Cryochemically Processed Li1+yMn1.95Ni0.025Co0.025O4 (y = 0, 0.1) Cathode Materials for Li-Ion Batteries
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials Preparation
2.2. Materials Characterization
2.3. Electrochemical Measurments
3. Results and Discussion
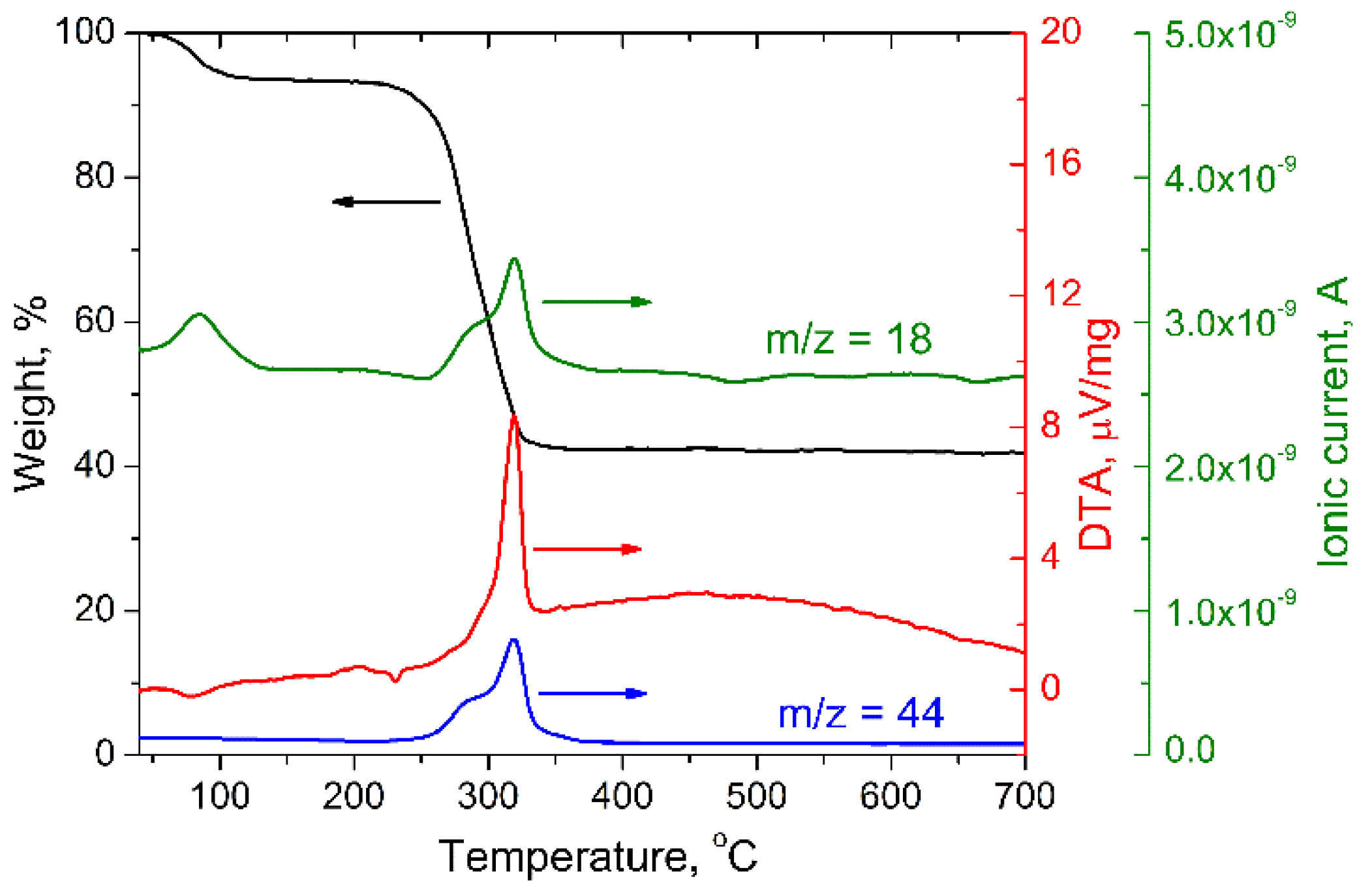
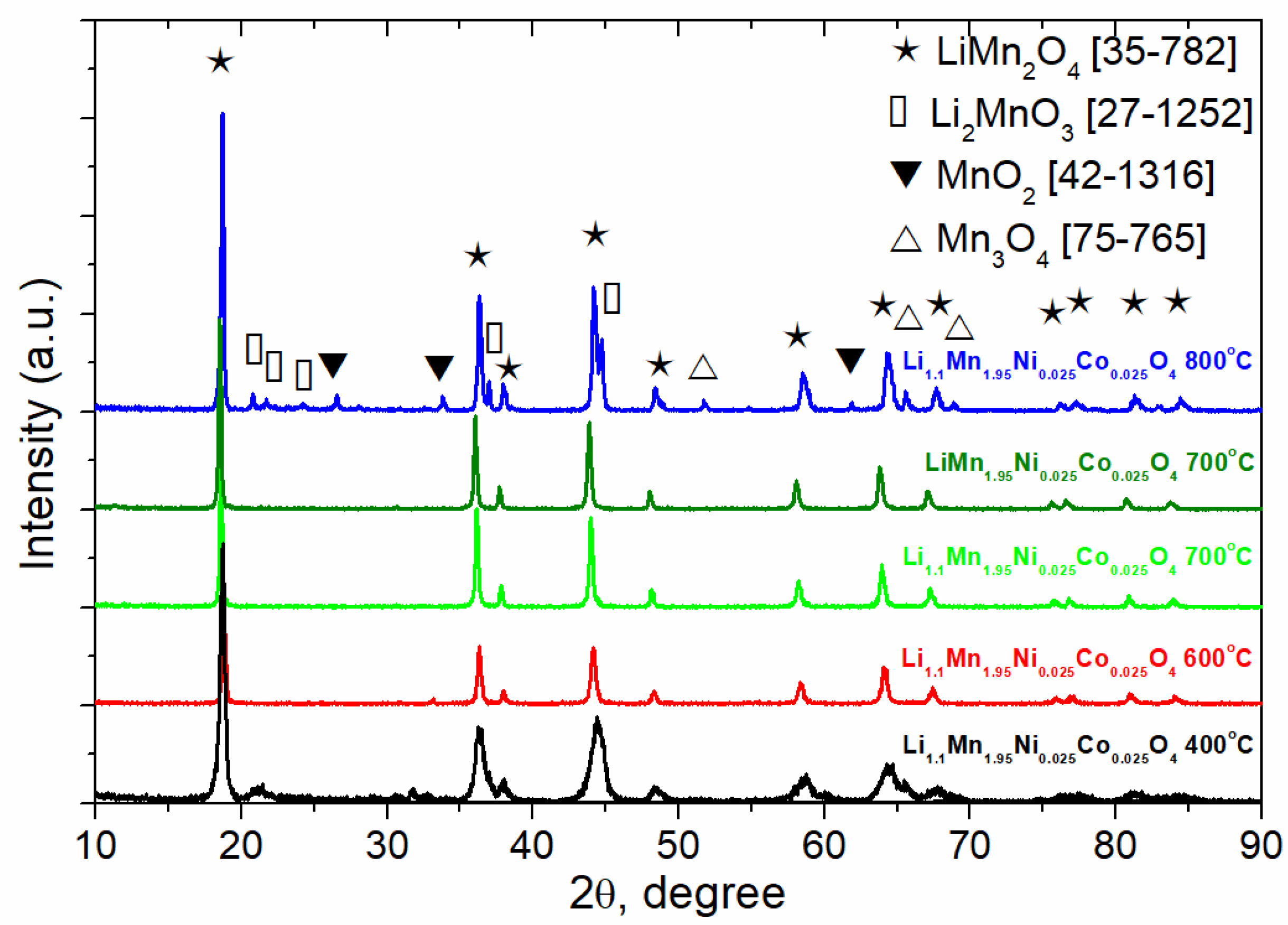
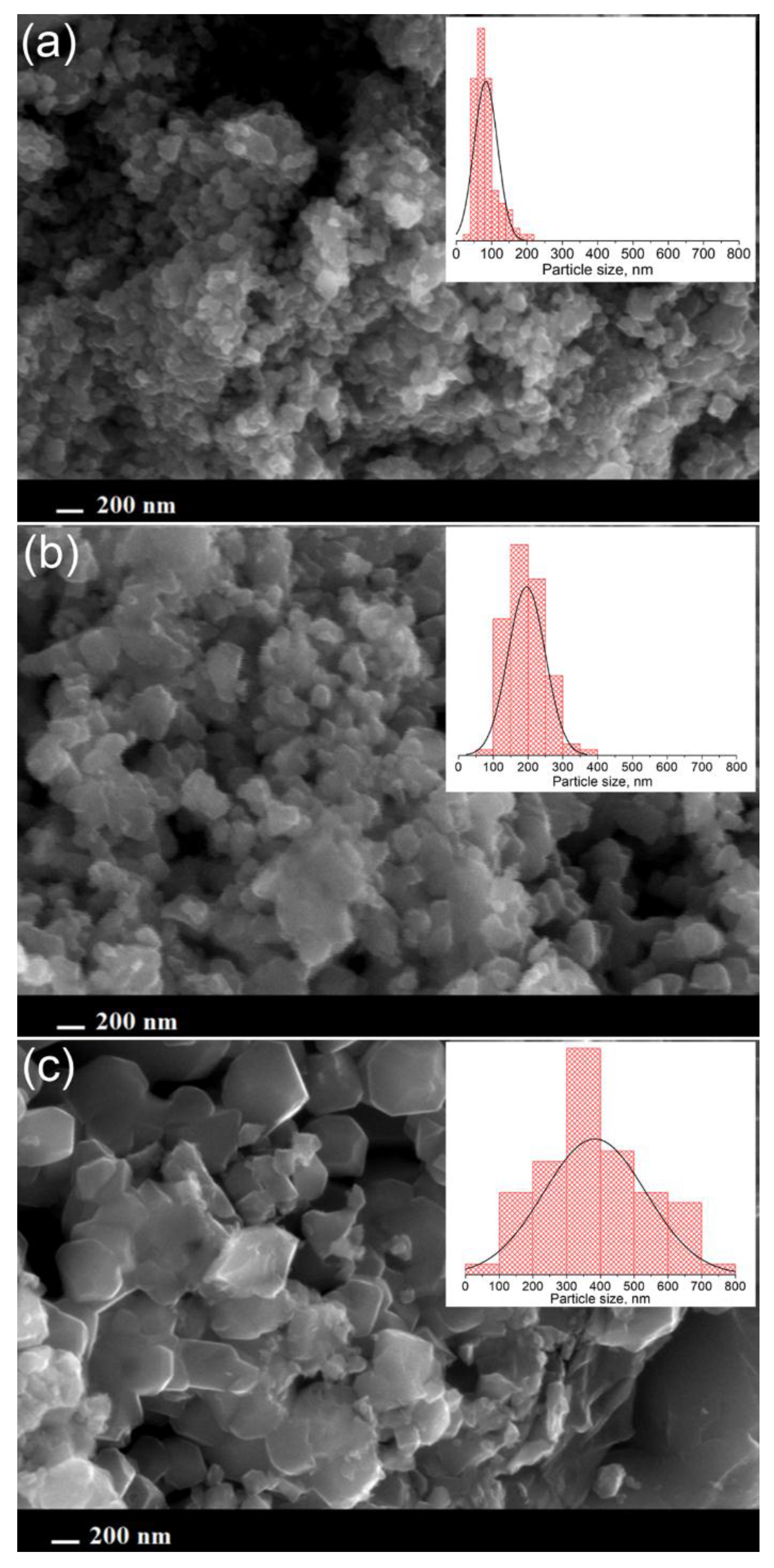
3.1. Materials Characterization
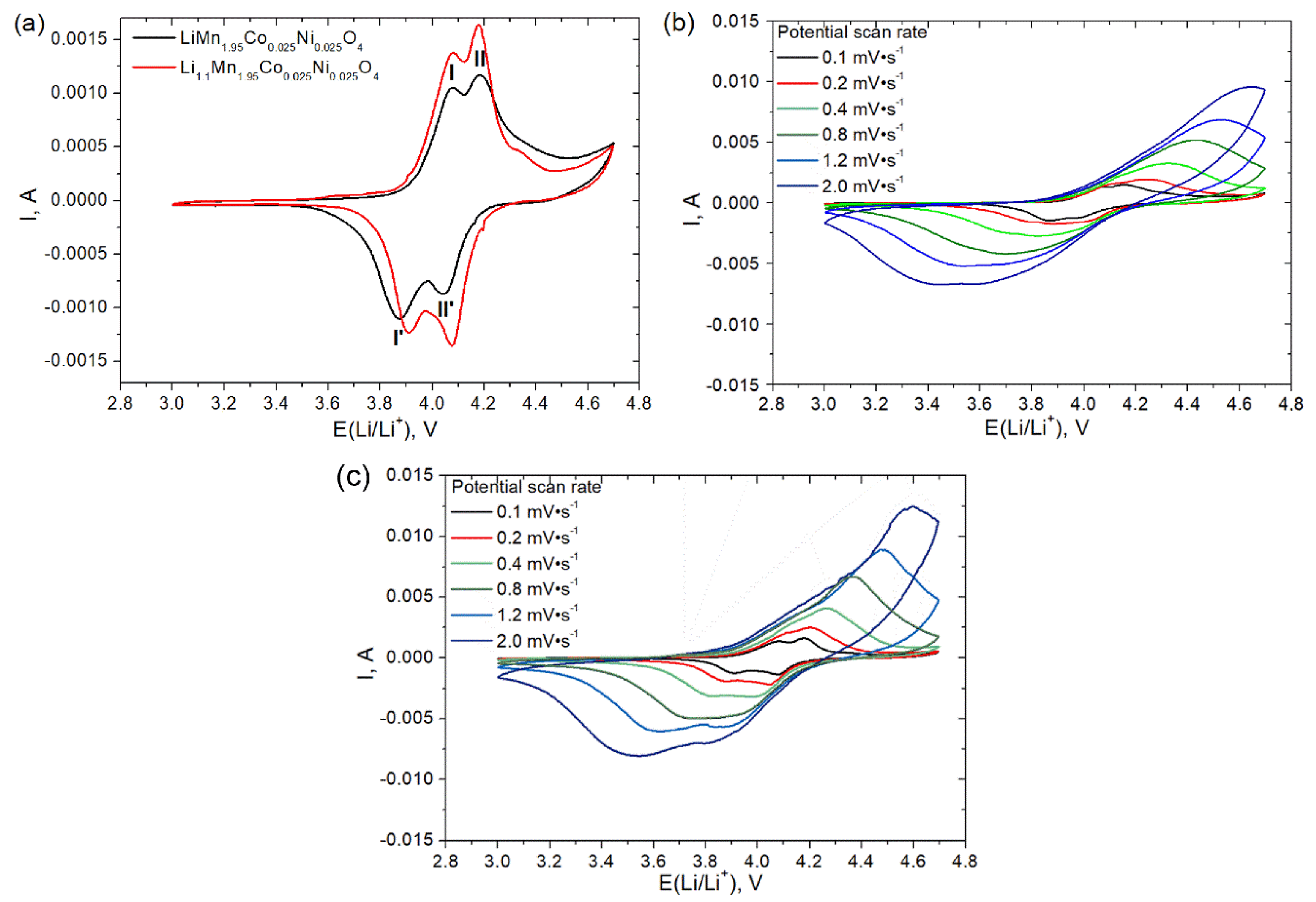
3.2. Electrochemical Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Whittingham, M.S. Lithium batteries and cathode materials. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4271–4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thackeray, M.M.; David, W.I.F.; Bruce, P.G.; Goodenough, J.B. Lithium insertion into manganese spinels. Mater. Res. Bull. 1983, 18, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunoda, M.; Oshima, Y.; Yoshinaga, M.; Shirasu, T. Prismatic lithium-ion rechargeable battery with manganese spinel and nickel-cobalt oxide cathode. NEC Res. Dev. 2000, 41, 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Guyomard, D.; Tarascon, J.M. The carbon Li1+xMn2O4 system. Solid State Ion. 1994, 69, 222–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohzuku, T.; Kitagawa, M.; Hirai, T. Electrochemistry of manganese-dioxide in lithium nonaqueous cell 3. X-ray diffractional study on the reduction of spinel-related manganese-dioxide. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1990, 137, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarascon, J.M.; Mckinnon, W.R.; Coowar, F.; Bowmer, T.N.; Amatucci, G.; Guyomard, D. Synthesis conditions and oxygen stoichiometry effects on Li insertion into the spinel LiMn2O4. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1994, 141, 1421–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, P.; Popov, B.N.; White, R.E. Electrochemical investigations of cobalt-doped LiMn2O4 as cathode material for lithium-ion batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1998, 145, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, H.J.; Donepudi, V.S.; Prakash, J. Preparation and characterization of partially substituted LiMyMn2-yO4 (M = Ni, Co, Fe) spinel cathodes for Li-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2002, 48, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, A.; Iqbal, Y.; Khan, A.M.; Ahmed, S. Low content Ni and Cr co-doped LiMn2O4 with enhanced capacity retention. Ionics 2017, 23, 1995–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebin, B.; Gurmen, S.; Lindbergh, G. Electrochemical properties of nanocrystalline LiCuxMn2−xO4 (x = 0.2–0.6) particles prepared by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis method. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 136, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goktepe, H.; Sahan, H.; Patat, S.; Ulgen, A. Enhanced cyclability of triple-metal-doped LiMn2O4 spinel as the cathode material for rechargeable lithium batteries. Ionics 2009, 15, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahan, H.; Goktepe, H.; Patat, S. Synthesis and cycling performance of double metal doped LiMn2O4 cathode materials for rechargeable lithium ion batteries. Inorg. Mater. 2008, 44, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcantara, R.; Jaraba, M.; Lavela, P.; Lloris, J.M.; Vicente, C.P.; Tirado, J.L. Synergistic effects of double substitution in LiNi0.5−yFeyMn1.5O4 spinel as 5 V cathode materials. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2005, 152, A13–A18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakuda, T.; Uematsu, K.; Toda, K.; Sato, M. Electrochemical performance of Al-doped LiMn2O4 prepared by different methods in solid-state reaction. J. Power Sources 2007, 167, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.D.; Wang, Z.B.; Chen, F.; Wu, J.; Zhang, X.G.; Gu, D.M. Crystal structure and multicomponent effects in Li1+xMn2−x−yAlyO4 cathode materials for Li-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2014, 262, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J. Electrochemical properties of tetravalent Ti-doped spinel LiMn2O4. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2011, 15, 1263–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.M.; Tu, J.P.; Chen, X.T.; Li, Y.; Zhao, X.B.; Cao, G.S. Effects of Ni-ion doping on electrochemical characteristics of spinel LiMn2O4 powders prepared by a spray-drying method. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2007, 11, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.H.; Wu, Z.F.; Li, J.C.; Liu, X.; Fang, D.L. Synthesis and electrochemical performance of a LiMn1.83Co0.17O4 shell/LiMn2O4 core cathode material. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 8455–8463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.; Huang, Y.; Liu, L.; Jia, D.; Guo, Z. Synthesis and electrochemical performance of LiCrxMn2−xO4 (x = 0,0.02,0.05,0.08,0.10) powders by ultrasonic coprecipitation. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2006, 10, 929–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Yuan, A.; Tian, L.; Wang, Y. Improved high-rate cyclability of sol–gel derived Cr-doped spinel LiCryMn2−yO4 in an aqueous electrolyte. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2011, 41, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirunakaran, R.; Sivashanmugam, A.; Gopukumar, S.; Rajalakshmi, R. Cerium and zinc: Dual-doped LiMn2O4 spinels as cathode material for use in lithium rechargeable batteries. J. Power Sources 2009, 187, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, C. Structure and Performance of Dual-doped LiMn2O4 Cathode Materials Prepared via Microwave Synthesis Method. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 125, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Xu, Y.; Tao, T.; Goodenough, J.B. Synthesis and electrochemical characterization of multi-cations doped spinel LiMn2O4 used for lithium ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2012, 199, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Tanaike, O.; Kodama, M.; Hatori, H. High rate capability of the Mg-doped Li–Mn–O spinel prepared via coprecipitated precursor. J. Power Sources 2007, 168, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, W.H.; Eom, J.Y.; Yin, R.Z.; Han, D.W.; Kim, W.K.; Kwon, H.S. Synergistic effects of various morphologies and Al doping of spinel LiMn2O4 nanostructures on the electrochemical performance of lithium-rechargeable batteries. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 15337–15342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Noguchi, H.; Yoshio, M. Synthesis and electrochemical studies on Li–Mn–O compounds prepared at high temperatures. J. Power Sources 2002, 126, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, B.J.; Santhanam, R.; Hu, S.G. Synthesis and characterization of multidoped lithium manganese oxide spinel Li1.02Co0.1Ni0.1Mn1.8O4 for rechargeable lithium batteries. J. Power Sources 2002, 108, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajakumar, S.; Thirunakaran, R.; Sivashanmugam, A.; Yamaki, J.; Gopukumar, S. Synthesis and characterization of 5 V LiCo(x)Ni(y)Mn2−x−yO4 (x = y = 0.25) cathode materials for use in rechargeable lithium batteries. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2011, 41, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sun, Z.; Xie, J.; Chen, H.; Wu, N.; Wu, B. Study of electrochemical performances of multi-doped spinel Li1.1Mn1.85Co0.075Ni0.075O4 at 4.3 and 5 V. Ionics 2013, 19, 1867–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.J.; Li, J.C.; Liu, X.; Huang, P.F.; Xu, T.R.; Qian, M.C.; Zheng, C.H. Synthesis of a Co–Ni doped LiMn2O4 spinel cathode material for high-power Li-ion batteries by a sol–gel mediated solid-state route. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 640, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shlyakhtin, O.A.; Oh, Y.J. Inorganic cryogels for energy saving and conversion. J. Electroceram. 2009, 23, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tretyakov, Y.D.; Shlyakhtin, O.A. Recent progress in cryochemical synthesis of oxide materials. J. Mater. Chem. 1999, 9, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, X.; Chen, G.; Nie, Z.; He, S.; Pi, X.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, J.; Zuo, T. Preparation and performance of LiFePO4 and LiFePO4/C cathodes by freeze-drying. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 497, 377–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.H.; Shlyakhtin, O.A.; Kim, J.; Yoon, Y.S. Structural and electrochemical properties of Li1+xNi0.5Mn0.5O2+δ (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.7) cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2005, 140, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shlyakhtin, O.A.; Yoon, Y.S.; Choi, S.H.; Oh, Y.J. Freeze drying synthesis of LiNi0.5Mn0.5O2 cathode materials. Electrochim. Acta 2004, 50, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brylev, O.A.; Shlyakhtin, O.A.; Kulova, T.L.; Skundin, A.M.; Tretyakov, Y.D. Influence of chemical prehistory on the phase formation and electrochemical performance of LiCoO2 materials. Solid State Ion. 2003, 156, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurilenko, K.A.; Shlyakhtin, O.A.; Brylev, O.A.; Drozhzhin, O.A. The effect of synthesis conditions on the morphology, cation disorder and electrochemical performance of Li1+xNi0.5Mn0.5O2. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 152, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.W.; Duh, J.G.; Sheen, S.R. LiMn2O4 cathode doped with excess lithium and synthesized by co-precipitation for Li-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2003, 115, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molenda, J.; Marzec, J.; Świerczek, K.; Ojczyk, W.; Ziemnicki, M.; Molenda, M.; Drozdek, M.; Dziembaj, R. The effect of 3d substitutions in the manganese sublattice on the charge transport mechanism and electrochemical properties of manganese spinel. Solid State Ion. 2004, 171, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raveendranath, K.; Ravi, J.; Tomy, R.M.; Jayalekshmi, S.; Mangalaraja, R.V.; Lee, S.T. Evidence of Jahn–Teller distortion in LixMn2O4 by thermal diffusivity measurements. Appl. Phys. A 2008, 90, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Liu, D.; Dong, H.; Zhang, Y. Synthesis and electrochemical performance of Ni and F doped LiMn2O4 cathode materials. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 75333–75340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, J.; Ren, H.; Tang, H.; Yu, R.; Wang, D. Multi-shelled LiMn2O4 hollow microspheres as superior cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2016, 3, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.J.; Joo, J.-B.; Lee, J.K.; Choi, W. Surface modification of cathodes with nanosized amorphous MnO2 coating for high-power application in lithium-ion batteries. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2014, 728, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, K.; Nkosi, F.P.; Viswanathan, E.; Mathe, M.K.; Damodaran, K.; Ozoemena, K.I. Microwave-enhanced electrochemical cycling performance of the LiNi0.2Mn1.8O4 spinel cathode material at elevated temperature. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 13074–13083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.C.; Xu, B.; Cheng, J.H.; Pan, C.J.; Hwang, B.J.; Meng, Y.S. Electronic, Structural, and Electrochemical Properties of LiNixCuyMn2−x−yO4 (0 < x < 0.5, 0 < y < 0.5) High-Voltage Spinel Materials. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 2832–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, Z.; Olalde-Velasco, P.; Chin, T.; Battaglia, V.; Harris, S.J.; Pan, F.; Yang, W. Effect of excess lithium in LiMn2O4 and Li1.15Mn1.85O4 electrodes revealed by quantitative analysis of soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 110, 093902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunjuzwa, N.; Kebede, M.A.; Ozoemenaa, K.I.; Mathe, M.K. Stable nickel-substituted spinel cathode material(LiMn1.9Ni0.1O4) for lithium-ion batteries obtained by using a low temperature aqueous reductiontechnique. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 111882–111888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
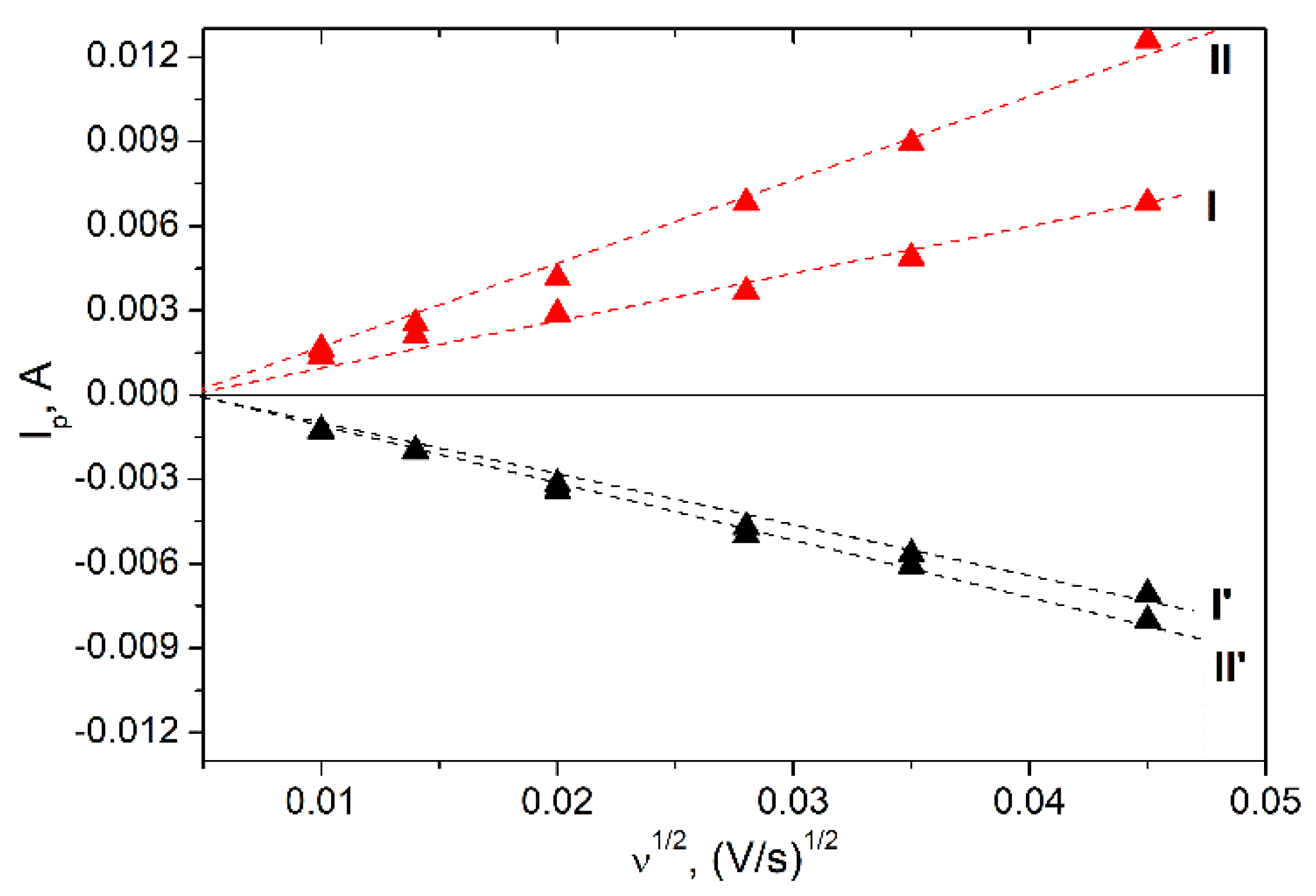
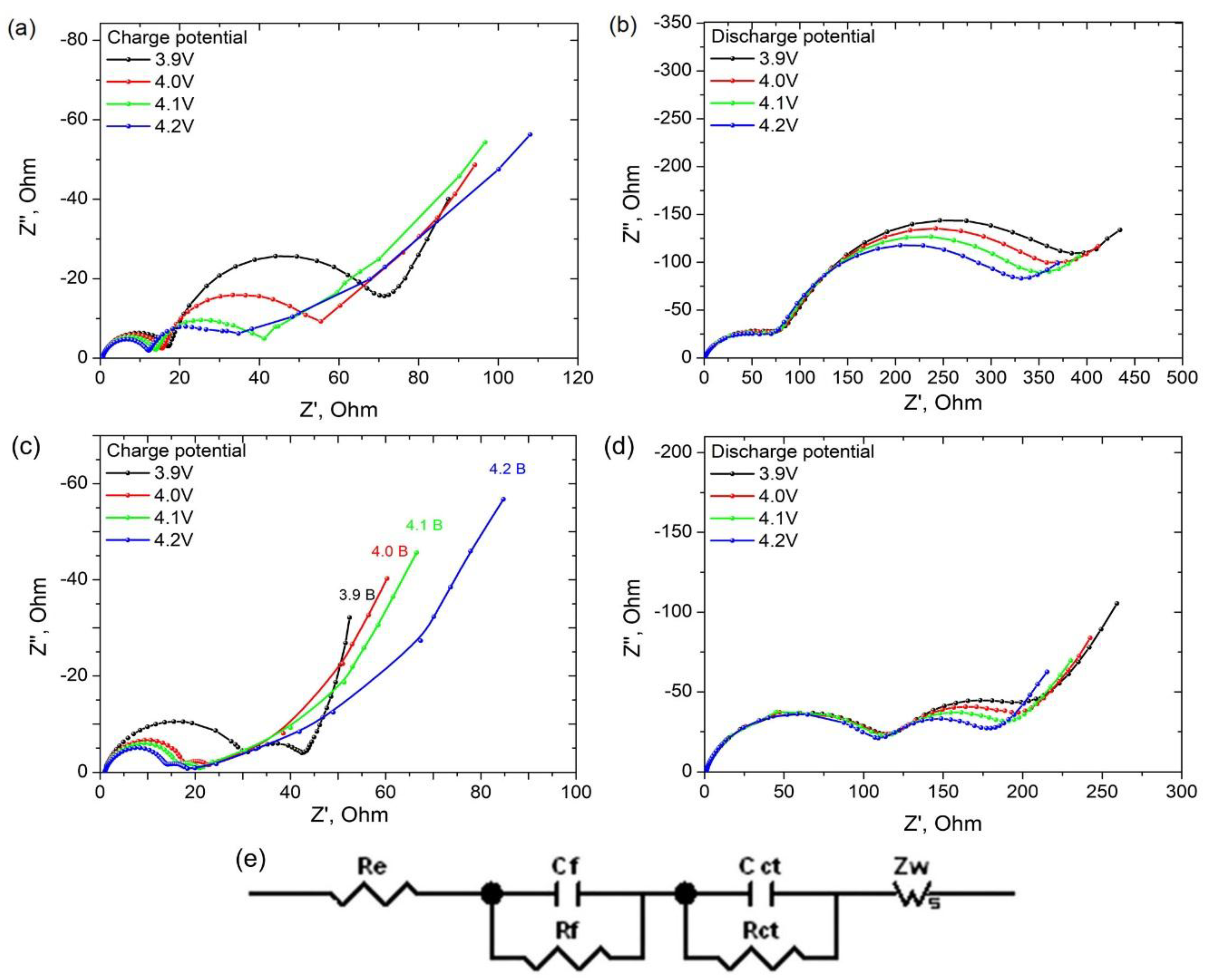
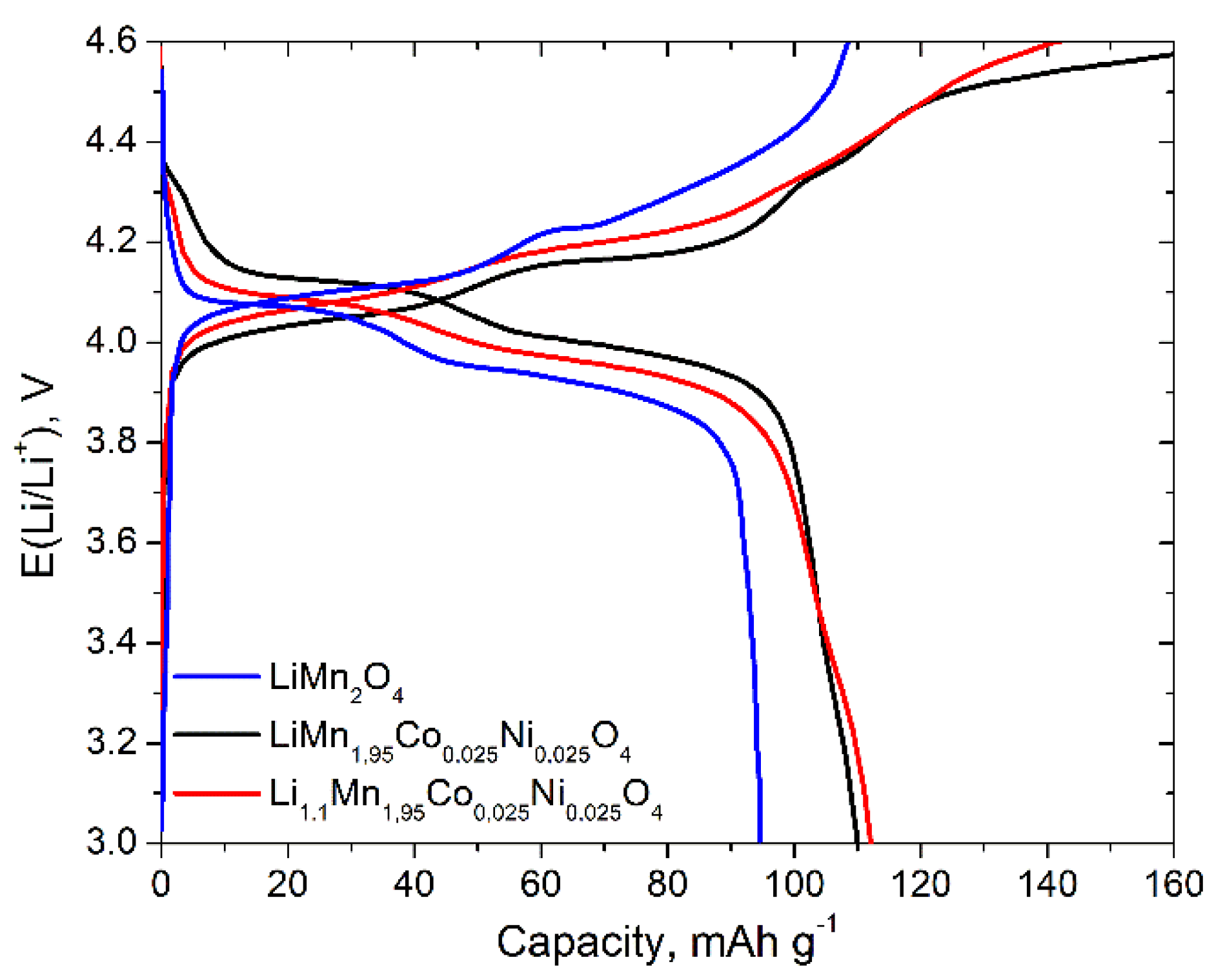
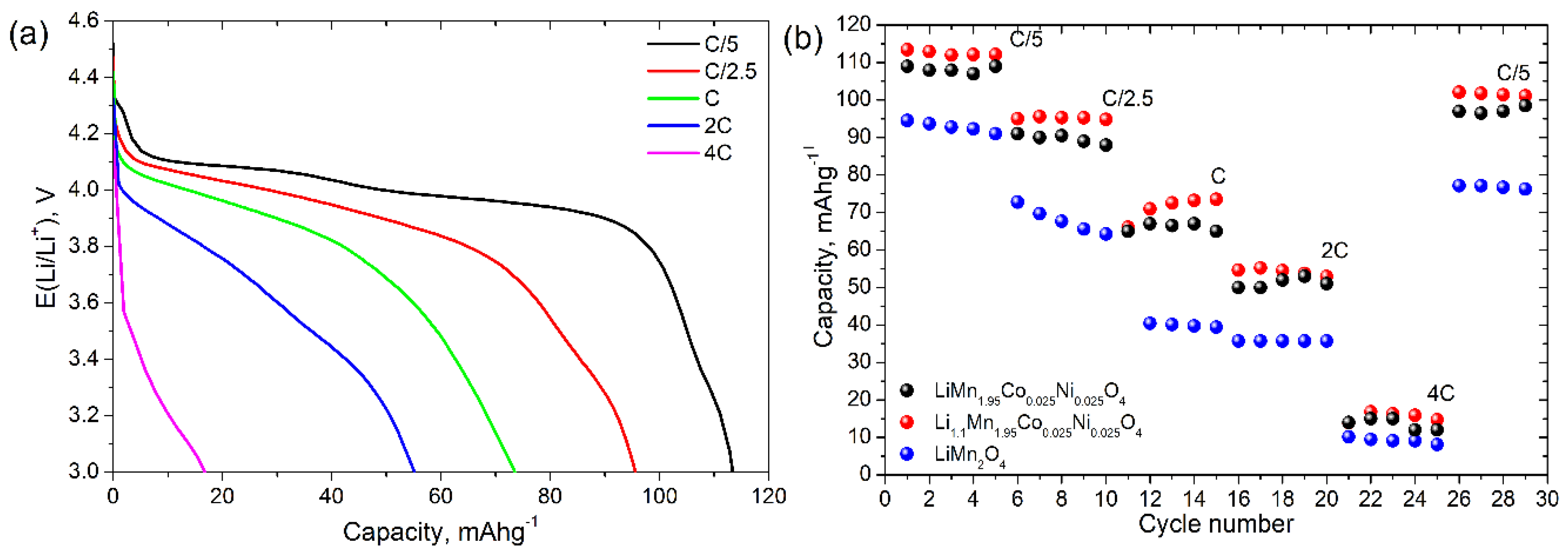
| Sample | a, Å | V, Å3 |
|---|---|---|
| LiMn2O4 | 8.2390 (5) | 559.27 (5) |
| LiMn1.95Co0.025Ni0.025O4 | 8.2301 (5) | 557.46 (5) |
| Li1.1Mn1.95Co0.025Ni0.025O4 | 8.2200 (5) | 555.42 (6) |
| Sample | Potential, V | Peak I’ | Peak II’ | Peak I | Peak II |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LiMn1.95Co0.025Ni0.025O4 | E (Li/Li+), V | 3.88 | 3.98 | 4.07 | 4.18 |
| DLi+, cm2 s−1 | 1.00 × 10−14 | 3.27 × 10−14 | 1.34 × 10−14 | 1.47 × 10−14 | |
| Li1.1Mn1.95Co0.025Ni0.025O4 | E (Li/Li+), V | 3.92 | 4.07 | 4.07 | 4.18 |
