Enhancement of First Hydrogenation of Ti1V0.9Cr1.1 BCC Alloy by Cold Rolling and Ball Milling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
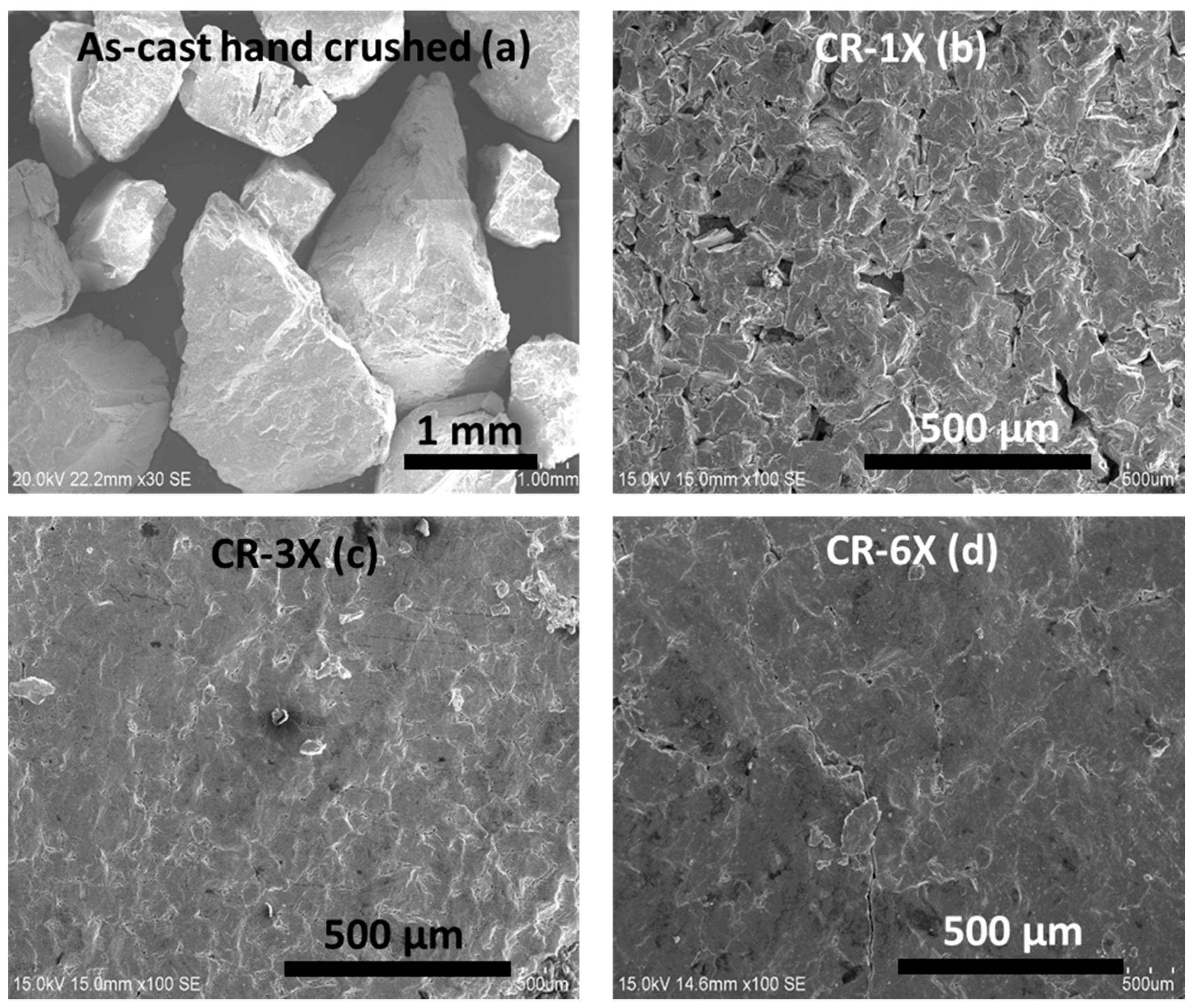
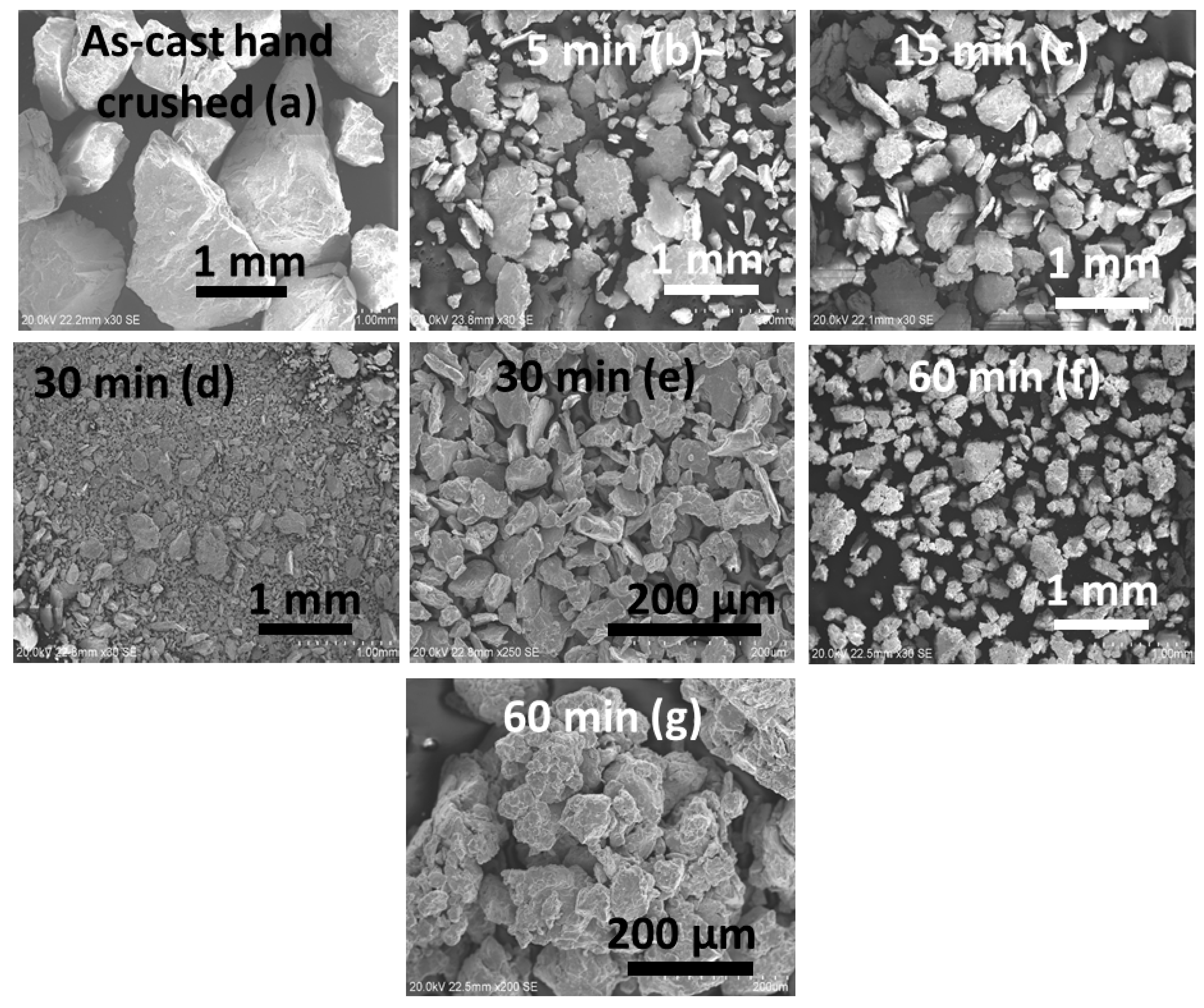
3.1. Morphology
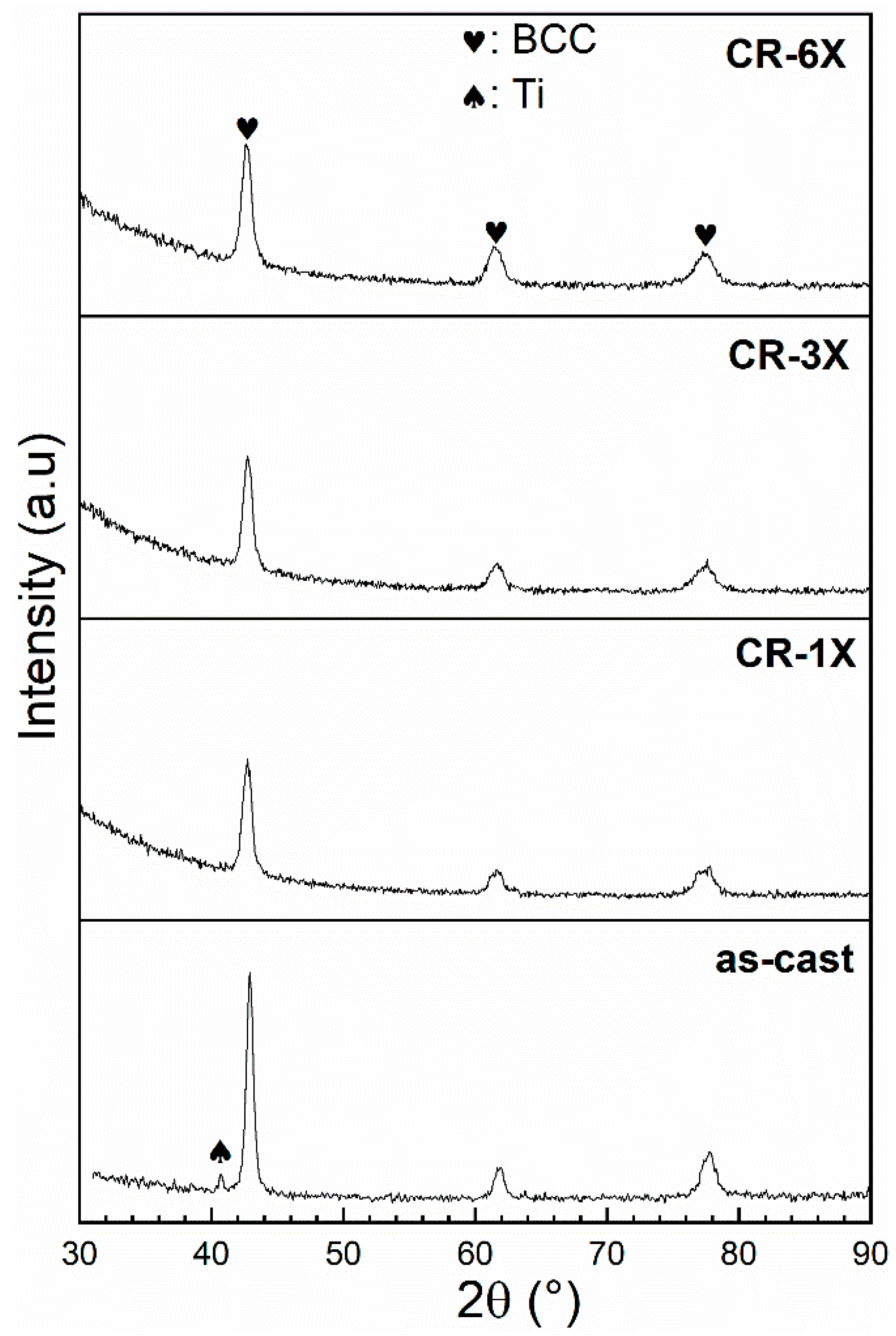
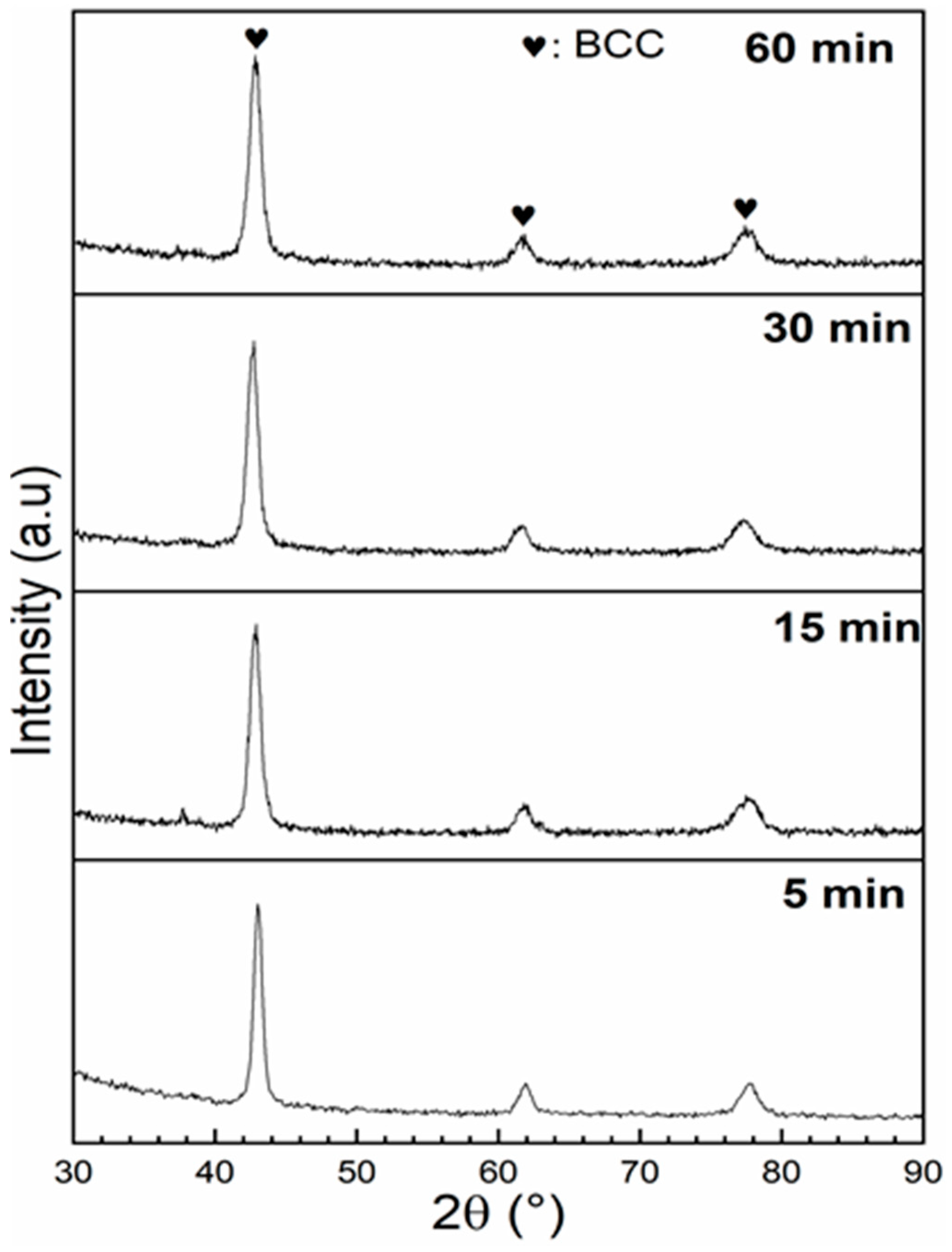
3.2. Crystal Structure
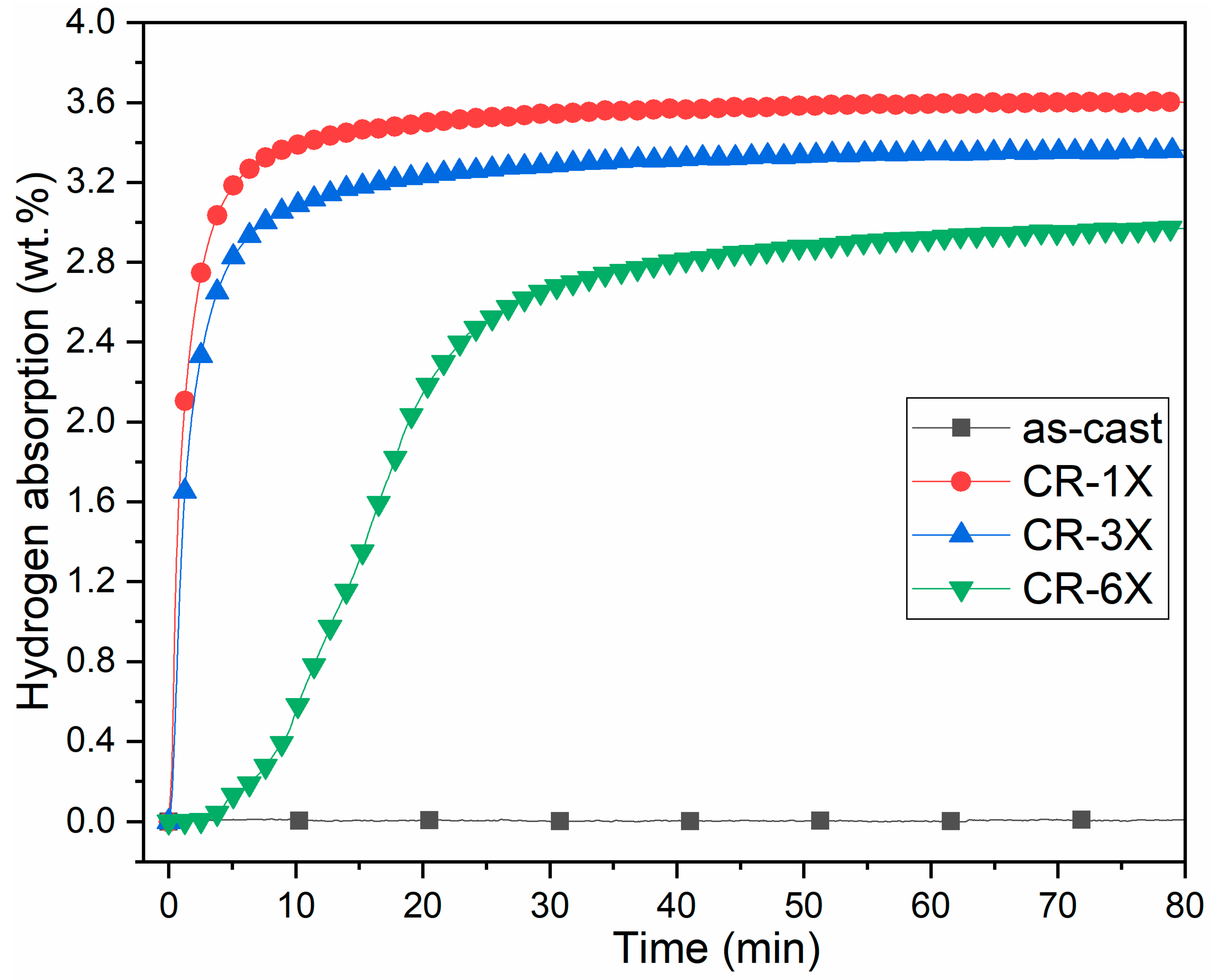
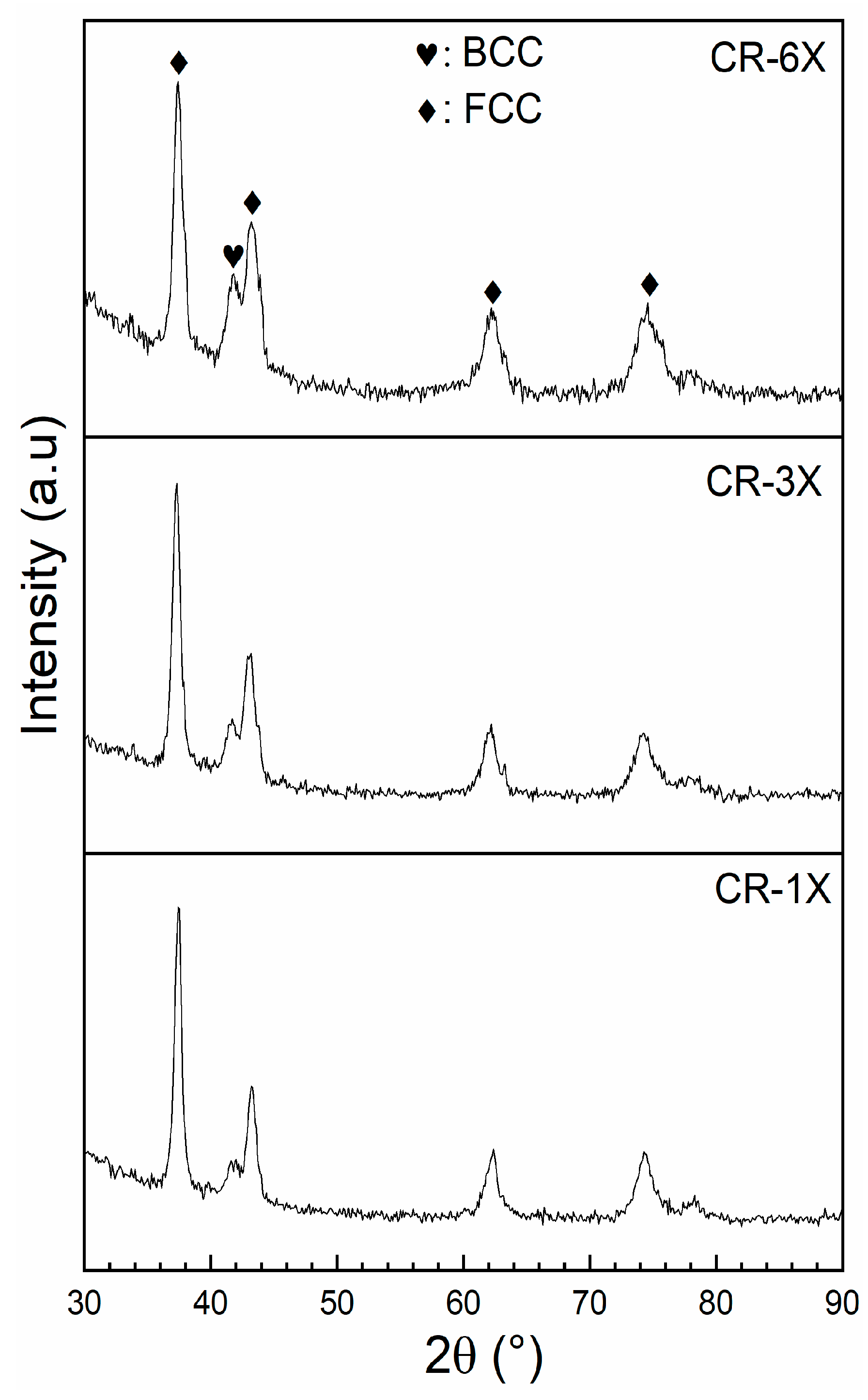
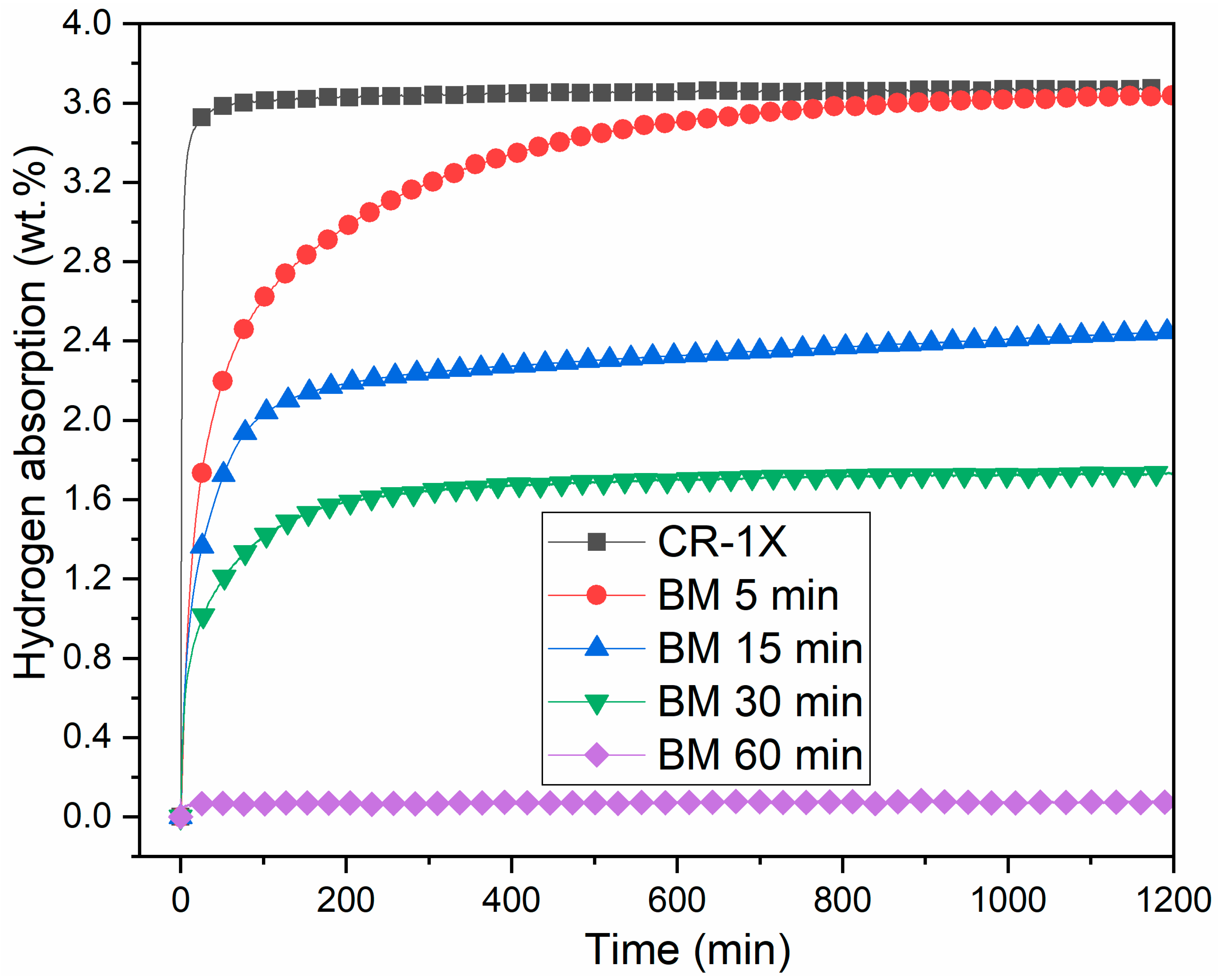
3.3. First Hydrogenation
3.4. Effect of Ball Milling on Ti1V0.9Cr1.1 Alloy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Von Colbe, J.B.; Ares, J.-R.; Barale, J.; Baricco, M.; Buckley, C.; Capurso, G.; Gallandat, N.; Grant, D.M.; Guzik, M.N.; Jacob, I.; et al. Application of hydrides in hydrogen storage and compression: Achievements, outlook and perspectives. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 7780–7808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusman, N.A.A.; Dahari, M. A review on the current progress of metal hydrides material for solid-state hydrogen storage applications. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 12108–12126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelyapina, M.G. Metal hydrides for energy storage. In Handbook of Ecomaterials; Martínez, L.M.T., Kharissova, O.V., Kharisov, B.I., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzolai, G.; Coluzzi, B.; Biscarini, A.; Mazzolai, F.M.; Tuissi, A.; Agresti, F.; Lo Russo, S.; Maddalena, A.; Palade, P.; Principi, G. Hydrogen-storage capacities and H diffusion in bcc TiVCr alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 466, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miraglia, S.; de Rango, P.; Rivoirard, S.; Fruchart, D.; Charbonnier, J.; Skryabina, N. Hydrogen sorption properties of compounds based on BCC Ti1−xV1−yCr1+x+y alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 536, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, T.; Kazumi, T.; Kamegawa, A.; Takamura, H.; Okada, M. Protium absorption properties and protide formations of Ti–Cr–V alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2003, 356, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriiwa, T.; Maruyama, T.; Kamegawa, A.; Okada, M. Effects of V content on hydrogen storage properties of V–Ti–Cr alloys with high desorption pressure. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 9082–9087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, S.; Jain, A.; Kumar, S.; Zhang, T.; Isobe, S.; Miyaoka, H.; Kojima, Y.; Ichikawa, T. Study of cyclic performance of V-Ti-Cr alloys employed for hydrogen compressor. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 2881–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelyapina, M.G.; Skryabina, N.E.; Surova, L.S.; Dost, A.; Ievlev, A.V.; Privalov, A.F.; Fruchart, D. Proton NMR study of hydrogen mobility in (TiCr1.8)1−xVx hydrides. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 778, 962–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.C.; Lin, K.M.; Wu, K.C.; Hsiung, H.H.; Tsai, H.K. Cyclic hydrogen absorption–desorption characteristics of TiCrV and Ti0.8Cr1.2V alloys. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2007, 32, 4966–4972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, H.; Arashima, H.; Kubo, K.; Kabutomori, T. The influence of microstructure on hydrogen absorption properties of Ti–Cr–V alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2002, 330–332, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huot, J. Kinetics and thermodynamics. In Hydrogen Technology: Mobile and Portable Applications; Léon, A., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 471–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, K. Handbook of Hydrogen Storage: New Materials for Future Energy Storage; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sleiman, S.; Huot, J. Microstructure and Hydrogen Storage Properties of Ti1V0.9Cr1.1 Alloy with Addition of x wt % Zr (x = 0, 2, 4, 8, and 12). Inorganics 2017, 5, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamble, A.; Sharma, P.; Huot, J. Effect of doping and particle size on hydrogen absorption properties of BCC solid solution 52Ti-12V-36Cr. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 11523–11527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellon, D.; Martinez, A.; Barreneche, D.; dos Santos, D. A structural study of the hydrogen absorption properties by replacing vanadium with zirconium in metal alloys. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2016, 687, 012057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelyapina, M.; Dost, A.; Skryabina, N.; Privalov, A.; Vogel, M.; Fruchart, D. Effect of Zr7Ni10 additive on hydrogen mobility in (TiCr1.8)1−xVx (x = 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8): An 1H NMR SFG study. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 7929–7937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skryabina, N.E.; Fruchart, D.; Medvedeva, N.A.; de Rango, P.; Mironova, A.A. Correlation between the Hydrogen Absorption Properties and the Vanadium Concentration of Ti-V-Cr Based Alloys. In Solid State Phenomena; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Bäch, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 257, pp. 165–172. [Google Scholar]
- Kamble, A.G.; Sharma, P.; Huot, J. Investigation of crystal structure, microstructure and hydrogenation behavior of heat-treated Ti52V12Cr36 alloy. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2019, 3, 794–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.Y.; Wang, F.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.M.; Yao, Q.R.; Deng, J.Q.; Tang, C.Y.; Rao, G.H. Hydrogen storage properties and thermal stability of V35Ti20Cr45 alloy by heat treatment. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 14887–14895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, M.; Wang, F.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, H. Effect of heat treatment on hydrogen storage properties and thermal stability of V68Ti20Cr12 alloy. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2017, 27, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couillaud, S.; Enoki, H.; Amira, S.; Bobet, J.-L.; Akiba, E.; Huot, J. Effect of ball milling and cold rolling on hydrogen storage properties of nanocrystalline TiV1.6Mn0.4 alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 484, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huot, J.; Enoki, H.; Akiba, E. Synthesis, phase transformation, and hydrogen storage properties of ball-milled TiV0.9Mn1.1. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 453, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.K.; Shim, G.; Cho, S.-W. Effects of mechanical milling on hydrogen storage properties of Ti0.32Cr0.43V0.25 alloy. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2007, 32, 4961–4965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varin, R.A.; Czujko, T.; Wronski, Z.S. Nanomaterials for Solid State Hydrogen Storage; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sleiman, S.; Huot, J. Effect of particle size, pressure and temperature on the activation mechanism of hydrogen absorption in TiVZrHfNb high entropy alloy. Unpublished work.
- Shelyapina, M.; Fruchart, D.; De Rango, P.; Charbonnier, J.; Rivoirard, S.; Skryabina, N.; Miraglia, S.; Hlil, E.; Wolfers, P. First-Principles Investigation of the Stability of the Ti-V-Cr Ternary Alloys and Their Related Hydrides. In AIP Conference Proceedings; American Institute of Physics: College Park, MD, USA, 2006; Volume 837, pp. 104–111. [Google Scholar]
- Huot, J. Enhancing Hydrogen Storage Properties of Metal Hybrides: Enhancement by Mechanical Deformations; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Vega, L.E.R.; Leiva, D.R.; Leal Neto, R.M.; Silva, W.B.; Silva, R.A.; Ishikawa, T.T.; Kiminami, C.S.; Botta, W.J. Mechanical activation of TiFe for hydrogen storage by cold rolling under inert atmosphere. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 2913–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Araujo-Silva, R.A.; Jorge, A.M., Jr.; Vega, L.E.R.; Leal Neto, R.M.; Leiva, D.R.; Botta, W.J. Hydrogen desorption/absorption properties of the extensively cold rolled β Ti–40Nb alloy. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 20133–20144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tousignant, M.; Huot, J. Hydrogen sorption enhancement in cold rolled LaNi5. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 595, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patselov, A.; Rybin, V.; Greenberg, B.; Mushnikov, N. Hydrogen absorption in as-cast bcc single-phase Ti–Al–Nb alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 505, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajavi, S.; Rajabi, M.; Huot, J. Effect of cold rolling and ball milling on first hydrogenation of Ti0.5Zr0.5 (Mn1−xFex) Cr1, x = 0, 0.2, 0.4. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 775, 912–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, J.; Tougas, B.; Huot, J. Mechanical activation of air exposed TiFe + 4 wt% Zr alloy for hydrogenation by cold rolling and ball milling. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 20795–20800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruker AXS. Topas V6: General Profile and Structure Analysis Software for Powder Diffraction Data—User’s Manual; Bruker AXS: Karlsruhe, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, L.; Wu, C.; Yang, S.; Zhou, J.; Chen, Y.; Yang, F.; Xu, Y.; Liu, P. Decaying behaviors of V40(TiCr) 51Fe8Mn hydrogen storage alloys with different particle sizes. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 645, S178–S183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | Phase | Unit Cell Volume (Å3) | Lattice Parameter (Å) | Crystallite Size (nm) | Microstrain (%) | Phase Abundance (%) | Rwp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As-cast | BCC Ti | 28.04 (2) 36.25 (1) | 3.0379 (9) a = 2.961 (4) c = 4.773 (1) | 24 (2) 13 (2) | 0.26 (1) | 97 (3) 3 (3) | 7.76 |
