A Study on Preparation and Stabilizing Mechanism of Hydrophobic Silica Nanofluids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Nanofluid
2.3. Characterization
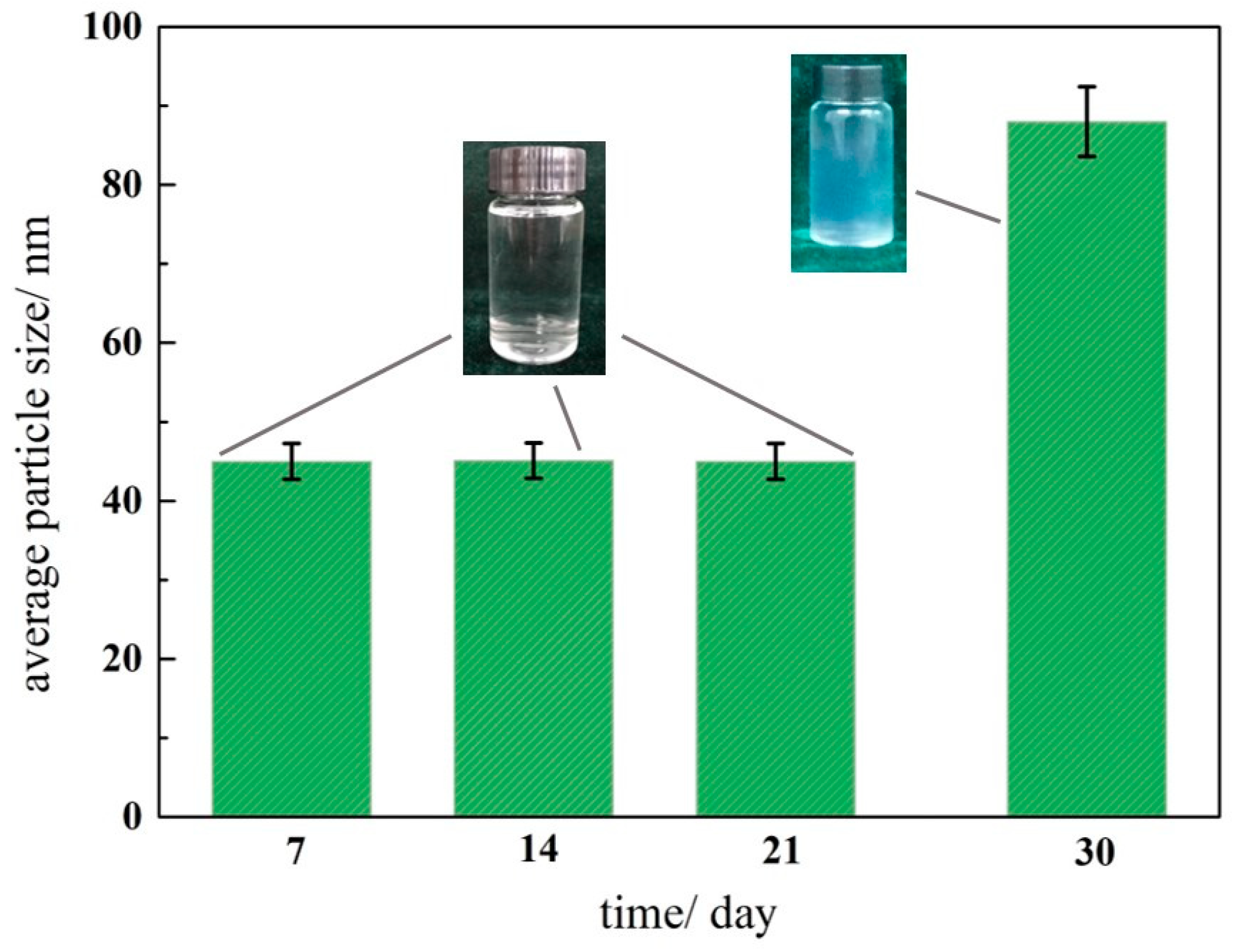
3. Results and Discussion
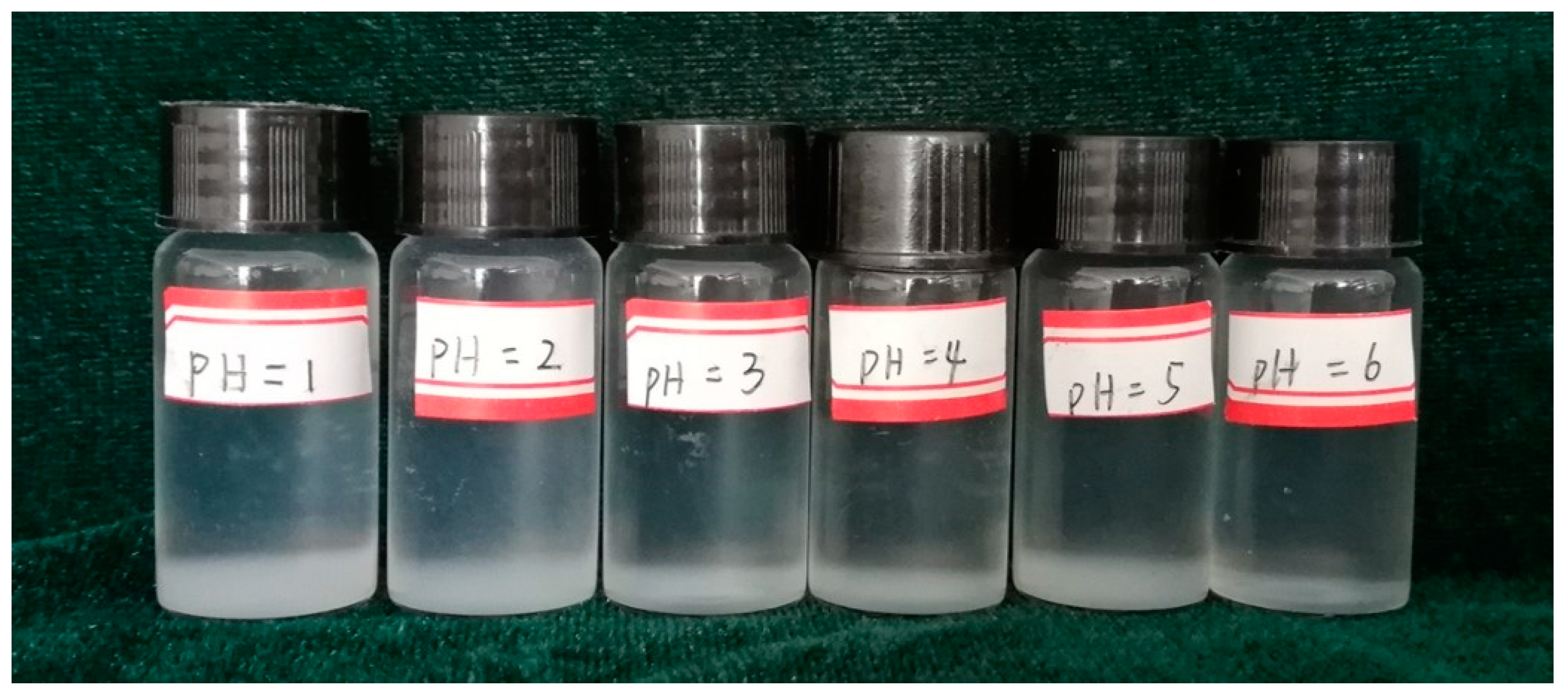
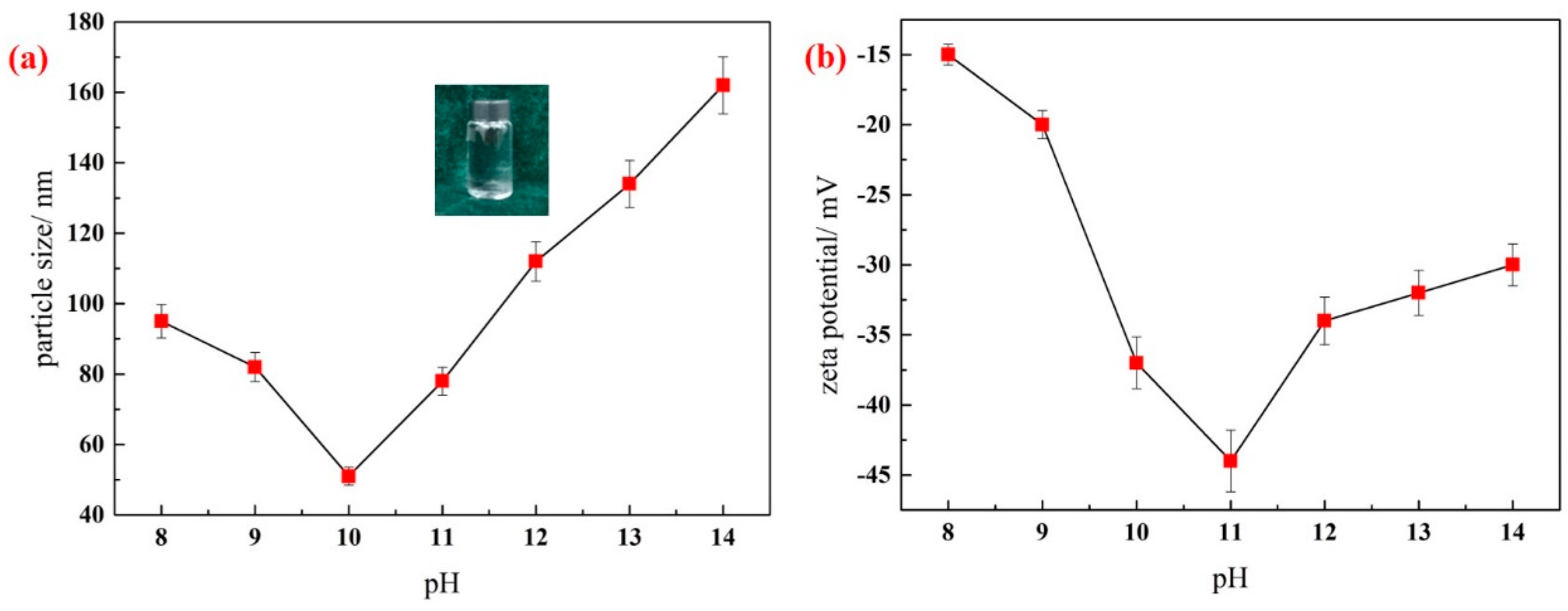
3.1. The Influence of pH on Stability of Silica Nanofluid
