Performance Evaluation of Vegetable Oil-Based Nano-Cutting Fluids in Environmentally Friendly Machining of Inconel-800 Alloy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
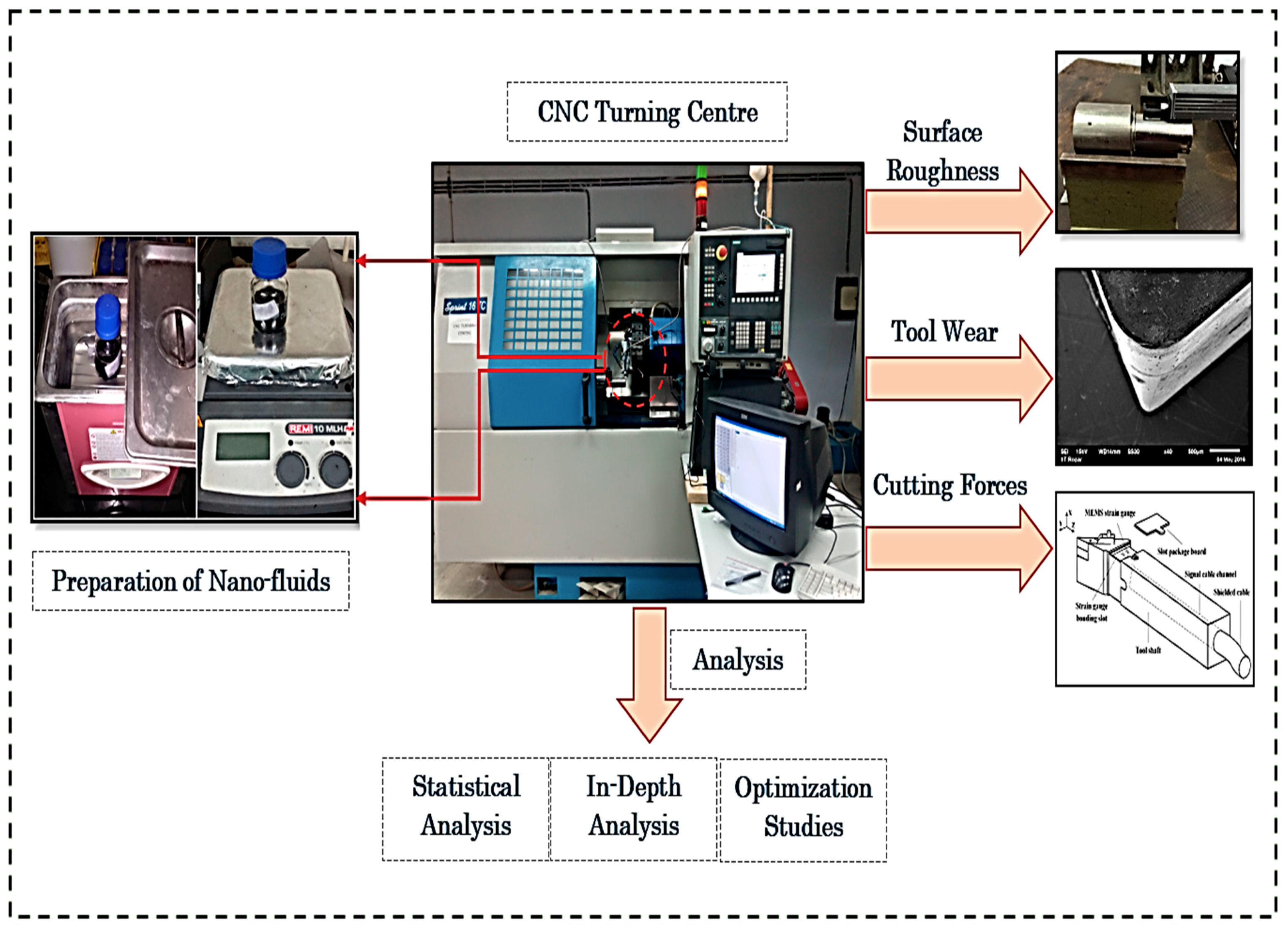
2.1. Workpiece, Cutting tool, and Machine Tool Details
2.2. Cooling-Lubrication Conditions
2.3. Preparation of Nanofluids
2.4. Machining Characteristic Measurements
