The Effect of Zn Content on the Mechanical Properties of Mg-4Nd-xZn Alloys (x = 0, 3, 5 and 8 wt.%)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
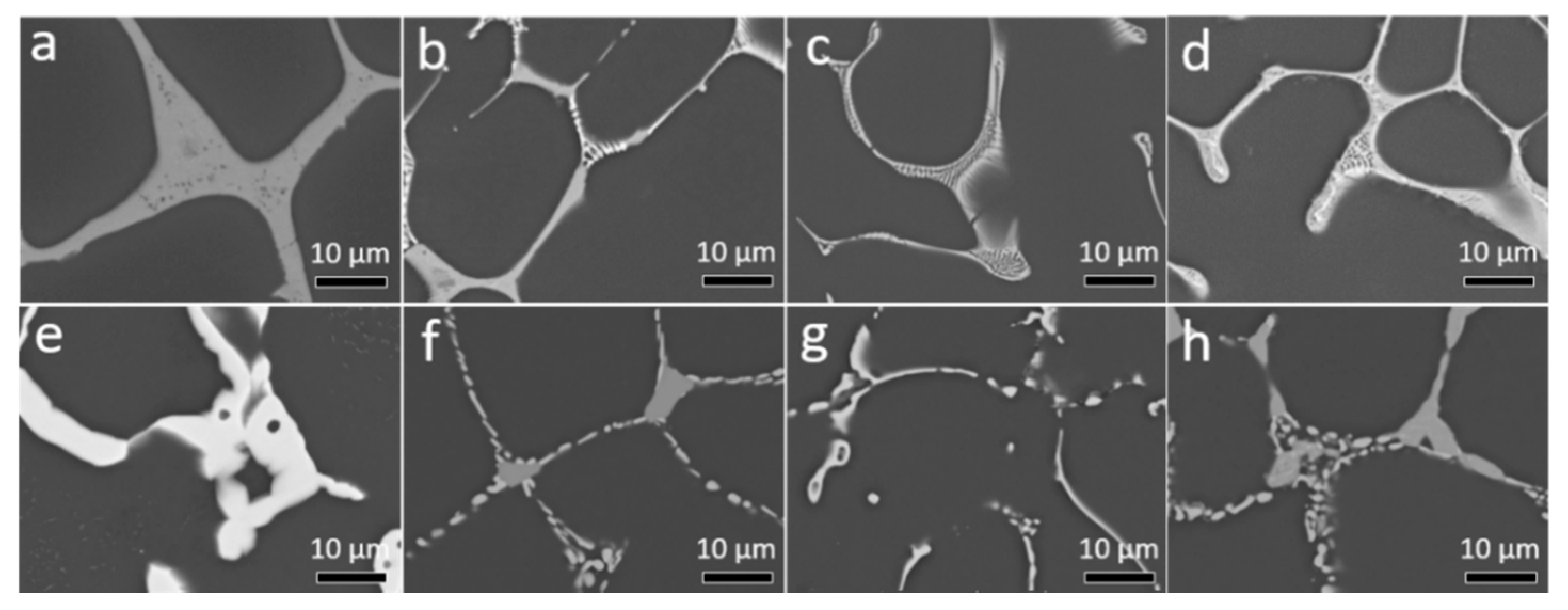
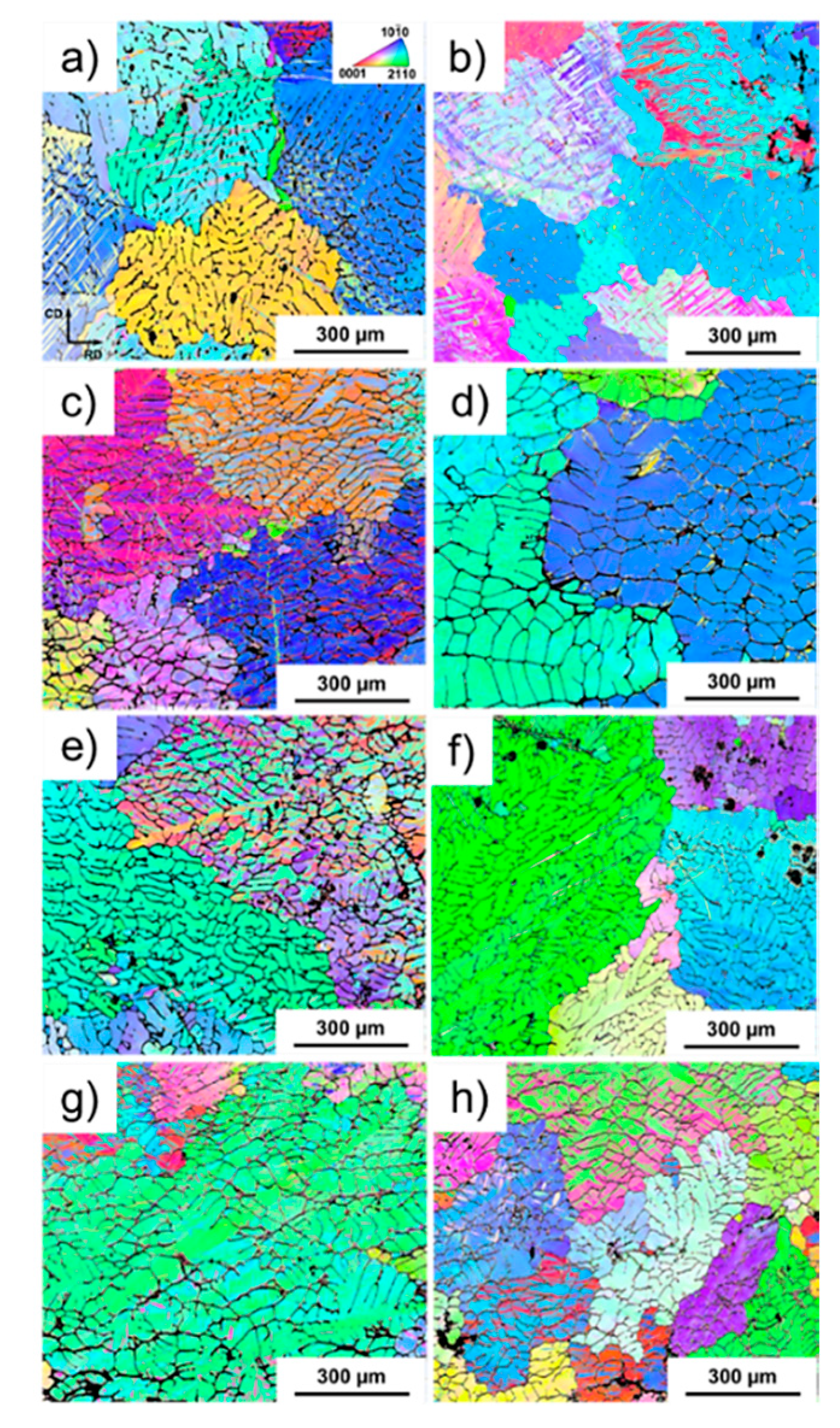
3.1. Metallography
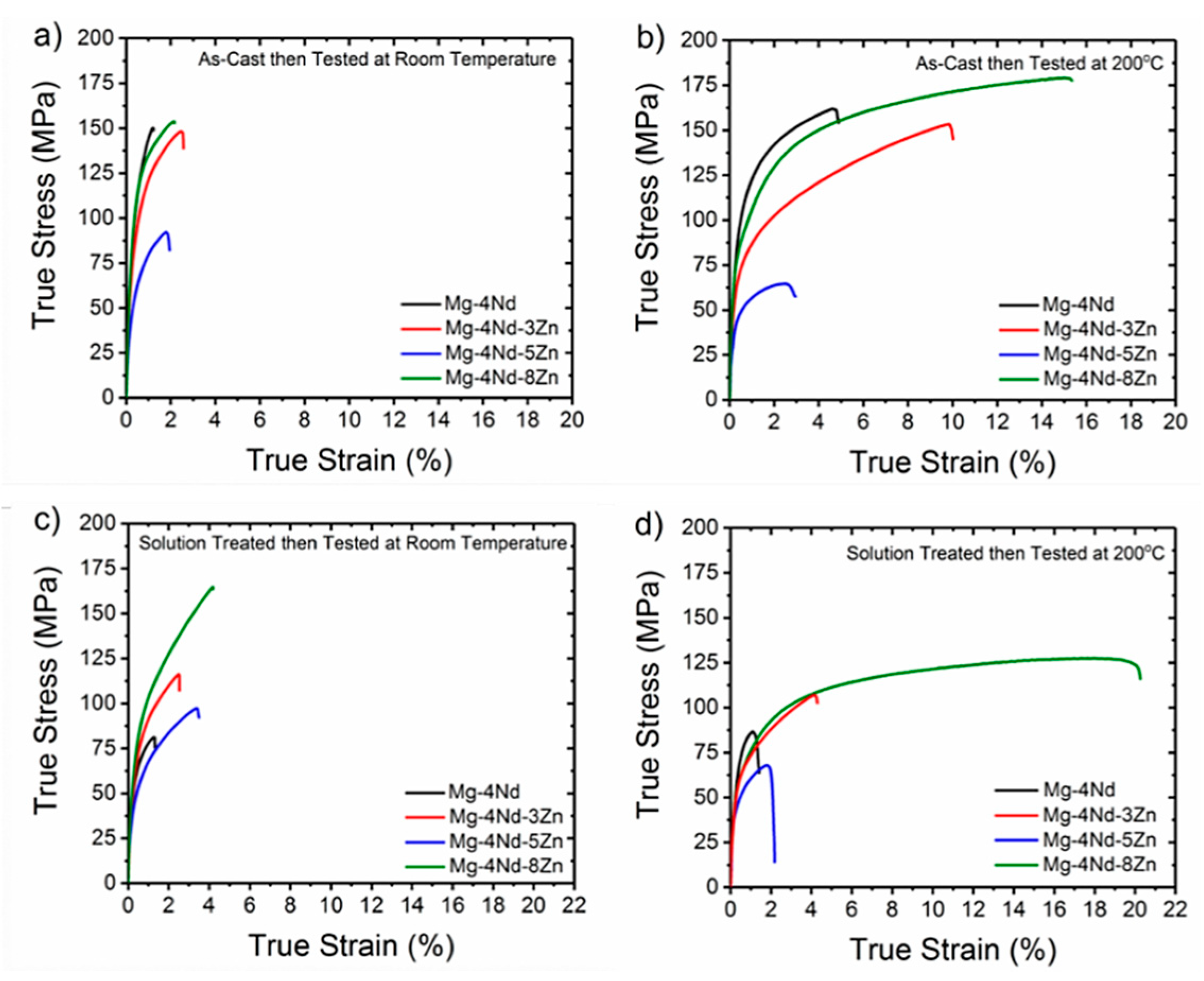
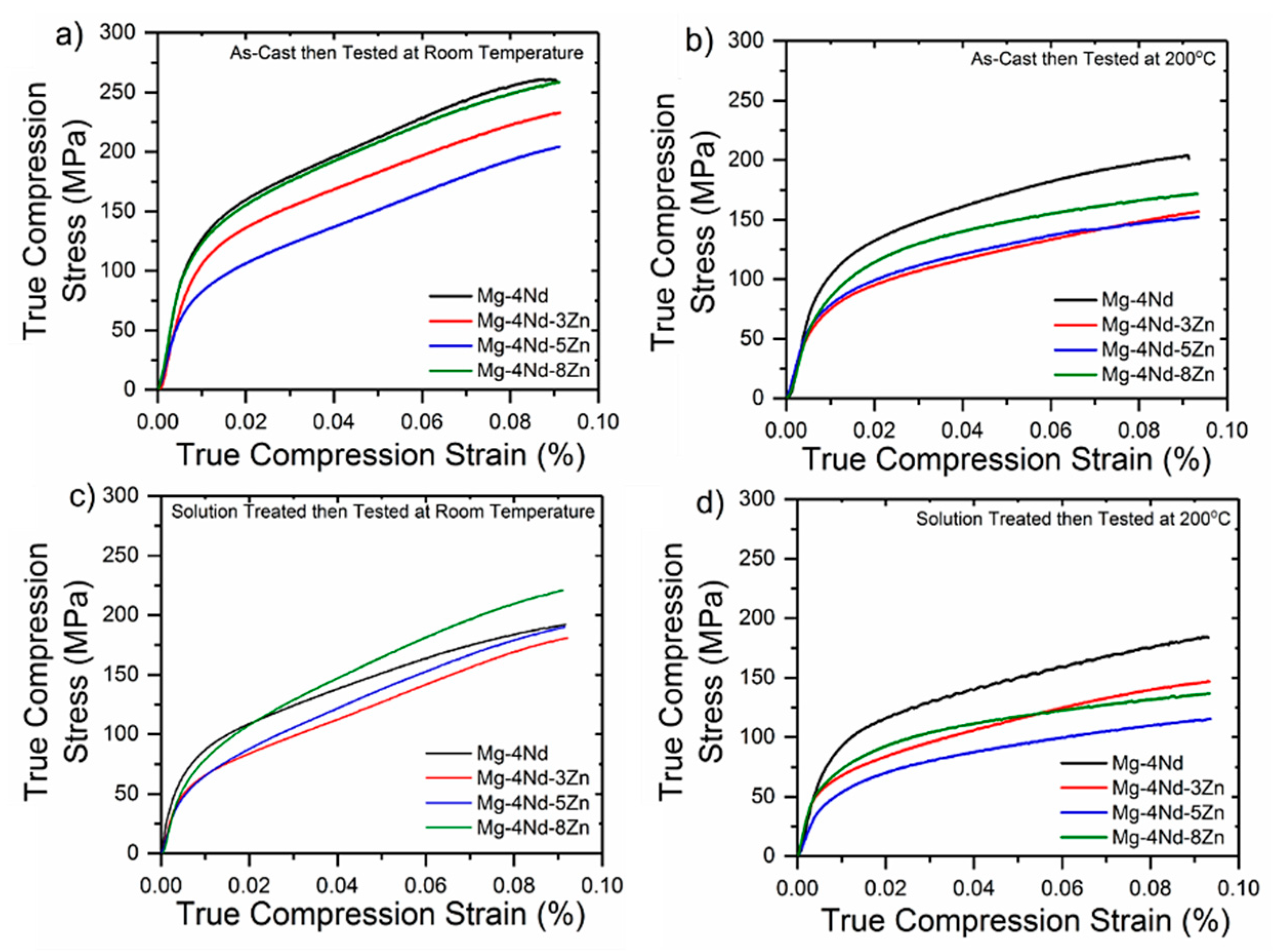
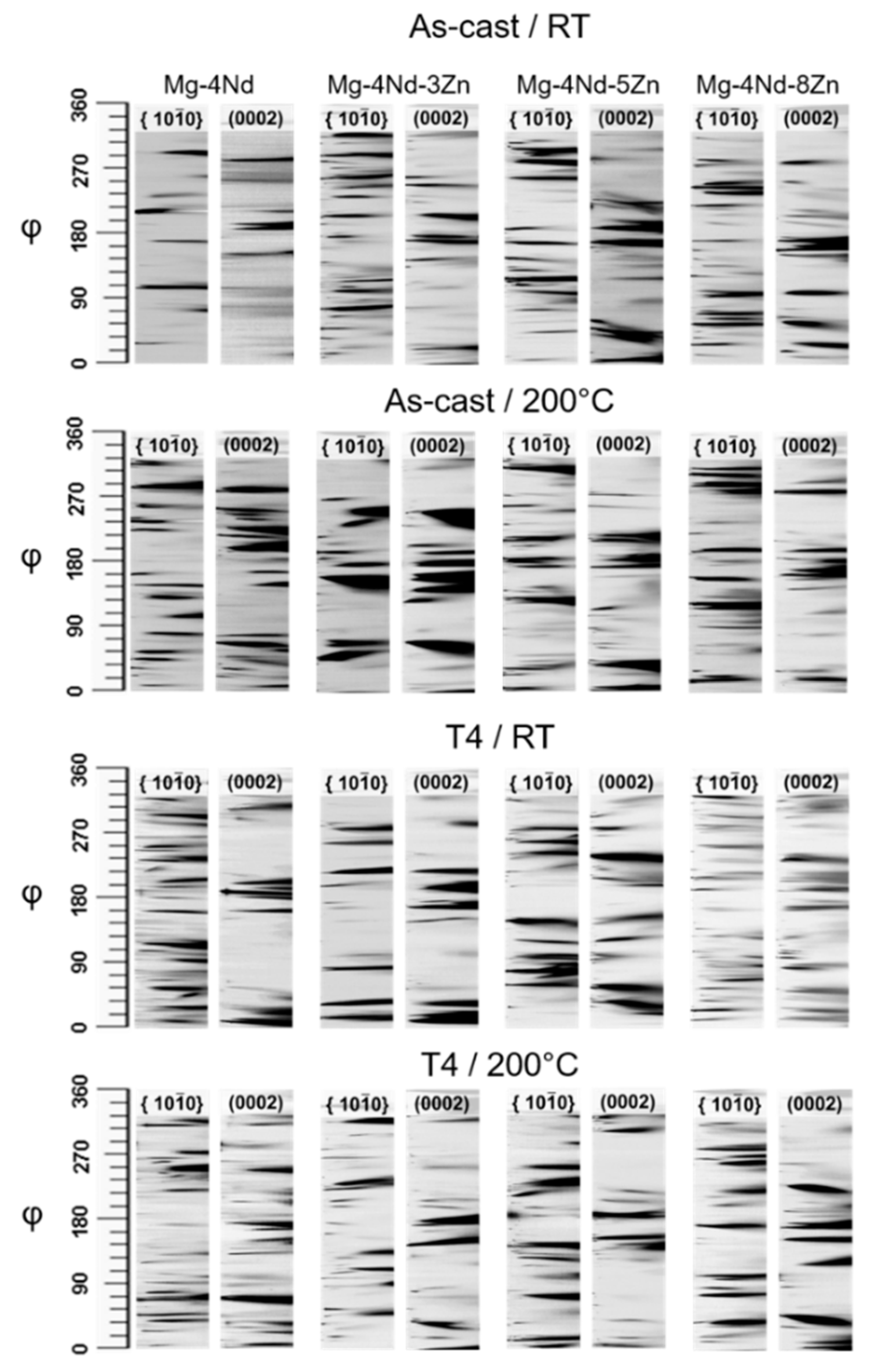
3.2. Mechanical Properties
3.3. In Situ Compression Experiments
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pekguleryuz, M.; Kainer, K.; Kaya, A. Fundamentals of Magnesium Alloy Metallurgy; Woodhead: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Avedesian, M.M.; Baker, H. Magnesium and Magnesium Alloys; ASM Specialty Handbook; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Feyerabend, F.; Fischer, J.; Holtz, J.; Witte, F.; Willumeit, R.; Drücker, H.; Vogt, C.; Hort, N. Evaluation of short-term effects of rare earth and other elements used in magnesium alloys on primary cells and cell lines. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 1834–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.M.; Peng, L.M.; Zeng, X.Q.; Ding, W.J.; Zhu, Y.P. Comparison of the microstructure and mechanical properties of a ZK60 alloy with and without 1.3 wt.% gadolinium addition. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 433, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Ding, W. Influence of temperature and strain rate on serration type transition in NZ31 Mg alloy. J. Alloy. Compd. 2007, 427, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homma, T.; Mendis, C.L.; Hono, K.; Kamado, S. Effect of Zr addition on the mechanical properties of as-extruded Mg-Zn-Ca-Zr alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 2356–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.Y.; Tezuka, H.; Kamio, A. Mechanical Properties and Structure of Ignition-Proof Mg-Ca-Zr Alloys Produced by Squeeze Casting. Mater. Trans. 1997, 38, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Liu, M.; Wu, G.; Ding, W.; Zhu, Y. Tensile properties of extruded ZK60–RE alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 349, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.T.; Zhang, Z.D.; Liu, C.M.; Wang, Q.W. Effect of Nd and Y on the microstructure and mechanical properties of ZK60 alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 445–446, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanford, N.; Atwell, D.; Beerb, A.; Davies, C.; Barnett, M.R. Effect of microalloying with rare-earth elements on the texture of extruded magnesium-based alloys. Scr. Mater. 2008, 59, 772–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langelier, B.; Nasiri, A.M.; Lee, S.Y.; Gharghouri, M.A.; Esmaeili, S. Improving microstructure and ductility in the Mg-Zn alloy system by combinational Ce-Ca microalloying. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 620, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leontis, T.E. The properties of sand cast magnesium-rare earth