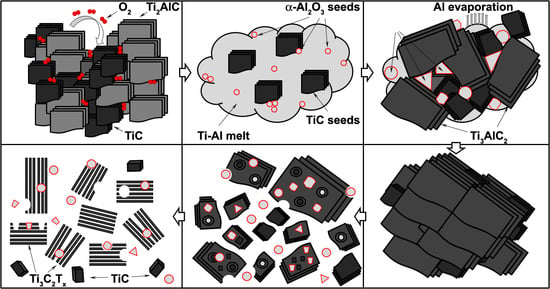
The Influence of Oxygen Concentration during MAX Phases (Ti3AlC2) Preparation on the α-Al2O3 Microparticles Content and Specific Surface Area of Multilayered MXenes (Ti3C2Tx)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. MAX Phase and MXene Synthesis
2.3. Characterization
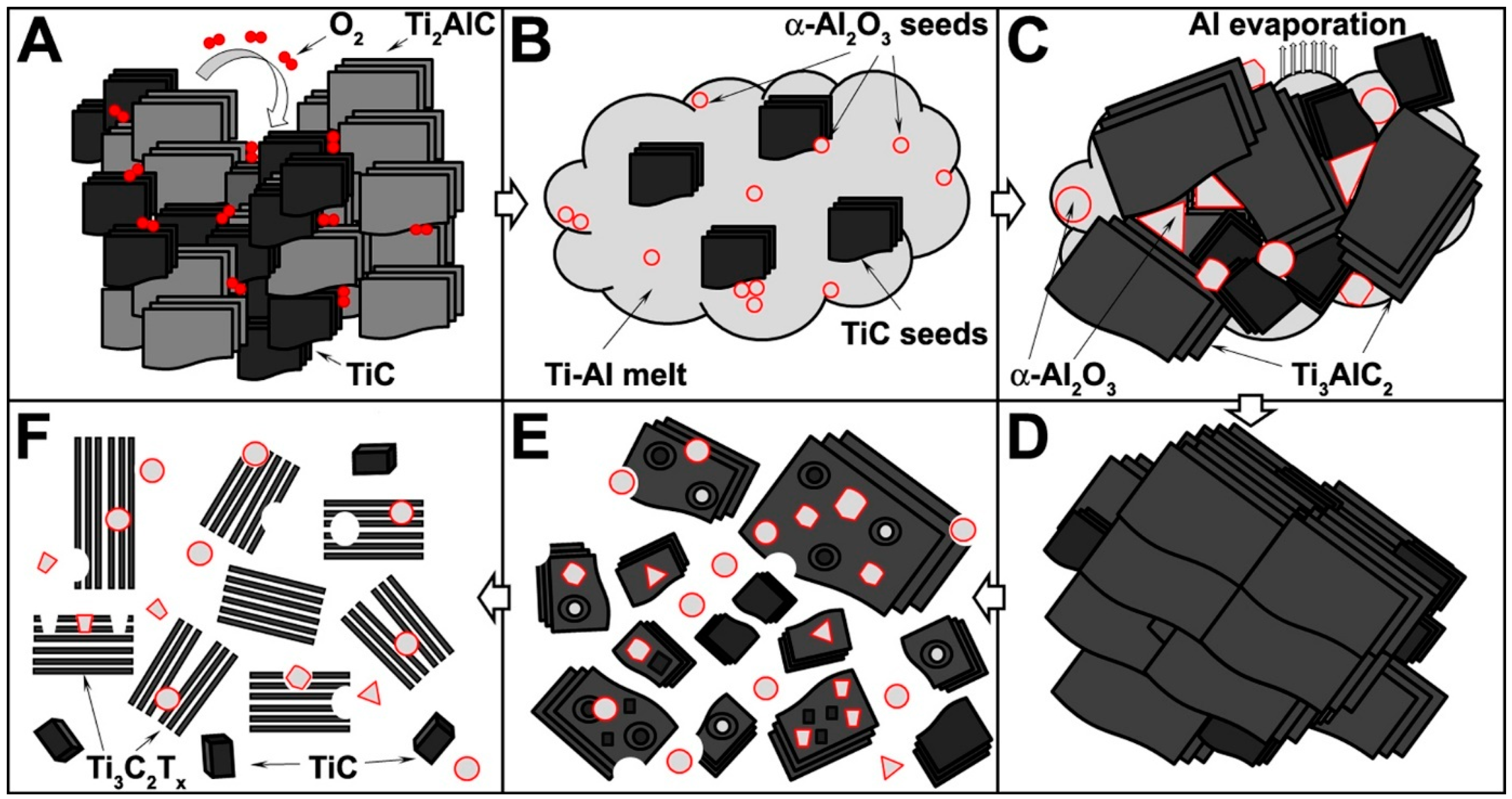
3. Results and Discussion
- (1)
- increased O2 concentration led to increased formation of Al2O3;
- (2)
- increased Al2O3 formation led to a decreased availability of Al atoms for Ti3AlC2 synthesis;
- (3)
- decreased Al atoms content led to increased formation of TiC due to stoichiometry disturbance.
