Abstract
In this work, Y2O3 based composite crucibles with different Al2O3 contents were designed and characterized. The stability behaviors and interaction mechanisms between molten Ti-47Al-2Cr-2Nb alloy and Y2O3-Al2O3 composite crucibles were investigated at high temperature. Results showed that the surface morphology of crucibles and the degree of interfacial reactions between the composite crucibles and the metal melts varied with the change of Al2O3 content in the crucible matrix. The pure Y2O3 crucible was the densest and its chemical stability was the highest. With the increase in Al2O3 content, the number of pores on the crucibles surface gradually increased and the interfacial reactions between the composite crucibles and the molten alloys became weaker. When the content of Al2O3 in composite crucibles increased from 3.5 wt % to 10.5 wt %, the thickness of the interface layer of melt-crucible decreased from 150 µm to 50 µm, and the equilibrium contact angles between metal and crucibles gradually decreased from 69.3° to 64.2° at 1873 K.
1. Introduction
Intermetallic TiAl-based alloys with the advantages of low density, high specific strength and elastic modulus, excellent creep properties and high resistance to oxidation, have extensive application in aerospace, automotive and energy industries [1,2,3,4]. They are acknowledged to be the most promising candidates to replace Ni-based superalloys [5]. However, the applications of TiAl-based alloys are restricted due to low ductility and fracture toughness at low temperature [6]. Therefore, some methods must be developed for optimizing the comprehensive properties of TiAl-based alloys.
The melting process of an alloy is one of the most important factors affecting the properties of the alloy [7]. Many meaningful studies have been conducted to improve the quality of TiAl-based alloys. Researchers suggested that the molten TiAl-based alloys have high reactivity, which led to some interactions between the molten alloys and crucible materials during melting and casting, resulting in deterioration of the internal and external quality of castings [8]. Therefore, the selection of refractories during the process of melting is crucial for obtaining high-quality alloys.
Previous investigations have shown that oxide ceramic materials have a better and more extensive application, of which Al2O3, CaO, ZrO2 and Y2O3 are the most commonly used [9,10,11,12,13,14]. One characteristic of the CaO mold shell is that it is extremely easy to absorb the tide of water, which requires strict control of the humidity of the crucibles. Therefore, the control of the humidity increase the difficulty of the operation and hinder its application [15]. ZrO2 is thermodynamically stable and economical. However, a large number of inclusions were found in metals during the melting of a TiAl-based alloy with the ZrO2 crucible and this indicated that it had serious chemical reactions with the TiAl-based alloy at high temperature [16]. Al2O3 crucibles are used in the precision casting of TiAl-based alloys because of the high Al2O3 content in crucibles, which reduces the activity of TiAl-based alloys and their solid solubility to oxygen [17]. In addition, the thermal expansion coefficient of A12O3 and TiAl-based alloys is very similar, which reduces the probability of fracture due to the low plasticity of TiAl-based alloys at room temperature. Therefore, the prospect of Al2O3 crucible in the casting of TiAl-based alloys is favored [18,19]. However, many studies have shown that the Al2O3 crucible also reacted with the melt during the melting process [20]. According to the study of Kostov and Frierich, Y2O3 presents the most thermodynamic stability among common metallic oxides, and it is a suitable material for crucibles used in the melting and casting of TiAl-based alloys [21]. Nevertheless, the poor thermal shock resistance of pure Y2O3 products and high production cost make it difficult to be widely used in industrial production [22].
Therefore, in order to find an appropriate crucible material, the composite crucibles were prepared by adding different amounts of Al2O3 powder and mixing different particle sizes of Y2O3. That can keep its stability during the smelting of high active TiAl-based alloys and make it cheap. The objective of this study was to demonstrate the mechanisms of the interactions between the chemical composition of Y2O3-Al2O3 composite crucibles and TiAl-based alloys, and then compare the stability of the composite crucibles with different Al2O3 contents during smelting.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Composite Crucibles
In this study, four different types of composite crucible with various components were designed and characterized. The compositions of the crucibles are listed in Table 1. The content of Y2O3 (purity 99.9%) (Beijing VPS-Tech Co., Ltd., Beijing, China) sand, which was 200 mesh and 60–80 mesh size of the main crystalline phase powder of the crucibles, was 30 wt % and 35 wt %, respectively. The content of 5 µm Al2O3 (purity 99.9%) (Beijing VPS-Tech Co., Ltd., Beijing, China) and 325 mesh Y2O3 active powder as the substrate of the crucible was 35 wt %. The compositions of the Al2O3-A, Al2O3-B, and Al2O3-C composite crucible with 5 µm Al2O3 powder instead of 325 mesh Y2O3 powder were 3.5 wt %, 7.0 wt % and 10.5 wt %, respectively. The crucibles were made of Y2O3 and Al2O3 powder by gelcasting with the dimensions of 25 mm o.d.× 18 mm i.d.× 30 mm length specified. For gelcasting, acrylamide [C2H3CONH2] (AM) (Beijing Lanyi Chemical Products Co., Ltd., Beijing, China) was used as a monomer, N,N′-methylenebisacrylamide [(C2H3CONH)2CH2] (MBAM) (Beijing Lanyi Chemical Products Co., Ltd., Beijing, China) as a coupling agent, N,N,N′,N′-tetramethylethylenediamine (TEMED) as a catalyst, ammonium persulphate (Beijing Chemical Works, Beijing, China) as an initiator and ammonium polyacrylate (Beijing Chemical Works, Beijing, China) as a dispersant. The crucible’s sintering temperature is 1873 K and the holding time is 4 h.

Table 1.
Designated composition of composite crucibles with different Al2O3 contents.
2.2. Melting Procedure
The master alloy, with nominal composition of Ti-47Al-2Cr-2Nb (at %), was prepared by an arc-melting method using Nb sheet (99.87%), commercial Ti sponge (99.76%), Al ingot (99.99%) and Cr granule (99.98%) as raw materials. The melting procedure was performed in a modified Bridgeman vacuum directional solidification furnace equipped with a removable composite crucible. Before each heating cycle, the chamber was evacuated down to ~10−3 Pa and backfilled with pure argon (O2 < 10 ppm; N2 < 50 ppm; H2 < 5 ppm; CH4 < 4 ppm) up to 0.05 MPa. The superheating temperature was 1873 K, measured and controlled by a thermocouple thermometer. The alloy ingots collected in composite crucibles were superheated for 10 min. Afterwards, the molten alloy was allowed to solidify in the composite crucible down to 300 K.
In order to further clarify the mechanism of interaction between molten metal and crucible, high temperature wetting experiments between TiAl-based alloys and crucibles were conducted by using composite ceramic substrates which were made under the same conditions of making composite crucibles. The oxide ceramic substrates with cylindrical shape were prepared by the dry pressing method using a uni-axial pressure machine (YLJ-40T, Shenyang Keji Automation Equipment Co., Ltd., Shenyang, China). Then, the Y2O3 and Al2O3 mixture powders were ground. Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) (Beijing Lanyi Chemical Products Co., Ltd., Beijing, China) with a content of 5 wt % was added as a binder. The wetting experiment was carried out by the improved sessile drop equipment. Before heating, the furnace chamber was vacuumed to 9.9 × 10−4 Pa and further backfilled with a deeply purified Ar (99.999%) atmosphere to prevent active elements from evaporation and oxidation. When the temperature reached 1873 K, the alloy with the size of 3 × 3 × 3 mm3 in the top of the equipment was dropped. The spreading process was recorded by a CCD camera (Canon, EOS 80D, Tokyo, Japan). The contact angles were obtained by the ADSA-SESDROP and FTA32 software (Jilin University, Shenyang, China) [4,5].
After the melting experiment and wetting experiment, the microstructures of the alloys were examined by an electron probe micro-analyzer (EPMA, JXA-8100, JEOL, Tokyo, Japan), and the microstructures of crucibles were observed via scanning electron microscopy (SEM, JSM 6010, Japan Electronics Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). Energy-dispersive spectrometry (EDS Oxford INCAPentaFET-x3, Japan Electronics Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) was used to analyse the chemical composition and impurity elements at specified positions from the surface to the inside of the ingots to establish the homogeneity. The phase identification of the compounds on the alloy matrix and contact interface was performed by X-ray diffraction (XRD, D/max 2200PC, Rigaku, Tokyo, Japan) with Cu Kα radiation by scanning on the designated area.
