Improving the Magnetic Properties of Non-Oriented Electrical Steels by Secondary Recrystallization Using Dynamic Heating Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
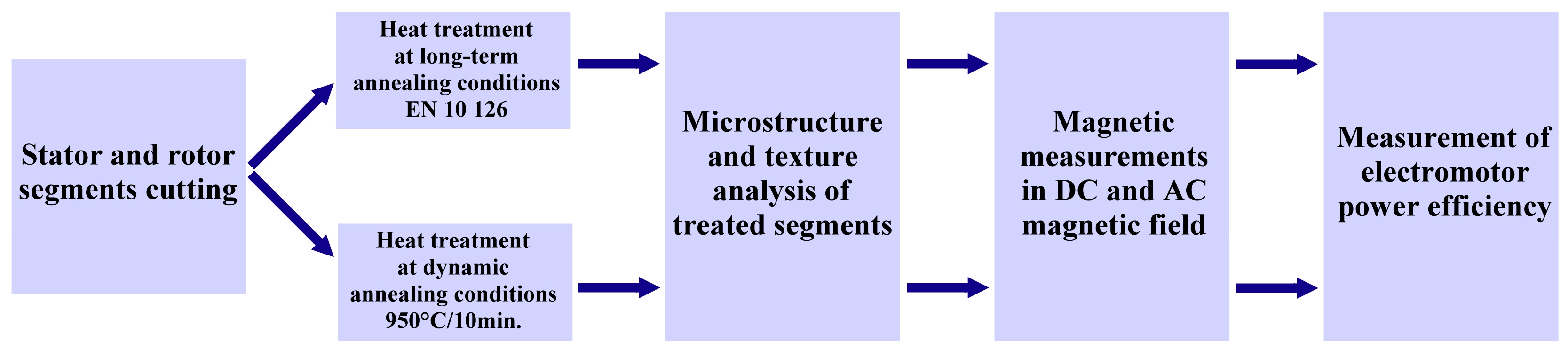
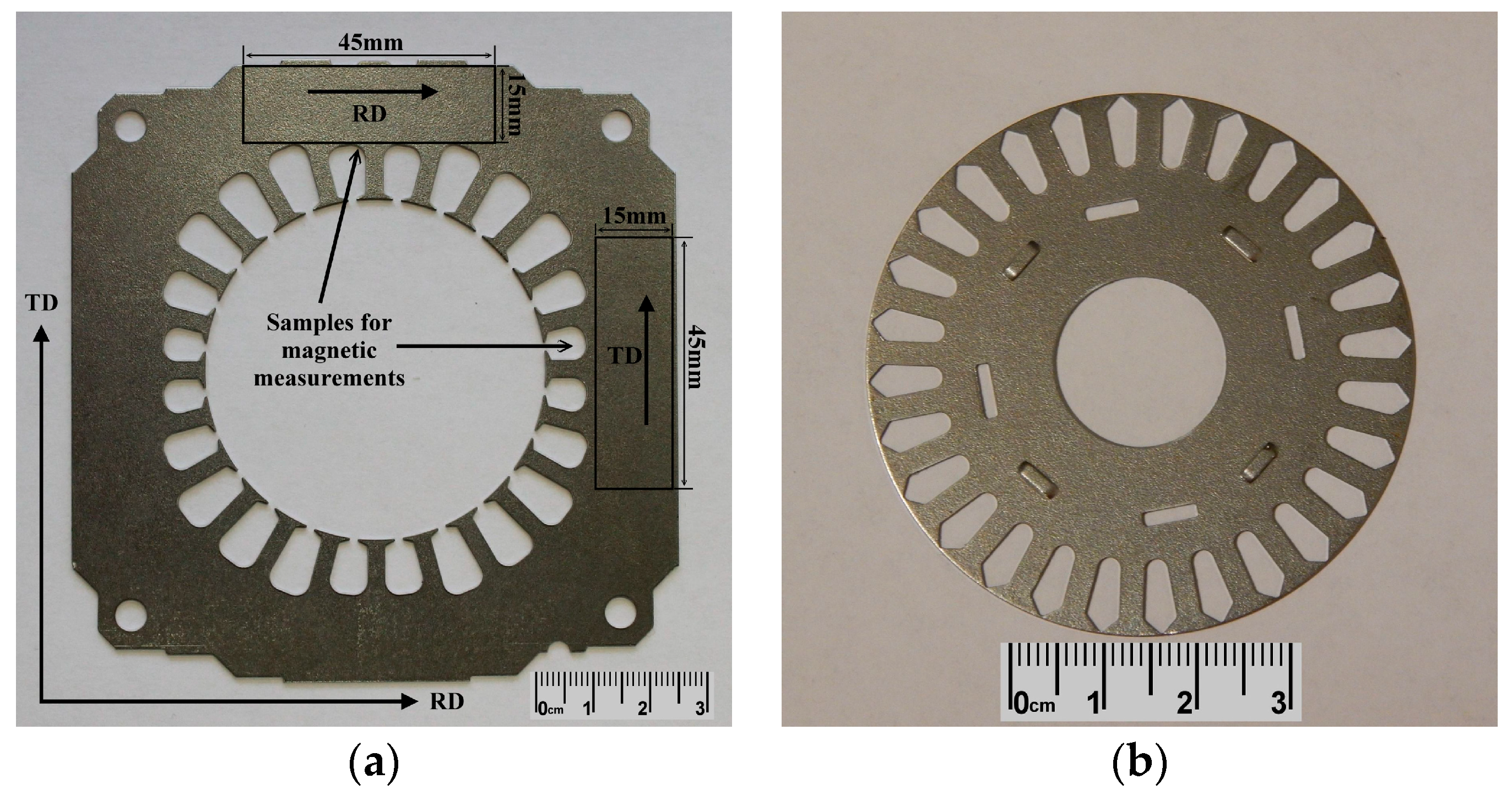
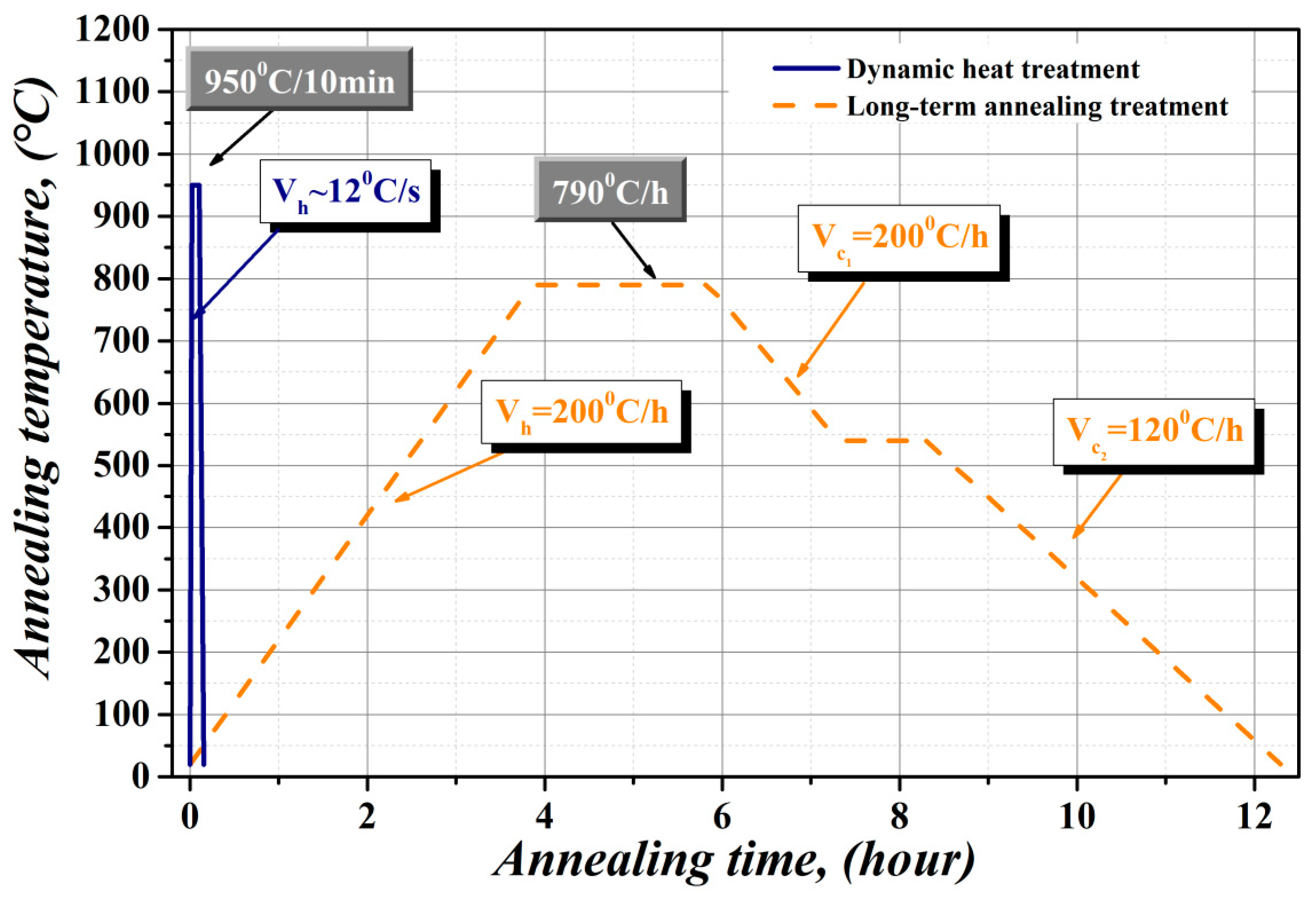
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