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K.; Morozov, S.V.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Dubonos, S.V.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Firsov, A.A. Electric Field Effect in Atomically Thin Carbon Films. Science 2004, 306, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anasori, B.; Lukatskaya, M.R.; Gogotsi, Y. 2D metal carbides and nitrides (MXenes) for energy storage. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukatskaya, M.R.; Mashtalir, O.; Ren, C.E.; Dall’Agnese, Y.; Rozier, P.; Taberna, P.L.; Naguib, M.; Simon, P.; Barsoum, M.W.; Gogotsi, Y. Cation Intercalation and High Volumetric Capacitance of Two-Dimensional Titanium Carbide. Science 2013, 341, 1502–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsoum, M.W. MAX Phases: Properties of Machinable Ternary Carbides and Nitrides, 1st ed.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Berlin, Germany, 2013; ISBN 978-3-527-33011-9. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, M.; Hu, T.; Li, Z.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, R.; Yang, J.; Cui, C.; Wang, X. Surface Functional Groups and Interlayer Water Determine the Electrochemical Capacitance of Ti3C2TxMXene. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 3578–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naguib, M.; Kurtoglu, M.; Presser, V.; Lu, J.; Niu, J.; Heon, M.; Hultman, L.; Gogotsi, Y.; Barsoum, M.W. Two-Dimensional Nanocrystals Produced by Exfoliation of Ti3AlC2. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 4248–4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Agnese, Y.; Lukatskaya, M.R.; Cook, K.M.; Taberna, P.-L.; Gogotsi, Y.; Simon, P. High capacitance of surface-modified 2D titanium carbide in acidic electrolyte. Electrochem. Commun. 