Hygrothermal Analysis of Laminated Composite Skew Conoids
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Formulations
2.1. Displacement Fields and Strains
2.2. Constitutive Equation
- Transformed reduced stiffness matrix can be formed with the material properties.
- () and fiber orientation () of lamina [45].
- ΔT = Change in temperature.
- ΔC = Change in moisture concentration.
- ; ; = transformed swelling or contraction coefficients due to moisture.
- ; ; = transformed thermal expansion or contraction coefficients due to temperature.
3. Finite Element Formulations
Skew Transformations
4. Results and Discussion
- Simply supported (SSSS):At ;At ;
- Clamped (CCCC):At and ;
- Clamped-simply supported (CSCS):At and ;At ; and at ;
4.1. Convergence Study
4.2. Comparison Study
4.3. Parametric Study
5. Conclusions
- The value of non-dimensional deflection of conoids under hygrothermal loadings increases along with the hl/hh ratio.
- The value of non-dimensional deflection of moderately thick shell under hygrothermal loadings decreases with an increase in the skew angle.
- The non-dimensional deflection of shells under temperature and moisture loading decreases with the increase in the number of plies.
- The non-dimensional maximum deflection of skew conoids under hygrothermal loading increases with the decreases in the a/h ratio.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kirchhoff, G. Über das Gleichgewicht und die Bewegung einer elastischen Scheibe. J. Die Reine Angew. Math. 1850, 40, 51–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mindlin, R.D. Influence of Rotatory Inertia and Shear on Flexural Motions of Isotropic, Elastic Plates. J. Appl. Mech. ASME 1951, 18, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Reissner, E. The effect of transverse shear deformation on the bending of elastic plates. J. Appl. Mech. 1945, 12, A68–A77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, J.N. A simple higher-order theory for laminated composite plates. J. Appl. Mech. 1984, 51, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, K.H.; Christensen, R.M.; Wu, E.M. A High-Order Theory of Plate Deformation Part 1: Homogeneous Plates. J. Appl. Mech. 1977, 44, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PELL, W.H. Thermal deflections of anisotropic thin plates. Q. Appl. Math. 1946, 4, 27–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitney, J.M.; Ashton, J.E. Effect of Environment on the Elastic Response of Layered Composite Plates. AIAA J. 1971, 9, 1708–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipes, R.B.; Vinson, J.R.; Chou, T.W. On the Hygrothermal Response of Laminated Composite Systems. J. Compos. Mater. 