, G.d.A. Adsorption of Anionic Dye on the Acid-Functionalized Bentonite. Materials 2020, 13, 3600. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13163600
Fernandes JV, Rodrigues AM, Menezes RR, Neves GdA. Adsorption of Anionic Dye on the Acid-Functionalized Bentonite. Materials. 2020; 13(16):3600. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13163600
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernandes, Jucielle Veras, Alisson Mendes Rodrigues, Romualdo Rodrigues Menezes, and Gelmires de Araújo Neves. 2020. "Adsorption of Anionic Dye on the Acid-Functionalized Bentonite" Materials 13, no. 16: 3600. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13163600
APA StyleFernandes, J. V., Rodrigues, A. M., Menezes, R. R., & Neves, G. d. A. (2020). Adsorption of Anionic Dye on the Acid-Functionalized Bentonite. Materials, 13(16), 3600. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13163600








