Interlaminar Shear Strength and Failure Analysis of Aluminium-Carbon Laminates with a Glass Fiber Interlayer after Moisture Absorption
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Analysis
2.1. Material
2.2. Hygrothermal Conditioning
2.3. ILSS Test
2.4. Fractography
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Moisture Absorption
3.2. Interlaminar Shear Strength
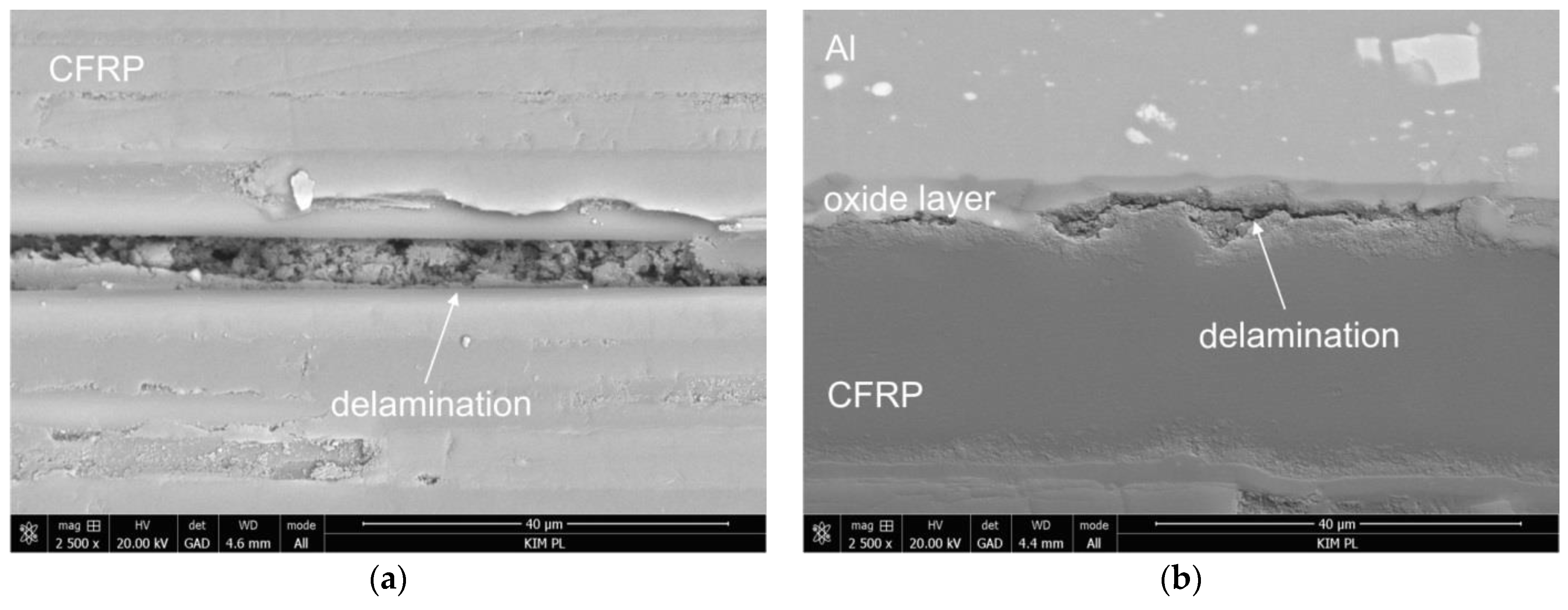
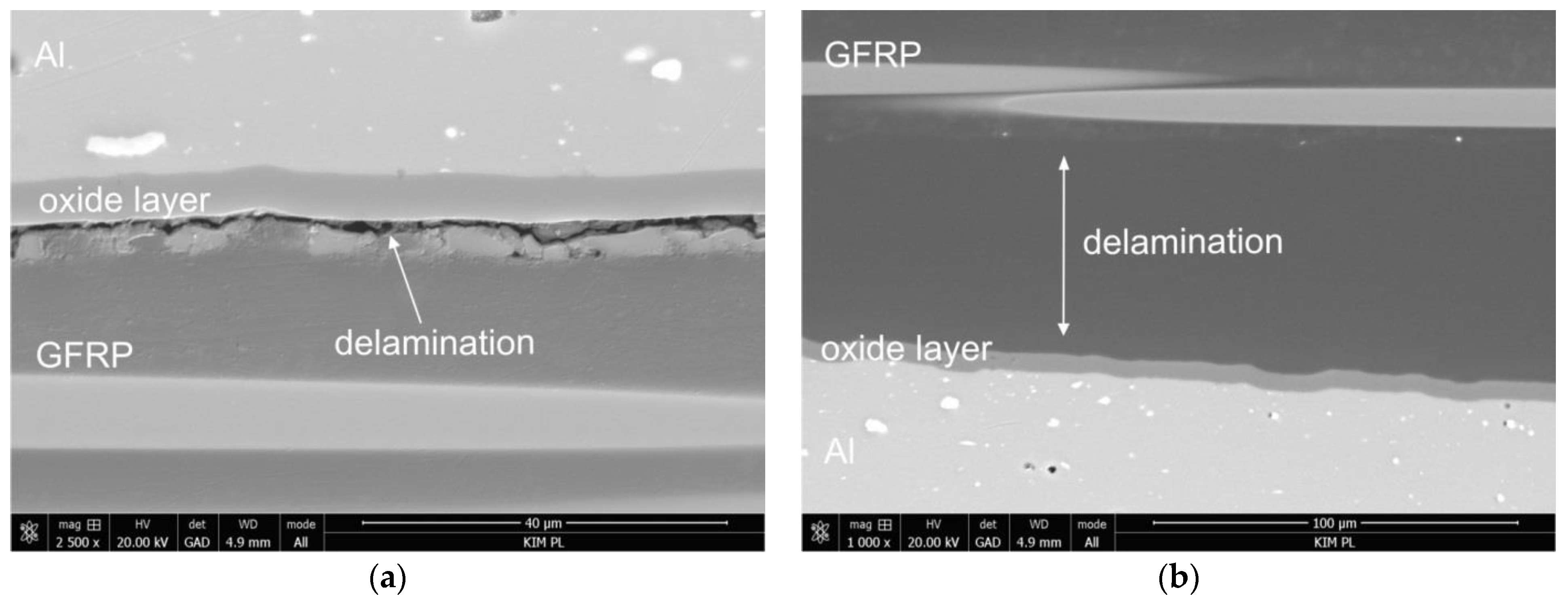
3.3. Failure Analysis
4. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Data Availability
References
- Vlot, A.; Gunnink, J.W. Fibre Metal Laminates: An Introduction; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001; Volume 1, pp. 39–51, 197–233. [Google Scholar]
- Dadej, K.; Bieniaś, J.; Surowska, B. Residual fatigue life of carbon fibre aluminium laminates. Int. J. Fatigue 2017, 100, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubczak, P.; Bieniaś, J.; Majerski, K.; Ostapiuk, M.; Surowska, B. The Impact Behavior of Aluminum Hybrid Laminates. Aircraft Engineering and Aerospace Technology. Aircr. Eng. Aerosp. Technol. 2014, 86, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieniaś, J.; Jakubczak, P. Impact damage growth in carbon fibre aluminium laminates. Compos. Struct. 2017, 172, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botelho, E.C.; Pardini, L.C.; Rezende, M.C. Evaluation of hygrothermal effects on the shear properties of Carall composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 452–453, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botelho, E.C.; Silva, R.A.; Pardini, L.C.; Rezende, M.C. A review on the development and properties of continuous fibre/epoxy/aluminum hybrid composites for aircraft structures. Mater. Res. 2006, 9, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botelho, E.C.; Almeida, R.S.; Pardini, L.C.; Rezende, M.C. Influance of hydrothermal conditioning on the elastic properties of Carall laminates. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2007, 14, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexopoulos, N.D.; Dalakouras, C.J.; Skarvelis, P.; Kourkoulis, S.K. Accelerated corrosion exposure in ultra thin sheets of 2024 aircraft aluminium alloy for Glare applications. Corros. Sci. 2012, 55, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgonje, B.; Ypma, M.S. Long term behaviour of Glare. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2003, 10, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Ali, A.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Lv, Y. Characterization of effects of heat treated anodized film on the properties of hygrothermally aged AA5083-based fibre-metal laminates. Corros. Sci. 2017, 167, 112–122. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.X.; Takao, Y.; Matsubara, T. Galvanic corrosion-resistant carbon fibre metal laminates. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Composite Materials, Kyoto, Japan, 8–13 July 2007; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Z.; Nie, X. Galvanic corrosion property of contacts between carbon fibre cloth materials and typical metal alloys in an aggressive environment. Surface and Coatings Technology. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 215, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieniaś, J.; Jakubczak, P.; Surowska, B. Properties and characterization of fibre metal laminates. In Hybrid Polymer Composite Materials: Properties and Characterisation; Kumar, T.V., Kumari, T.M., Asokan, P., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Duxford, UK, 2017; pp. 253–278. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, C.H.; Springer, G. Moisture absorption and desorption of composite materials. J. Compos. Mater. 1976, 10, 2–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Duan, L.; Zheng, Z.; Sapkota, B. Characterization of seawater hydrothermal conditioning effects on the properties of titanium-based fibre-metal laminates for marine applications. Compos. Struct. 2016, 158, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jedidi, J.; Jacquemin, F.; Vautrin, A. Accelerated hygrothermal cyclical tests for carbon/epoxy laminates. Compos. Part A 2006, 37, 636–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Botelho, E.C.; Almeida, R.S.; Pardini, L.C.; Rezende, M.C. Elastic properties of hydrothermally conditioned glare laminate. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2007, 45, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.S.; Ahn, K.J.; Nam, J.-D.; Chun, H.J. Hygroscopic aspects of epoxy/carbon fibre composite laminates in aircraft environments. Compos. Part A 2001, 32, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jedidi, J.; Jacquemin, F.; Vautrin, A. Design of accelerated hygrothermal cycles on polymer matrix composites in the case of supersonic aircraft. Compos. Struct. 2005, 68, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, B.P.; Tatar, J.; Douglas, E.P.; Hamilton, H.R. Effects of hygrothermal conditioning on epoxy adhesives used in FRP composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 96, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botelho, E.C.; Rezende, M.C.; Pardini, L.C. Hydrothermal effects evaluation using the losipescu shear test for Glare laminates. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2008, 30, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Majerski, K.; Surowska, B.; Bieniaś, J. The comparision of effects of hydrothermal conditioning on mechanical properties of fibre metal lamintes and fibre reinforced polymers. Compos. Part B 2018, 142, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.F.; Botelho, E.C.; Ancelotti, A.C., Jr.; Damato, C.A. Enviromental conditioning effects on the mechanical properties of titanium fibre-metal laminates. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Composite Materials, Montreal, QC, Canada, 28 July–2 August 2013; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Poodts, E.; Ghelli, D.; Brugo, T.; Panciroli, R.; Minak, G. Experimental characterization of a fiber metal laminate for underwater applications. Compos. Struct. 2015, 129, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Angra, S. Experimental evaluation of hygrothermal degradation of stainless steel fibre metal laminate. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2018, 21, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Choi, W.J.; Choi, H.S. The effects void contents on the long-term hydrothermal behaviors of glass/epoxy and Glare laminates. Compos. Struct. 2010, 92, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekar, M.; Ishak, M.R.; Jawaid, M.; Leman, Z.; Sapuan, S.M. An experimental review on the mechanical properties and hydrothermal behaviour of fibre metal laminates. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2017, 36, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botelho, E.C.; Pardini, L.C.; Rezende, M.C. Hydrothermal effects on damping behavior of metal/glass fibre/epoxy hybrid composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 399, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Joshi, S.C. Response of hygrothermally aged Glare 4A laminates under static and cyclic loadings. Mater. Des. 2015, 87, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, H.; Fu, X.; Zhang, X.; Tao, J.; Xu, J. Hygrothermal characterization of polyimide–titanium-based fibre metal laminate. Polym. Compos. 2018, 39, 2819–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moleiro, F.; Carrera, E.; Li, G.; Cinefra, M.; Reddy, J.N. Hygro-thermo-mechanical modelling of multilayered plates: Hybrid composite laminates, fibre metal laminates and sandwich plates. Compos. Part B 2019, 177, 107388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moleiro, F.; Mota Soares, C.M.; Carrera, E. Three-dimensional exact hygro-thermo-elastic solutions for multilayered plates: Composite laminates, fibre metal laminates and sandwich plates. Compos. Struct. 2019, 216, 260–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, C.; Trendafilova, I.; Zucchelli, A.; Contreras, J. The effect of nylon nanofibers on the dynamic behaviour and the delamination resistance of GFRP composites. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 148, 14001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ASTM D 5229. ASTM D 5229. Standard Test Method for Moisture Absorption Properties and Equilibrium Conditioning of Polymer Matrix Composite Materials; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- EN ISO14130:1997. Fibre-Reinforced Plastic Composites—Determination of Apparent Interlaminar Shear Strength by Short-Beam Method. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, A.A.; Silva, D.; Travessa, D.N.; Botelho, E.C. The effect of thermal cycles on the mechanical properties of fibre-metal laminates. Mater. Des. 2012, 42, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suri, C.; Perreux, D. The effects of mechanical damage in a glass fibre/epoxy composite on the absorption rate. Compos. Eng. 1995, 5, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scida, D.; Assarar, M.; Poilâne, C.; Ayad, R. Influence of hygrothermal ageing on the damage mechanisms of flax-fibre reinforced epoxy composite. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 48, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbruggen, M.L.C.E. Aramid Reinforced Aluminium Laminates: ARALL. Adhesion Problems and Environmental Effects. Vol. B: Environmental Effects; Report LR-504; Delft University of Technology: Delft, The Netherlands, 1986; Volume 1, pp. 9–74. [Google Scholar]
- Guermazi, N.; Ben Tarjem, A.; Ksouri, I.; Ayedi, H.F. On the durability of FRP composites for aircraft structures in hygrothermal conditioning. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 85, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinz, S.; Omoori, T.; Hojo, M.; Schulte, K. Damage characterization of fibre metal laminates under interlaminar shear load. Compos. Part A 2009, 40, 925–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
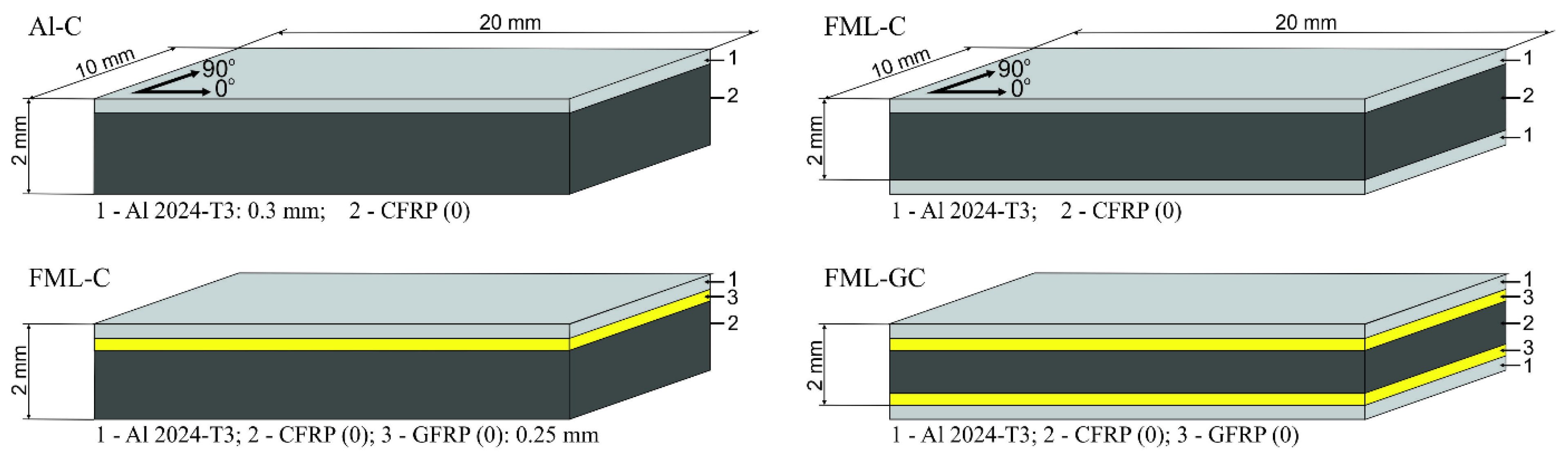








| Laminate Type | Before Hygrothermal Conditioning | |||
| Al-C | Al-GC | FML-C | FML-GC | |
| Fmax [N] | 2728 (±125 *) CV ** = 4.59 | 2374 (±69) CV = 2.91 | 2366 (±84) CV = 3.55 | 2326 (±40) CV = 1.72 |
| ILSS [MPa] | 93.0 (±2.3) | 86.4 (±2.6) | 84.6 (±2.4) | 81.5 (±1.7) |
| Laminate Type | After Hygrothermal Conditioning | |||
| Al-C | Al-GC | FML-C | FML-GC | |
| Fmax [N] | 2299 (±90) CV = 3.91 | 1991 (±130) CV = 6.54 | 2400 (±82) CV = 3.44 | 2351 (±75) CV = 3.18 |
| ILSS [MPa] | 82.3 (±2.7) | 66.8 (±4.1) | 85.9 (±2.0) | 81.8 (±1.4) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bieniaś, J.; Jakubczak, P.; Droździel, M.; Surowska, B. Interlaminar Shear Strength and Failure Analysis of Aluminium-Carbon Laminates with a Glass Fiber Interlayer after Moisture Absorption. Materials 2020, 13, 2999. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13132999
Bieniaś J, Jakubczak P, Droździel M, Surowska B. Interlaminar Shear Strength and Failure Analysis of Aluminium-Carbon Laminates with a Glass Fiber Interlayer after Moisture Absorption. Materials. 2020; 13(13):2999. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13132999
Chicago/Turabian StyleBieniaś, Jarosław, Patryk Jakubczak, Magda Droździel, and Barbara Surowska. 2020. "Interlaminar Shear Strength and Failure Analysis of Aluminium-Carbon Laminates with a Glass Fiber Interlayer after Moisture Absorption" Materials 13, no. 13: 2999. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13132999
APA StyleBieniaś, J., Jakubczak, P., Droździel, M., & Surowska, B. (2020). Interlaminar Shear Strength and Failure Analysis of Aluminium-Carbon Laminates with a Glass Fiber Interlayer after Moisture Absorption. Materials, 13(13), 2999. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13132999







