The Role of Long Period Stacking Ordered Phase in Dynamic Recrystallization of a Mg–Gd–Y–Zn–Zr Alloy during Multi-Directional Forging Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
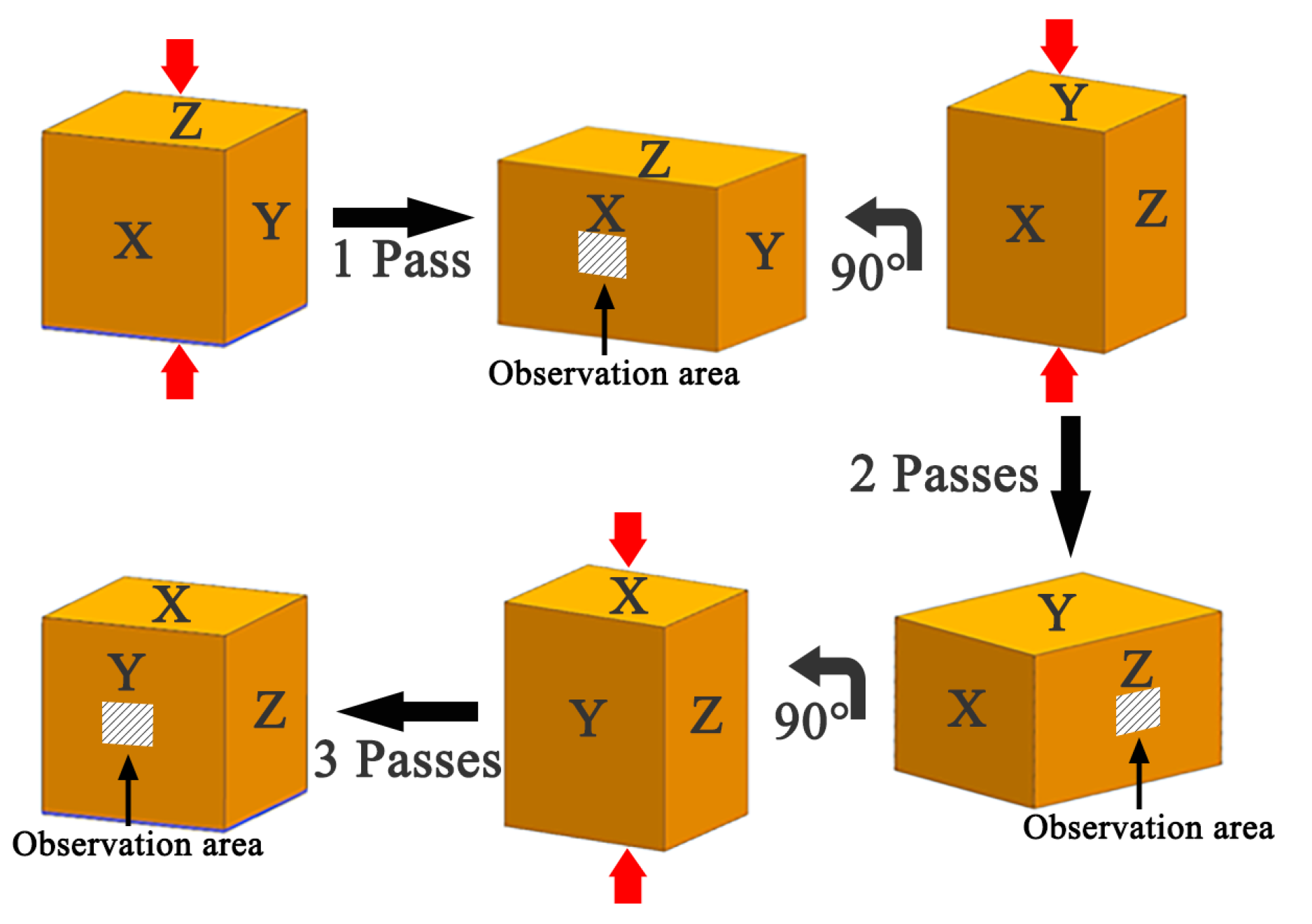
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
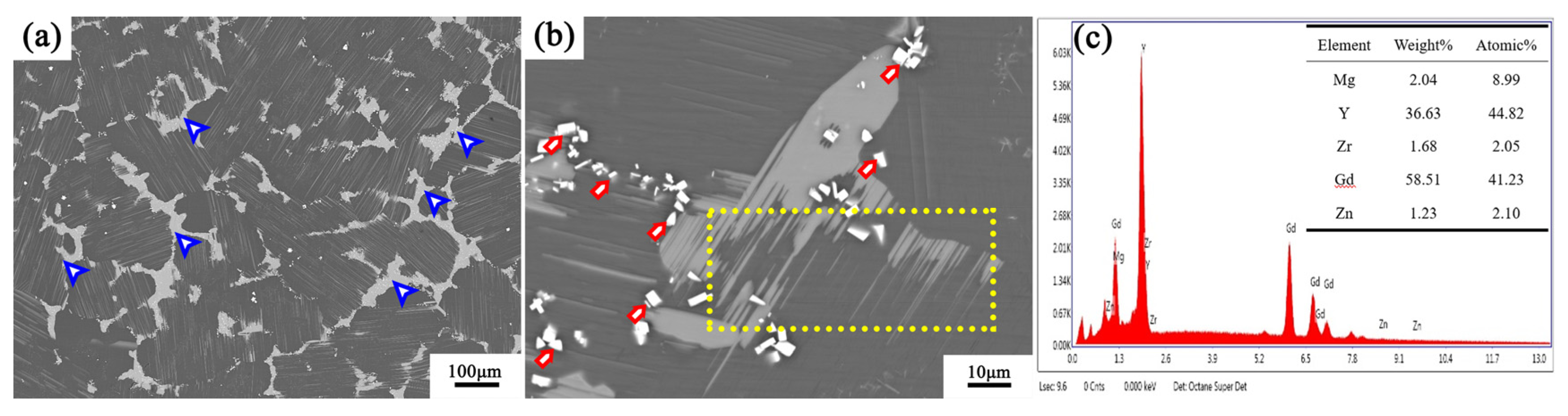
3.1. Microstructure of the Initial Alloy
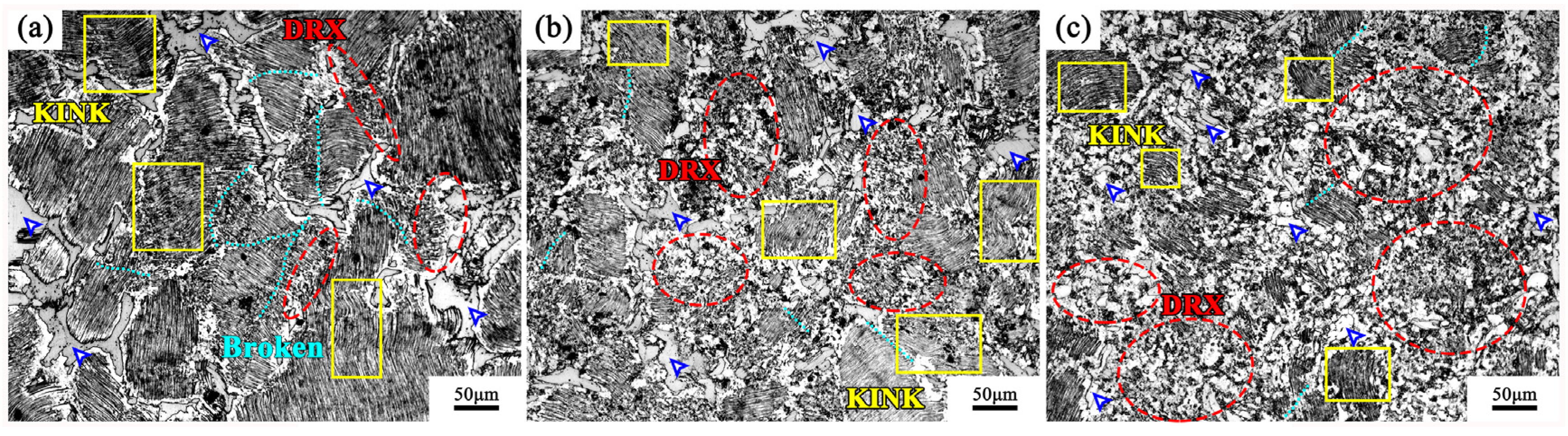
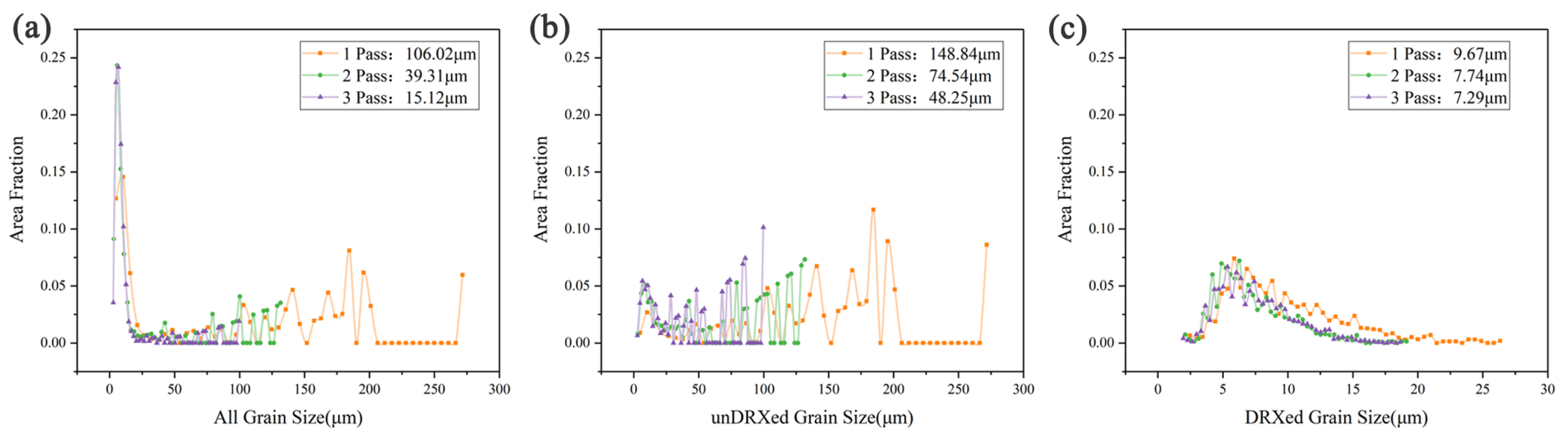
3.2. Microstructure Evolution of the MDFed Alloys
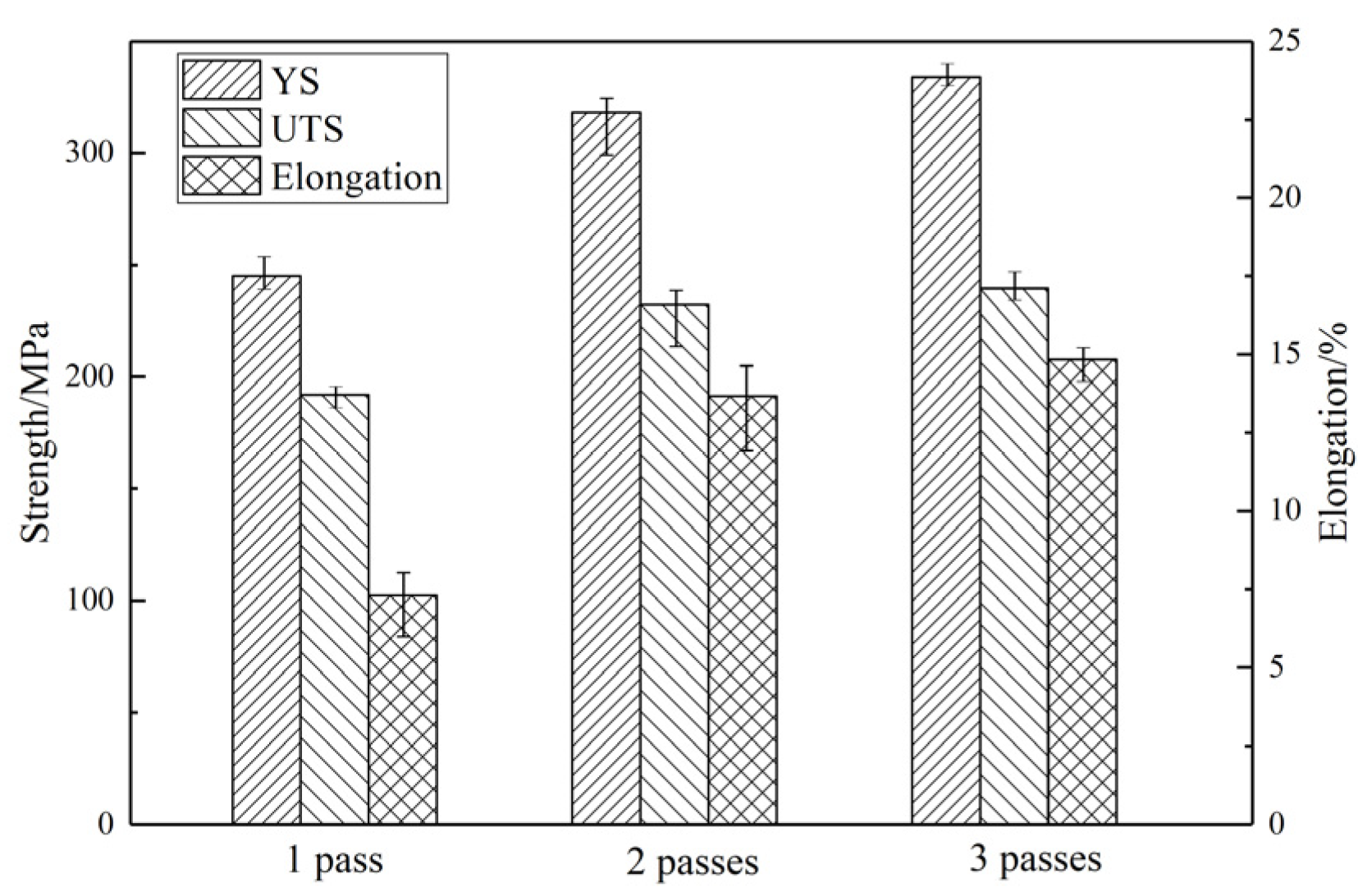
3.3. Mechanical Performance
4. Discussion
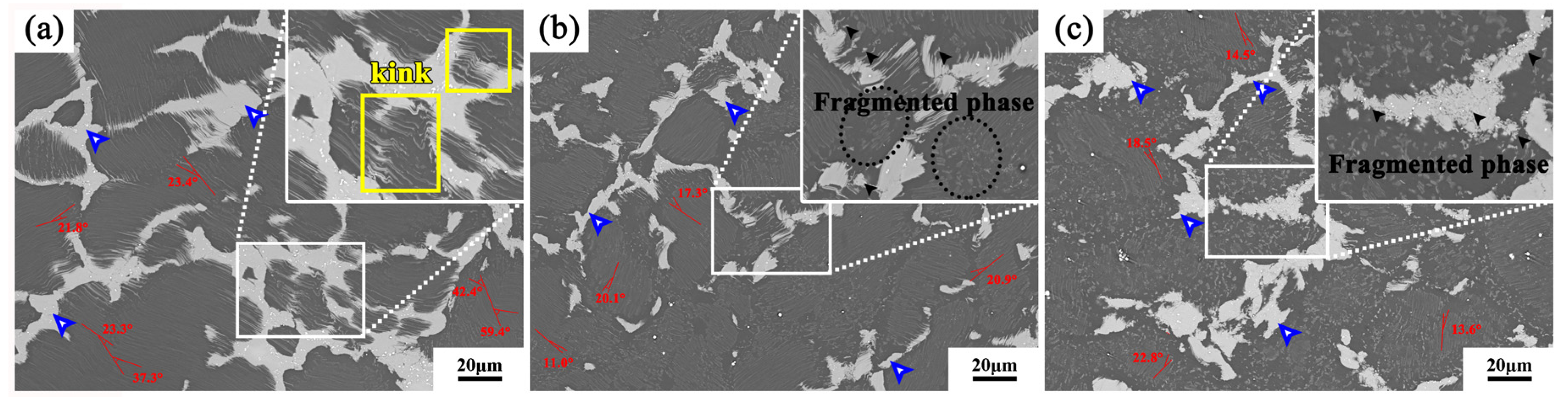
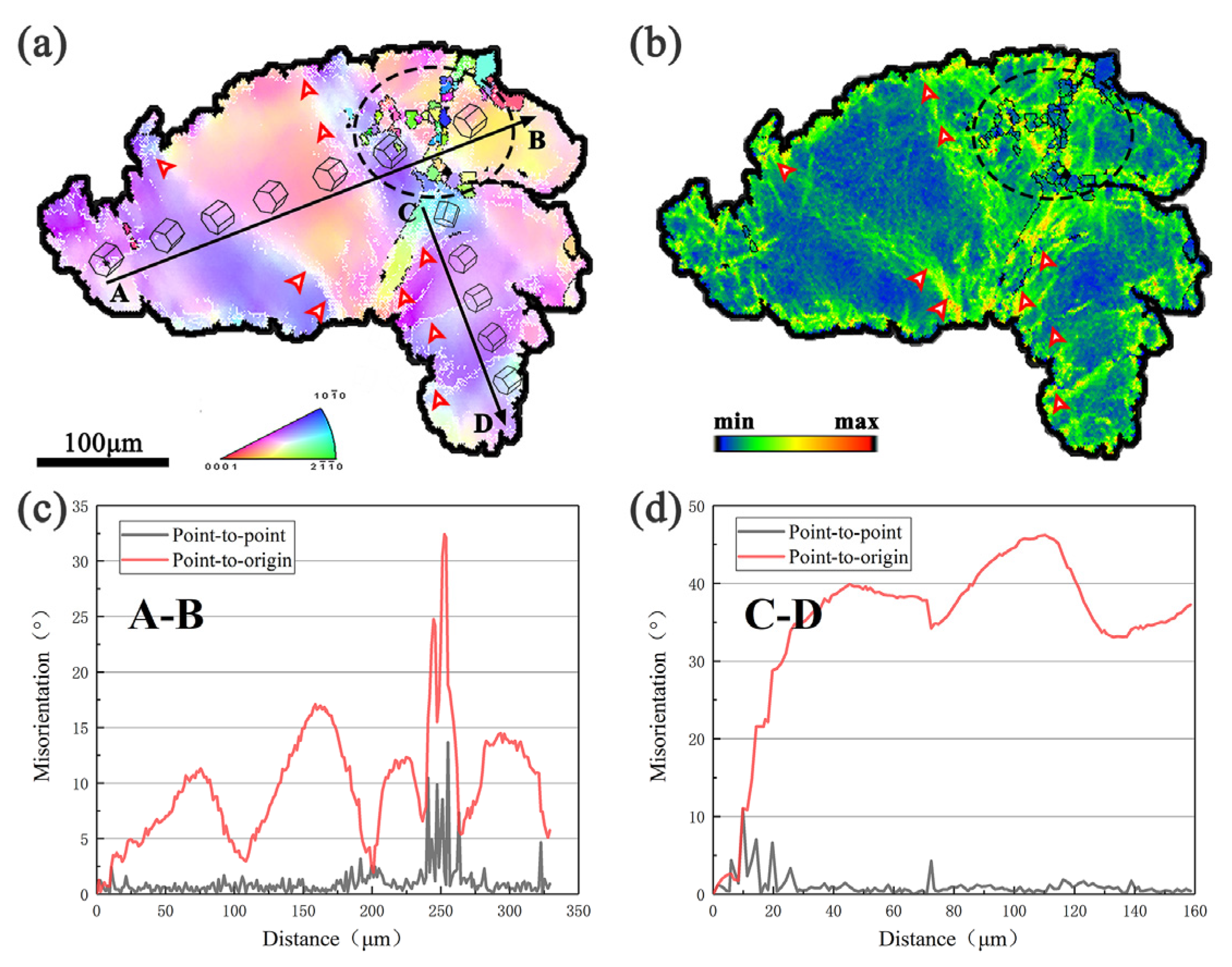
4.1. Lamellar LPSO Phase with Kinks Induced Dynamic Recrystallization
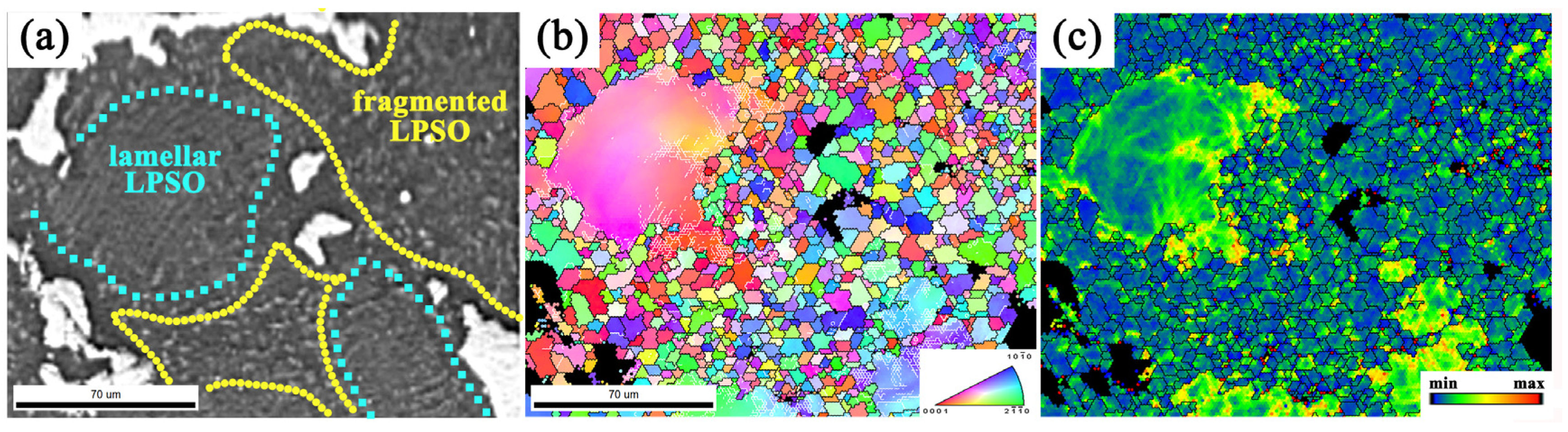
4.2. Fragmentation of Lamellar LPSO Phase Induced Dynamic Recrystallization
4.3. Block-Shaped Phase Induced Dynamic Recrystallization
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- As the number of processing passes increases, the dynamic crystallization fraction increases, and the grains are refined. After 3 passes, the dynamic recrystallization fraction reaches 0.703. The grain size decreases significantly from 106.02 to 15.13 µm, and the structure is more uniform.
- (2)
- Dynamic recrystallization weakens the texture and significantly improves the mechanical properties. In 3 passes, the texture intensity is reduced to 2.62, the tensile strength is increased to 325.3 MPa, and the elongation increased to 14.67%.
- (3)
