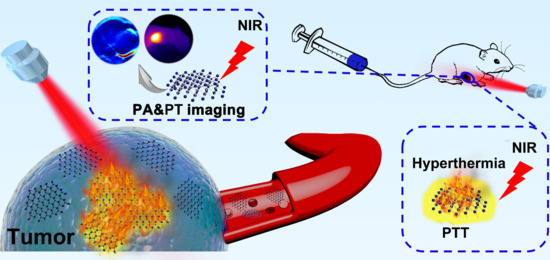
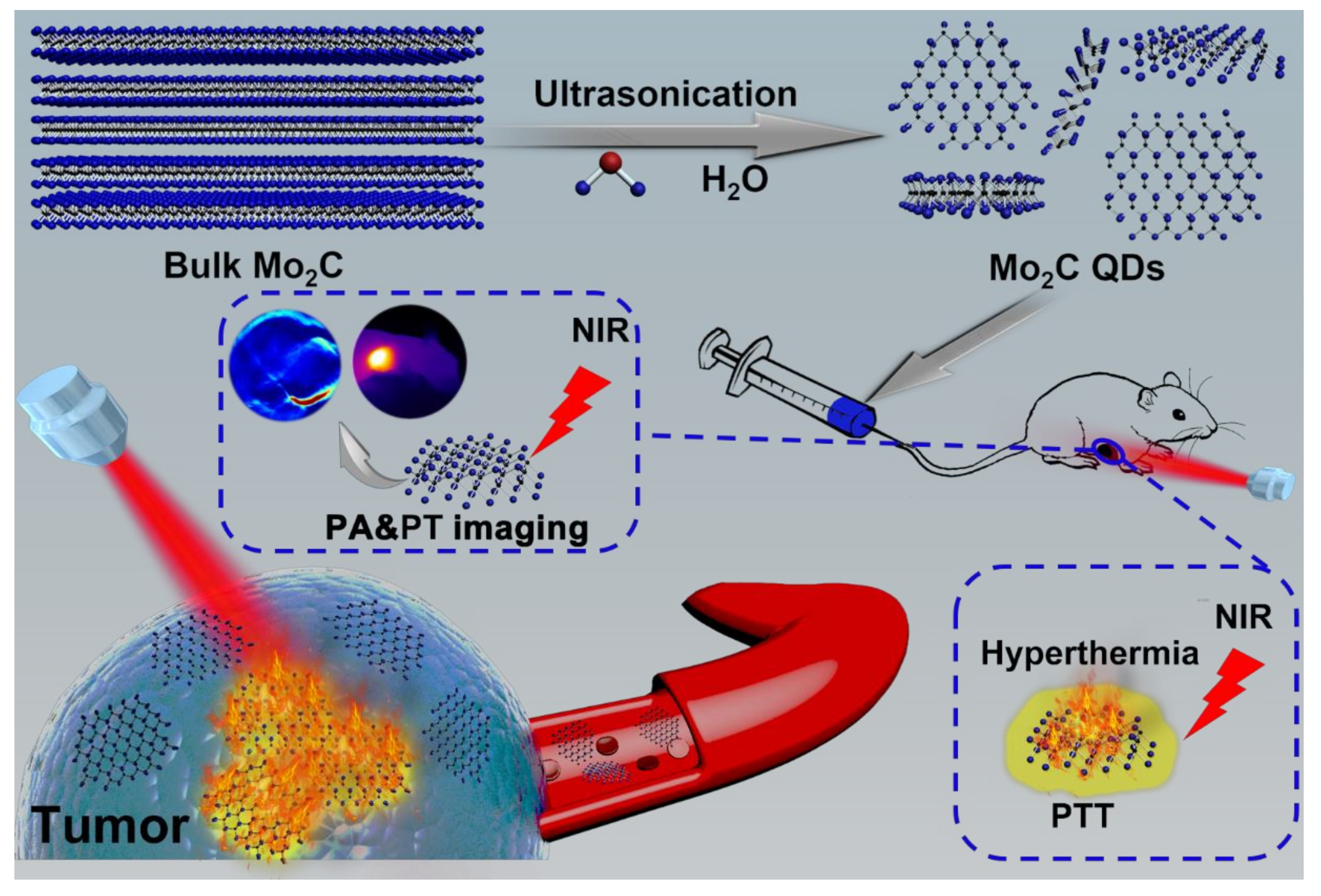
A Semimetal-Like Molybdenum Carbide Quantum Dots Photoacoustic Imaging and Photothermal Agent with High Photothermal Conversion Efficiency
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Mo2C QDs
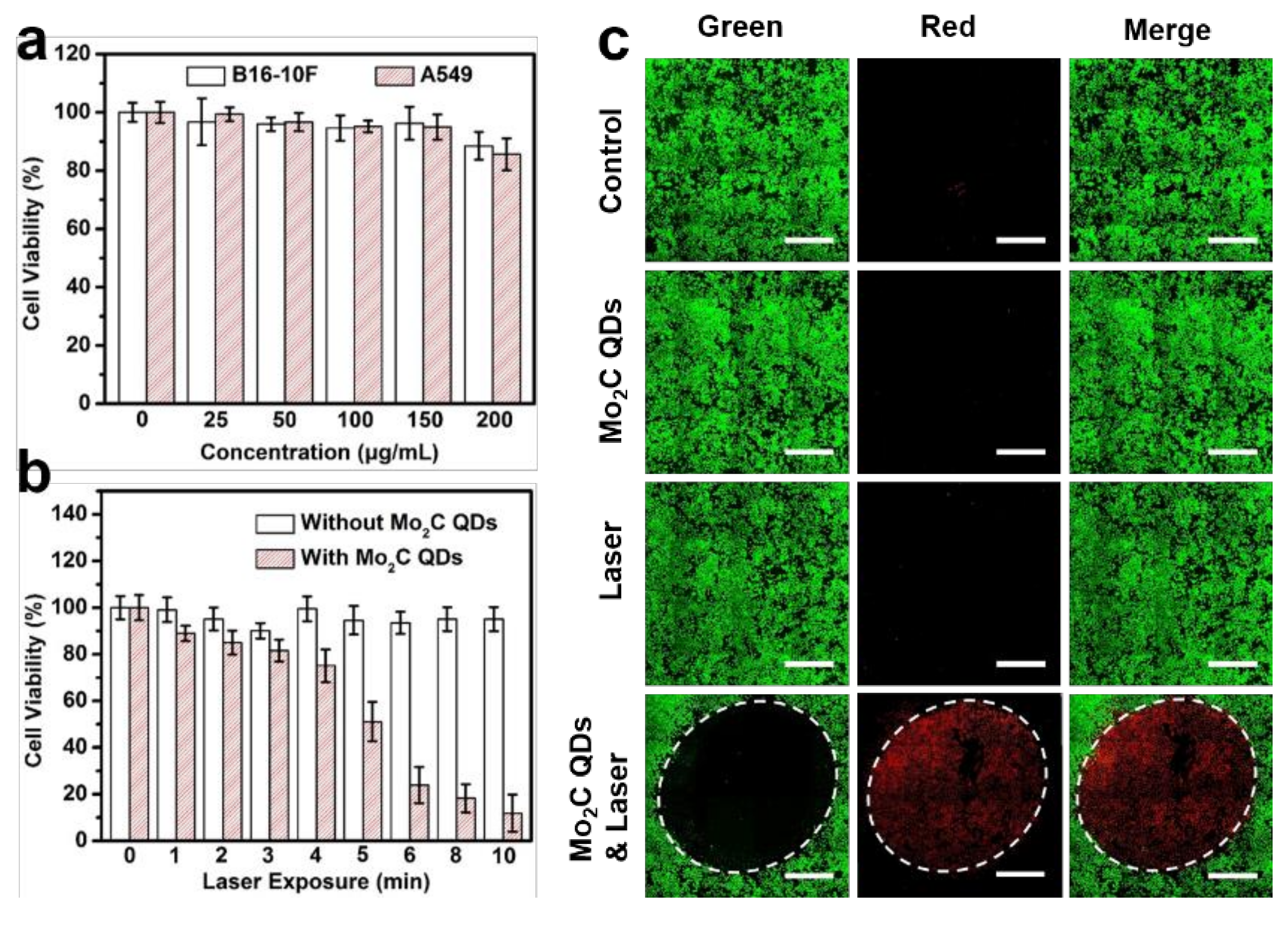
2.2. In Vitro Phototoxicity Assay and Confocal Imaging
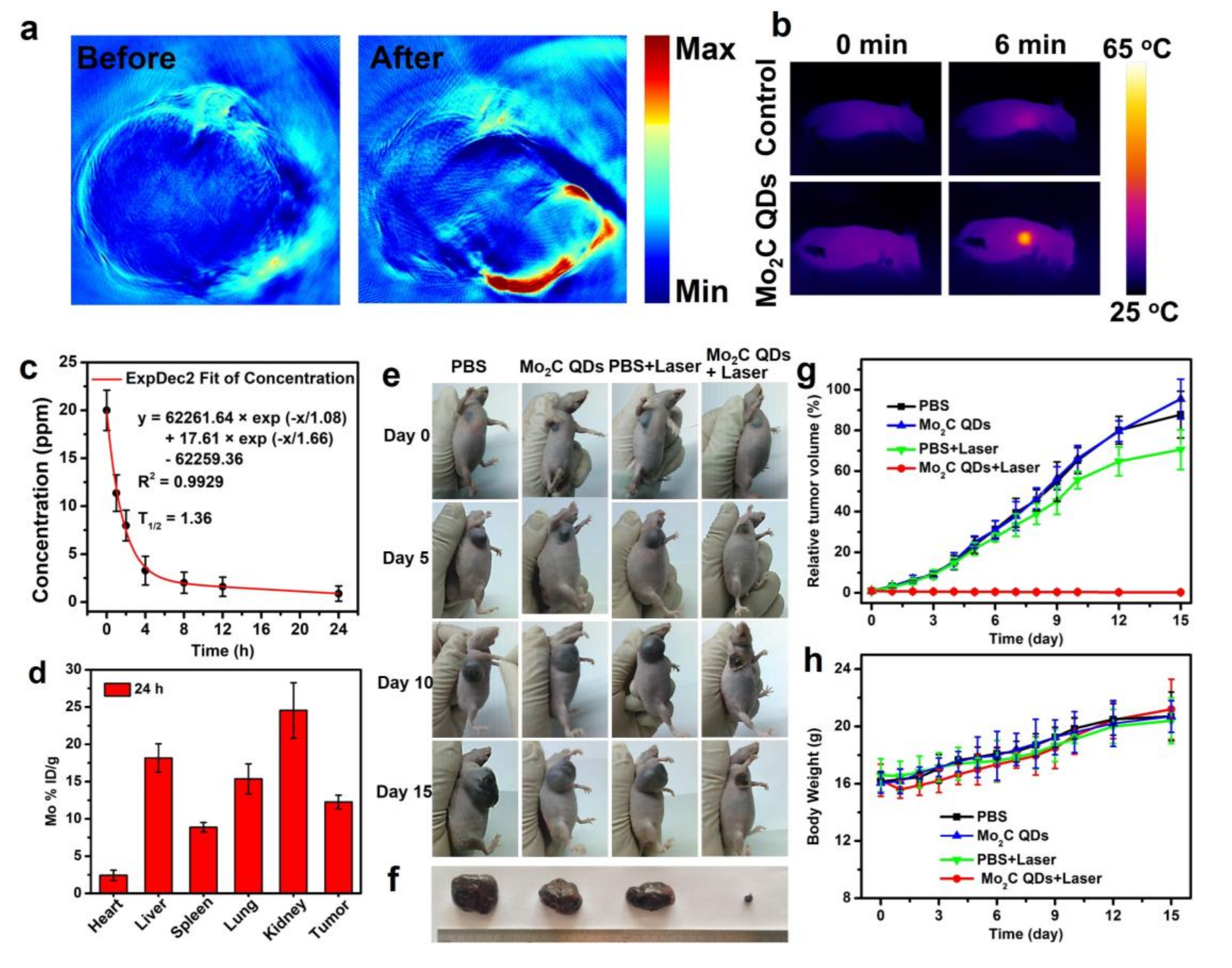
2.3. In Vitro and In Vivo PA Imaging
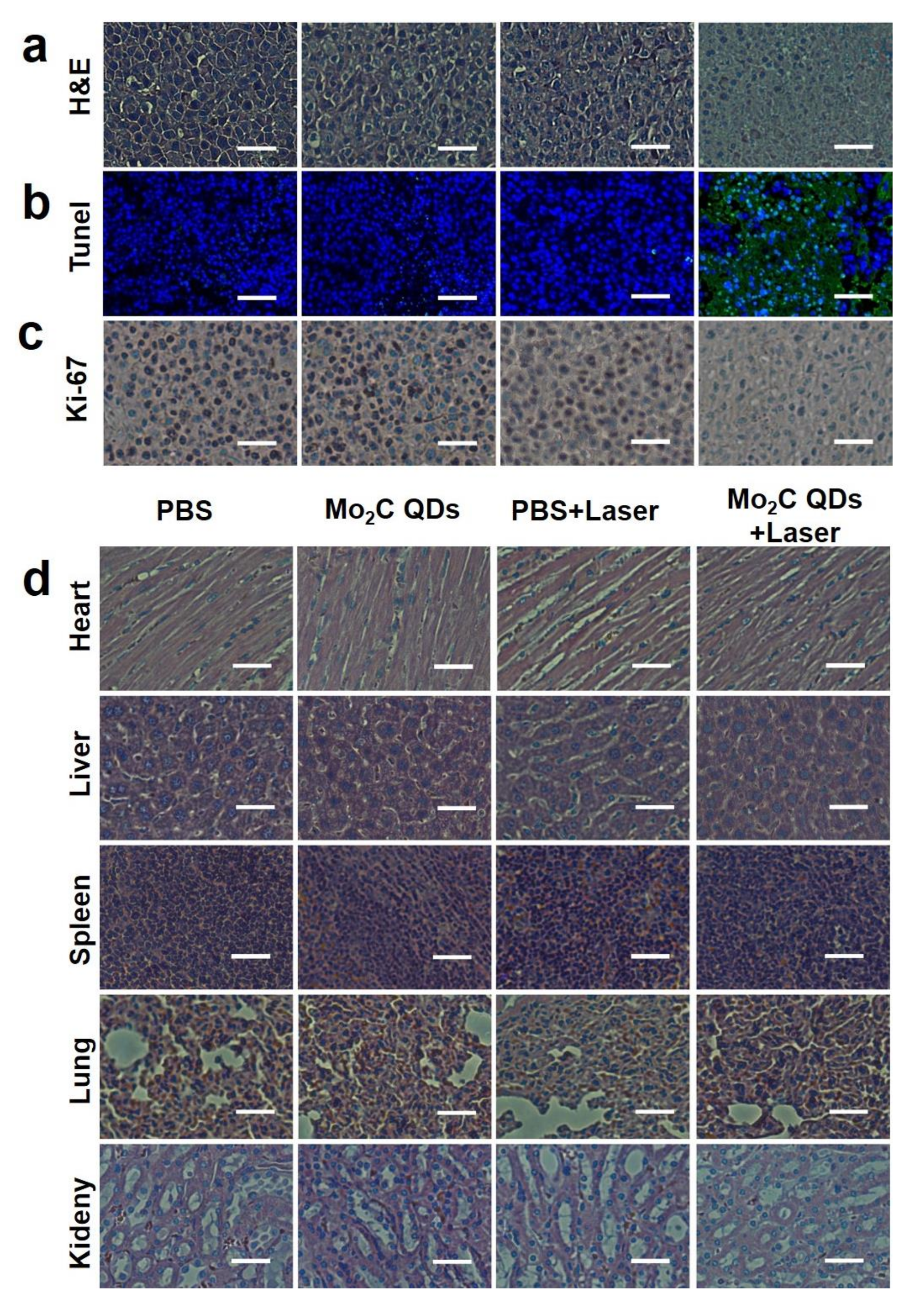
2.4. In Vivo Photothermal Therapy
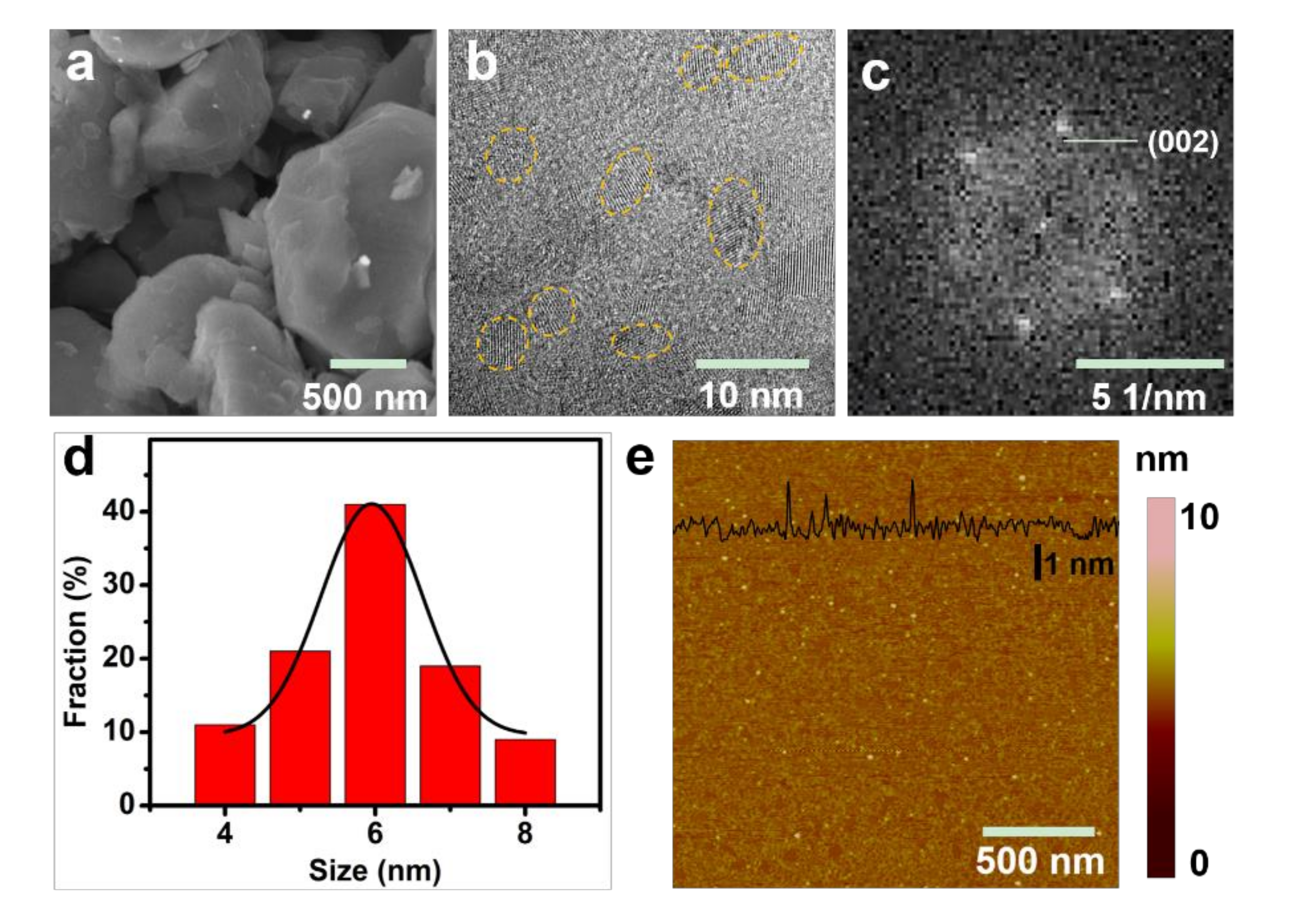
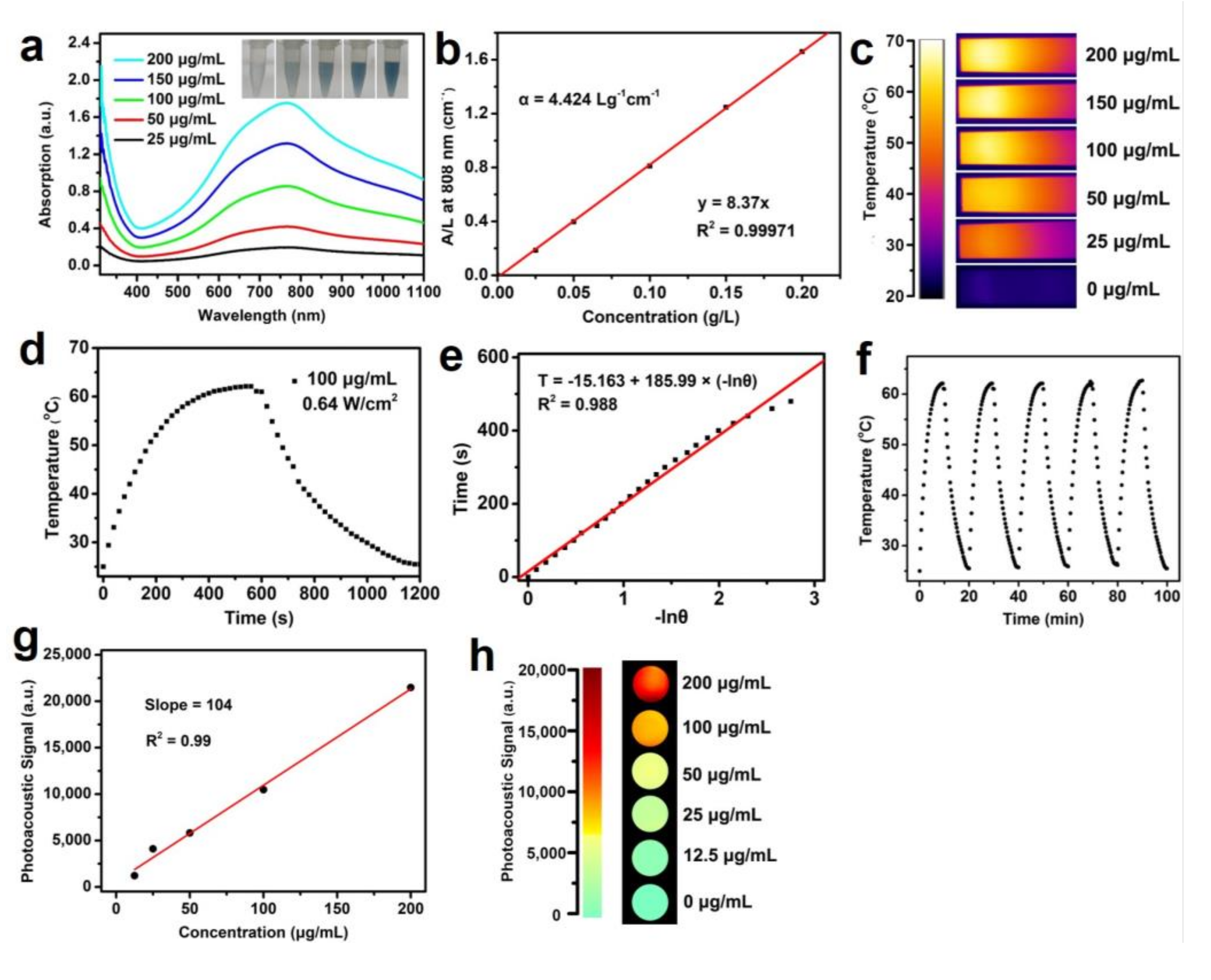
3. Results and Discussions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yoo, D.; Lee, J.H.; Shin, T.H.; Cheon, J. Theranostic magnetic nanoparticles. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 863–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.N.; Li, W.Y.; Cobley, C.M.; Chen, J.Y.; Xia, X.H.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, M.X.; Cho, E.C.; Brown, P.K. Gold nanocages: From synthesis to theranostic applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 914–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardhan, R.; Lal, S.; Joshi, A.; Halas, N.J. Theranostic nanoshells: From probe design to imaging and treatment of cancer. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 936–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Feng, L.Z.; Shi, X.Z.; Liu, Z. Nano-graphene in biomedicine: Theranostic applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 530–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Lee, S.; Chen, X.Y. Nanoparticle-based