Control of MnS Inclusions in High- and Low-Sulfur Steel by Tellurium Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Steel Content and Other Experimental Material
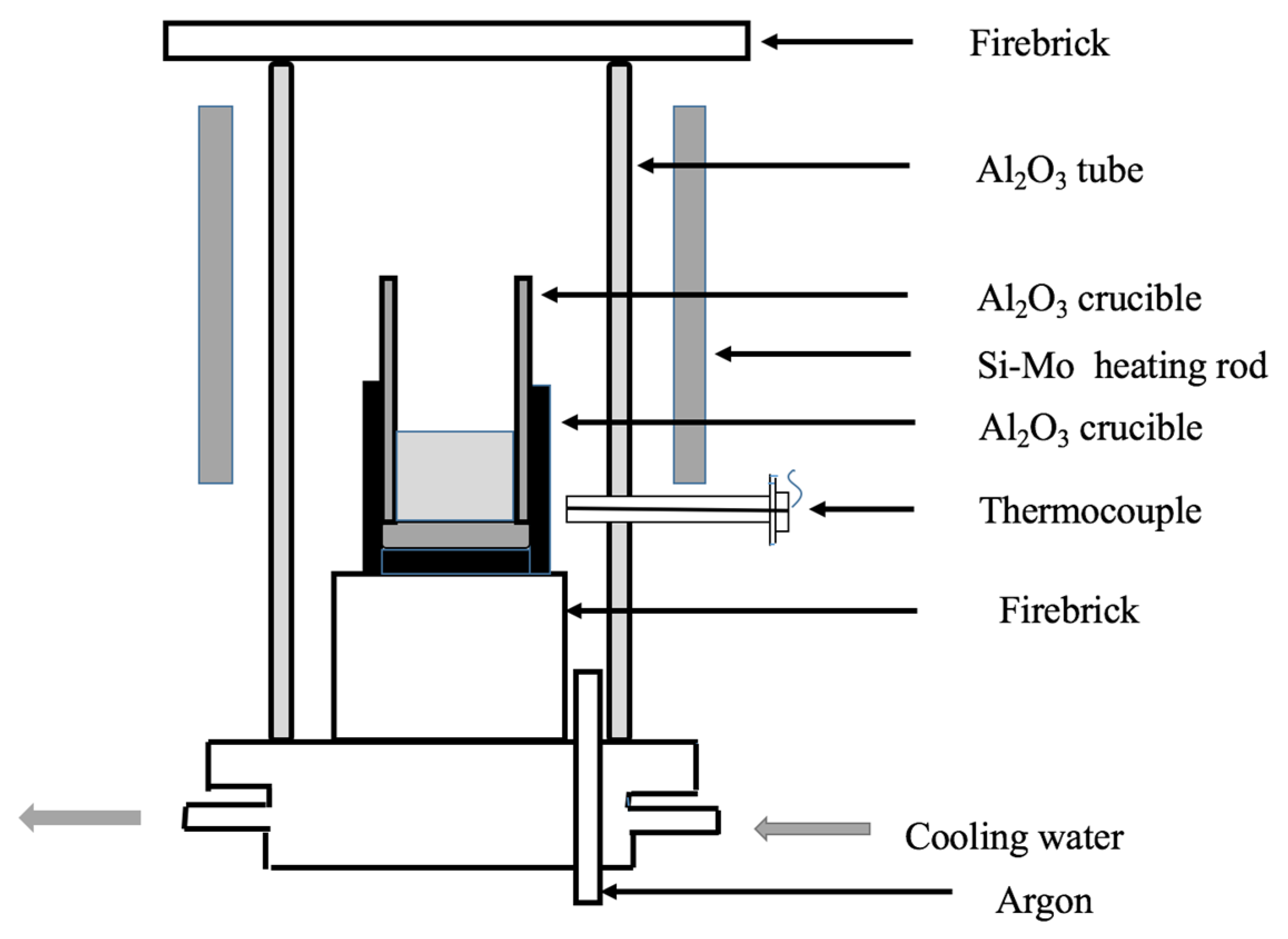
2.2. Experimental Procedure
3. Results
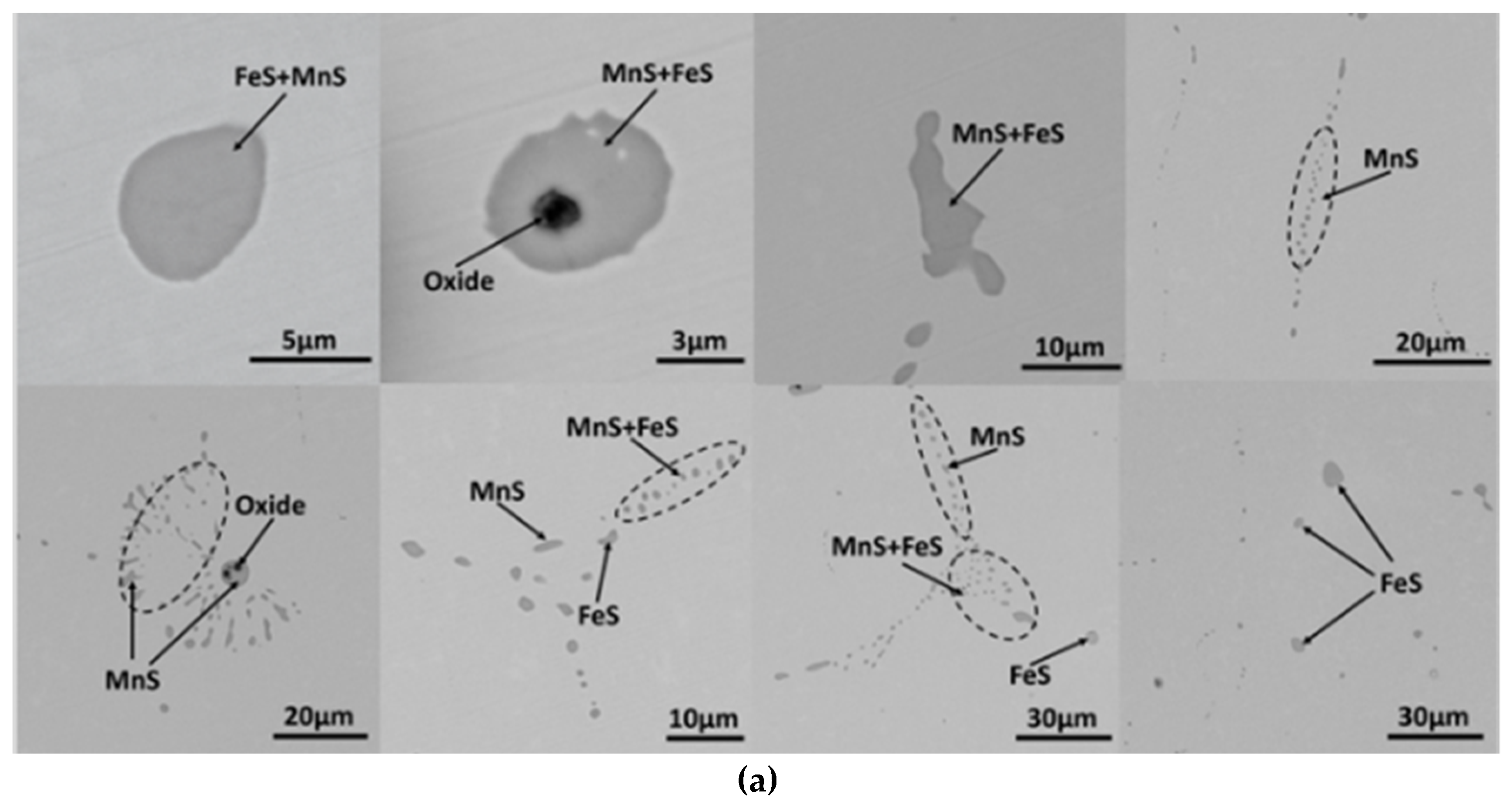
