A Comprehensive Evaluation of Rejuvenator on Mechanical Properties, Durability, and Dynamic Characteristics of Artificially Aged Asphalt Mixture
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Experimental
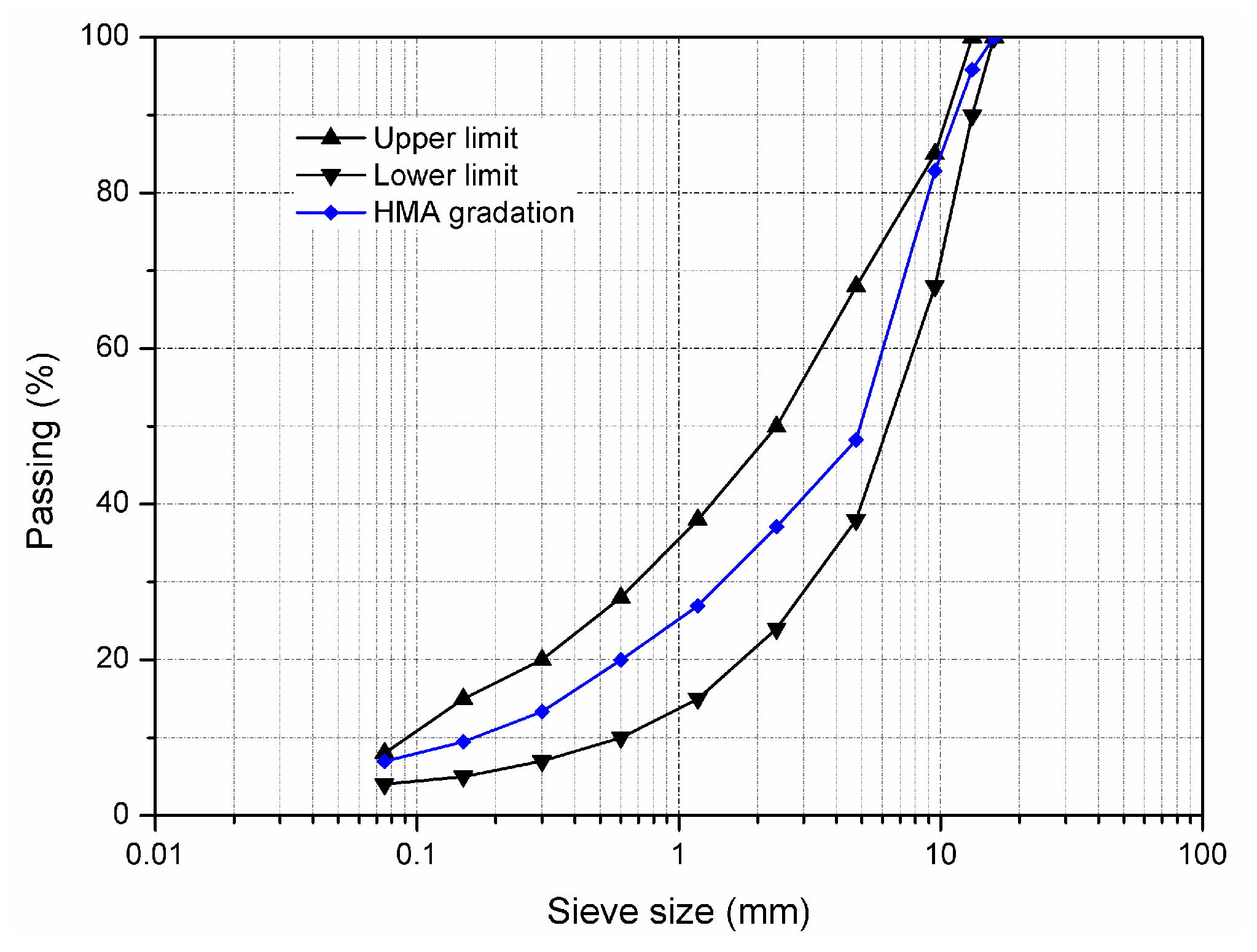
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Physical Properties Test of Asphalt Binder