theranostic agents. Adv. Drug Deliver. Rev. 2010, 62, 1064–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, W.; Cong, L.; Guo, Z.; Xie, Y.; Wang, L.; Tang, R.; Feng, Q.; Hamada, Y.; et al. Thermo-triggered release of CRISPR-cas9 system by lipid-encapsulated gold nanoparticles for tumor therapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 1491–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angell, C.; Kai, M.; Xie, S.; Dong, X.; Chen, Y. Bioderived DNA nanomachines for potential uses in biosensing, diagnostics, and therapeutic applications. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1701189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janib, S.M.; Moses, A.S.; MacKay, J.A. Imaging and drug delivery using theranostic nanoparticles. Adv. Drug Deliver. Rev. 2010, 62, 1052–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.K.; Park, J.; Jon, S. Targeting strategies for multifunctional nanoparticles in cancer imaging and therapy. Theranostics 2012, 2, 3–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, G.; Xie, J.; Chen, X. Rethinking cancer nanotheranostics. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 17024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, P.; Xiao, H.; Yu, C.; Liu, J.; Cheng, Z.; Song, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Wang, J.; Gu, Z.; et al. Enhanced cisplatin chemotherapy by iron oxide nanocarrier-mediated generation of highly toxic reactive oxygen species. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 928–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Cheng, L.; Dong, Z.; Chao, Y.; Lei, H.; Zhao, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z. Degradable vvanadium disulfide nanostructures with unique optical and magnetic functions for cancer theranostics. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 129, 13171–13176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthu, M.S.; Singh, S. Targeted nanomedicines: Effective treatment modalities for cancer, AIDS and brain disorders. Nanomedicine 2009, 4, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, C.; Santos-Martinez, M.J.; Radomski, A.; Corrigan, O.I.; Radomski, M.W. Nanoparticles: pharmacological and toxicological significance. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 150, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanhai, W.R.; Sakamoto, J.H.; Canady, R.; Ferrari, M. Seven challenges for nanomedicine. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 242–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swierczewska, M.; Han, H.S.; Kim, K.; Park, J.H.; Lee, S. Polysaccharide-based nanoparticles for theranostic nanomedicine. Adv. Drug Deliver. Rev. 2016, 99, 70–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawant, R.R.; Jhaveri, A.M.; Koshkaryev, A.; Zhu, L.; Qureshi, F.; Torchilin, V.P. Targeted transferrin-modified polymeric micelles: Enhanced efficacy in vitro and in vivo in ovarian carcinoma. Mol. Pharmaceut. 2014, 11, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, G.X.; Guo, W.S.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, T.B.; Li, S.Y.; Chen, S.Z.; Eltahan, A.S.; Wang, D.L.