3. Results
3.1. Microstructure
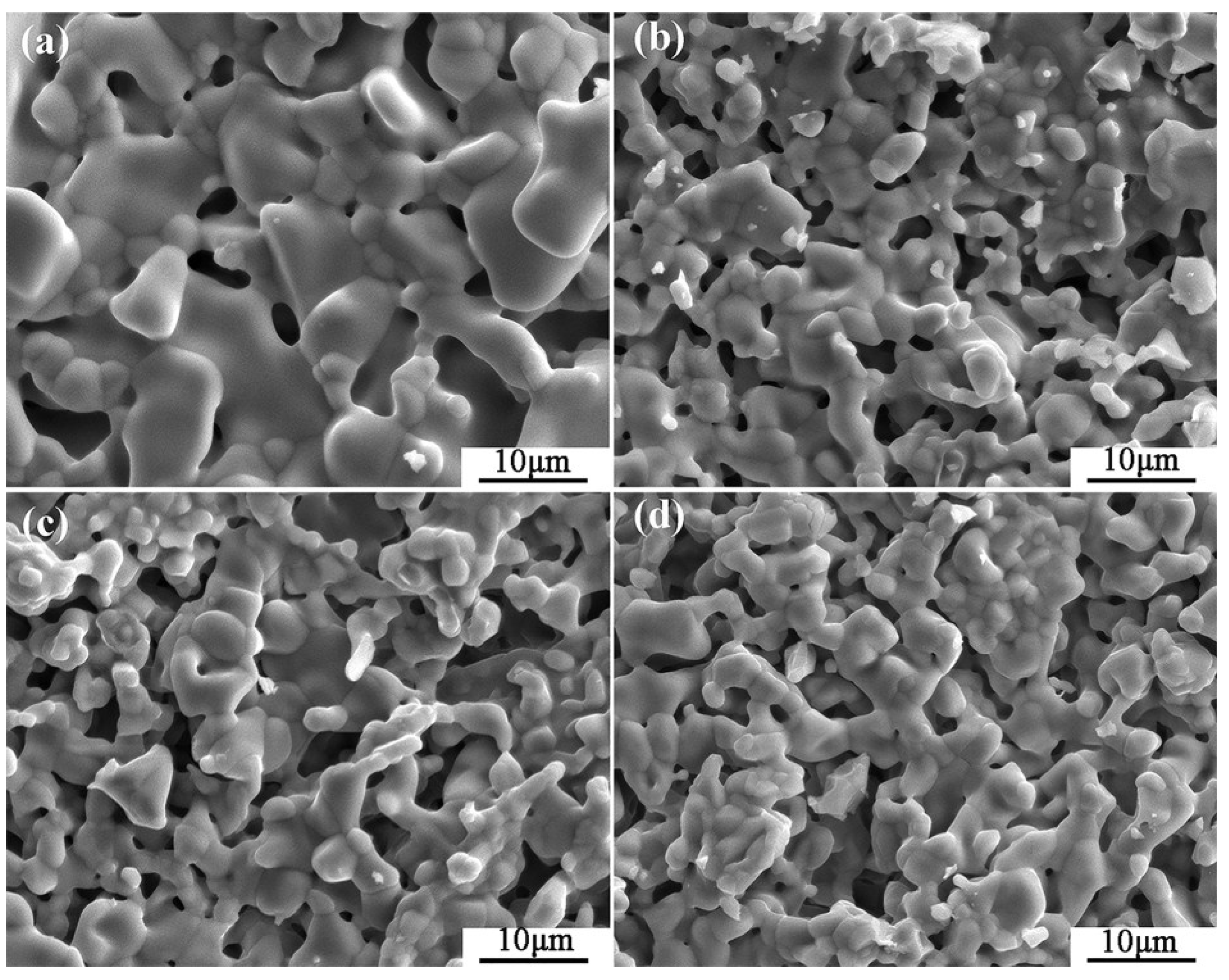
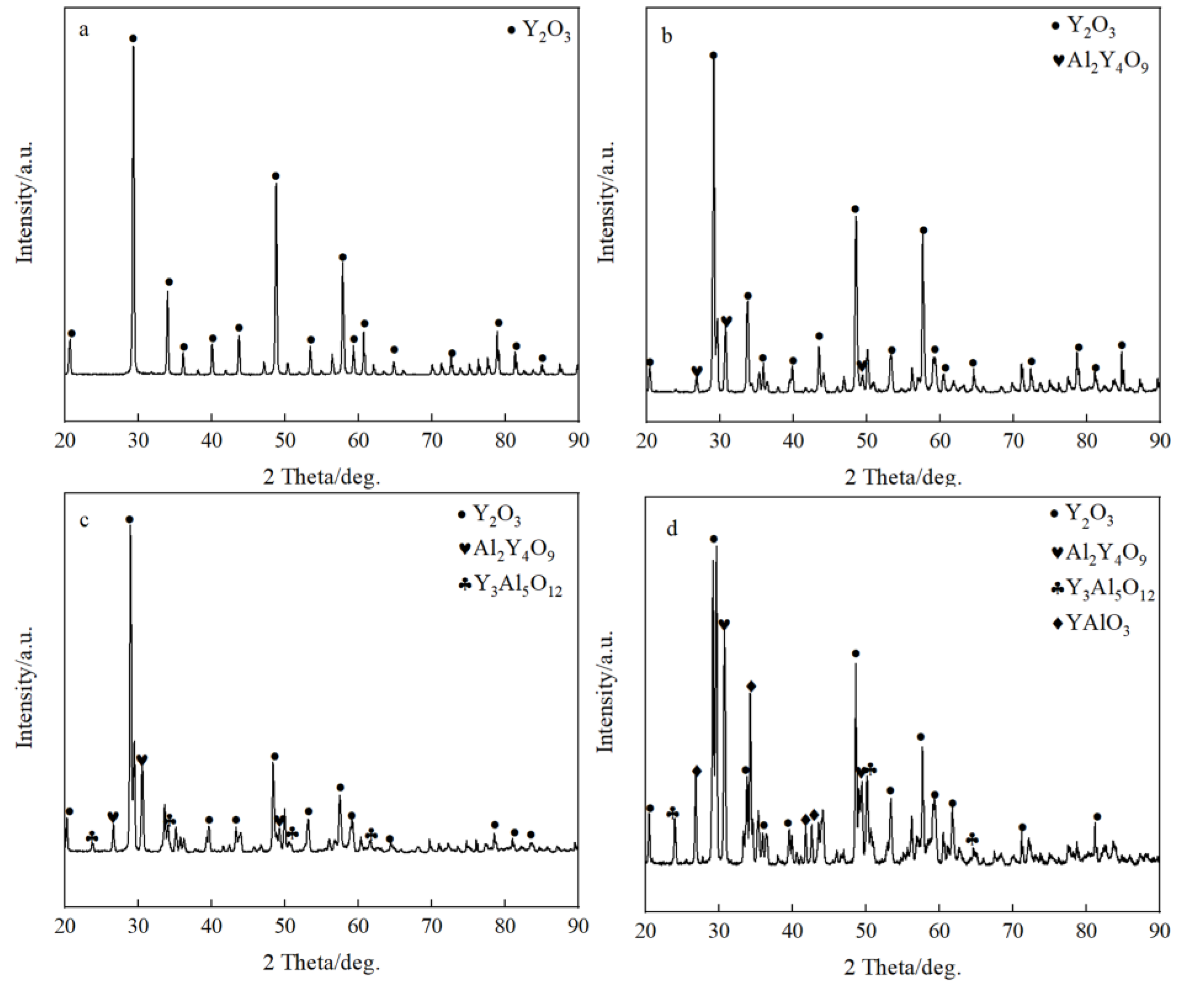
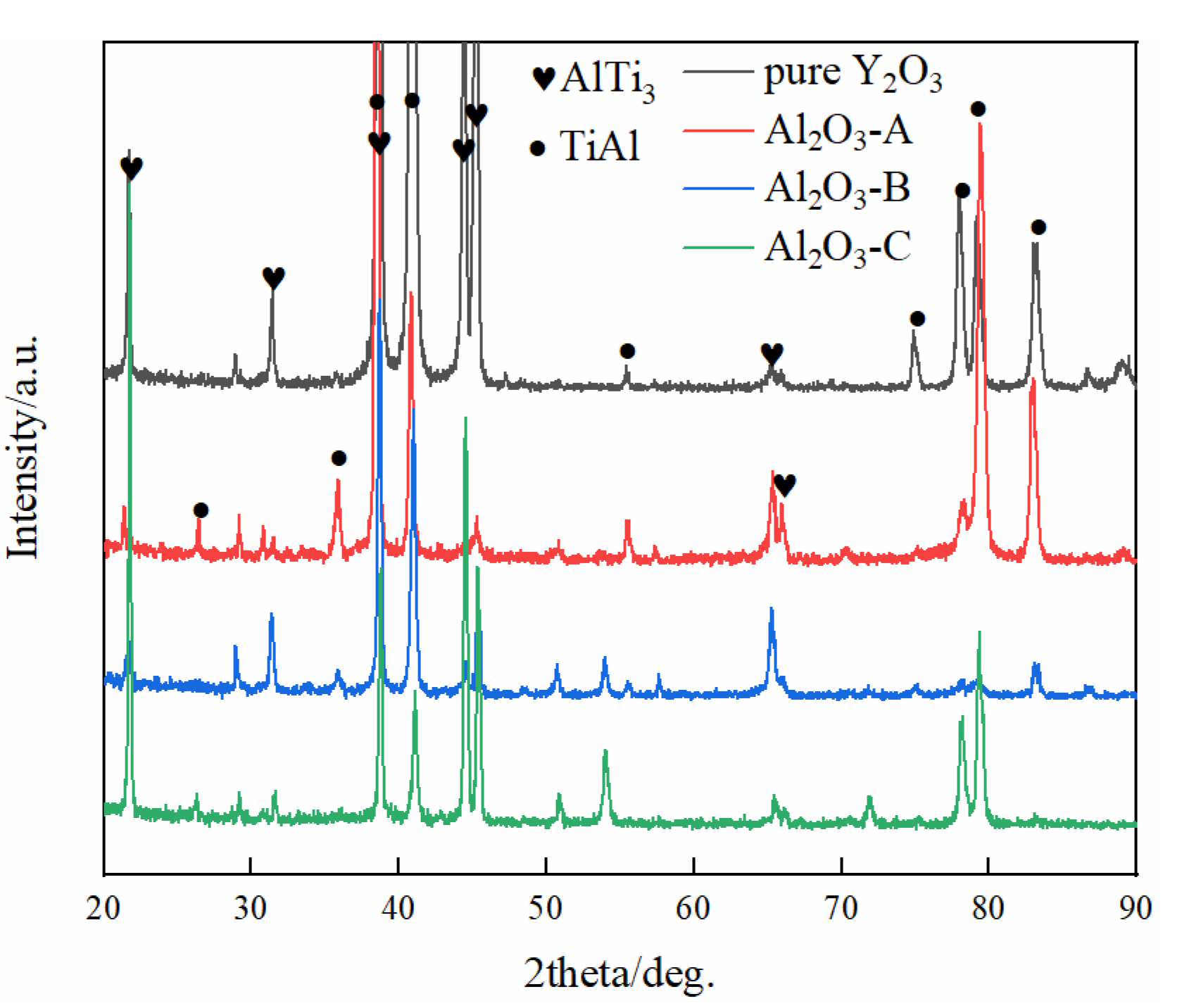
The typical microstructures of four composite crucibles after sintering are shown in Figure 1. The corresponding porosities of the composite crucibles are shown in Table 2. The morphology of the pure Y2O3 crucible (Figure 1a), which was a pure Y2O3 crucible without addition of Al2O3, presented the least amount of connected pores and the densest surface. Compared with several other crucibles, it was the most thoroughly sintered. The degree of sintering of the Al2O3-A crucible was less than that of the pure Y2O3 crucible. The number of surface connected pores increased and the porosity increased from 5.88% to 9.93%. The surface microstructures of the Al2O3-B and Al2O3-C crucibles were very similar, with similar porosity values of 11.52% and 11.34%, respectively. Compared to the Al2O3-A crucible, the number of surface connected pores increased