FEM Investigation of the Stress Distribution over Mandibular Bone Due to Screwed Overdenture Positioned on Dental Implants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
- Analysis was performed on sagittal and axial planes.
- Occlusion over all transversal planes.
- Load of 200 N for anterior area, 600 N for premolars, and 800 N for molars.
- Only a static load condition has been studied.
- joint constraint between the overlapping faces of the bone components;
- joint constraint between the overlapping faces between fixture and connection screw;
- joint constraint between the threading of the fixture and the bone.
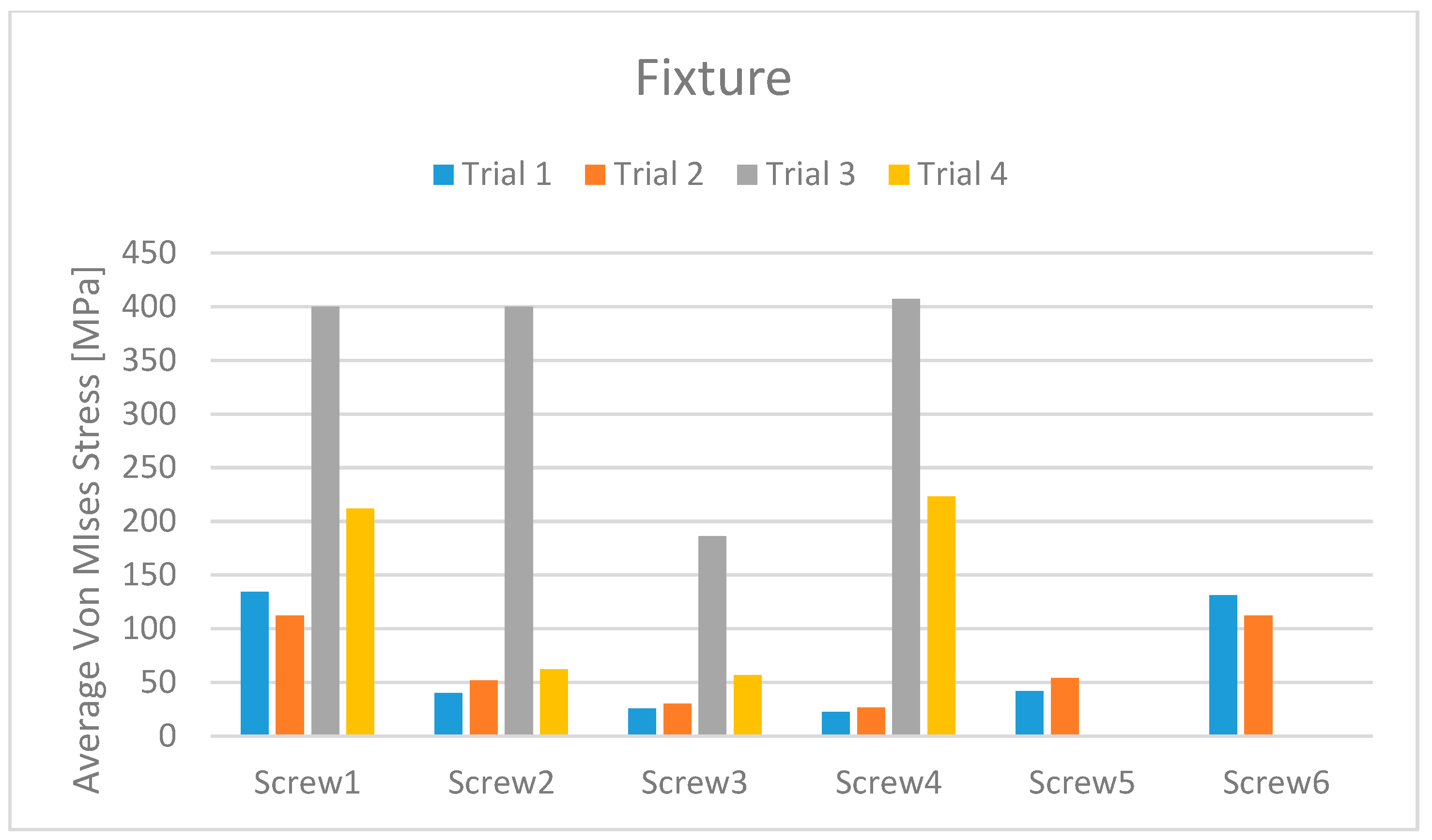
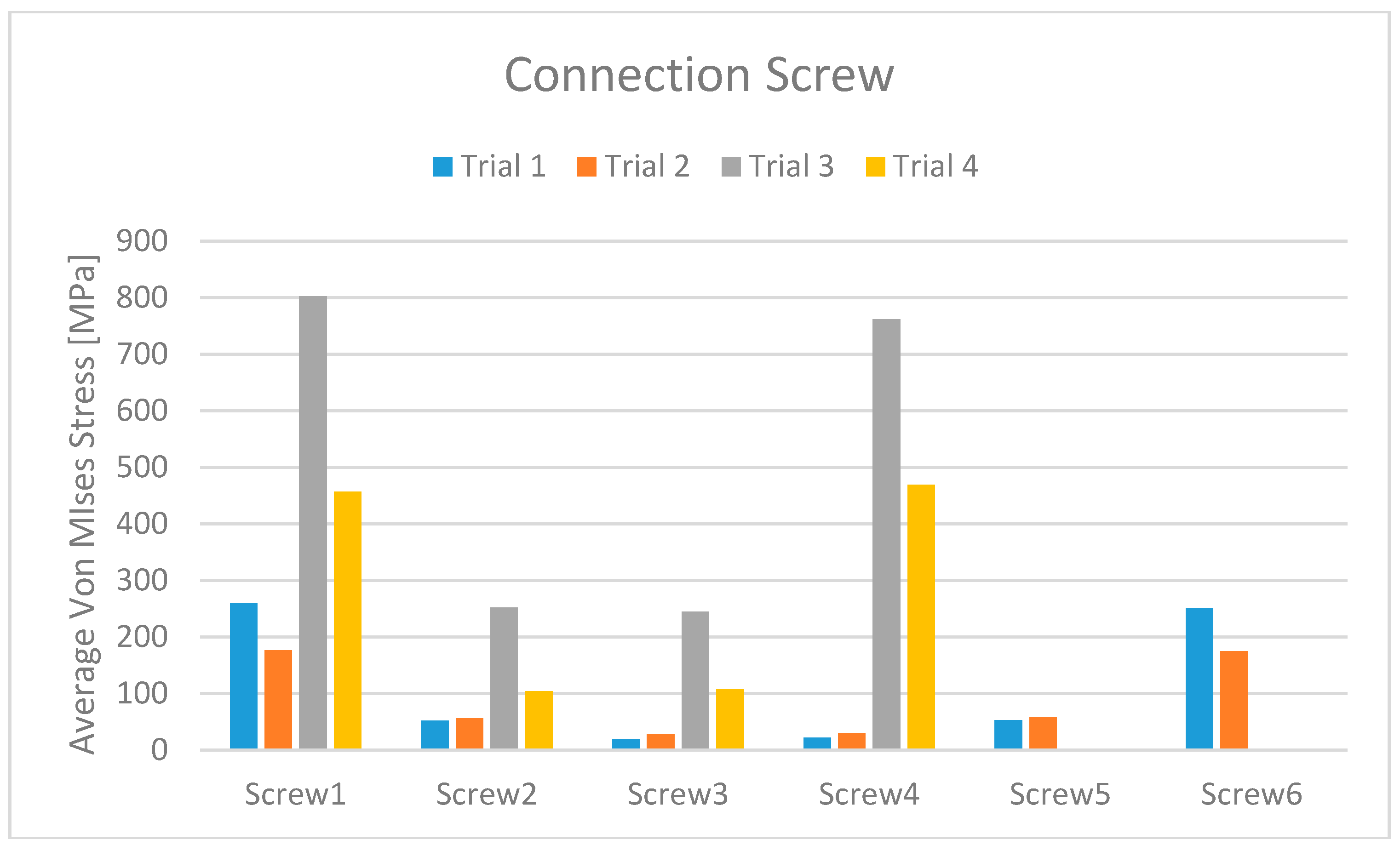
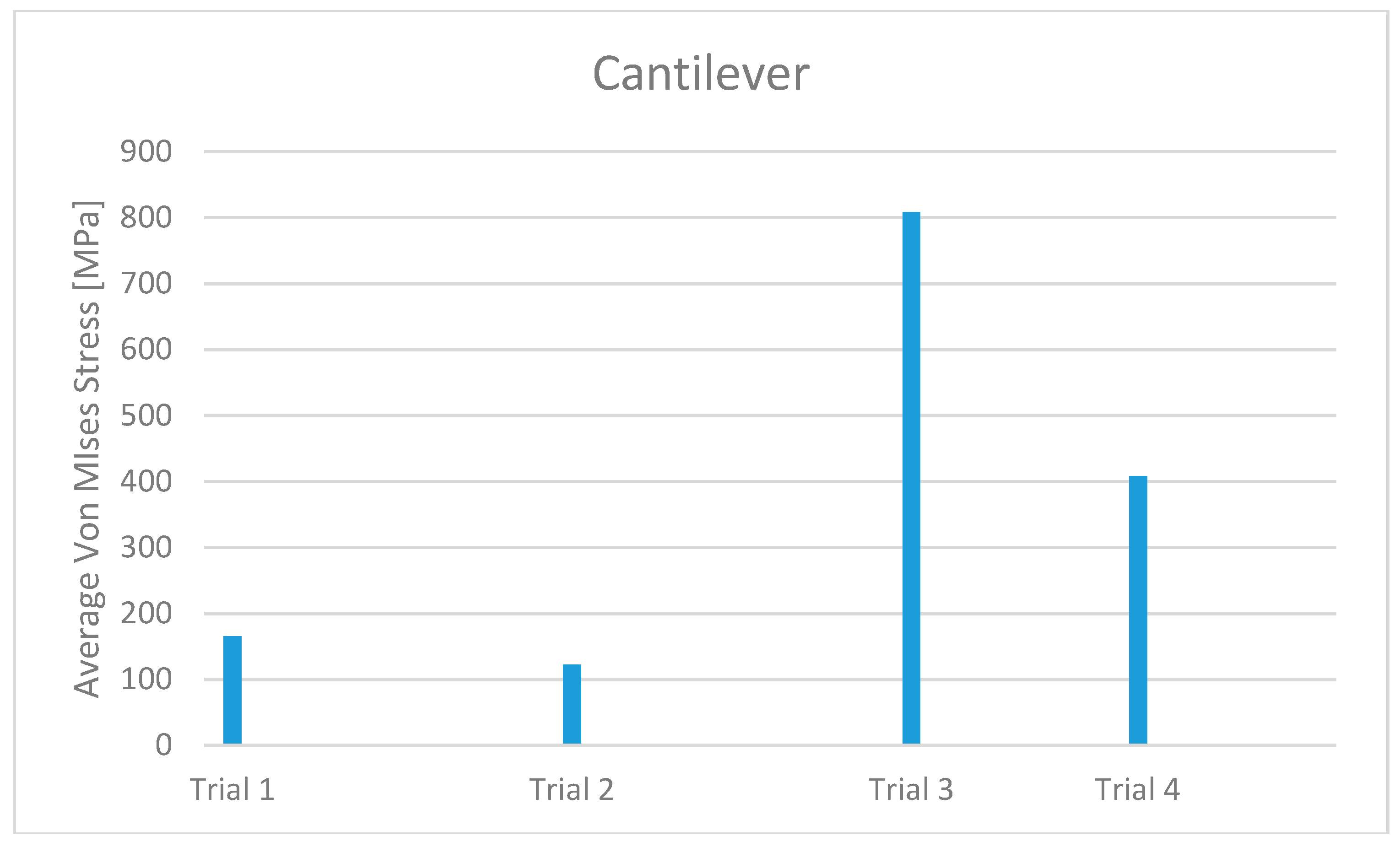
3. Results
- The use of the six-screw implant is exclusively available for those patients with a jaw size that facilitates the installation of screws in the posterior part of the dental arch.
- The possibility of installation of screws in the area of the molars greatly increases the risk of positioning them incorrectly, given the reduced space which is available to the implant surgeon. Recall that an incorrect positioning of the prosthesis-supporting abutments almost always generates a failure of the implant and, therefore, it is obvious that great care is needed when evaluating the six-screw solution as optimal.
- The use of two extra screws leads to an increase in the cost of the installation that cannot be neglected, especially if the advantages obtainable are not so clear.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Von Meyer, H. Die architectur der spongiosa. Arch. Anat. Physiol. 1867, 47, 615–628. [Google Scholar]
- Tallgren, A. The continuing reduction of the residual alveolar ridges in complete denture wearers: A mixed-longitudinal study covering 25 years. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1972, 27, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cawood, J.I.; Howell, R.A. Reconstructive preprosthetic surgery: I. Anatomical considerations. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1991, 20, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cawood, J.I.; Howell, R.A. A classification of the edentulous jaws. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1988, 17, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervino, G.; Romeo, U.; Lauritano, F.; Bramanti, E.; Fiorillo, L.; D’Amico, C.; Milone, D.; Laino, L.; Campolongo, F.; Rapisarda, S.; et al. Fem and Von Mises Analysis of OSSTEM® Dental Implant Structural Components: Evaluation of Different Direction Dynamic Loads. Open Dent. J. 2018, 12, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicciù, M.; Risitano, G.; Maiorana, C.; Franceschini, G. Parametric analysis of the strength in the “Toronto” osseous-prosthesis system. Minerva Stomatol. 2009, 58, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cicciu, M.; Bramanti, E.; Matacena, G.; Guglielmino, E.; Risitano, G. FEM evaluation of cemented-retained versus screw-retained dental implant single-tooth crown prosthesis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2014, 7, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bramanti, E.; Cervino, G.; Lauritano, F.; Fiorillo, L.; D’Amico, C.; Sambataro, S.; Denaro, D.; Famà, F.; Ierardo, G.; Polimeni, A.; et al. FEM and von mises analysis on prosthetic crowns structural elements: Evaluation of different applied materials. Sci. World J. 2017, 2017, 1029574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauritano, F.; Runci, M.; Cervino, G.; Fiorillo, L.; Bramanti, E.; Cicciù, M. Three-dimensional evaluation of different prosthesis retention systems using finite element analysis and the Von Mises stress test. Minerva Stomatol. 2016, 65, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cicciù, M.; Cervino, G.; Bramanti, E.; Lauritano, F.; Lo Gudice, G.; Scappaticci, L.; Rapparini, A.; Guglielmino, E.; Risitano, G. FEM analysis of mandibular prosthetic overdenture supported by dental implants: Evaluation of different retention methods. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2015, 2015, 943839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarone, F.; Apicella, A.; Nicolais, L.; Aversa, R.; Sorrentino, R. Mandibular flexure and stress build-up in mandibular full-arch fixed prostheses supported by osseointegrated implants. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2003, 14, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burch, J.G. Patterns of change in human mandibular arch width during jaw excursions. Arch. Oral Biol. 1972, 17, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, S.; Spalj, S.; Lapter Varga, M.; Anic Milosevic, S.; Mestrovic, S.; Slaj, M. Maximum voluntary molar bite force in subjects with normal occlusion. Eur. J. Orthod. 