2.4. Performance Test of Asphalt Mixture
2.4.1. Moisture Susceptibility Test
2.4.2. Cantabro Abrasion Test
2.4.3. Wheel Tracking Test
2.4.4. Dynamic Uniaxial Compression Test
2.4.5. Three-Point Bending Test
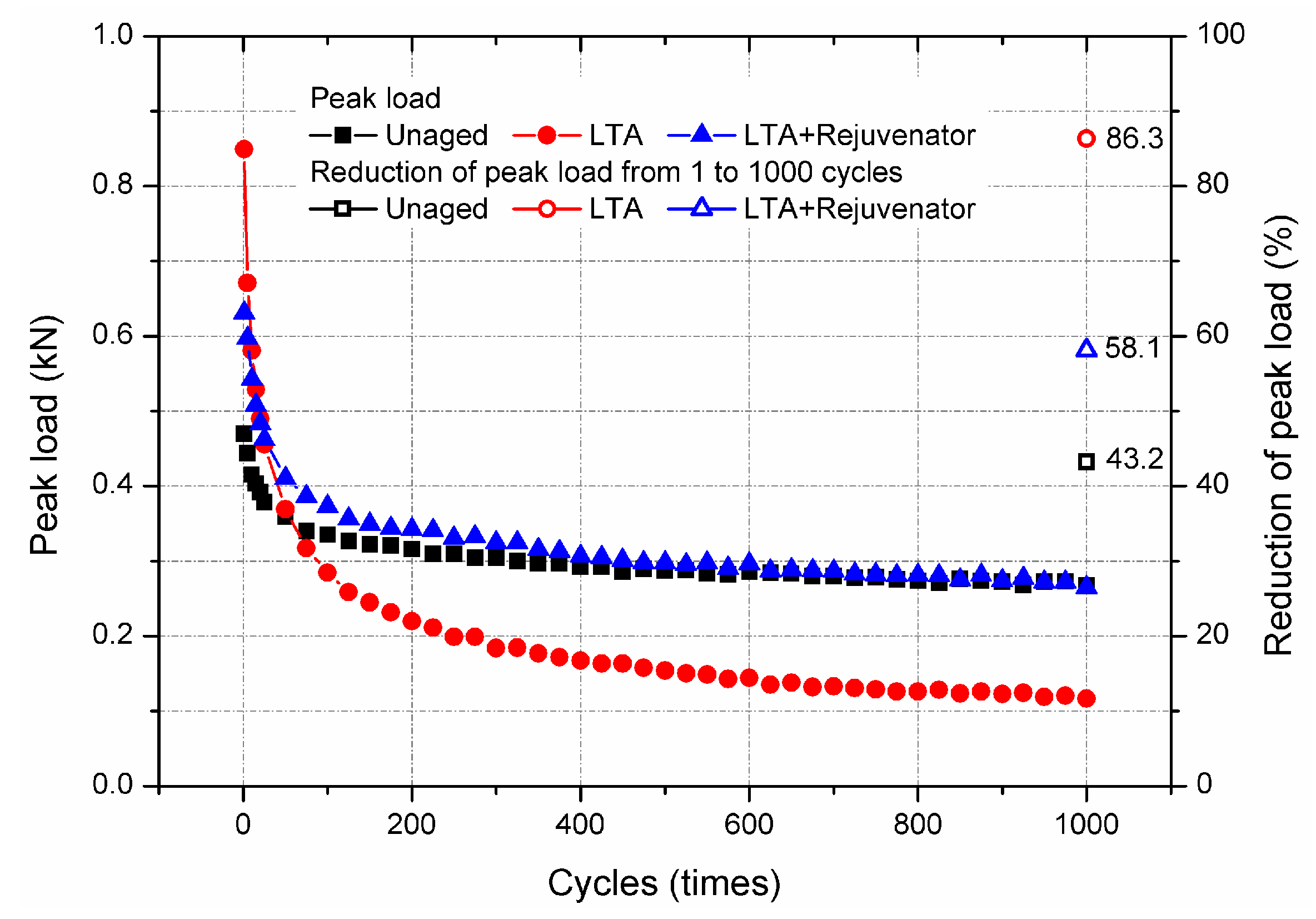
2.4.6. Overlay Tester
2.4.7. Four-Point Bending Fatigue Test