significantly, with more even dispersal, and the combination of oxide particles was looser. The XRD spectrum (Figure 2) shows that there was only Y2O3 in the pure Y2O3 crucible, and Al2O3-A crucible contained the Al2Y4O9 phase. In addition to the Al2Y4O9, Y3Al5O12 and YAlO3 phases were newly formed in the Al2O3-B and Al2O3-C crucible with higher Al2O3 addition.
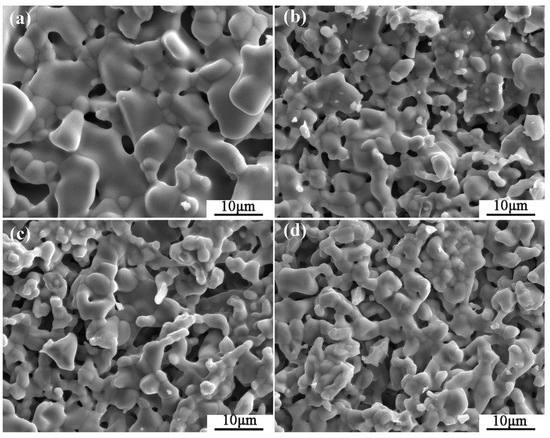
Figure 1.
The SEM micrographs of the composite crucibles with specific components. (a) The pure Y2O3 crucible; (b) Al2O3-A crucible, containing 3.5 wt % Al2O3; (c) Al2O3-B crucible, containing 7.0 wt % Al2O3; (d) Al2O3-C crucible, containing 10.5 wt % Al2O3.

Table 2.
The porosity of crucibles.
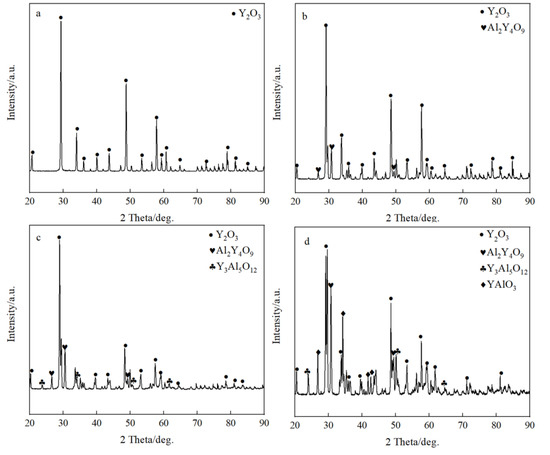
Figure 2.
The XRD spectrum of composite crucibles before the melting experiment. (a) The pure Y2O3 crucible; (b) Al2O3-A crucible, containing 3.5 wt % Al2O3; (c) Al2O3-B crucible, containing 7.0 wt % Al2O3; (d) Al2O3-C crucible, containing 10.5 wt % Al2O3.