2.5. Process Parameters and Design Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
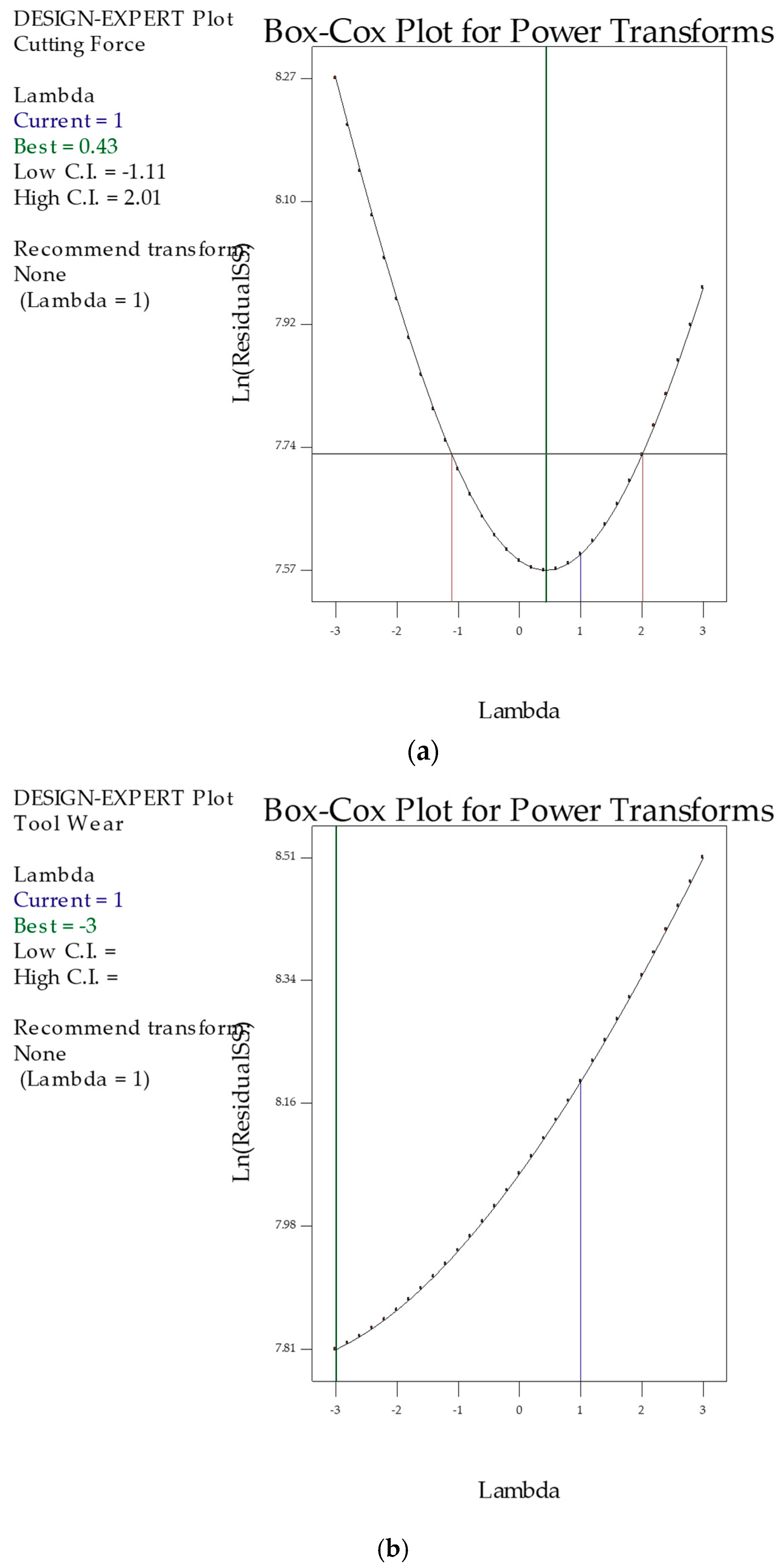
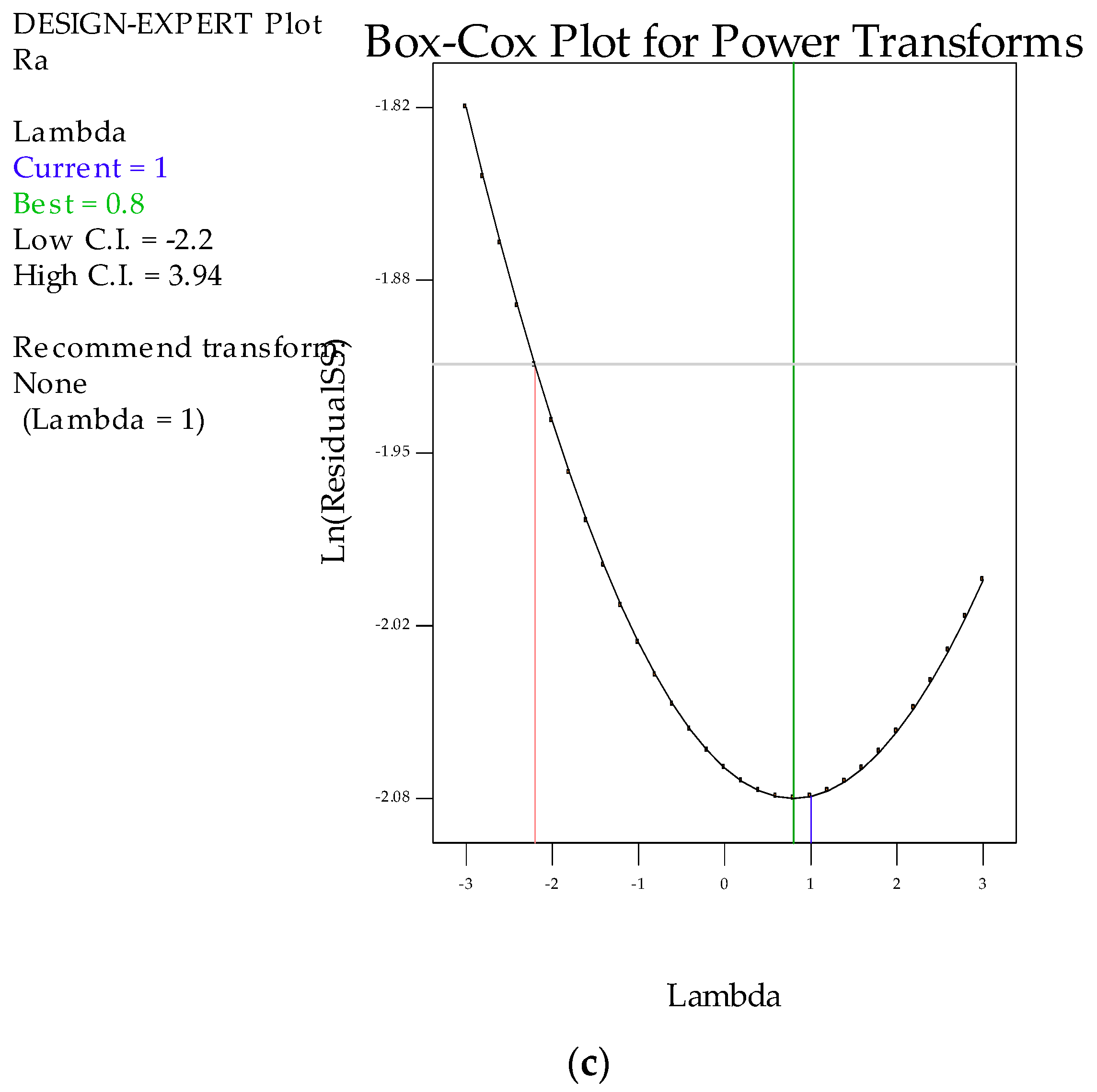
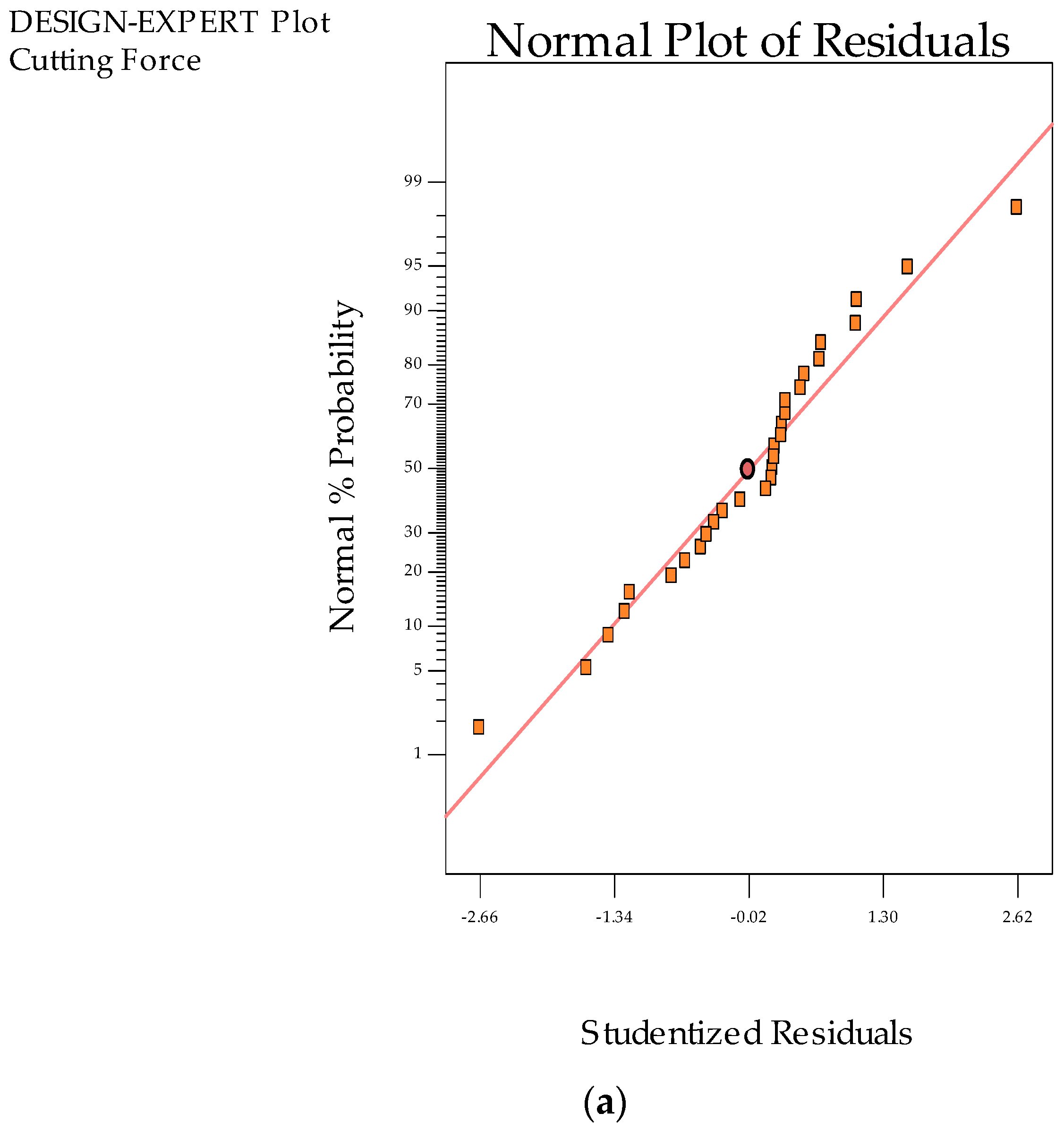
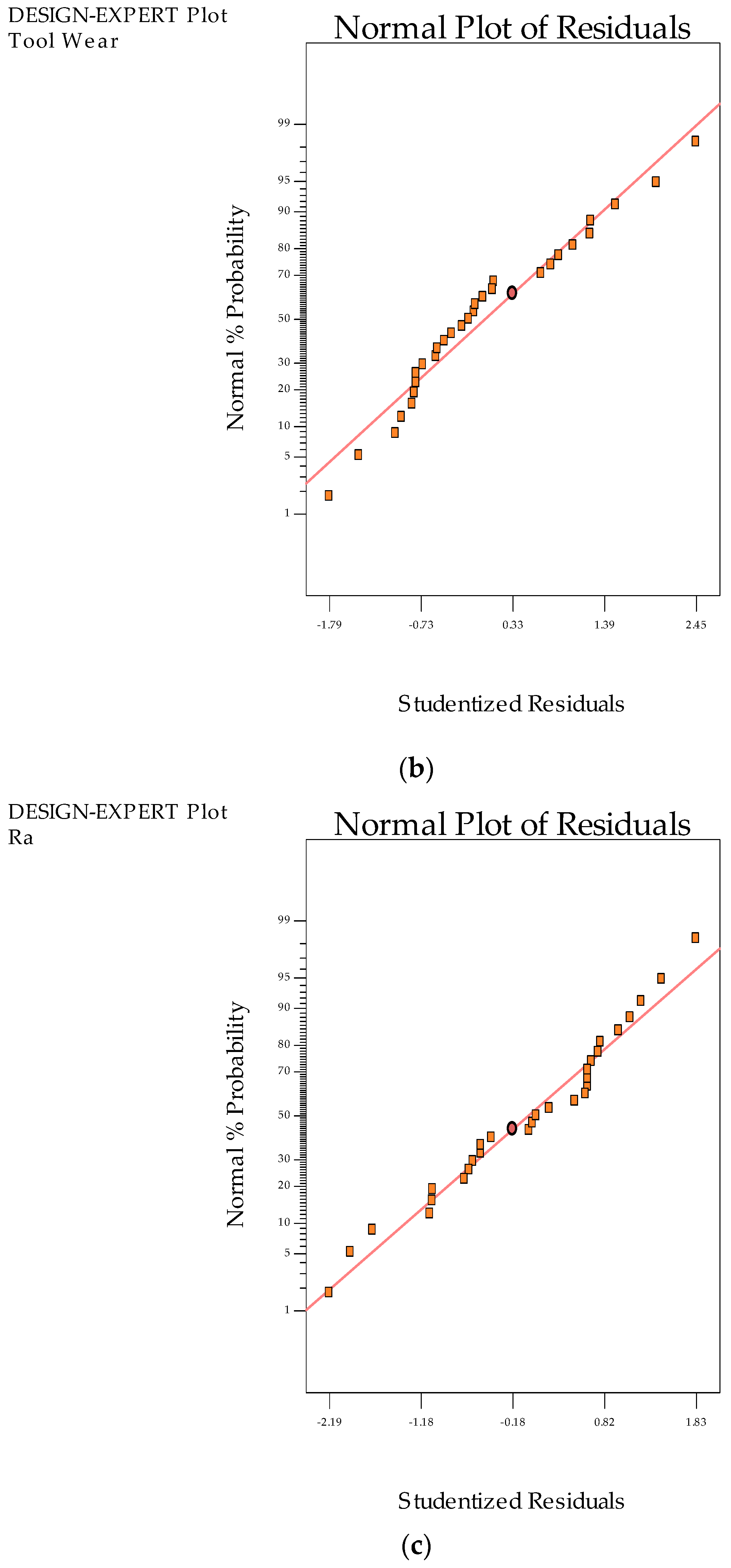
3.1. Statistical Analysis
3.2. Experimental Investigation
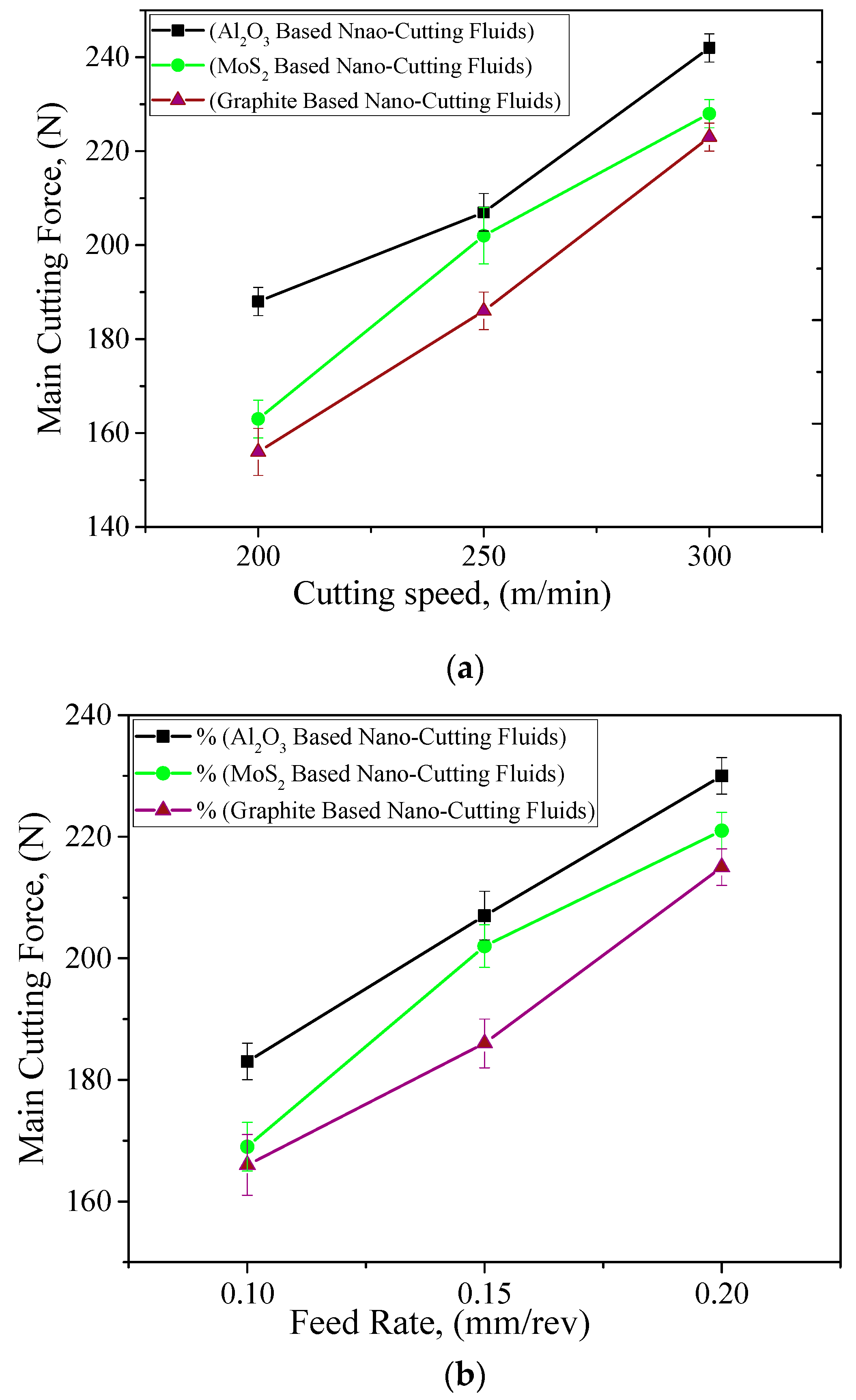
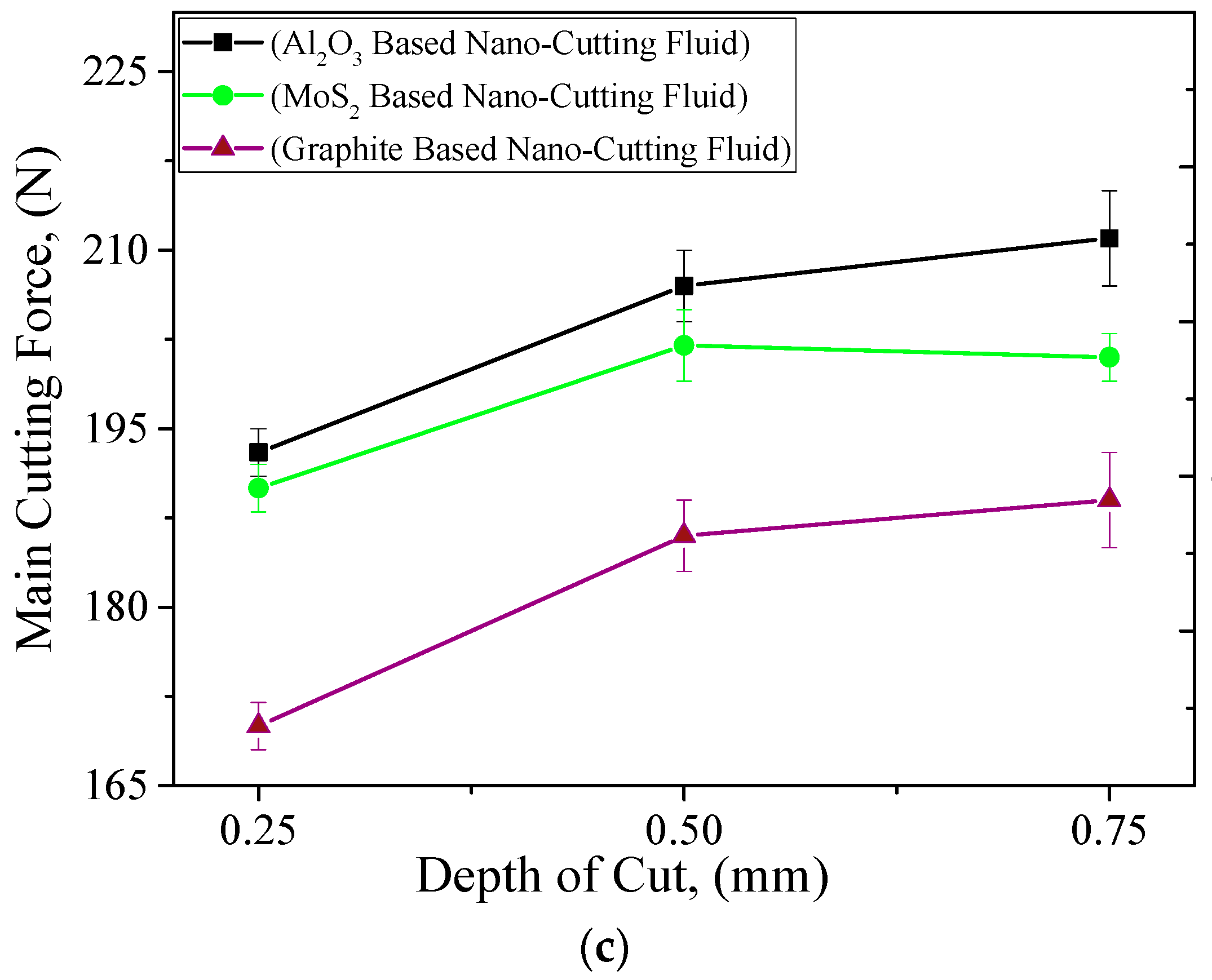