2014, 48, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natu, V.; Clites, M.; Pomerantseva, E.; Barsoum, M.W. MesoporousMXene powders synthesized by acid induced crumpling and their use as Na-ion battery anodes. Mater. Res. Lett. 2018, 6, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Zheng, S.; Qin, J.; Zhao, X.; Shi, H.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Wu, Z.-S. All-MXene-Based Integrated Electrode Constructed by Ti3C2Nanoribbon Framework Host and Nanosheet Interlayer for High-Energy-Density Li-S Batteries. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 2381–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.J.; Nicolosi, V. Graphene and MXene-based transparent conductive electrodes and supercapacitors. Energy Storage Mater. 2019, 16, 102–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, N.; Zhou, Z. Adsorptive environmental applications of MXenenanomaterials: A review. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 19895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Xu, D.; Zhu, Y.; Peng, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, F.; Fan, X. Hierarchical “nanoroll” like MoS2/Ti3C2Tx hybrid with high electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution activity. Appl. Catal. B 2019, 241, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Rufford, T.E.; Chen, X.; Li, N.; Lyu, M.; Dai, L.; Wang, L. Nitrogen-doped Ti3C2TxMXene electrodes for high-performance supercapacitors. Nano Energy 2017, 38, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Wu, X.; Zhou, P.; Zhou, T.; Zhao, J.; Miao, Z.; Zhou, J.; Zhuo, S. Fe3O4@Ti3C2MXene hybrids with ultrahigh volumetric capacity as an anode material for lithium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 11189–11197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Wang, L.; Zhou, A.