3.2. Melt-Crucible Interface
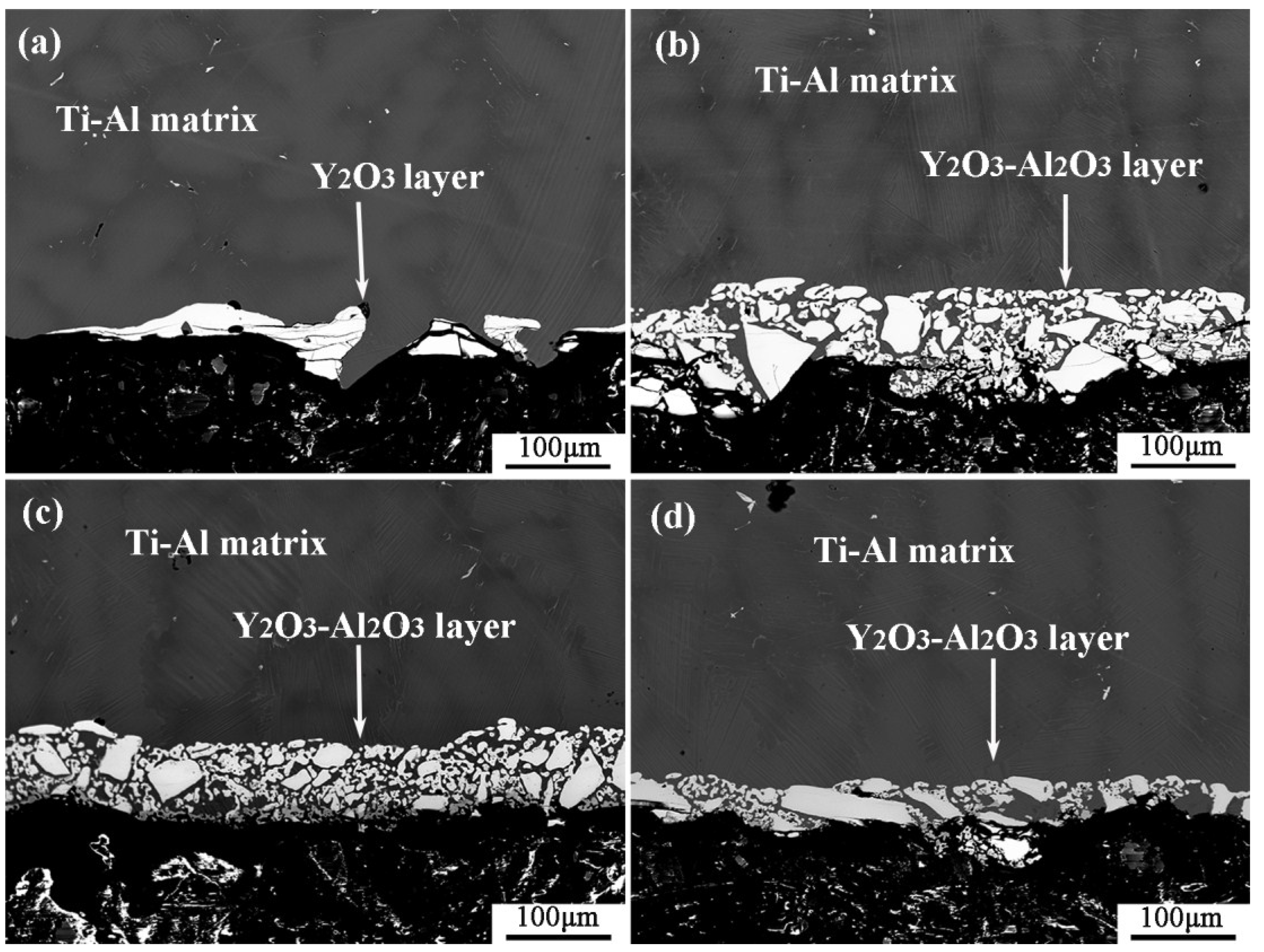
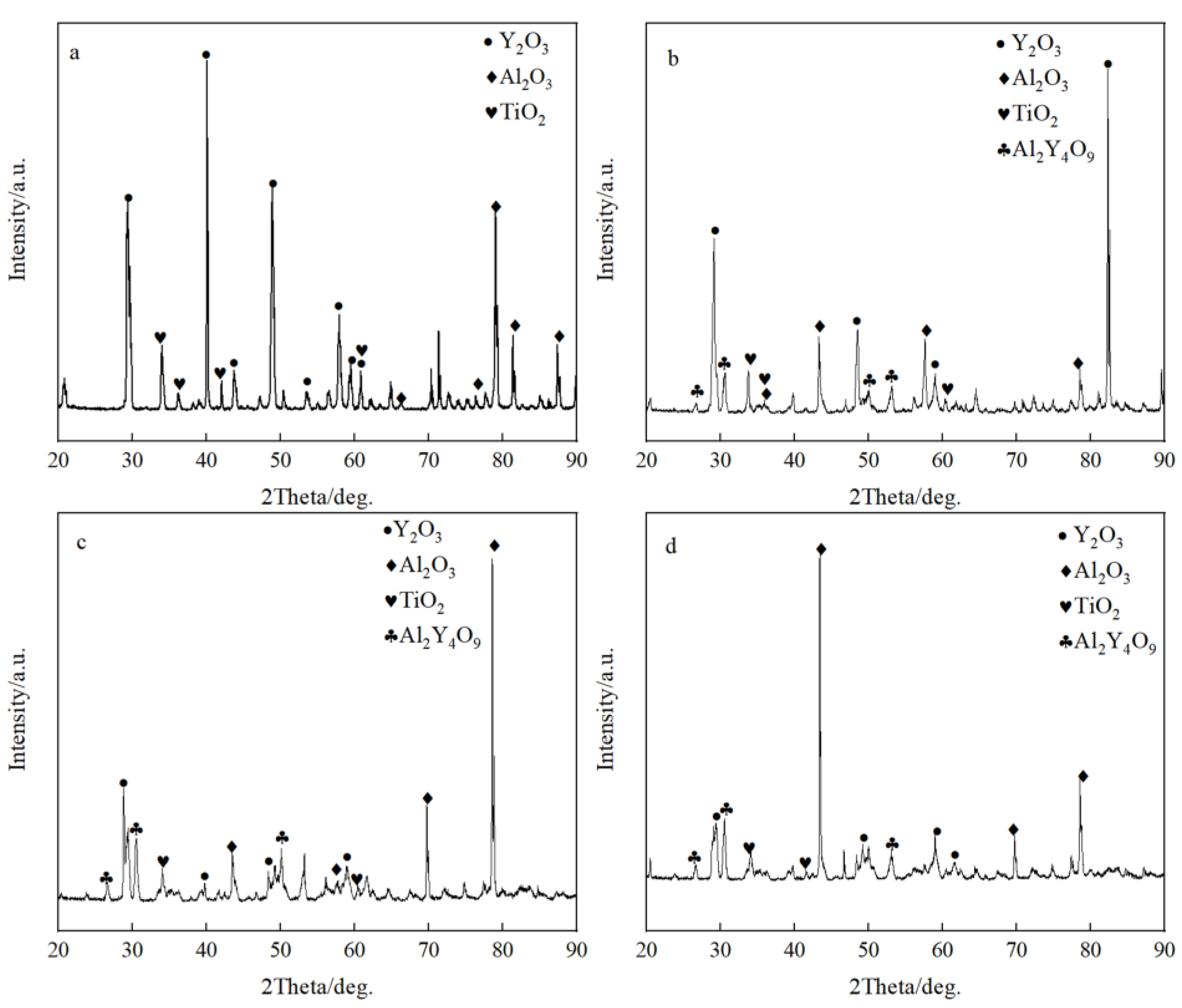
Figure 3 shows the microstructure of the metal-crucible contact interface after the melting experiment. The molten metal penetrated into the crucible at the interface and then adhered to oxide layer from the crucible. As shown in Figure 3a, the interface layer in the pure Y2O3 crucible was discontinuous. The greatest thickness was about 100 µm, while the thinnest was about only a few microns. It can be seen that the white substance bonded to the metal was almost a complete Y2O3 coarse sand particle. The interface layers of Al2O3-A, Al2O3-B and Al2O3-C crucible (Figure 3b–d) were continuous and uniform. Compared with the pure Y2O3 crucible, the oxide particles that adhered to the metal were relatively small. The thickness of the interface layer of the Al2O3-A crucible was the largest, about 150 µm, and the particles in the interface layer were fine and loose. The thickness of the interface layer of Al2O3-B crucible was about 100 µm, and the white particles were fine, but the arrangement was relatively close relative to that of the Al2O3-A crucible. The thickness of the interface layer of the Al2O3-C with the most Al2O3 powder was about 50 µm, and the proportion of fine white oxide particles decreased. The XRD diffraction pattern of the interface layer (Figure 4) showed that the interface layer of the pure Y2O3 crucible had Y2O3, Al2O3 and a small amount of TiO2, but at the interface of Al2O3-A, Al2O3-B and Al2O3-C crucibles, besides the above three substances, Al2Y4O9 was also detected.

Figure 3.
Microstructure of the melt-crucible contact interface. (a–d) represent the pure Y2O3, Al2O3-A, Al2O3-B and Al2O3-C crucibles, respectively.
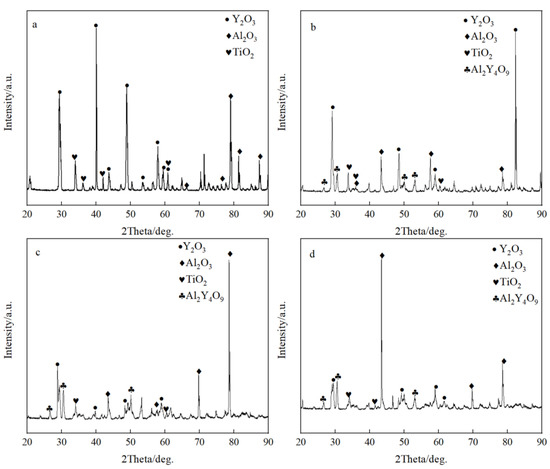
Figure 4.
