Development of a Monitoring Strategy for Laser-Textured Metallic Surfaces Using a Diffractive Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
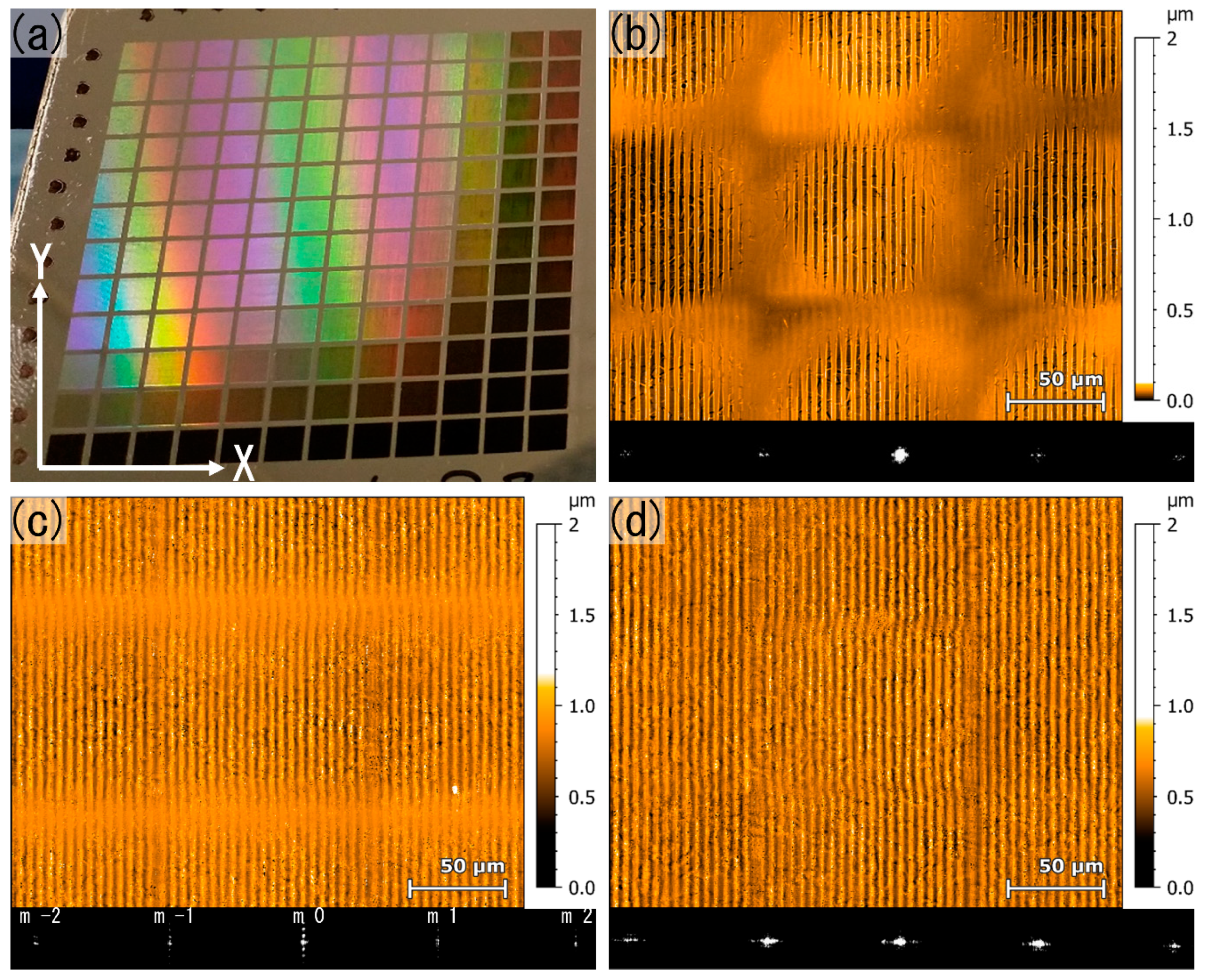
3.1. Development of an Optical Measurement System for Periodic Surface Structures
3.2. Direct Laser Interference Patterning of Steel Surface
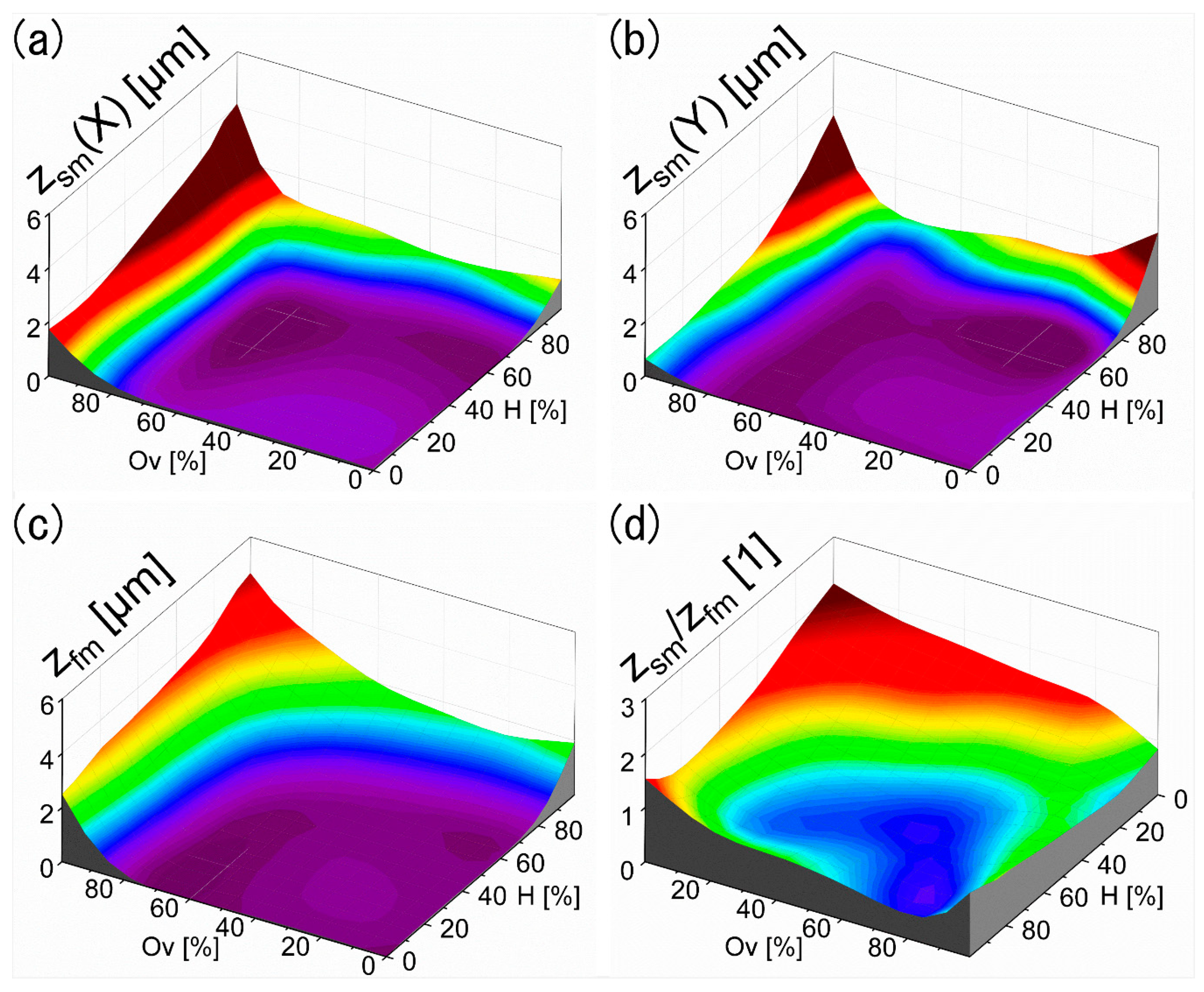
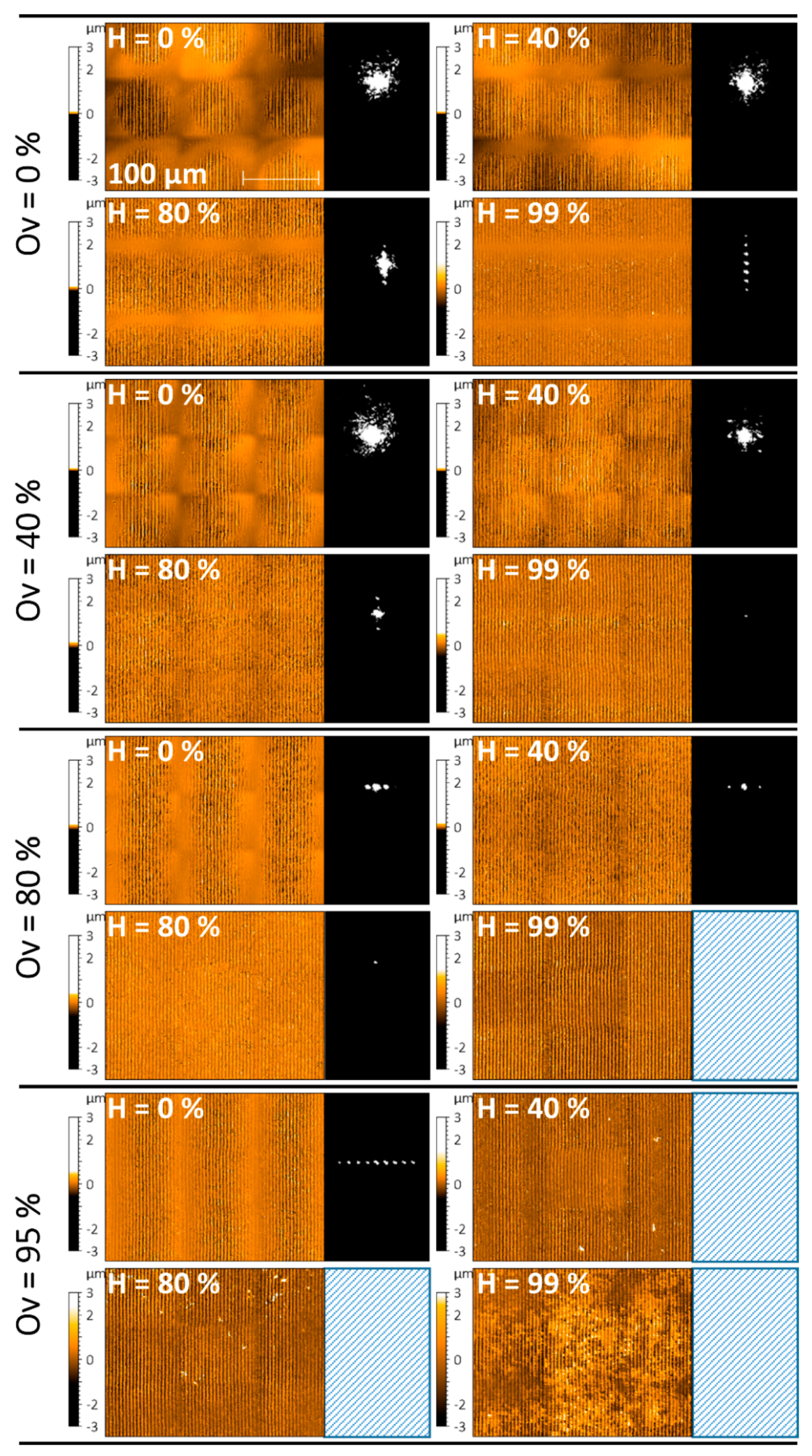
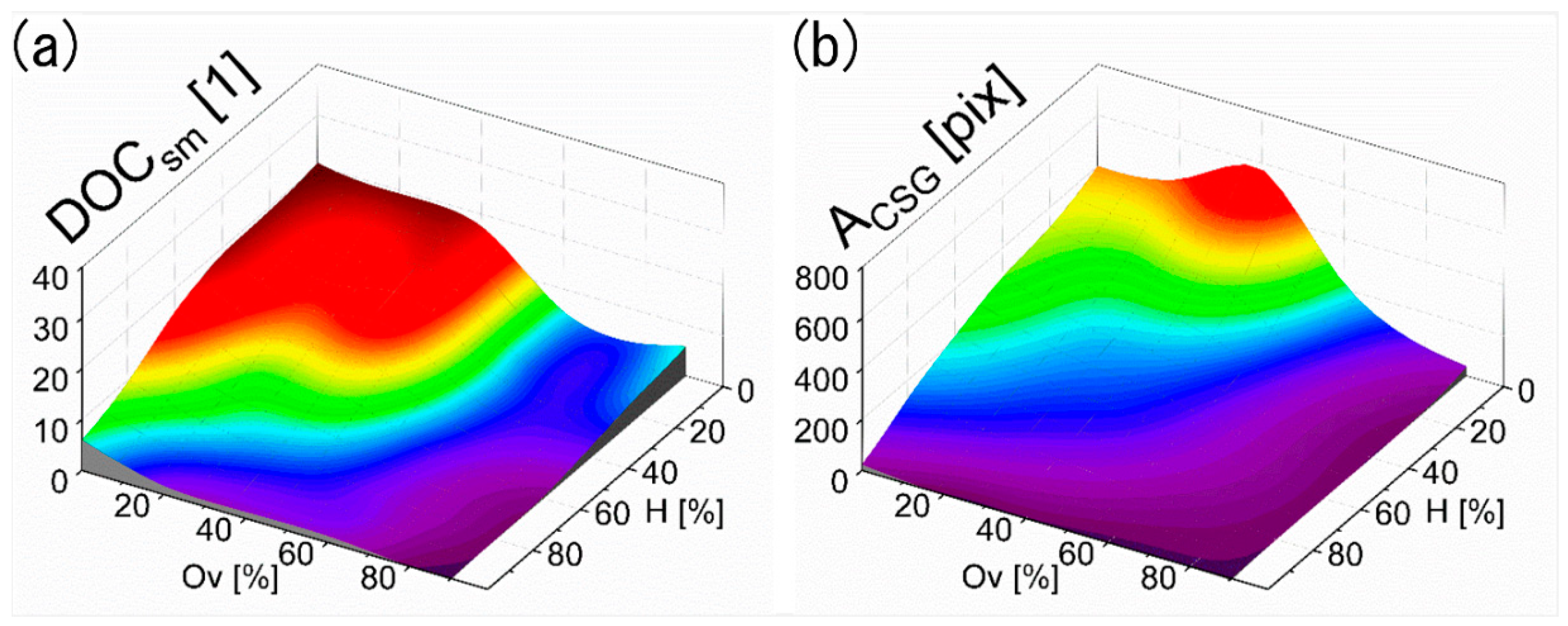
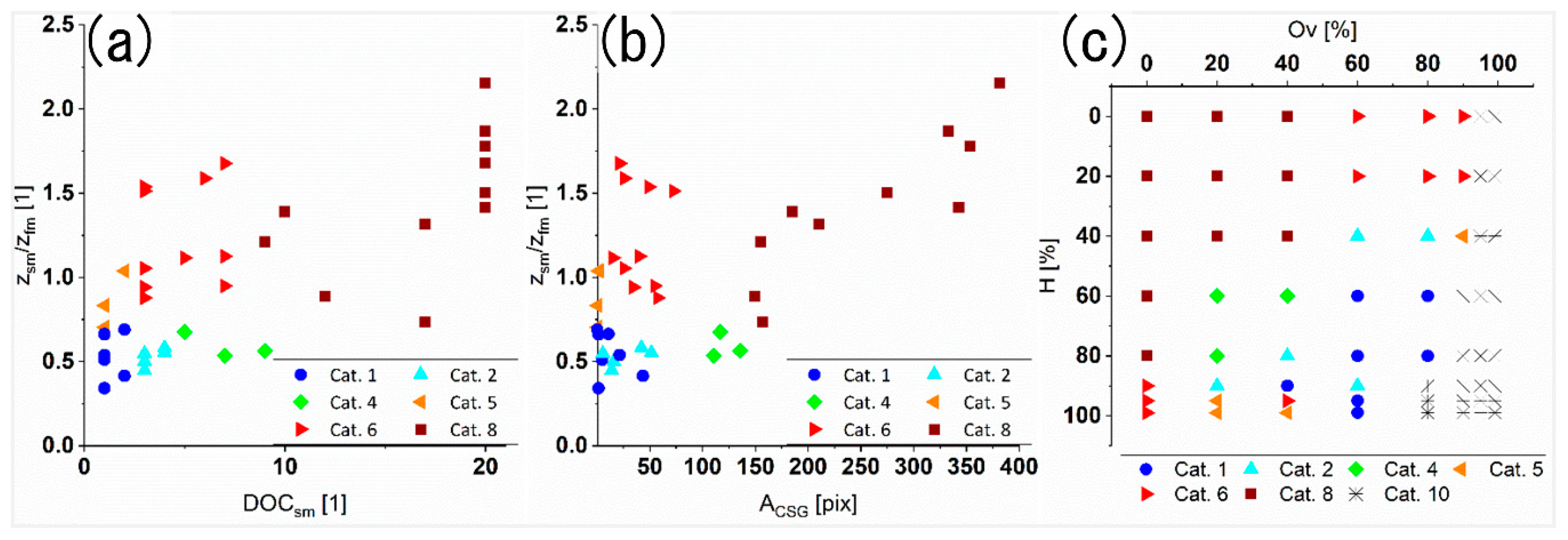
3.3. Characterization of the Laser Textured Surfaces Using the Developed Optical Module
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ensikat, H.J.; Ditsche-Kuru, P.; Neinhuis, C.; Barthlott, W. Superhydrophobicity in perfection: The outstanding properties of the lotus leaf. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2011, 2, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhushan, B.; Jung, Y.C.; Koch, K. Micro-, nano- and hierarchical structures for superhydrophobicity, self-cleaning and low adhesion. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2009, 367, 1631–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, G.S.; Green, D.W.; Schwarzkopf, L.; Li, X.; Cribb, B.W.; Myhra, S.; Watson, J.A. A gecko skin micro/nano structure—A low adhesion, superhydrophobic, anti-wetting, self-cleaning, biocompatible, antibacterial surface. Acta Biomater. 2015, 21, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jwad, T.; Walker, M.; Dimov, S. Erasing and rewriting of titanium oxide colour marks using laser-induced reduction/oxidation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 458, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Chu, J.; Huang, W. Realization of diverse displays for multiple color patterns on metal surfaces. App. Surf. Sci. 2014, 316, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruening, S.; Du, K.; Jarczynski, M.; Jenke, G.; Gillner, A. Ultra-fast laser micro processing by multiple laser spots. Procedia CIRP 2018, 74, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Héquet, A.; Humblot, V.; Berjeaud, J.-M.; Pradier, C.-M. Optimized grafting of antimicrobial peptides on stainless steel surface and biofilm resistance tests. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 84, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutey, A.H.A.; Gemini, L.; Romoli, L.; Lazzini, G.; Fuso, F.; Faucon, M.; Kling, R. Towards Laser-Textured Antibacterial Surfaces. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, T.L.; Rawlings, D.C. Aerodynamic microstructures having sub-microstructures. U.S. Patent US9868135B2, 16 January 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Walsh, M.J.; Anders, J.B.; Hefner, J.N. Combined riblet and lebu drag reduction system. U.S. Patent 4706910A, 17 November 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, V.W.; Tung, S.C. Overview