Tunable Perfect THz Absorber Based on a Stretchable Ultrathin Carbon-Polymer Bilayer
Abstract
1. Introduction
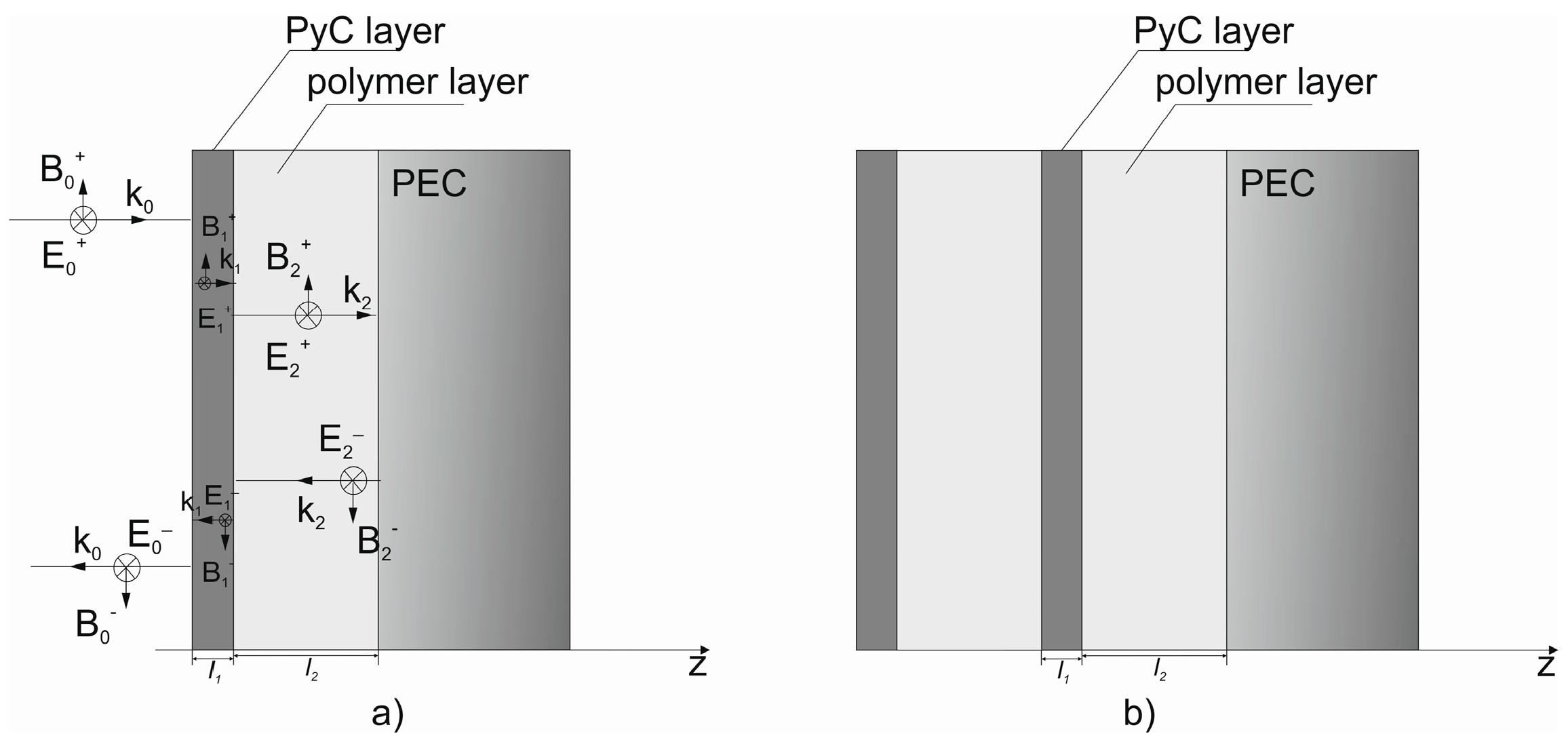
2. Theory and Numerical Simulations
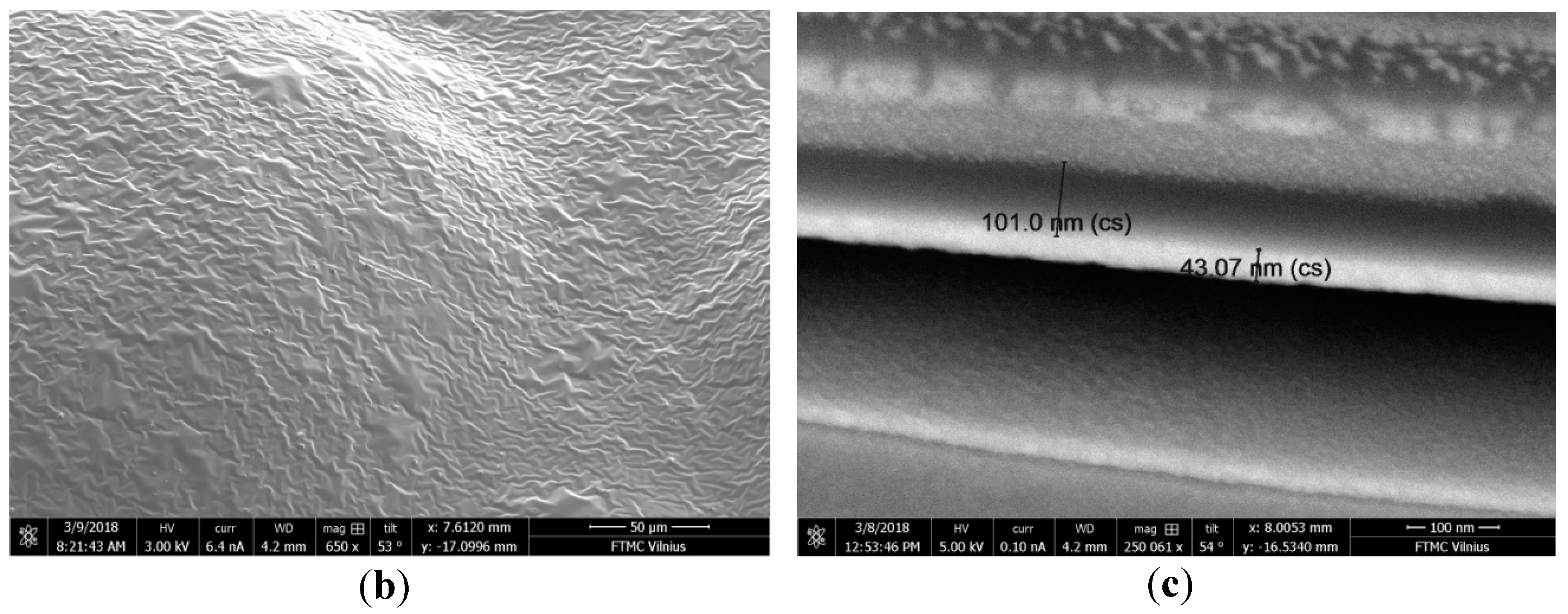
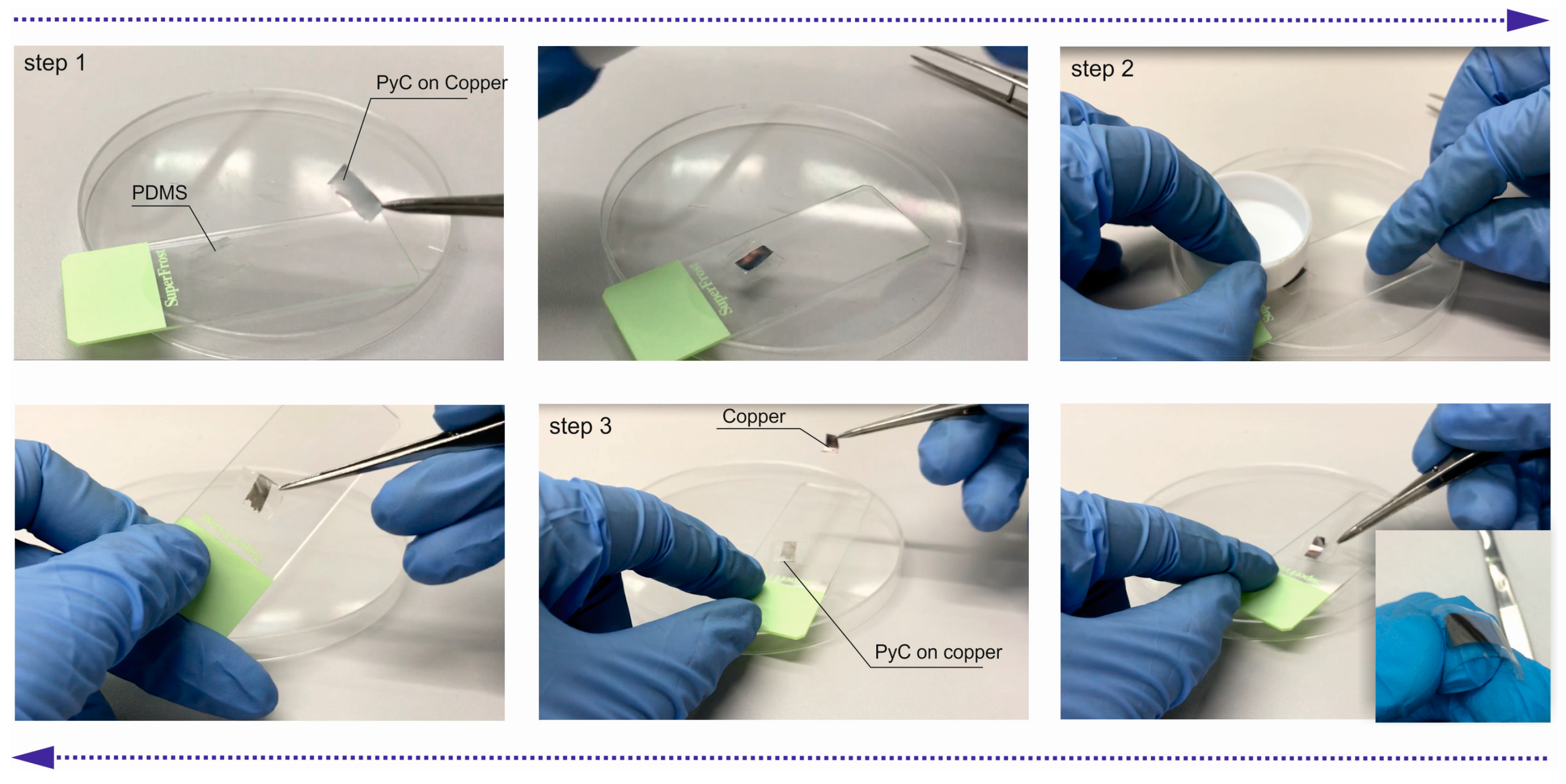
3. Materials and Methods
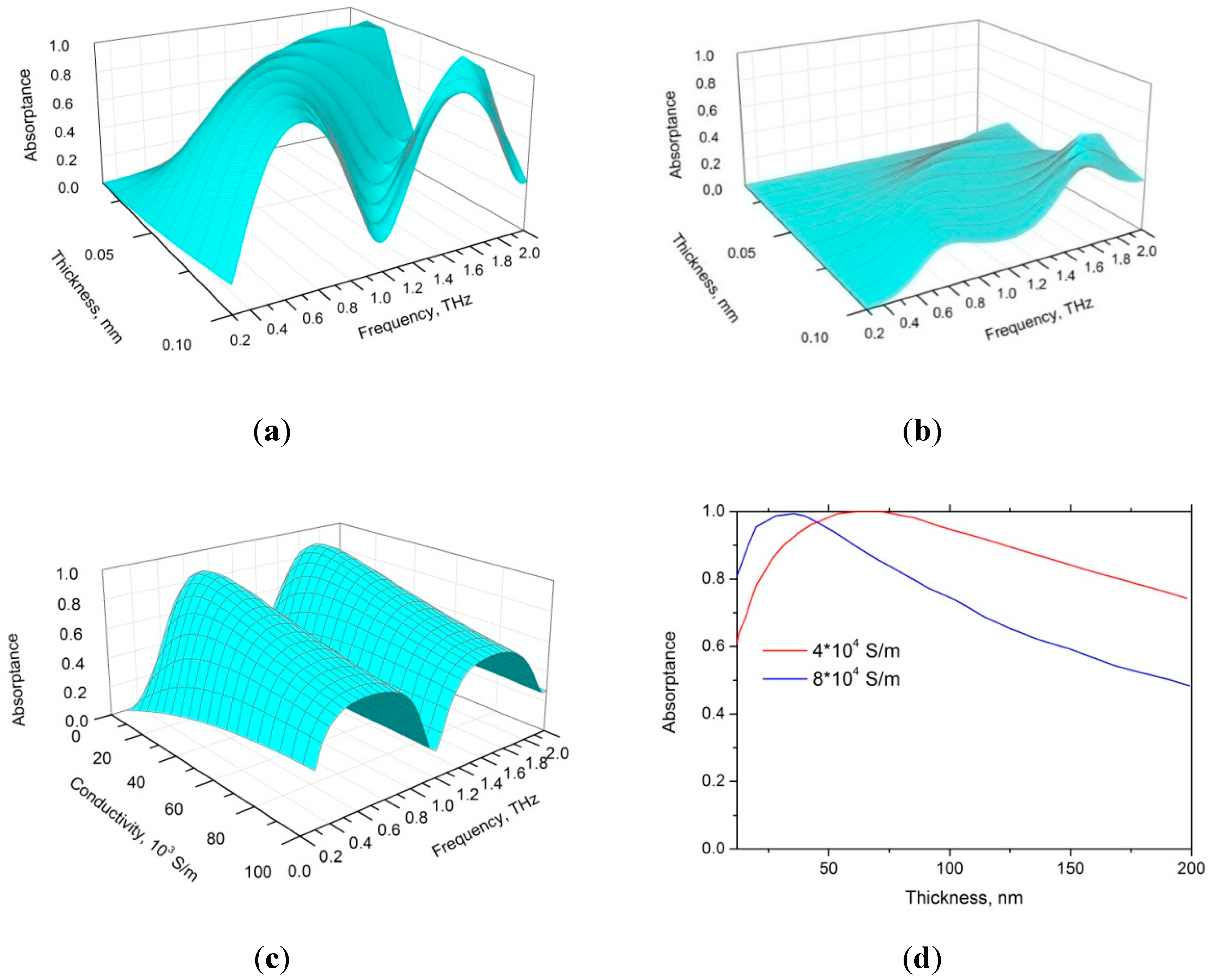
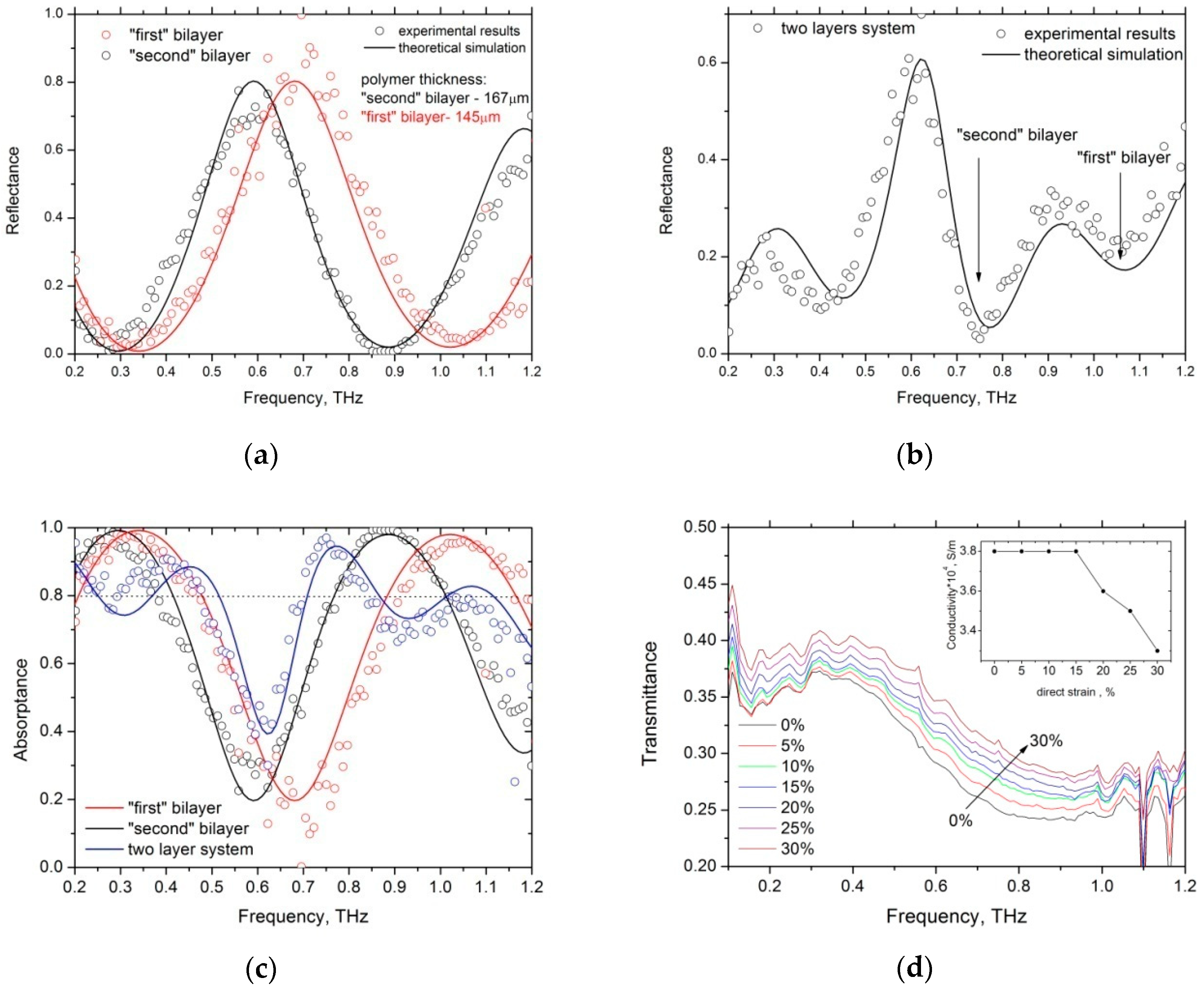
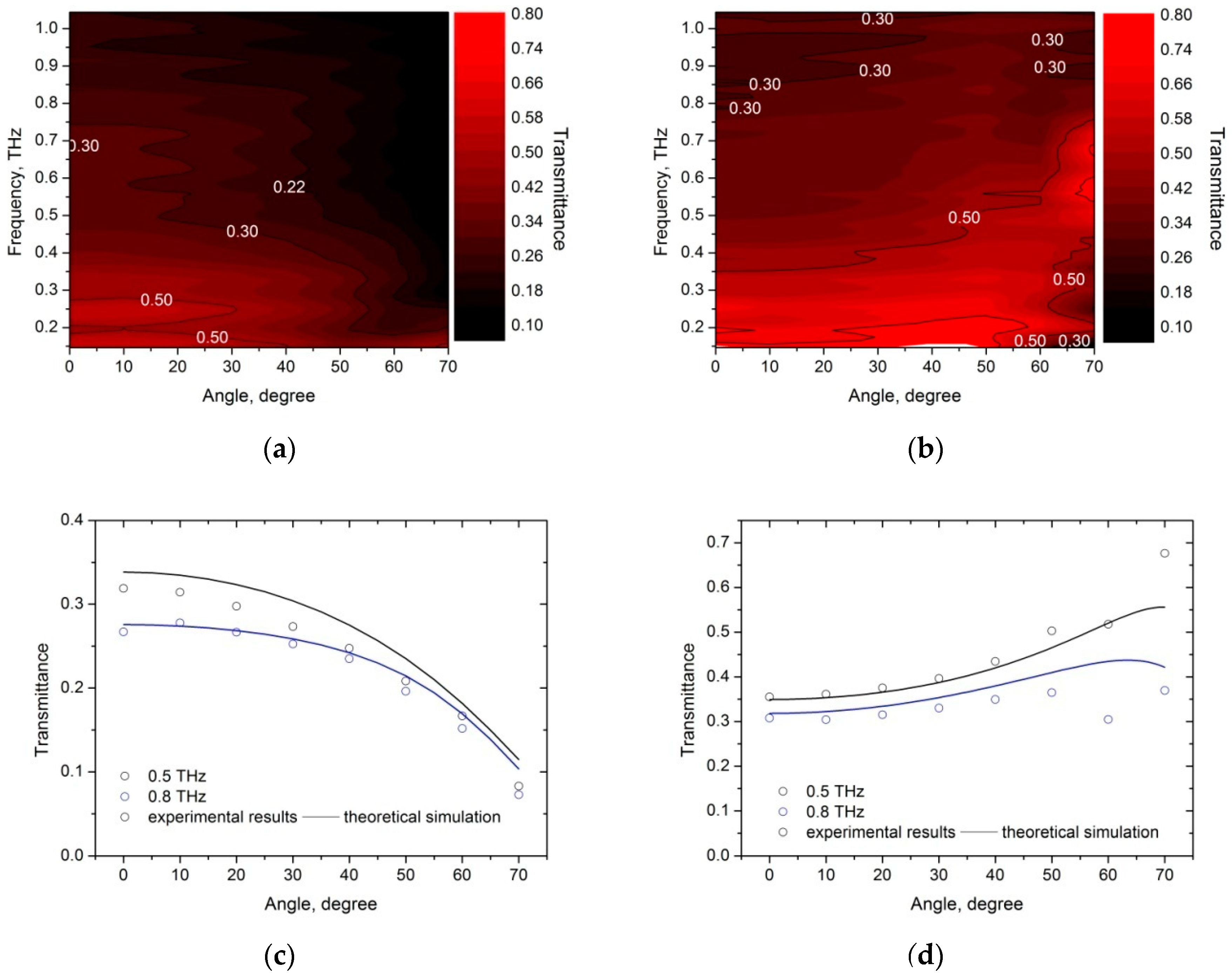
4. Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tonouchi, M. Cutting-edge terahertz technology. Nat. Photonics 2007, 1, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, P.H. THz Instruments for Space. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2007, 55, 2957–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagatsuma, T. Terahertz technologies: Present and future. IEICE Electron. Express 2011, 8, 1127–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, P.L.; Mc Creight, C.R. Infrared Detectors for Astrophysics. Phys. Today 2005, 58, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, S.S.; Vitiello, M.S.; Linfield, E.H.; Davies, A.G.; Hoffmann, M.C.; Booske, J.; Paoloni, C.; Gensch, M.; Weightman, P.; Williams, G.P. The 2017 terahertz science and technology roadmap. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2017, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batrakov, K.; Kuzhir, P.; Maksimenko, S.; Volunets, N.; Voronovich, S.; Paddubskaya, A.; Valusis, G.; Kaplas, T.; Svirko, Y.; Lambin, P. Enhanced microwave-to-terahertz absorption in graphene. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 108, 123101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzhir, P.; Paddubskaya, A.; Volynets, N.; Batrakov, K.; Kaplas, T.; Lamberti, P.; Kotsilkova, R.; Lambin, P. Main principles of passive devices based on graphene and carbon films in microwave—THz frequency range. J. Nanophotonics 2017, 11, 032504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, R.C.; Shi, T.; Silva, E.C.; Jovanovic, I.; Robinson, J.A. Radiation effects on two-dimensional materials. Phys. Status Solidi A 2016, 213, 3065–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, K.C.; Schwab, K.C. Ultrasensitive and Wide-Bandwidth Thermal Measurements of Graphene at Low Temperatures. Phys. Rev. X 2012, 2, 031006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balandin, A.A. Thermal properties of graphene and nanostructured carbon materials. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, K.C.; Wollman, E.E.; Ravi, H.; Chen, W.; Clerk, A.A.; Shaw, M.D.; Leduc, H.G.; Schwab, K.C. Measurement of the Electronic Thermal Conductance Channels and Heat Capacity