Effect of Residual Stress on S–N Curves and Fracture Morphology of Ti6Al4V Titanium Alloy after Laser Shock Peening without Protective Coating
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
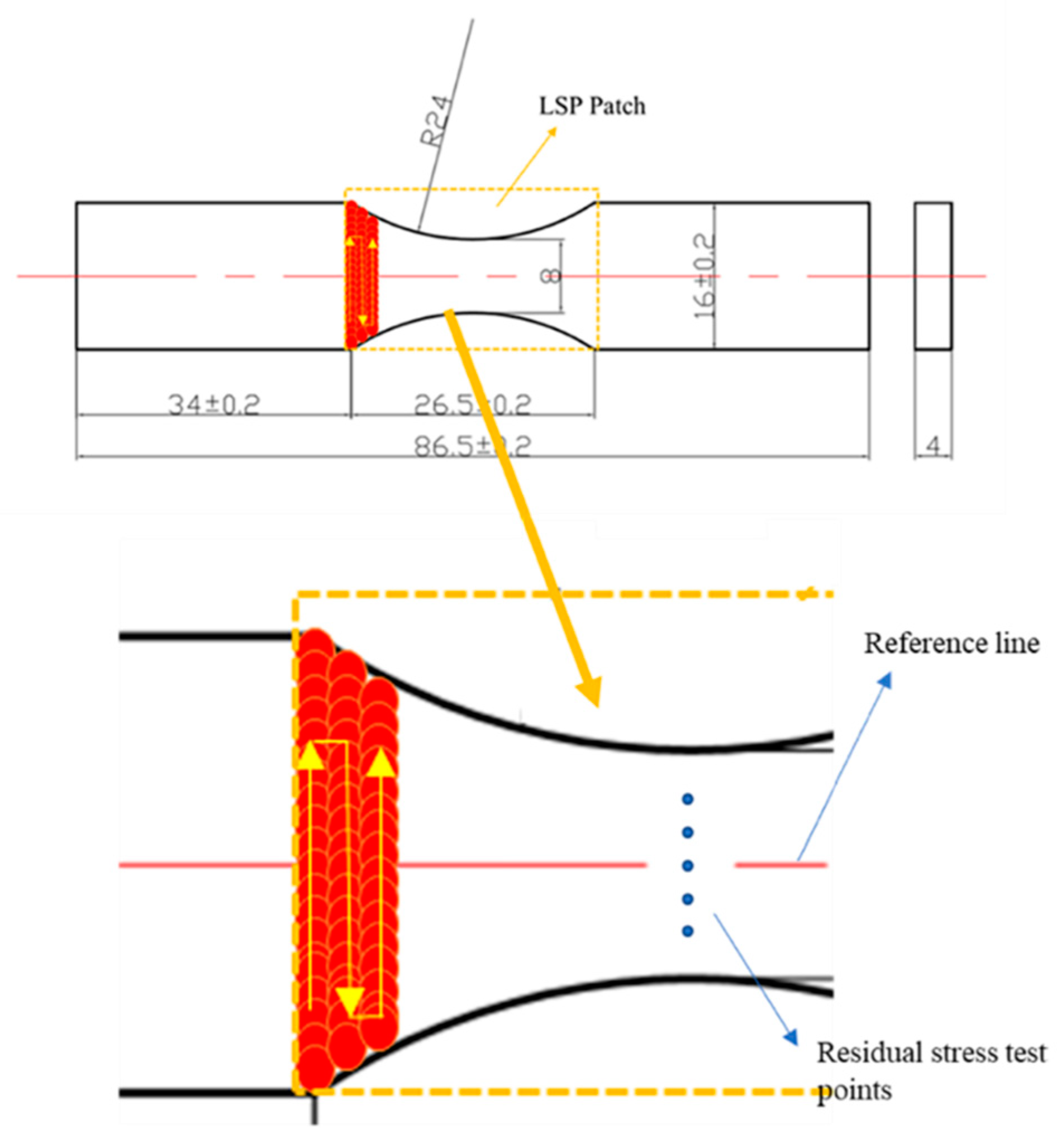
2.1. Materials and Specimens
2.2. LSP Processing
2.3. Residual Stress Test
2.4. High-Cycle Fatigue Test and Fractography Observation
3. Results and Discussion
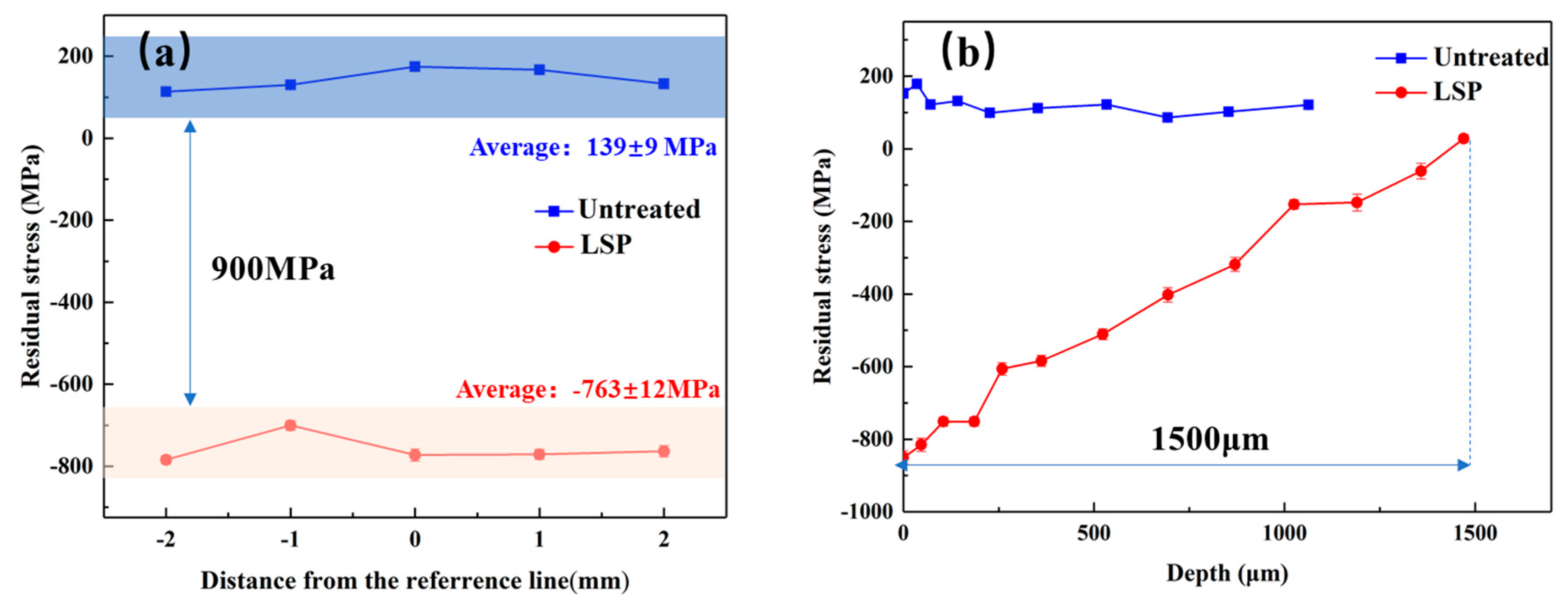
3.1. Residual Stress Distribution after LSP
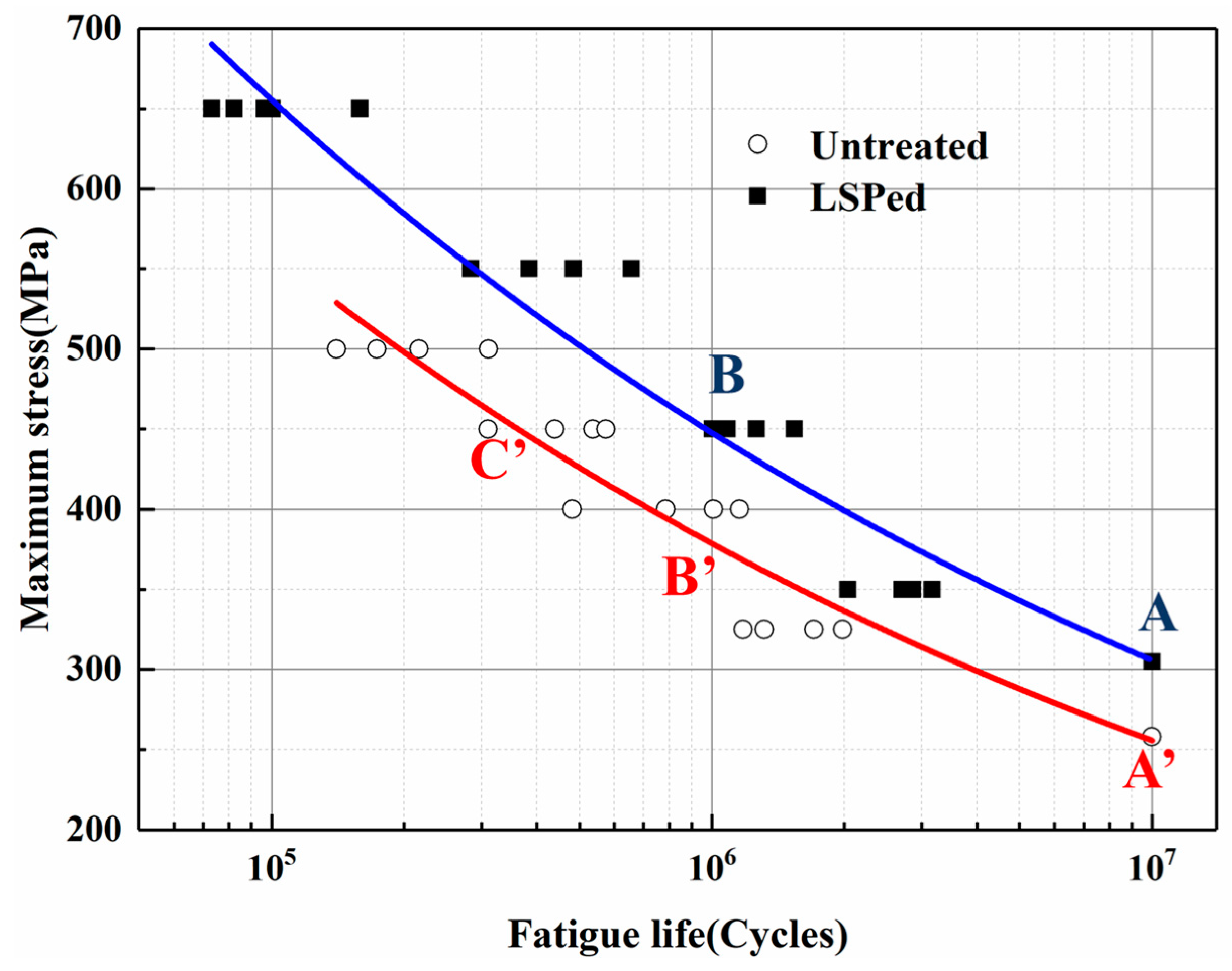
3.2. Characteristics of the S–N Curve after LSP
3.2.1. Fatigue Limit measured by the Up–Down Method
3.2.2. S–N Curves Measured by the Group Method
3.3. The Effect of Residual Stress on the S–N Curves
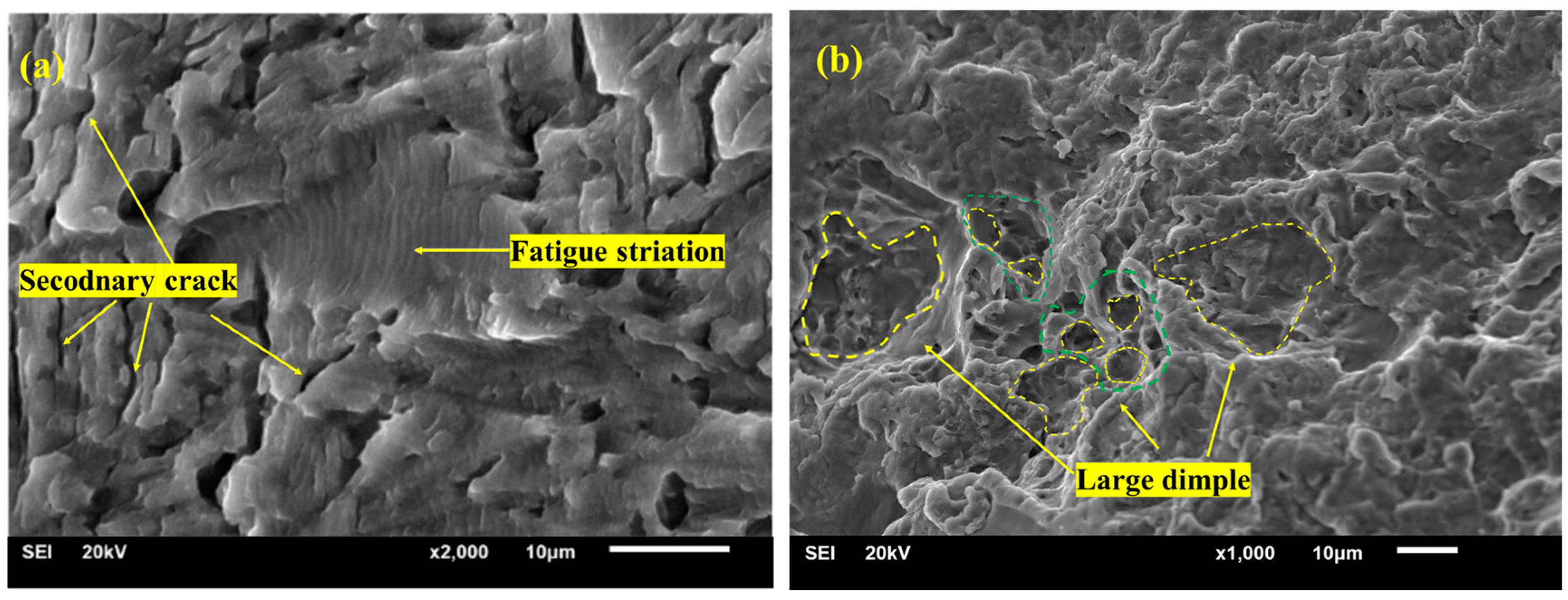
3.4. Fracture Feature after LSP
4. Conclusions
- There is a tensile residual stress appearing on the surface of the untreated specimen. After LSP, the surface residual stress is changed from tension stress to compressive stress. Besides, a deeper compressive residual stress layer is also introduced into the Ti6Al4V titanium alloy specimen.
- The fatigue limits of the untreated and LSP-ed titanium alloys are 264 MPa and 305 MPa respectively. The fatigue limit of the specimens treated by LSP was improved by 16%. After LSP, the S–N curve shifts upward.
- Due to the high-value compressive residual stress induced by LSP, the tensile stress produced by external loading is decreased. It is beneficial for the improvement of the crack initiation life. After LSP, the crack initiation sites of the samples moved to the subsurface. All in all, the LSP process can produce higher-amplitude compressive residual stress into the materials, which is an important factor in the improvement of the fatigue life of metallic components.