3.2.1. Cutting Forces
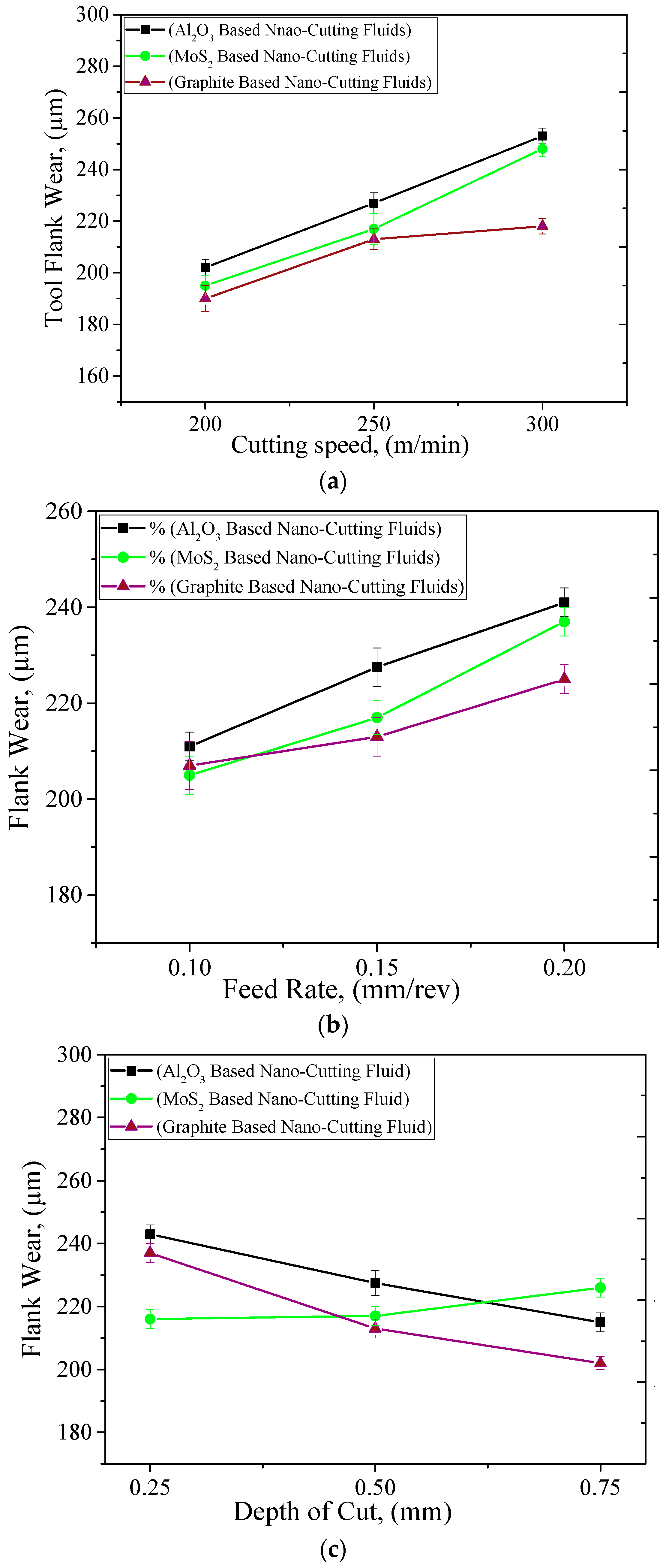
3.2.2. Tool Wear
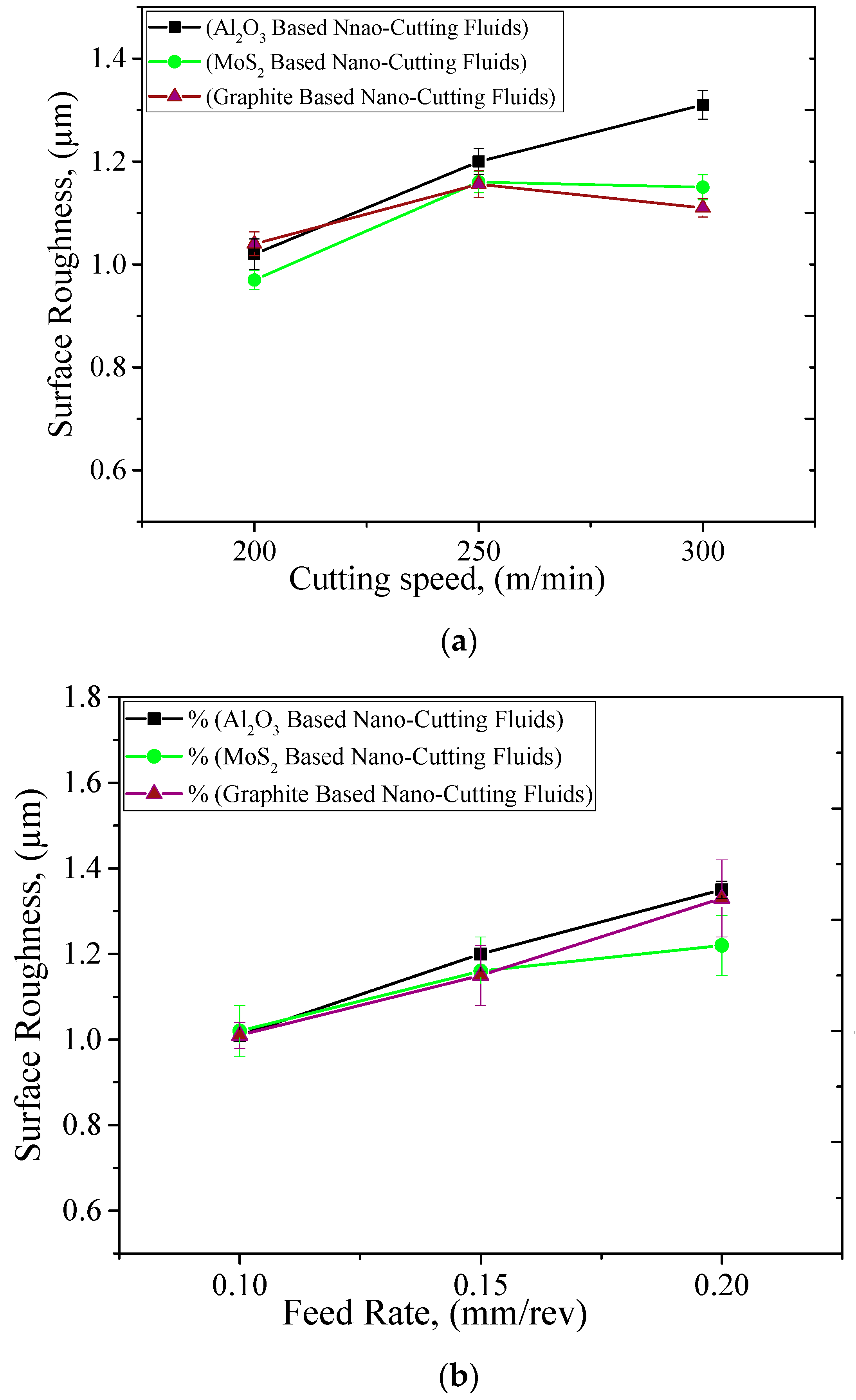
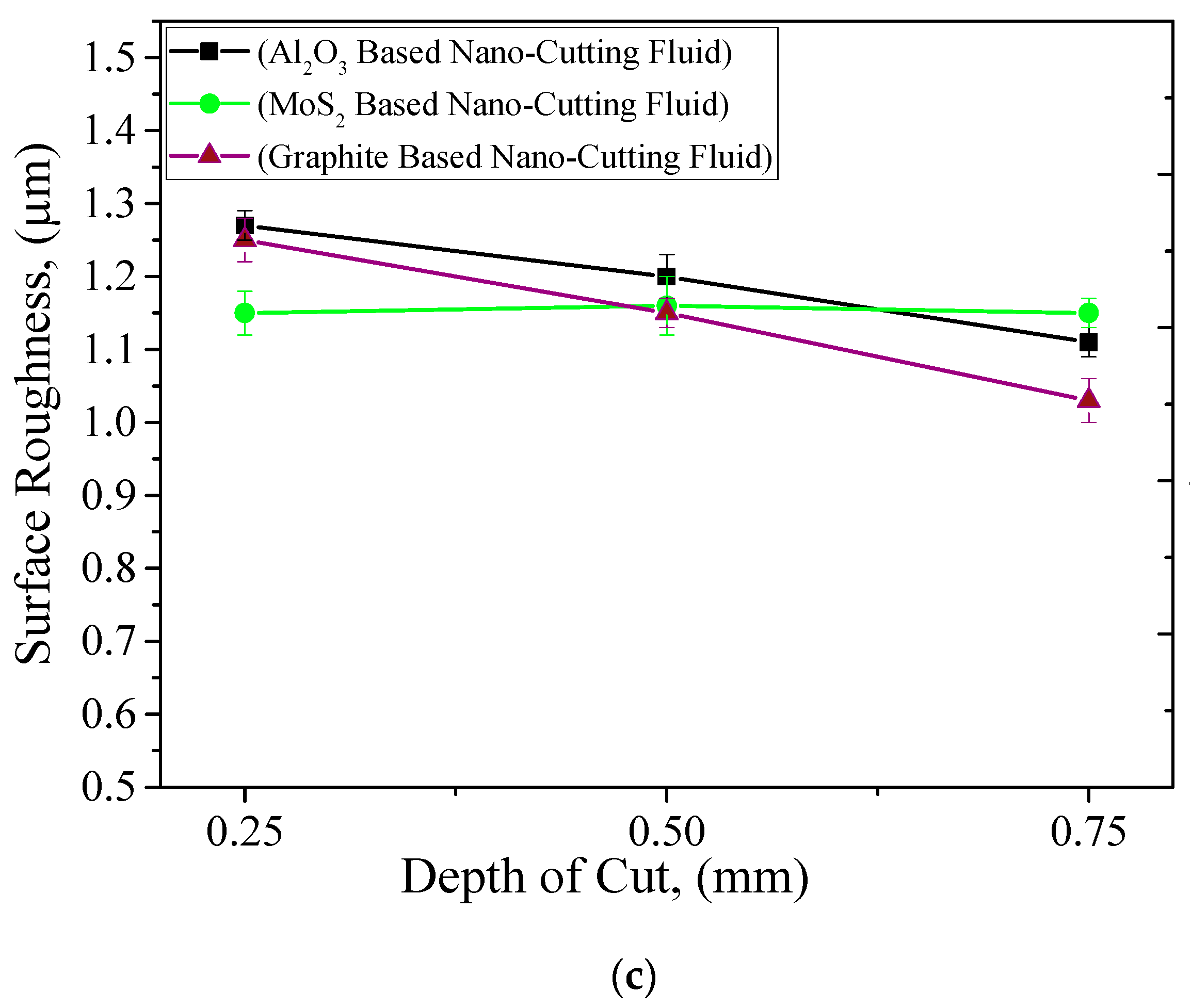
3.3. Surface Roughness
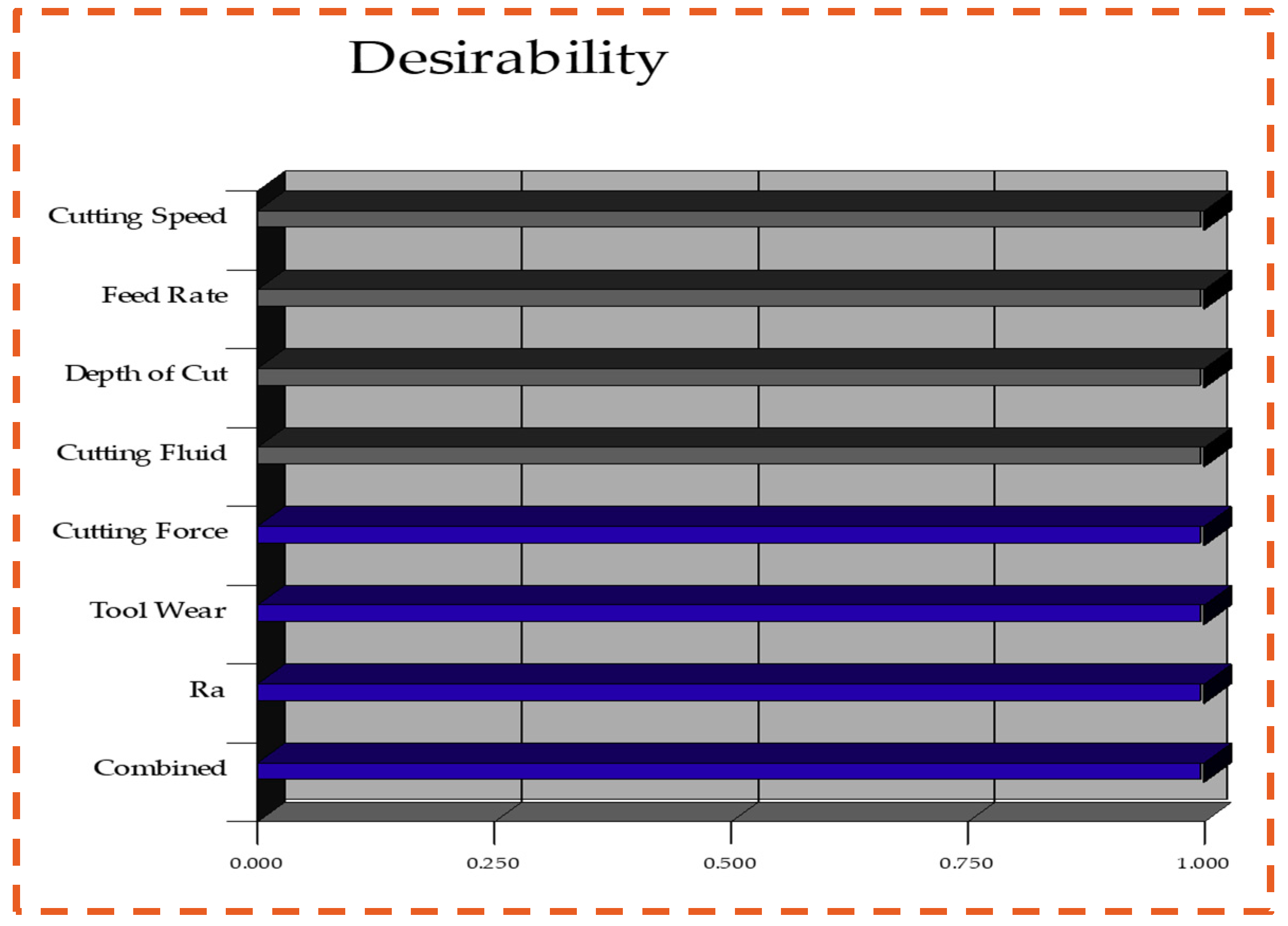
3.4. Optimization of Process Parameters: Composite Desirability Approach (CDA)
4. Conclusions
- Statistical analysis results: The results determined through experiments were statistically significant in terms of Box Cox transformation, R2 values, and ANOVA tests. Therefore, the prediction models are useful for researchers and academics to determine the values for their reference.
- Experimental investigation: The trend of almost all parameters were found to be the same, i.e., the cutting forces, tool wear, and surface roughness values were significantly affected with small changes in any one of these machining parameters.
- Comparison results: When the comparison was made between all cutting fluids, the overall performance of graphite-based nanofluids was found to be better in improving the machining characteristics. This is because of the good tribological and cooling properties of graphite-based nano-cutting fluids. Moreover, the chemical structure of graphite is more covalent and this drastically affects its performance as compared to other nanofluids.
- Optimization results: CDA is also a very efficient optimization method for determining the optimal solution, i.e., 200 m/min for the cutting speed, 0.10 mm/rev of feed rate, 0.70 mm of depth of cut, and graphite-based nano-cutting fluids.
