Abstract
BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α was prepared via the sol-gel method using zirconium nitrate, ytterbium trioxide, cerium nitrate and barium acetate as raw materials. Subsequently, it reacted with the binary NaCl~KCl salt to obtain BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α-NaCl~KCl composite electrolyte. The structure, morphology, conductivity and fuel cell performance of the obtained samples were investigated. Scanning electron microscope (SEM) images showed that BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α and NaCl~KCl combined with each other to form a homogeneous 3-D reticulated structure. The highest power density and conductivity of BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α-NaCl~KCl was 393 mW·cm−2 and 3.0 × 10−1 S·cm−1 at 700 °C, respectively.
1. Introduction
Fuel cells have many merits, such as diversity of fuel options, being environmentally friendly and having high energy efficiency [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8]. BaCeO3 and SrCeO3-based perovskite oxides have excellent protonic conductivities under hydrogen- or water-containing atmosphere at 400–1000 °C [9,10,11,12,13,14,15]. The oxygen vacancies appear when Ce4+ is substituted with trivalent metal cations [16]. Owing to the concentrations of oxygen vacancies and point defect pairs, two opposing factors, the optimum doping level of BaCeO3 and SrCeO3-based electrolytes is usually 10% [17]. Among these doped metal cations, Y3+ and Yb3+ doped BaCeO3 or SrCeO3 have relatively high conductivities [17,18]. The synthetic methods of BaCeO3 and SrCeO3-based electrolytes are solid-state reactions, citrate-nitrate combustions, microemulsions and sol-gel methods [19,20]. The solid-state reaction method requires a high temperature (1550–1700 °C) and the particle size of the product is larger. By comparison, the sol-gel method can mix raw materials at the nanometre level. Moreover, the sintering temperature can be reduced to 200–300 °C.
Intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cells have many advantages, such as good selectivity, durability and low cost [21,22,23,24]. The excellent protonic conduction of BaCeO3-based electrolytes is mainly reflected at high temperatures (700–1000 °C). Also, the conductivities of BaCeO3-based electrolytes are relatively low at intermediate temperatures (400–700 °C). In applying BaCeO3-based electrolytes to intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cells, electrolyte membranes and composite electrolytes have attracted intensive attention in recent years [25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32]. Park et al. reported that the conductivities of composite BaZr0.85Y0.15O3−δ-Nd0.1Ce0.9O2−δ electrolyte are higher than that of single BaZr0.85Y0.15O3−δ above 600 °C [28]. Huang et al. found the conductivities of BaCe0.7Zr0.1Y0.2O3−δ-Li2CO3-Na2CO3 composite electrolyte >0.1 S·cm−1 at 600 °C [32]. Our previous studies indicated that SrCeO3-based oxides-inorganic salt composite electrolytes have good intermediate temperature electrochemical properties [33,34]. Usually, BaCeO3-based electrolytes have higher conductivities than SrCeO3-based ones. To date, there are only a few reports on composite electrolytes of BaCeO3-based ceramic/carbonate [32]. BaCeO3-based electrolytes/chloride composite electrolytes have not been developed and investigated thoroughly.
In this study, BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α was prepared via the sol-gel method and the composite electrolyte of BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α-NaCl~KCl was also synthesized. The morphology, physical chemistry change, and the structure of BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α were studied using SEM, Thermogravimetric Analysis and Differential Scanning Calorimetry (TGA-DSC) and X–ray diffractometer (XRD). The intermediate temperature electrochemical properties of BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α and BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α-NaCl~KCl were also investigated.
2. Materials and Methods
BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α was prepared via the sol-gel method using zirconium nitrate, ytterbium trioxide, cerium nitrate and barium acetate as the raw materials. The stoichiometric metal ion salts (Ba2+:Ce4+:Yb3+ = 10:9:1) were dissolved in deionized water. Citric acid was added (three times as much as the metal ion salts). The pH of the above solution was adjusted to 8.0 with ammonia and heated at 90 °C for 6 h until gelatinous. The xerogel was obtained at 130 °C and heated for the ashing treatment [35,36,37]. The calcination of the resultant ash was carried out at 1250 °C and 1550 °C for 5 h, respectively, to obtain BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α.
A 1:1 mole ratio of NaCl to KCl was heated at 700 °C to form the molten salt [38]. The weight ratio of BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α:NaCl~KCl = 80:20 was mixed and ground. Then, the mixing powders were sintered at 750 °C for 2 h to obtain BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α-NaCl~KCl.