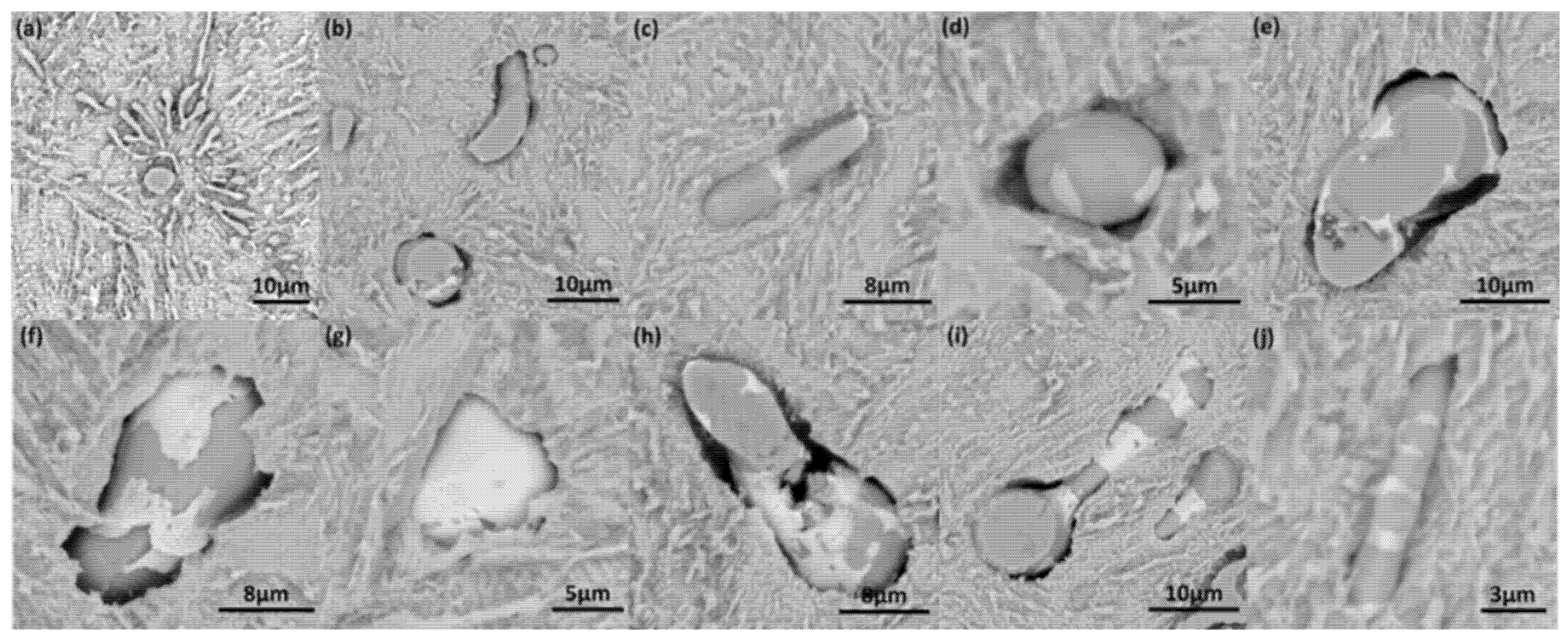
3.1. MnS Inclusion Morphology in Original Steel
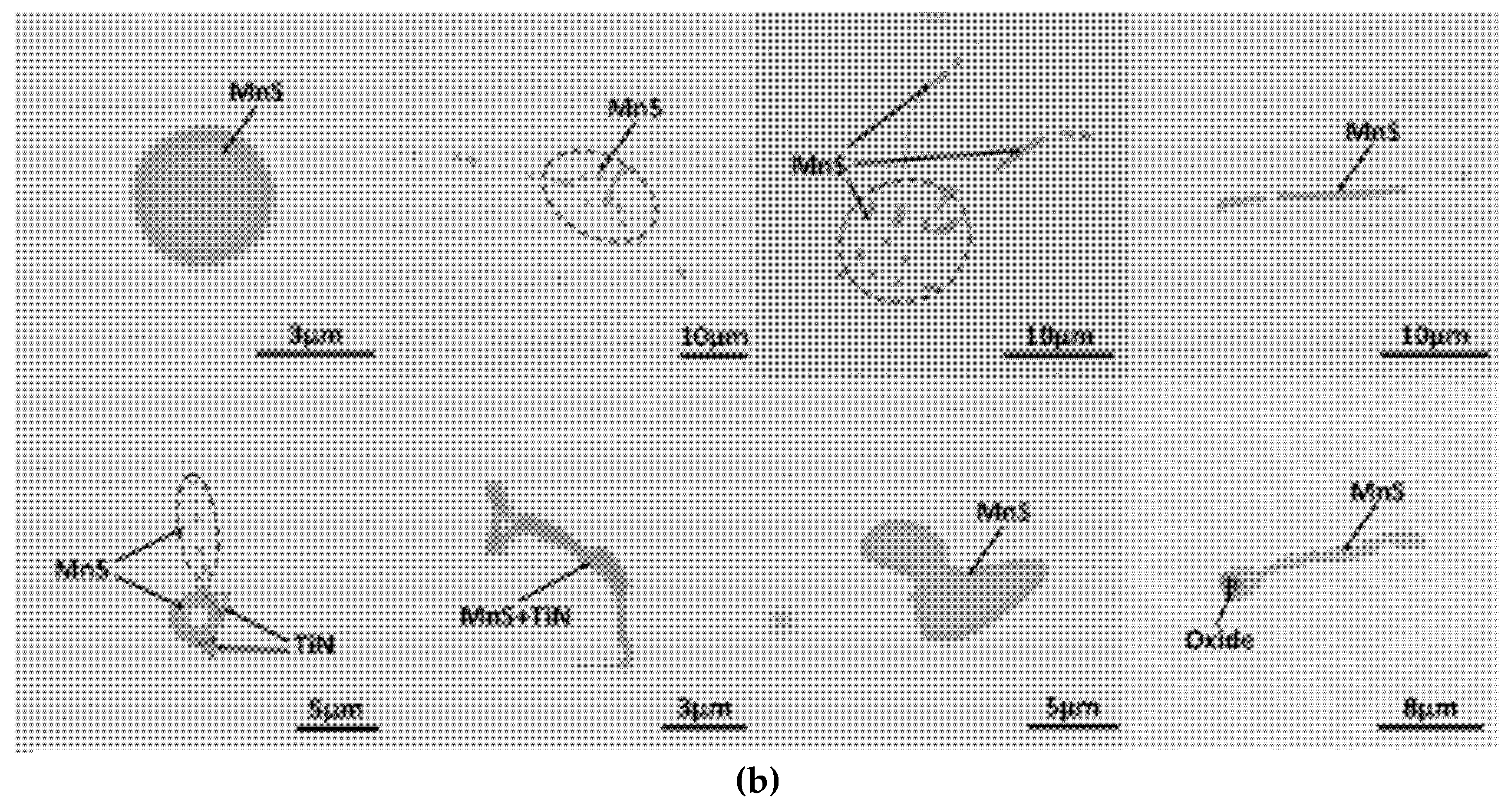