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, J.C.; et al. Near-infrared emission CuInS/ZnS quantum dots: All-in-one theranostic nanomedicines with intrinsic fluorescence/photoacoustic imaging for tumor phototherapy. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 9637–9645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lammers, T.; Aime, S.; Hennink, W.E.; Storm, G.; Kiessling, F. Theranostic nanomedicine. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 1029–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Huang, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhuang, X.; Hu, S.; Ju, H.; Yu, B.; Tian, J. A programmed nanoparticle with self-adapting for accurate cancer cell eradication and therapeutic self-reporting. Theranostics 2017, 7, 1245–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Feng, W.; Chang, J.; Tan, Y.W.; Li, J.; Chen, M.; Sun, Y.; Li, F. Temperature-feedback upconversion nanocomposite for accurate photothermal therapy at facile temperature. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, K.; Dupuy, D. Thermal ablation of tumours: Biological mechanisms and advances in therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roper, D.K.; Ahn, W.; Hoepfner, M. Microscale heat transfer transduced by surface plasmon resonant gold nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 3636–3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hessel, C.M.; Pattani, V.P.; Rasch, M.; Panthani, M.G.; Koo, B.; Tunnell, J.W.; Korgel, B.A. Copper selenide nanocrystals for photothermal therapy. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 2560–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Wang, Y.; Gao, S.; Chen, Y.; Shi, J. Theranostic 2D tantalum carbide (MXene). Adv. Mater. 