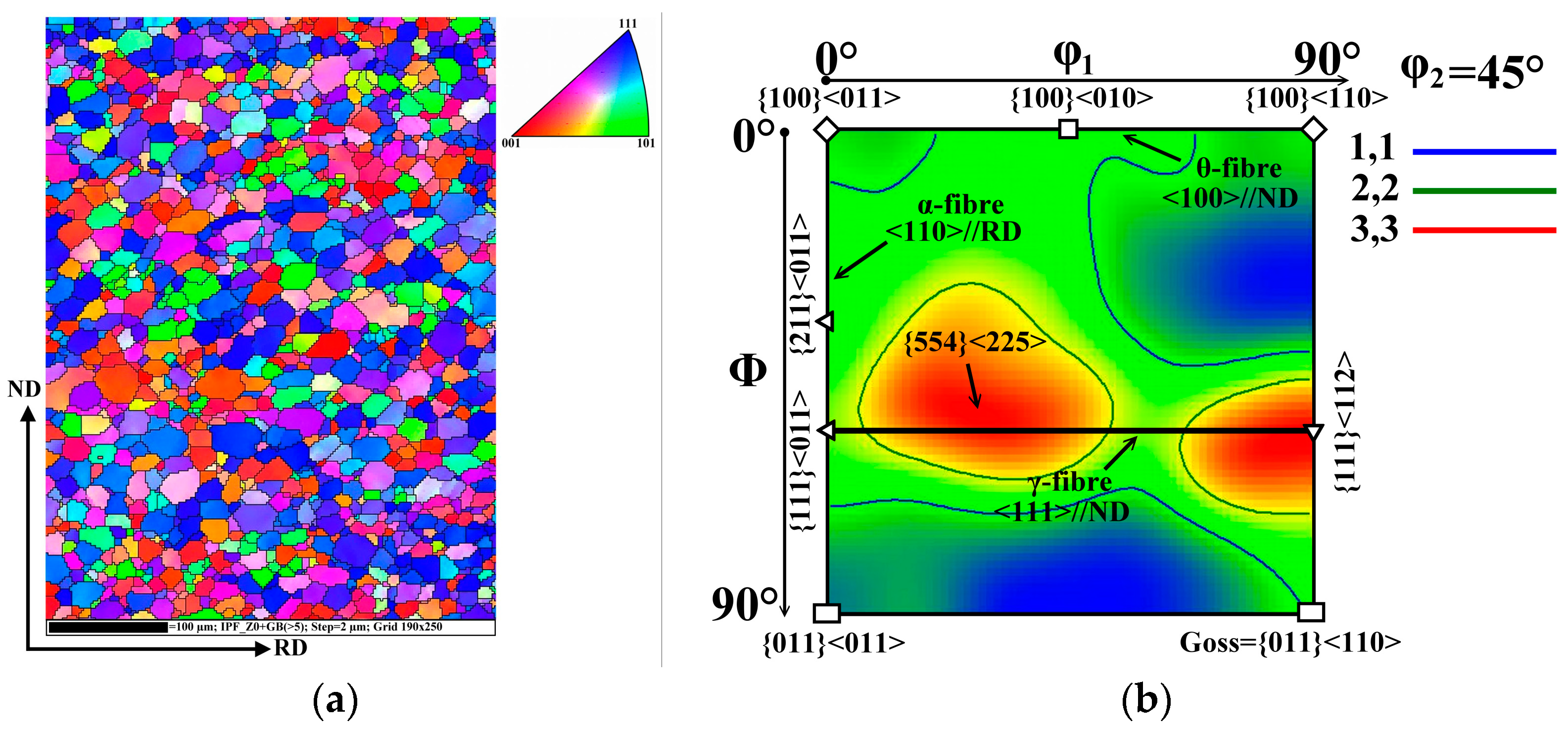
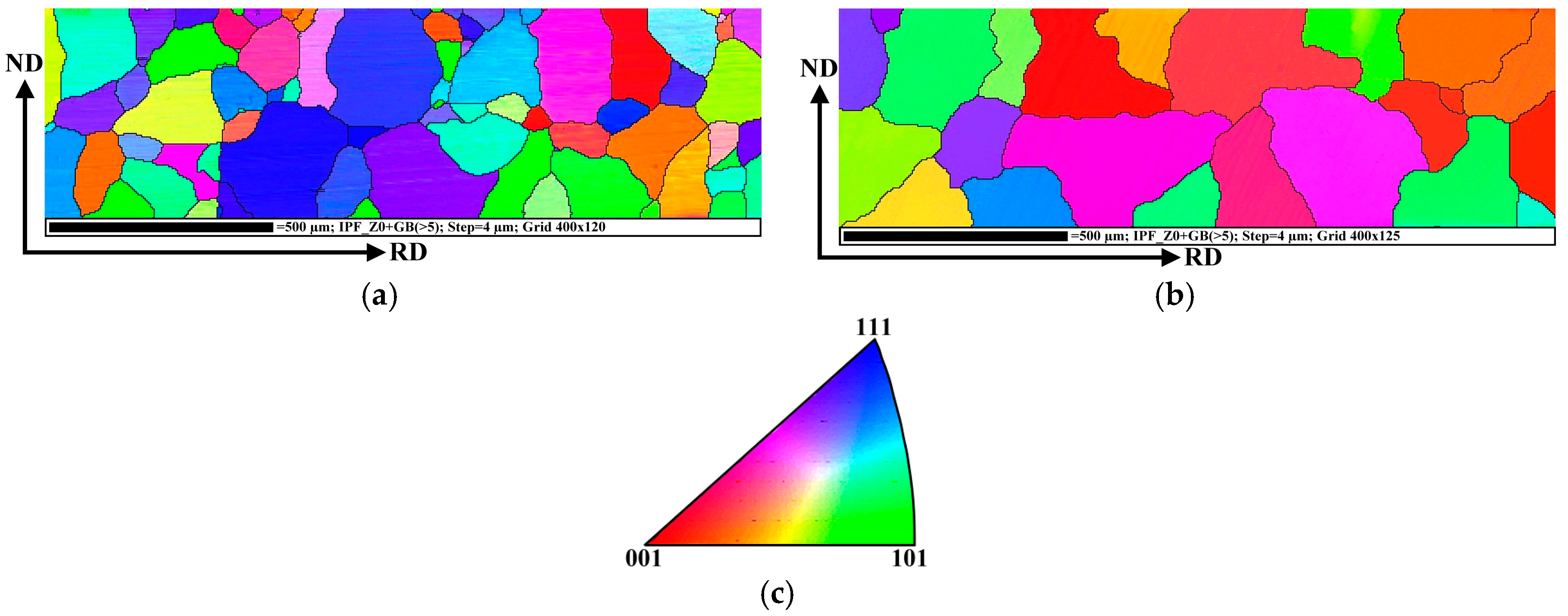
3.1. Microstructure
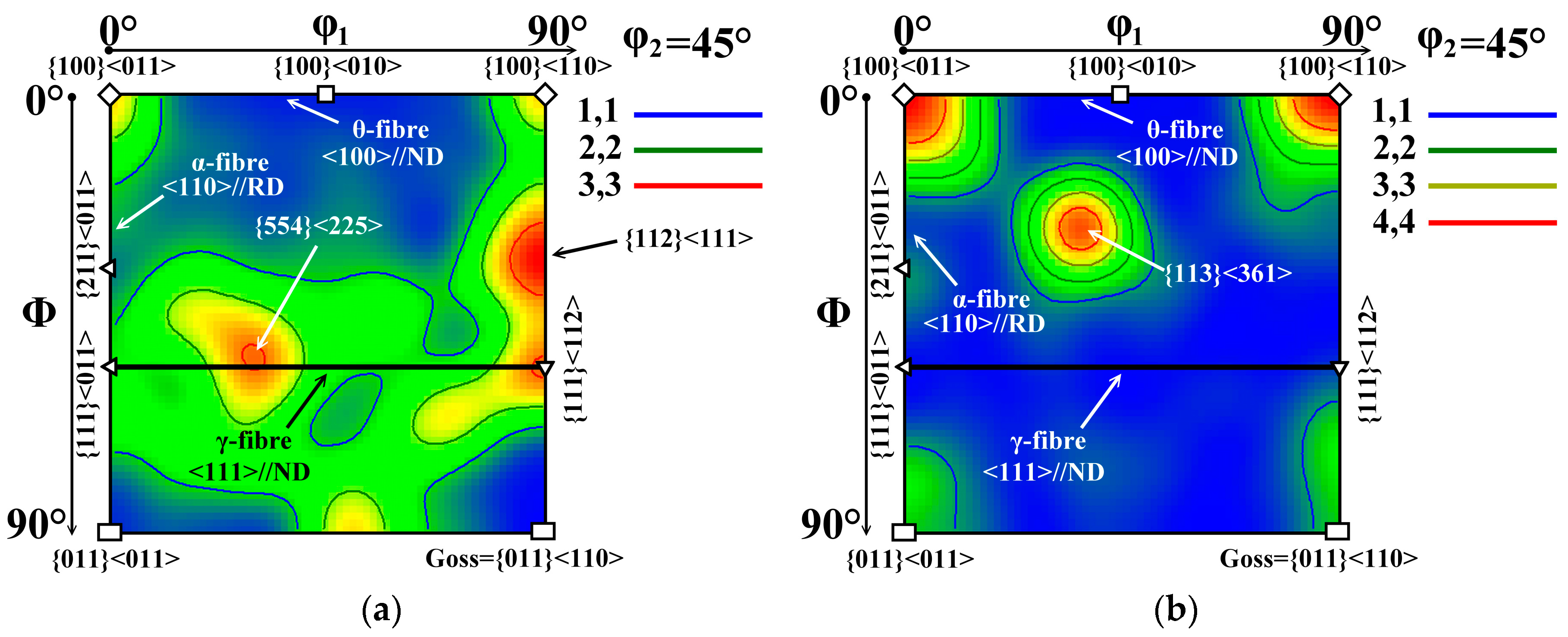
3.2. Texture
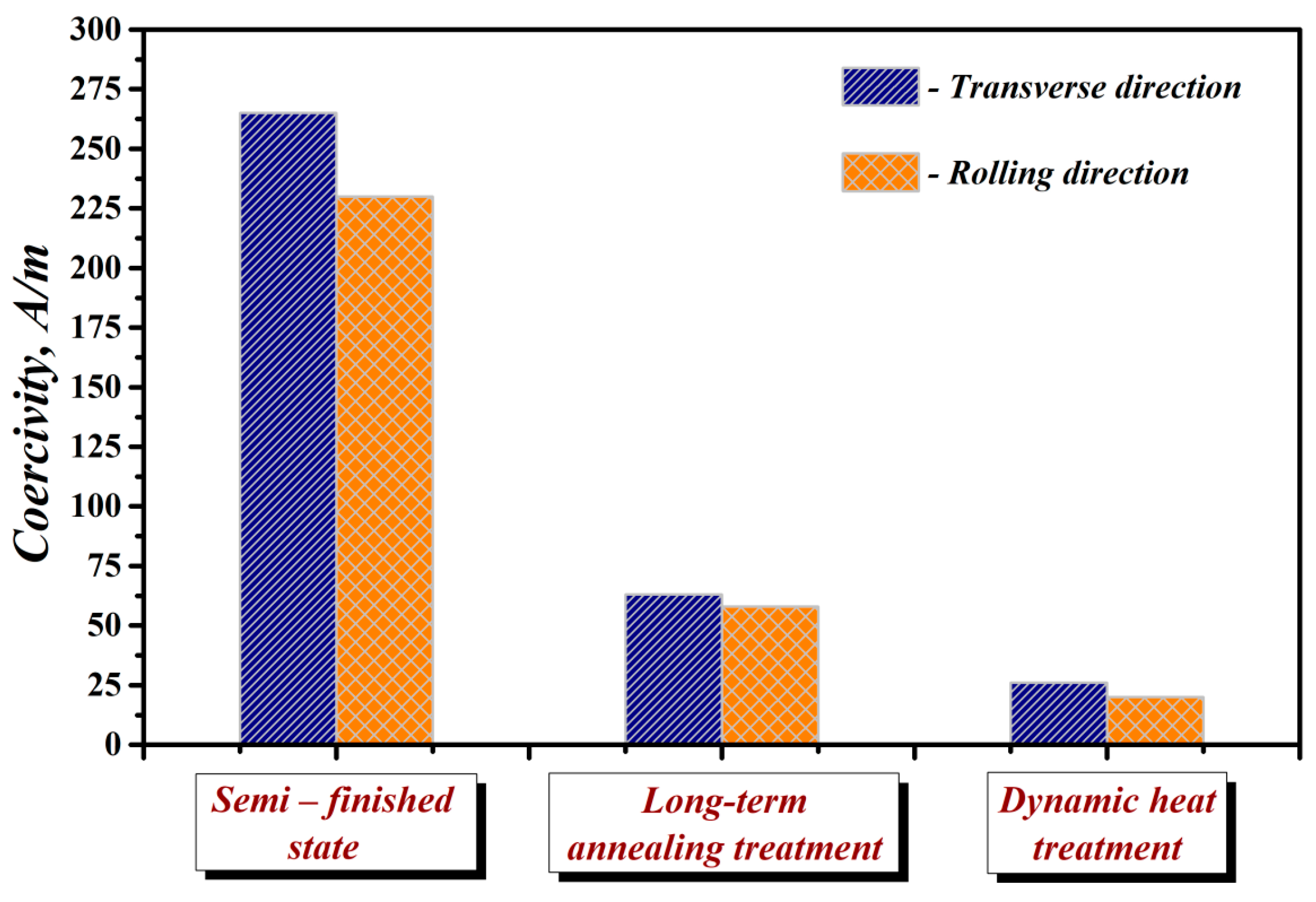