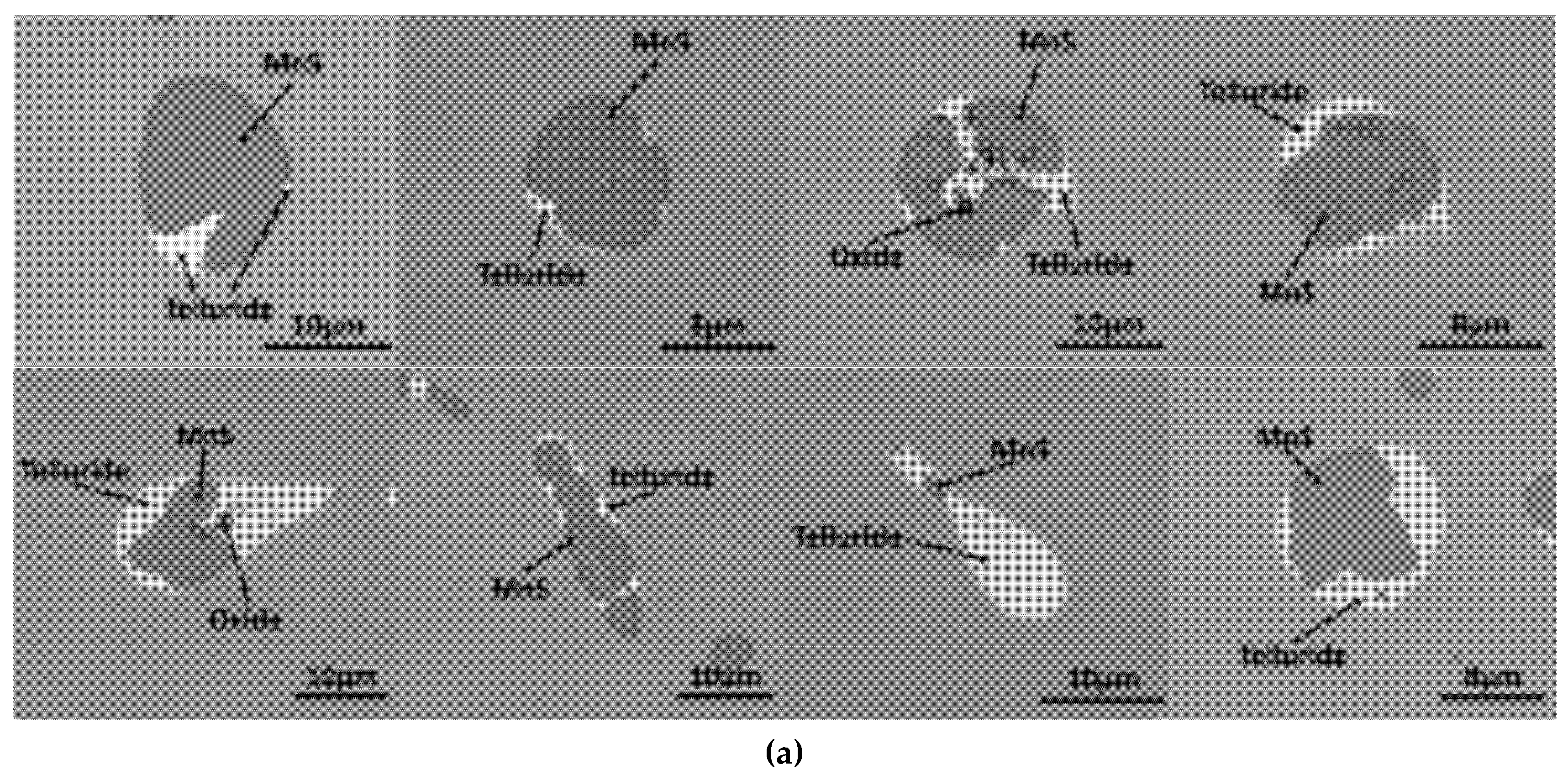
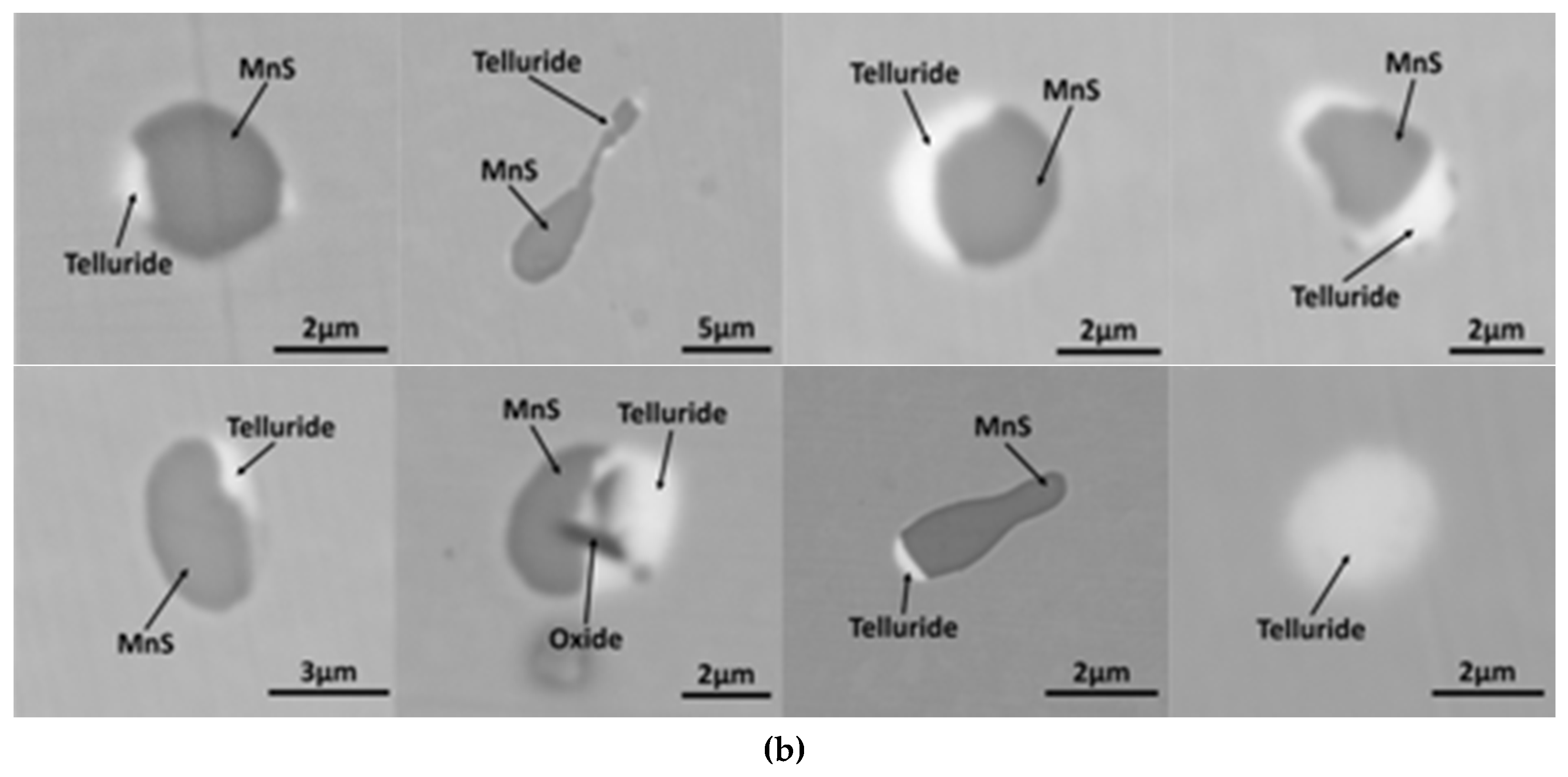
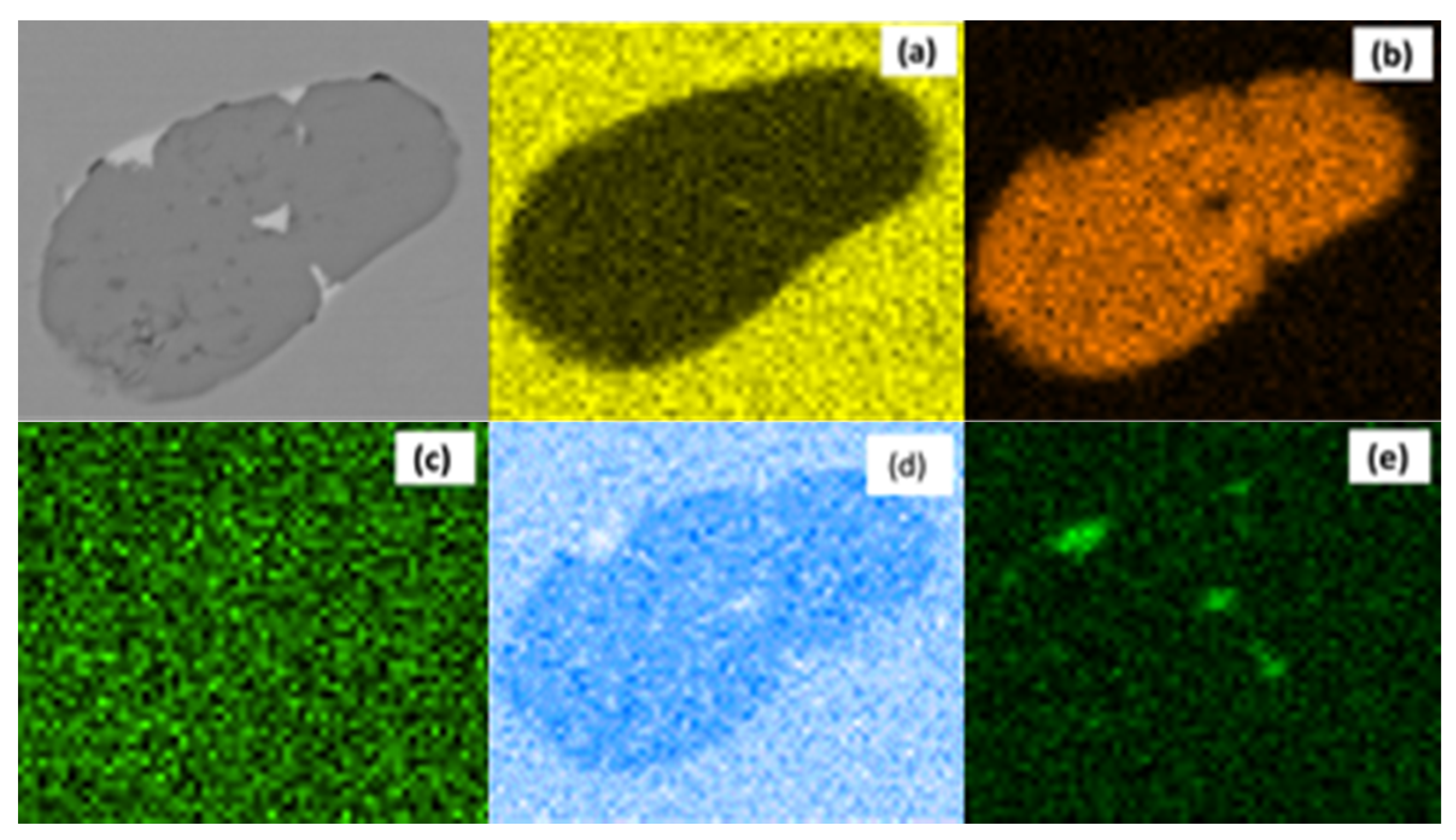
3.2. MnS Inclusion Morphology with Te Addition