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Z.; Hu, Q.; Qin, G. MoS2-Decorated Ti3C2MXeneNanosheet as Anode Material in Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, 2654–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Hu, Q.; Zheng, M.; Chi, Y.; Qin, X.; Pang, H.; Xu, Q. MXene–2D layered electrode materials for energy storage. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2018, 28, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, T.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, P.; Yuan, X. Synthesis and mechanism of ternary carbide Ti3AlC2 by in situ hot pressing process in TiC–Ti–Al system. Adv. Appl. Ceram. 2013, 112, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouquerol, J.; Rouquerol, F.; Llewellyn, P.; Maurin, G.; Sing, K. Adsorption by Powders and Porous Solids, 2nd ed.; Academic Press/Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; ISBN 978-0-08-097035-6. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, W.; Sun, H.; Yang, B.; Xu, B.; Ma, W.; Liu, D.; Dai, Y. Preparation of titanium carbide powders by carbothermal reduction of titania/charcoal at vacuum condition. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2010, 28, 628–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchior, S.; Raju, A.K.; Ike, I.S.; Erasmus, R.M.; Kabongo, G.; Sigalas, I.; Iyuke, S.E.; Ozoemena, K.I. High-voltage symmetric supercapacitor based on 2D titanium carbide (MXene, Ti2CTx)/carbon nanospherecomposites in neutral aqueous electrolyte. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ma, J.; Zhu, S.; Cheng, J.; Qiao, Z.; Yang, J.; Liu, W. High temperature tribological properties of Ti3AlC2 ceramic against SiC under different atmospheres. Mater. Des. 2015, 67, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Benitez, R.; Basu, S.; Karaman, I.; Radovic, M. Processing and characterization of porous Ti2AlC with controlled porosity and pore size. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 6266–6277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhabeb, M.; Malesky, K.; Anasori, B.; Lelyukh, P.; Clark, L.; Sin, S.; Gogotsi, Y. Guidelines for Synthesis and Processing of Two-Dimensional Titanium Carbide (Ti3C2TxMXene). Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 7633–7644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syamsai, R.; Kollu, P.; Heong, S.K.; Grace, A.N. Synthesis and properties of 2D-titanium carbide MXene sheets towards electrochemical energy storage applications. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 13119–13126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadabadi, H.; Aftabtalab, A.; Zafaria, S.; Shaker, S.; Ahmadipour, M.; Venkateswara Rao, K. High purity Alpha Alumina nanoparticle: Synthesis and characterization. IJSER 2013, 4, 1593–1596. [Google Scholar]
- Prikhna, T.; Ostash, O.; Sverdun, V.; Karpest, M.; Zimych, T.; Ivasyshin, A.; Cabioc’h, T.; Chartier, P.; Dub, S.; Javorska, L.; et al. Presence of Oxygen in Ti–Al–C MAX Phases-Based Materials and their Stability in Oxidizing Environment at Elevated Temperatures. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2018, 133, 789–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk, M.; Jaroniec, M. Gas Adsorption Characterization of Ordered Organic−Inorganic Nanocomposite Materials. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 3169–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Wei, P.