1976, 10, 129–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, J.N.; Hsu, Y.S. Effects of shear deformation and anisotropy on the thermal bending of layered composite plates. J. Therm. Stresses 1980, 3, 475–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.H.; Tauchert, T.R. Thermoelastic analysts of laminated plates. 2: Antisymmetric cross-ply and angle-ply laminates. J. Therm. Stresses 1980, 3, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doxsee, L.E. A higher-order theory of hygrothermal behavior of laminated composite shells. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1989, 25, 339–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Yen, W.J. Hygrothermal effects on the stability of a cylindrical composite shell panel. Comput. Struct. 1989, 33, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sai Ram, K.S.; Sinha, P.K. Hygrothermal effects on the bending characteristics of laminated composite plates. Comput. Struct. 1991, 40, 1009–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauchert, T.R. Thermally Induced Flexure, Buckling, and Vibration of Plates. Appl. Mech. Rev. 1991, 44, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajab, A.A.K.D.; An, J.N.R. Thermal Effects on the Response of Cross-Ply Laminated Shallow Shells. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1992, 29, 653–667. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, J.S.M.; Bhaskar, K.; Varadan, T.K. A new theory for accurate thermal/mechanical flexural analysis of symmetric laminated plates. Compos. Struct. 1999, 45, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenkour, A.M.; Fares, M.E. Thermal bending analysis of composite laminated cylindrical shells using a refined first-order theory. J. Therm. Stresses 2000, 23, 505–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganapathi, M.; Patel, B.P.; Pawargi, D.S. Dynamic analysis of laminated cross-ply composite non-circular thick cylindrical shells using higher-order theory. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2002, 39, 5945–5962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khare, R.K.; Kant, T.; Garg, A.K. Closed-form thermo-mechanical solutions of higher-order theories of cross-ply laminated shallow shells. Compos. Struct. 2003, 59, 313–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenkour, A.M. Analytical solution for bending of cross-ply laminated plates under thermo-mechanical loading. Compos. Struct. 2004, 65, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brischetto, S.; Carrera, E. Coupled thermo-mechanical analysis of one-layered and multilayered isotropic and composite shells. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2010, 56, 249–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, A.K.; Pandey, R.; Shukla, K.K. Nonlinear flexural response of laminated composite plates under hygro-thermo-mechanical loading. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2010, 15, 2634–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, A.; Singh, B.N.; Anand, S. Nonlinear bending response of laminated composite spherical shell panel with system randomness subjected to hygro-thermo-mechanical loading. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2011, 53, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Chakrabarti, A. Hygrothermal Analysis of Laminated Composite Plates by Using Efficient Higher Order Shear Deformation Theory. J. Solid Mech. 2011, 3, 85–95. [Google Scholar]
- Brischetto, S. Hygrothermoelastic analysis of multilayered composite and sandwich shells. J. Sandw. Struct. Mater. 2013, 15, 168–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, J.S.M.; Alsubari, S.; Aminanda, Y. A Higher Order Theory for Bending of Cross Ply Laminated Cylindrical Shell under Hygrothermal Loads. Adv. Mater. Res. 2015, 1115, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, J.S.M.; Alsubari, S.; Aminanda, Y. Hygrothermoelastic analysis of orthotropic cylindrical shells. Lat. Am. J. Solids Struct. 2016, 13, 573–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, M.; Sahu, S.K.; Asha, A.V. Experimental and numerical studies on free vibration of laminated composite shallow shells in hygrothermal environment. Compos. Struct. 2015, 127, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenkour, A.M.; Alghanmi, R.A. Bending of symmetric cross-ply multilayered plates in hygrothermal environments. J. Math. Models Eng. (MME) 2016, 24, 94–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Yao, W. Hygrothermal analysis of laminated composite plates in terms of an improved C0-type global–local model. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2017, 63, 328–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadid, H.A. An analytical and experimental investigation into the bending theory of elastic conoidal shell. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, C.K. A conoidal shell analysis by modified isoparametric element. Comput. Struct. 1984, 18, 921–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, B.; Bandyopadhyay, J.N. Bending analysis of conoidal shells using curved quadratic isoparametric element. Comput. Struct. 1989, 33, 717–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, B.; Bandyopadhyay, J.N. Approximate bending analysis of conoidal shells using the galerkin method. Comput. Struct. 1990, 36, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A.; Bandyopadhyay, J.N.; Sinha, P.K. Finite Element Analysis of Laminated Composite Conoidal Shell Structures. Comput. Struct. 1992, 43, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.K.; Bandyopadhyay, J.N. Theoretical and experimental studies on conoidal shells. Comput. Struct. 1993, 49, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, B.; Bandyopadhyay, J.N. Bending analysis of conoidal shells with cut-outs. Comput. Struct. 1994, 53, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, H.S.; Chakravorty, D. Design aids and selection guidelines for composite conoidal shell roofs—A finite element application. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2007, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, H.S.; Chakravorty, D. Bending analysis of stiffened composite conoidal shell roofs through finite element application. J. Compos. Mater. 2011, 45, 525–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Chakrabarti, A.; Bhargava, P. Finite element analysis of laminated composite and sandwich shells using higher order zigzag theory. Compos. Struct. 2013, 106, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anish; Kumar, A. Ultimate Strength Analysis of Laminated Composite Sandwich Plates. Structures 2018, 14, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Chakrabarti, A.; Bhargava, P. Vibration analysis of laminated composite skew cylindrical shells using higher order shear deformation theory. J. Vib. Control 2015, 21, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.I.; Kumar, A.; Chakrabarti, A. Static analysis of doubly curved singly ruled truncated FGM cone. Compos. Struct. 