2011, 33, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashman, R.B.; Van Buskirk, W.C. The elastic properties of a human mandible. Adv. Dent. Res. 1987, 1, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, J.L.; Meunier, A. The elastic anisotropy of bone. J. Biomech. 1987, 20, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrektsson, T.; Zarb, G.; Worthington, P.; Eriksson, A.R. The long-term efficacy of currently used dental implants: A review and proposed criteria of success. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 1986, 1, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, E.J. Alternative prosthodontic technique for tissue-integrated prostheses. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1987, 57, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, T.Y. Combined elastic and von mises stress-strain relations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1955, 41, 908–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandridis, C.; Caputo, A.A.; Thanos, C.E. Distribution of stresses in the human skull. J. Oral Rehabil. 1985, 12, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Velde, T.; Collaert, B.; De Bruyn, H. Immediate loading in the completely edentulous mandible: Technical procedure and clinical results up to 3 years of functional loading. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2007, 18, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rancitelli, D.; Borgonovo, A.E.; Cicciù, M.; Re, D.; Rizza, F.; Frigo, A.C.; Maiorana, C. Maxillary sinus septa and anatomic correlation with the Schneiderian membrane. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2015, 26, 1394–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maridati, P.; Stoffella, E.; Speroni, S.; Cicciu, M.; Maiorana, C. Alveolar Antral Artery Isolation during Sinus Lift Procedure with the Double Window Technique. Open Dent. J. 2014, 8, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangert, B.; Jemt, T.; Jorneus, L. Forces and moments on branemark implants. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 1989, 4, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pruim, G.J.; de Jongh, H.J.; ten Bosch, J.J. Forces acting on the mandible during bilateral static bite at different bite force levels. J. Biomech. 1980, 13, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassler, C.R.; Rybicki, E.F.; Cummings, K.D.; Clark, L.C. Quantitation of compressive stress and its effects upon bone remodeling [proceedings]. Bull. Hosp. Jt. Dis. 1977, 38, 90–93. [Google Scholar]
- Pilliar, R.M.; Deporter, D.A.; Watson, P.A.; Valiquette, N. Dental implant design—Effect on bone remodeling. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1991, 25, 467–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaillancourt, H.; Pilliar, R.M.; McCammond, D. Factors affecting crestal bone loss with dental implants partially covered with a porous coating: A finite element analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 1996, 11, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Skalak, R. Biomechanical considerations in osseointegrated prostheses. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1983, 49, 843–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegaroiu, R.; Kusakari, H.; Nishiyama, S.; Miyakawa, O. Influence of prosthesis material on stress distribution in bone and implant: A 3-dimensional finite element analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 1998, 13, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Benzing, U.R.; Gall, H.; Weber, H. Biomechanical aspects of two different implant-prosthetic concepts for edentulous maxillae. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 1995, 10, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hobkirk, J.A.; Psarros, K.J. The influence of occlusal surface material on peak masticatory forces using osseointegrated implant-supported prostheses. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 1992, 7, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cibirka, R.M.; Razzoog, M.E.; Lang, B.R.; Stohler, C.S. Determining the force absorption quotient for restorative materials used in implant occlusal surfaces. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1992, 67, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailath, G.; Stoiber, B.; Watzek, G.; Matejka, M. Bone resorption at the entry of osseointegrated implants—A biomechanical phenomenon. Finite element study. Kunstz. Stomatol. 1989, 86, 207–216. [Google Scholar]