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, F.; Cao, Y.; Wang, H.; Yu, H.; Peng, F. A hydrothermal etching route to synthesis of 2D MXene (Ti3C2, Nb2C): Enhanced exfoliation and improved adsorption performance. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 18886–18893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, B.; Anjum, D.H.; Hedhili, M.N.; Gogotsi, Y.; Alshareef, H.N. H2O2 assisted room temperature oxidation of Ti2C MXene for Li-ion battery anodes. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 7580–7587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yuan, X.; Lin, C.; Yang, Y.; Xu, L.; Du, X.; Xie, J.; Lin, J.; Sun, J. Achieving High Pseudocapacitance of 2D Titanium Carbide (MXene) by Cation Intercalation and Surface Modification. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 160272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.; Huang, H.; Jiang, Q. Chemically functionalized two-dimensional titanium carbide MXene by in situ grafting-intercalating with diazonium ions to enhance supercapacitive performance. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2018, 115, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhuang, Z.; Lv, F.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, L.; Luo, M.; Zhu, J.; Lang, Z.; Feng, S.; Chen, W.; et al. The Marriage of the FeN4 Moiety and MXene Boosts Oxygen Reduction Catalysis: Fe 3d Electron Delocalization Matters. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1803220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
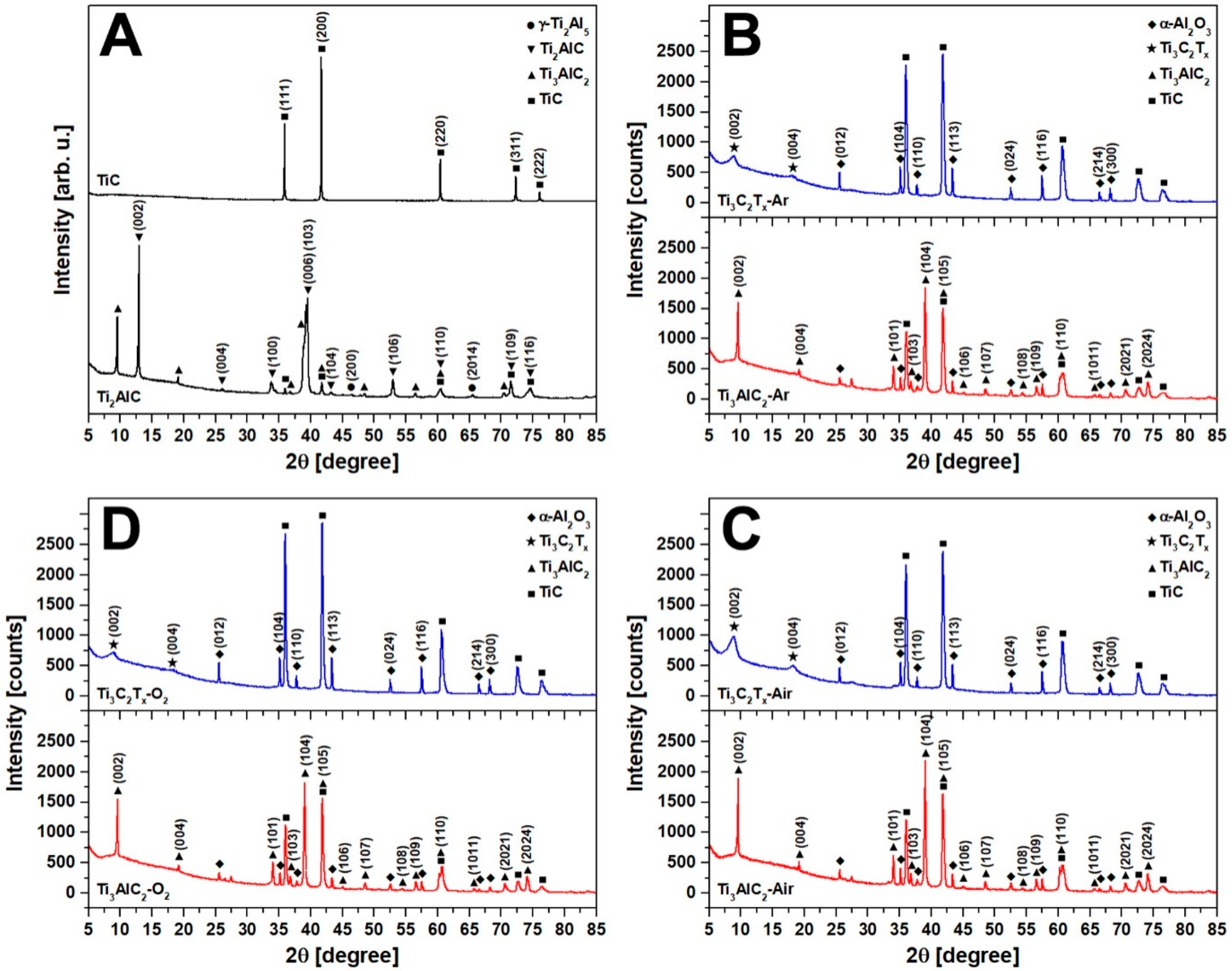
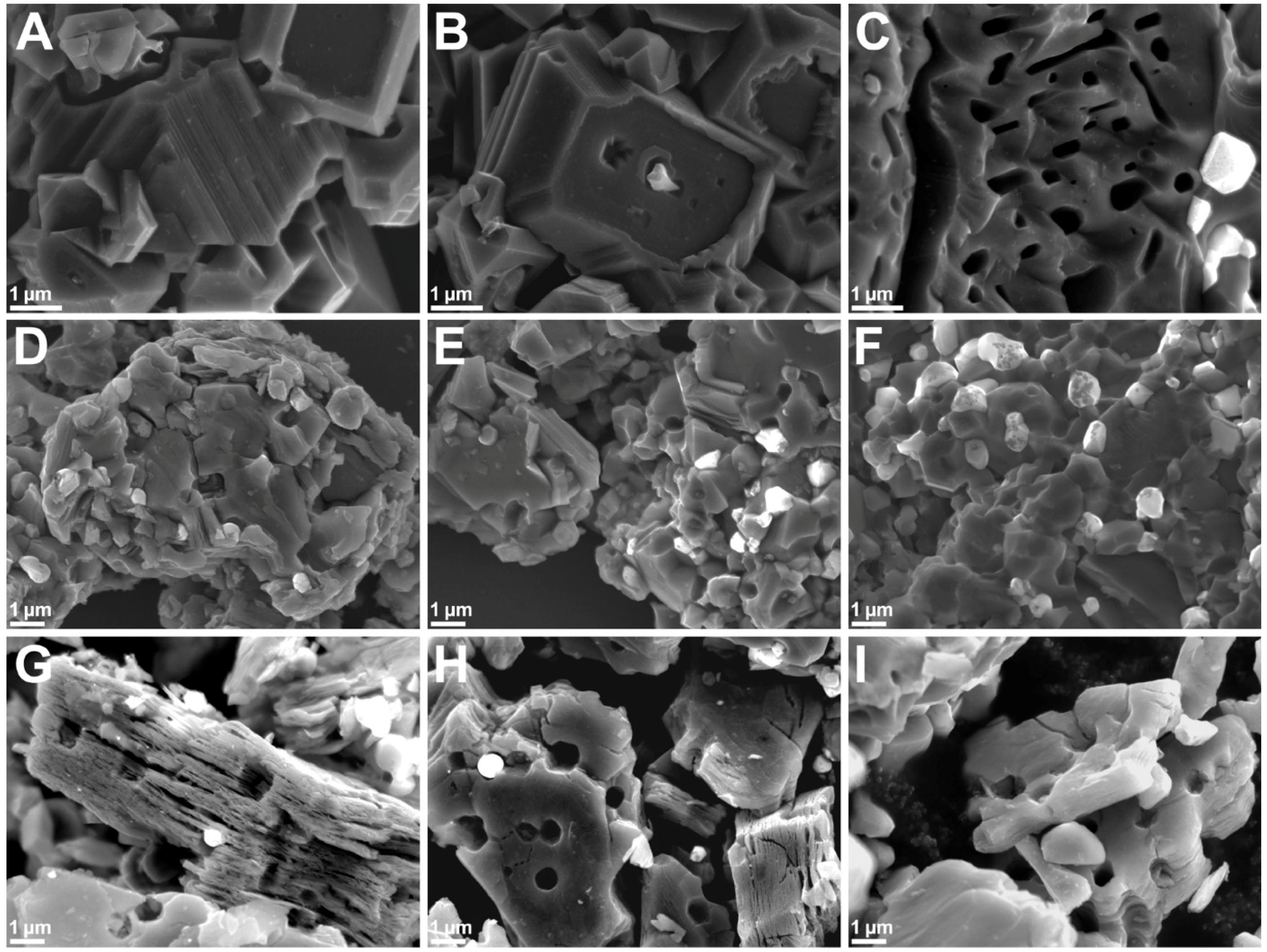
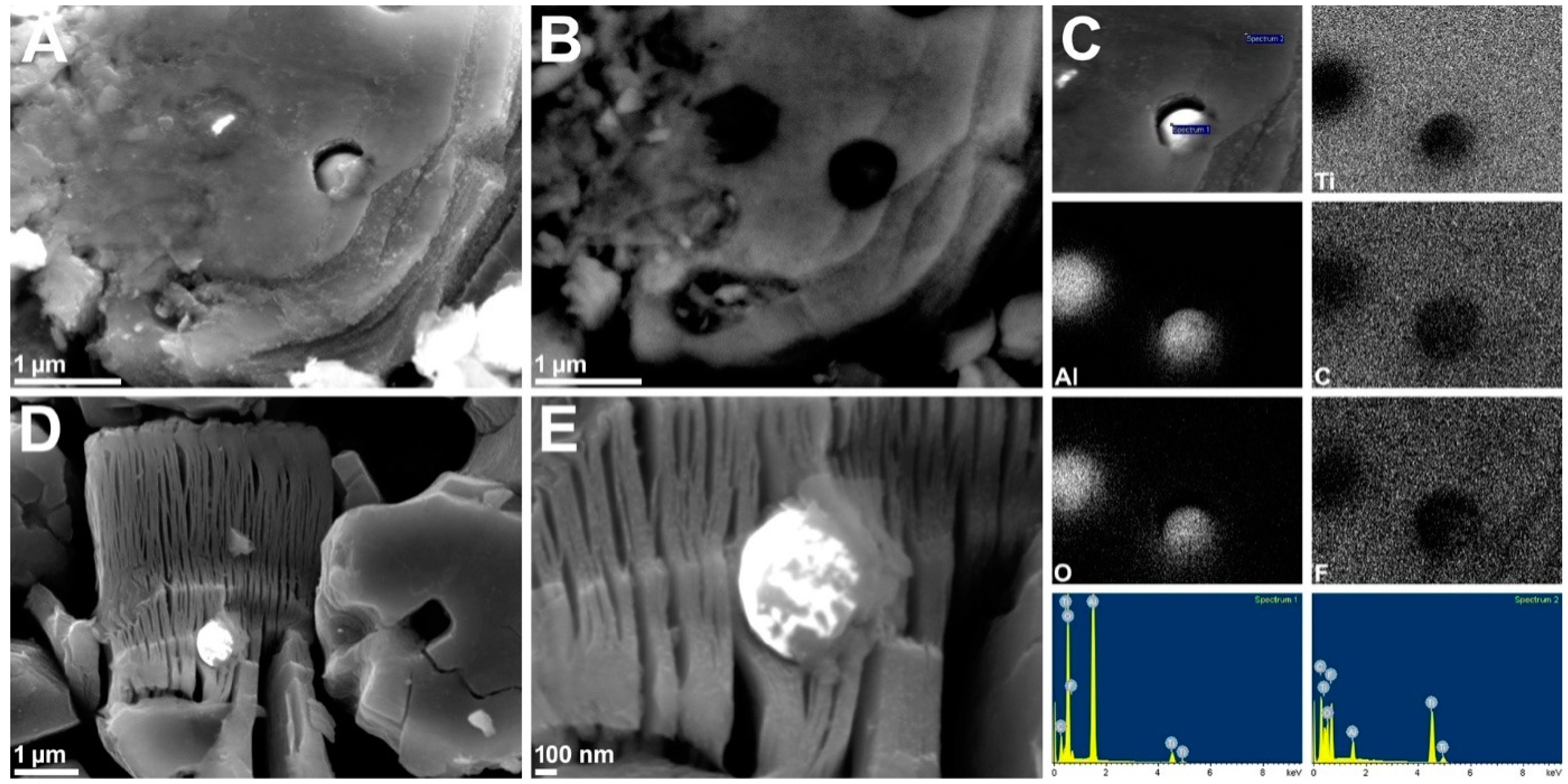
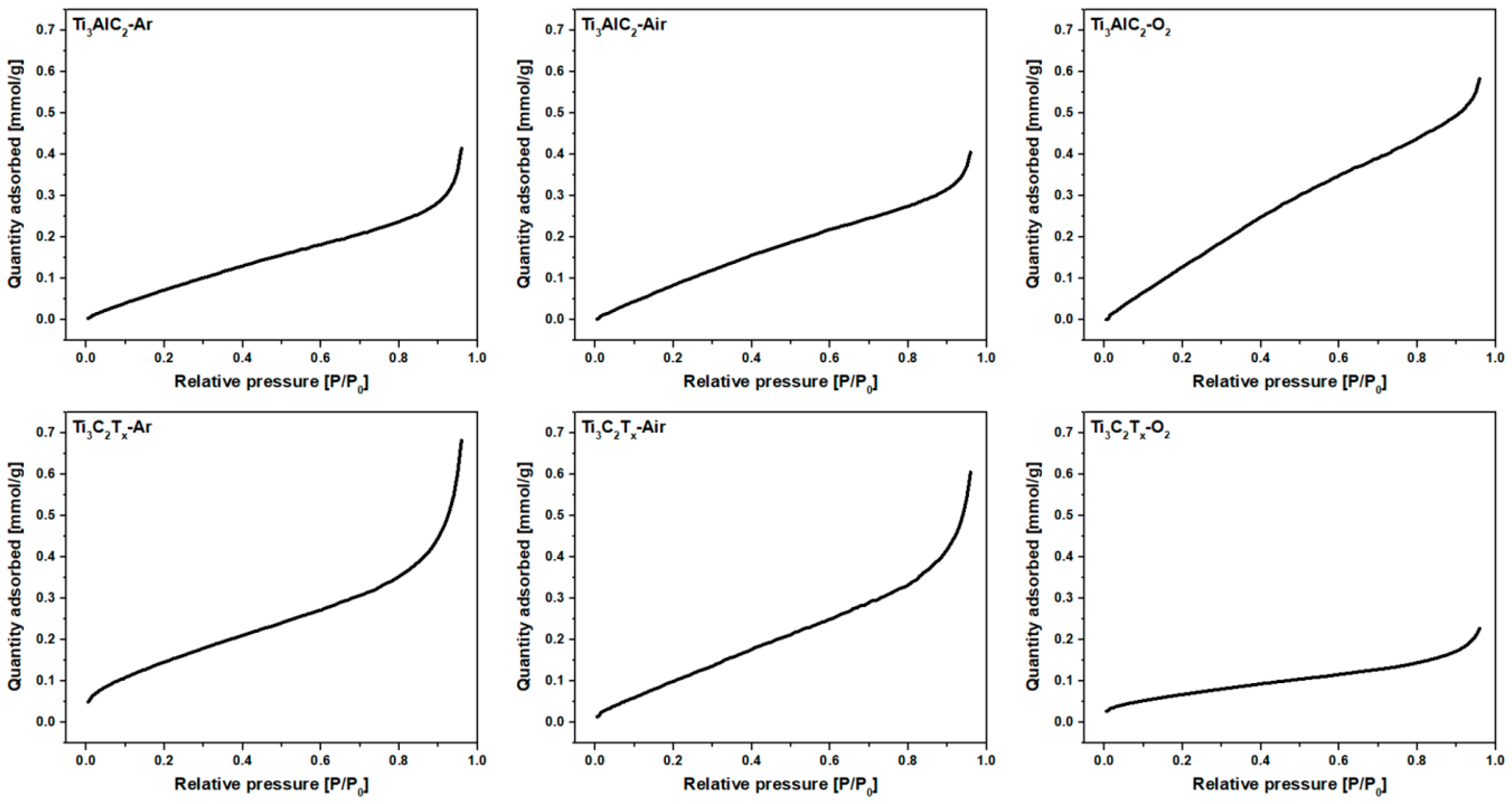