- The kinked lamellar phase rotates the grains, promotes dislocation plugging, and forms grain boundaries more easily, which is a potential nucleation site for dynamically recrystallized grains; the fragmented lamellar phase promotes the dynamic recrystallization process through the particle-stimulated nucleation mechanism, and stress concentration occurs around the block-shaped phase to promote dynamic recrystallization, making the microstructure more uniform.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mordike, B.L.; Ebert, T. Magnesium: Properties-applications-potential. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 302, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Liao, M.; Wang, Q. Lightweight Design of the Transmission Case Based on Topology Optimization. J. Agric. Mech. Res. 2018, 4, 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, W.; Gollapudi, S.; Charit, I.; Murty, K.L. Formability of a wrought Mg alloy evaluated by impression testing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 712, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Luo, J. Analysis of the application of magnesium alloy materials in marine gearboxes. Shandong Ind. Technol. 2015, 000, 18–19. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M. Research on Extrusion Process of Magnesium Alloy Box. Master’s Degree, North University of China, Taiyuan, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Stanford, N. Micro-alloying Mg with Y, Ce, Gd and La for texture modification—A comparative study. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 2669–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, V.M. Materials processing by simple shear. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1995, 197, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Wang, Q.D.; Ye, B.; Zhou, H. Enhanced microstructure homogeneity and mechanical properties of AZ31–Si composite by cyclic closed-die forging. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 558, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebesberger, T.; Stüwe, H.P.; Vorhauer, A.; Wetscher, F.; Pippan, R. Structure of Cu deformed by high pressure torsion. Acta Mater. 2005, 53, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.S.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, Z.D.; Ma, M.L.; Li, X.G.; Zhang, K. Microstructure, texture and mechanical properties of coarse-grained Mg–Gd–Y–Nd–Zr alloy processed by multidirectional forging. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 623, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.B.; Zhang, Z.M.; Yu, J.M.; Che, X.; Meng, M.; Zhang, J.L. Microstructure, texture evolution and mechanical properties of multi-directional forged Mg-13Gd-4Y–2Zn-0.5Zr alloy under decreasing temperature. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 823, 153776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohlen, J.; Nürnberg, M.R.; Senn, J.W.; Letzig, D.; Agnew, S.R. The texture and anisotropy of Mg-zinc-rare earth alloy sheets. Acta. Mater. 2007, 55, 2101–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homma, T.; Knito, N.; Kamado, S. Fabrication of extraordinary high-strength Mg alloy by hot extrusion. Scr. Mater. 