Enhanced Singular Value Truncation Method for Non-Destructive Evaluation of Structural Damage Using Natural Frequencies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Development
2.1. Natural Frequency Sensitivity for Damage Detection
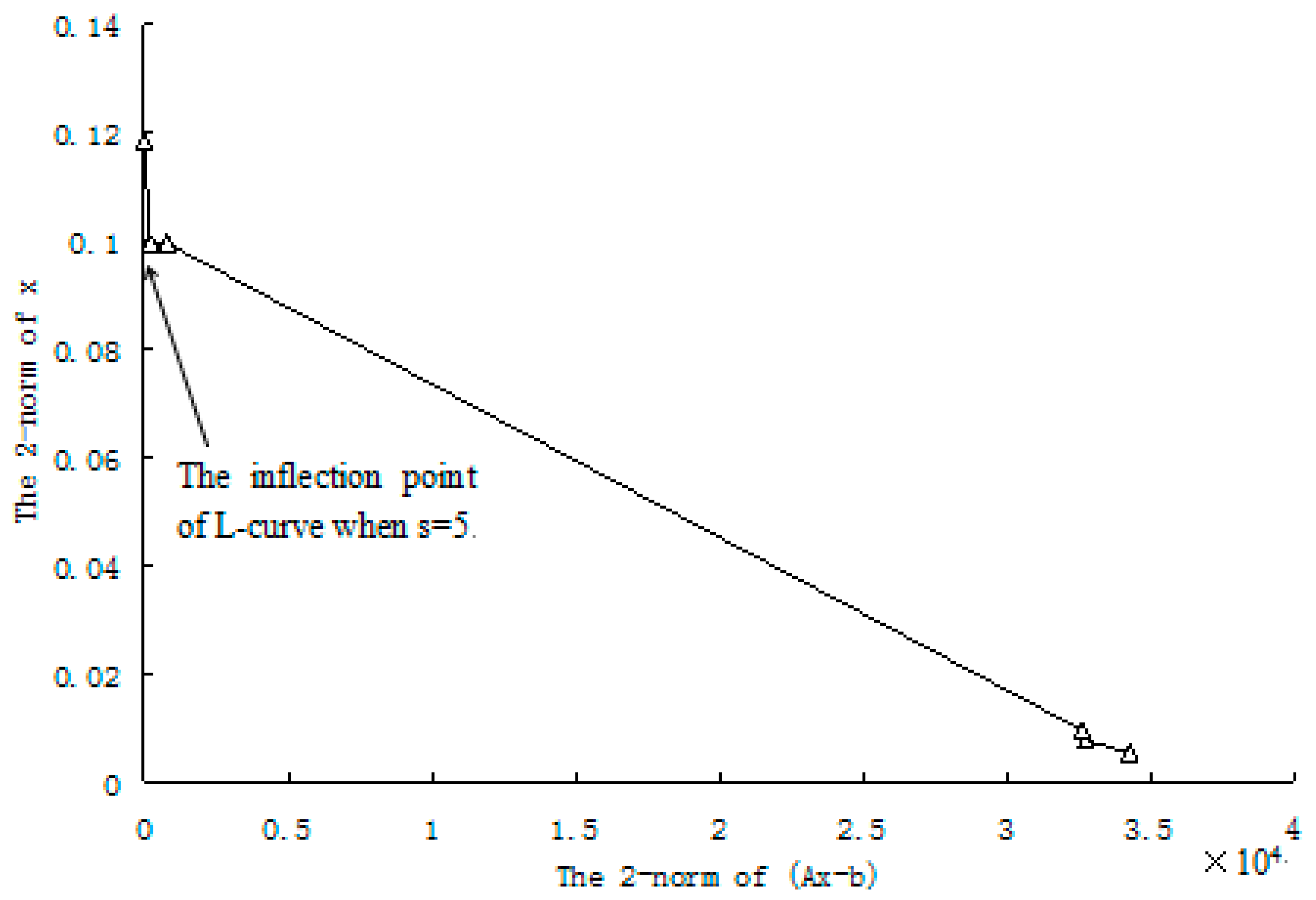
2.2. Enhanced Singular Value Truncation Method
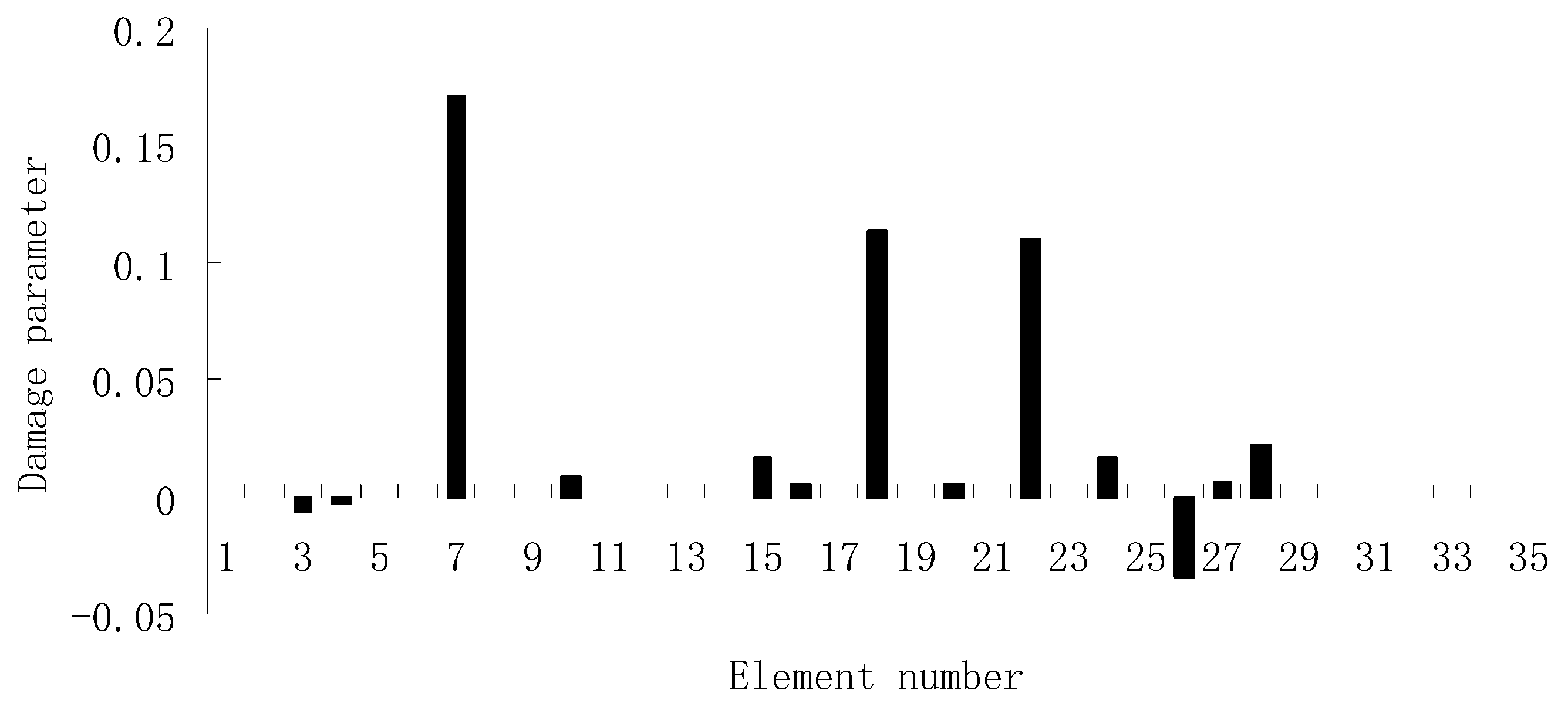
3. Numerical Examples
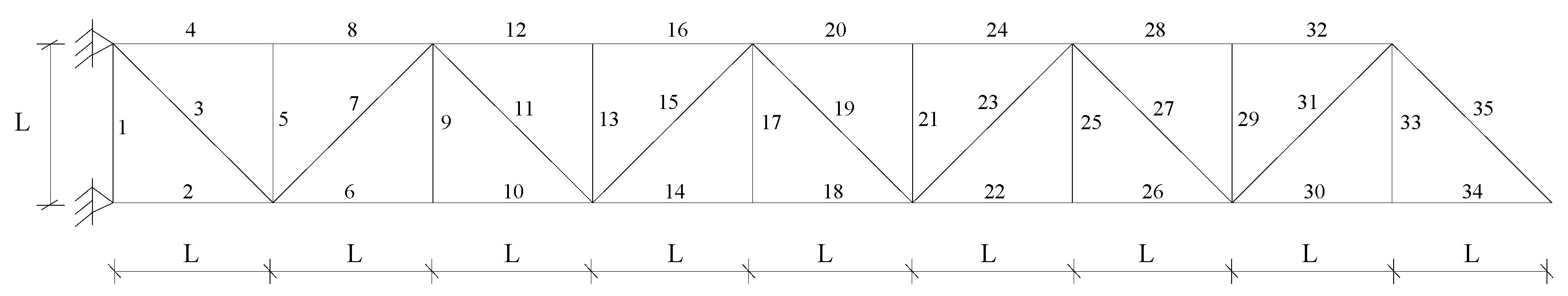
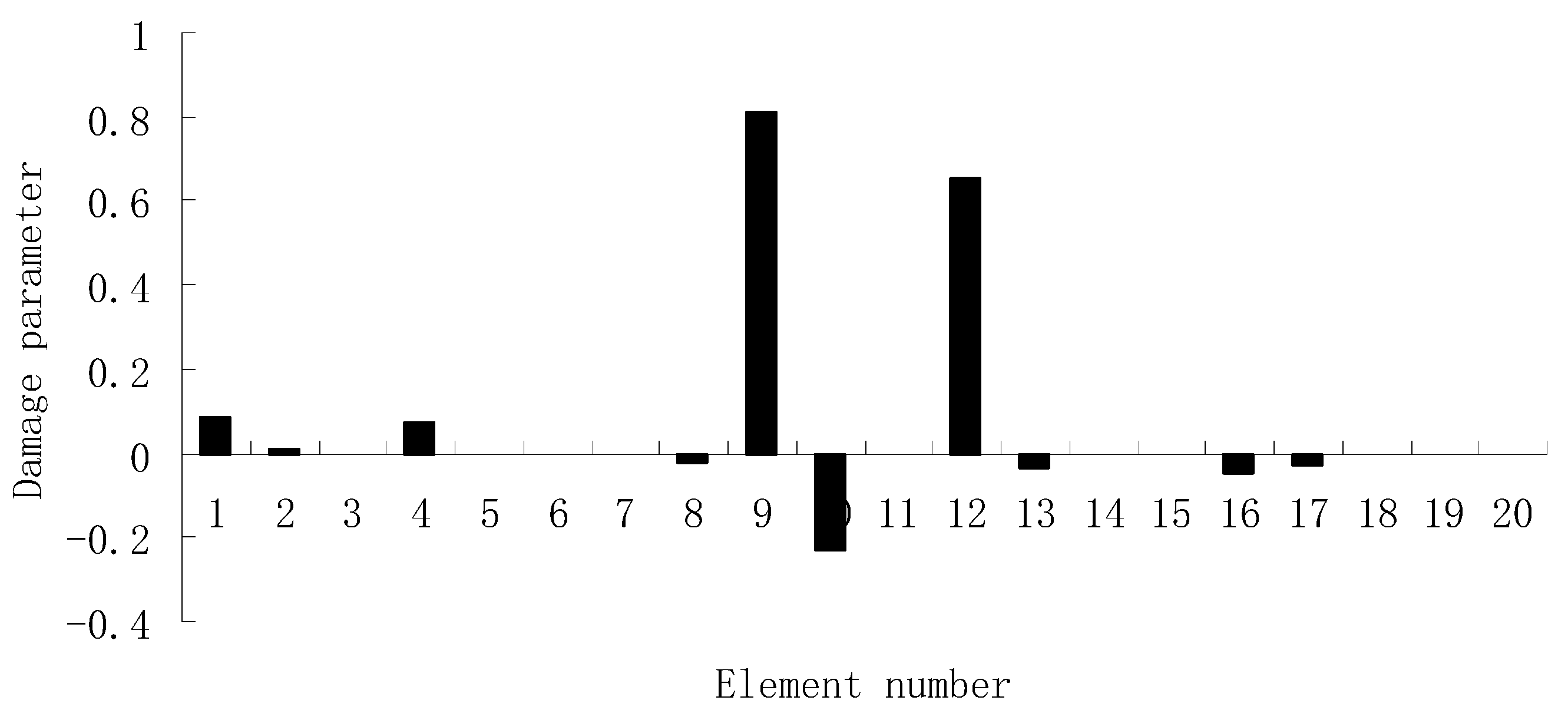
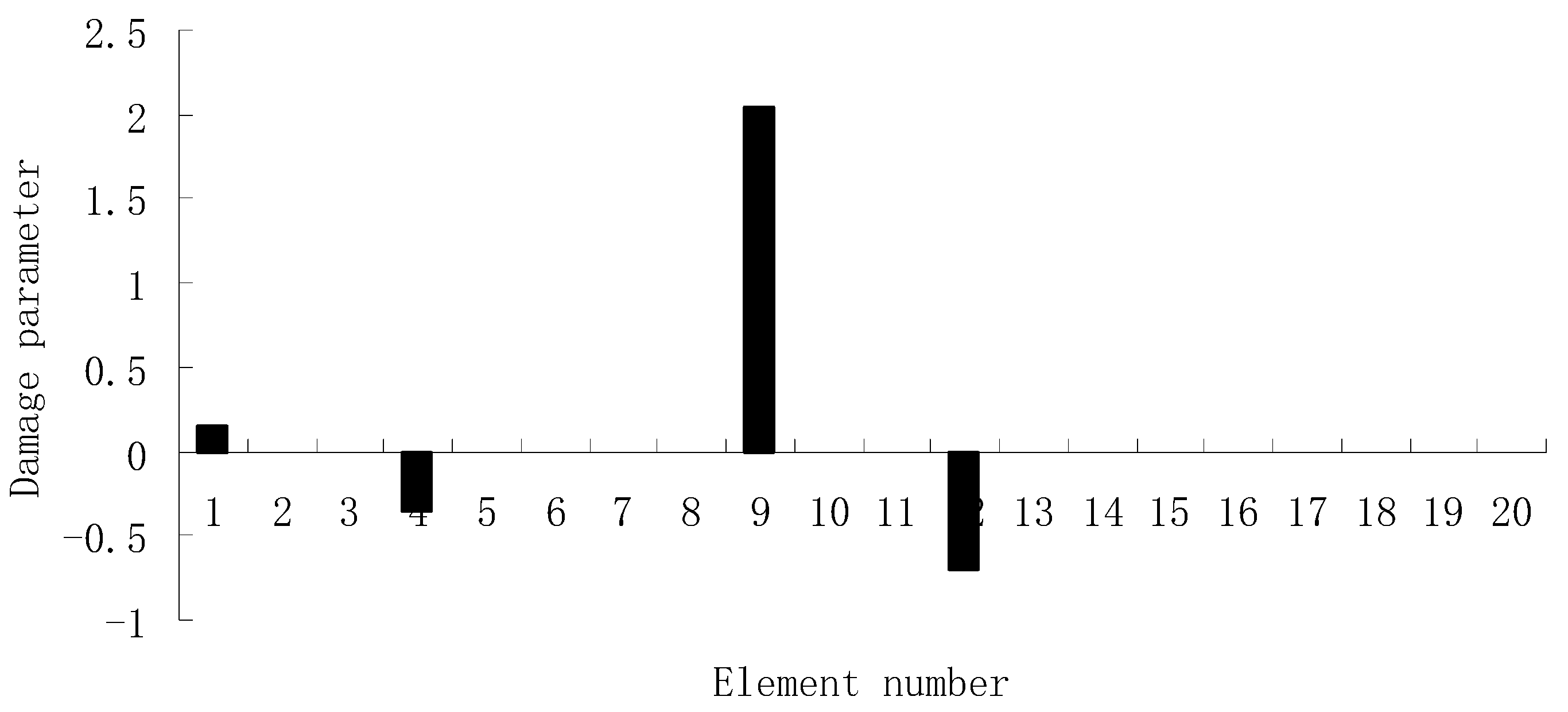
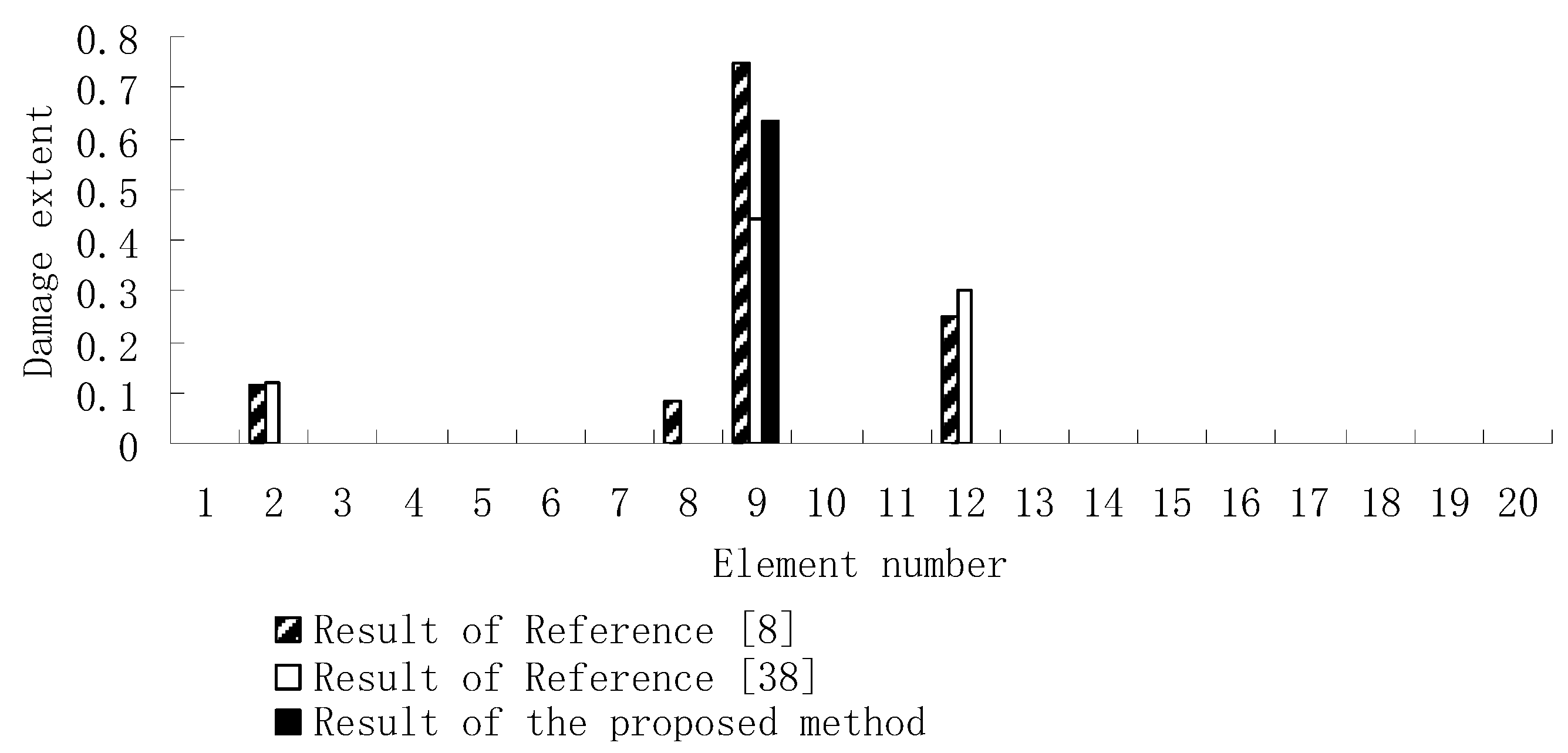
3.1. A Truss Structure
3.2. A Plate Structure
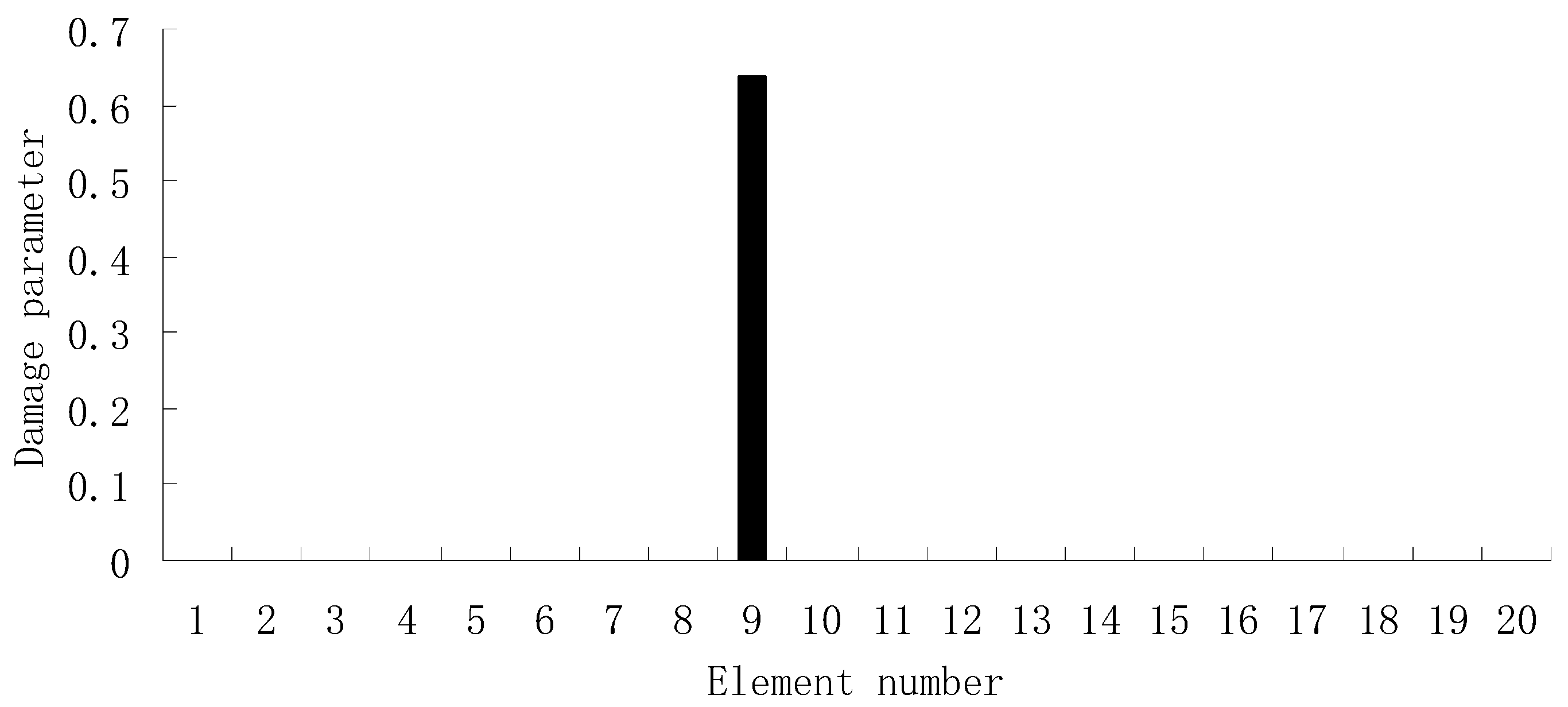
4. Experimental Validation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salawu, O.S. Detection of structural damage through changes in frequency: a review. Eng. Struct. 1997, 19, 718–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.W.; Liu, J.K. A coupled method for structural damage identification. J. Sound Vib. 2006, 296, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, A.; Williams, J.E.; Contursi, T. Structural damage detection by a sensitivity and statistical-based method. J. Sound Vib. 1996, 216, 791–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Cheng, L.; Yam, L.H.; Yan, Y.J. Application of eigenvalue perturbation theory for detecting small structural damage using dynamic responses. Compos. Struct. 