- Wiskott, H.W.; Belser, U.C. Lack of integration of smooth titanium surfaces: A working hypothesis based on strains generated in the surrounding bone. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 1999, 10, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, S. The implant neck: Smooth or provided with retention elements. A biomechanical approach. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 1999, 10, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmgren, E.P.; Seckinger, R.J.; Kilgren, L.M.; Mante, F. Evaluating parameters of osseointegrated dental implants using finite element analysis—A two-dimensional comparative study examining the effects of implant diameter, implant shape, and load direction. J. Oral Implantol. 1998, 24, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, R.L.; Borgersen, S.E. Nonlinear finite element contact analysis of dental implant components. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 1993, 8, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jorneus, L.; Jemt, T.; Carlsson, L. Loads and designs of screw joints for single crowns supported by osseointegrated implants. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 1992, 7, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Haack, J.E.; Sakaguchi, R.L.; Sun, T.; Coffey, J.P. Elongation and preload stress in dental implant abutment screws. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 1995, 10, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Versluis, A.; Korioth, T.W.; Cardoso, A.C. Numerical analysis of a dental implant system preloaded with a washer. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 1999, 14, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clelland, N.L.; Ismail, Y.H.; Zaki, H.S.; Pipko, D. Three-dimensional finite element stress analysis in and around the screw-vent implant. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 1991, 6, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Branemark, P.I.; Adell, R.; Breine, U.; Hansson, B.O.; Lindstrom, J.; Ohlsson, A. Intra-osseous anchorage of dental prostheses: I. Experimental studies. Scand. J. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1969, 3, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branemark, P.I.; Hansson, B.O.; Adell, R.; Breine, U.; Lindstrom, J.; Hallen, O.; Ohman, A. Osseointegrated implants in the treatment of the edentulous jaw. Experience from a 10-year period. Scand. J. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Suppl. 1977, 16, 1–132. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Adell, R.; Eriksson, B.; Lekholm, U.; Branemark, P.I.; Jemt, T. Long-term follow-up study of osseointegrated implants in the treatment of totally edentulous jaws. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 1990, 5, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jemt, T.; Lekholm, U. Oral implant treatment in posterior partially edentulous jaws: A 5-year follow-up report. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 1993, 8, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van Steenberghe, D.; Lekholm, U.; Bolender, C.; Folmer, T.; Henry, P.; Herrmann, I.; Higuchi, K.; Laney, W.; Linden, U.; Astrand, P. Applicability of osseointegrated oral implants in the rehabilitation of partial edentulism: A prospective multicenter study on 558 fixtures. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 1990, 5, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Esposito, M.; Hirsch, J.M.; Lekholm, U.; Thomsen, P. Biological factors contributing to failures of osseointegrated oral implants. (II). Etiopathogenesis. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 1998, 106, 721–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, D.H. The failure of retainers in bridge prostheses. An analysis of 2000 retainers. Br. Dent. J. 1970, 128, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walton, J.N.; Gardner, F.M.; Agar, J.R. A survey of crown and fixed partial denture failures: Length of service and reasons for replacement. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1986, 56, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, S. Failures and length of service in fixed prosthodontics after long-term function. A longitudinal clinical study. Swed. Dent. J. 1989, 13, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grundling, N.L.; Jooste, C.H.; Terblanche, E. Three-dimensional finite element model of a human mandible incorporating six osseointegrated implants for stress analysis of mandibular cantilever prostheses. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 1995, 10, 51–57. [Google Scholar]