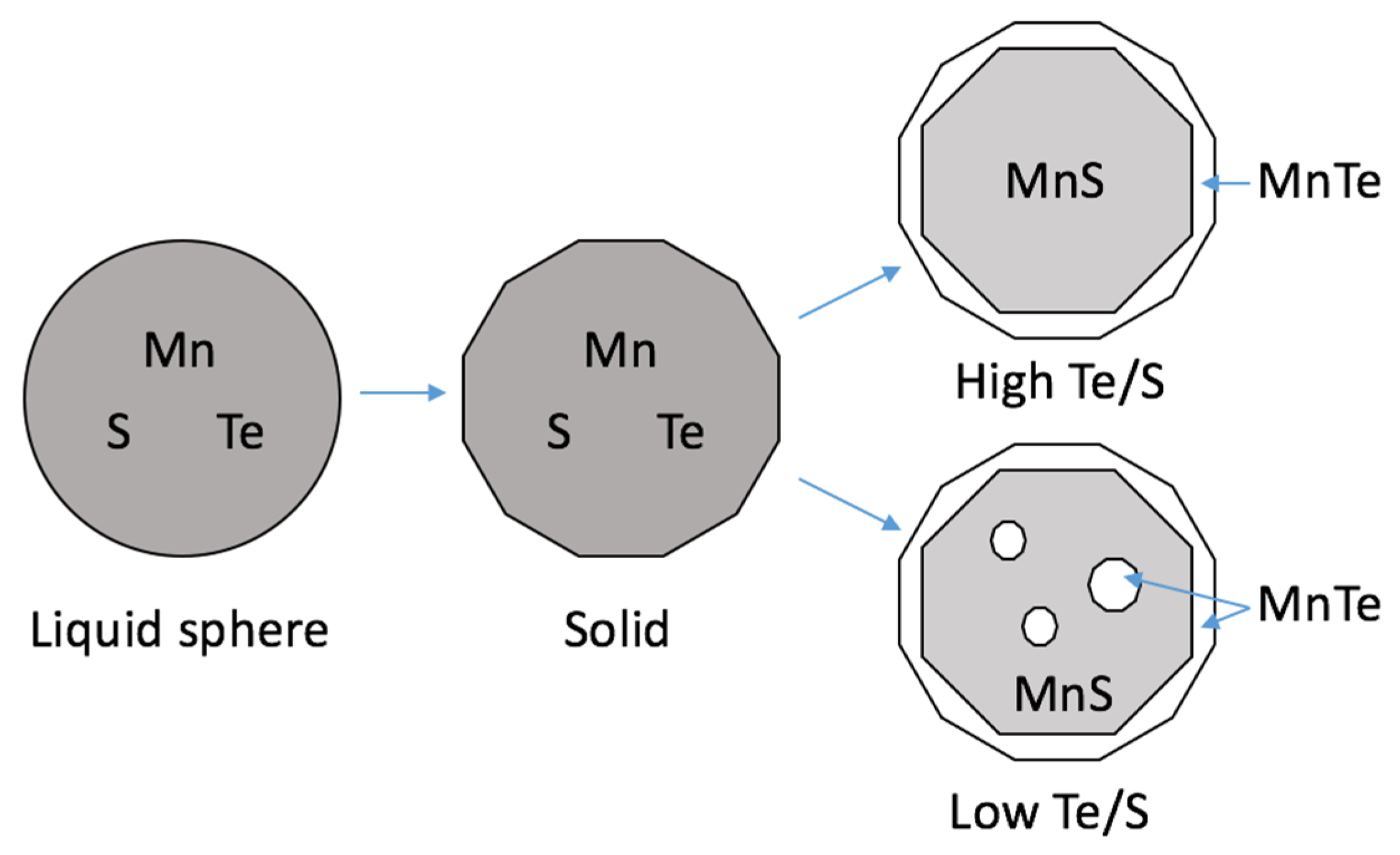
4. Discussion
Mechanism of Te Treatment
5. Conclusions
- (1)
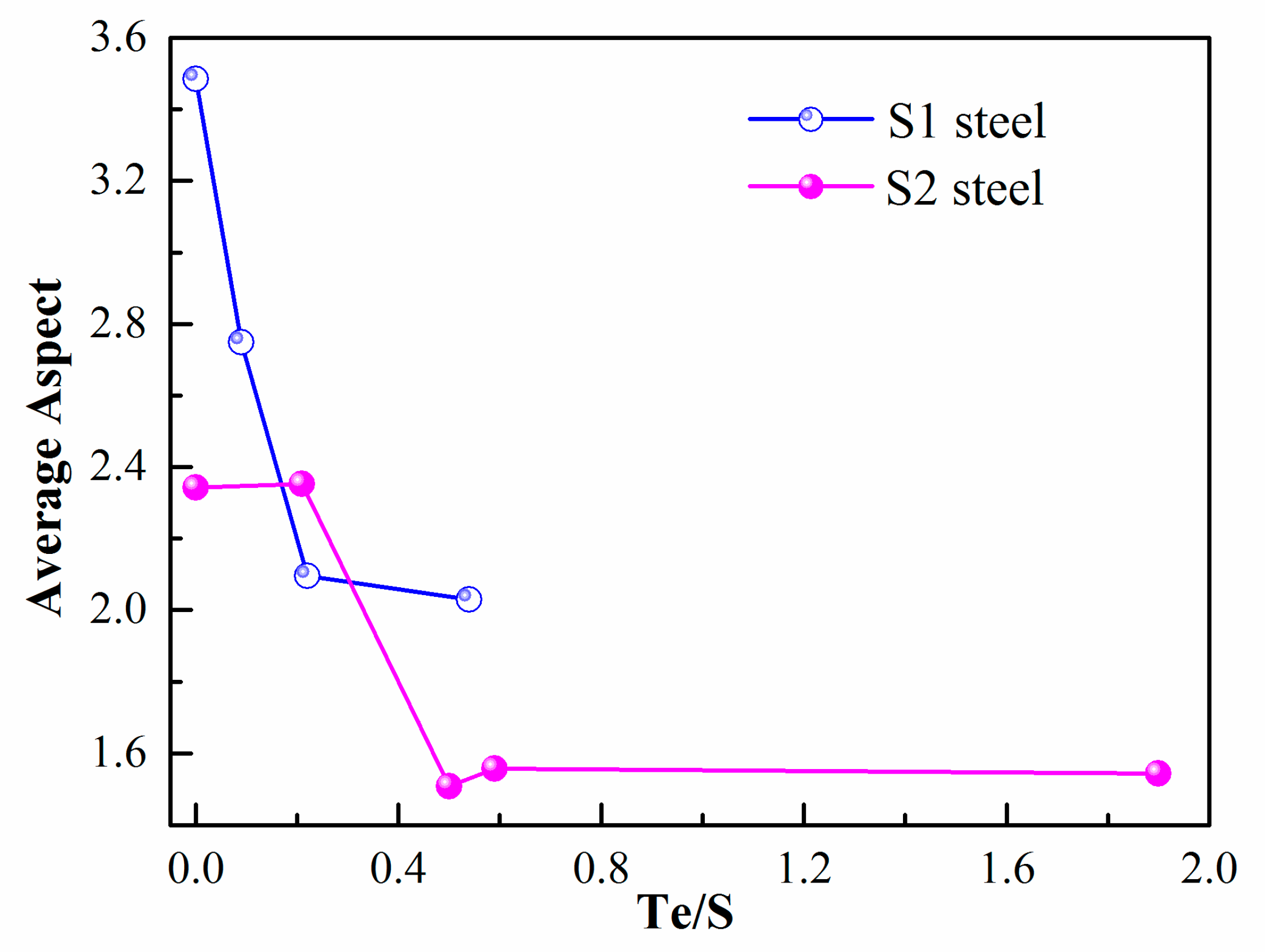
- Through the experiment, both in high- and low-sulfur steel, the aspect ratio and size changed dominantly with the addition of Te. The best Te/S to reach the lowest average aspect of inclusion was about 0.5 for both high- and low-sulfur steel in this experimental setup.