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jha, A.K.; Singh, S.K.; Kiranmayee, M.S.; Sreekumar, K.; Sinha, P.P. Failure analysis of titanium alloy (Ti6Al4V) fastener used in aerospace application. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2010, 17, 1457–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiga, C.; Davim, J.; Loureiro, A. Properties and applications of titanium alloys: A brief review. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2012, 32, 133–148. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, X.; Guo, H.; Wang, T.; Yao, Z. Effects of β treatments on microstructures and mechanical properties of TC4-DT titanium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 533, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Jiang, C.; Lu, W.; Ke, Z.; Chen, Y. Investigation on the residual stress and microstructure of (TiB + TiC)/Ti–6Al–4V composite after shot peening. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 3423–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altenberger, I.; Nalla, R.K.; Sano, Y.; Wagner, L.; Ritchie, R.O. On the effect of deep-rolling and laser-peening on the stress-controlled low- and high-cycle fatigue behavior of Ti–6Al–4V at elevated temperatures up to 550 °C. Int. J. Fatigue 2012, 44, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.C.; Zhang, Y.K.; Lu, J.Z.; Xuan, F.Z.; Wang, Z.D.; Tu, S.T. Improvement of fatigue life of Ti–6Al–4V alloy by laser shock peening. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 3411–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; He, W.; Zhou, L.; Li, Q.; Wang, X. Experiment investigation of laser shock peening on TC6 titanium alloy to improve high cycle fatigue performance. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 594, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.Z.; Huang, S.; Zuo, L.D.; Meng, X.K.; Sheng, J.; Tian, Q.; Han, Y.H.; Zhu, W.L. Effects of laser peening on residual stresses and fatigue crack growth properties of Ti–6Al–4V titanium alloy. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2014, 52, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, C.; Lara, L.R.D.; Díaz, M.; Gil-Santos, A.; Porro, J.A.; Ocaña, J.L. Effect of advancing direction on fatigue life of 316L stainless steel specimens treated by double-sided laser shock peening. Int. J. Fatigue 2015, 79, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Li, L.; Guo, W.; Peng, P.; Zhai, T.; Che, Z.; Li, B.; Guo, C.; Zhu, Y. Laser shock peening induced fatigue crack retardation in Ti-17 titanium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 737, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattoura, M.; Mannava, S.R.; Qian, D.; Vasudevan, V.K. Effect of laser shock peening on residual stress, microstructure and fatigue behavior of ATI 718Plus alloy. Int. J. Fatigue 2017, 102, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; He, W.; Zang, S.; Wang, X.; Zhao, J. Effect study and application to improve high cycle fatigue resistance of TC11 titanium alloy by laser shock peening with multiple impacts. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 253, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhou, K.; Li, G. Effect of laser shock peening and annealing temperatures on stability of AA2195 alloy near-surface microstructure. Opt. Laser Technol. 