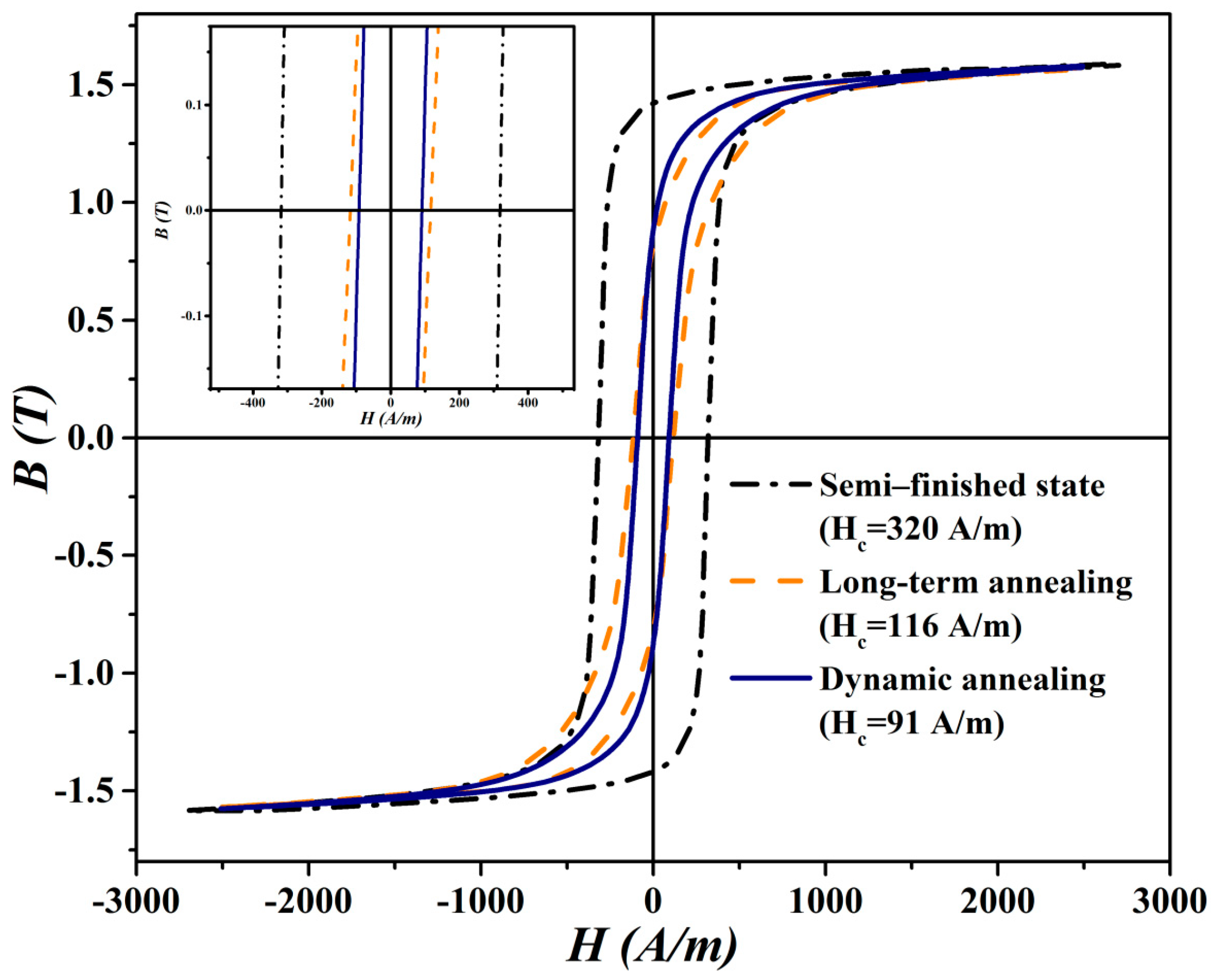
3.3. Magnetic Measurements
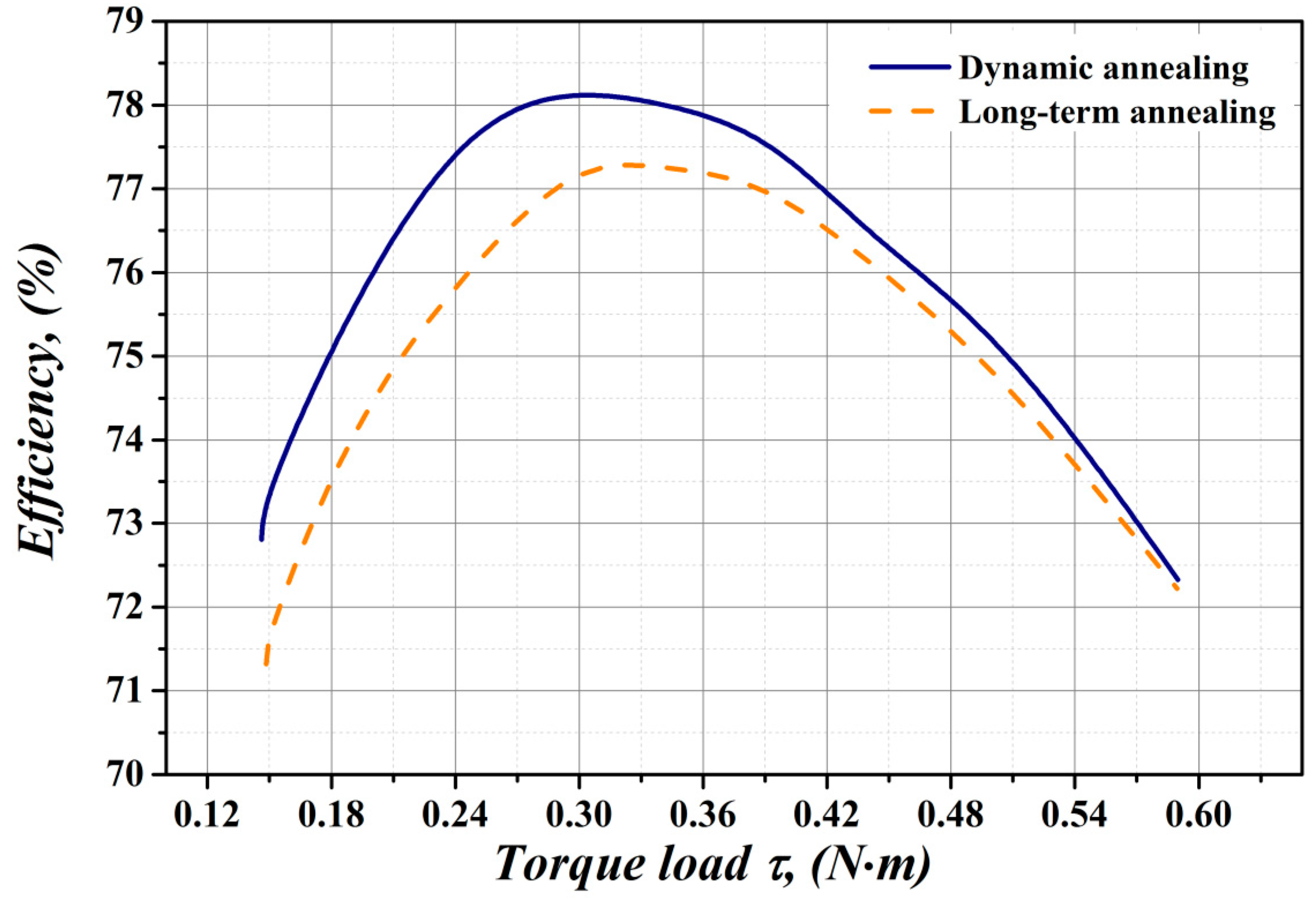
3.4. Measurement of Efficiency
4. Summary and Conclusions
- The rapid heating at dynamic annealing conditions of semi-finished NO silicon steels leads to a significant increase of average grain size of the obtained microstructure. The distinct evolution of coarse-grained microstructure is related to the strain-induced grain boundary migration mechanism under the influence of steep temperature gradient through the steel sheet cross-section.