Thermogravimetric Analysis and Differential Scanning Calorimetry (TGA-DSC, Universal V 3.7A, TA Instruments, New Castle, DE, USA) were conducted before and after the ashing treatment of the BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α precursor. The temperature ranged between 25 °C and 1100 °C with a heating rate of 15 °C·min−1. The structures of BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α (1250 °C, 1550 °C) and BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α-NaCl~KCl were determined by X–ray diffractometer (XRD, X’pert Pro MPD, Holland’s company, Amsterdam, Netherlands). From the X-ray spectrogram, the average crystallite size (DXRD) can be calculated from:
where λ is the X-ray wavelength of Cu-Kα radiation (λ = 0.15405 nm), b is the corrected half-width of the diffraction peak and θ is the diffraction angle (°) [35]. The external and cross-sectional surfaces of BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α (1550 °C) and BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α-NaCl~KCl were imaged using a scanning electron microscope (SEM, S-4700, Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan).
DXRD = 0.89λ/bcos θ
For conductivity measurements, BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α (1550 °C) and BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α-NaCl~KCl pellets were processed into wafers (diameter = 16 mm, thickness = 1.0 mm). The electrodes (area = 0.50 cm2) were comprised of 20 wt% Pd and 80 wt% Ag and the wires were pure Ag. The conductivities were investigated utilizing an electrochemical analyzer over the frequency range from 1 Hz to 100 KHz in the air at 400–700 °C as well as with the oxygen partial pressures (pO2) from 1 × 10−20 to 1 atm at 700 °C [8]. The electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) of BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α (1550 °C) and BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α-NaCl~KCl were studied under open circuit conditions. Finally, H2/O2 fuel cells were fabricated and tested.
3. Results and Discussion
TGA-DSC plots for the BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α precursor were measured before and after the ashing treatment. In Figure 1a, the DSC curve has a sharp exothermic peak between 260 °C and 300 °C accompanied by 45% weight loss, mainly attributed to the decomposition of citric acid and ammonium salt. The weight loss is gentle, declining from 510 °C to 580 °C, which is attributed to the decomposition of the nitrate. As seen in Figure 1b, there was a decline in weight loss around 550 °C, which is ascribed to the incomplete decomposition of the nitrate [39,40]. There was almost no weight loss after 1070 °C indicating that the BaCeO3 phase had begun to form.
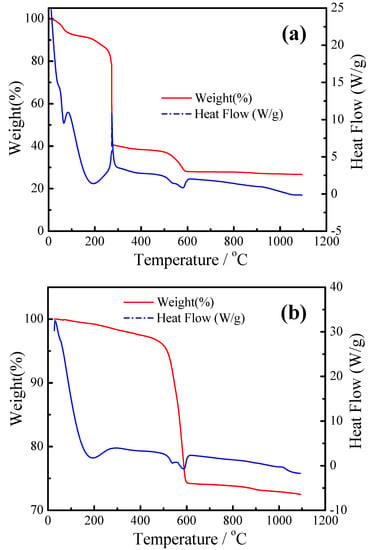
Figure 1.
Thermogravimetric Analysis and Differential Scanning Calorimetry (TGA-DSC) plots for the BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α precursor before (a) and after (b) ashing treatment.
The XRD patterns of BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α (1250 °C, 1550 °C) and BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α-NaCl~KCl are shown in Figure 2. The XRD patterns show that the sintered BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α (1250 °C, 1550 °C) samples are all orthorhombic BaCeO3 phases. The average crystallite sizes (DXRD) of BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α (1250 °C, 1550 °C) samples are 45.9573 nm and 50.2176 nm, respectively. Combined with the results of Figure 1, the first sintering temperature of 1250 °C is suitable. There are some small additional peaks in the BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α-NaCl~KCl XRD spectrum, suggesting that NaCl~KCl inorganic salts exist as crystalline phases in the composite electrolyte [35].