2.4.8. Dynamic Modulus Test
3. Result and Discussion
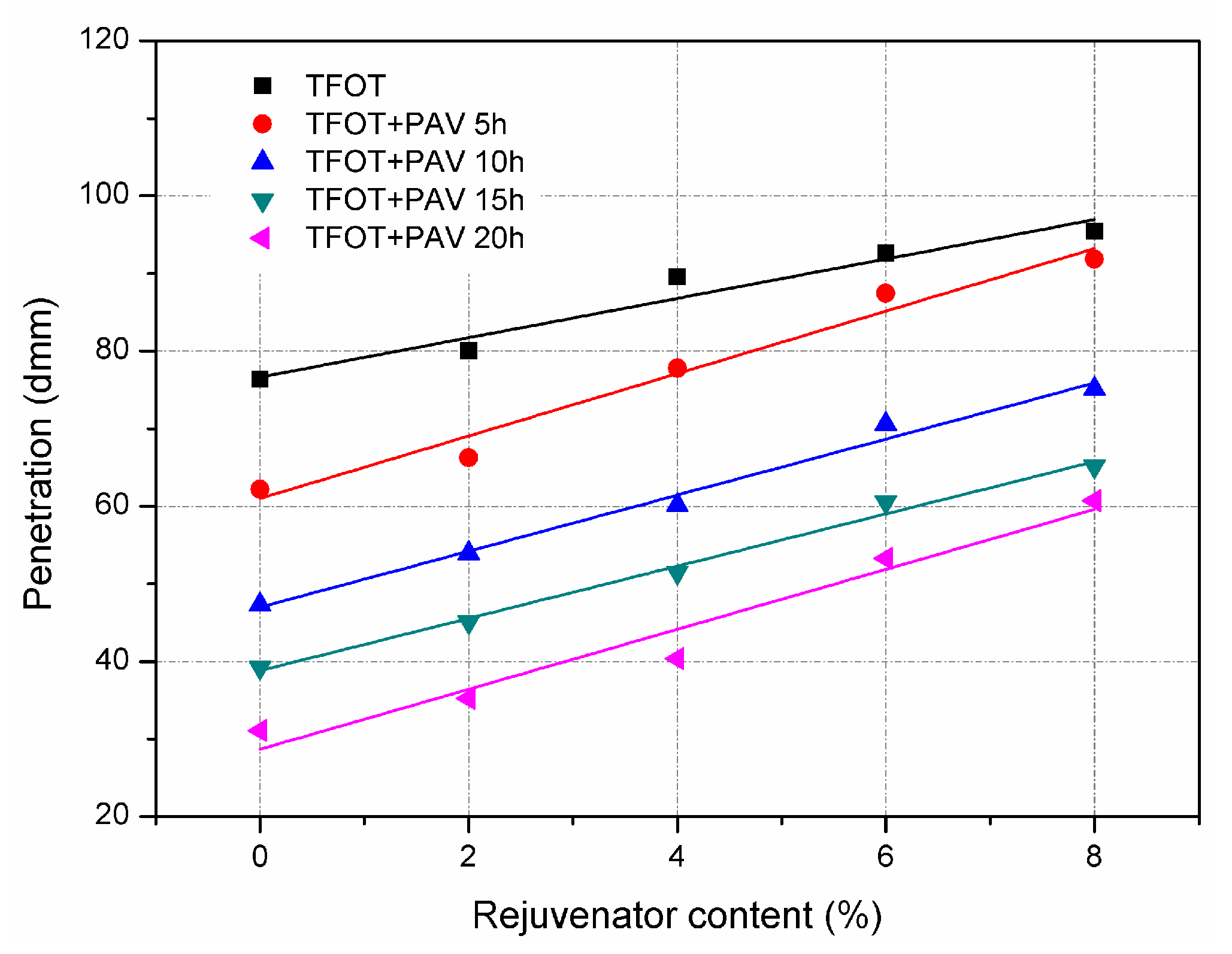
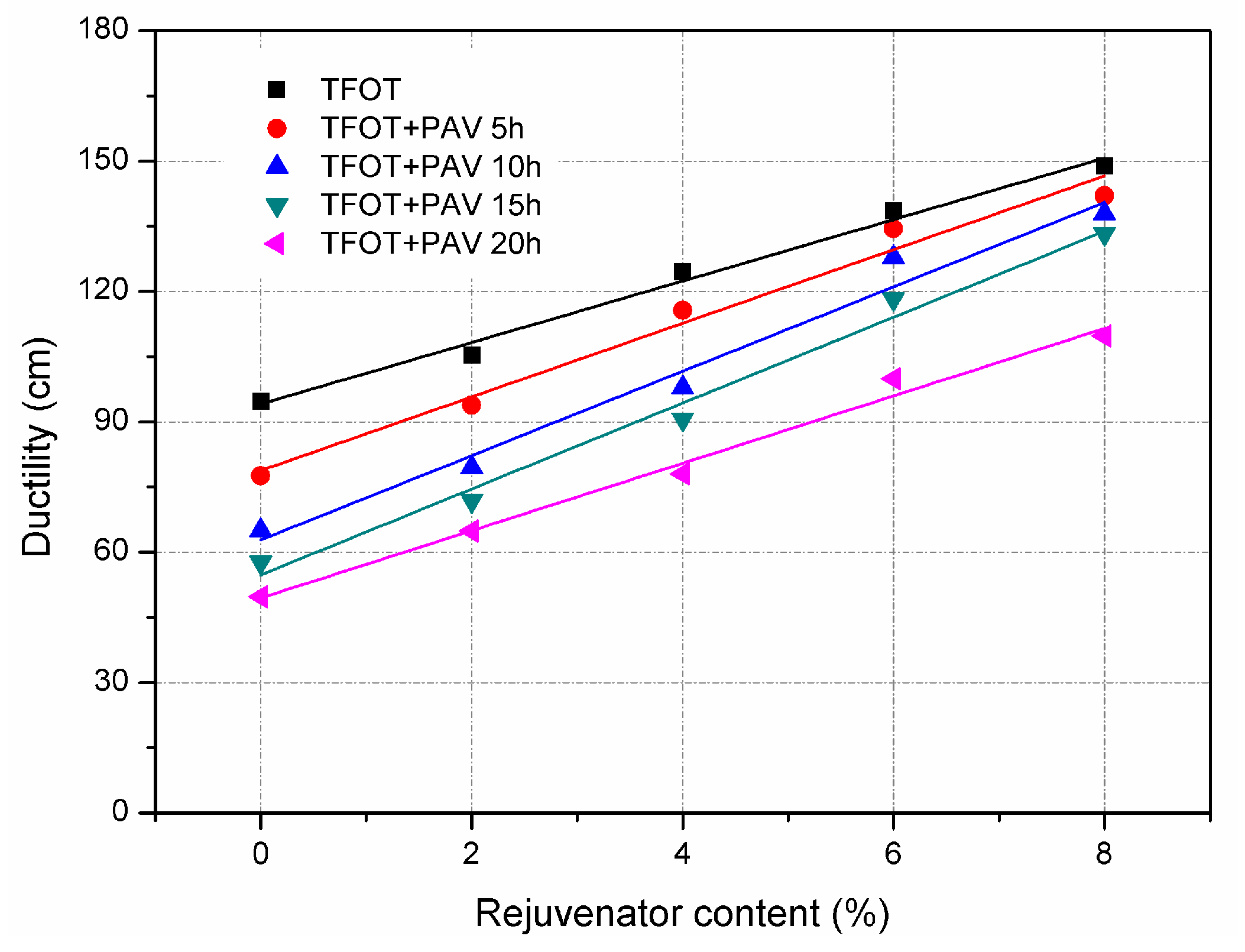
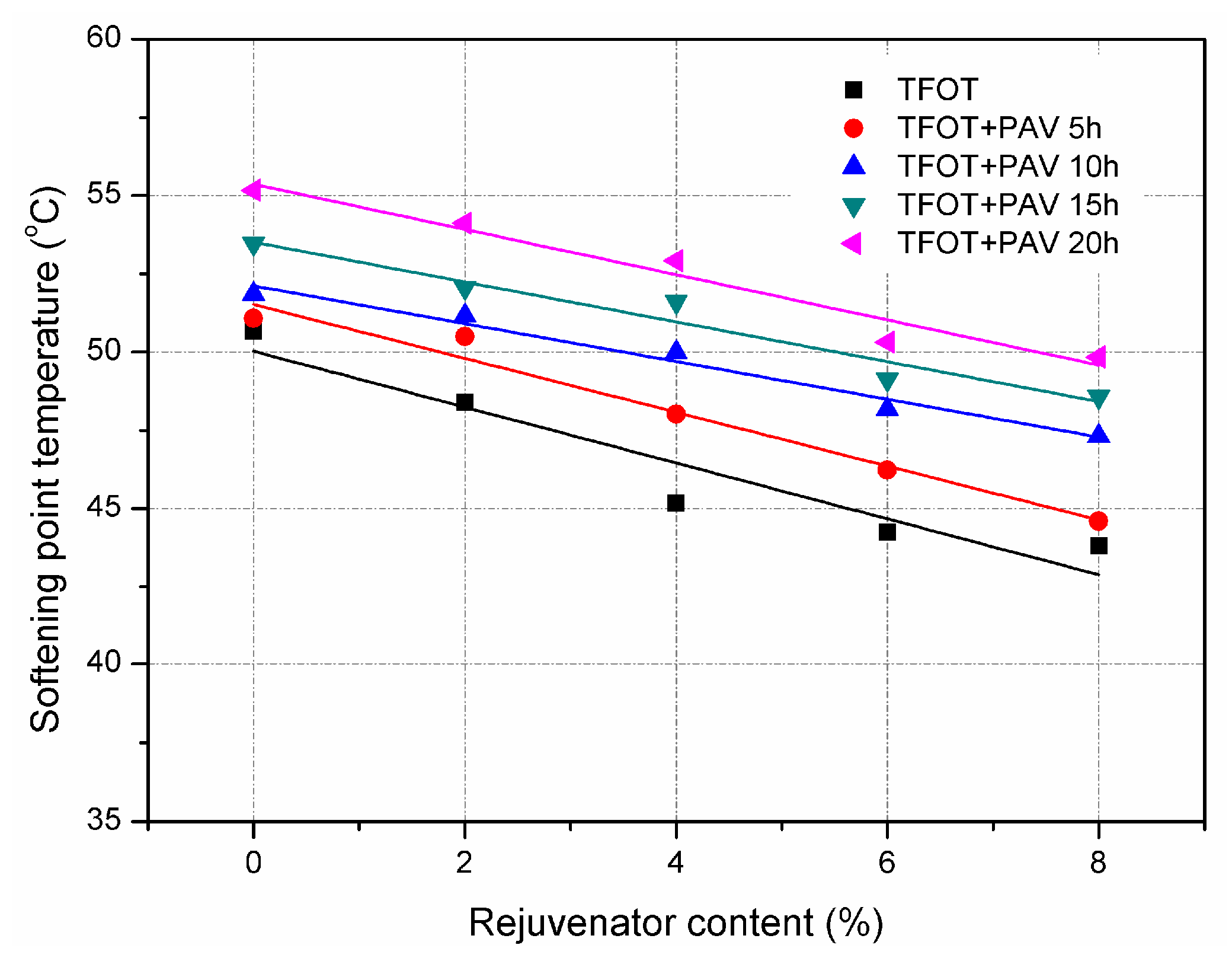
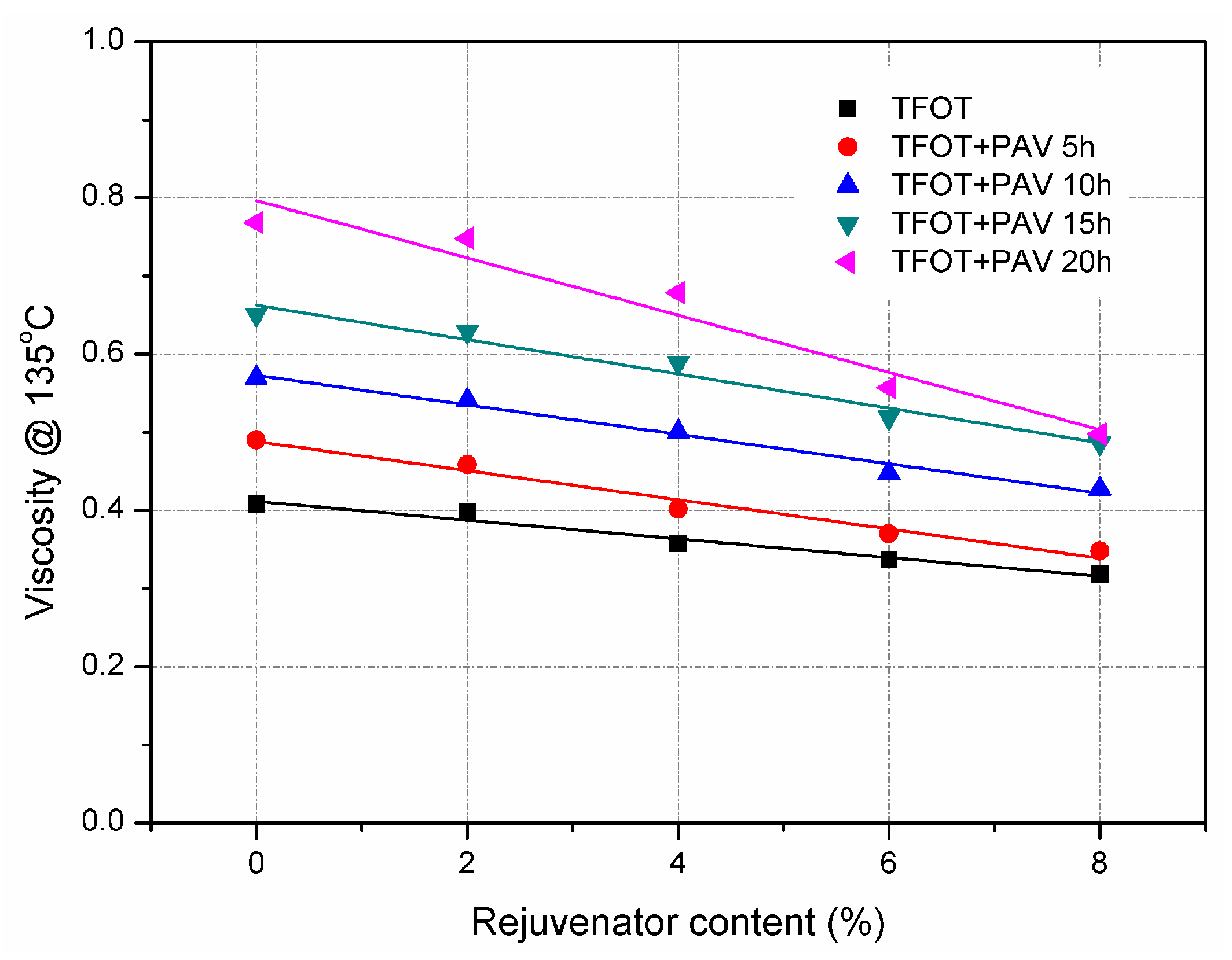
3.1. Effect of Rejuvenator on Physical Properties of Aged Asphalt Binder