alloys. J. Met. 1949, 185, 968–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokhlin, L.L. Magnesium Alloys Containing Rare Earth Metals; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2003; ISBN 0-415-28414-7. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, P.H.; Peng, L.M.; Jiang, H.Y.; Chang, J.W.; Zhai, C.Q. Effects of heat treatments on the microstructures and mechanical properties of Mg-3Nd-0.2Zn-0.4Zr (wt.%) alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 486, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Chen, R.S.; Ke, W. Microstructure and mechanical properties of a sand-cast Mg-Nd-Zn alloy. Mater. Des. 2014, 58, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Wang, W.; Huang, H.; Pei, J.; Qu, H.; Yuan, G.; Li, Y. The degradation and transport mechanism of a Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr stent in rabbit common carotid artery: A 20-month study. Acta Biomater. 2018, 69, 372–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonardelli, I.; Gey, N.; Wenk, H.R.; Humbert, M.; Vogel, S.C.; Lutterotti, L. In situ observation of texture evolution during α→β and β→α phase transformations in titanium alloys investigated by neutron diffraction. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 5718–5727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwanpinij, P.; Stark, A.; Li, X.; Römer, F.; Herrmann, K.; Lippmann, T.; Bleck, W. In Situ High Energy X-ray Diffraction for Investigating the Phase Transformation in Hot Rolled TRIP-Aided Steels. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2014, 16, 1044–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liss, K.D.; Yan, K. Thermo-mechanical processing in a synchrotron beam. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 528, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzolin, R.H.; Tolnai, D.; Mendis, C.L.; Stark, A.; Schell, N.; Pinto, H.; Kainer, K.U.; Hort, N. In situ synchrotron radiation diffraction study of the role of Gd, Nd on the elevated temperature compression behavior of ZK40. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 640, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzolin, R.H.; Mendis, C.L.; Tolnai, D.; Stark, A.; Schell, N.; Pinto, H.; Kainer, K.U.; Hort, N. In situ synchrotron radiation diffraction investigation of the compression behaviour at 350 °C of ZK40 alloys with addition of CaO and Y. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 664, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavras, S.; Subroto, T.; Buzolin, R.H.; Hort, N.; Tolnai, D. The Role of Zn Additions on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Mg-Nd-Zn Alloys. Int. J. Metalcast. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, F.R.; Hort, N.; Salgado Ordorica, M.A.; Kainer, K.U. Magnesium Permanent Mold Castings Optimization. Mater. Sci. Forum 2011, 690, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIN 50125, Testing of Metallic Materials—Tensile Test Pieces; DIN: Berlin, Germany, 2009.