2017, 1703284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghidiu, M.; Lukatskaya, M.R.; Zhao, M.Q.; Gogotsi, Y.; Barsoum, M.W. Conductive two-dimensional titanium carbide ‘clay’ with high volumetric capacitance. Nature 2014, 516, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naguib, M.; Gogotsi, Y. Synthesis of two-dimensional materials by selective extraction. Accounts Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Liu, Y.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, X.; Yakobson, B.I.; Goddard, W.A.; Guo, X.; Hauge, R.H.; et al. Atomic H-induced Mo2C hybrid as an active and stable bifunctional electrocatalyst. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, R.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, P.; Liu, Q.; Wang, J. Ultrafine molybdenum carbide nanoparticles composited with carbon as a highly active hydrogen-evolution electrocatalyst. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 14723–14727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halim, J.; Kota, S.; Lukatskaya, M.R.; Naguib, M.; Zhao, M.Q.; Moon, E.J.; Pitock, J.; Nanda, J.; May, S.J.; Gogotsi, Y.; et al. Synthesis and characterization of 2D molybdenum carbide (MXene). Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 3118–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Chen, L.; Guo, J.; Kang, N.; Ma, X.L.; Cheng, H.M.; Ren, W. Large-area high-quality 2D ultrathin Mo2C superconducting crystals. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, W.H.; Dong, H.F.; Bunshi, F.; Cao, Y.; Lu, H.; Ma, X.; Zhang, X.J. Tunable fabrication of molybdenum disulfide quantum dots for intracellular microRNA detection and multiphoton bioimaging. Small 2015, 11, 4158–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Zou, Y.; Hu, W.; Li, Y.; Gu, Y.; Cao, B.; Guo, N.; Wang, L.; Song, J.; Zhang, S.; et al. Near-infrared plasmonic 2D semimetals for applications in communication and biology. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 1793–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Wang, X.; Yu, L.; Chen, Y.; Shi, J. Two-dimensional ultrathin MXene ceramic nanosheets for photothermal conversion. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luther, J.M.; Jain, P.K.; Ewers, T.; Alivisatos, A.P. Localized surface plasmon resonances arising from free carriers in doped quantum dots. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, J.T.; Tabakman, S.M.; Liang, Y.Y.; Wang, H.L.; Casalongue, H.S.; Vinh, D.; Dai, H.J. Ultrasmall reduced graphene oxide with high near-infrared absorbance for photothermal therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 6825–6831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikoobakht, B.; Wang, J.P.; El-Sayed, M.A. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering of molecules adsorbed on gold nanorods: Off-surface plasmon resonance condition. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2002, 366, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, J.H.; Liu, Q.; Huang, H.; Chen, M.; Li, K.; Li, C.; Yu, X.F.; Chu, P.K. Rose-bengal-conjugated gold nanorods for in vivo photodynamic and photothermal oral cancer therapies. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 1954–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Xie, H.; Tang, S.; Yu, X.F.; Guo, Z.; Shao, J.; Zhang, H.; Huang, H.; Wang, H.; Chu, P.K. Ultrasmall black phosphorus quantum dots: Synthesis and use as photothermal agents. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 11526–11530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.; Favazza, C.; Wang, L.V. In vivo photoacoustic tomography of chemicals: High-resolution functional and molecular optical imaging at new depths. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 2756–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Cai, X.; Yao, H.; Gao, W.; Zheng, Y.; An, X.; Shi, J.; Chen, H. A facile one-pot synthesis of a two-dimensional MoS2/Bi2S3 composite theranostic nanosystem for multi-modality tumor imaging and therapy. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2775–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Chen, C.; Liu, H.; Fu, C.; Tan, L.; Wang, S.; Fu, S.; Liu, X.; Meng, X.; Liu, H. Multifunctional carbon–silica nanocapsules with gold core for synergistic photothermal and chemo-Cancer therapy under the guidance of bimodal imaging. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 4252–4261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.Y.; Ma, L.; Li, L.H.; Zhang, J.Y.; Lim, R.X.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Y. A new modality for cancer treatment-nanoparticle mediated microwave induced photodynamic therapy. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2016, 12, 1835–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, K.; Li, J.; Yin, J.; Ma, Q.; Yan, B.