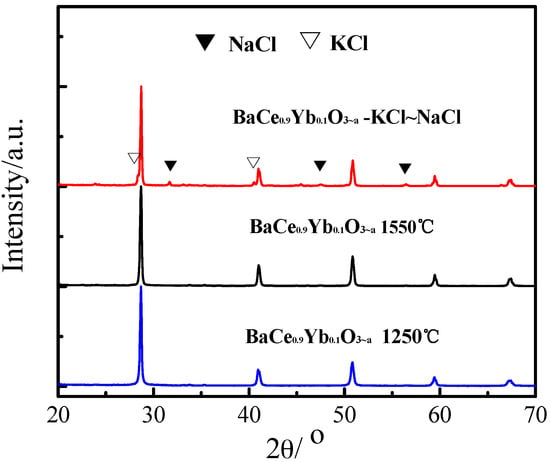
Figure 2.
X–ray diffractometer (XRD) patterns of BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α (1250 °C, 1550 °C) and BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α-NaCl~KCl.
The SEM external and cross-sectional surface images of BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α calcined at 1550 °C for 5 h (Figure 3a,b) and BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α-NaCl~KCl sintered at 750 °C for 2 h (Figure 3c,d) are displayed in Figure 3. As seen in Figure 3a,b, the degree of BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α particle agglomeration is good. However, the fractured surface image of BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α shows that there are still some holes after being calcined at 1550 °C for 5 h, as shown in Figure 3b. It has been proved by our experiments that they are closed holes. In Figure 3c,d, it is clearly visible that the particles of BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α are aggregated into clumps after the addition of NaCl~KCl inorganic salts sintered at 750 °C for 2 h. The regular polyhedron zones correspond to the BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α. Contrastingly, the amorphous areas point to the NaCl~KCl inorganic salt phase. Combined with the results of Figure 2, NaCl~KCl inorganic salts exist as both crystalline and amorphous phases [31,32].
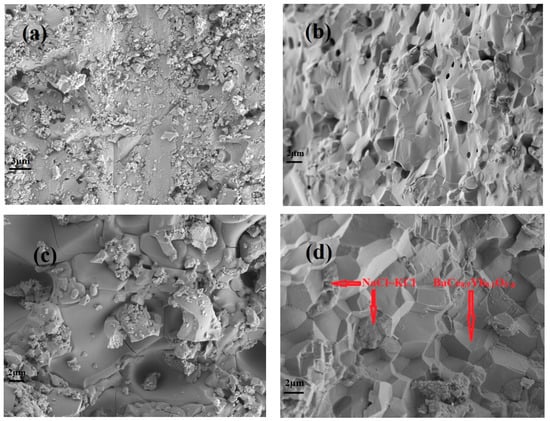
Figure 3.
Scanning electron microscope (SEM) photos of BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α calcined at 1550 °C for 5 h (a,b) external and cross-sectional surfaces, and BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α-NaCl~KCl sintered at 750 °C for 2 h (c,d) external and cross-sectional surfaces.
Figure 4 shows the log (σT)~1000 T−1 plots of BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α (1550 °C) and BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α-NaCl~KCl in the air from 400 °C to 700 °C. As seen in Figure 4, the conductivities of composite BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α-NaCl~KCl electrolytes are higher than that of the single BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α. The conductivities of BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α-NaCl~KCl vary from 2.0 × 10−4 S·cm−1 to 3.0 × 10−1 S·cm−1 in the range of 400–700 °C which is equivalent to BaZr0.85Y0.15O3−α-Li2CO3-K2CO3 in the air at 650 °C [31]. The single BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α electrolyte shows a linear Arrhenius curve in the air at 400–700 °C, whereas the conductivities of BaZr0.85Y0.15O3−α-Li2CO3-K2CO3 start to increase dramatically above 600 °C. The results indicate that the molten NaCl~KCl salt provides more ion transport channels at high temperatures [31,32,41].
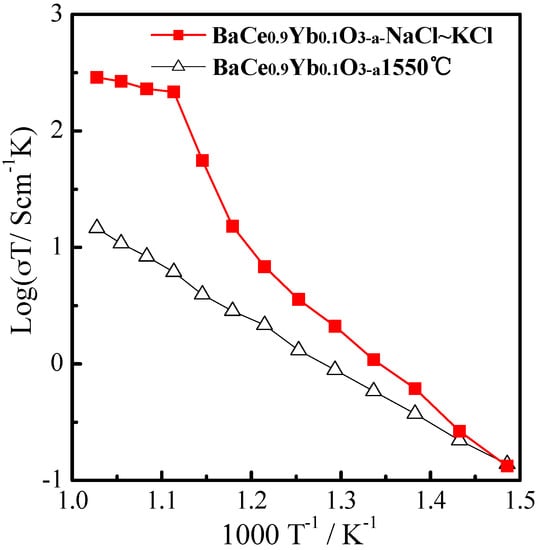
Figure 4.