of Graphene at Low Temperature. Phys. Rev. X 2013, 3, 041008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crossno, J.; Shi, J.K.; Liu, X.; Harzheim, A.; Lucas, A.; Sachdev, S.; Kim, P. Observation of the Dirac fluid and the breakdown of the Wiedemann-Franz law in graphene. Science 2016, 351, 1058–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppens, F.H.L.; Mueller, T.; Avouris, P.; Ferrari, A.C.; Vitiello, M.S.; Polini, M. Photodetectors based on graphene, other two-dimensional materials and hybrid systems. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 780–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobet, M.; Majerus, B.; Henrard, L.; Lambin, P. Perfect electromagnetic absorption using graphene and epsilon-near-zero metamaterials. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 93, 235424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, S.; Bauer-Gogonea, S.; Ploss, B. The physics of pyroelectric infrared devices. Appl. Phys. B 1992, 54, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min Woo, J.; Kim, M.-S.; Kim, H.W.; Jang, J.-H. Graphene based salisbury screen for terahertz absorber. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 081106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Jin, H.; Zeng, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z. Flexible and easy-to-tune broadband electromagnetic wave absorber based on carbon resistive film sandwiched by silicon rubber/multi-walled carbon nanotube composites. Carbon 2017, 121, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroll, J.; Darmo, J.; Unterrainer, K. High-performance terahertz electro-optic detector. Electron. Lett. 2004, 40, 763–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.-X.; Parrott, E.P.J.; Paul, D.J.; Zeitler, J.A. Determination of complex refractive index of thin metal films from terahertz time-domain spectroscopy. J. App. Phys. 2008, 104, 053110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismach, A.; Druzgalski, C.; Penwell, S.; Schwartzberg, A.; Zheng, M.; Javey, A.; Bokor, J.; Zhang, Y. Direct chemical vapor deposition of graphene on dielectric surfaces. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 1542–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Shin, D.; Bae, S.; Hong, B.H. Graphene transfer: key for applications. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 5527–5537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplas, T.; Svirko, Y. Direct deposition of semitransparent conducting pyrolytic carbon films. J. Nanophotonics 2012, 6, 