- (2)
- The mechanism is discussed from a sequential solidification point of view. The MnS and MnTe were supposed to react as a second liquid phase and then, during its cooling, MnTe diffused to the shell while MnS remained in the core to form the core–shell inclusion.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramanujachar, K.; Subramanian, S.V. Micromechanisms of tool wear in machining free cutting steels. Wear 1996, 197, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobih, M.; Crouse, P.L.; Li, L. Elimination of striation in laser cutting of mild steel. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2007, 40, 6908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.J.; Wang, X.H.; Jiang, M.; Wan, W.J.; Huang, F.X. Effect of heat treatment conditions on shape control of large-sized elongated MnS inclusions in resulfurized free-cutting steels. ISIJ Int. 2011, 51, 1995–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, C.; Dahle, F. Effect of aluminum on the properties of medium carbon cast steel. Trans. Am. Foundrym. Soc. 1938, 46, 65–132. [Google Scholar]
- Speich, G.R.; Spitzig, W.A. Effect of volume fraction and shape of sulfide inclusions on through-thickness ductility and impact energy of high-strength 4340 plate steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1982, 13, 2239–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imagumbai, M. Consideration on distribution and size of dendritic type II MnS-inclusion in steel dendrite structure. ISIJ int. 1994, 34, 992–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temmel, C.; Ingesten, N.G.; Karlsson, B. Fatigue anisotropy in cross-rolled, hardened medium carbon steel resulting from MnS inclusions. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2006, 37, 2995–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikawa, K.; Ishida, K.; Nishizawa, T. Effect of titanium addition on the formation and distribution of MnS inclusions in steel during solidification. ISIJ Int. 1997, 37, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Chang, C.H.; Lee, H.G. Evolution of inclusions and resultant microstructural change with Mg addition in Mn/Si/Ti deoxidized steels. Scr. Mater. 2005, 53, 1253–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, A.M.; Li, S.R.; Guo, J.; Li, P.H.; Ding, K.M.; He, X.L. Effect of zirconium addition on the impact toughness of the heat affected zone in a high strength low alloy pipeline steel. Mater. Charact. 2008, 59, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, C. Role of Ca treatment in hydrogen induced cracking of hot rolled API pipeline steel in acid sour media. Met. Mater. Int. 2013, 19, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.I.; Nara, S.; Kato, Y.; Mamoru, S. Shape control of alumina inclusions by double calcium addition treatment. J. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. 2007, 93, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.T.; Jeon, S.H.; Lee, I.S.; Park, Y.S. Effects of rare earth metals addition on the resistance to pitting corrosion of super duplex stainless steel—Part 1. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 1897–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waudby, P.E. Rare earth additions to steel. Int. Met. Rev. 1978, 23, 74–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kano, T.; Hanyuda, T. Improvement of machinability improvement function of inclusion on sulfide-containing steel which applied Ca treatment. Denki Seiko (Electr. Furn. Steel) 2004, 75, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holappa, L.; Hämäläinen, M.; Liukkonen, M.; Lind, M. Thermodynamic examination of inclusion modification and precipitation from calcium treatment to solidified steel. Ironmaking Steelmaking 2003, 30, 111–115. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, S.; Nakajima, K.; Mizoguchi, S.; Hasegawa, H. In-situ observation of the precipitation of manganese sulfide in low-carbon magnesium-killed steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2002, 33, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Yang, S.; Fu, J. The Effect of Tellurium on the Formation of MnTe-MnS Composite Inclusions in Non-Quenched and Tempered Steel. Metals 2018, 8, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Malfliet, A.; Wollants, P.; Blanpain, B.; Guo, M. Effect of surfactant Te on the formation of MnS inclusions in steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2017, 48, 2447–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaguchi, H.; Onodera, N. The Effect of Tellurium on the Machinability of AISI 12L14+Te Steel. Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. 1988, 28, 1051–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, J.M.; Riewald, P.G.; Van Vlack, L.H. The System MnSe-MnS. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1967, 50, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Steel | Content | C | Si | Mn | P | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | wt.% | 0.10–0.18 | <0.15 | 0.8–1.2 | 0.05–0.1 | 0.23–0.33 |
| 2 | wt.% | 0.17–0.23 | 0.17–0.37 | 0.80–1.10 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.035 |
| Heats | S, wt.% | Te, wt.% | Te/S | Heats | S, wt.% | Te, wt.% | Te/S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1T0 | 0.3 | 0 | 0 | S2T0 | 0.02 | 0 | 0 |
| S1T1 | 0.3 | 0.015 | 0.05 | S2T1 | 0.02 | 0.004 | 0.2 |
| S1T2 | 0.3 | 0.06 | 0.2 | S2T2 | 0.02 | 0.006 | 0.3 |
| S1T3 | 0.3 | 0.15 | 0.5 | S2T3 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.5 |
| S2T4 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 1 |
| Heats | S, wt.% | Te, wt.% | Te/S | Heats | S, wt.% | Te, wt.% | Te/S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1T0 | 0.28 | 0 | 0 | S2T0 | 0.020 | 0 | 0 |
| S1T1 | 0.28 | 0.024 | 0.09 | S2T1 | 0.020 | 0.0042 | 0.21 |
| S1T2 | 0.26 | 0.057 | 0.22 | S2T2 | 0.014 | 0.007 | 0.5 |
| S1T3 | 0.26 | 0.14 | 0.54 | S2T3 | 0.019 | 0.01 | 0.53 |
| S2T4 | 0.01 | 0.019 | 1.9 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, F.; Guo, H.; Liu, W.; Yang, S.; Zhang, S.; Li, J. Control of MnS Inclusions in High- and Low-Sulfur Steel by Tellurium Treatment. Materials 2019, 12, 1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12071034
Wang F, Guo H, Liu W, Yang S, Zhang S, Li J. Control of MnS Inclusions in High- and Low-Sulfur Steel by Tellurium Treatment. Materials. 2019; 12(7):1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12071034
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Feng, Hao Guo, Wei Liu, Shufeng Yang, Shuo Zhang, and Jingshe Li. 2019. "Control of MnS Inclusions in High- and Low-Sulfur Steel by Tellurium Treatment" Materials 12, no. 7: 1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12071034
APA StyleWang, F., Guo, H., Liu, W., Yang, S., Zhang, S., & Li, J. (2019). Control of MnS Inclusions in High- and Low-Sulfur Steel by Tellurium Treatment. Materials, 12(7), 1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12071034