- The unconventional dynamic heat treatment of the investigated electric motor core segments resulted in a stronger texture optimization tendency (i.e. the weakening or total absence the γ-fibre and forming strong rotated cube texture) than in the case of using conventional long-term annealing process.
- The improvement of the texture characteristics illustrated that the used dynamic heat treatment can optimize soft magnetic properties of the investigated semi-finished steel, namely its magnetic isotropy in combination with magnetic coercivity.
- The magnetic properties measured at 50 Hz frequency clearly showed that the evolved microstructures and textures of the segments heat treated by two different procedures are directly responsible for their final magnetic characteristics. The segments which were unconventionally heat treated at higher temperature with rapid heating were characterised by lower value of watt losses (4.33 W/kg), compared to those of the segments which were conventionally heat treated at lower temperature with much slower heating (5.45 W/kg).
- The measurement of efficiency of electric motors constructed from the segments heat treated under two different heat treatment conditions have clearly shown, that in comparison to the conventional heat treatment technology, the application of our unconventional dynamic heat treatment leads to a significant efficiency improvement by more than 1.2%.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Steiner Petrovič, D. Non-oriented electrical steel sheets. Mater. Technol. 2010, 44, 317–325. [Google Scholar]
- Moses, A.J. Electrical steels: Past, present and future developments. IEE Proc. 1990, 137, 233–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, D.; Park, H. Developmental trajectories in electrical steel technology using patent information. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, Y.; Kohno, M.; Honda, A. Recent development of non-oriented electrical steel sheet for automobile electrical devices. JMMM 2008, 320, 2430–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuning, N.; Steentjes, S.; Hameyer, K. Effect of grain size and magnetic texture on iron-loss components in NO electrical steel at different frequencies. JMMM 2019, 469, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidor, J.J.; Verbeken, K.; Gomes, E.; Schneider, J.; Calvillo, P.R.; Kestens, L.A.I. Through process texture evolution and magnetic properties of high Si non-oriented electrical steels. Mater. Charact. 2012, 71, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.H.; Jung, J.; Yoon, J.I.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, H.S. Modeling the evolution of recrystallization texture for a non-grain oriented electrical steel. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2018, 149, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Zhang, N.; Yang, P.; Mao, W.M. Retaining {100} texture from initial columnar grains in electrical steels. Scr. Mater. 2012, 67, 899–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, G.; Singh, C.D.; Deepa, M.; Dhua, S.K.; Saxena, A. Recrystallization behavior and texture of non-oriented electrical steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 734, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuning, N.; Steentjes, S.; Schulte, M.; Bleck, W.; Hameyer, K. Effect of elastic and plastic tensile mechanical loading on the magnetic properties of NGO electrical steel. JMMM 2016, 417, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner Petrovič, D.; Mandrino, D. XPS characterization of the oxide scale on fully processed nonoriented electrical steel sheet. Mater. Charact. 2011, 62, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, J.; Schneider, J. Influence of deformation process on the improvement of non-oriented electrical steel. JMMM 2003, 254–255, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, J.; Schneider, J.; Verbeken, K.; Houbaert, Y. On the correlation between microstructure and magnetic losses in electrical steel. JMMM 2008, 320, 2490–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilinski, E. Recent developments in semiprocessed cold rolled magnetic lamination steel. JMMM 2006, 304, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, M.; Jamshidian, M.; Ziaei-Rad, S.; Raabe, D.; Roters, F. Constitutive modeling of strain induced grain boundary migration via coupling crystal plasticity and phase-field methods. Int. J. Plast. 2017, 99, 19–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillamore, I.L.; Smith, C.J.E.; Watson, T.W. Oriented nucleation in the formation of annealing texture in iron. Met. Sci. J. 1967, 1, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatchinson, W.B. Development and control of annealing textures in low-carbon steels. Int. Met. Rev. 1984, 29, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, S.F.; Gallego, J.; Landgraf, F.J.G.; Kestenbach, H.J. Orientation dependence of stored energy of cold work in semi-processed electrical steels after temper rolling. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 427, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovac, F.; Stoyka, V.; Petryshynets, I. Strain induced grain growth in non-oriented electrical steels. JMMM 2008, 320, e627–e630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CEN. Cold Rolled Electrical Non-Alloy and Alloy Steel and Strip Delivered in the Semi-Processed State; STN EN 10341; CEN: Brussels, Belgium, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, A.D.; Bertoldi, P.; Leonhard, W. Energy Efficiency Improvements in Electric Motors and Drives, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1997; pp. 102–112. [Google Scholar]