| Sample | Specific Surface Area (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Average Pore Width (BJH) (nm) | Average Slit-Pore Width (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti3AlC2-Ar | 10.57 | 0.0133 | 6.58 | 2.5 |
| Ti3AlC2-Air | 12.95 | 0.0134 | 5.51 | 2.1 |
| Ti3AlC2-O2 | 22.46 | 0.0195 | 5.12 | 1.7 |
| Ti3C2Tx-Ar | 13.70 | 0.0219 | 6.86 | 3.2 |
| Ti3C2Tx-Air | 13.64 | 0.0196 | 6.30 | 2.9 |
| Ti3C2Tx-O2 | 5.96 | 0.0075 | 5.38 | 2.5 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scheibe, B.; Kupka, V.; Peplińska, B.; Jarek, M.; Tadyszak, K. The Influence of Oxygen Concentration during MAX Phases (Ti3AlC2) Preparation on the α-Al2O3 Microparticles Content and Specific Surface Area of Multilayered MXenes (Ti3C2Tx). Materials 2019, 12, 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030353
Scheibe B, Kupka V, Peplińska B, Jarek M, Tadyszak K. The Influence of Oxygen Concentration during MAX Phases (Ti3AlC2) Preparation on the α-Al2O3 Microparticles Content and Specific Surface Area of Multilayered MXenes (Ti3C2Tx). Materials. 2019; 12(3):353. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030353
Chicago/Turabian StyleScheibe, Błażej, Vojtech Kupka, Barbara Peplińska, Marcin Jarek, and Krzysztof Tadyszak. 2019. "The Influence of Oxygen Concentration during MAX Phases (Ti3AlC2) Preparation on the α-Al2O3 Microparticles Content and Specific Surface Area of Multilayered MXenes (Ti3C2Tx)" Materials 12, no. 3: 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030353
APA StyleScheibe, B., Kupka, V., Peplińska, B., Jarek, M., & Tadyszak, K. (2019). The Influence of Oxygen Concentration during MAX Phases (Ti3AlC2) Preparation on the α-Al2O3 Microparticles Content and Specific Surface Area of Multilayered MXenes (Ti3C2Tx). Materials, 12(3), 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12030353