061703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEvoy, N.; Peltekis, N.; Kumar, S.; Rezvani, E.; Nolan, H.; Keeley, G.P.; Blau, W.J.; Duesberg, G.S. Synthesis and analysis of thin conducting pyrolytic carbon films. Carbon 2012, 50, 1216–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplas, T.; Kuzhir, P. Ultra-thin Graphitic Film: Synthesis and Physical Properties. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batrakov, K.; Kuzhir, P.; Maksimenko, S.; Paddubskaya, A.; Voronovich, S.; Kaplas, T.; Svirko, Y. Enhanced microwave shielding effectiveness of ultrathin pyrolytic carbon films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 073117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, E.M.; De, S.; Lyon, P.E.; Nirmalraj, P.N.; Scardaci, V.; Joimel, J.; Blau, W.J.; Boland, J.J.; Coleman, J.N. The spatial uniformity and electromechanical stability of transparent, conductive films of single walled nanotubes. Carbon 2009, 47, 2466–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.; Kim, H.; Lee, Y.; Xu, X.; Park, J.-S.; Zheng, Y.; Balakrishnan, J.; Lei, T.; Kim, H.R.; Song, Y.; et al. Roll-to-roll production of 30-inch graphene films for transparent electrodes. Nat. Nanotech. 2010, 5, 574–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhi, L.; Mullen, K. Transparent, Conductive Graphene Electrodes for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Nano Lett. 2007, 8, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, M.; Lutz, T.; Keeley, G.P.; Kumar, S.; Boese, M.