The XRD spectrum of the interface. (a–d) represent the pure Y2O3, Al2O3-A, Al2O3-B and Al2O3-C crucibles, respectively.
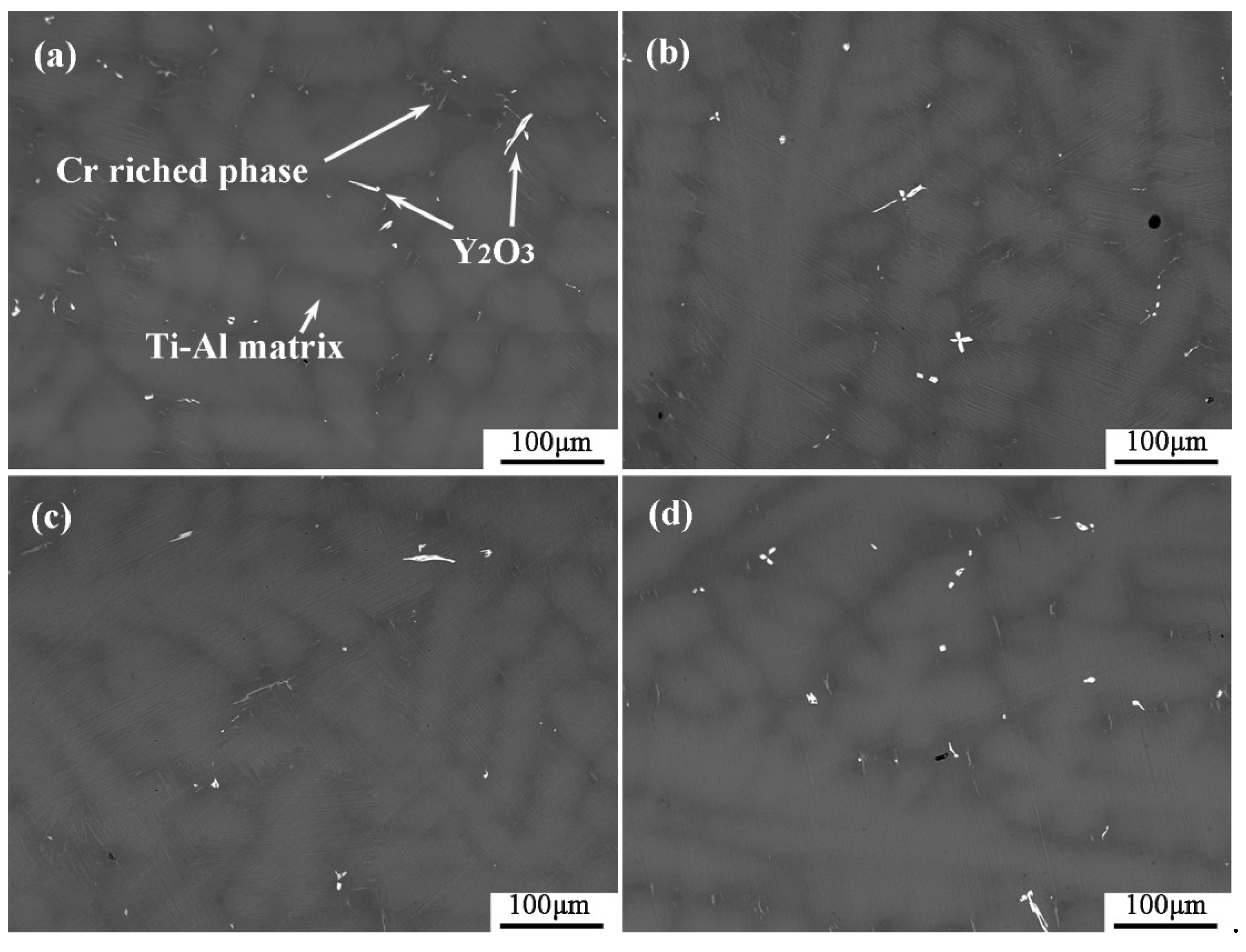
Figure 5 shows the microstructures of the interior of the alloys after the melting experiment. A large number of coarse grayish dendrites were distributed in the dark gray matrix, and a small number of irregular phases with bright white and grey contrast were dispersedly distributed among them. The grey precipitates were mainly distributed in the deep gray between dendrites, presented as tiny needles. Bright white precipitates were mainly distributed among dendrites, and there were a small number of dendrites. Some of them were elongated, some were plum-like flowers, and some were distributed small particles. The XRD spectra of the interior of metal particles after melting experiments are shown in Figure 6. There were only two phases of TiAl and AlTi3. The presumed results may not be shown in diffraction patterns due to too little precipitation. The EDS analysis of the precipitated bright with white contrast and gray matter contrast is shown in Table 3. The atomic percentage of heavy Cr in the gray contrast reached 23–25%, and it is known that it was a rich Cr phase precipitate, and the Cr in the matrix was easily segregated in the interdendritic area. The ratio of Y and O in white contrast material was close to 1:1, and at the same time, contained a small amount of Al. It is speculated that it was an oxide that contained Y and Al, and it was formed during the melting process of the metal from the crucible to the metal melt.
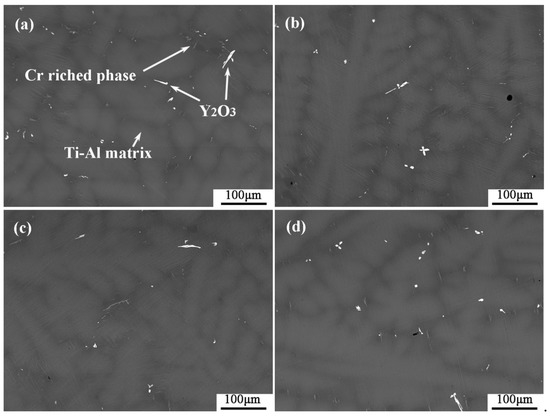
Figure 5.
(a–d) are the internal microstructures of the metal particles obtained from the alloy melting experiments of pure Y2O3, Al2O3-A, Al2O3-B and Al2O3-C crucibles.
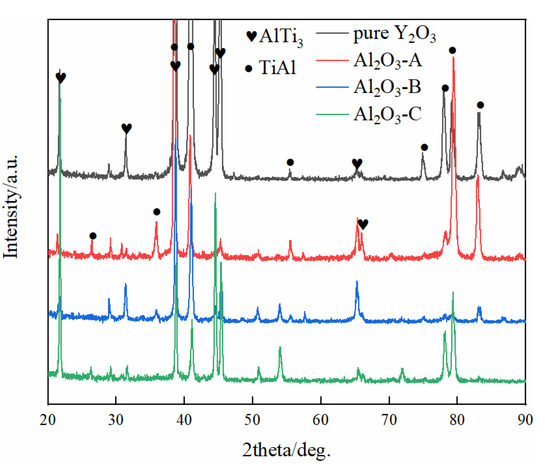
Figure 6.
The XRD spectra of the interior of metal particles.

Table 3.
The internal components of the metal particles.