3.2. Effect of Rejuvenator on Engineering Properties and Durability of Aged Asphalt Mixture
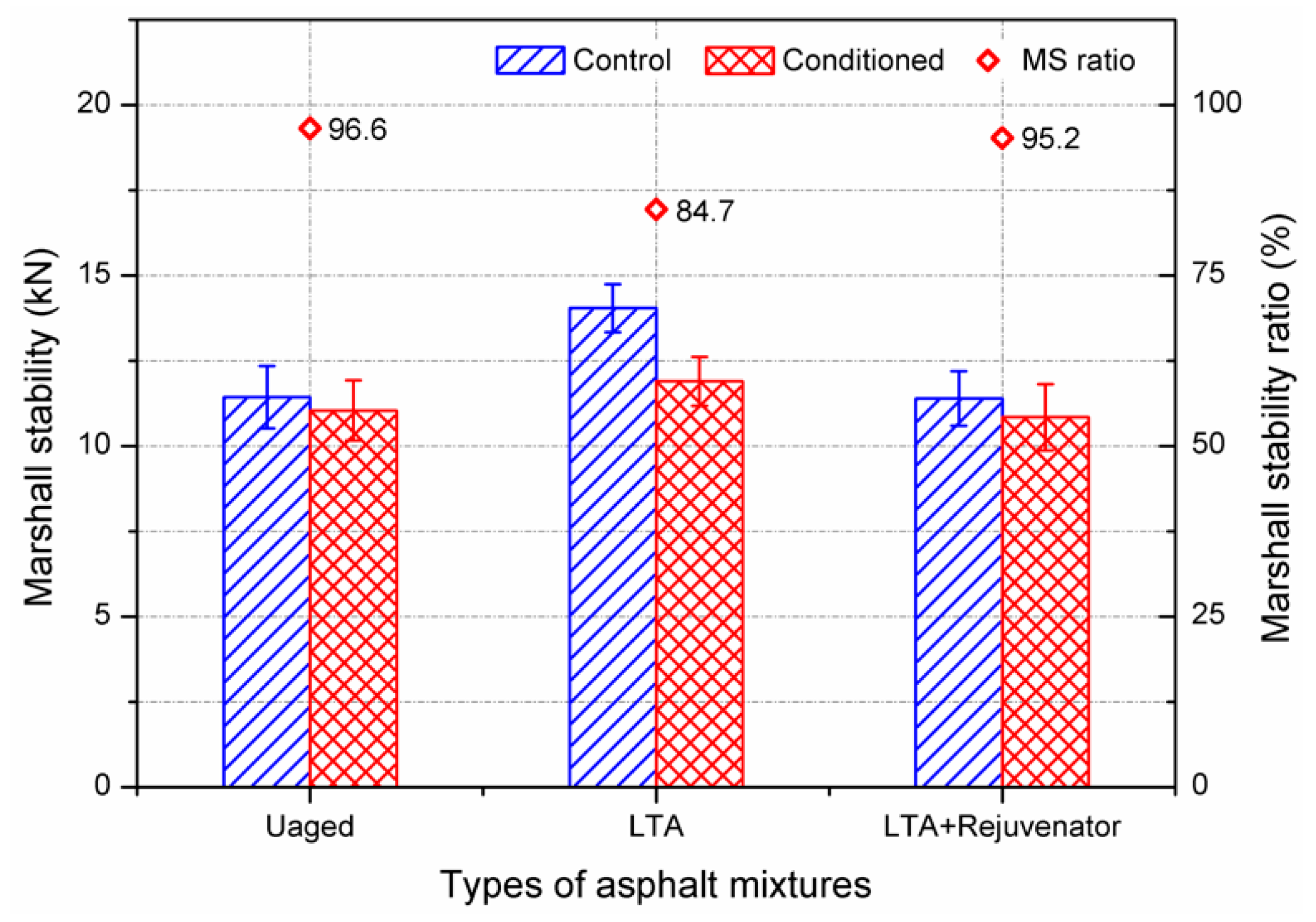
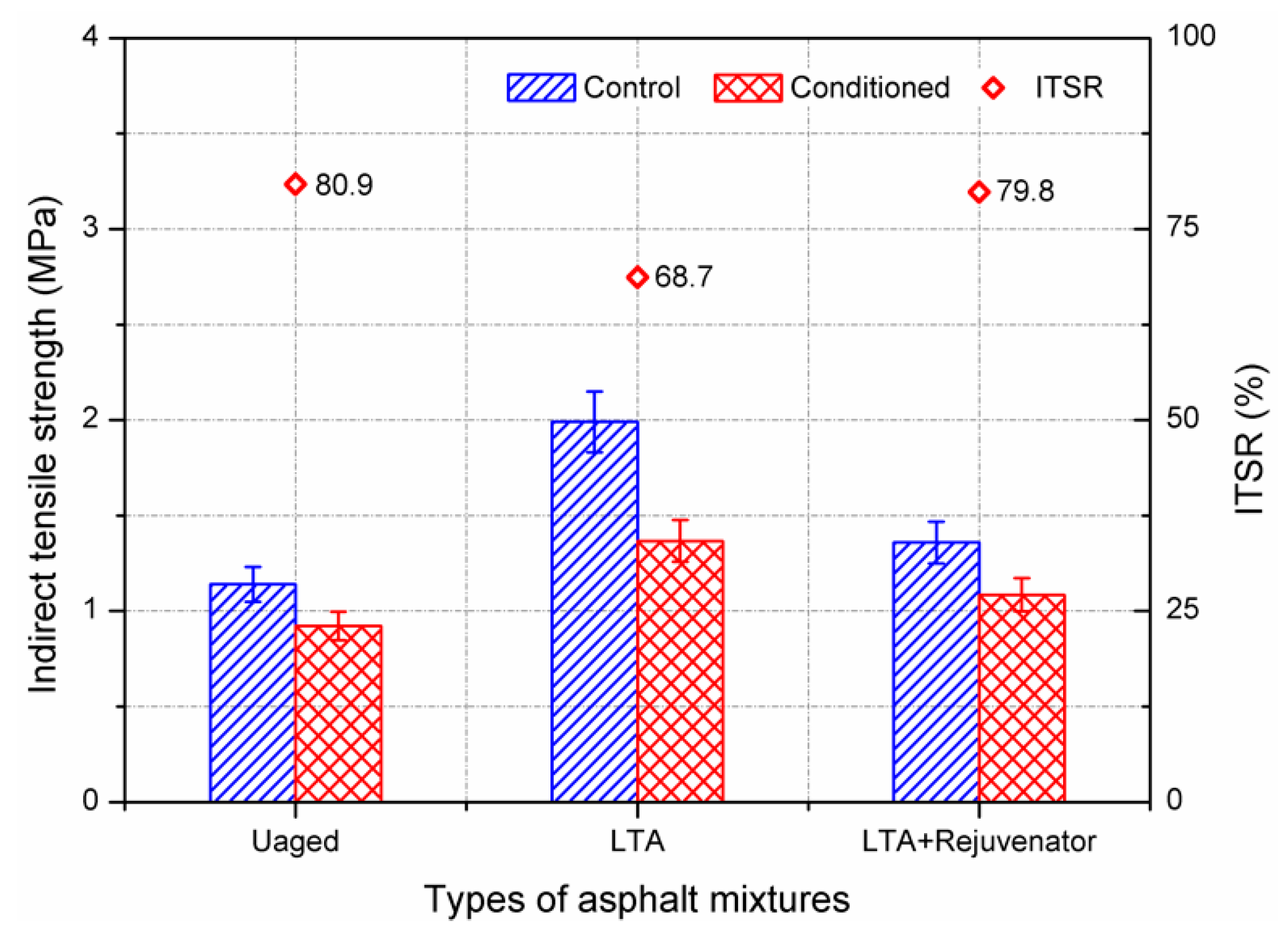
3.2.1. Moisture Susceptibility Test
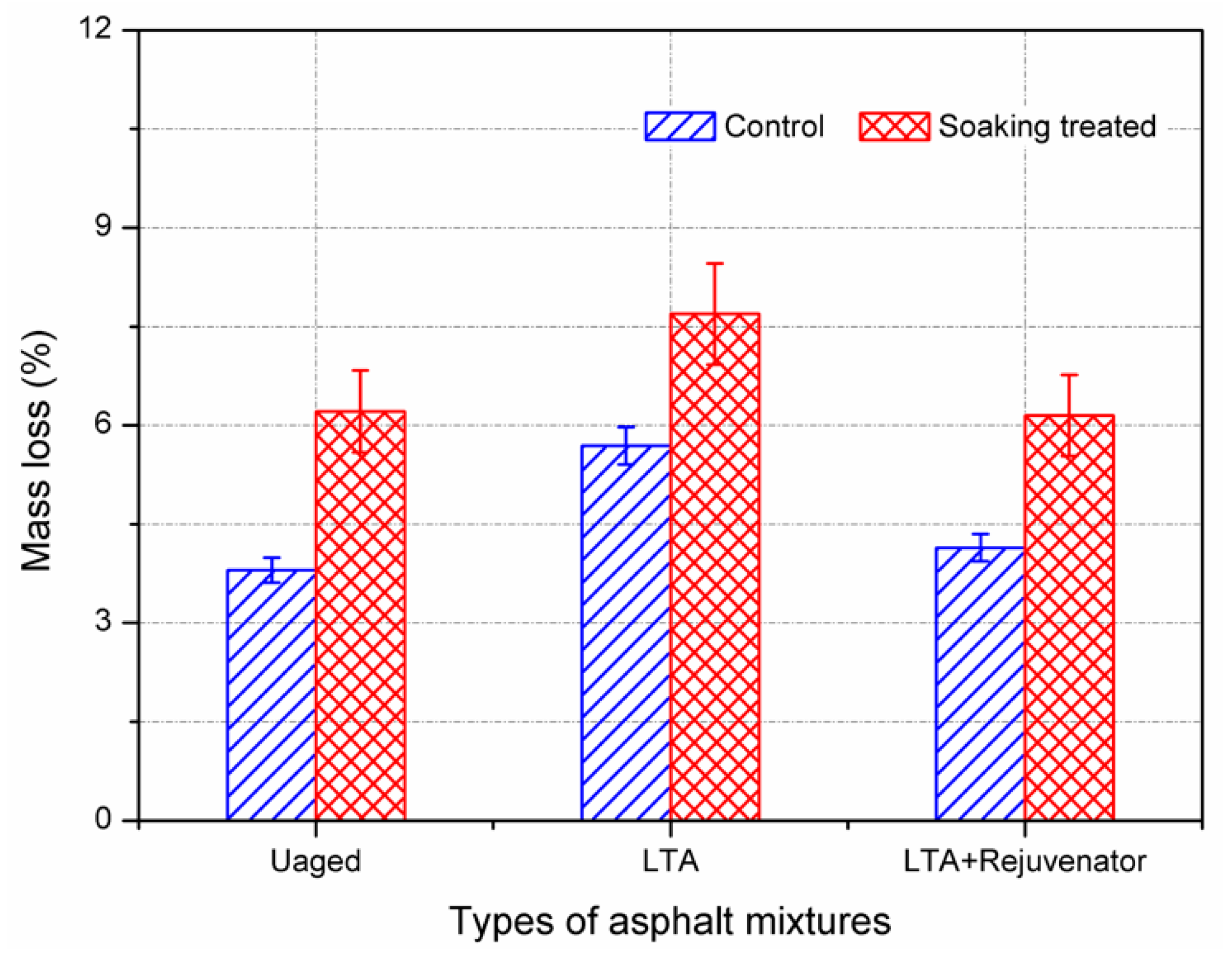
3.2.2. Cantabro Abrasion Test
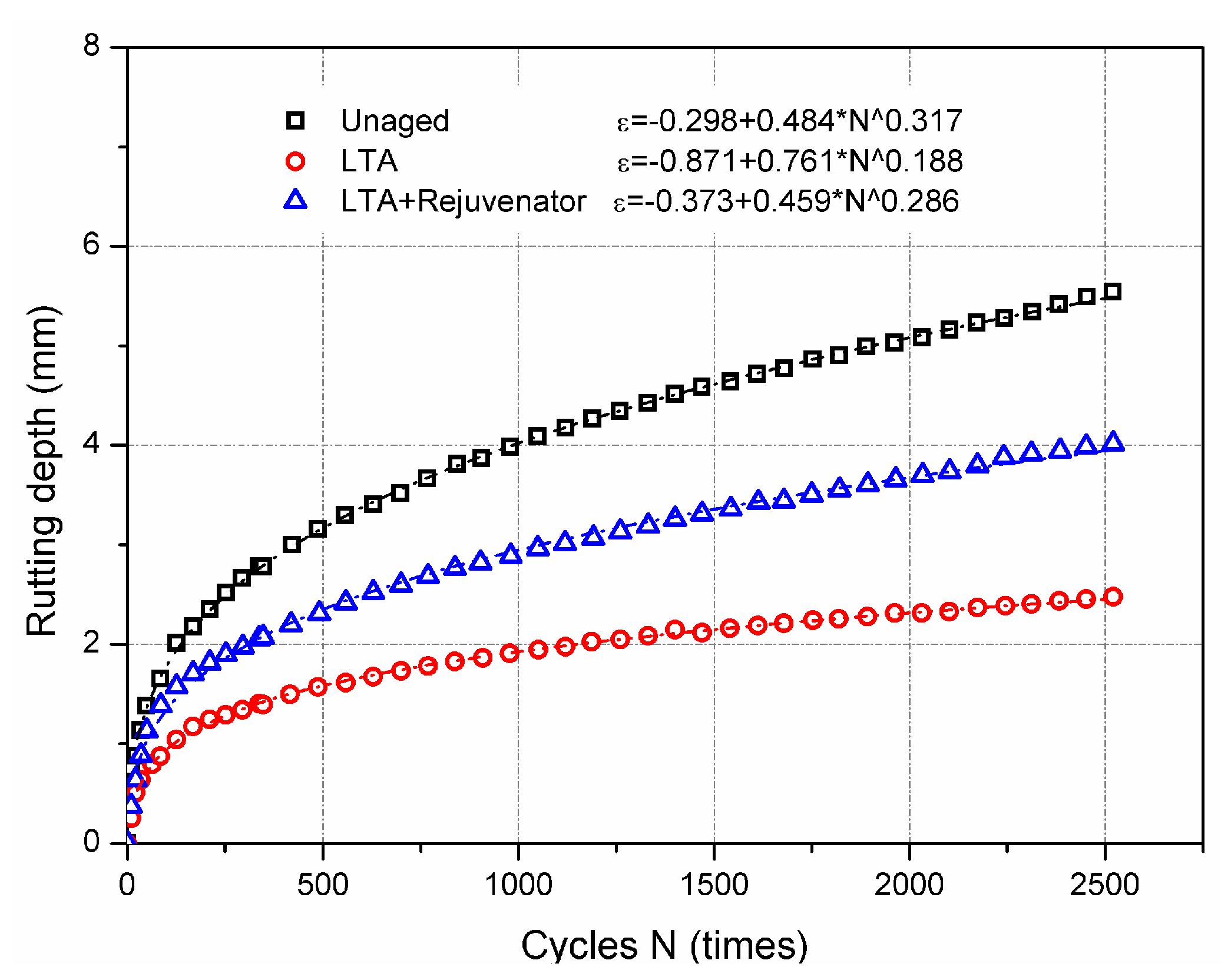
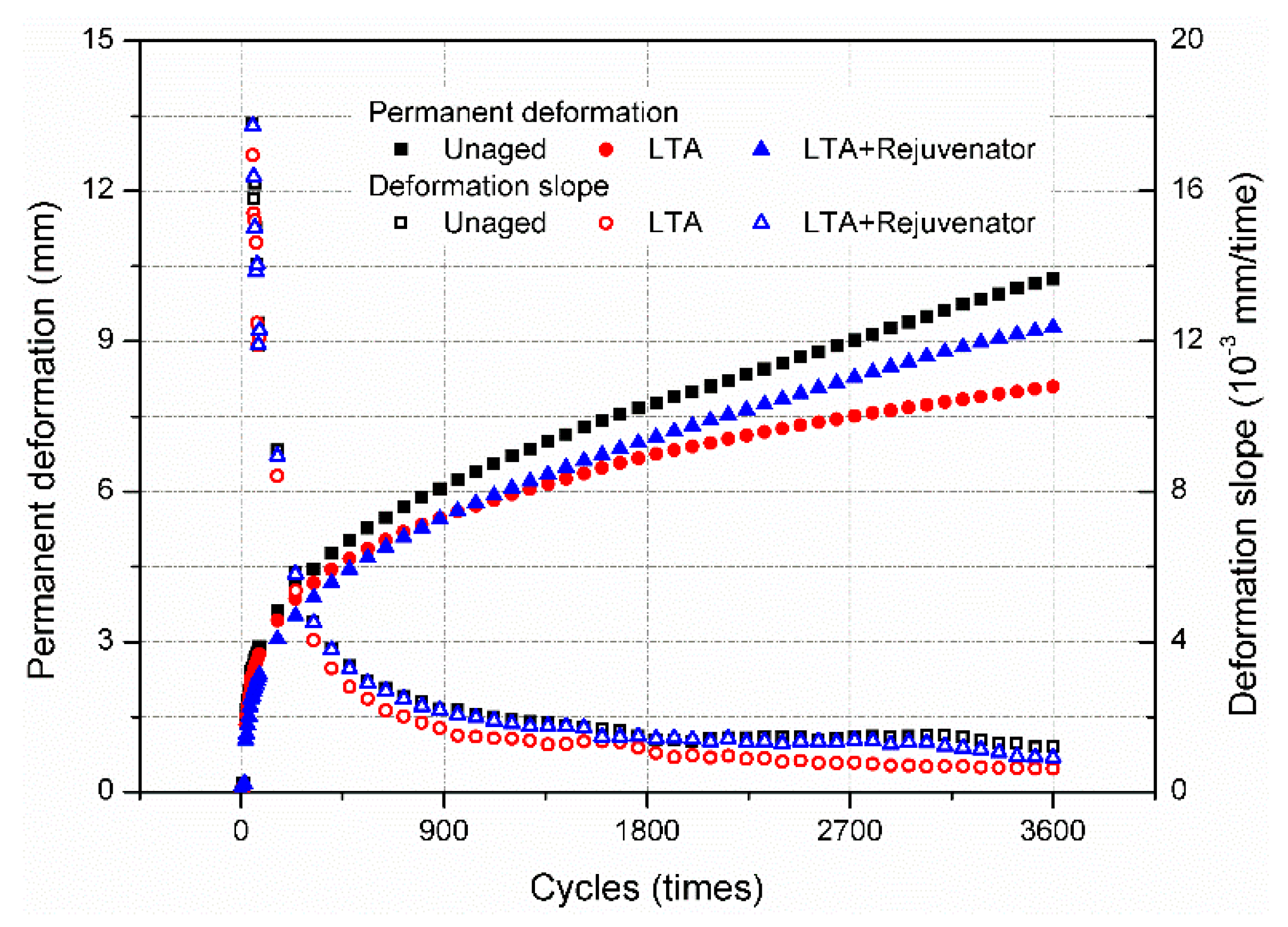