of automotive engine friction and reduction trends–Effects of surface, material, and lubricant-additive technologies. Friction 2016, 4, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moebius, M.; Vora, K.; Kang, S.; Munoz, P.; Deng, G.; Mazur, E. Direct Laser Writing of 3D Gratings and Diffraction Optics. In Proceedings of the 2015 Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics (CLEO), San Jose, CA, USA, 10–15 May 2015; p. SW1K.6. [Google Scholar]
- England, G.; Kolle, M.; Kim, P.; Khan, M.; Munoz, P.; Mazur, E.; Aizenberg, J. Bioinspired micrograting arrays mimicking the reverse color diffraction elements evolved by the butterfly Pierella luna. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 15630–15634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebollar, E.; Sanz, M.; Pérez, S.; Hernández, M.; Martín-Fabiani, I.; Rueda, D.R.; Ezquerra, T.A.; Domingo, C.; Castillejo, M. Gold coatings on polymer laser induced periodic surface structures: Assessment as substrates for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 15699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebollar, E.; Hernández, M.; Sanz, M.; Pérez, S.; Ezquerra, T.A.; Castillejo, M. Laser-induced surface structures on gold-coated polymers: Influence of morphology on surface-enhanced Raman scattering enhancement. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonse, J.; Krüger, J.; Höhm, S.; Rosenfeld, A. Femtosecond laser-induced periodic surface structures. J. Laser Appl. 2012, 24, 042006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottmann, J.; Wagner, R. Sub-wavelength ripple formation on dielectric and metallic materials induced by tightly focused femto-second laser radiation. In Proc. SPIE 6101, Photon Processing in Microelectronics and Photonics V; SPIE: Santa Clara, CA, USA; 21–26 January 2006, p. 61061R.