2018, 184, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaubey, A.K.; Kumar, A.; Mishra, S.S. Dynamic Analysis of Laminated Composite Rhombic Elliptic Paraboloid due to Mass Variation. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2018, 31, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R. Mechanics of Composite Materials; McGraw-Hill Book Company: New York, NY, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Whitney, J.M.; Pagano, N.J. Shear Deformation in Heterogeneous Anisotropic Plates 1. J. Appl. Mech. 1970, 37, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, A.H.; Chakrabarti, A. A new plate bending element based on higher-order shear deformation theory for the analysis of composite plates. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 2003, 39, 883–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prathap, G.; Naganarayana, B.P. Consistent thermal stress evaluation in finite elements. Comput. Struct. 1995, 54, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
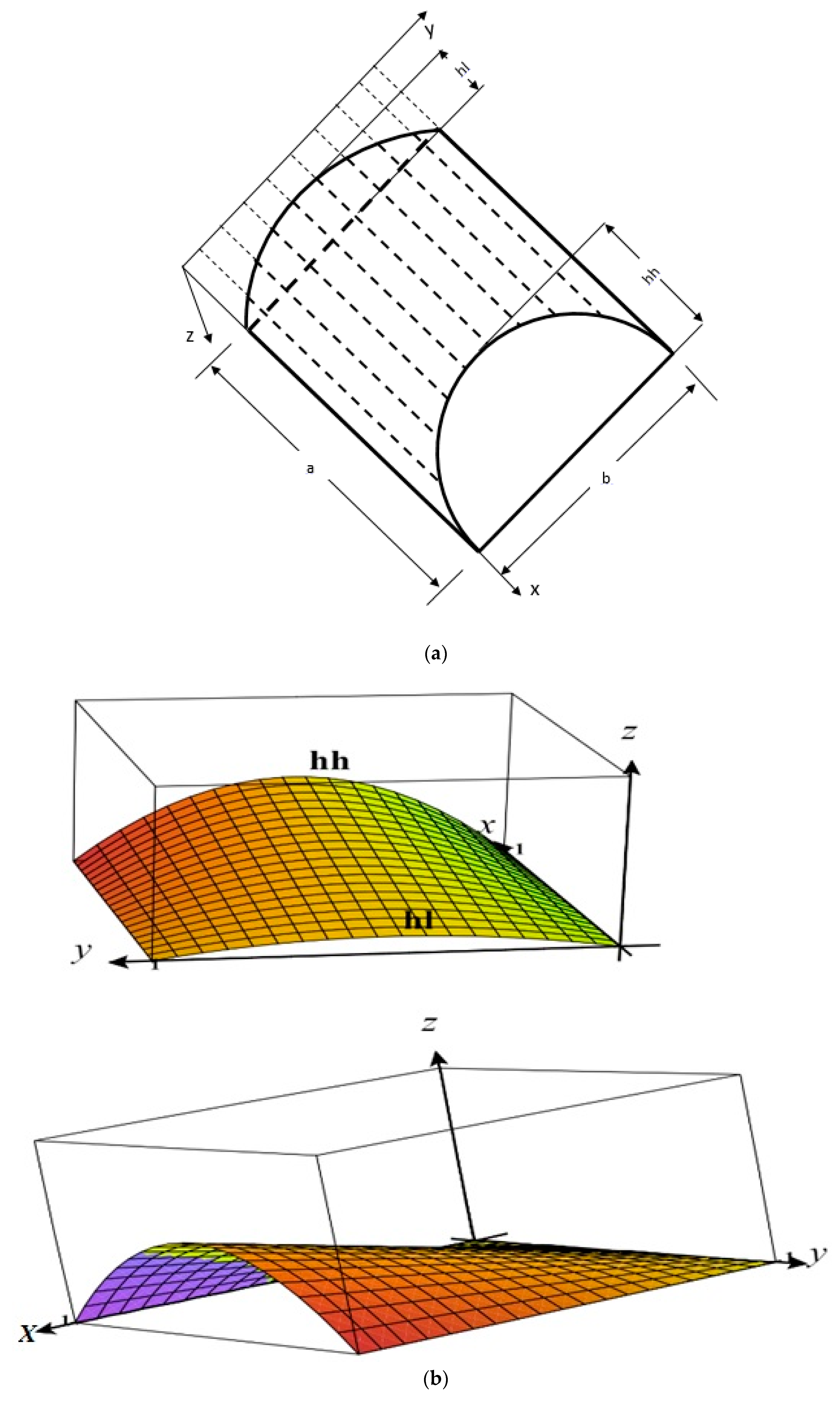
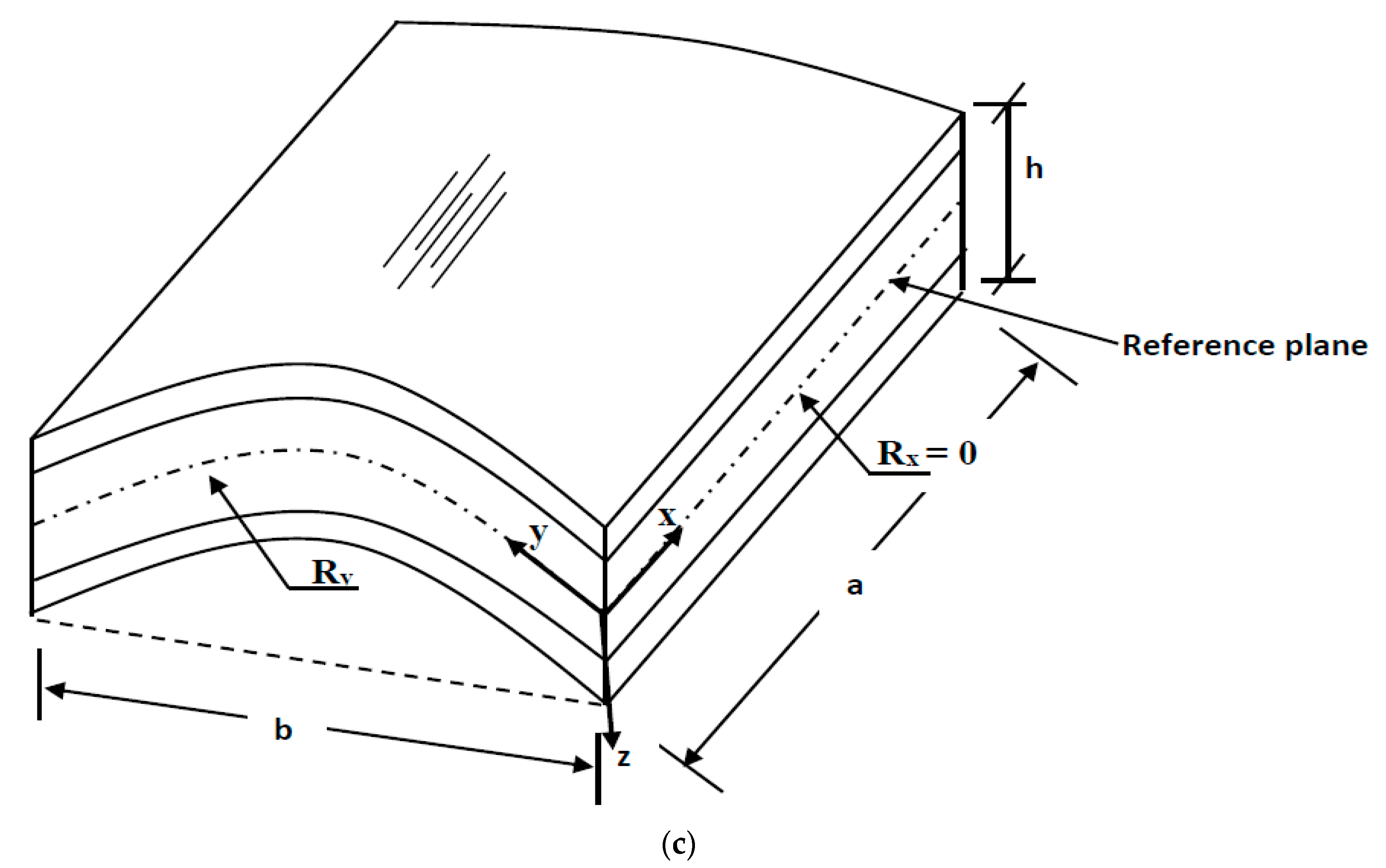
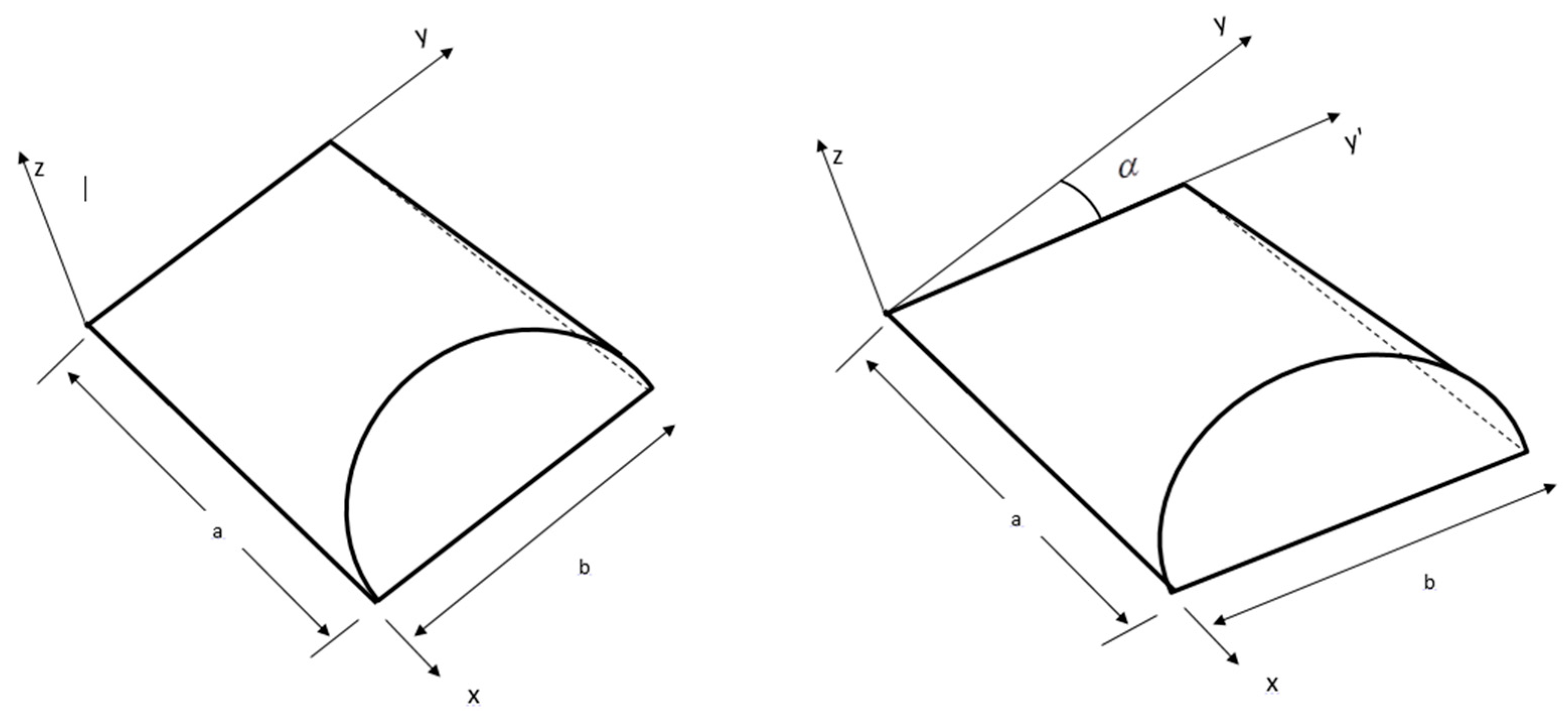
| h/a | Reference | Theory | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.10 | Present (8 × 8) | 0.7174 | 0.5917 | 0.5544 | 0.0285 | |
| Present (12 × 12) | 0.7175 | 0.5880 | 0.5511 | 0.0282 | ||
| Present (16 × 16) | 0.7176 | 0.5866 | 0.5499 | 0.0282 | ||
| Present (20 × 20) | 0.7176 | 0.5866 | 0.5498 | 0.0280 | ||
| Pagano [46] | 3D Elasticity | 0.7405 | 0.5900 | |||
| Chakrabarti and Sheikh [47] | HSDT | 0.7140 | 0.5806 | 0.2722 | 0.0279 | |
| Chakrabarti and Sheikh [47] | FSDT | 0.6700 | 0.5219 | 0.2582 | 0.0254 |
| Thickness Ratio | Brischetto and Carrera [21] | Present |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | 5.9448 | 5.9424 |
| 50 | 1.4857 | 1.4857 |
| 10 | 0.0587 | 0.0590 |
| 5 | 0.0141 | 0.0144 |
| Reference | 0°/90°/0° | 0° | 0°/90° | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a/b = 1 | a/b = 1.5 | a/b = 2 | a/b = 1 | a/b = 1 | |
| Present | 1.0174 | 0.8585 | 0.6319 | 1.0226 | 1.1080 |
| Singh and Chakrabarti [24] | 1.0429 | 0.8802 | 0.6566 | 1.0332 | 1.1520 |
| Prathap and Naganarayana [48] | 1.0249 | 0.8802 | 0.6566 | 1.0332 | 1.1434 |