2009, 61, 644–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.F.; Zhu, Y.M.; Morton, A.J. On the structure, transformation and deformation of long-period stacking ordered phases in Mg-Y-Zn alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2014, 45, 3338–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Wu, Y.; Peng, L.; Chen, J.; Zeng, X.; Ding, W. Formation of lamellar phase with 18R-type LPSO structure in an as-cast Mg96Gd3Zn1 (at%) alloy. Mater. Lett. 2016, 169, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Fan, Y.; Gao, H.; Zhai, C.; Zhu, Y. The effect of Ca and rare earth elements on the microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion behavior of AZ91D. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 408, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.X.; Tan, Z.; Huo, Q.H.; Xiao, Z.Y.; Fang, Z.W.; Yang, X.Y. Dynamic recrystallization behaviors of Mg-Gd-Y-Zn-Zr alloy with different morphologies and distributions of LPSO phases. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 715, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.B.; Chen, R.S.; Han, E.H. Effects of ageing treatment on microstructures and properties of Mg-Gd-Y-Zr alloys with and without Zn additions. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 465, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Chen, X.H.; Wang, L.; Wang, W.Y.; Liu, Z.K.; Liu, J.X.; Hui, X.D. High strength Mg-Zn-Y alloys reinforced synergistically by Mg12ZnY phase and Mg3Zn3Y2 particle. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 703, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.J.; Xu, C.; Meng, J.; Zhang, X.H.; Kamado, S. Effects of pre-annealing on microstructure and mechanical properties of as-extruded Mg-Gd-Y-Zn-Zr alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 729, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Liu, G.; Liu, X.; Hao, H.; Zhang, X. Significant texture weakening of Mg-8Gd-5Y-2Zn alloy by Al addition. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 701, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asqardoust, S.; Zarei-Hanzaki, A.; Fatemi, S.M.; Moradjoy-Hamedani, M. High temperature deformation behaviour and microstructural evolutions of a high Zr containing WE Mg alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 669, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Lin, D.L.; Zeng, X.Q.; Lu, C. Microstructure and mechanical properties of ultrafine grained Mg97Y2Zn1alloy processed by equal channel angular pressing. J. Alloys Compd. 2007, 440, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.S.; Zhang, W.B.; Bian, L.P.; Cheng, W.L.; Niu, X.F.; Xu, C.X.; Wu, S.J. Study of Mg-Gd-Zn-Zr alloys with long period stacking ordered structures. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 585, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.S.; Chen, C.J.; Cheng, W.L.; Bian, L.P.; Wang, H.X.; Xu, C.X. High-strength Mg93.96Zn2Y4Sr0.04alloy with long-period stacking ordered structure. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 559, 416–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.M.; Ma, A.B.; Jiang, J.H.; Yang, D.H.; Yuan, Y.C.; Zhang, L.Y. Formation of profuse long period stacking ordered microcells in Mg-Gd-Zn-Zr alloy during multi-pass ECAP process. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 601, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Ikeda, K.I.; Shi, Q.; Chiu, Y.L. Kink boundaries and their role in dynamic recrystallisation of a Mg-Zn-Y alloy. Mater. Charact. 2019, 148, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.J.; Liu, C.M.; Gao, Y.H.; Jiang, S.N.; Han, X.Z.; Chen, Z.Y. Evolution of LPSO phases and their effect on dynamic recrystallization in a Mg-Gd-Y-Zn-Zr alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2017, 48, 3060–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Chen, Z.Y.; Shao, J.B.; Wang, R.K.; Mao, L.H.; Liu, C.M. The role of long period stacking ordered phase in dynamic recrystallization of a Mg-Zn-Y alloy during hot compression. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 818, 152814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Zhang, Z.M.; Zhang, G.S.; Yan, Z.M.; Yu, J.M. Grain Refinement and Texture Evolution of Mg-Gd-Y-Zn-Zr Alloy Processed by Repetitive Usetting-extrusion at Decreasing Temperature. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2018, 47, 1422–1428. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, M.; Kimura, T.; Koike, J.; Maruyama, K. Strengthening effect of Zn in heat resistant Mg-Y-Zn solid solution alloys. Scr. Mater. 2003, 48, 997–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, E.; Kawamura, Y.; Hayashi, K.; Inoue, A. Long-period ordered structure in a high-strength nanocrystalline Mg-1 at% Zn-2 at% Y alloy studied by atomic-resolution Z-contrast STEM. Acta Mater. 2020, 50, 3845–3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Ko, W.S.; Sandlobes, S.; Heidelmann, M.; Grabowski, B.; Raabe, D. The role of metastable LPSO building block clusters in phase transformations of an Mg-Y-Zn alloy. Acta Mater. 