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Targeted delivery of CXCR4-siRNA by scFv for HER2+ breast cancer therapy. Biomaterials 2015, 59, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.W.; Ding, L.; Xu, H.J.; Shen, Z.; Ju, H.X.; Jia, L.; Bao, L.; Yu, J.S. Cell-specific and pH-activatable rubyrin-loaded nanoparticles for highly selective near-infrared photodynamic therapy against cancer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 18850–18858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dai, W.; Dong, H.; Zhang, X. A Semimetal-Like Molybdenum Carbide Quantum Dots Photoacoustic Imaging and Photothermal Agent with High Photothermal Conversion Efficiency. Materials 2018, 11, 1776. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11091776
Dai W, Dong H, Zhang X. A Semimetal-Like Molybdenum Carbide Quantum Dots Photoacoustic Imaging and Photothermal Agent with High Photothermal Conversion Efficiency. Materials. 2018; 11(9):1776. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11091776
Chicago/Turabian StyleDai, Wenhao, Haifeng Dong, and Xueji Zhang. 2018. "A Semimetal-Like Molybdenum Carbide Quantum Dots Photoacoustic Imaging and Photothermal Agent with High Photothermal Conversion Efficiency" Materials 11, no. 9: 1776. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11091776
APA StyleDai, W., Dong, H., & Zhang, X. (2018). A Semimetal-Like Molybdenum Carbide Quantum Dots Photoacoustic Imaging and Photothermal Agent with High Photothermal Conversion Efficiency. Materials, 11(9), 1776. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11091776