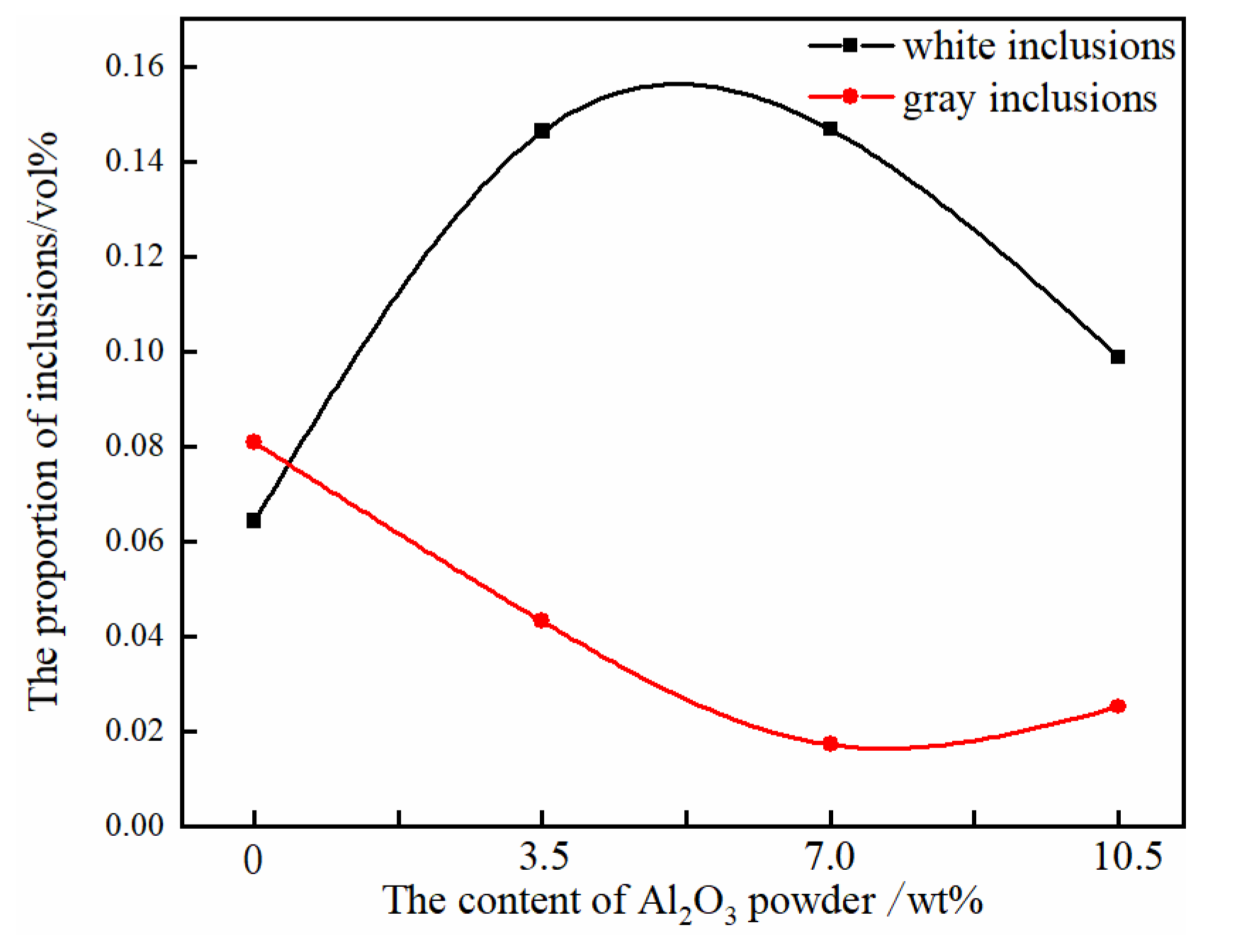
The percentage of the gray interlining Cr rich and the white interlining yttrium aluminum oxide in the alloy interface area was calculated, which was used to indicate the content of inclusions in the TiAl alloy. The results showed that (Figure 7) with the increase of the addition of Al2O3 powder, the white inclusion content in the metal increased first and then decreased. The content of white inclusions in the pure Y2O3 crucible with no Al2O3 powder was the lowest. After adding a small amount of Al2O3 powder, the number of inclusions increased rapidly. With the increase of the addition of Al2O3, the content of white inclusions decreased. After the addition of Al2O3, the content of the rich Cr phase of the gray contrast decreased first, followed by a rebound trend, and the content of the precipitated phase was the lowest when the proportion of Al2O3 powder was 7.0 wt %.
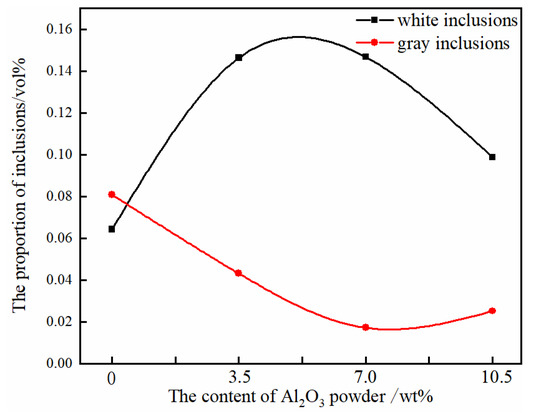
Figure 7.
The number of precipitates in metal particles.
4. Discussion
The surface microstructure and the porosity of the crucibles showed that the addition of Al2O3 affected the degree of sintering of the crucibles. As shown in Figure 1 and Table 2, the sintering degree of Y2O3 crucible decreased with the addition of Al2O3, and the porosity increased with the addition of Al2O3 before maintaining a relatively stable value. According to the results obtained by H.R. Zhang [23], Y2O3 and Al2O3 reacted in the process of high-temperature sintering to form dense and solid Y3Al5O12, which increased the sintering degree of the crucibles. In this study, the XRD (Figure 2) detected Al2Y4O9, Y3Al5O12 and YAlO3 phases in the composite crucibles with Al2O3 added before the melting experiment. The system Y2O3-Al2O3 features Al2Y4O9, YAlO3 and Y3Al5O12, with mole ratios Y2O3: Al2O3 of 2:1, 1:1, and 3:5, respectively. The reaction temperature and ratio of Y2O3 and Al2O3 affect the type of final product [24]. Kolitsch, U. et al. suggested that YAlO3 is a stable phase in the temperature range from 1873 K to 1673 K and possibly down to ambient temperature [25]. However, a reversible phase transition of Al2Y4O9 at around 1650 K has been reported [26]. The reactions between Y2O3 and Al2O3 produced several different products as described above during the sintering process because Y2O3-Al2O3 is a rather complex (and partly metastable) system. The Al2O3 powder with size of 5 µm was added to the Al2O3-A, Al2O3-B and Al2O3-C crucibles, and an alternative part of the 325 mesh Y2O3 powder formed the mixed fine powder. Because the particle size of Al2O3 powder was much smaller than that of the 325 mesh Y2O3 powder, and the 325 mesh Y2O3 of 3.5 wt % in the Al2O3-A crucible was replaced by Al2O3 powder of 5 µm, and the surface grain of the small crucible formed by sintering was finer than that on the surface of the pure Y2O3 crucible. The proportion of Al2O3 powder in Al2O3-B and Al2O3-C crucibles continued to increase. The particles were in close contact with each other, and the sintering degree was good. Therefore, compared to the Al2O3-A crucible, the porosity of the Al2O3-B and Al2O3-C crucible was only slightly increased, and the surface micromorphology of the two was similar.
The interfacial reactions between melt metals and ceramic crucibles are very complicated physical-chemical process. The experimental results in this study showed that the alloy melting experiments were carried out in the crucibles with different compositions under the same experimental conditions, and the amount of oxide inclusions in the metal was different after the experiment. The amount of oxide inclusions in the alloy melted with pure Y2O3 crucible was the smallest. However, in the composite crucibles, the amount of oxide inclusions decreased with the addition of Al2O3. When the amount of Al2O3 added was 3.5 wt %, the proportion of inclusions in the metal was largest.