- Sertgoz, A.; Guvener, S. Finite element analysis of the effect of cantilever and implant length on stress distribution in an implant-supported fixed prosthesis. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1996, 76, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindquist, L.W.; Carlsson, G.E.; Jemt, T. A prospective 15-year follow-up study of mandibular fixed prostheses supported by osseointegrated implants. Clinical results and marginal bone loss. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 1996, 7, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, F.A.; Williams, K.R.; Draughn, R.; Strohaver, R. Design of prosthetic cantilever bridgework supported by osseointegrated implants using the finite element method. Dent. Mater. 1998, 14, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, H.J.; Starmans, F.J.; Steen, W.H.; Bosman, F. Location of implants in the interforaminal region of the mandible and the consequences for the design of the superstructure. J. Oral Rehabil. 1994, 21, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meijer, G.J.; Starmans, F.J.; de Putter, C.; van Blitterswijk, C.A. The influence of a flexible coating on the bone stress around dental implants. J. Oral Rehabil. 1995, 22, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clift, S.E.; Fisher, J.; Watson, C.J. Finite element stress and strain analysis of the bone surrounding a dental implant: Effect of variations in bone modulus. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. H 1992, 206, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
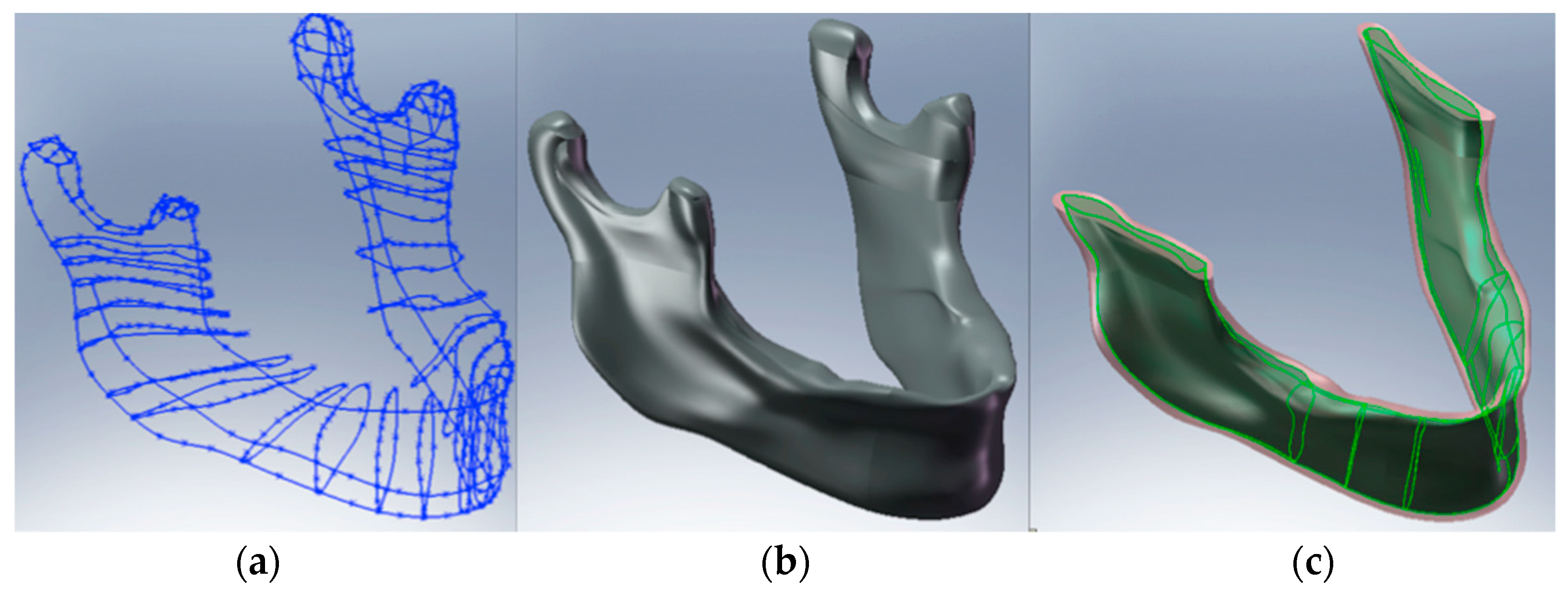
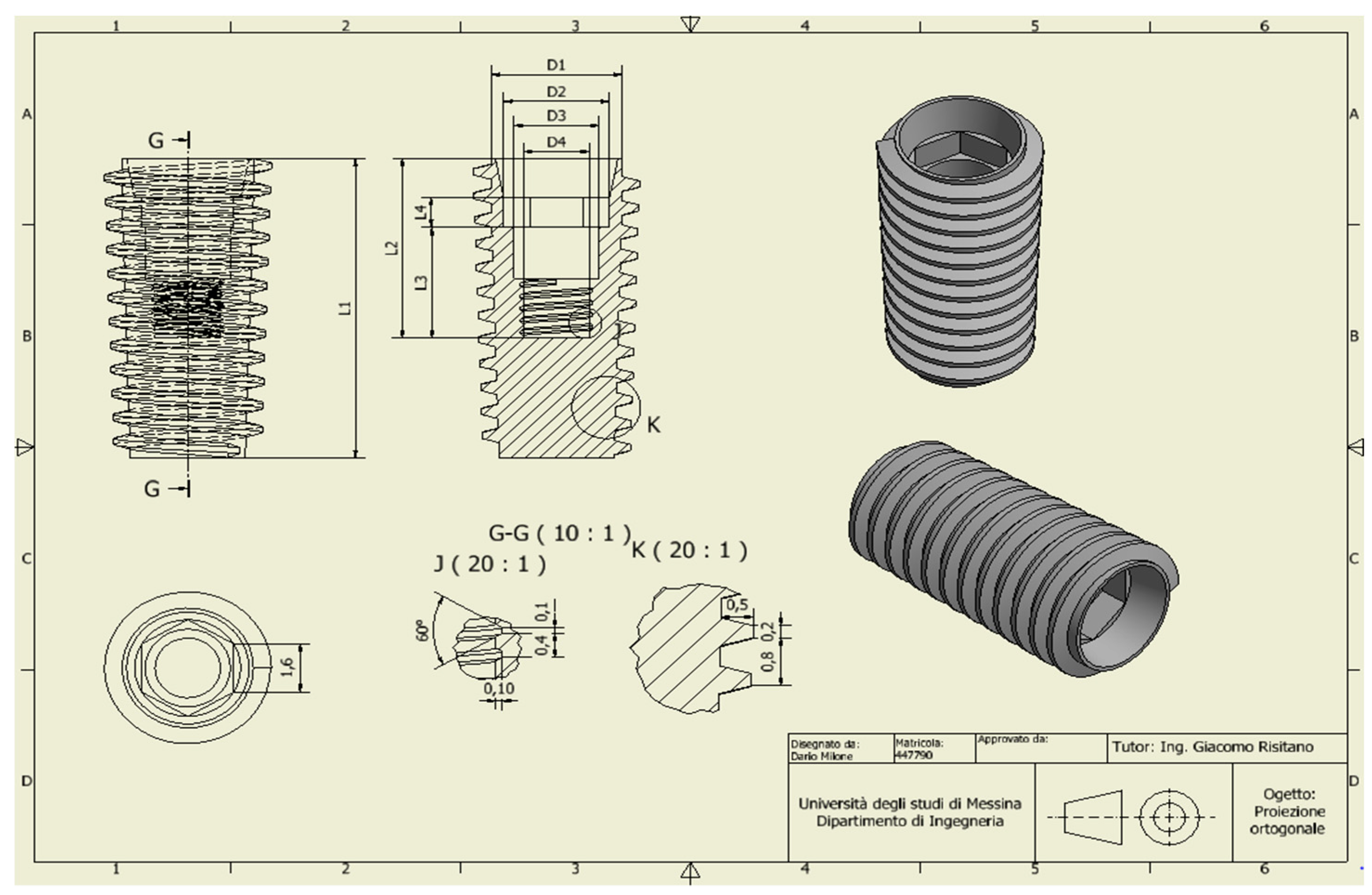
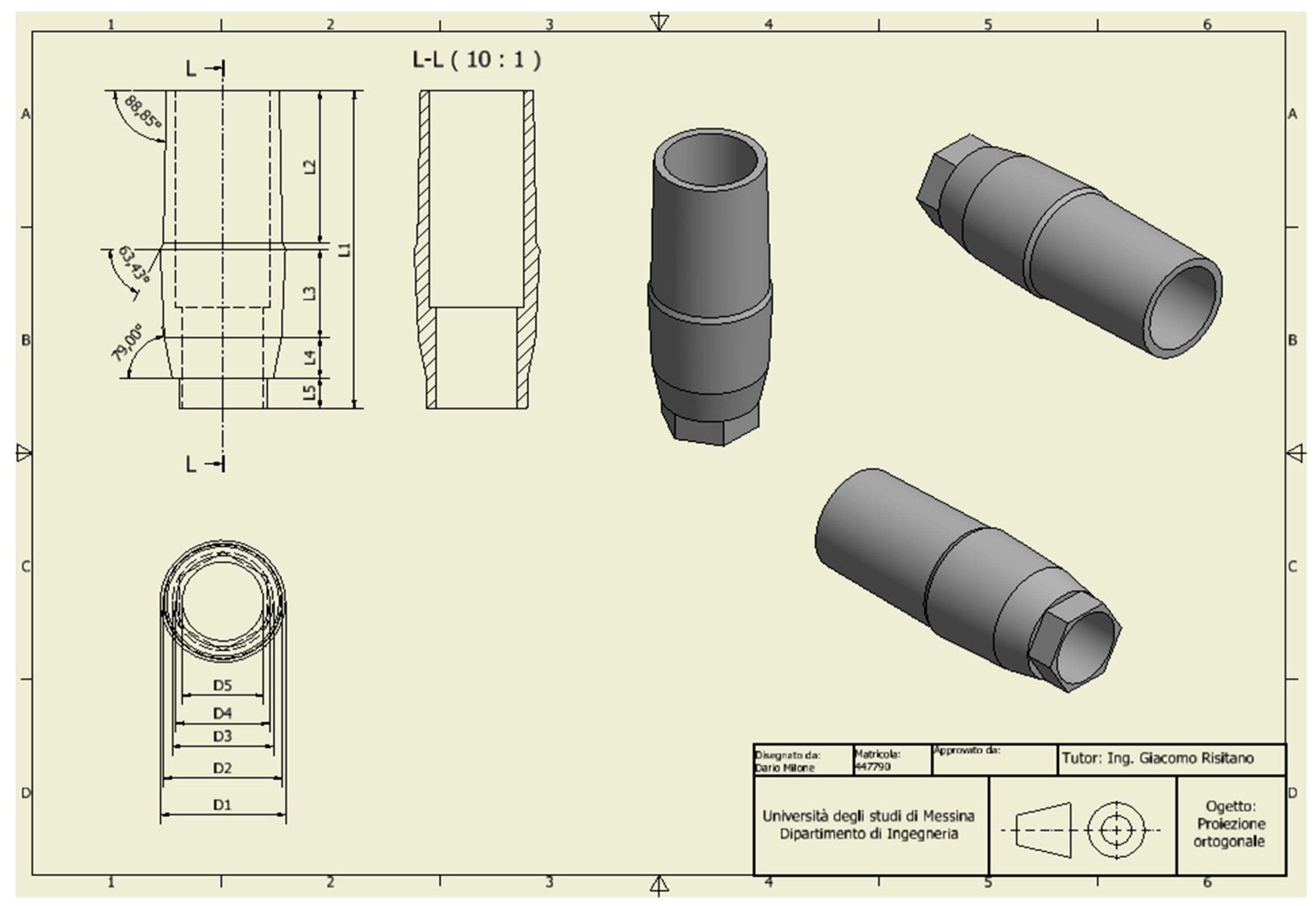
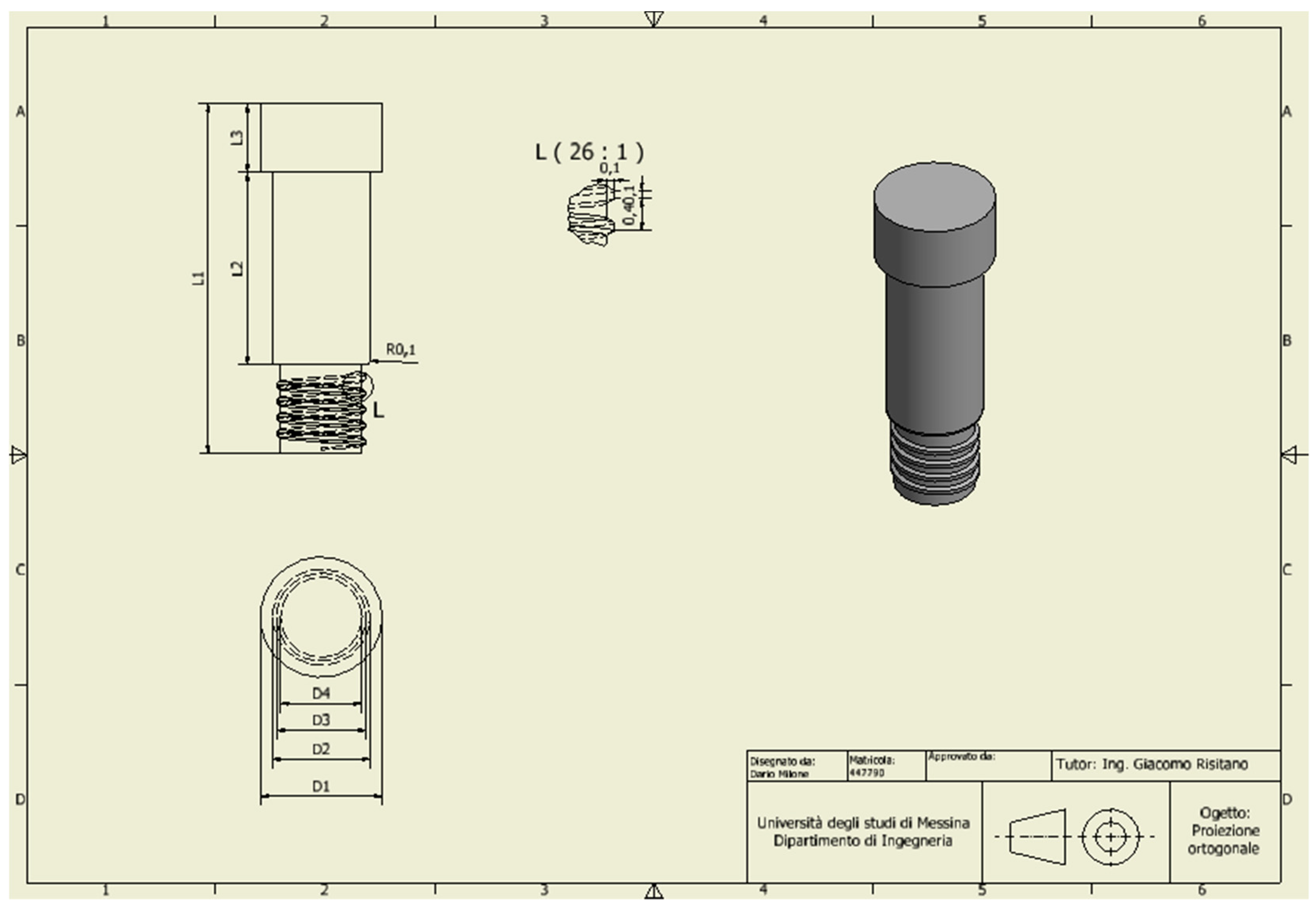
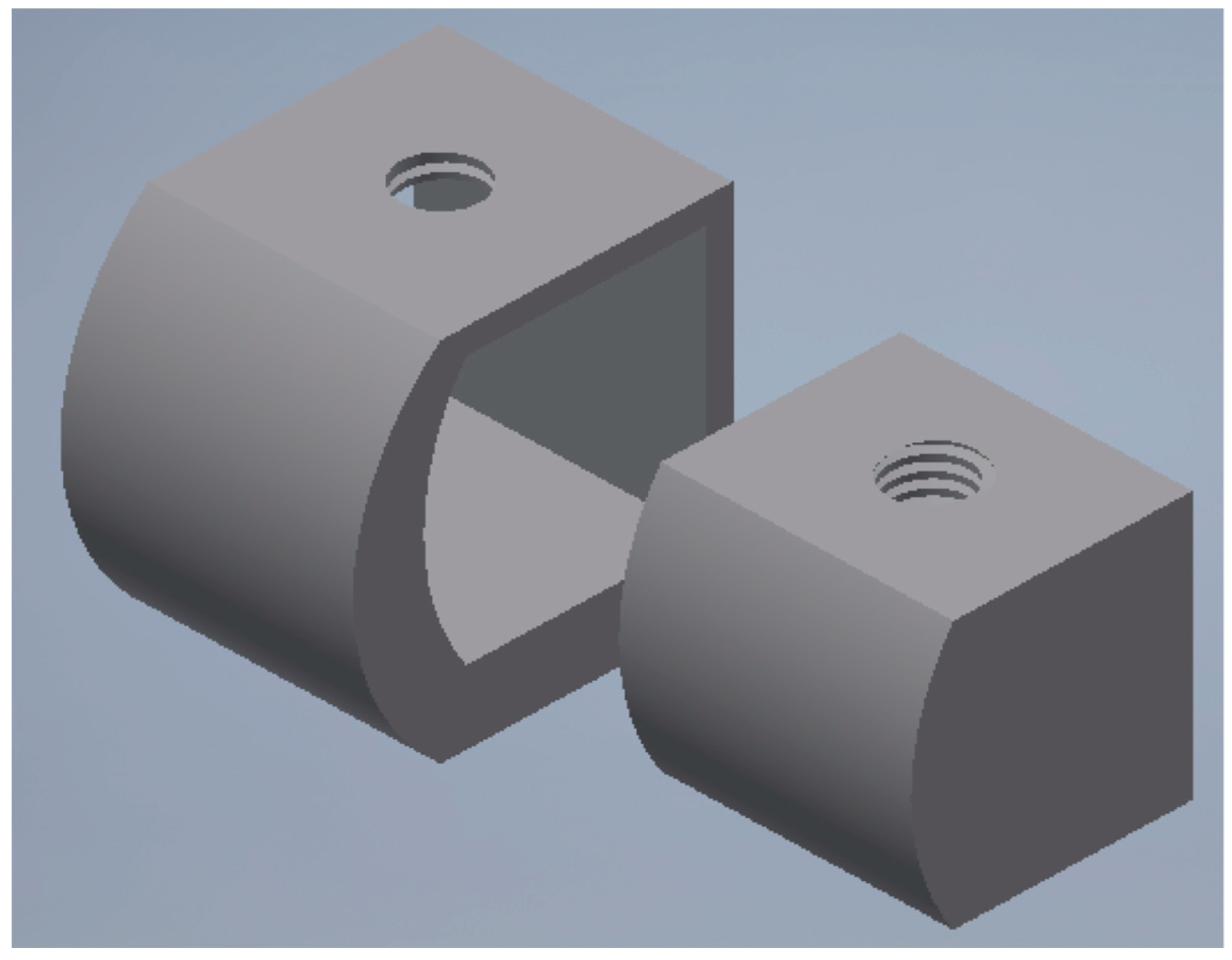
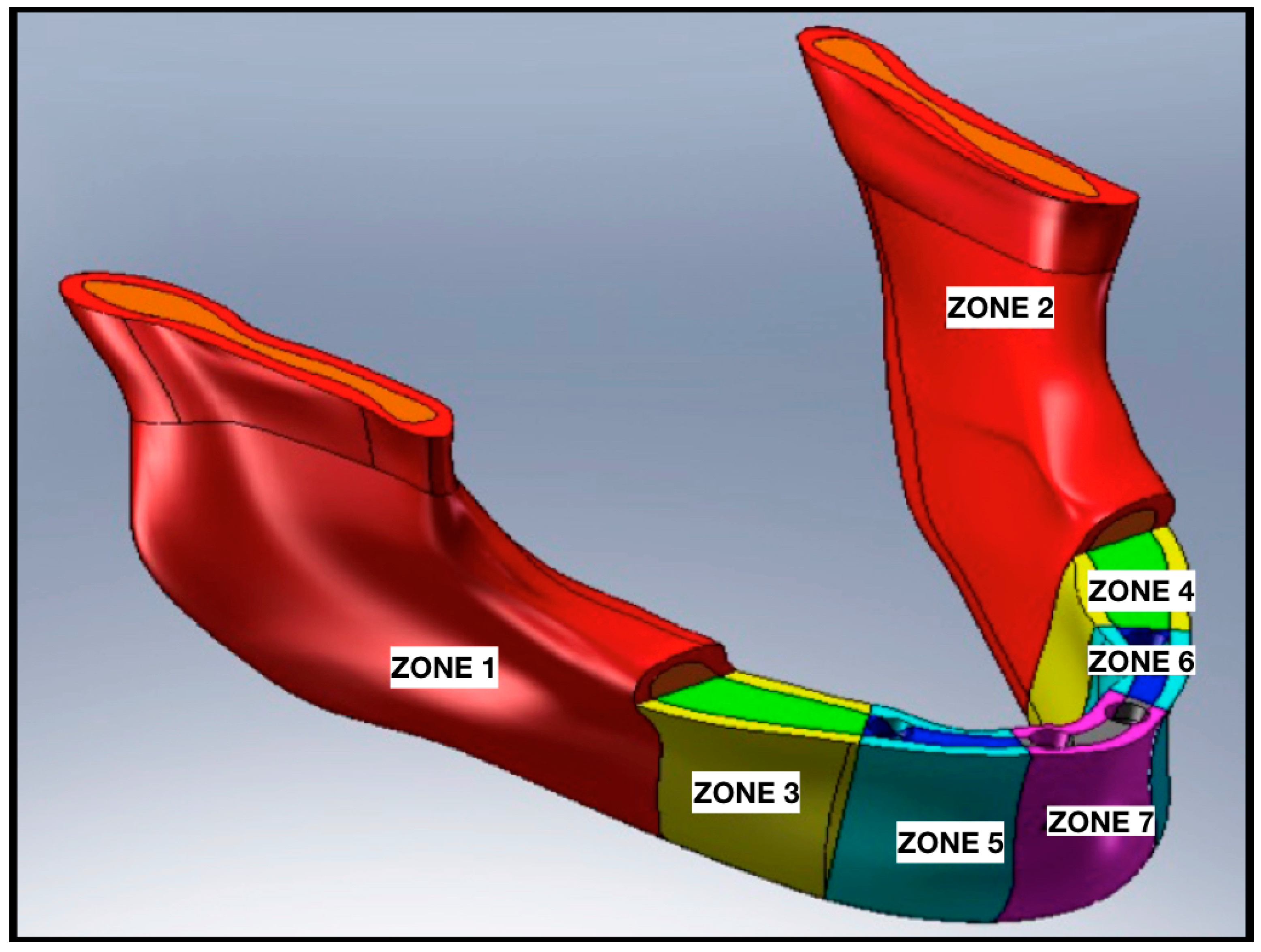
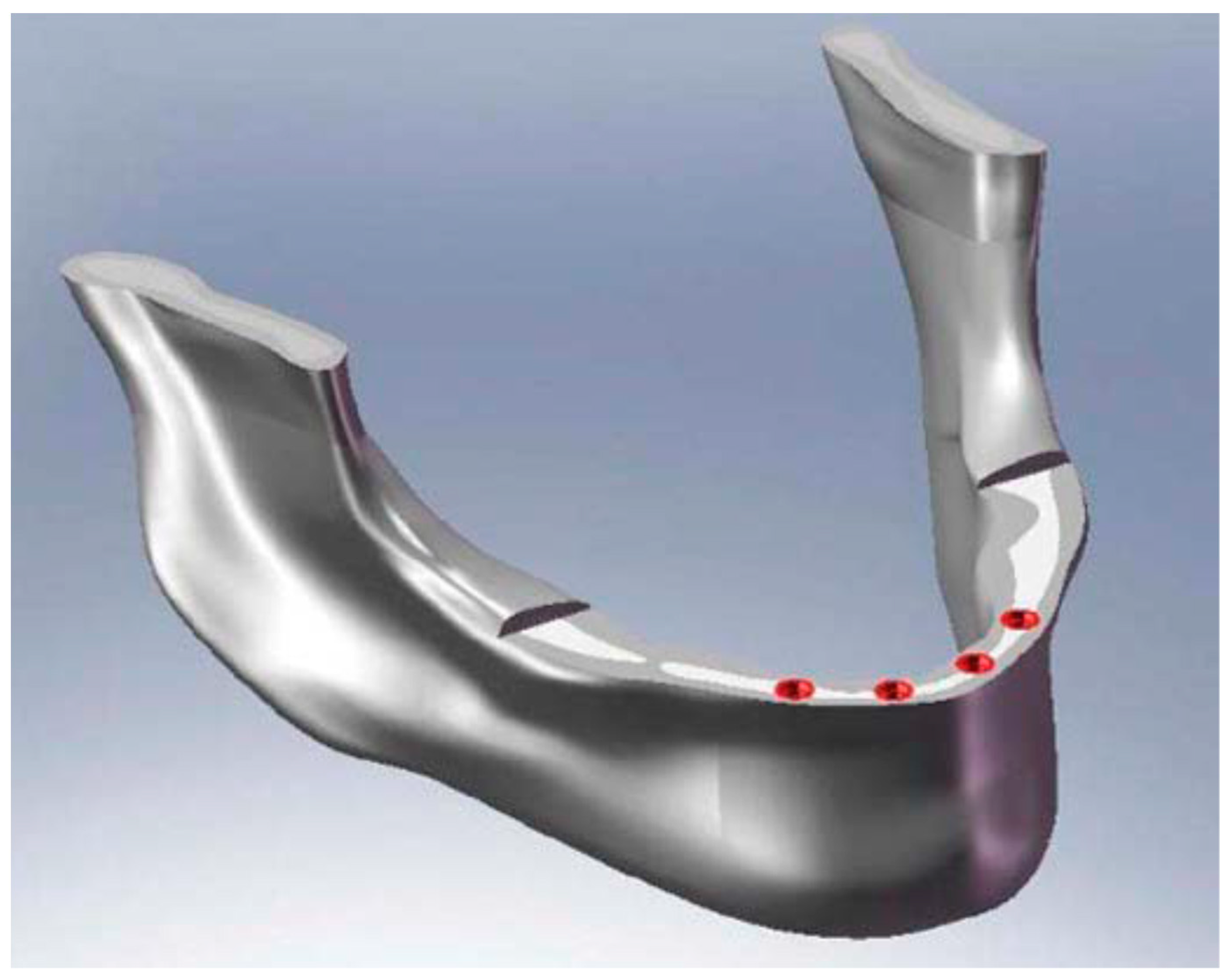
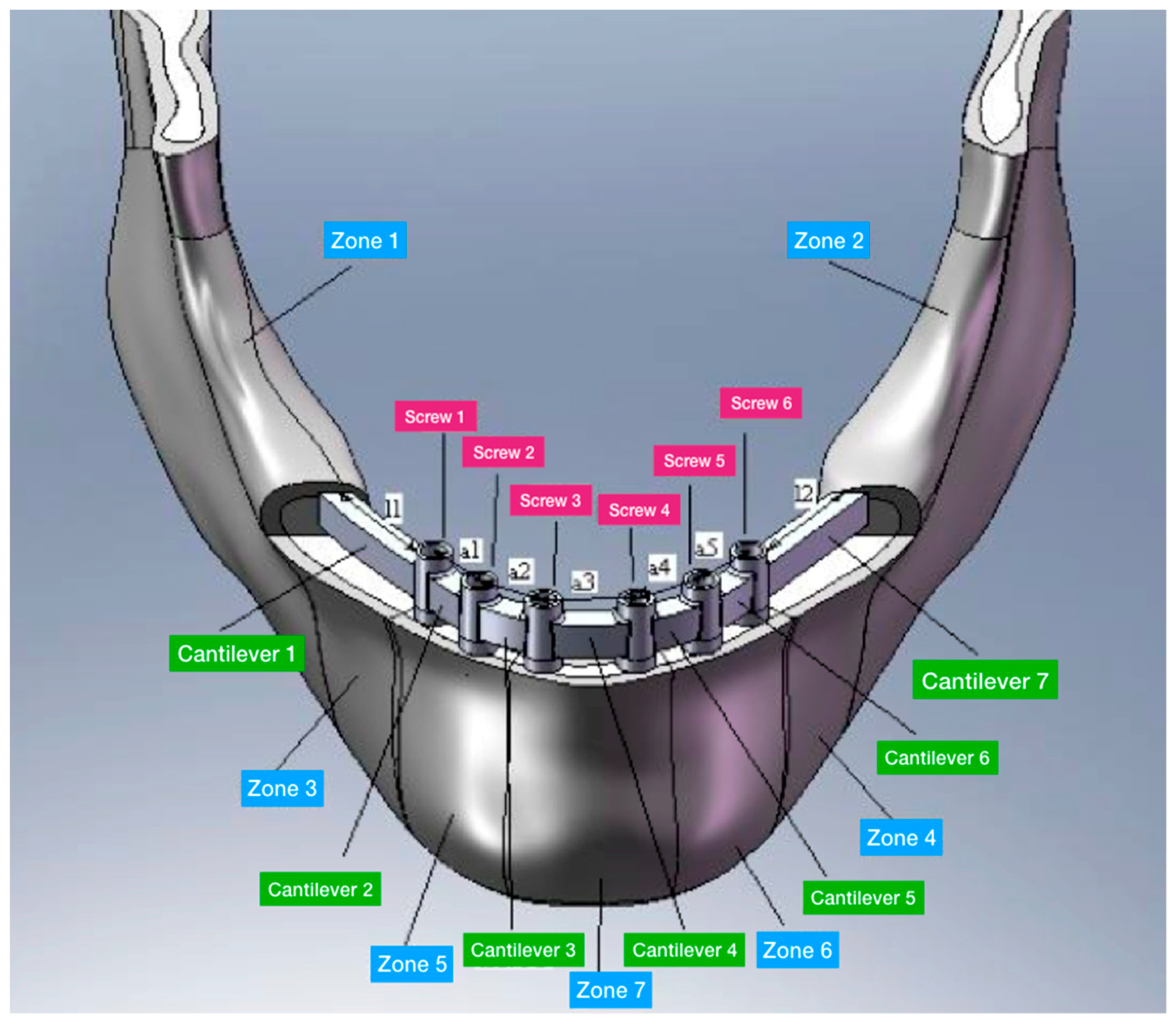

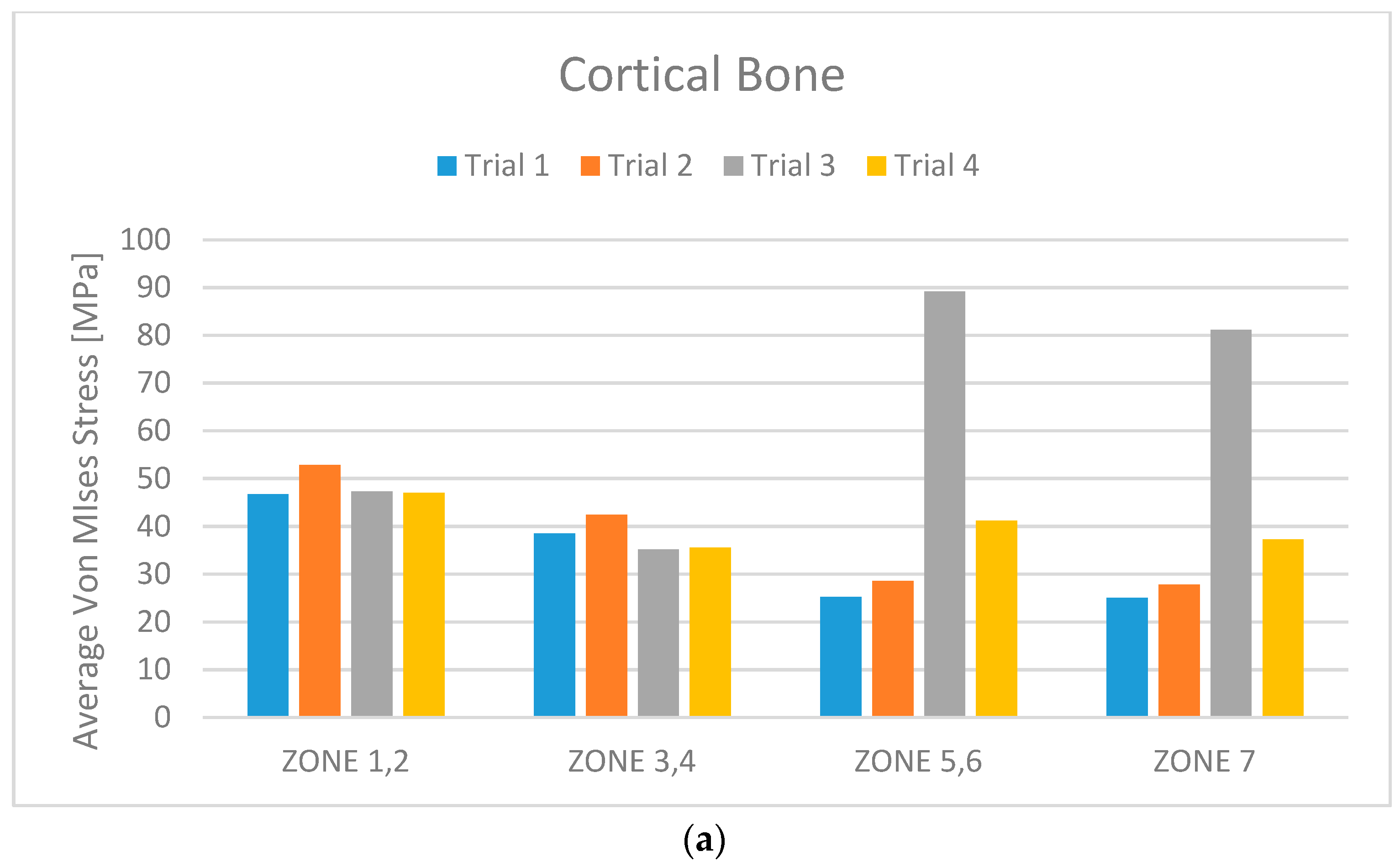
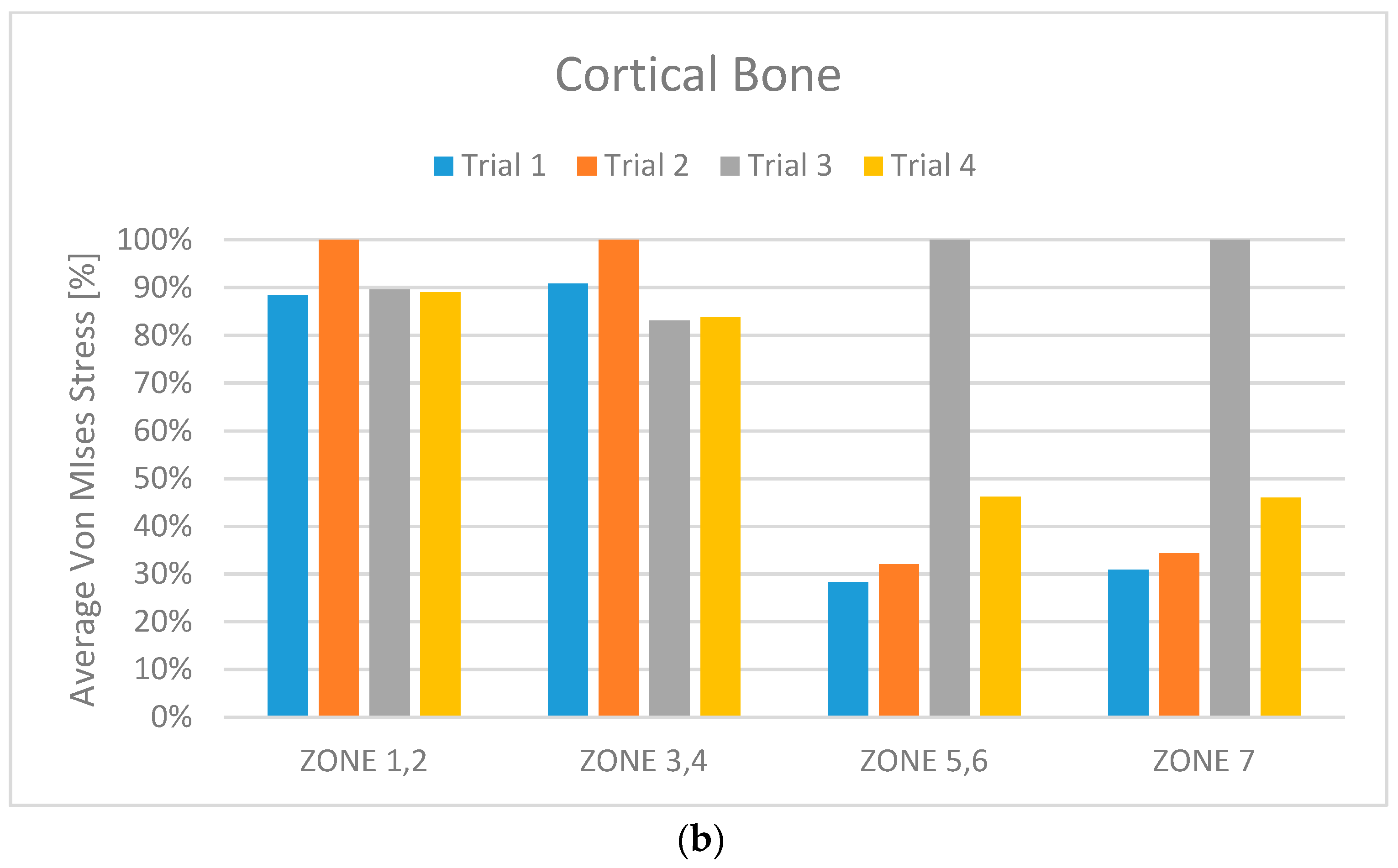
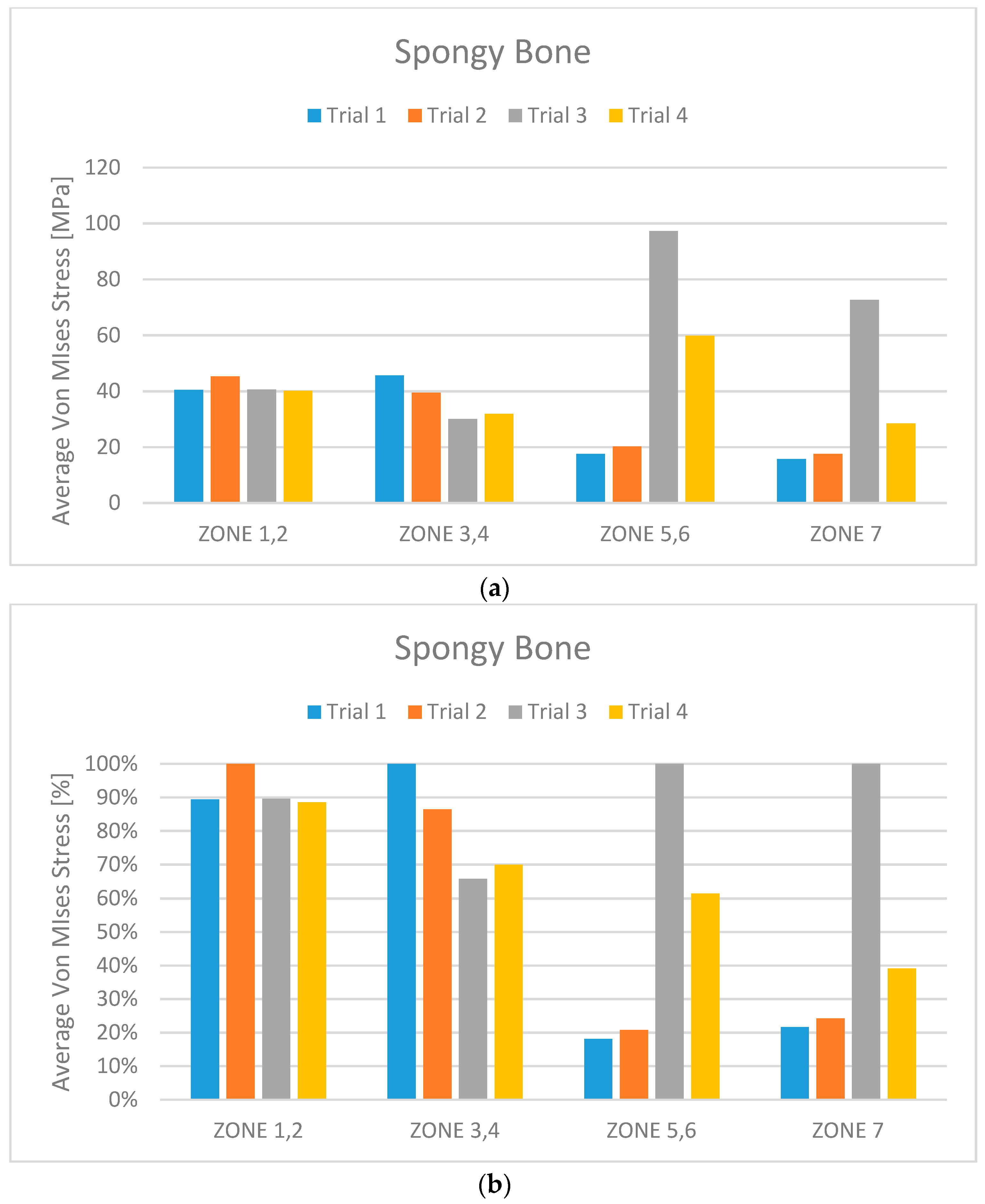

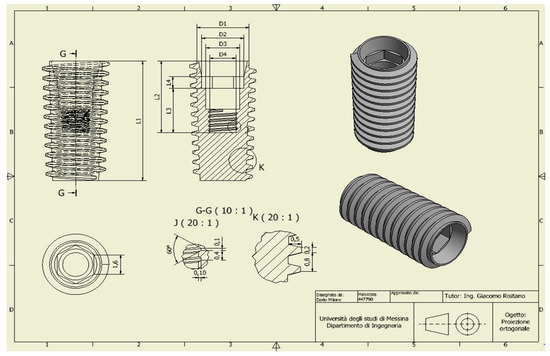
| No. Area | Cortical Bone | Spongy Bone | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E (MPa) | G (MPa) | υ | E (MPa) | G (MPa) | υ | |
| Zone 1 | 1.68 × 1010 | 6.24 × 109 | 0.345 | 7.27 × 108 | 2.71 × 108 | 0.345 |