| CR-1X | BCC | 28.24 (3) | 3.0453 (1) | 28 (5) | 0.40 (1) | 100 | 5.95 |
| CR-3X | BCC | 28.34 (4) | 3.0487 (1) | 25 (4) | 0.40 (1) | 100 | 6.07 |
| CR-6X | BCC | 28.26 (4) | 3.0459 (1) | 21 (3) | 0.42 (2) | 100 | 6.55 |
| Sample | Phase | Unit Cell Volume (Å3) | Lattice parameter (Å) | Crystallite Size (nm) | Microstrain (%) | Phase Abundance (%) | Rwp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CR-1X | FCC BCC | 79.03 (1) 30.84 (8) | 4.2914 (2) 3.136 (3) | 20.2 (2) 7 (2) | 0.34 (1) 0.43 (1) | 84 (2) 16 (2) | 5.34 |
| CR-3X | FCC BCC | 78.90 (1) 30.65 (9) | 4.289 (2) 3.130 (7) | 17.3 (1) 4.0 (6) | 0.40 (1) 0.33 (1) | 76 (3) 24 (3) | 5.28 |
| CR-6X | FCC BCC | 78.61 (1) 30.67 (7) | 4.284 (2) 3.130 (2) | 29 (6) 4.9 (6) | 0.53 (2) 0.36 (8) | 72 (2) 28 (2) | 4.93 |
| Sample | Phase | Unit Cell Volume (Å3) | Lattice Parameter (Å) | Crystallite Size (nm) | Microstrain (%) | Phase Abundance (%) | Rwp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As-cast | BCC Ti | 28.04 (2) 36.25 (1) | 3.0379 (9) a = 2.961(4) c = 4.773 (1) | 24 (2) 13 (2) | 0.26 (1) | 97 (3) 3 (3) | 7.76 |
| BM 5 min | BCC | 28.29 (3) | 3.0471 (9) | 20.5 (1) | 0.30 (1) | 100 | 5.20 |
| BM 15 min | BCC | 28.18 (3) | 3.0432 (1) | 16.1 (1) | 0.40 (2) | 100 | 7.84 |
| BM 30 min | BCC | 28.28 (3) | 3.0468 (1) | 14.5 (8) | 0.40 (1) | 100 | 7.46 |
| BM 60 min | BCC | 28.32 (3) | 3.0481 (1) | 12.2 (6) | 0.40 (1) | 100 | 7.30 |