2019, 119, 105569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Luo, K.Y.; Dai, F.Z.; Lu, J.Z. Effects of scanning path and overlapping rate on residual stress of 316L stainless steel blade subjected to massive laser shock peening treatment with square spots. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 481, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakaran, S.; Kalainathan, S.; Shukla, P.; Vasudevan, V.K. Residual stress, phase, microstructure and mechanical property studies of ultrafine bainitic steel through laser shock peening. Opt. Laser Technol. 2019, 115, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, B.; Li, B.; Lin, D.; Liao, Y. Enhanced room temperature stretch formability of AZ31B magnesium alloy sheet by laser shock peening. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 756, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Zhou, L.; Nie, X.; Li, Y.; He, W. The compound process of laser shock peening and vibratory finishing and its effect on fatigue strength of Ti-3.5Mo-6.5Al-1.5Zr-0.25Si titanium alloy. J. Alloy. Compd. 2019, 783, 828–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.Y.; Yin, Y.F.; Wang, C.Y.; Chai, Q.F.; Cai, J.; Lu, J.Z.; Lu, Y.F. Effects of laser shock peening with different coverage layers on fatigue behaviour and fractural morphology of Fe-Cr alloy in NaCl solution. J. Alloy. Compd. 2019, 773, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luong, H.; Hill, M.R. The effects of laser peening and shot peening on high cycle fatigue in 7050-T7451 aluminum alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.K. Improvement of fatigue property in 7050-T7451 aluminum alloy by laser peening and shot peening. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 3823–3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabeen, S.; Preuss, M.; Withers, P.J. Evolution of a laser shock peened residual stress field locally with foreign object damage and subsequent fatigue crack growth. Acta Mater. 2015, 83, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiozawa, K.; Lu, L. Very high-cycle fatigue behaviour of shot-peened high-carbon–chromium bearing steel. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2010, 25, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.D.; Wu, H.L.; Yao, Y.Z. Titanium Alloys Handbook; Chongqing Science and Technology Press: Chongqing, China, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.K.; Wu, X.R. Experimental investigation and fatigue life prediction for 7475-T7351 aluminum alloy with and without shot peening-induced residual stresses. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 3737–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.Z.; Meng, X.K.; Huang, S.; Sheng, J.; Lu, J.Z.; Yang, Z.R.; Su, C. Effects of warm laser peening at elevated temperature on the low-cycle Cross Mark fatigue behavior of Ti6Al4V alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. 2015, 643, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Standardization Management Committee, Recommended National Standards of the People’s Republic of China: Metallic Materials—Fatigue Testing-Statistical Planning and Analysis Data. Available online: https://wenku.baidu.com/view/5455ccb477eeaeaad1f34693daef5ef7bb0d125e.html (accessed on 25 June 2009).
- National Aircraft Standards Committee, Standards of the Ministry of Aviation of the People’s Republic of China: Statistical Analysis Method for Material Fatigue Test. Available online: http://www.doc88.com/p-1836397254353.html (accessed on 1 October 1986).