The log (σT)~1000 T−1 plots of BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α (1550 °C) and BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α-NaCl~KCl in the air from 400 °C to 700 °C.
Figure 5 shows the conductivities of BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α (1550 °C) and BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α-NaCl~KCl as a function of pO2 from 1 × 10−20 to 1 atm at 700 °C. The log σ ~ log pO2 plot is usually used to estimate the ionic and electronic conduction of an electrolyte. Pikalova et al. reported that BaCe0.89Gd0.1Cu0.01O3−α has a predominantly proton-conducting character at intermediate and low pO2 values [9]. As shown in Figure 5, the conductivity is a horizontal line parallel to the X-axis, which indicates that the samples are almost pure ionic conductors. This may be ascribed to the molten salts acting as fast conduction paths for ionic charge carriers, which corresponds with related reports on composite electrolytes [25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32].
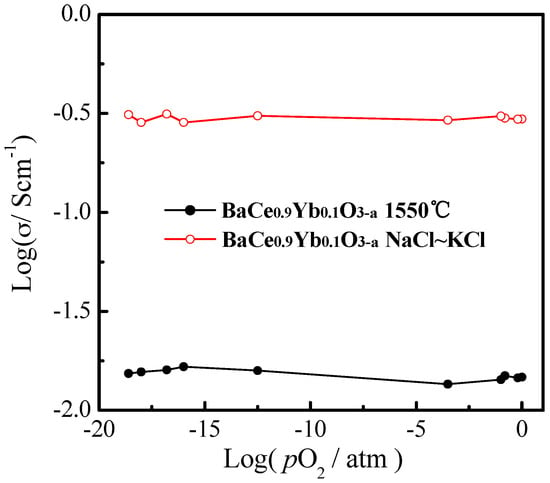
Figure 5.
The conductivities of BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α (1550 °C) and BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α-NaCl~KCl as a function of pO2 at 700 °C.
Figure 6 presents the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) of BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α (1550 °C) and BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α-NaCl~KCl under open-circuit conditions at 700 °C. Usually, the AC impedance curve includes a semicircle and a radial at high (1 KHz–100 KHz) and low (1 Hz–1 KHz) frequencies which correspond to the ohmic and total resistances, respectively. Additionally, the difference between them from the intercept with the real axis at high frequencies to the juncture point of the semicircle and radial, represents polarization resistance (Rp) [18]. The semicircle gradually disappears as the temperature increases [42,43]. In Figure 6, the polarization resistance (Rp) for BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α (1550 °C) and BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α-NaCl~KCl are 1.72 Ω·cm2 and 0.31 Ω·cm2, respectively. This result indicates that the molten salt cannot only generate fast transport ways but also enhance its long-range mobility, which leads to lower resistance and higher performance.
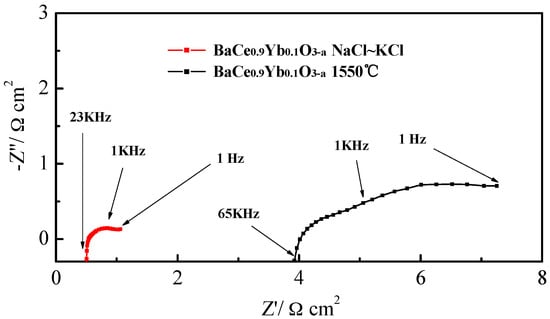
Figure 6.
The electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) of BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α (1550 °C) and BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α-NaCl~KCl under open-circuit conditions at 700 °C.
Figure 7 shows the I–V–P curves of BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α (1550 °C) and BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α-NaCl~KCl at 700 °C. The following reactions occur in the cathode and anode compartments:
and
cathode reaction: 2H+ + O2 + 4e− = H2O + O2−
anode reaction: 2H2 + O2− = 2H+ + H2O + 4e−.