2016, 112, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.Z.; Yu, J.M.; Liu, K.; Yu, H.S.; Zhang, F.; Wu, Y.J.; Zhang, Z.M.; Luo, N.N.; Wang, H.H. The evolution of long-period stacking ordered phase and its effect on dynamic recrystallization in Mg-Gd-Y-Zn-Zr alloy processed by repetitive upsetting-extrusion. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 828, 154454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, B.J.; Peng, J.; Wang, Y.J.; An, X.Q.; Zhong, L.P.; Tang, A.T.; Pan, F.S. Dynamic recrystallization behavior and hot workability of Mg-2.0Zn-0.3Zr-0.9Y alloy by using hot compression test. Mater. Des. 2014, 53, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, G.L.; Fang, D.Q.; Zhang, W.C.; Sudagar, J.; Zhang, Q.X.; Lian, J.S.; Jiang, Z.H. Microstructure and mechanical properties of an extruded Mg-2Dy-0.5Zn alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2012, 28, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, J.B.; Barrett, C.S. Structure and nature of kink bands in zinc. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 1949, 1, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.J.; Liu, C.M.; Gao, Y.H.; Jiang, S.N.; Chen, Z.Y. Improved workability and ductility of the Mg-Gd-Y-Zn-Zr alloy via enhanced kinking and dynamic recrystallization. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 749, 878–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, J.D.; Henry, D.T.; Davis, B. Particle effects on recrystallization in magnesium–manganese alloys: Particle-stimulated nucleation. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 2739–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variance | UTS | YS | FE |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 pass | 92.89 | 49.62 | 1.29 |
| 2 passes | 127.81 | 142.36 | 1.56 |
| 3 passes | 64.22 | 37.65 | 0.22 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Meng, Y.; Yu, H.; Xu, W.; Zhang, S.; Jia, L.; Wu, G. The Role of Long Period Stacking Ordered Phase in Dynamic Recrystallization of a Mg–Gd–Y–Zn–Zr Alloy during Multi-Directional Forging Process. Materials 2020, 13, 3290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13153290
Liu H, Meng Y, Yu H, Xu W, Zhang S, Jia L, Wu G. The Role of Long Period Stacking Ordered Phase in Dynamic Recrystallization of a Mg–Gd–Y–Zn–Zr Alloy during Multi-Directional Forging Process. Materials. 2020; 13(15):3290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13153290
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Huiling, Yingze Meng, Huisheng Yu, Wenlong Xu, Siyang Zhang, Leichen Jia, and Guoqin Wu. 2020. "The Role of Long Period Stacking Ordered Phase in Dynamic Recrystallization of a Mg–Gd–Y–Zn–Zr Alloy during Multi-Directional Forging Process" Materials 13, no. 15: 3290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13153290
APA StyleLiu, H., Meng, Y., Yu, H., Xu, W., Zhang, S., Jia, L., & Wu, G. (2020). The Role of Long Period Stacking Ordered Phase in Dynamic Recrystallization of a Mg–Gd–Y–Zn–Zr Alloy during Multi-Directional Forging Process. Materials, 13(15), 3290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13153290