2007, 78, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.W.; Liu, J.K. Structural damage identification by adding given masses. Eng. Mech. 2009, 26, 159–163. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Khiem, N.T.; Toan, L.K. A novel method for crack detection in beam-like structures by measurements of natural frequencies. J. Sound Vib. 2014, 333, 4084–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Lu, Z.; Huang, M.; Liu, J. Improved artificial bee colony algorithm for crack identification in beam using natural frequencies only. Inverse Prob. Sci. Eng. 2017, 25, 218–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnanunni, C.G.; Raj, R.S.; Nandan, D.; Midhun, C.K.; Sajith, A.S.; Ameen, M. Sensitivity-based damage detection algorithm for structures using vibration data. J. Civ. Struct. Health Monit. 2019, 9, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, A.J.; Han, J.H. Frequency-based damage detection in cantilever beam using vision-based monitoring system with motion magnification technique. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2018, 29, 3923–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, J.; Ramakrishnan, K.R.; Singh, H.K. A novel method of vibration modes selection for improving accuracy of frequency-based damage detection. Composites Part B 2019, 159, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercolani, G.D.; Felix, D.H.; Ortega, N.F. Crack detection in prestressed concrete structures by measuring their natural frequencies. J. Civ. Struct. Health Monit. 2018, 8, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicanic, N.; Chen, H.P. Damage identification in framed structures using natural frequencies. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 1997, 40, 4451–4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Hao, H.; Brownjohn, J.M.W.; Xia, P.Q. Damage identification of structures with uncertain frequency and mode shape data. Earthquake Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2002, 31, 1053–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udwadia, F.E. Structural identification and damage detection from noisy modal data. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2005, 18, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, P.; Yang, Y.; Xu, D. An improved EMD method for modal identification and a combined static-dynamic method for damage detection. J. Sound Vib. 2018, 420, 242–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakha, M.A. On the Moore–Penrose generalized inverse matrix. Appl. Math. Comput. 2004, 158, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrar, C.R.; Doebling, S.W.; Nix, D.A. Vibration—Based structural damage identification. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 2001, 359, 131–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggiero, E.J.; Park, G.; Inman, D.J. Multi-input multi-output vibration testing of an inflatable torus. Mech. Syst. Sig. Process. 