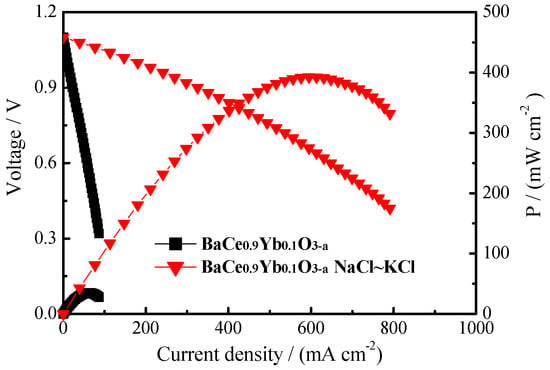
Figure 7.
The I–V–P curves of BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α (1550 °C) and BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α-NaCl~KCl at 700 °C.
The H2/O2 fuel cell using BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α-NaCl~KCl (thickness = 1.0 mm) as electrolyte achieves the highest power density (Ph) of 393 mW·cm−2 when the voltage is 0.64 V at 700 °C. The SrCe0.6Zr0.3Lu0.1O3−α only has 34.8 mW·cm−2 under the same conditions. The Ph value of our result is higher than the fuel cell performance of 60 wt% Ce0.8Sm0.2O1.9-40 wt% (Li/Na)2CO3 (575 °C) and BaCe0.7In0.15Ta0.05Y0.1O3−δ (thickness = 25 µm, 700 °C), however, lower than 80 wt% BaCe0.7Zr0.1Y0.2O3−δ-20 wt% (Li/Na)2CO3 (thickness = 0.4 mm, 600 °C) as shown in Table 1 [18,32,44]. This may be due to the different electrolyte and inorganic salt types and fuel cell construction.

Table 1.
The highest power densities of BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α-NaCl~KCl and similar electrolytes in the literature.
4. Conclusions
In this study, BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α was prepared via the sol-gel method. The first sintering temperature for the BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α precursor was determined using TGA-DSC. XRD and SEM results indicated that NaCl~KCl inorganic salts exist as both crystalline and amorphous phases. The polarization resistances (Rp) for BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α (1550 °C) and BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α-NaCl~KCl were 1.72 Ω·cm2 and 0.31 Ω·cm2 under open-circuit conditions at 700 °C, respectively. The highest power density and conductivity of BaCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α-NaCl~KCl were 393 mW·cm−2 and 3.0 × 10−1 S·cm−1 at 700 °C, respectively.
Author Contributions
H.W. and X.J. conceived and designed the experiments; F.W. and X.J. performed the experiments; H.W. and F.W. analyzed the data; X.J. contributed the used materials and analysis tools; H.W. wrote the paper.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation (No. 51402052, 21602029) of China, The Natural Science Project of Anhui Province (No. KJ2018A0337), Excellent Youth Foundation of Anhui Educational Committee (No. gxyq2018046), Horizontal cooperation project of Fuyang municipal government and Fuyang Normal College (No. XDHX2016019, XDHXTD201704).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lo Faro, M.; Trocino, S.; Zignani, S.C.; Italiano, C.; Vita, A.; Aricò, A.S. Study of a solid oxide fuel cell fed with n-dodecane reformate. Part II: Effect of the reformate composition. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 1751–1757. [Google Scholar]
- Fragiacomo, P.; De. Lorenzo, G.; Corigliano, O. Performance Analysis of an intermediate temperature solid oxide electrolyzer test bench under a CO2-H2O feed stream. Energies 2018, 11, 2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Ren, C.; Yu, L.; Jin, C. High performance intermediate temperature micro-tubular SOFCs with Ba0.9Co0.7Fe0.2Nb0.1O3−δ as cathode. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2013, 38, 15348–15353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, M.; Matsumoto, S.; Iwami, M.; Nishimoto, S.; Kameshima, Y. Electrochemical performances of Ni1−xCux/SDC cermet anodes for intermediate-temperature SOFCs using syngas fuel. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 13625–13631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De. Lorenzo, G.; Fragiacomo, P. Electrical and thermal analysis of an intermediate temperature IIR-SOFC system fed by biogas. Energy Sci. Eng. 2018, 6, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milewski, J.; Wołowicz, M.; Lewandowski, J. Comparison of SOE/SOFC system configurations for a peak hydrogen power plant. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 3498–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-S.; Bae, H.B.; Jung, W.; Chung, S.-Y. Manipulation of nanoscale intergranular phases for high proton conduction and decomposition tolerance in BaCeO3 polycrystals. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 1110–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Z.; Sun, W.; Jin, Z.; Miao, L.; Liu, W. Barium- and strontium-containing anode materials toward ceria-based solid oxide fuel cells with high open circuit voltages. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2018, 1, 3521–3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikalova, E.; Medvedev, D. Effect of anode gas mixture humidification on the electrochemical performance of the BaCeO3-based protonic ceramic fuel cell. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 4016–4025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.Y.; Park, J.-Y.; Lim, H.-T. Investigation of electronic transport property and durability of BCY-BZY electrolyte cells using embedded probes. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 236, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, S.; Li, C.; Rainwater, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Liu, M. Atmospheric plasma-sprayed BaZr0.1Ce0.7Y0.1Yb0.1O3−δ(BZCYYb) electrolyte membranes for intermediate- temperature solid oxide fuel cells. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 19231–19236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilov, N.; Pikalova, E.; Lyagaeva, J.; Antonov, B.; Medvedev, D.; Demin, A.; Tsiakaras, P. Grain and grain boundary transport in BaCe0.5Zr0.3Ln0.2O3−δ(Ln-Y or lanthanide) electrolytes attractive for protonic ceramic fuel cells application. J. Power Sources 2017, 366, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Chen, L.; Yuan, H.; Ji, L.; Xiong, C.; Ma, J.; Zhu, X. Fabrication and characterization of BaZr0.1Ce0.7Y0.2O3−δ based anode supported solid oxide fuel cells by tape casting combined with spray coating. Mater. Lett. 2017, 189, 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyagaeva, J.; Vdovin, G.; Hakimova, L.; Medvedev, D.; Demin, A.; Tsiakaras, P. BaCe0.5Zr0.3Y0.2–xYbxO3−δ proton-conducting electrolytes for intermediate-temperature solid oxide fuel cells. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 251, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Medvedev, D.; Shao, Z. Gas humidification impact on the properties and performance of perovskite-type functional materials in proton-conducting solid oxide cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 1802592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minakshi, M.; Nallathamby, K.; Mitchell, D.R.G. Electrochemical characterization of an aqueous lithium rechargeable battery: The effect of CeO2 additions to the MnO2 cathode. J. Alloy Compd. 2009, 479, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Miao, H.; Wang, H. Novel SrCe1−xYbxO3−α-(Na/K)Cl composite electrolytes for intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cells. Solid State Ion. 2017, 311, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, L.; Li, Q.; Song, T.; Su, J.; Cai, B.; He, H. High performance In, Ta and Y-doped BaCeO3 electrolyte membrane for proton-conducting solid oxide fuel cells. Solid State Ion. 2018, 323, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Han, Y.; Shi, R.; Sheng, L.; Guan, Q.; Liu, J. BaCe0.9Er0.1O3−α-NaCl-KCl composite as electrolyte for intermediate temperature solid oxide fuel cells. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2019, 14, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, B.; Yang, Q.; Chen, C.; Wang, W.; Ma, G. Preparation via microemulsion method and proton conduction at intermediate-temperature of BaCe1−xYxO3−α. Electrochem. Commun. 2009, 11, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilela, C.; Martins, A.P.C.; Sousa, N.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Figueiredo, F.M.L.; Freire, C.S.R. Poly(bis[2-(methacryloyloxy)ethyl]phosphate)/bacterial cellulose nanocomposites: Preparation, characterization and application as polymer electrolyte membranes. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Qiao, Z.; Feng, C.; Kim, J.; Wang, B.; Zhu, B. Study on zinc oxide-based electrolytes in low-temperature solid oxide fuel cells. Materials 2018, 11, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.; Zhu, J.; Lin, Z. Effects of electrode composition and thickness on the mechanical performance of a solid oxide fuel cell. Energies 2018, 11, 1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernuy-Lopez, C.; Rioja-Monllor, L.; Nakamura, T.; Ricote, S.; O’Hayre, R.; Amezawa, K.; Einarsrud, M.; Grande, T. Effect of cation ordering on the performance and chemical stability of layered double perovskite cathodes. Materials 2018, 11, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morejudo, S.H.; Zanón, R.; Escolástico, S.; Yuste-Tirados, I.; Malerød-Fjeld, H.; Vestre, P.K.; Coors, W.G.; Martínez, A.; Norby, T.; Serra, J.M.; et al. Direct conversion of methane to aromatics in a catalytic co-ionic membrane reactor. Science 2016, 353, 563–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, C.; Tong, J.; Shang, M.; Nikodemski, S.; Sanders, M.; Ricote, S.; Almonsoori, A.; O’Hayre, R. Readily processed protonic ceramic fuel cells with high performance at low temperatures. Science 2015, 349, 1321–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Dang, J.; Hou, J.; Qian, J.