- Guay, J.-M.; Calà Lesina, A.; Baxter, J.; Killaire, G.; Ramunno, L.; Berini, P.; Weck, A. Topography Tuning for Plasmonic Color Enhancement via Picosecond Laser Bursts. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2018, 6, 1800189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkranz, A.; Hans, M.; Gachot, C.; Thome, A.; Bonk, S.; Mücklich, F. Direct Laser Interference Patterning: Tailoring of Contact Area for Frictional and Antibacterial Properties. Lubricants 2016, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieda, M.; Siebold, M.; Lasagni, A.F. Fabrication of sub-micron surface structures on copper, stainless steel and titanium using picosecond laser interference patterning. App. Surf. Sci. 2016, 387, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stärk, M.; Schlickeiser, F.; Nissen, D.; Hebler, B.; Graus, P.; Hinzke, D.; Scheer, E.; Leiderer, P.; Fonin, M.; Albrecht, M.; et al. Controlling the magnetic structure of Co/Pd thin films by direct laser interference patterning. Nanotechnology 2015, 26, 205302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasagni, A.F. Advanced Design of Periodical Structures by Laser Interference Metallurgy in the Micro/Nano Scale on Macroscopic Areas; Shaker Verlag GmbH: Aachen, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Voisiat, B.; Gedvilas, M.; Indrišiūnas, S.; Račiukaitis, G. Picosecond-Laser 4-Beam-Interference Ablation as a Flexible Tool for Thin Film Microstructuring. Phys. Procedia 2011, 12, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geometrische Produktspezifikation (GPS)-Oberflächenbeschaffenheit: Flächenhaft–Teil 6: Klassifizierung von Methoden zur Messung der Oberflächenbeschaffenheit; DIN EN ISO 25178-6; Deutsches Institut für Normung e.V., Beuth Verlag GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2010.
- Leach, R. Introduction to Surface Texture Measurement. In Optical Measurement of Surface Topography; Leach, R., Ed.; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Purtonen, T.; Kalliosaari, A.; Salminen, A. Monitoring and Adaptive Control of Laser Processes. Phys. Procedia 2014, 56, 1218–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smilde, H.-J.H.; den Boef, A.; Kubis, M.; Jak, M.; van Schijndel, M.; Fuchs, A.; van der Schaar, M.; Meyer, S.; Morgan, S.; Wu, J.; et al. Evaluation of a novel ultra small target technology supporting on-product overlay measurements. In Proc. SPIE 8324, Metrology, Inspection, and Process Control for Microlithography XXVI; SPIE: San Jose, CA, USA; 12–16 February 2012, p. 83241A.
- Pollentier, I.; Cheng, S.Y.; Baudemprez, B.; Laidler, D.; van Dommelen, Y.; Carpaij, R.; Yu, J.; Uchida, J.; Viswanathan, A.; Chin, D.; et al. In-line lithography cluster monitoring and control using integrated scatterometry. In Proc. SPIE 5378, Data Analysis and Modeling for Process Control; SPIE: Santa Clara, CA, USA; 22–27 February 2004, p. 105.
- El Kodadi, M.; Soulan, S.; Besacier, M.; Schiavone, P. Real time scatterometry for profile control during resist trimming process. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 2009, 27, 3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuzer, M.; Whitworth, G.L.; Francone, A.; Gomis-Bresco, J.; Kehagias, N.; Sotomayor-Torres, C.M. In-line metrology for roll-to-roll UV assisted nanoimprint lithography using diffractometry. APL Mater. 2018, 6, 058502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Morales, A.I.; Alamri, S.; Kunze, T.; Lasagni, A.F. Influence of processing parameters on surface texture homogeneity using Direct Laser Interference Patterning. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 107, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, V.; Rank, A.; Lasagni, A.F. Large Area One-Step Fabrication of Three-Level Multiple-Scaled Micro and Nanostructured Nickel Sleeves for Roll-to-Roll Hot Embossing: Large Area Fabrication of Three-Level microstructures. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2017, 19, 1700126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanasiou, C.-E.; Hongler, M.-O.; Bellouard, Y. Unraveling Brittle-Fracture Statistics from Intermittent Patterns Formed During Femtosecond Laser Exposure. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2017, 8, 054013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulané-Petermann, L. Processes of bioadhesion on stainless steel surfaces and cleanability: A review with special reference to the food industry. Biofouling 1996, 10, 275–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jullien, C.; Bénézech, T.; Carpentier, B.; Lebret, V.; Faille, C. Identification of surface characteristics relevant to the hygienic status of stainless steel for the food industry. J. Food Eng. 2003, 56, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akl, M.A.; Ahmed, M.A.; Ramadan, A. Validation of an HPLC-UV method for the determination of ceftriaxone sodium residues on stainless steel surface of pharmaceutical manufacturing equipments. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2011, 55, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siva Reddy, V.; Kaushik, S.C.; Ranjan, K.R.; Tyagi, S.K. State-of-the-art of solar thermal power plants—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 27, 258–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geometrische Produktspezifikation (GPS)-Oberflächenbeschaffenheit: Flächenhaft; DIN EN ISO 25178; Deutsches Institut für Normung e.V., Beuth Verlag GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2012.