2004, 18, 1187–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodano, H.A.; Park, G.; Inman, D.J. An investigation into the performance of macro-fiber composites for sensing and structural vibration applications. Mech. Syst. Sig. Process. 2004, 18, 683–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foti, D.; Diaferio, M.; Giannoccaro, N.I.; Mongelli, M. Ambient vibration testing, dynamic identification and model updating of a historic tower. NDT and E Int. 2012, 47, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumaier, A. Solving ill-conditioned and singular linear systems: A tutorial on regularization. SIAM Rev. 1998, 40, 636–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basseville, M.; Mevel, L.; Goursat, M. Statistical model-based damage detection and localization: subspace-based residuals and damage-to-noise sensitivity ratios. J. Sound Vib. 2004, 275, 769–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.P. Application of regularization methods to damage detection in large scale plane frame structures using incomplete noisy modal data. Eng. Struct. 2008, 30, 3219–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, B.; Paultre, P.; Proulx, J. Consistent regularization of nonlinear model updating for damage identification. Mech. Syst. Sig. Process. 2009, 23, 1965–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Law, S.S. Adaptive Tikhonov regularization for damage detection based on nonlinear model updating. Mech. Syst. Sig. Process. 2010, 24, 1646–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Gardoni, P.; Hurlebaus, S.A. probabilistic damage detection approach using vibration-based nondestructive testing. Struct. Saf. 2012, 38, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Lin, R.; Meng, Z.; He, G.; You, L.; Zhou, Y. A modified truncation singular value decomposition method for solving ill-posed problems. J. Algorithms Comput. Technol. 2018, 1748301818813609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcucci, R.; Mottet, L.; Pain, C.; Guo, Y.K. Optimal reduced space for Variational Data Assimilation. J. Comput. Phys. 2019, 379, 51–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golub, G.H.; Van Loan, C.F. An analysis of the total least squares problem. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 1980, 17, 883–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markovsky, I.; Van Huffel, S. Overview of total least-squares methods. Signal Process. 2007, 87, 2283–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.; Xiao, W.; Xie, L. Total least squares method for robust source localization in sensor networks using TDOA measurements. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2011, 7, 172902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Jin, Y.; Li, L. An improved weighted total least squares method with applications in linear fitting and coordinate transformation. J. Surv. Eng. 2011, 137, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, L.; Liu, Z.; Wang, G. A robust total Kalman filter algorithm with numerical evaluation. Surv. Rev. 2019, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, P.C. Analysis of discrete ill-posed problems by means of the L-curve. SIAM Rev. 1992, 34, 561–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, P.C.; O’Leary, D.P. The use of the L-curve in the regularization of discrete ill-posed problems. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 1993, 14, 1487–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichel, L.; Sadok, H. A new L-curve for ill-posed problems. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2008, 219, 493–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.S.; Tsai, T.; PEVLIN, V. Structural damage detection by the system identification technique. Shock Vibr. Bull. 1985, 55, 57–65. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, H.; Xia, Y. Vibration-based damage detection of structures by genetic algorithm. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2002, 16, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
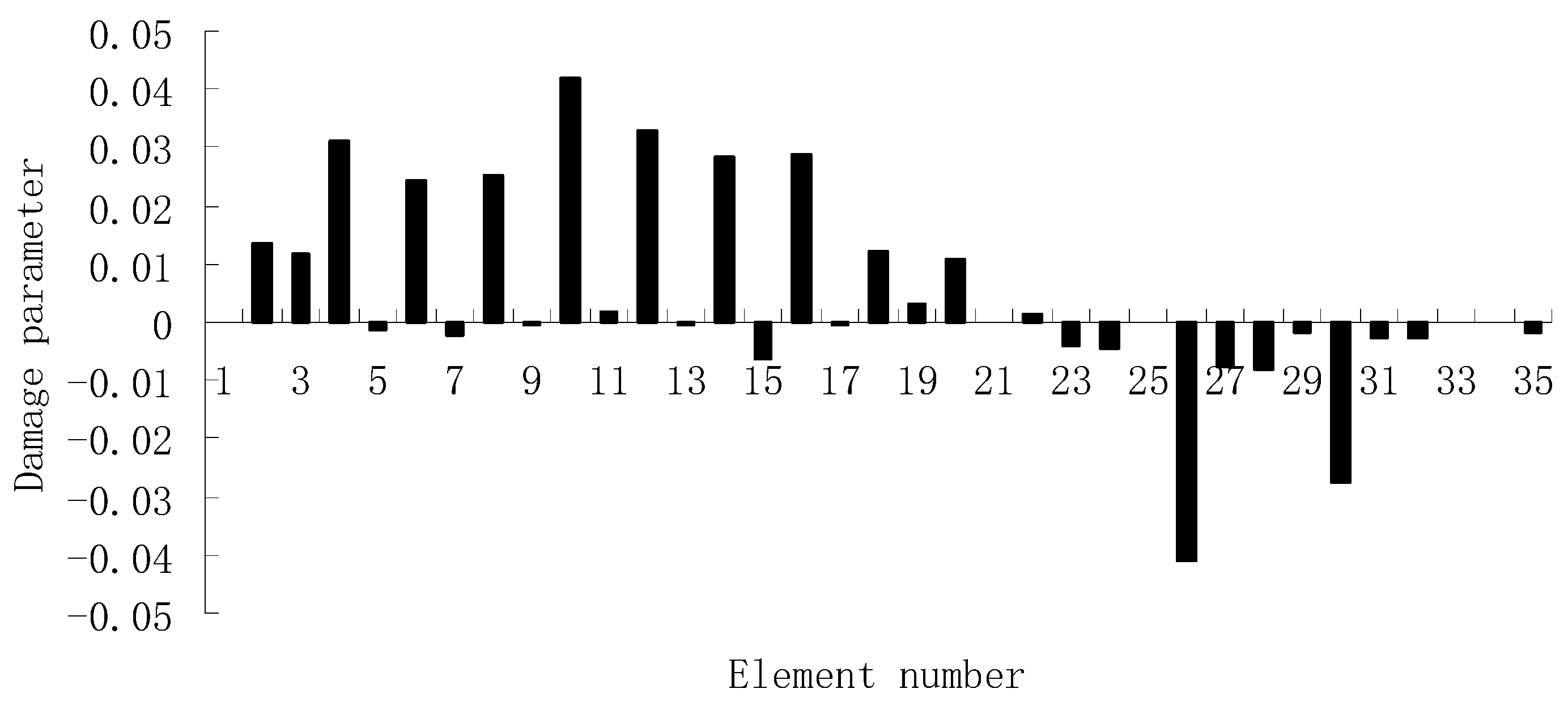
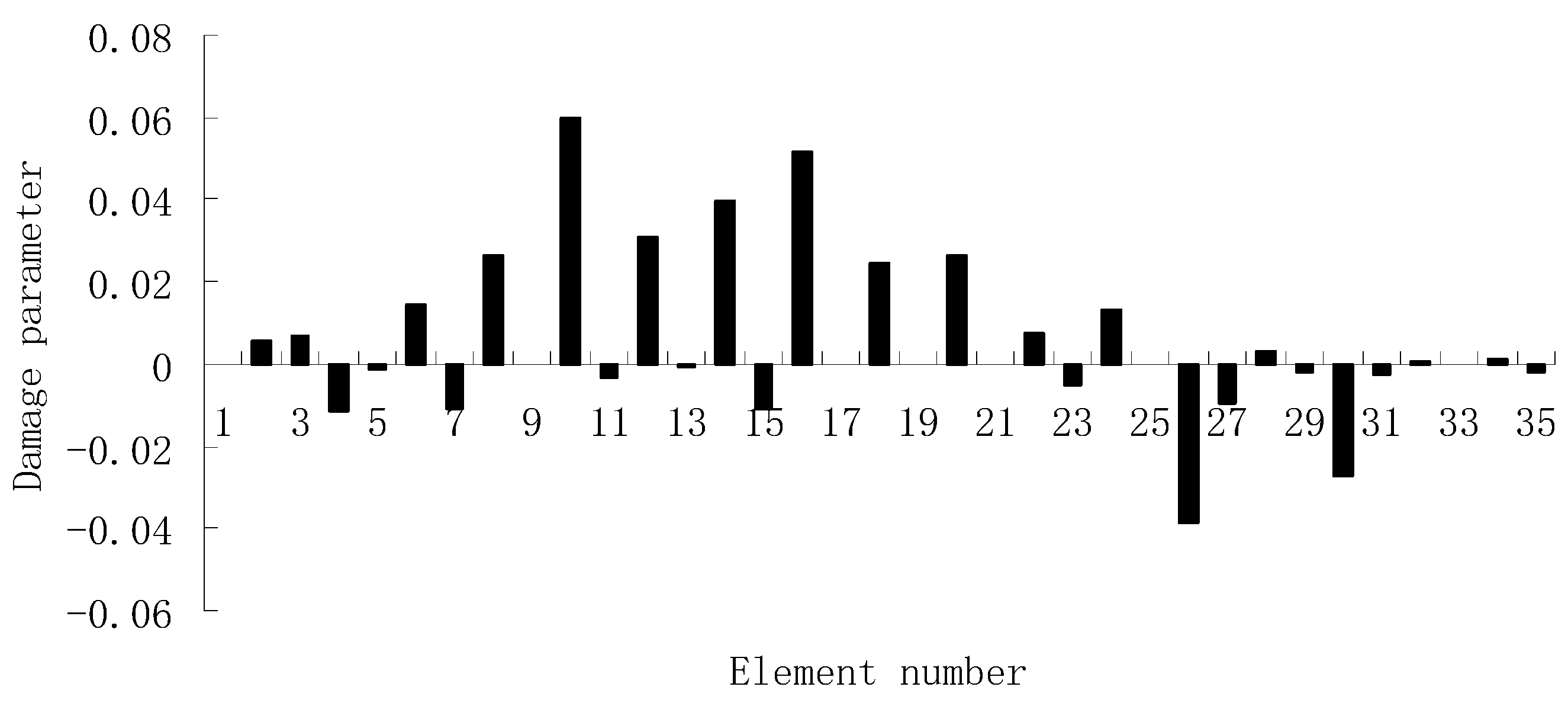
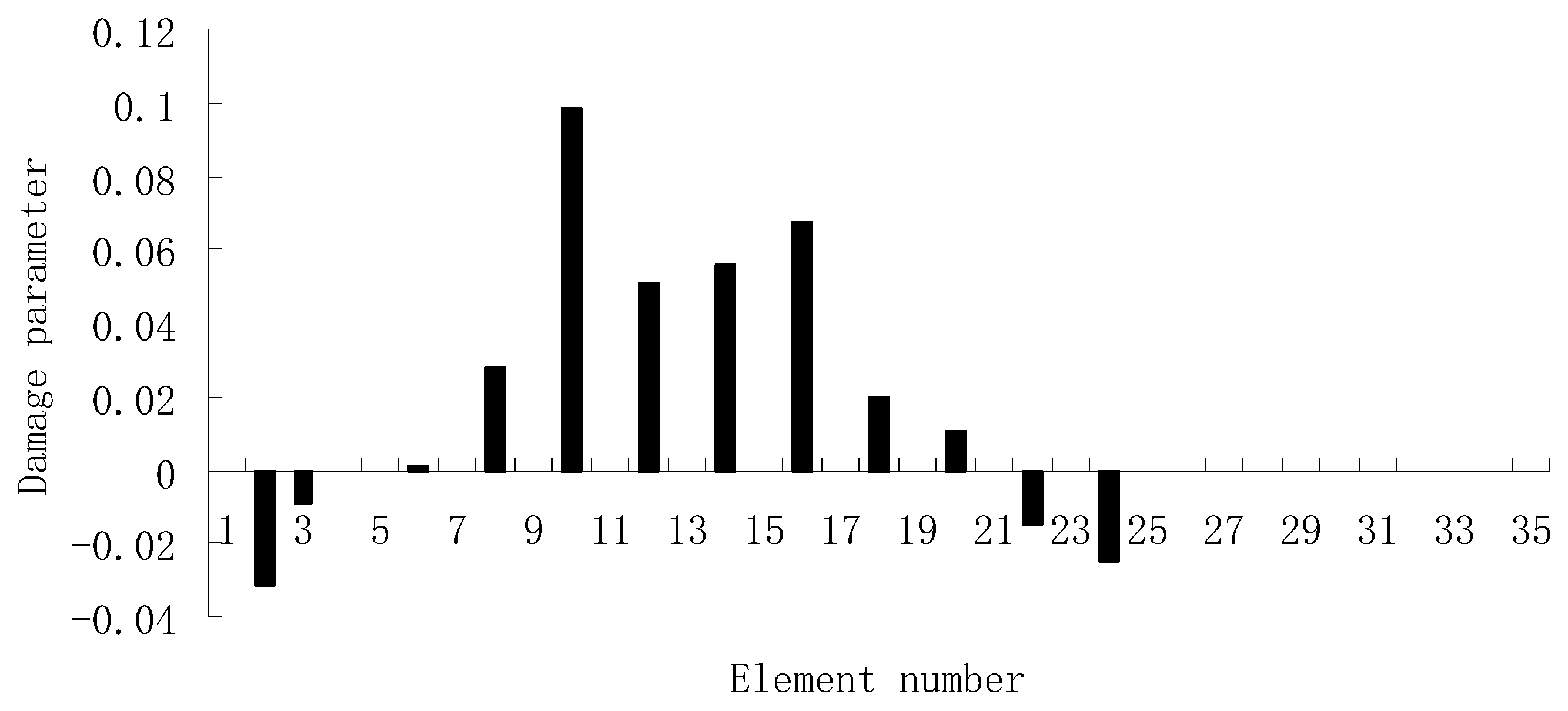
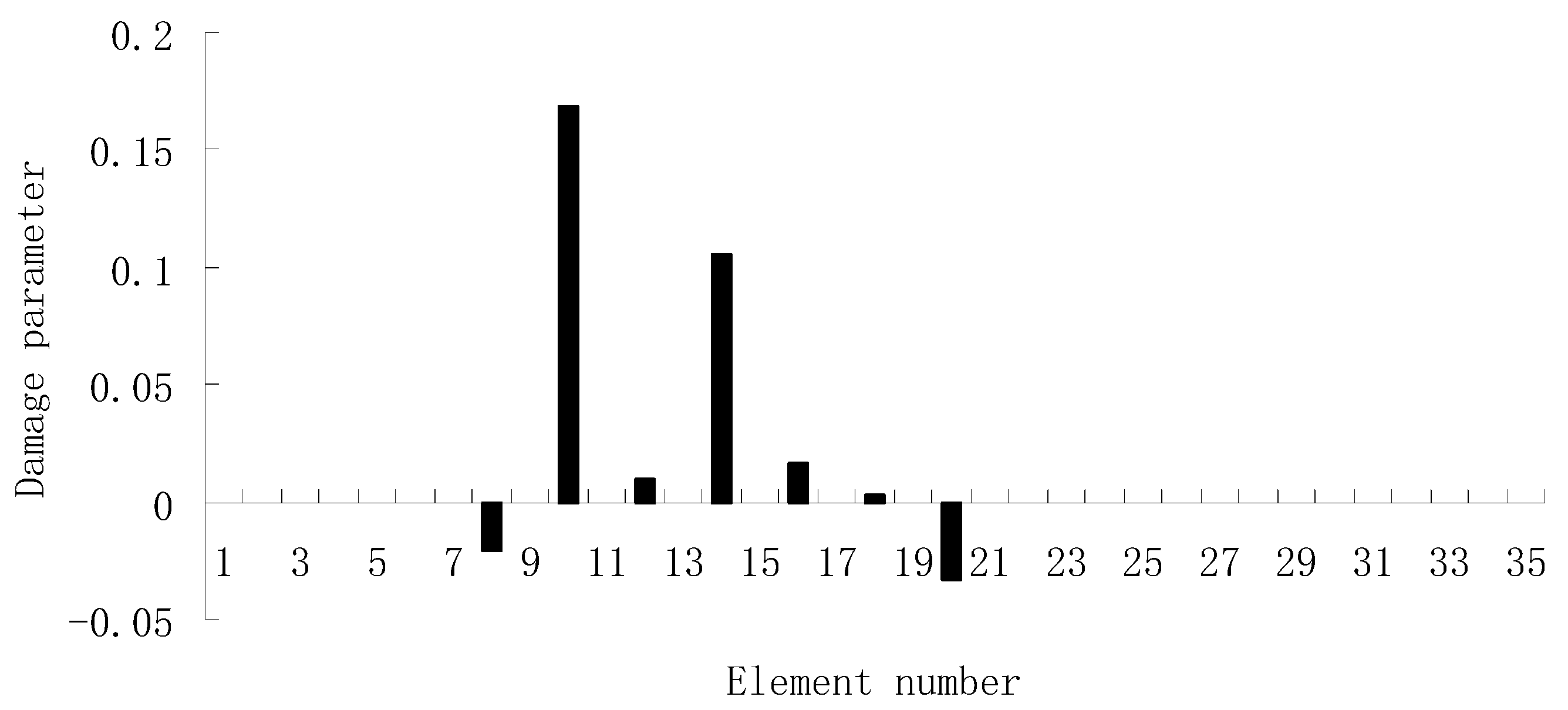
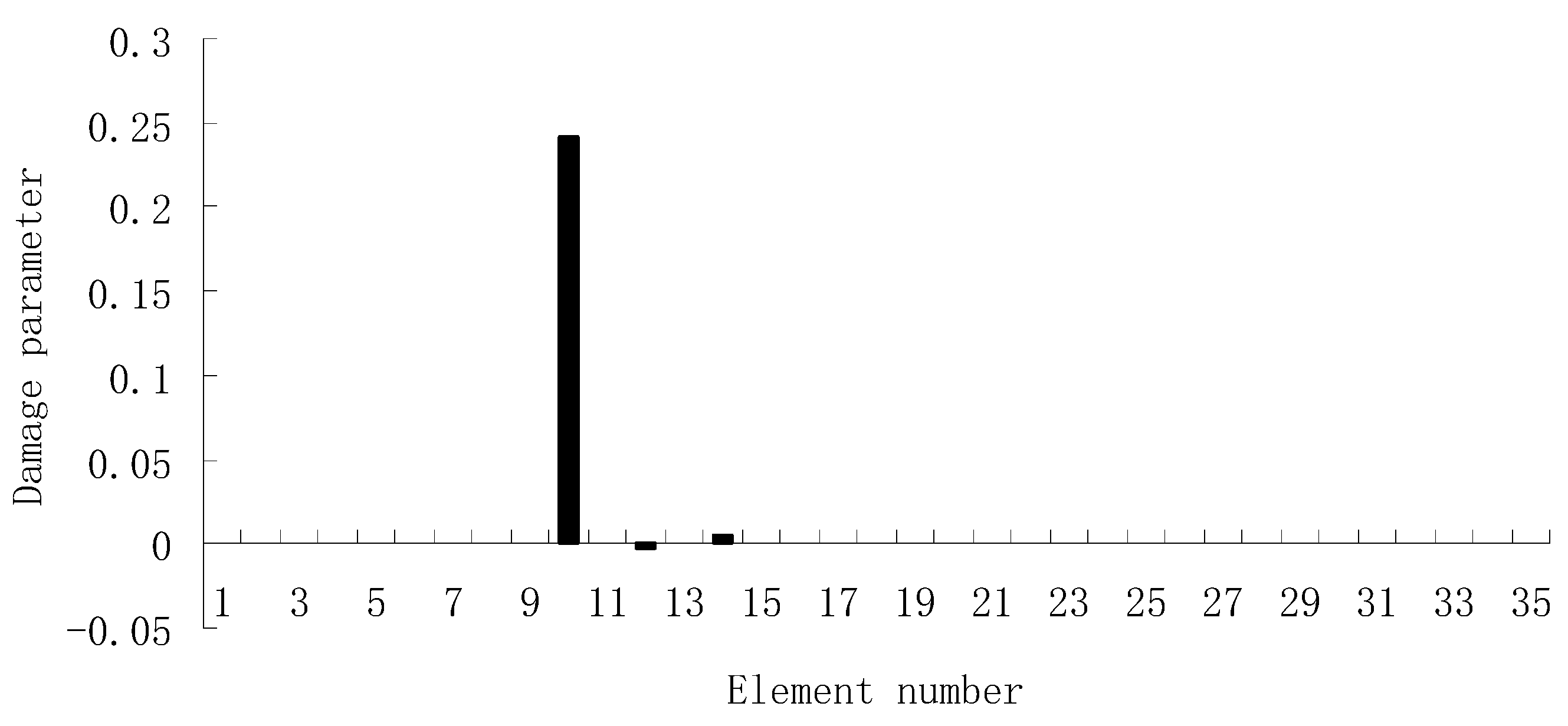