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Liu, W. Study on new BaCe0.7In0.3O3−δ-Gd0.1Ce0.9O2−δ composite electrolytes for intermediate-temperature solid oxide fuel cells. J. Alloy Compd. 2015, 639, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.-Y.; Lee, T.-H.; Jo, S.; Yang, J.; Song, S.-J.; Lim, H.-T.; Kim, J.H.; Park, J.-Y. Electrical and physical properties of composite BaZr0.85Y0.15O3−δ-Nd0.1Ce0.9O2−δ electrolytes for intermediate temperature-solid oxide fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2016, 336, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondao, A.I.B.; Patricio, S.G.; Figueiredo, F.M.L.; Marques, F.M.B. Composite electrolytes for fuel cells: Long-term stability under variable atmosphere. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 5460–5469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, N.C.T.; Rajesh, S.; Marques, F.M.B. Synthesis and electrochemical assessment of Ce0.5Yb0.5O1.75 ceramics and derived composite electrolytes. Mater. Res. Bull. 2015, 70, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.-Y.; Lee, T.-H.; Kim, J.-T.; Lee, N.; Seo, Y.; Song, S.-J.; Park, J.-Y. Highly conductive barium zirconate-based carbonate composite electrolytes for intermediate temperature-protonic ceramic fuel cells. J. Alloy Compd. 2014, 585, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hei, Y.; Huang, J.; Wang, C.; Mao, Z. Novel doped barium cerate-carbonate composite electrolyte material for low temperature solid oxide fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 14328–14333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yuan, M.; Wang, H.; Liu, J. High-performance intermediate temperature fuel cells of new SrCe0.9Yb0.1O3−α-inorganic salt composite electrolytes. J. Alloy Compd. 2016, 677, 38–41. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, R.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Wu, F.; Miao, H. Intermediate temperature fuel cell durability of Eu-doped SrCeO3-SrZrO3 solid solution/NaCl-KCl composite electrolyte. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 16931–16935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Meng, B.; Tan, X. Stability and electrical conductivity of BaCe0.85Tb0.05M0.1O3−δ (M = Co, Fe, Y, Zr, Mn) high temperature proton conductors. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 13278–13284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Wu, F.; Miao, H.; Cui, Y. Low temperature synthesis of SrCe0.9Eu0.1O3−α by sol-gel method and SrCe0.9Eu0.1O3−α-NaCl-KCl composite electrolyte for intermediate temperature fuel cells. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2017, 12, 11594–11601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, G.S.; Bauri, R. Y and In-doped BaCeO3-BaZrO3 solid solutions: Chemically stable and easily sinterable proton conducting oxides. J. Alloy Compd. 2016, 688, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Fechler, N.; Antonietti, M. Salt melt synthesis of ceramics, semiconductors and carbon nanostructures. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 8237–8265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, A.; Oh, S.; Nguyen, V.H.; Daiko, Y.; Kawamura, G.; Muto, H. Anhydrous proton conductivity of KHSO4-H3PW12O40 composites and the correlation with hydrogen bonding distance under ambient pressure. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 9364–9369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soo, M.T.; Prastomo, N.; Matsuda, A.; Kawamura, G.; Muto, H.; Noor, A.F.M.; Lockman, Z.; Cheong, K.Y. Elaboration and characterization of sol-gel derived ZrO2 thin films treated with hot water. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 5250–5258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Li, S.; Mellander, B.E. The oretical approach on ceria-based two-phase electrolytes for low temperature (300–600 °C) solid oxide fuel cells. Electrochem. Commun. 2008, 10, 302–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presto, S.; Viviani, M. Effect of CuO on microstructure and conductivity of Y-doped BaCeO3. Solid State Ion. 2016, 295, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, M.L.; Minakshi, M.; Singh, N.K. Synthesis and characterization of solid polymer electrolyte based on activated carbon for solid state capacitor. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 137, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhang, H.; Fan, L.; Wang, C.; Zhu, B. Ceria-carbonate composite for low temperature solid oxide fuel cell: Sintering aid and composite effect. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 12309–12316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).