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Duesberg, G.S. Transparent ultrathin conducting carbon films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 6186–6190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gires, F.; Tournois, P.R. Interferometre utilisable pour la compression d’impulsions lumineuses modulees en frequence. Acad. Sci. Paris 1964, 258, 6112–6615. [Google Scholar]
- Chamber, B.; Tennant, A. Optimised design of Jaumann radar absorbing materials using a genetic algorithm. IEEE Proc. Radar Sonar Navig. 1996, 143, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadezky, A.; Muckenhuber, H.; Grothe, H.; Niessner, R.; Pöschl, U. Raman Microspectroscopy of Soot and Related Carbonaceous Materials: Spectral Analysis and Structural Information. Carbon 2005, 43, 1731–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childres, I.; Jauregui, L.A.; Park, W.; Cao, H.; Chen, Y.P. Raman Spectroscopy of Graphene and Related Materials. Available online: https://www.physics.purdue.edu/quantum/files/Raman_Spectroscopy_of_Graphene_NOVA_Childres.pdf (accessed on 30 October 2013).
- Cancado, L.G.; Takai, K.; Enoki, T. General equation for the determination of the crystallite size La of nanographite by Raman spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 163106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaskela, A.; Nasibulin, A.G.; Timmermans, M.Y.; Aitchison, B.; Papadimitratos, A.; Tian, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Jiang, H.; Brown, D.P.; Zakhidov, A.; et al. Aerosol-Synthesized SWCNT Networks with Tunable Conductivity and Transparency by a Dry Transfer Technique. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 4349–4355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, I.D.; McCluckey, D.K.; Tan, C.K.L.; Trancey, M.C. Mechanical characterization of bulk Sylgard 184 for microfluidics and microengineering. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2014, 24, 035017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kats, M.A.; Blanchard, R.; Genevet, P.; Capasso, F. Nanometre optical coatings based on strong interference effects in highly absorbing media. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, V.-C.; Chu, C.H.; Sun, G.; Tsai, D.P. Advances in optical metasurfaces: Fabrication and applications. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 13148–13182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.D.; Liu, M.H.; Hu, X.W.; Kong, L.H.; Cheng, L.L.; Chen, Z.Q. Broadband and ultra-thin terahertz metamaterial absorber based on multi-circular patches. Eur. Phys. J. B 2013, 86, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paddubskaya, A.; Demidenko, M.; Batrakov, K.; Valušis, G.; Kaplas, T.; Svirko, Y.; Kuzhir, P. Tunable Perfect THz Absorber Based on a Stretchable Ultrathin Carbon-Polymer Bilayer. Materials 2019, 12, 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12010143
Paddubskaya A, Demidenko M, Batrakov K, Valušis G, Kaplas T, Svirko Y, Kuzhir P. Tunable Perfect THz Absorber Based on a Stretchable Ultrathin Carbon-Polymer Bilayer. Materials. 2019; 12(1):143. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12010143
Chicago/Turabian StylePaddubskaya, Alesia, Marina Demidenko, Konstantin Batrakov, Gintaras Valušis, Tommi Kaplas, Yuri Svirko, and Polina Kuzhir. 2019. "Tunable Perfect THz Absorber Based on a Stretchable Ultrathin Carbon-Polymer Bilayer" Materials 12, no. 1: 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12010143
APA StylePaddubskaya, A., Demidenko, M., Batrakov, K., Valušis, G., Kaplas, T., Svirko, Y., & Kuzhir, P. (2019). Tunable Perfect THz Absorber Based on a Stretchable Ultrathin Carbon-Polymer Bilayer. Materials, 12(1), 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12010143