3.2.3. High Temperature Performance
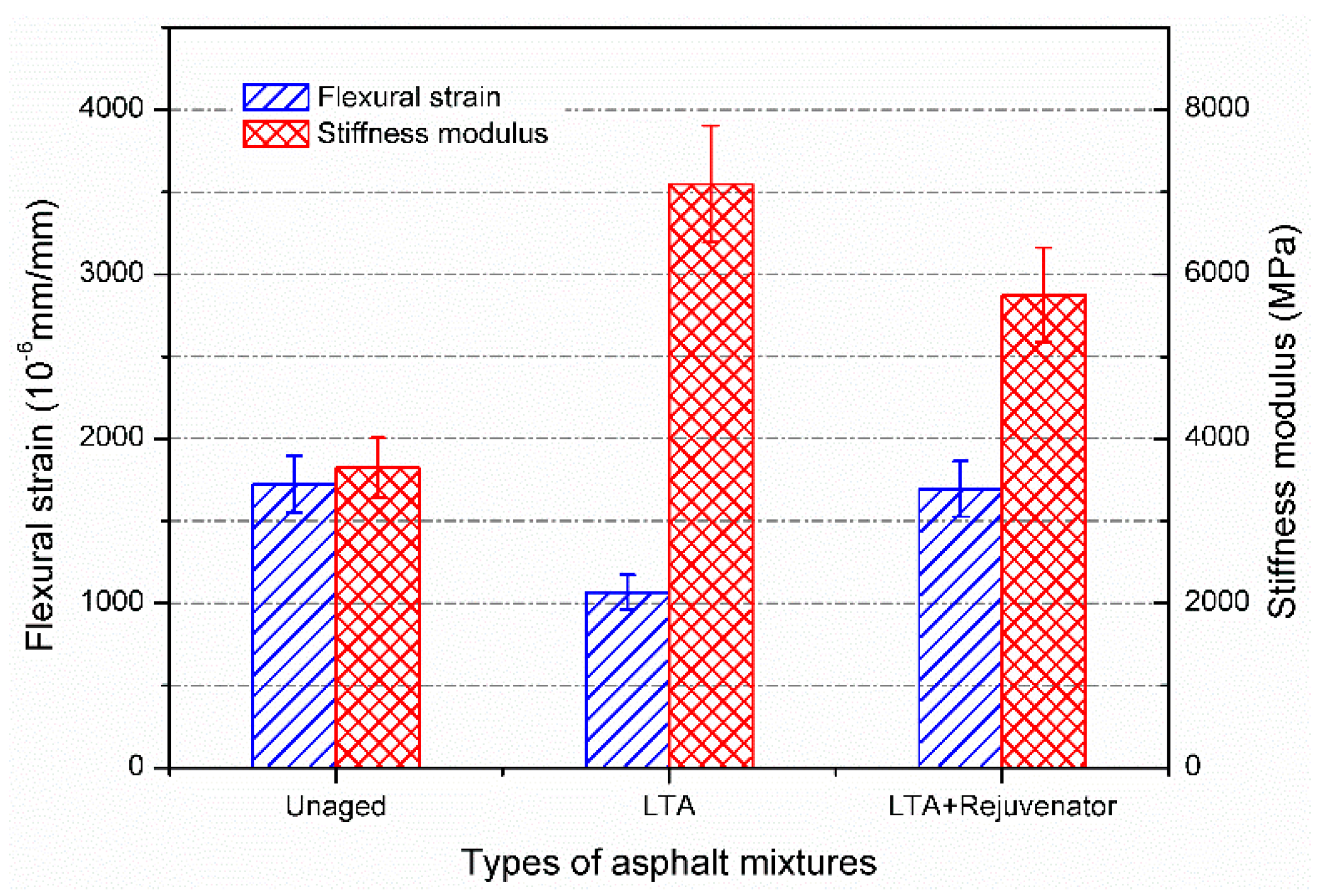
3.2.4. Cracking Resistance
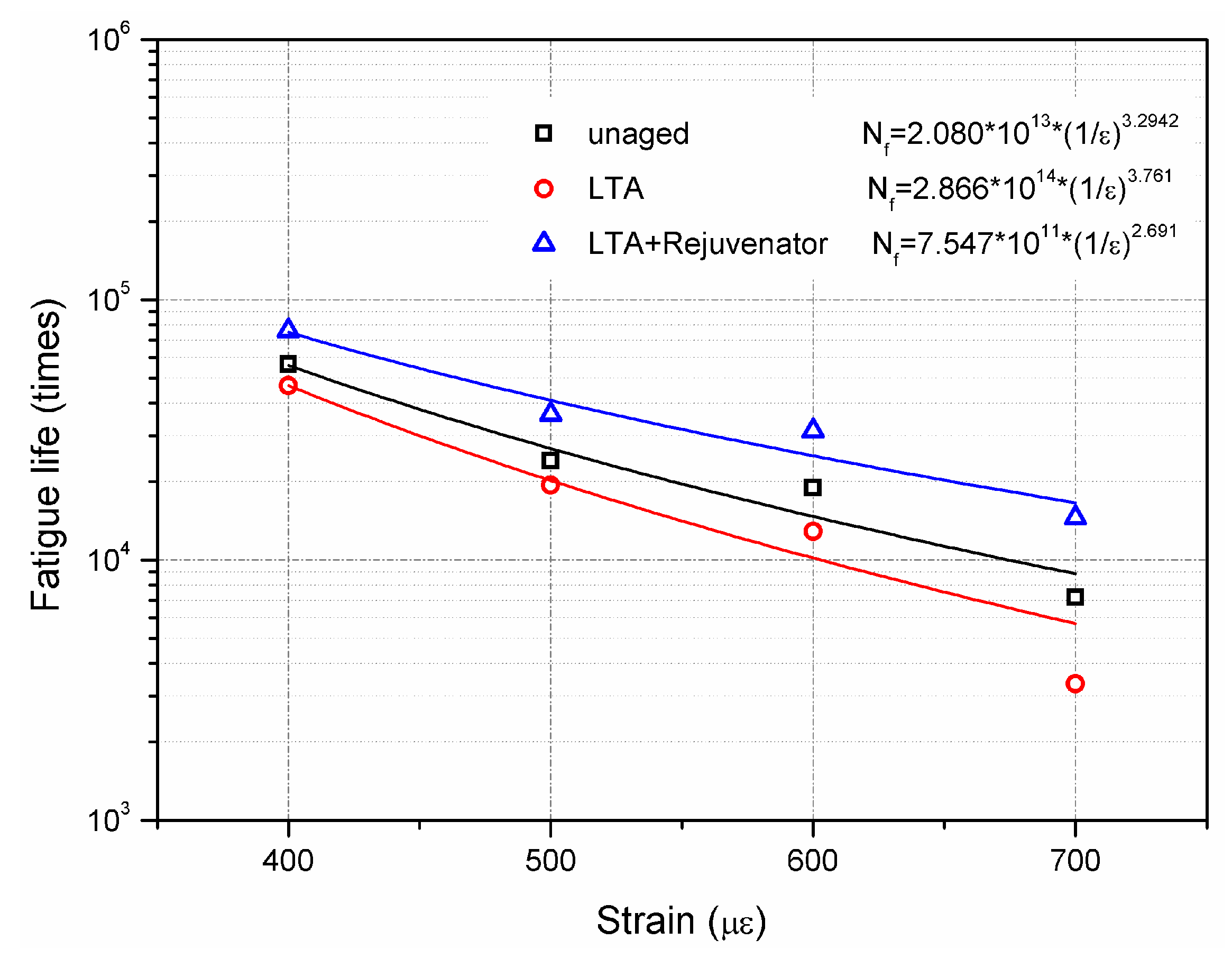
3.2.5. Fatigue Property
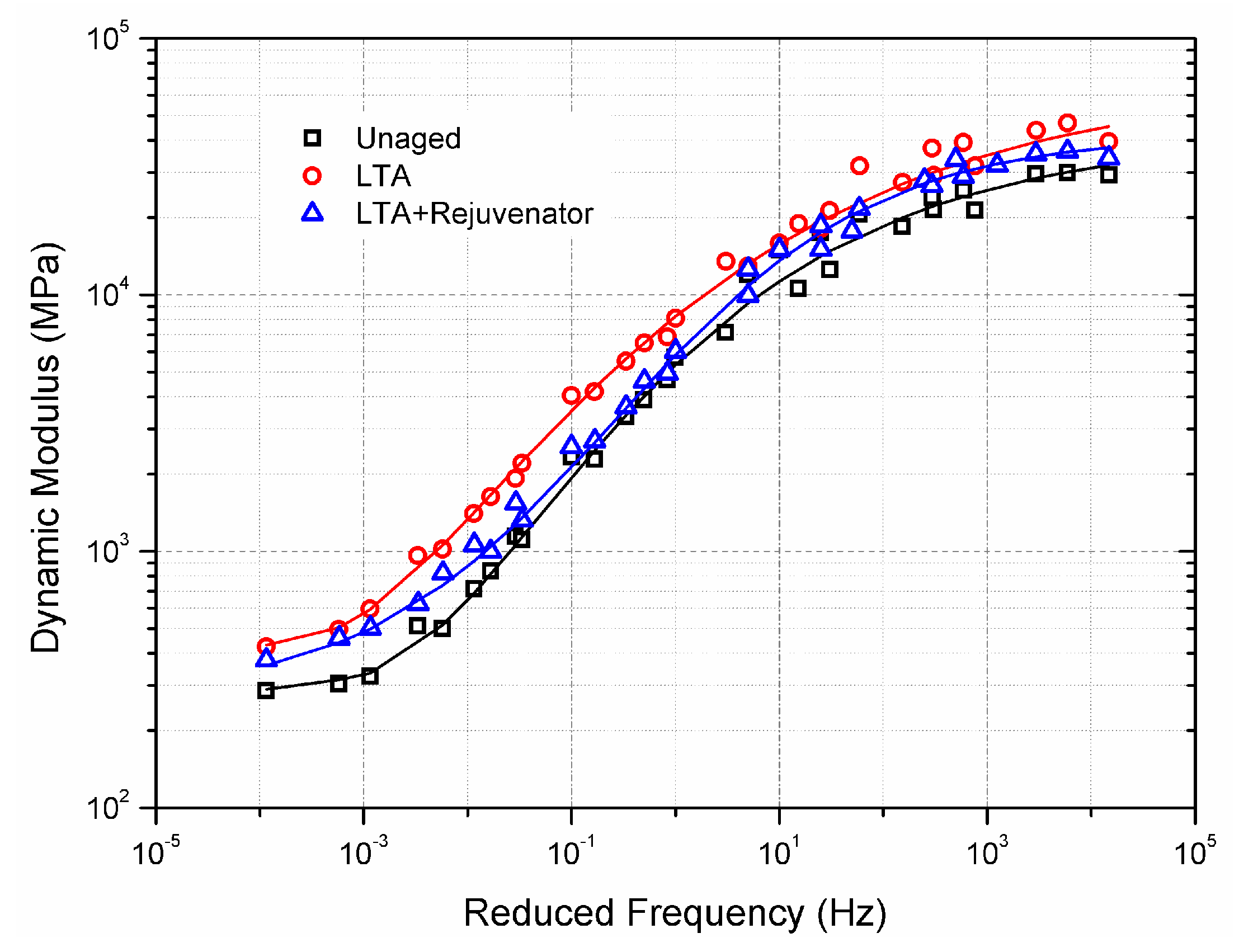
3.3. Dynamic Characteristics
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Aged asphalt binder can be recovered to some extent by incorporating with rejuvenator. However, the effect of ageing and rejuvenator on asphalt binder differs from the physical properties concerned.
- (2)
- Rejuvenated asphalt mixture has comparable resistance to moisture damage and ravelling. ITSR value is recommended as an indicator for evaluating the moisture susceptibility for recycling asphalt pavement.
- (3)
- With similar flexural strain, rejuvenated asphalt mixture has greater modulus and inferior ability to resist reflective cracking than the unaged mixture.
- (4)
- Rejuvenated asphalt mixture, which is less sensitive to strain level, shows better fatigue property than unaged mixture.