- Petryshynets, I.; Kovac, F.; Marcin, J.; Skorvanek, I. Magnetic properties of temper rolled NO FeSi steels with enhanced rotation texture. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2013, 49, 4303–4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petryshynets, I.; Kovac, F.; Marcin, J.; Skorvanek, I. Improved processing technique for preparation of non-oriented electrical steels with low coercivity. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2014, 126, 182–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kováč, F.; Petryshynets, I.; Puchy, V.; Šebek, M.; Marcin, J.J. Preparation of NO silicon steels with columnar microstructure and low watt losses. J. Electr. Eng. 2015, 66, 86–89. [Google Scholar]
- Petryshynets, I.; Kováč, F.; Falat, L.; Puchý, V.; Šebek, M. Magnetic losses evolution of ferric Fe-Si steel subjected to temper rolling at elevated temperature. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2018, 133, 1065–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdi, M.; He, Y.; Hilinski, E.J.; Edrisy, A. Effect of skin pass rolling reduction rate on the texture evolution of a non-oriented electrical steel after inclined cold rolling. JMMM 2017, 429, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Hilinski, E.J. Texture and magnetic properties of non-oriented electrical steels processed by an unconventional cold rolling scheme. JMMM 2016, 405, 337–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbeken, K.; Kestens, L. Strain-induced selective growth in an ultra low carbon steel after a small rolling reduction. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 1679–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Xu, Y.-B.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Wang, Y.; Lu, X.; Misra, R.D.K.; Wang, G.-D. Evolution of recrystallization microstructure and texture during rapid annealing in strip-cast non-oriented electrical steels. JMMM 2015, 381, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, X.; Mi, X.; Zhang, S.; Volinsky, A.A. Rapid annealing effects on microstructure, texture, and magnetic properties of non-oriented electrical steel. Met. Mater. Int. 2012, 18, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotterill, P.; Mould, P.R. Recrystallization and Grain Growth in Metals, 1st ed.; Surrey University Press: London, UK, 1976; pp. 266–300. [Google Scholar]
- Sidor, Y.; Kovac, F.; Kvackaj, T. Grain growth phenomena and heat transport in non-oriented electrical steels. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 1711–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homma, H.; Nakamura, S.; Yoshinaga, N. On {h,1,1}<1/h,1,2>, the recrystallization texture of heavily cold rolled BCC steel. Mater. Sci. Forum 2004, 470, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobernado, P.; Petrov, R.H.; Kestens, L.A.I. Recrystallized {311}<136> orientation in ferrite steel. Scr. Mater. 2012, 66, 623–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diligent, S.; Gautier, E.; Lemoine, X.; Berveiller, M. Lattice orientation dependence of the stored energy during cold-rolling of polycrystalline steels. Acta Mater. 2001, 49, 4079–4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, M.F.; Teixeira, J.C.; Langraf, F.J.G. The optimum grain size for minimizing energy losses in iron. JMMM 2006, 301, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PermKumar, R.; Samajdar, I.; Viswanathan, N.N.; Singal, V.; Seshadri, V. Relative effect(s) of texture and grain size on magnetic properties in a low silicon non-grain oriented electrical steel. JMMM 2003, 264, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample Type | Watt losses in AC Magnetic Field P (W/kg) | Coercivity in AC Magnetic Field HC (A/m) | Coercivity in DC Magnetic Field HC (A/m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Semi-finished state | 13.8 | 320 | 230 |
| Long-term annealing treatment | 5.45 | 116 | 58 |
| Dynamic annealing treatment | 4.33 | 91 | 20 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Petryshynets, I.; Kováč, F.; Petrov, B.; Falat, L.; Puchý, V. Improving the Magnetic Properties of Non-Oriented Electrical Steels by Secondary Recrystallization Using Dynamic Heating Conditions. Materials 2019, 12, 1914. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12121914
Petryshynets I, Kováč F, Petrov B, Falat L, Puchý V. Improving the Magnetic Properties of Non-Oriented Electrical Steels by Secondary Recrystallization Using Dynamic Heating Conditions. Materials. 2019; 12(12):1914. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12121914
Chicago/Turabian StylePetryshynets, Ivan, František Kováč, Branislav Petrov, Ladislav Falat, and Viktor Puchý. 2019. "Improving the Magnetic Properties of Non-Oriented Electrical Steels by Secondary Recrystallization Using Dynamic Heating Conditions" Materials 12, no. 12: 1914. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12121914
APA StylePetryshynets, I., Kováč, F., Petrov, B., Falat, L., & Puchý, V. (2019). Improving the Magnetic Properties of Non-Oriented Electrical Steels by Secondary Recrystallization Using Dynamic Heating Conditions. Materials, 12(12), 1914. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12121914