| Activated BM | Phase | Unit Cell Volume (Å3) | Lattice Parameter (Å) | Crystallite Size (nm) | Microstrain (%) | Phase Abundance (%) | Rwp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 min | FCC BCC | 78.97 (7) 31.06 (7) | 4.2903 (1) 3.144 (2) | 15.4 (8) 3.8 (5) | 0.35 (1) 0.34 (1) | 79 (2) 21 (2) | 4.12 |
| 15 min | FCC BCC | 78.38 (1) 29.33 (5) | 4.280 (2) 3.0841 (2) | 15.8 (2) 8.6 (1) | 0.42 (2) 1.09 (4) | 36 (2) 64 (2) | 5.12 |
| 30 min | FCC BCC | 78.49 (2) 28.75 (5) | 4.282 (3) 3.0634 (2) | 14.0 (2) 5.1 (3) | 0.29 (3) 0.49 (3) | 23 (2) 77 (2) | 5.17 |
| 60 min | BCC | 28.15 (3) | 3.0418 (9) | 12.4 (6) | 0.40 (1) | 100 | 4.63 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sleiman, S.; Aliouat, A.; Huot, J. Enhancement of First Hydrogenation of Ti1V0.9Cr1.1 BCC Alloy by Cold Rolling and Ball Milling. Materials 2020, 13, 3106. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13143106
Sleiman S, Aliouat A, Huot J. Enhancement of First Hydrogenation of Ti1V0.9Cr1.1 BCC Alloy by Cold Rolling and Ball Milling. Materials. 2020; 13(14):3106. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13143106
Chicago/Turabian StyleSleiman, Salma, Anis Aliouat, and Jacques Huot. 2020. "Enhancement of First Hydrogenation of Ti1V0.9Cr1.1 BCC Alloy by Cold Rolling and Ball Milling" Materials 13, no. 14: 3106. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13143106
APA StyleSleiman, S., Aliouat, A., & Huot, J. (2020). Enhancement of First Hydrogenation of Ti1V0.9Cr1.1 BCC Alloy by Cold Rolling and Ball Milling. Materials, 13(14), 3106. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13143106