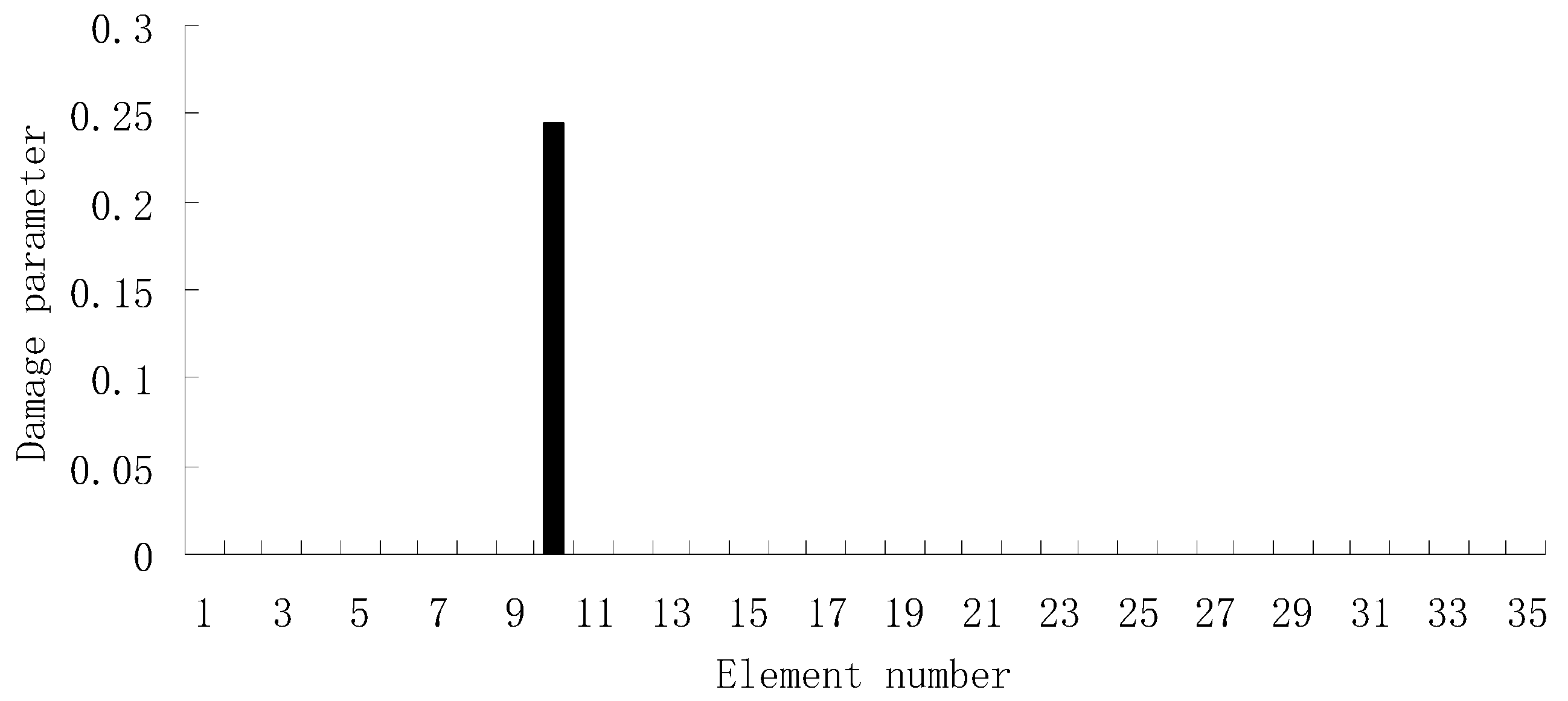

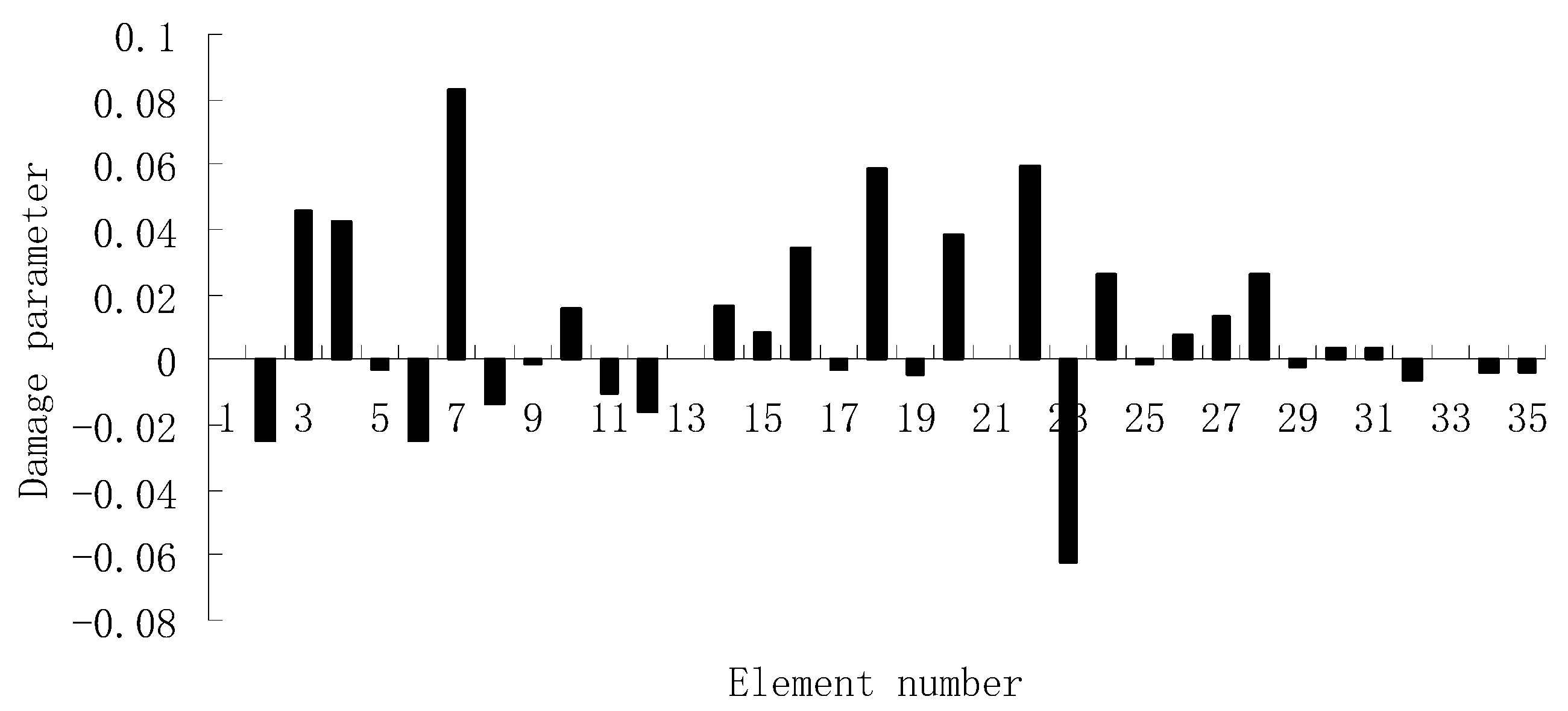

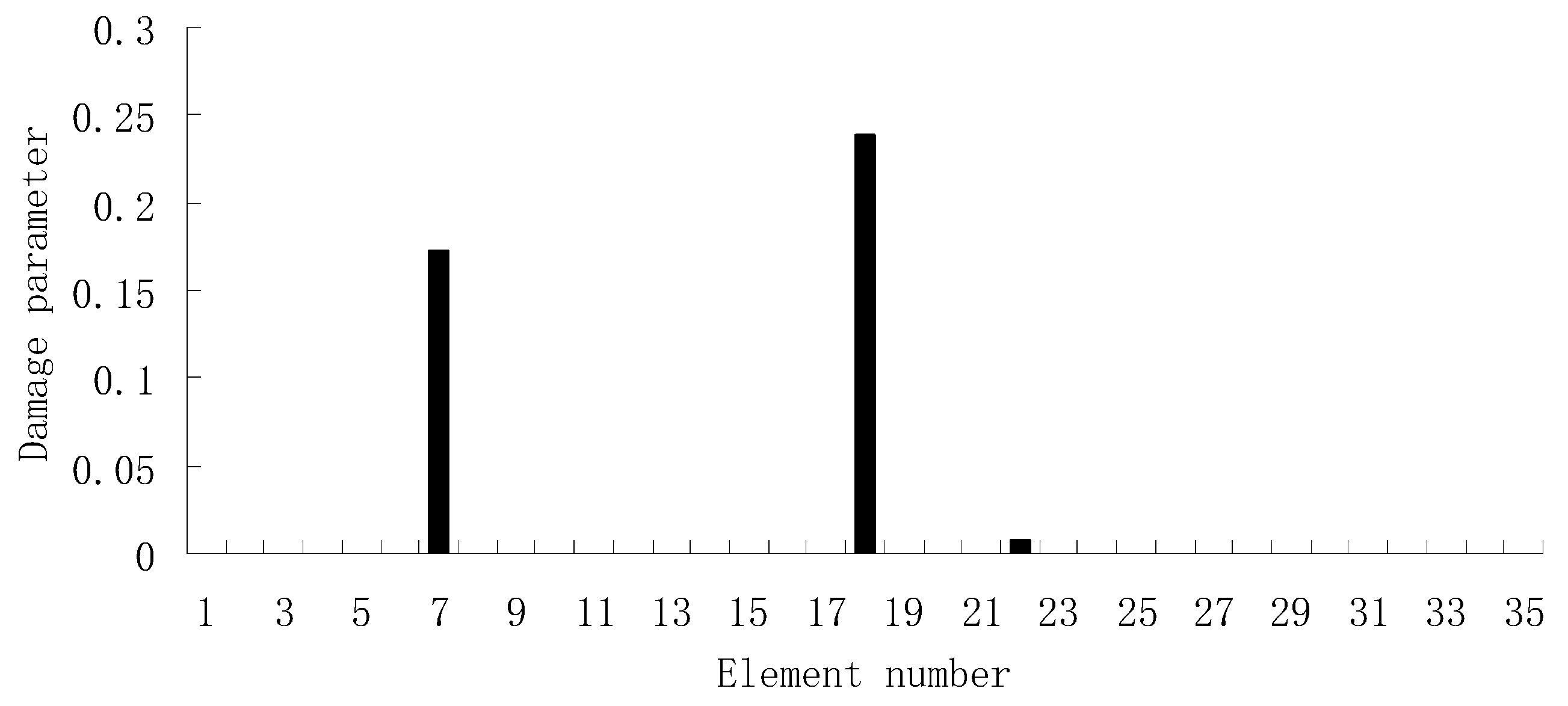
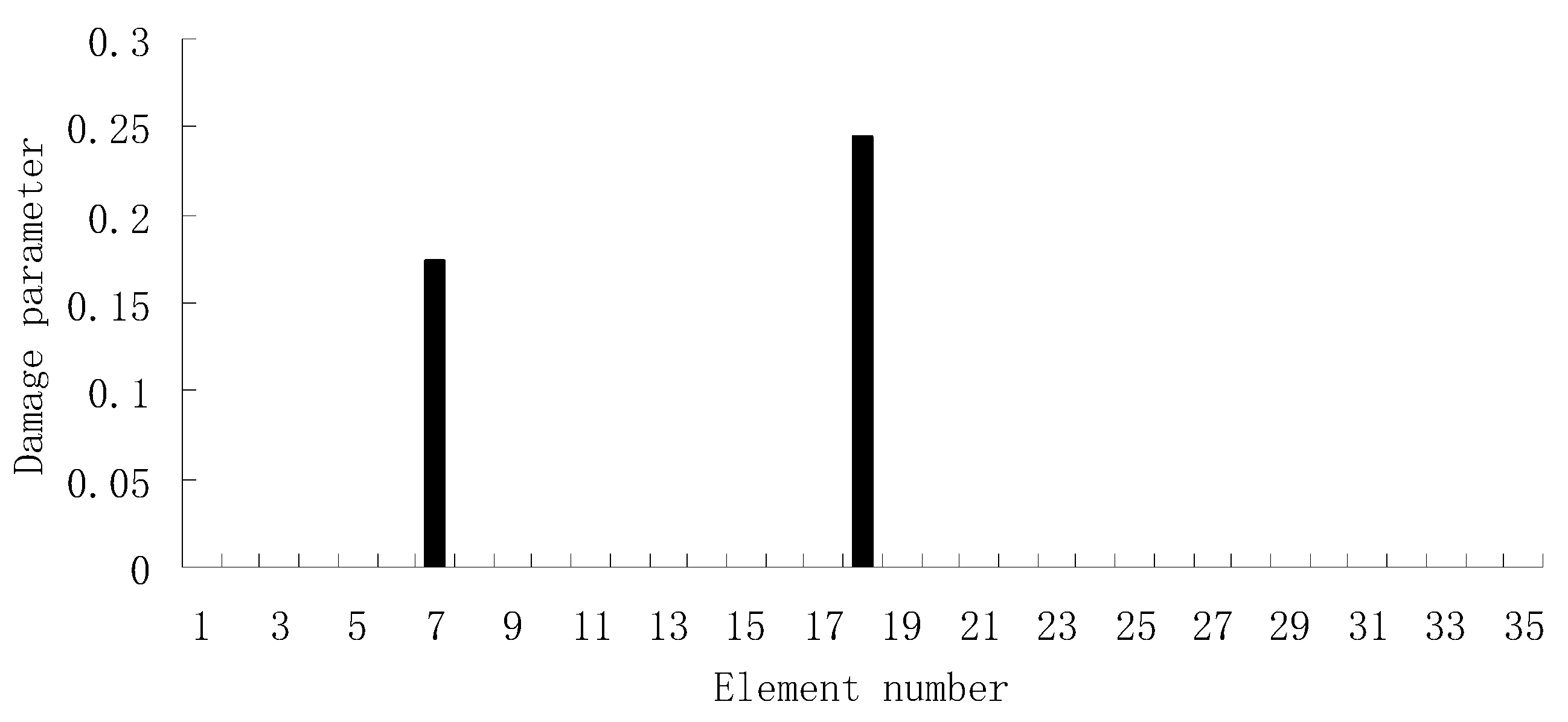
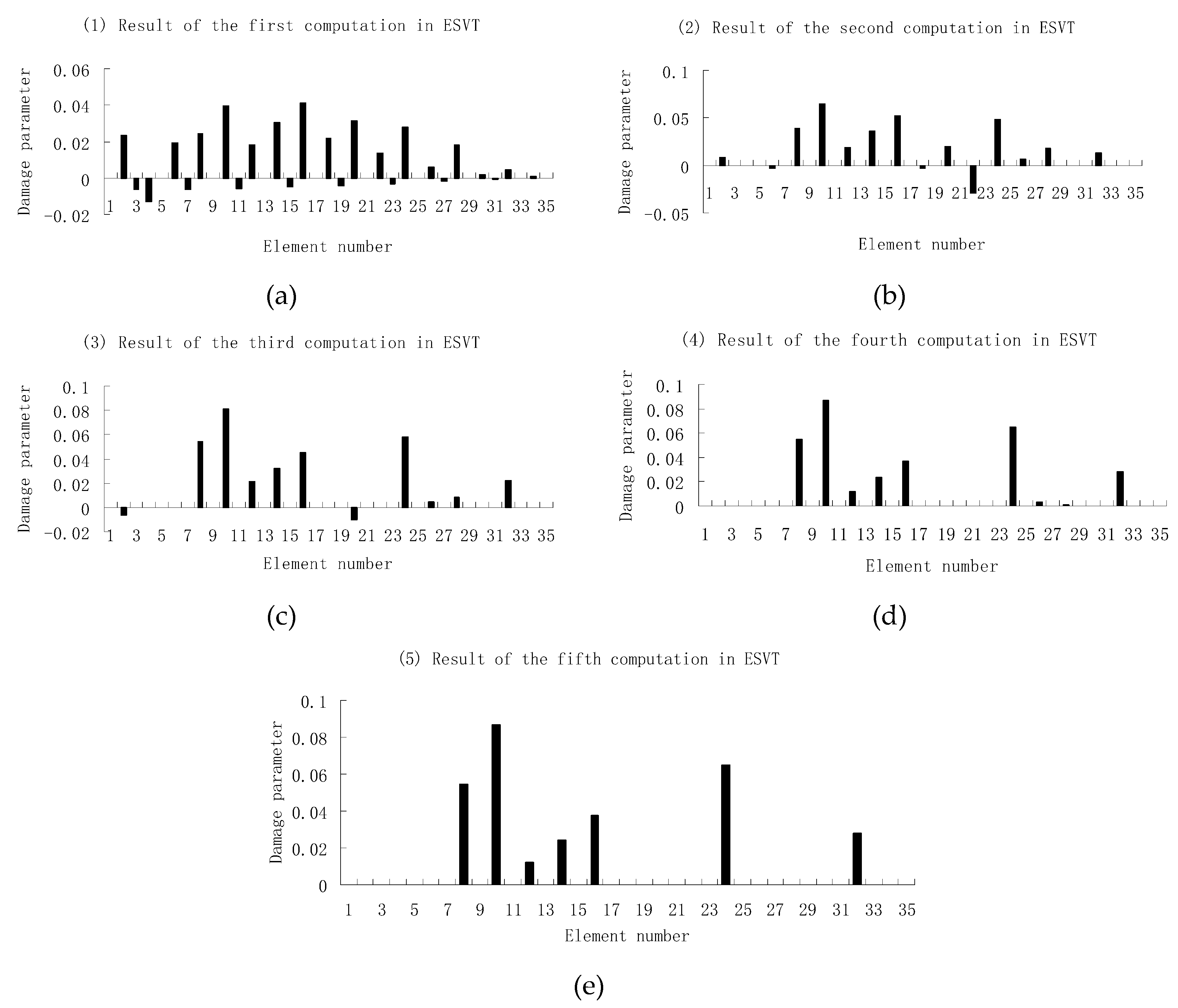

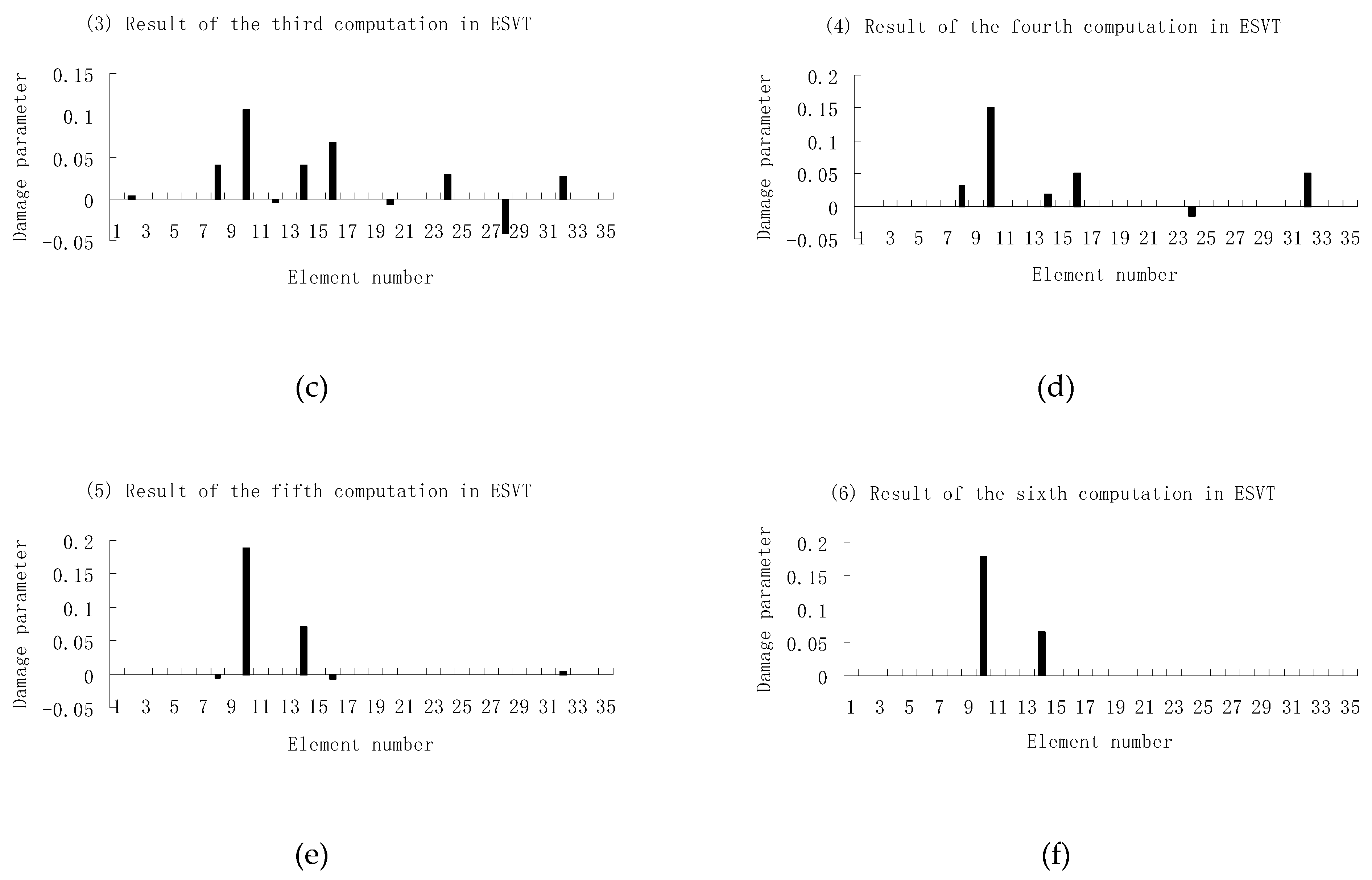
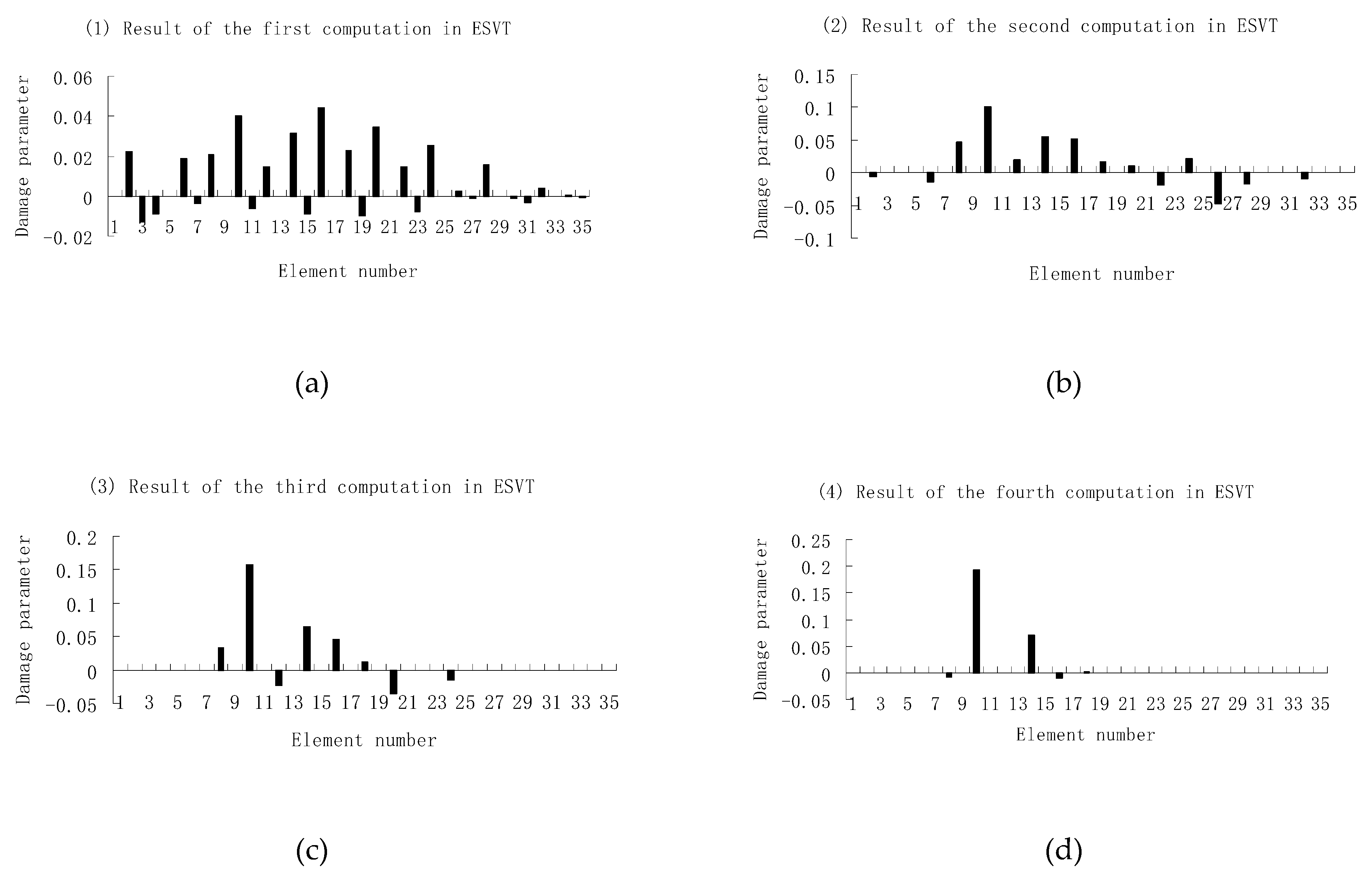
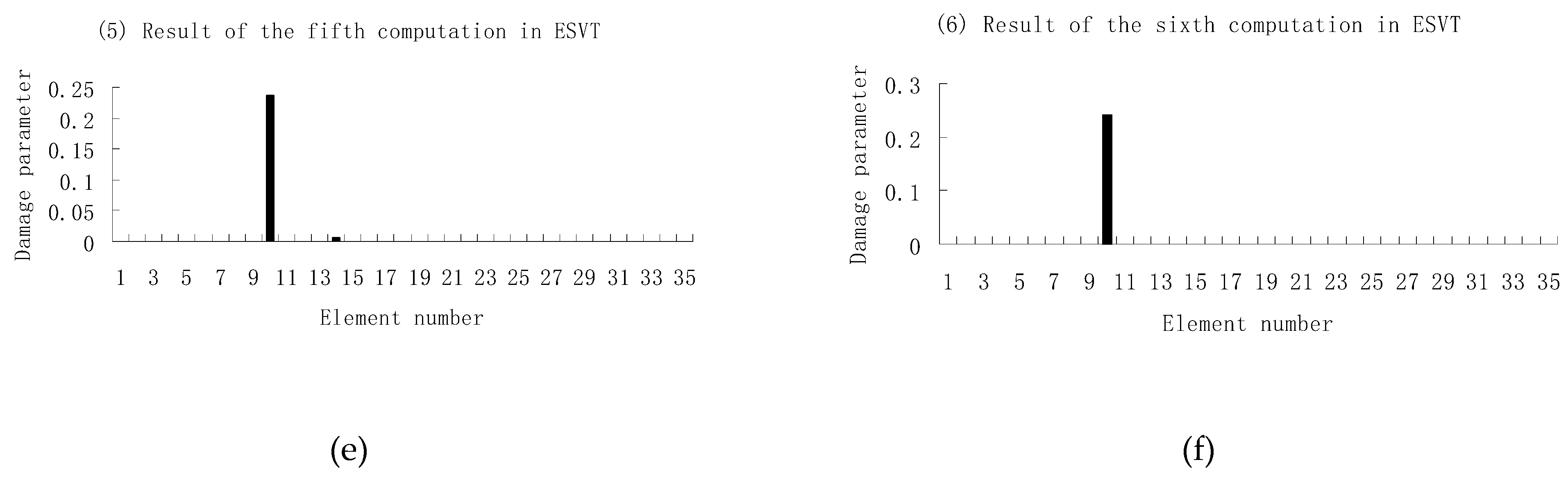
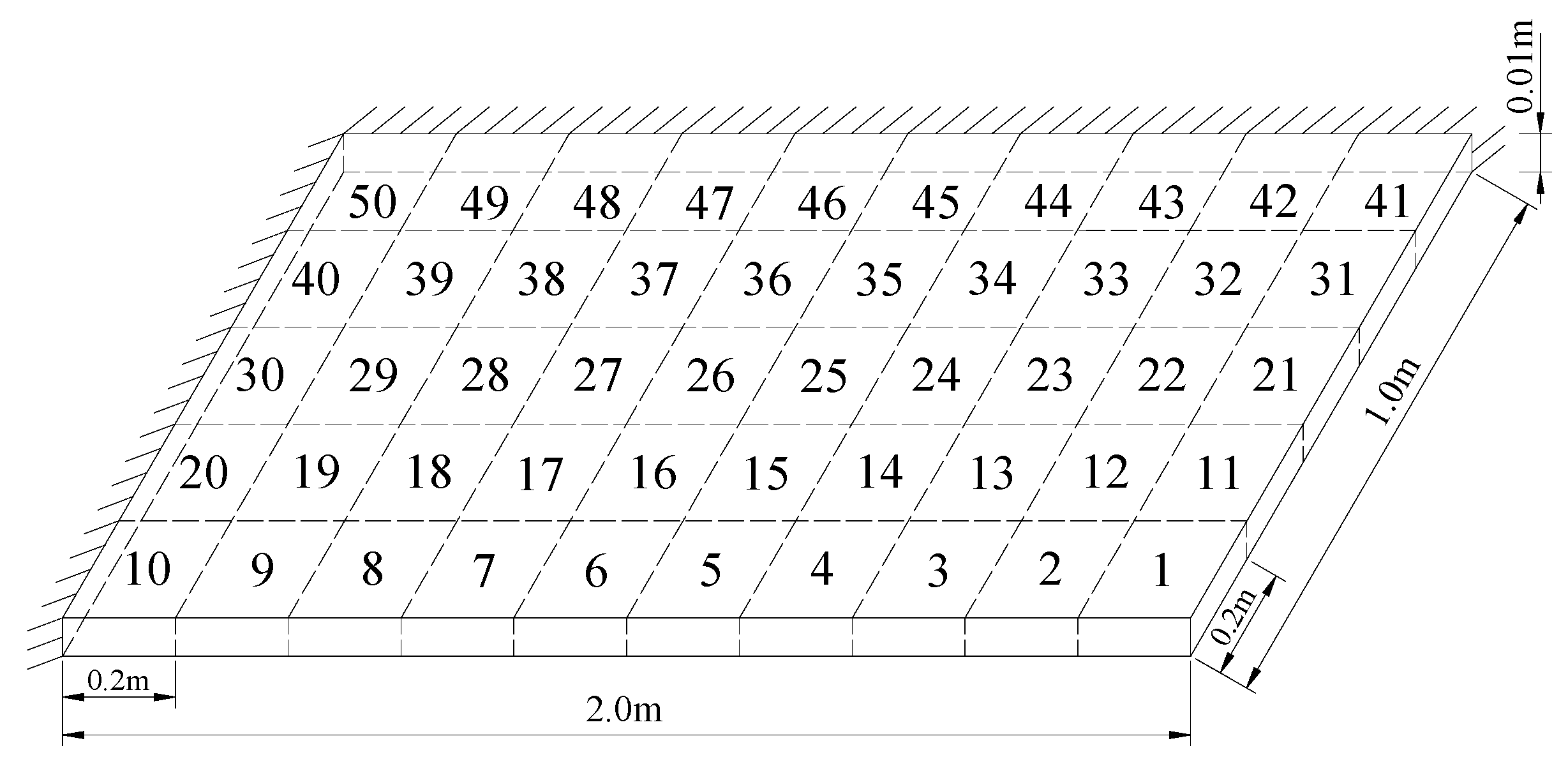
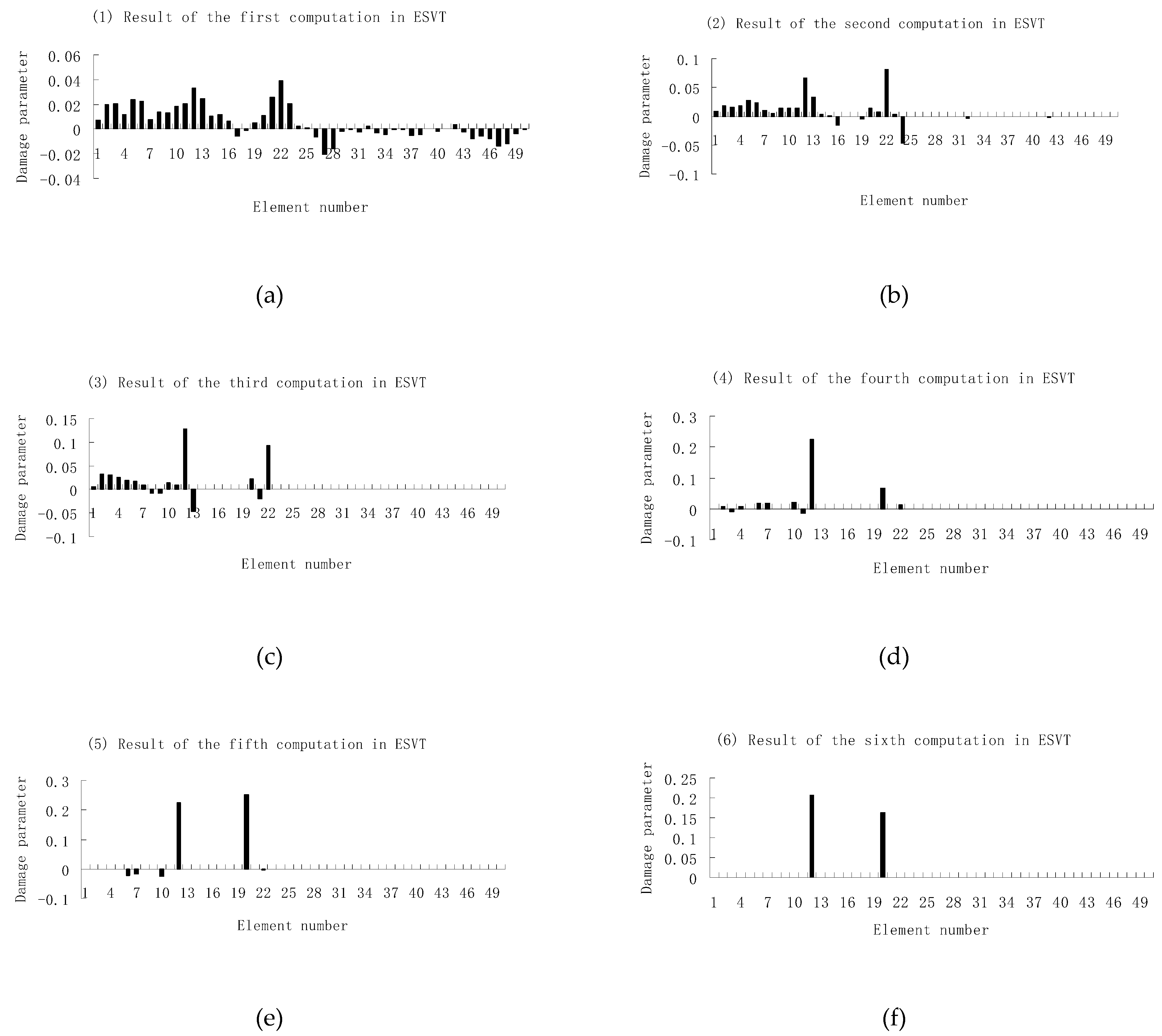
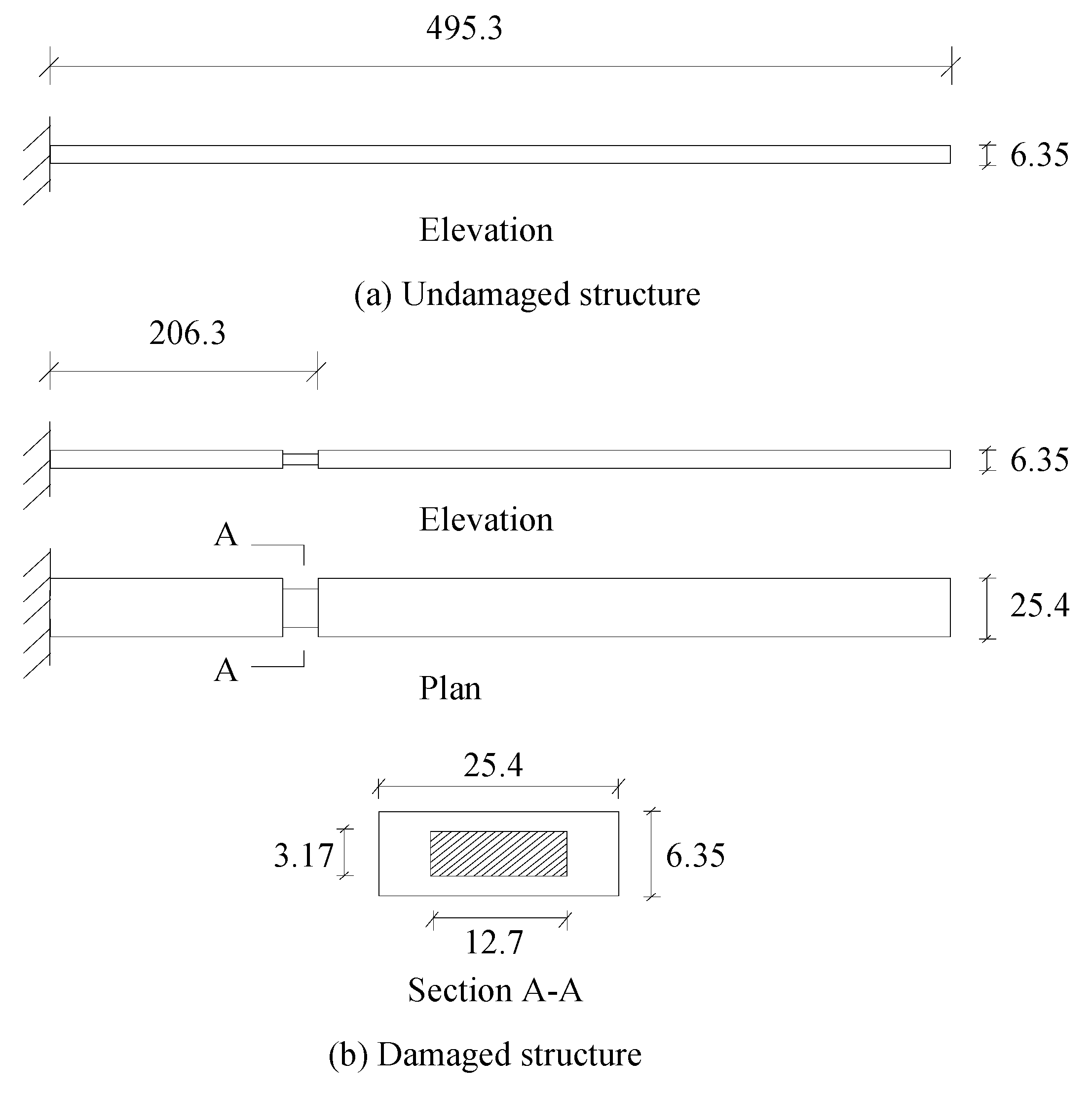
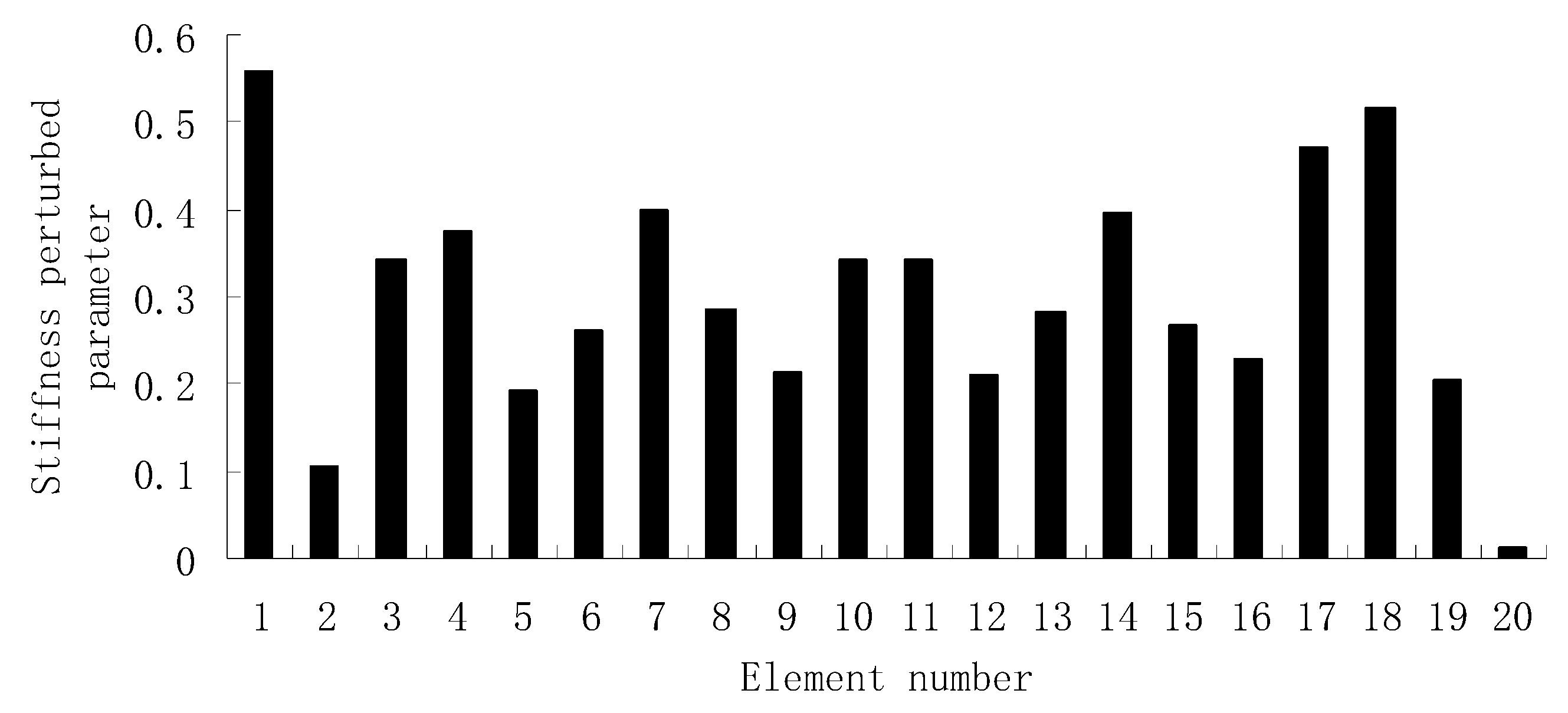

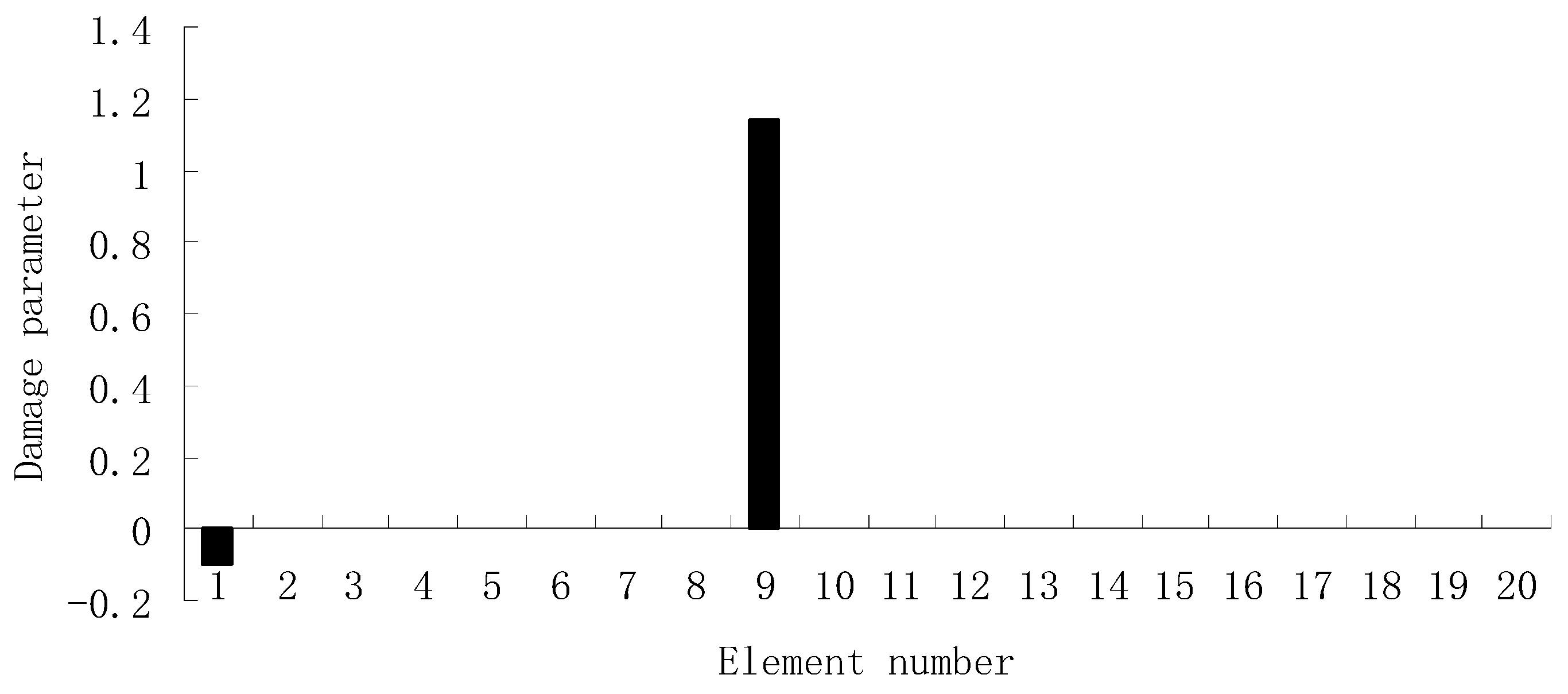
| Natural Frequencies | Undamaged Structure | Damage Case 1 | Damage Case 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 24.034 | 23.8588 | 23.9621 |
| 2 | 119.9908 | 119.3298 | 117.8529 |
| 3 | 195.9065 | 193.7641 | 194.9649 |
| 4 | 274.2121 | 273.7942 | 270.9942 |
| 5 | 436.9691 | 436.5461 | 436.3045 |
| 6 | 569.0272 | 568.812 | 565.0954 |
| Natural Frequencies | Analytical Values (Hz) | Experimental Values (Undamaged) | Experimental Values (Damaged) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 23.7 | 19.53 | 19.00 |
| 2 | 148.5 | 122.05 | 115.85 |
| 3 | 415.7 | 339.26 | 332.36 |
| 4 | 814.2 | 661.73 | 646.91 |
| 5 | 1345.3 | 1085.22 | 1037.46 |
| 6 | 2008.7 | 1594.59 | 1591.36 |
| Natural Frequencies | Analytical Values of Original FEM (Hz) | Experimental Values (Undamaged Beam) | Analytical Values of Modified FEM (Hz) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 23.7 (21.4%*) | 19.53 | 19.0 (2.7%) |