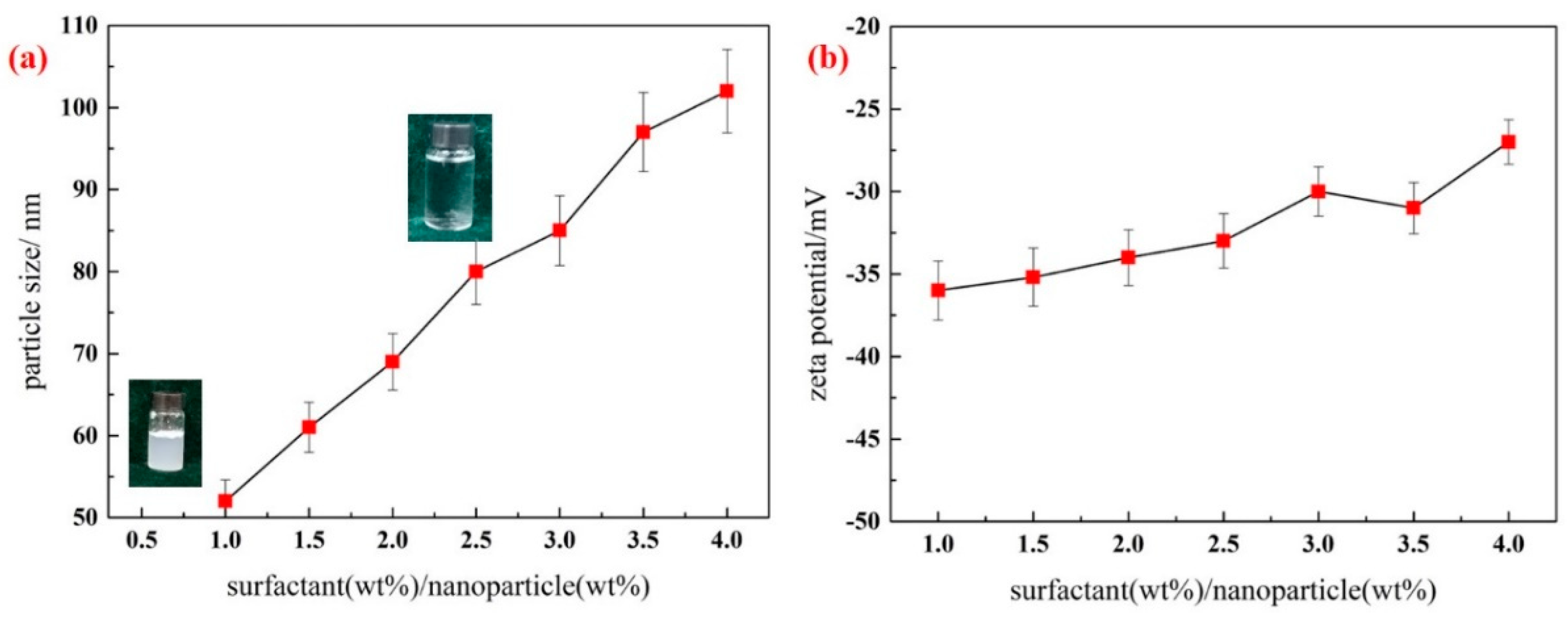
3.2. The Influence of Surfactant Dosage on Stability of Silica Nanofluid
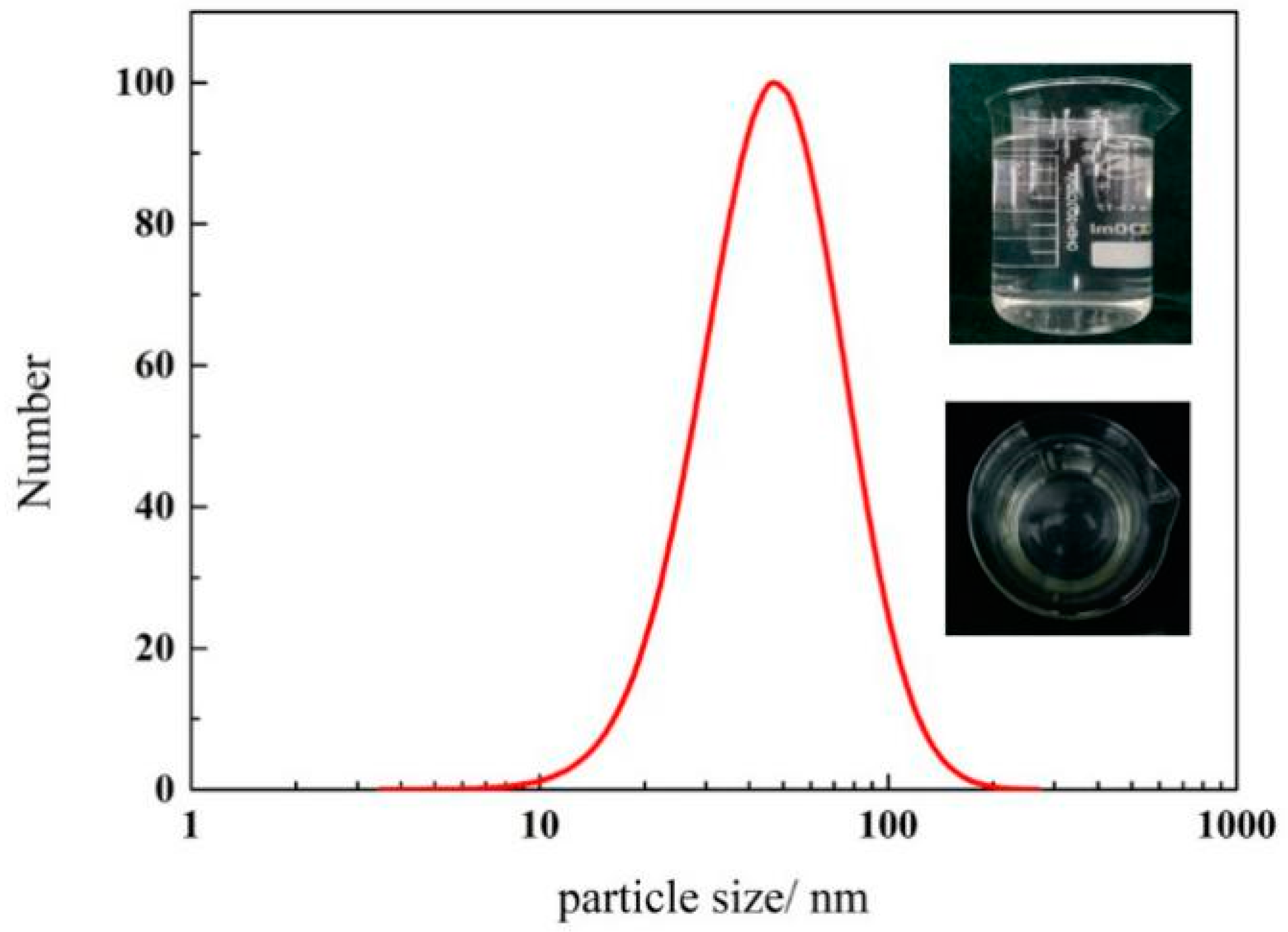