- Future recommendations: Even though the results obtained from this study were highly useful for practical applications, some future avenues are still pending to improve the machining performance of Inconel-800 alloy. For instance, the high-pressure cooling (HPC) approach could be integrated with the nano-cutting fluids and the results compared with the MQL technique.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Darshan, C.; Jain, S.; Dogra, M.; Gupta, M.K.; Mia, M. Machinability improvement in Inconel-718 by enhanced tribological and thermal environment using textured tool. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, A.; Gangopadhyay, S. State-of-the-art in surface integrity in machining of nickel-based super alloys. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2016, 100, 25–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, B.C.; Alemayehu, H.; Ghosh, S.; Rao, P.V. A comparative study of recent lubri-coolant strategies for turning of Ni-based superalloy. J. Manuf. Process. 2017, 30, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Pruncu, C.; Mia, M.; Singh, G.; Singh, S.; Prakash, C.; Sood, P.; Gill, H. Machinability investigations of inconel-800 super alloy under sustainable cooling conditions. Materials 2018, 11, 2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- M’Saoubi, R.; Outeiro, J.C.; Chandrasekaran, H.; Dillon Jr, O.W.; Jawahir, I.S. A review of surface integrity in machining and its impact on functional performance and life of machined products. Int. J. Sustain. Manuf. 2008, 1, 203–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krolczyk, G.M.; Maruda, R.W.; Krolczyk, J.B.; Wojciechowski, S.; Mia, M.; Nieslony, P.; Budzik, G. Ecological trends in machining as a key factor in sustainable production—A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 218, 601–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruda, R.W.; Krolczyk, G.M.; Feldshtein, E.; Pusavec, F.; Szydlowski, M.; Legutko, S.; Sobczak-Kupiec, A. A study on droplets sizes, their distribution and heat exchange for minimum quantity cooling lubrication (MQCL). Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2016, 100, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mia, M.; Singh, G.; Gupta, M.K.; Sharma, V.S. Influence of Ranque-Hilsch vortex tube and nitrogen gas assisted MQL in precision turning of Al 6061-T6. Precis. Eng. 2018, 53, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.K.; Sood, P.K.; Sharma, V.S. Optimization of machining parameters and cutting fluids during nano-fluid based minimum quantity lubrication turning of titanium alloy by using evolutionary techniques. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 135, 1276–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldırım, Ç.V.; Kıvak, T.; Erzincanlı, F. Tool wear and surface roughness analysis in milling with ceramic tools of Waspaloy: A comparison of machining performance with different cooling methods. J. Brazilian Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2019, 41, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarikaya, M.; Güllü, A. Multi-response optimization of minimum quantity lubrication parameters using Taguchi-based grey relational analysis in turning of difficult-to-cut alloy Haynes 25. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 91, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Pruncu, C.I.; Gupta, M.K.; Mia, M.; Khan, A.M.; Jamil, M.; Pimenov, D.Y.; Sen, B.; Sharma, V.S. Investigations of machining characteristics in the upgraded MQL-assisted turning of pure titanium alloys using evolutionary algorithms. Materials 2019, 12, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, K.K.; Kumar, R. Anurag An Experimental Investigations in Turning of Incoloy 800 in Dry, MQL and Flood Cooling Conditions. Procedia Manuf. 2018, 20, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruda, R.W.; Krolczyk, G.M.; Wojciechowski, S.; Zak, K.; Habrat, W.; Nieslony, P. Effects of extreme pressure and anti-wear additives on surface topography and tool wear during MQCL turning of AISI 1045 steel. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2018, 32, 1585–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruda, R.W.; Feldshtein, E.; Legutko, S.; Krolczyk, G.M. Research on emulsion mist generation in the conditions of Minimum Quantity Cooling Lubrication (MQCL). Teh. Vjestn. Tech. Gaz. 2015, 22, 1213–1218. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A.K.; Tiwari, A.K.; Dixit, A.R. Effects of Minimum Quantity Lubrication (MQL) in machining processes using conventional and nanofluid based cutting fluids: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 127, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Singh, R.K.; Dixit, A.R.; Tiwari, A.K. Characterization and experimental investigation of Al2O3 nanoparticle based cutting fluid in turning of AISI 1040 steel under minimum quantity lubrication (MQL). Mater. Today Proc. 2016, 3, 1899–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, M.; Khan, A.M.; Hegab, H.; Gong, L.; Mia, M.; Gupta, M.K.; He, N. Effects of hybrid Al2O3-CNT nanofluids and cryogenic cooling on machining of Ti–6Al–4V. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 102, 3895–3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Sani, A.S.; Rahim, E.A.; Sharif, S.; Sasahara, H. Machining performance of vegetable oil with phosphonium- and ammonium-based ionic liquids via MQL technique. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 209, 947–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Lv, T.; Wang, M.; Xu, X. Effects of machining and oil mist parameters on electrostatic minimum quantity lubrication–EMQL turning process. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. Green Technol. 2018, 5, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, A.; Paipa Suarez, M.; Falco Sales, W.; Rocha Machado, Á. Turning of Inconel 718 with whisker-reinforced ceramic tools applying vegetable-based cutting fluid mixed with solid lubricants by MQL. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2019, 266, 530–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mia, M.; Razi, M.H.; Ahmad, I.; Mostafa, R.; Rahman, S.M.S.; Ahmed, D.H.; Dey, P.R.; Dhar, N.R. Effect of time-controlled MQL pulsing on surface roughness in hard turning by statistical analysis and artificial neural network. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 91, 3211–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.M.; Jamil, M.; Ul Haq, A.; Hussain, S.; Meng, L.; He, N. Sustainable machining. Modeling and optimization of temperature and surface roughness in the milling of AISI D2 steel. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2019, 71, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmini, R.; Vamsi Krishna, P.; Krishna Mohana Rao, G. Effectiveness of vegetable oil based nanofluids as potential cutting fluids in turning AISI 1040 steel. Tribol. Int. 2016, 94, 490–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.M.; Jamil, M.; Salonitis, K.; Sarfraz, S.; Zhao, W.; He, N.; Mia, M.; Zhao, G.L. Multi-objective optimization of energy consumption and surface quality in nanofluid SQCl assisted face milling. Energies 2019, 12, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.K.; Sood, P.K. Machining Behavior of High Strength Temperature Resistant Alloys Under MQL Environment; National Institute of Technology: Hamirpur, India, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Vasantharaja, P.; Vasudevan, M. Optimization of A-TIG welding process parameters for RAFM steel using response surface methodology. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Des. Appl. 2015, 232, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutnichenko, O.; Bushlya, V.; Zhou, J.; Ståhl, J.-E. Tool wear and machining dynamics when turning high chromium white cast iron with pcBN tools. Wear 2017, 390, 253–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegab, H.; Umer, U.; Soliman, M.; Kishawy, H.A. Effects of nano-cutting fluids on tool performance and chip morphology during machining Inconel 718. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 96, 3449–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegab, H.; Kishawy, H. Towards sustainable machining of inconel 718 using nano-fluid minimum quantity lubrication. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2018, 2, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltaggaz, A.; Hegab, H.; Deiab, I.; Kishawy, H.A. Hybrid nano-fluid-minimum quantity lubrication strategy for machining austempered ductile iron (ADI). Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. 2018, 12, 1273–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegab, H.; Kishawy, H.A.; Umer, U.; Mohany, A. A model for machining with nano-additives based minimum quantity lubrication. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 102, 2013–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegab, H.; Umer, U.; Deiab, I.; Kishawy, H. Performance evaluation of Ti–6Al–4V machining using nano-cutting fluids under minimum quantity lubrication. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 95, 4229–4241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegab, H.; Kishawy, H.A.; Gadallah, M.H.; Umer, U.; Deiab, I. On machining of Ti-6Al-4V using multi-walled carbon nanotubes-based nano-fluid under minimum quantity lubrication. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 97, 1593–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltaggaz, A.; Zawada, P.; Hegab, H.A.; Deiab, I.; Kishawy, H.A. Coolant strategy influence on tool life and surface roughness when machining ADI. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 94, 3875–3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegab, H.; Darras, B.; Kishawy, H.A. Sustainability assessment of machining with nano-cutting fluids. Procedia Manuf. 2018, 26, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishawy, H.A.; Hegab, H.; Deiab, I.; Eltaggaz, A. Sustainability assessment during machining Ti-6Al-4V with Nano-additives-based minimum quantity lubrication. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2019, 3, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.K.; Sood, P.K.; Singh, G.; Sharma, V.S. Sustainable machining of aerospace material—Ti (grade-2) alloy: Modeling and optimization. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 147, 614–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
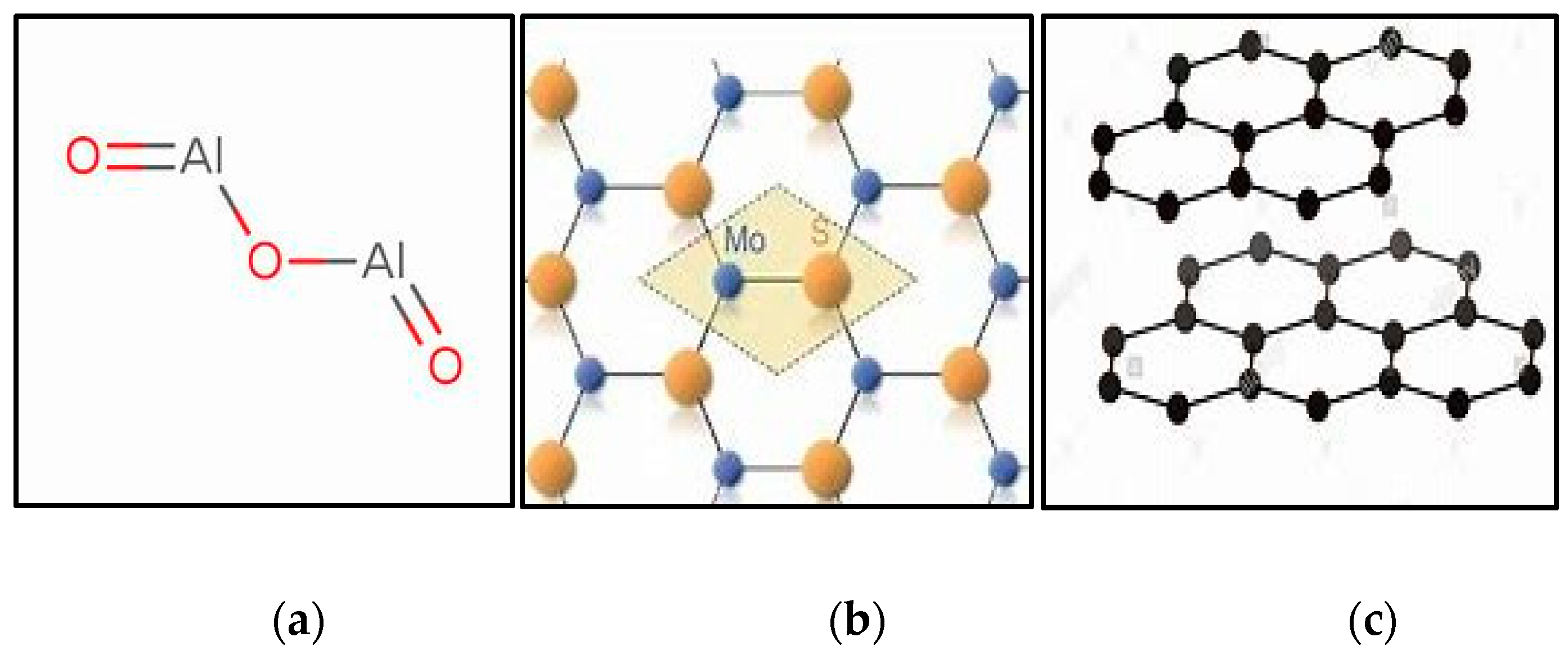

| Ni | Cr | Fe | C | Al | Ti | Al + Ti |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30.0–35.0 | 19.0–23.0 | 39.5 min | 0.10 max | 0.15–0.60 | 0.15–0.60 | 0.30–1.20 |
| Heat Treatment | Intermediate Treatment | Final Treatment | Rockwell Hardness |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1050 °C for 2 h, air-cooling | 850 °C for 6 h, air-cooling | 700 °C for 2 h, air-cooling | RC |
| Inclination Angle | −6° |
|---|---|
| Orthogonal rake angle | 6° |
| Orthogonal clearance angle | 80° |
| Auxiliary cutting-edge angle | 15° |
| Principal cutting-edge angle | 90° |
| Nose radius | 0.4 mm |
| Shape | Rhombic |
| Properties | Vegetable Base Oil | Al2O3 Nanofluid | MoS2 Nanofluid | Graphite Nanofluid |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Bright and clear | White | Black | Grayish Black |
| Viscosity (CP) (at 20 °C) | 68.16 | 120.23 | 100.56 | 83.12 |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/mK) | 0.1432 | 0.2085 | 0.2362 | 0.2663 |
| Parameters | Coded Value | Units | Low Level (−1) | Middle Level (0) | High Level (+1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cutting Speed (Vc) | A | m/min | 200 | 250 | 300 |
| Feed Rate (f) | B | mm/rev | 0.1 | 0.15 | 0.20 |
| Depth of cut (ap) | C | mm | 0.25 | 0.50 | 0.75 |
| Cooling condition | D | - | Al2O3 | MoS2 | Graphite |
| Sr. No. | Cutting Speed | Feed Rate | Depth of Cut | Cutting Fluid | Cutting Force | Tool Wear | Surface Roughness | Desirability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 200 | 0.10 | 0.70 | 3 | 143 | 181 | 0.87 | 1.00 |
| 2 | 202 | 0.10 | 0.64 | 3 | 141 | 183 | 0.88 | 0.88 |
| 3 | 201 | 0.10 | 0.63 | 3 | 140 | 183 | 0.88 | 0.74 |
| 4 | 201 | 0.10 | 0.70 | 3 | 145 | 182 | 0.87 | 0.72 |
| 5 | 200 | 0.10 | 0.62 | 2 | 141 | 182 | 0.88 | 0.65 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gupta, M.K.; Jamil, M.; Wang, X.; Song, Q.; Liu, Z.; Mia, M.; Hegab, H.; Khan, A.M.; Collado, A.G.; Pruncu, C.I.; et al. Performance Evaluation of Vegetable Oil-Based Nano-Cutting Fluids in Environmentally Friendly Machining of Inconel-800 Alloy. Materials 2019, 12, 2792. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12172792
Gupta MK, Jamil M, Wang X, Song Q, Liu Z, Mia M, Hegab H, Khan AM, Collado AG, Pruncu CI, et al. Performance Evaluation of Vegetable Oil-Based Nano-Cutting Fluids in Environmentally Friendly Machining of Inconel-800 Alloy. Materials. 2019; 12(17):2792. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12172792
Chicago/Turabian StyleGupta, Munish Kumar, Muhammad Jamil, Xiaojuan Wang, Qinghua Song, Zhanqiang Liu, Mozammel Mia, Hussein Hegab, Aqib Mashood Khan, Alberto Garcia Collado, Catalin Iulian Pruncu, and et al. 2019. "Performance Evaluation of Vegetable Oil-Based Nano-Cutting Fluids in Environmentally Friendly Machining of Inconel-800 Alloy" Materials 12, no. 17: 2792. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12172792
APA StyleGupta, M. K., Jamil, M., Wang, X., Song, Q., Liu, Z., Mia, M., Hegab, H., Khan, A. M., Collado, A. G., Pruncu, C. I., & Imran, G. M. S. (2019). Performance Evaluation of Vegetable Oil-Based Nano-Cutting Fluids in Environmentally Friendly Machining of Inconel-800 Alloy. Materials, 12(17), 2792. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12172792