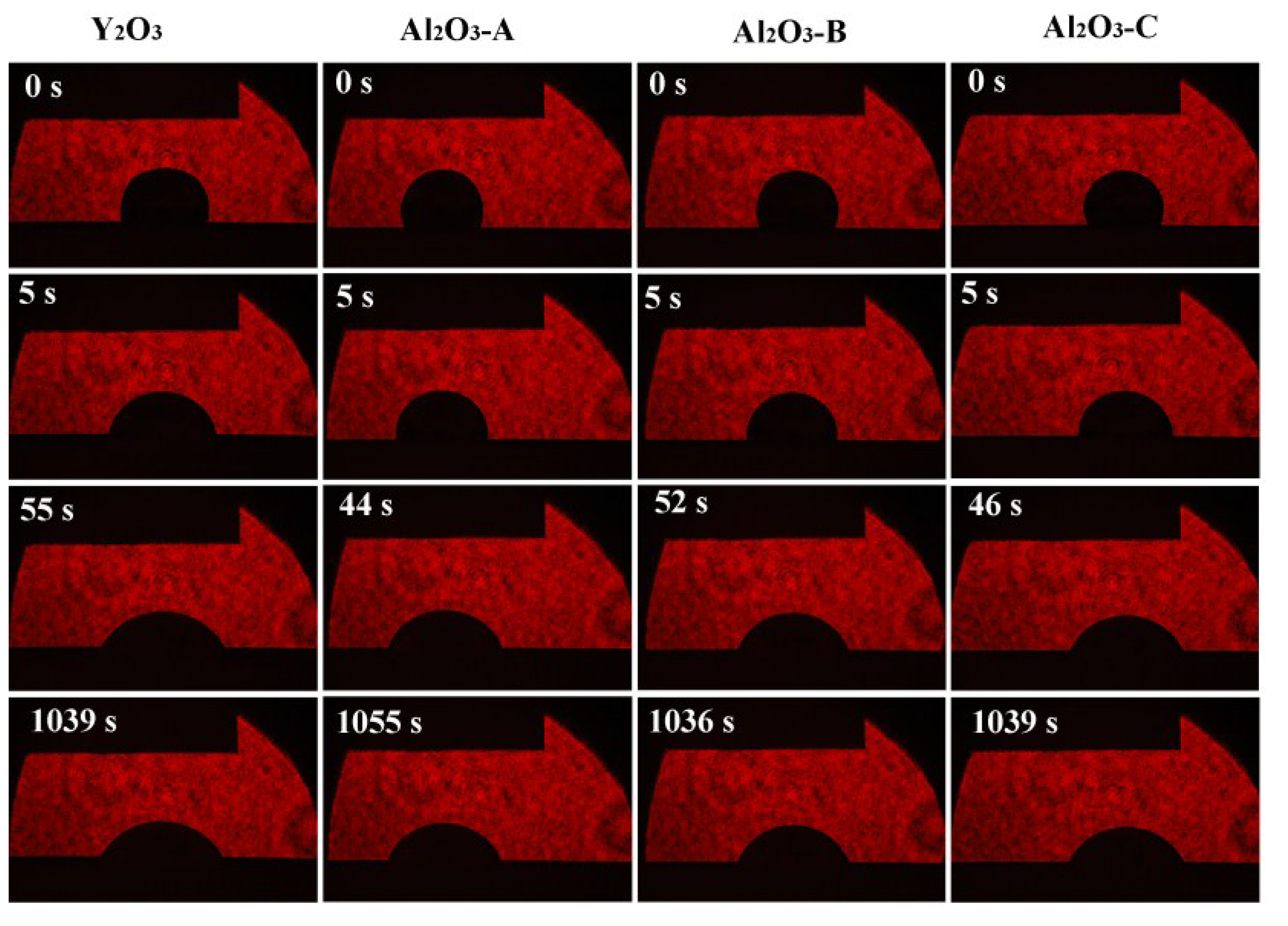
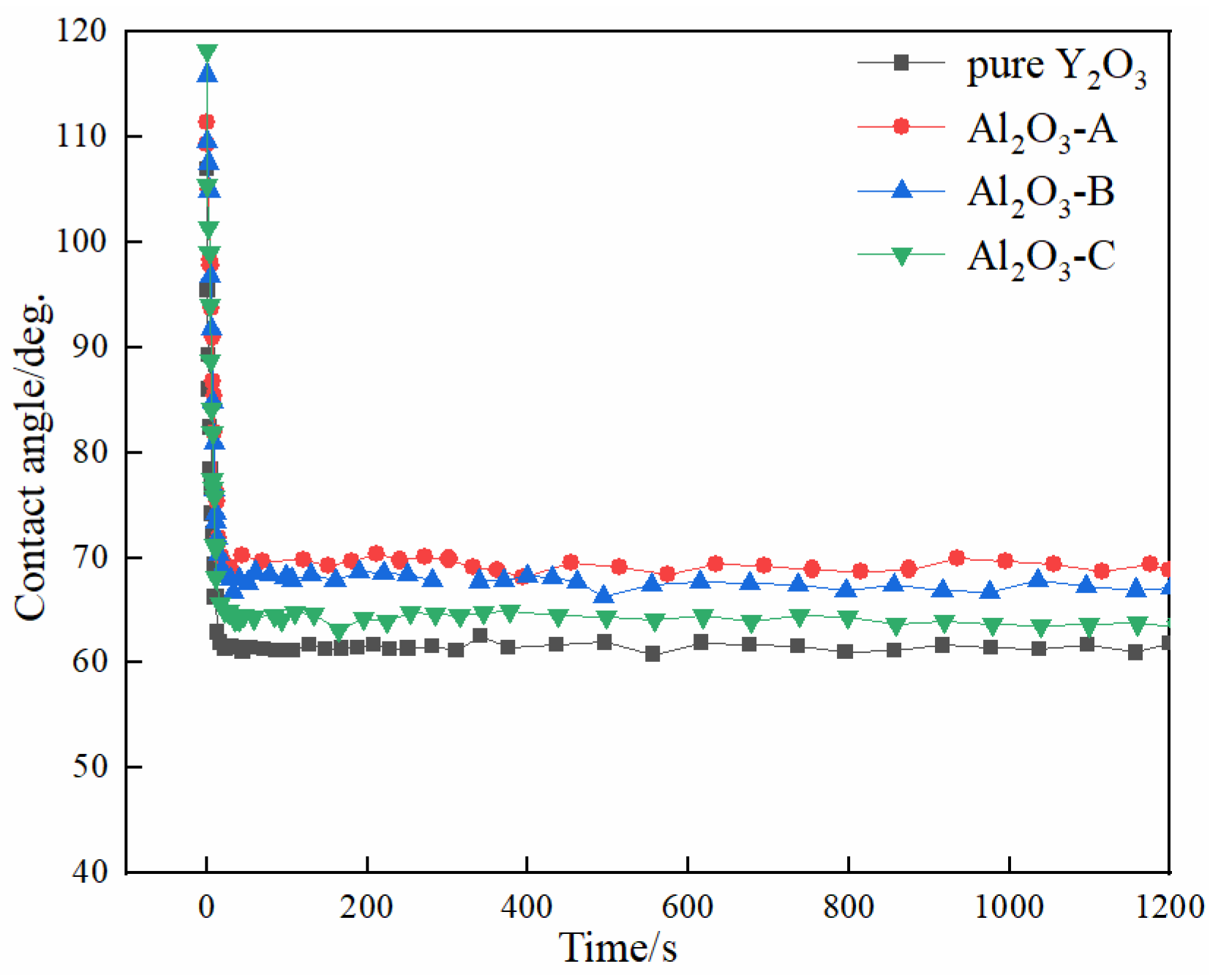
From the chemical point of view, the pure Y2O3 crucible without Al2O3 was more thermodynamically stable than composite crucibles with Al2O3. The Al2O3 and TiO2 detected in the interfacial layer (Figure 4) were presumably speculated to be formed by the combination of free O and Ti atoms and Al atoms in the melt during the metal melting experiment. In the metal melting experiment, the amount of oxide inclusions in the pure Y2O3 crucible entering the metal was the least because Y2O3 has higher chemical stability than Al2O3 and is less likely to react chemically with the molten alloy. Therefore, the number of oxide inclusions in the alloy obtained by Al2O3-A, Al2O3-B and Al2O3-C crucibles was higher than that of the pure Y2O3 crucible. Secondly, from the physical effect, the high temperature metal melt has a physical erosion effect on the crucible. The microstructure of the crucible surface (Figure 1) showed that the Y2O3 particles were the largest on the surface of the pure Y2O3 crucible, the porosity was the smallest and the surface was the most compact. In order to further clarify the mechanism of interaction between molten metal and the crucible, high temperature wetting experiments between metal and crucibles were performed. As shown in Figure 8 and Figure 9, the initial contact angles and the equilibrium contact angles of the molten metal and crucible varied with the change in composition. The initial contact angles of the pure Y2O3, Al2O3-A, Al2O3-B and Al2O3-C were 107°, 111.4°, 115.9° and 118.2°, respectively. The equilibrium contact angles were 61.5°, 69.3°, 67.7° and 64.2°, respectively. During the melting experiment, the high temperature metal melt contacted well with the crucible, and the crucible itself had high strength. Liquid metal can quickly form a protective film on the surface of the crucible, thus preventing more oxide particles from the crucible falling into the metal melt. The Al2O3-C crucible surface microstructure had fine grains, and the highest content of Al2O3 added to produce more Y3Al5O12. Y3Al5O12 belongs to cubic crystal system, with garnet structure, high temperature resistance and strength at high temperatures, and its wettability was similar to that of the pure Y2O3 crucible, so it can reduce the loss to the oxide crucible alloy. The degree of interaction between the melt and composite crucible (Al2O3-A and Al2O3-B) is stronger than that between the pure Y2O3 crucible and the melt, and weaker than that between the Al2O3-C crucible and the melt. The crucible structure was relatively loose, and the wettability between metal and interface was relatively poor. Therefore, the corrosion of metal in the crucible was considerable, and the content of oxide inclusions in molten alloys was higher than that in pure Y2O3 and Al2O3-C.