| Zone 2 | 1.68 × 1010 | 2.34 × 109 | 0.345 | 7.27 × 108 | 2.71 × 108 | 0.345 |
| Zone 3 | 1.93 × 1010 | 7.41 × 109 | 0.236 | 8.35 × 108 | 3.37 × 108 | 0.236 |
| Zone 4 | 1.93 × 1010 | 7.41 × 109 | 0.236 | 8.35 × 108 | 3.37 × 108 | 0.236 |
| Zone 5 | 2.40 × 1010 | 9.71 × 109 | 0.236 | 1.04 × 109 | 4.21 × 108 | 0.236 |
| Zone 6 | 2.40 × 1010 | 9.71 × 109 | 0.236 | 1.04 × 109 | 4.21 × 108 | 0.236 |
| Zone 7 | 2.04 × 1010 | 8.25 × 109 | 0.236 | 8.83 × 108 | 3.57 × 108 | 0.236 |
| Titanium Alloy (grade 4) | E (MPa) = 1.05 × 1011 | G (MPa) = 4.60 × 1010 | υ = 0.33 | |||
| ZONE | Trial 01 | Trial 02 | Trial 03 | Trial 04 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a1 | 10 mm | 13 mm | - | - |
| a2 | 6 mm | 6 mm | 6 mm | 12 mm |
| a3 | 7.5 mm | 7.5 mm | 7.5 mm | 7.5 mm |
| a4 | 6 mm | 6 mm | 6 mm | 12 mm |
| a5 | 10 mm | 13 mm | - | - |
| l1 | 8.5 mm | 5.5 mm | 18.5 mm | 12.5 mm |
| l2 | 8.5 mm | 5.5 mm | 18.5 mm | 12.5 mm |
| Bone Area | Prosthesis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area | Cortical Bone | Spongy Bone | Screw | 0.5 mm |
| Zones 1,2 | 2 mm | 2 mm | ||
| Zones 3–7 | 1.5 mm | 1.5 mm | Cantilever | 0.8 mm |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cicciù, M.; Cervino, G.; Milone, D.; Risitano, G. FEM Investigation of the Stress Distribution over Mandibular Bone Due to Screwed Overdenture Positioned on Dental Implants. Materials 2018, 11, 1512. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11091512
Cicciù M, Cervino G, Milone D, Risitano G. FEM Investigation of the Stress Distribution over Mandibular Bone Due to Screwed Overdenture Positioned on Dental Implants. Materials. 2018; 11(9):1512. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11091512
Chicago/Turabian StyleCicciù, Marco, Gabriele Cervino, Dario Milone, and Giacomo Risitano. 2018. "FEM Investigation of the Stress Distribution over Mandibular Bone Due to Screwed Overdenture Positioned on Dental Implants" Materials 11, no. 9: 1512. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11091512
APA StyleCicciù, M., Cervino, G., Milone, D., & Risitano, G. (2018). FEM Investigation of the Stress Distribution over Mandibular Bone Due to Screwed Overdenture Positioned on Dental Implants. Materials, 11(9), 1512. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11091512