- (5)
- Compared to unaged and LTA mixtures, rejuvenated mixture shows less dependence on frequency at high temperature regions and stronger dependence at low temperature regions.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, J.; Hong, J.; Xiao, Y. Dynamic characteristics of 100% cold recycled asphalt mixture using asphalt emulsion and cement. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 156, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, T.B.; Baaj, H. The use of rejuvenating agents in production of recycled hot mix asphalt: A systematic review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 114, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinis-Almeida, M.; Castro-Gomes, J.; Sangiorgi, C.; Zoorob, S.E.; Afonso, M.L. Performance of warm mix recycled asphalt containing up to 100% RAP. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 112, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, A. Summary report on the ageing of asphalt-aggregate system. Transp. Res. Board 1989, 10, 1–121. [Google Scholar]
- Airey, G.D. State of the art report on ageing test methods for bituminous pavement materials. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2003, 4, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaumanis, M.; Mallick, R.B. Review of very high-content reclaimed asphalt use in plant-produced pavements: state of the art. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2015, 16, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Leng, B.; Wu, S.; Sang, Y. Physical, chemical and rheological properties of waste edible vegetable oil rejuvenated asphalt binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 66, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Xiao, F.; Putman, B.; Leng, B.; Wu, S. High temperature properties of rejuvenating recovered binder with rejuvenator, waste cooking and cotton seed oils. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 59, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, J.S.; Lachance, A. Mechanistic and volumetric properties of asphalt mixtures with recycled asphalt pavement. Transport. Res. Rec. 2005, 1929, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molenaar, A.A.A.; Hagos, E.T.; van de Ven, M.F.C. Effects of ageing on the mechanical characteristics of bituminous binders in PAC. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2010, 22, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Airkhanian, S.N.; Wu, B. Fatigue and stiffness evaluations of reclaimed asphalt pavement in hot mix asphalt mixtures. J. Test. Eval. 2011, 39, 234–242. [Google Scholar]
- Zaumanis, M.; Mallick, R.B.; Frank, R. Evaluation of different recycling agents for restoring aged asphalt binder and performance of 100% recycled asphalt. Mater. Struct. 2015, 48, 2475–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Hussain, B.U.; Enad, M.; Hajj, E.Y. Estimating allowable RAP in asphalt mixes to meet target low temperature PG requirements. J. Assoc. Asphalt Paving Technol. 2010, 79, 473–495. [Google Scholar]
- Kuang, D.; Jiao, Y.; Ye, Z.; Lu, Z.; Chen, H.; Yu, J.; Liu, N. Diffusibility enhancement of rejuvenator by epoxidized soybean oil and its influence on the performance of recycled hot mix asphalt mixtures. Materials 2017, 10, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaumanis, M.; Mallick, R.B.; Frank, R. Determining optimum rejuvenator dose for asphalt recycling based on superpave performance grade specifications. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 69, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, M.C.; Zaumanis, M.; Mazza, E.; Partl, M.N.; Poulikakos, L.D. Ageing effect on rheology and cracking behaviour of reclaimed binder with bio-based rejuvenators. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 189, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ongel, A.; Hugener, M. Impact of rejuvenators on ageing properties of bitumen. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 94, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Huang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y. Evaluation of the diffusion and distribution of the rejuvenator for hot asphalt recycling. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 98, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; van de Ven, M.F.C.; Molenaar, A.A.A.; Wu, S. Assessment of effectiveness of rejuvenators on artificially aged mortar. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2016, 28, 04016079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, Z.; Li, C.; Xiao, Y.; Wu, S.; Pan, P. The Rejuvenating Effect in Hot Asphalt Recycling by Mortar Transfer Ratio and Image Analysis. Materials 2017, 10, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- JTG F41—Technical Specification for Highway Asphalt Pavement Recycling; Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2008. (In Chinese)
- Im, S.; Zhou, F.; Lee, R.; Scullion, T. Impacts of rejuvenators on performance and engineering properties of asphalt mixtures containing recycled materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 53, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, S.; Karki, P.; Zhou, F. Development of new mix design method for asphalt mixtures containing RAP and rejuvenators. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 115, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaumanis, M.; Mallick, R.B.; Poulikakos, L.; Frank, R. Influence of six rejuvenators on the performance properties of reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP) binder and 100% recycled asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 71, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, P.; Wu, S.; Hu, X.; Liu, G.; Li, B. Effect of material composition and environmental condition on thermal characteristics of conductive asphalt concrete. Materials 2017, 10, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- JTG F40—Technical Specifications for Construction Highway Asphalt Pavements; Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2004. (In Chinese)
- JTG E20—Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China. Standard Test Methods of Bitumen and Bituminous Mixtures for Highway Engineering; Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2011. (In Chinese)
- ASTM D36/D36M-14e1—Standard Test Method for Softening Point of Bitumen (Ring-and-Ball Apparatus); ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014.
- ASTM D113-17—Standard Test Method for Ductility of Bituminous Materials; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017.
- ASTM D5/D5M-13—Standard Test Method for Penetration of Bituminous Materials; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013.
- ASTM D4402/D4402M-15—Standard Test Method for Viscosity Determination of Asphalt at Elevated Temperatures Using a Rotational Viscometer; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015.
- BS EN 12697-25—Bituminous Mixtures Test Methods: Cyclic Compression Test; British Standard Institute: London, UK, 2016.
- Tex-248-F—Test Procedure for Overlay Test; Texas Department of Transportation: Austin, TX, USA, 2009.
- Hu, X.; Wang, N.; Pan, P.; Bai, T. Performance evaluation of asphalt mixture using brake pad waste as mineral filler. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 138, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modarres, A.; Hamedi, H. Developing laboratory fatigue and resilient modulus models for modified asphalt mixes with waste plastic bottles (PET). Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 68, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AASHTO TP 62-07—Standard Test Method for Determining Dynamic Modulus of Hot-Mix Asphalt (HMA); American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials: Washington, DC, USA, 2007.
- Ruan, L.; Luo, R.; Hu, X.; Pan, P. Effect of bell-shaped loading and haversine loading on the dynamic modulus and resilient modulus of asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 161, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellinen, T.; Zofka, A.; Marasteanu, M.; Funk, N. Asphalt mixture stiffness predictive models. J. Assoc. Asphalt Paving Technol. 2007, 76, 575–625. [Google Scholar]
| Properties | Rejuvenator | Test Method |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Liquid | |
| Color | Brown | |
| pH | 5.6 | pH test paper |
| Viscosity (25 °C), SFS | 15 | ASTM D-244 |
| Solute component (wt %) | 60 | ASTM D-244 |
| Regeneration component (wt %) | 8 | ASTM D-2006-70 |
| Asphaltene component (wt %) | 0.75 |
| Marshall Stability Test | Indirect Tensile Strength Test | |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Soaking for 0.5 h at 60 °C | Soaking for 2 h at 25 °C |
| Conditioned | Soaking for 48 h at 60 °C | Freezing at −18 °C for 16 h + Thawing at 60 °C for 24 h + Soaking for 2 h at 25 °C |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, P.; Kuang, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhang, X. A Comprehensive Evaluation of Rejuvenator on Mechanical Properties, Durability, and Dynamic Characteristics of Artificially Aged Asphalt Mixture. Materials 2018, 11, 1554. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11091554
Pan P, Kuang Y, Hu X, Zhang X. A Comprehensive Evaluation of Rejuvenator on Mechanical Properties, Durability, and Dynamic Characteristics of Artificially Aged Asphalt Mixture. Materials. 2018; 11(9):1554. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11091554
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Pan, Yi Kuang, Xiaodi Hu, and Xiao Zhang. 2018. "A Comprehensive Evaluation of Rejuvenator on Mechanical Properties, Durability, and Dynamic Characteristics of Artificially Aged Asphalt Mixture" Materials 11, no. 9: 1554. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11091554
APA StylePan, P., Kuang, Y., Hu, X., & Zhang, X. (2018). A Comprehensive Evaluation of Rejuvenator on Mechanical Properties, Durability, and Dynamic Characteristics of Artificially Aged Asphalt Mixture. Materials, 11(9), 1554. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11091554