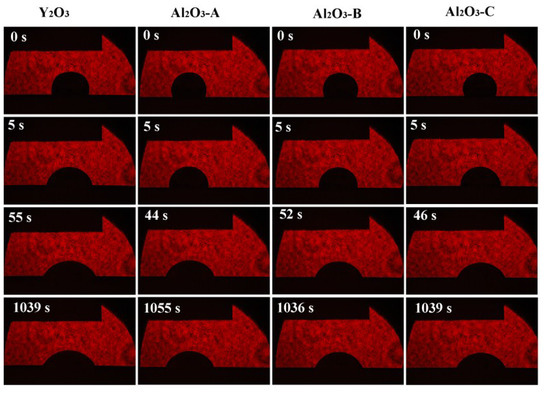
Figure 8.
Wetting process of the Ti-47Al-2Cr-2Nb alloys on substrates with various compositions at 1873 K.
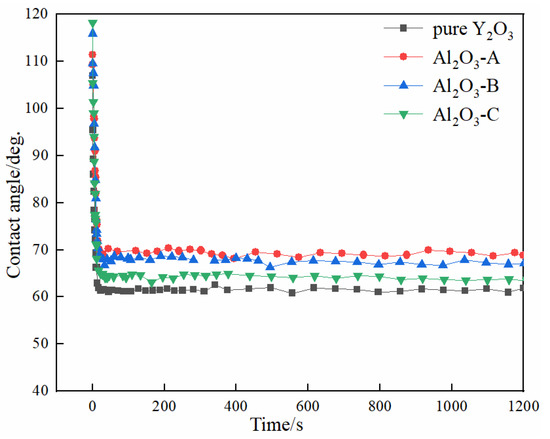
Figure 9.
Variation of contact angle with time at 1873 K.
5. Conclusions
The TiAl-based alloy was melted in Y2O3-based composite crucibles with an Al2O3 content of 0 wt %, 3.5 wt %, 7.0 wt % and 10.5 wt %, based on which the interfacial reactions and associated mechanisms between TiAl-based alloy and composite crucibles were discussed. The primary conclusions of this work were as follows.
The chemical stability of the pure Y2O3 crucible was the best. After the melting experiment, the number of inclusions in the interior of the metal particles and the reactants at the interface layer with the pure yttrium crucible were the lowest. With the increase in the amount of Al2O3, the interfacial reaction between the composite crucible and the molten alloy became weaker. When the content of Al2O3 in the composite crucible increased from 3.5 wt % to 10.5 wt %, the thickness of the interface layer of the melt-crucible decreased from 150 µm to 50 µm. The addition of Al2O3 increased the wettability of the composite crucible with the metal melt. The equilibrium contact angles between metal and crucible under 1873 K decreased from 69.3° to 64.2°.
Author Contributions
H.Z. (Huarui Zhang) and H.Z. (Hu Zhang) conceived and designed the experiments; Y.C. and M.G. performed the experiments; Q.L. and J.L. analyzed the data; Y.C. and C.Y. contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools; Q.L. and H.Z. (Huarui Zhang) wrote the paper.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Science & Technology Pillar Program of China (No. 2013BAB11B04) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51404017 and 51604014).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Science & Technology Pillar Program of China (No. 2013BAB11B04) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51404017 and 51604014). Furthermore, the authors wish to express their appreciation to the State Key Laboratory of Refractories and Metallurgy, Wuhan University of Science and Technology, and the group of Prof. Shen of Jilin University for the help with the wetting experiments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Barbosa, J.; Ribeiro, C.S.; Monteiro, A.C. Influence of superheating on casting of γ-TiAl. Intermetallics 2007, 15, 945–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imayev, R.M.; Imayev, V.M.; Oehring, M.; Appel, F. Alloy design concepts for refined gamma titanium aluminide based alloys. Intermetallics 2007, 15, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renjie, C.; Ming, G.; Hu, Z.; Shengkai, G. Interactions between tial alloys and yttria refractory material in casting process. J. Mater. Process. Tech. 2010, 210, 1190–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Dong, S.; Guo, J.; Ding, H.; Su, Y.; Fu, H. Investigation of macro/microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of directionally solidified high-Nb Tial-based alloy. Mater. Des. 2016, 89, 492–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voisin, T.; Monchoux, J.-P.; Hantcherli, M.; Mayer, S.; Clemens, H.; Couret, A. Microstructures and mechanical properties of a multi-phase β-solidifying TiAl alloy densified by spark plasma sintering. Acta Mater. 2014, 73, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, J.; Zhang, L.; Ge, G.; Lin, J. Characterization of microstructure evolution in β-γ TiAl alloy containing high content of niobium using constitutive equation and power dissipation map. Mater. Des. 2016, 107, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.W. Inhomogeneous microstructure in highly alloyed cast TiAl-based alloys, caused by microsegregation. Scr. Mater. 2005, 52, 1021–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Gao, M.; Li, Q.; Bian, W.; Tao, T.; Zhang, H. High-temperature wettability and interactions between y-containing Ni-based alloys and various oxide ceramics. Materials 2018, 11, 749–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kima, M.; Ohb, M.; Leec, J.; Inuid, H.; Yamaguchid, M.; Weea, D. Composition and growth rate effects in directionally solidified TiAl alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1997, 239, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapin, J.; Gabalcová, Z. Solidification behaviour of TiAl-based alloys studied by directional solidification technique. Intermetallics 2011, 19, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.F.; Lin, J.P.; Zhang, L.Q.; Su, Y.Q.; Chen, G.L. Microstructural control of TiAl–Nb alloys by directional solidification. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetsui, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Harada, H. Achieving high strength and low cost for hot-forged TiAl based alloy containing β phase. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 552, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, R.J.; Tang, X.X.; Gao, M.; Zhang, H.; Gong, S.K. Microstructure and composition of cast Ti–47Al–2Cr–2Nb alloys produced by yttria crucibles. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 541, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Tang, X.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S. Comparison of directional solidification of γ-TiAl alloys in conventional Al2O3 and novel Y2O3-coated Al2O3 crucibles. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2013, 33, 925–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, F.; Barbosa, J.; Ribeiro, C.S. Induction melting of γ-TiAl in CaO crucibles. Intermetallics 2008, 16, 1292–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetsui, T. Development of a TiAl turbocharger for passenger vehicles. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 2002, 329, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, D.E.; Christodoulou, L.; Kampe, S.L.; Sadler, R. Investment-cast processing of xdtm near-γ titanium aluminides. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1991, 144, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, S.-Y.; Kim, Y.-J. Modeling of titanium aluminides turbo-charger casting. Intermetallics 2007, 15, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myounggyun, K.; Kim, S.; Youngjig, K. Effect of mold material and binder on metal-mold interfacial reaction for investment castings of titanium alloys. Mater. Trans. 2005, 43, 745–750. [Google Scholar]
- Kostov, A.; Friedrich, B. Predicting thermodynamic stability of crucible oxides in molten titanium and titanium alloys. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2006, 38, 374–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, J.P.; Harding, R.A.; Campbell, J. Investigation into refractories as crucible and mould materials for melting and casting γ-TiAl alloys. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2013, 16, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.; Fujii, H.; Nogi, K. Wetting, Wetting, adhesion and diffusion in Cu-Al/SiO system at 1473k. Scr. Mater. 2005, 52, 1259–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.R.; Tang, X.X.; Zhou, L.; Gao, M.; Zhou, C.G.; Zhang, H. Interactions between Ni-44Ti-5Al-2Nb-Mo alloy and oxide ceramics during directional solidification process. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 6451–6458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mah, T.I.; Petry, M.D. Eutectic composition in the pseudobinary of Y4Al2O9 and Y2O3. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 75, 2006–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolitsch, U.; Seifert, H.J.; Ludwig, T.; Aldinger, F. Phase equilibria and crystal chemistry in the Y2O3-Al2O3-SiO2 system. J. Mater. Res. 1999, 14, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamane, H.; Omori, M.; Hiral, T. Thermogravimetry and Rietveld analysis for the high-temperature X-ray powder diffraction pattern of Y4Al2O9. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1995, 14, 470–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).