3.3. The Influence of Nanoparticle Concentration on Stability of Silica Nanofluid
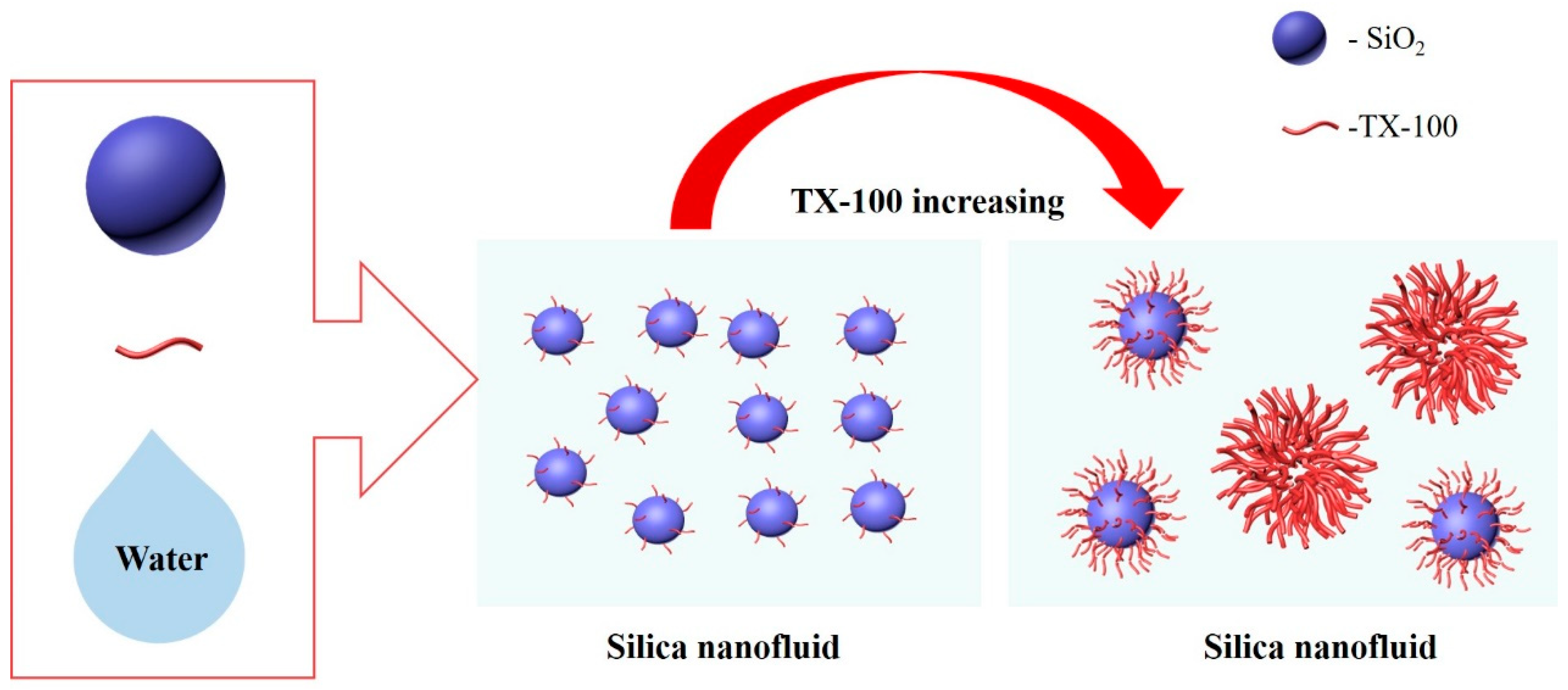
3.4. The Stability Mechanism of Silica Nanofluid
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- A silica nanofluid was prepared using the two-step method. TX-100 was used as the dispersant to allow the dispersion of hydrophobic silica nanoparticles in water.