- Lasagni, A.F.; Alamri, S.; Rößler, F.; Lang, V.; Voisiat, B. Design of Perfectly Ordered Periodic Structures on Polymers Using Direct Laser Interference Patterning. In Wrinkled Polymer Surfaces; González-Henríquez, C.M., Rodríguez-Hernández, J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 157–180. [Google Scholar]
- Bonse, J.; Hohm, S.; Kirner, S.V.; Rosenfeld, A.; Kruger, J. Laser-Induced Periodic Surface Structures—A Scientific Evergreen. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2017, 23, 7581030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voisiat, B.; Teutoburg-Weiss, S.; Rank, A.; Lasagni, A.F. DLIP holographic structuring: from basic concept to advanced monitoring methods and industrial scale production. In Proc. SPIE 10906, Laser-Based Micro-and Nanoprocessing XIII; Klotzbach, U., Kling, R., Watanabe, A., Eds.; SPIE: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2019; Volume 109060W, p. 31. [Google Scholar]
- Rößler, F.; Günther, D.; Lasagni, A.F. Fabrication of Hierarchical Micro Patterns on PET Substrates Using Direct Laser Interference Patterning: Fabrication of Hierarchical Micro Patterns. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2016, 18, 1755–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rößler, F.; Kunze, T.; Lasagni, A.F. Fabrication of diffraction based security elements using direct laser interference patterning. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 22959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar-Morales, A.I.; Alamri, S.; Lasagni, A.F. Micro-fabrication of high aspect ratio periodic structures on stainless steel by picosecond direct laser interference patterning. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2018, 252, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamri, S.; Aguilar-Morales, A.I.; Lasagni, A.F. Controlling the wettability of polycarbonate substrates by producing hierarchical structures using Direct Laser Interference Patterning. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 99, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, V.; Voisiat, B.; Lasagni, A.F. High Throughput Direct Laser Interference Patterning of Aluminum for Fabrication of Super Hydrophobic Surfaces. Materials 2019, 12, 1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradski, G. The OpenCV Library. Dr. Dobb’s Journal of Software Tools 2000, 25, 120–125. [Google Scholar]