| DLi+, cm2 s−1 | 1.01 × 10−14 | 2.39 × 10−14 | 1.27 × 10−14 | 1.92 × 10−14 |
| Sample | Potential, V | 3.9 | 4.0 | 4.1 | 4.2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LiMn1.95Co0.025Ni0.025O4 | Charge, DLi+, cm2 s−1 | 4.49 × 10−12 | 1.09 × 10−12 | 4.11 × 10−13 | 2.84 × 10−13 |
| Discharge, DLi+, cm2 s−1 | 2.28 × 10−14 | 2.73 × 10−14 | 2.60 × 10−12 | 2.90 × 10−12 | |
| Li1.1Mn1.95Co0.025Ni0.025O4 | Charge, DLi+, cm2 s−1 | 1.42 × 10−12 | 1.19 × 10−12 | 9.09 × 10−13 | 4.10 × 10−13 |
| Discharge, DLi+, cm2 s−1 | 5.33 × 10−14 | 7.99 × 10−14 | 6.31 × 10−14 | 7.33 × 10−14 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Normakhmedov, O.O.; Brylev, O.A.; Petukhov, D.I.; Kurilenko, K.A.; Kulova, T.L.; Tuseeva, E.K.; Skundin, A.M. Cryochemically Processed Li1+yMn1.95Ni0.025Co0.025O4 (y = 0, 0.1) Cathode Materials for Li-Ion Batteries. Materials 2018, 11, 1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071162
Normakhmedov OO, Brylev OA, Petukhov DI, Kurilenko KA, Kulova TL, Tuseeva EK, Skundin AM. Cryochemically Processed Li1+yMn1.95Ni0.025Co0.025O4 (y = 0, 0.1) Cathode Materials for Li-Ion Batteries. Materials. 2018; 11(7):1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071162
Chicago/Turabian StyleNormakhmedov, Ofok O., Oleg A. Brylev, Dmitrii I. Petukhov, Konstantin A. Kurilenko, Tatiana L. Kulova, Elena K. Tuseeva, and Alexander M. Skundin. 2018. "Cryochemically Processed Li1+yMn1.95Ni0.025Co0.025O4 (y = 0, 0.1) Cathode Materials for Li-Ion Batteries" Materials 11, no. 7: 1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071162
APA StyleNormakhmedov, O. O., Brylev, O. A., Petukhov, D. I., Kurilenko, K. A., Kulova, T. L., Tuseeva, E. K., & Skundin, A. M. (2018). Cryochemically Processed Li1+yMn1.95Ni0.025Co0.025O4 (y = 0, 0.1) Cathode Materials for Li-Ion Batteries. Materials, 11(7), 1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071162