- (2)
- The pH value markedly influenced the silica nanofluid. Silica nanoparticles could not be dispersed uniformly under acidic conditions. The pH value of 10 was considered optimal.
- (3)
- Optimal TX-100 dosage and concentration were determined. According to the results, the silica nanofluid exhibited the highest stability when the surfactant-to- silica nanoparticle ratio was 1 and the nanofluid concentration was 0.1 wt. %.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| ζ | zeta potential/mV |
| c | concentration/% |
| d | particle size/nm |
| D | reserve time/day |
| RSD | relative standard deviation |
References
- Patel, H.E.; Das, S.K.; Sundararajan, T.; Sreekumaran Nair, A. Thermal conductivities of naked and monolayer protected metal nanoparticle based nanofluids: Manifestation of anomalous enhancement and chemical effects. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 83, 2931–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Y.; Li, Q. Investigation on Convective Heat Transfer and Flow Features of Nanofluids. J. Heat Transf. 2003, 125, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, J.H.; Cho, H.H.; Koo, J.H.; Yoon, S.G.; Lee, J.K. Heat transfer characteristics of liquid-solid suspension flow in a horizontal pipe. KSME Int. J. 2000, 14, 1159–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, R.L. Principles of Enhanced Heat Transfer; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Deng, L.; Zhou, P.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Lu, J.R. Tuning the Self-Assembly of Short Peptides via Sequence Variations. Langmuir 2013, 29, 13457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.H.; Cao, F.Y.; Yang, B. Synthesis and thermal characterization of phase-changeable indium/polyalphaolefin nanofluids. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 243104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Bang, I.C.; Buongiorno, J.; Hu, L.W. Study of pool boiling and critical heat flux enhancement in Nanofluids. Bull. Pol. Acad. Sci. Tech. Sci. 2014, 55, 211–216. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.J.; Bang, I.C.; Buongiorno, J.; Hu, L.W. Surface wettability change during pool boiling of nanofluids and its effect on critical heat flux. Int. Heat Mass Transf. 2007, 50, 4105–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.B.; Wilson, C.; Borgmeyer, B.; Park, K.; Yu, Q.; Choi, S.U.S.; Tirumala, M. Effect of nanofluid on the heat transport capability in an oscillating heat pipe. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 143116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.B.; Wilson, C.; Yu, Q.; Park, K.; Choi, U.S.; Tirumala, M. An experimental investigation of heat transport capability in a nanofluid oscillating heat pipe. J. Heat Transf. 2006, 128, 1213–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawgo, R.S.; Grayson, A.C.R.; Li, Y.; Cima, M.J. BioMEMS for drug delivery. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2002, 6, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasan, D.T.; Nikolov, A.D. Spreading of nanofluids on solids. Nature 2003, 423, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.S.; Lin, C.C.; Tsai, C.Y.; Wang, C.C. Enhancement of thermal conductivity with Cu for nanofluids using chemical reduction method. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2006, 49, 3028–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.T.; Lin, Y.S.; Yin, Y.S. A novel one-step chemical method for preparation of copper nanofluids. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 277, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.; Wang, J.; Xi, T.; Liu, Y.; Ai, F.; Wu, Q. Thermal conductivity enhancement of suspensions containing nanosized alumina particles. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 91, 4568–4572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murshed, S.M.S.; Leong, K.C.; Yang, C. Enhanced thermal conductivity of TiO2—Water based nanofluids. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2005, 44, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colangelo, G.; Favale, E.; Risi, A.D.; Laforgia, D. Results of experimental investigations on the heat conductivity of nanofluids based on diathermic oil for high temperature applications. Appl. Energy 2012, 97, 828–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanese, M.; Iacobazzi, F.; Colangelo, G.; Risi, A.D. An investigation of layering phenomenon at the liquid–solid interface in Cu and CuO based nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 103, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colangelo, G.; Favale, E.; Miglietta, P.; Milanese, M.; Risi, A.D. Thermal conductivity, viscosity and stability of Al2O3-diathermic oil nanofluids for solar energy systems. Energy 2016, 95, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colangelo, G.; Favale, E.; Milanese, M.; Starace, G.; Risi, A.D. Experimental Measurements of Al2O3 and CuO Nanofluids Interaction with Microwaves. J. Energy Eng. 2016, 143, 04016045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouguerra, N.; Poncet, S.; Elkoun, S. Dispersion regimes in alumina/water-based nanofluids: Simultaneous measurements of thermal conductivity and dynamic viscosity. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 92, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacobazzi, F.; Milanese, M.; Colangelo, G.; Lomascolo, M.; Risi, A.D. An explanation of the Al2O3 nanofluid thermal conductivity based on the phonon theory of liquid. Energy 2016, 116, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, Y.; Lee, J.K.; Lee, J.K.; Jeong, Y.M.; Cheong, S.I.; Ahn, Y.C.; Kim, S.H. Production and dispersion stability of nanoparticles in nanofluids. Powder Technol. 2008, 186, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhu, D.; Wang, X. Evaluation on dispersion behavior of the aqueous copper nano-suspensions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 310, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.F.; Yu, X.L.; Xia, L.F.; Zhong, X. Influence factors on suspension stability of nanofluids. J. Zhejiang Univ. 2007, 41, 577–580. [Google Scholar]
- Haddad, Z.; Abid, C.; Oztop, H.F.; Mataoui, A. A review on how the researchers prepare their nanofluids. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2014, 76, 168–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timofeeva, E.V.; Moravek, M.R.; Singh, D. Improving the heat transfer efficiency of synthetic oil with silica nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 364, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazeli, S.A.; Hashemi, S.M.H.; Zirakzadeh, H.; Ashjaee, M. Experimental and numerical investigation of heat transfer in a miniature heat sink utilizing silica nanofluid. Superlattices Microstruct. 2012, 51, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolukbasi, A.; Ciloglu, D. Pool boiling heat transfer characteristics of vertical cylinder quenched by SiO2—Water nanofluids. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2011, 50, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dai, C.; Zhou, H.; Wang, X.; Lv, W.; Zhao, M. Investigation of Spontaneous Imbibition by Using a Surfactant-Free Active Silica Water-Based Nanofluid for Enhanced Oil Recovery. Energy Fuels 2017, 32, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Lv, W.; Zou, C.; Gao, M.; Zhao, M. Spontaneous Imbibition Investigation of Self-Dispersing Silica Nanofluids for Enhanced Oil Recovery in Low-Permeability Cores. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 2663–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekar, M.; Suresh, S.; Bose, A.C.; Chandrasekar, M.; Suresh, S.; Bose, A.C. Experimental investigations and theoretical determination of thermal conductivity and viscosity of AlO/water nanofluid. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2010, 34, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.F.; Zhu, D.S.; Wang, X.J.; Wang, N.; Gao, J.W.; Li, H. Thermal conductivity enhancement dependent pH and chemical surfactant for Cu-H2O nanofluids. Thermochim. Acta 2008, 469, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Xie, H.; Chen, L.; Li, Y. Enhancement of thermal conductivity of kerosene-based Fe3O4 nanofluids prepared via phase-transfer method. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2010, 355, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slósarczyk, A.; Szymuraoleksiak, J.; Mycek, B. The kinetics of pentoxifylline release from drug-loaded hydroxyapatite implants. Ceram. Int. 2001, 27, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fovet, Y.; Gal, J.Y.; Toumelin-Chemla, F. Influence of pH and fluoride concentration on titanium passivating layer: Stability of titanium dioxide. Talanta 2001, 53, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Zhu, D.S.; Yang, S. Investigation of pH and SDBS on enhancement of thermal conductivity in nanofluids. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2009, 470, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, M.; Lv, W.; Li, Y.; Dai, C.; Zhou, H.; Song, X.; Wu, Y. A Study on Preparation and Stabilizing Mechanism of Hydrophobic Silica Nanofluids. Materials 2018, 11, 1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081385
Zhao M, Lv W, Li Y, Dai C, Zhou H, Song X, Wu Y. A Study on Preparation and Stabilizing Mechanism of Hydrophobic Silica Nanofluids. Materials. 2018; 11(8):1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081385
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Mingwei, Wenjiao Lv, Yuyang Li, Caili Dai, Hongda Zhou, Xuguang Song, and Yining Wu. 2018. "A Study on Preparation and Stabilizing Mechanism of Hydrophobic Silica Nanofluids" Materials 11, no. 8: 1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081385
APA StyleZhao, M., Lv, W., Li, Y., Dai, C., Zhou, H., Song, X., & Wu, Y. (2018). A Study on Preparation and Stabilizing Mechanism of Hydrophobic Silica Nanofluids. Materials, 11(8), 1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081385