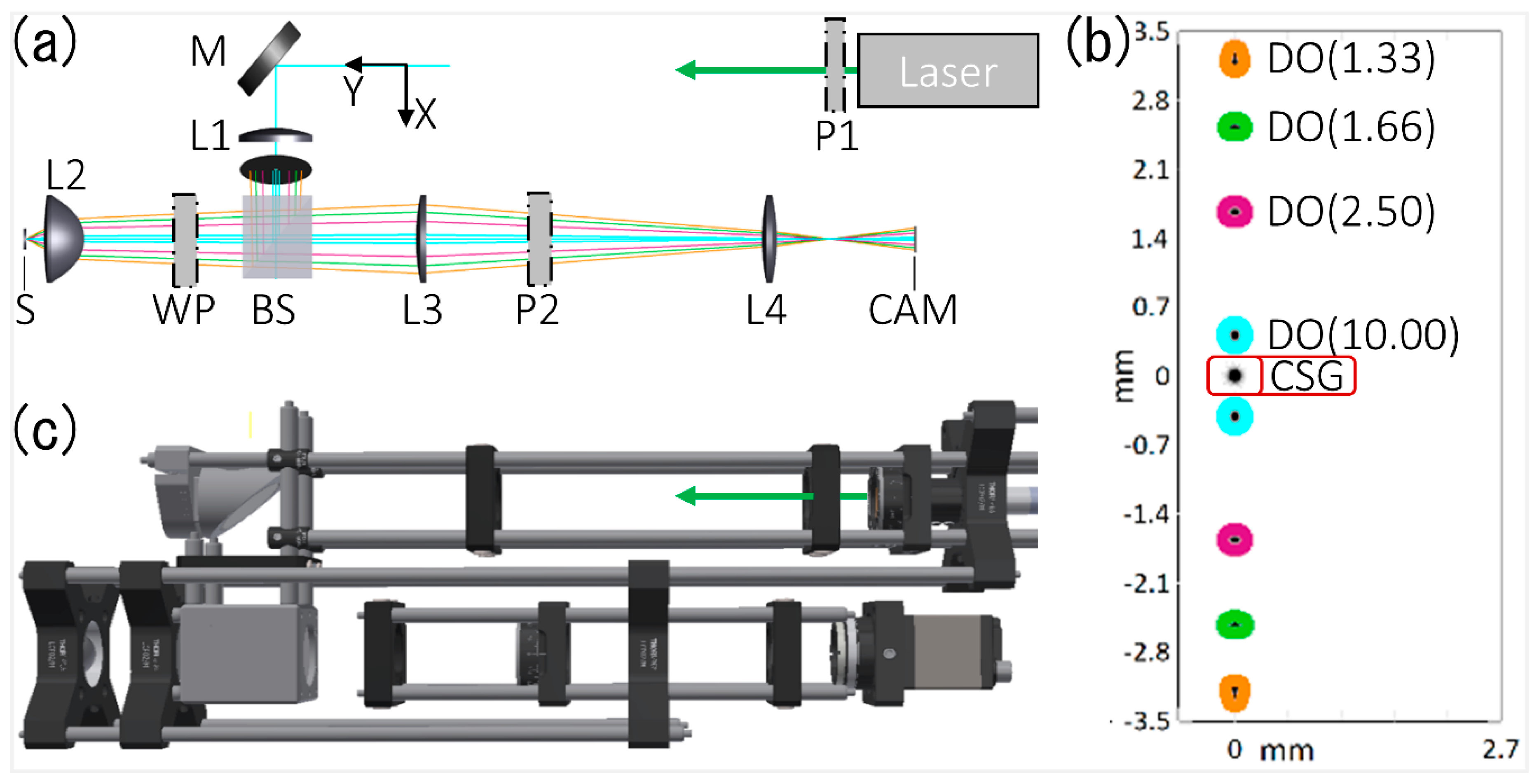

| ID | Object | X (mm) | Y (mm) | Parameter |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laser | Coherent light source | 0 | 0 | λ = 532 nm, 0.9 mW, 3.5 mm beam diameter |
| P1 | Polarizer | (0) | - | Linear Dichroic, λ = 400–700 nm |
| M | Coupling Mirror | 0 | 60 | For 532 nm wavelength |
| L1 | Lens | 20 | 60 | Plano-Convex, N-BK7, f = 75 mm |
| BS | Beam Splitter | 49 | 60 | Polarized for λ = 532 nm |
| WP | λ/4 Wave plate | (49) | - | Zero order for 532 nm |
| L2 | Lens | 49 | 140 | Asphere, N-BK7, f = 16 mm, NA = 0.79 |
| S | Sample | 49 | 146 | Textured sample with different spatial periods |
| L3 | Lens | 49 | −10 | Plano-Convex, N-BK7, f = 100 mm |
| P2 | Polarizer | (49) | - | Linear Dichroic, λ = 400–700 nm |
| L4 | Lens | 49 | −110 | Bi-Convex, N-BK7, f = 50 mm |
| CAM | Camera | 49 | −160 | Camera screen size: 2.7 mm × 3.4 mm |
| Category # | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zsm/Zfm | <0.7 | >0.7 | No Data | ||||||
| ACSG | <100 | >100 | <100 | >100 | |||||
| DOCsm | ≤2 | >2 | ≤2 | >2 | ≤2 | >2 | ≤2 | >2 | |
| CSG example in Figure 6 Ov,H | 80, 80 | 40, 80 | - | 40, 60 * | 40, 99 | 0, 99 | - | 40, 0 | - |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Teutoburg-Weiss, S.; Voisiat, B.; Soldera, M.; Lasagni, A.F. Development of a Monitoring Strategy for Laser-Textured Metallic Surfaces Using a Diffractive Approach. Materials 2020, 13, 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13010053
Teutoburg-Weiss S, Voisiat B, Soldera M, Lasagni AF. Development of a Monitoring Strategy for Laser-Textured Metallic Surfaces Using a Diffractive Approach. Materials. 2020; 13(1):53. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13010053
Chicago/Turabian StyleTeutoburg-Weiss, Sascha, Bogdan Voisiat, Marcos Soldera, and Andrés Fabián Lasagni. 2020. "Development of a Monitoring Strategy for Laser-Textured Metallic Surfaces Using a Diffractive Approach" Materials 13, no. 1: 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13010053
APA StyleTeutoburg-Weiss, S., Voisiat, B., Soldera, M., & Lasagni, A. F. (2020). Development of a Monitoring Strategy for Laser-Textured Metallic Surfaces Using a Diffractive Approach. Materials, 13(1), 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13010053