| NASTRAN [24] | 1.0028 | 0.8346 | 0.6108 | 1.0109 | 1.9374 |
| Reddy and Hsu [9] | 1.0949 | 0.9847 | 0.7643 | 1.0313 | 1.6765 |
| a/b | a/h = 10 | a/h = 20 | a/h = 50 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Present | Zenkour and Alghanmi [29] | Present | Zenkour and Alghanmi [29] | Present | Zenkour and Alghanmi [29] | |
| 1 | 2.7360 | 2.7749 | 2.1691 | 2.3654 | 1.9906 | 2.2355 |
| 1.5 | 3.2156 | 3.2273 | 2.9160 | 2.8521 | 2.8168 | 2.7148 |
| 2 | 3.0517 | 2.8496 | 2.9415 | 2.6631 | 2.8971 | 2.5849 |
| x/a | Das and Chakravorty 1 [38] | Hadid 2 [31] | Present |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.10 | 0.9142 | 0.9857 | 0.9694 |
| 0.40 | 2.0428 | 1.8285 | 1.8146 |
| 0.60 | 1.6000 | 1.4000 | 1.4771 |
| 0.70 | 1.3571 | 1.3000 | 1.2637 |
| 0.80 | 0.9714 | 1.0000 | 0.9946 |
| Lamination (°) | Maximum Non-Dimensional Downward Deflection | |
|---|---|---|
| Present Theory | Das and Chakravorty [38] | |
| 0/90 | 0.305 (0.20, 0.50) | 0.319 (0.19, 0.50) |
| 0/90/0 | 0.314 (0.30, 0.50) | 0.298 (0.13, 0.50) |
| 45/−45 | 0.696 (0.25, 0.50) | 0.722 (0.25, 0.50) |
| 45/−45/45 | 0.610 (0.27, 0.40) | 0.629 (0.25, 0.38) |
| Skew Angle | hl/hh | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.25 | 0.20 | 0.15 | 0.10 | 0.05 | 0.00 | |
| 0° | 0.242 (0.40, 0.50) | 0.259 (0.38, 0.50) | 0.279 (0.35, 0.50) | 0.306 (0.33, 0.50) | 0.341 (0.28, 0.50) | 0.386 (0.28, 0.50) |
| 15° | 0.203 (0.44, 0.53) | 0.215 (0.44, 0.51) | 0.229 (0.41, 0.51) | 0.245 (0.41, 0.51) | 0.265 (0.39, 0.51) | 0.288 (0.39, 0.51) |
| 30° | 0.359 (0.54, 0.67) | 0.352 (0.54, 0.67) | 0.343 (0.54, 0.67) | 0.333 (0.54, 0.67) | 0.323 (0.54, 0.67) | 0.312 (0.54, 0.67) |
| 45° | 0.384 (0.74, 0.57) | 0.381 (0.74, 0.57) | 0.378 (0.74, 0.57) | 0.373 (0.73, 0.58) | 0.368 (0.73, 0.58) | 0.363 (0.73, 0.58) |
| 60° | 0.220 (0.91, 0.43) | 0.221 (0.91, 0.43) | 0.222 (0.91, 0.43) | 0.223 (0.91, 0.43) | 0.223 (0.91, 0.43) | 0.222 (0.91, 0.43) |
| Skew Angle | Boundary Conditions | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSSS | CCCC | CSCS | CCSS | CCFF | CFCF | |
| 0° | 0.242 (0.40, 0.50) | 0.231 (0.40, 0.50) | 0.231 (0.43, 0.50) | 0.226 (0.40, 0.50) | 0.615 (0.43, 0.50) | 0.471 (1.00, 0.28) |
| 15° | 0.204 (0.44, 0.53) | 0.209 (0.42, 0.43) | 0.201 (0.42, 0.46) | 0.203 (0.42, 0.43) | 0.471 (0.45, 0.39) | 0.882 (1.07, 0.27) |