| 2 | 148.5 (21.7%) | 122.05 | 119.8 (1.8%) |
| 3 | 415.7 (22.5%) | 339.26 | 333.7 (1.6%) |
| 4 | 814.2 (23.0%) | 661.73 | 651.2 (1.6%) |
| 5 | 1345.3 (24.0%) | 1085.22 | 1068.7 (1.5%) |
| 6 | 2008.7 (26.0%) | 1594.59 | 1582.6 (0.8%) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Q.; Wang, C.; Li, N.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y. Enhanced Singular Value Truncation Method for Non-Destructive Evaluation of Structural Damage Using Natural Frequencies. Materials 2019, 12, 1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12071021
Yang Q, Wang C, Li N, Wang W, Liu Y. Enhanced Singular Value Truncation Method for Non-Destructive Evaluation of Structural Damage Using Natural Frequencies. Materials. 2019; 12(7):1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12071021
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Qiuwei, Chaojun Wang, Na Li, Wei Wang, and Yong Liu. 2019. "Enhanced Singular Value Truncation Method for Non-Destructive Evaluation of Structural Damage Using Natural Frequencies" Materials 12, no. 7: 1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12071021
APA StyleYang, Q., Wang, C., Li, N., Wang, W., & Liu, Y. (2019). Enhanced Singular Value Truncation Method for Non-Destructive Evaluation of Structural Damage Using Natural Frequencies. Materials, 12(7), 1021. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12071021