- Starker, P.; Wohlfahrt, H.; Macherauch, E. Subsurface crack initiation during fatigue as a result of residual stresses. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 1979, 1, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.D.; Zhan, Q.B.; Yang, H.M.; Dai, F.Z.; Cui, C.Y.; Sun, G.F.; Ruan, L. The effects of residual stress on fatigue behavior and crack propagation from laser shock processing-worked hole. Mater. Des. 2013, 44, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.D. Assessment method for fatigue strength of wheel based on improved Goodman curve. J. Railw. Sci. Eng. 2017, 14, 827–832. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, C.H.; Suslov, S.; Kim, B.J.; Stach, E.A.; Cheng, G.J. Fatigue performance improvement in AISI 4140 steel by dynamic strain aging and dynamic precipitation during warm laser shock peening. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 1014–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boytsov, B.V.; Kravtchenko, G.N.; Petukhov, J. Effect of Residual Stress and Overloading on Initiation and Fatigue Crack Propagation Mechanisms. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference, Beijing, China, 3–6 June 1987; pp. 749–756. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.F.; Ying-Yan, L.I.; Niu, L.S.; Shi, H. Effects of residual stress on the delay of fatigue crack initiation in the mixed-mode stress field for aluminum alloys. Hangkong Cailiao Xuebao/J. Aeronaut. Mater. 2003, 23, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.; Garbatov, Y.; Guedes Soares, C. Fatigue crack initiation assessment of welded joints accounting for residual stress. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2018, 41, 1823–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnubel, D.; Horstmann, M.; Ventzke, V.; Riekehr, S.; Staron, P.; Fischer, T.; Huber, N. Retardation of fatigue crack growth in aircraft aluminium alloys via laser heating—Experimental proof of concept. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 546, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Paddea, S.; Zhang, X. Fatigue crack propagation behaviour in wire+arc additive manufactured Ti-6Al-4V: Effects of microstructure and residual stress. Mater. Des. 2016, 90, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, C.; Lotz, T.; Martinez, M.; Artemev, A.; Alderliesten, R.; Benedictus, R. Fatigue crack growth in residual stress fields. Int. J. Fatigue 2016, 87, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadananda, K.; Vasudevan, A.K. Fatigue crack growth behavior of titanium alloys. Int. J. Fatigue 2005, 27, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Alloying Elements | Impurities Not Greater than | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al | V | Ti | Fe | C | N | H | O | Other Elements | |
| Individual | Sum | ||||||||
| 5.5~6.8 | 3.5~4.5 | 3.5~4.5 | 1.6~2.4 | 1.6~2.4 | 0.05 | 0.0125 | 0.13 | 0.1 | 0.4 |
| Material | Density/g·cm−3 | Poisson’s Ratio | Elastic Model/GPa | Shear Modulus/GPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti6Al4V | 4.44 | 0.34 | 109 | 44 |
| Technical Standard | Heat Treatment Mechanism | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GJB 494-1988 | Annealing: 700~850 °C, 0.5~2 h, air cooling | 925 | 870 | 12 |
| Condition | Wavelength (nm) | Spot Size (mm) | Overlap | Pulse Energy (J) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LSP | 1064 | 2.4 | 50% | 4 |
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Radiation | Cu-Kα |
| Aperture size(diameter) | 2 mm |
| Crystal plane | {213} |
| 2θ | 142° |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, X.; Li, X.; Zhou, L.; Feng, X.; Luo, S.; He, W. Effect of Residual Stress on S–N Curves and Fracture Morphology of Ti6Al4V Titanium Alloy after Laser Shock Peening without Protective Coating. Materials 2019, 12, 3799. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12223799
Pan X, Li X, Zhou L, Feng X, Luo S, He W. Effect of Residual Stress on S–N Curves and Fracture Morphology of Ti6Al4V Titanium Alloy after Laser Shock Peening without Protective Coating. Materials. 2019; 12(22):3799. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12223799
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Xinlei, Xiang Li, Liucheng Zhou, Xiaotai Feng, Sihai Luo, and Weifeng He. 2019. "Effect of Residual Stress on S–N Curves and Fracture Morphology of Ti6Al4V Titanium Alloy after Laser Shock Peening without Protective Coating" Materials 12, no. 22: 3799. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12223799
APA StylePan, X., Li, X., Zhou, L., Feng, X., Luo, S., & He, W. (2019). Effect of Residual Stress on S–N Curves and Fracture Morphology of Ti6Al4V Titanium Alloy after Laser Shock Peening without Protective Coating. Materials, 12(22), 3799. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12223799