| 30° | 0.360 (0.54, 0.67) | 0.165 (0.45, 0.35) | 0.165 (1.30, 0.74) | 0.158 (0.45, 0.35) | 0.442 (1.25, 0.87) | 1.444 (1.16, 0.28) |
| 45° | 0.385 (0.74, 0.57) | 0.102 (0.49, 0.27) | 0.124 (1.43, 0.60) | 0.096 (0.49, 0.27) | 0.789 (1.31, 0.71) | 0.665 (1.19, 0.19) |
| 60° | 0.221 (0.91, 0.43) | 0.047 (0.53, 0.18) | 0.069 (1.46, 0.41) | 0.044 (0.51, 0.15) | 0.781 (1.34, 0.50) | 0.444 (1.87, 0.50) |
| Skew Angle | 0°/90° | 45°/−45° | 0°/90°/0° | 45°/−45°/45° | 0°/90°/90°/0° |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0° | 0.323 | 0.249 | 0.201 | 0.210 | 0.132 |
| 15° | 0.266 | 0.264 | 0.172 | 0.188 | 0.125 |
| 30° | 0.176 | 0.223 | 0.115 | 0.144 | 0.080 |
| 45° | 0.084 | 0.132 | 0.104 | 0.080 | 0.108 |
| 60° | 0.094 | 0.125 | 0.105 | 0.125 | 0.098 |
| Skew Angle | a/h = 5 | a/h = 10 | a/h = 20 | a/h = 50 | a/h = 100 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0° | 7.742 | 6.527 | 4.878 | 4.241 | 4.849 |
| 15° | 3.253 | 2.691 | 2.101 | 1.885 | 2.036 |
| 30° | 1.084 | 0.888 | 0.697 | 1.031 | 1.799 |
| 45° | 0.200 | 0.169 | 0.222 | 0.431 | 0.770 |
| 60° | 0.102 | 0.095 | 0.104 | 0.145 | 0.220 |
| Stresses | hl/hh | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.25 | 0.20 | 0.15 | 0.10 | 0.05 | 0.00 | |
| −463.40 | −486.05 | −485.00 | −445.01 | −346.33 | −170.05 | |
| −2738.92 | −2569.06 | −2381.98 | −2172.71 | −1935.42 | −1663.12 | |
| 3838.81 | 3786.63 | 3561.32 | 3055.54 | 2115.01 | 545.88 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chaubey, A.; Kumar, A.; Fic, S.; Barnat-Hunek, D.; Sadowska-Buraczewska, B. Hygrothermal Analysis of Laminated Composite Skew Conoids. Materials 2019, 12, 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12020225
Chaubey A, Kumar A, Fic S, Barnat-Hunek D, Sadowska-Buraczewska B. Hygrothermal Analysis of Laminated Composite Skew Conoids. Materials. 2019; 12(2):225. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12020225
Chicago/Turabian StyleChaubey, Abhay, Ajay Kumar, Stanisław Fic, Danuta Barnat-Hunek, and Barbara Sadowska-Buraczewska. 2019. "Hygrothermal Analysis of Laminated Composite Skew Conoids" Materials 12, no. 2: 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12020225
APA StyleChaubey, A., Kumar, A., Fic, S., Barnat-Hunek, D., & Sadowska-Buraczewska, B. (2019). Hygrothermal Analysis of Laminated Composite Skew Conoids. Materials, 12(2), 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12020225