- Tolnai, D.; Szakács, G.; Requena, G.; Stark, A.; Schell, N.; Kainer, K.; Hort, N. Study of the Solidification of AS Alloys Combining in situ Synchrotron Diffraction and Differential Scanning Calorimetry. Mater. Sci. Forum 2013, 765, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easton, M.A.; Gibson, M.A.; Qiu, D.; Zhu, S.M.; Gröbner, J.; Schmid-Fetzer, R.; Nie, J.F.; Zhang, M.X. The role of Crystallography and Thermodynamics on Phase Selection in Binary Magnesium-Rare Earth (Ce or Nd) Alloys. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 4420–4430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Gavras, S.; Nagasekhar, A.V.; Caceres, C.H.; Easton, M.A. The Strength of the Spatially Interconnected Eutectic Network in HPDC Mg-La, Mg-Nd, and Mg-La-Nd Alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2014, 45, 4386–4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Alloy (wt.%) | Nd wt.% (XRF) | Zn wt.% (Spark Analyzer) |
|---|---|---|
| Mg-4Nd | 4.20 | – |
| Mg-4Nd-3Zn | 4.35 | 3.20 |
| Mg-4Nd-5Zn | 4.20 | 5.20 |
| Mg-4Nd-8Zn | 4.34 | 8.00 |
| Alloy (wt.%) | Grain Size in As-Cast Condition (mm) ± SD | Grain Size in Solution Treated Condition (mm) ± SD |
|---|---|---|
| Mg-4Nd | 0.99 ± 0.14 | 1.13 ± 0.07 |
| Mg-4Nd-3Zn | 0.55 ± 0.03 | 0.76 ± 0.04 |
| Mg-4Nd-5Zn | 0.36 ± 0.02 | 0.38 ± 0.01 |
| Mg-4Nd-8Zn | 0.20 ± 0.02 | 0.14 ± 0.02 |
| Alloy (wt.%) | Ave 0.2% PS ± SD (MPa) | Ave UTS ± SD (MPa) | Ave Elong ± SD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| As-Cast Tested at Room Temperature | |||
| Mg-4Nd | 103.4 ± 1.8 | 147.7 ± 17.0 | 1.2 ± 0.3 |
| Mg-4Nd-3Zn | 81.7 ± 2.1 | 143.6 ± 6.6 | 2.5 ± 0.3 |
| Mg-4Nd-5Zn | 50.0 ± 1.5 | 84.9 ± 10.1 | 1.7 ± 0.7 |
| Mg-4Nd-8Zn | 105.1 ± 1.9 | 151.4 ± 2.1 | 2.0 ± 0.1 |
| Solution Treated Tested at Room Temperature | |||
| Mg-4Nd | 53.6 ± 4.5 | 80.2 ± 28.5 | 2.0 ± 1.0 |
| Mg-4Nd-3Zn | 66.7 ± 11.7 | 113.0 ± 20.1 | 2.5 ± 0.7 |
| Mg-4Nd-5Zn | 46.1 ± 10.9 | 107.7 ± 31.1 | 3.2 ± 0.7 |
| Mg-4Nd-8Zn | 71.1 ± 3.1 | 163.9 ± 27.7 | 4.3 ± 1.7 |
| As-Cast Tested at 200 °C | |||
| Mg-4Nd | 96.8 ± 2.1 | 169.3 ± 12.1 | 4.9 ± 1.3 |
| Mg-4Nd-3Zn | 69.7 ± 2.7 | 152.8 ± 3.4 | 9.9 ± 1.4 |
| Mg-4Nd-5Zn | 44.9 ± 1.0 | 66.1 ± 3.2 | 3.2 ± 0.8 |
| Mg-4Nd-8Zn | 83.9 ± 3.2 | 177.7 ± 4.7 | 15.2 ± 0.5 |
| Solution Treated Tested at 200 °C | |||
| Mg-4Nd | 68.5 ± 15.5 | 83.4 ± 4.7 | 1.6 ± 0.3 |
| Mg-4Nd-3Zn | 62.3 ± 9.5 | 97.1 ± 8.6 | 3.7 ± 1.0 |
| Mg-4Nd-5Zn | 43.8 ± 1.3 | 66.9 ± 3.1 | 1.9 ± 0.4 |
| Mg-4Nd-8Zn | 61.4 ± 1.3 | 125.1 ± 2.6 | 17.8 ± 6.8 |
| Alloy (wt.%) | Ave 0.2% PS ± SD (MPa) | Ave UCS ± SD (MPa) | Ave Comp. ± SD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| As-Cast Tested at Room Temperature | |||
| Mg-4Nd | 103.2 (±5.0) | 257.4 (±11.3) | 8.3 (±0.7) |
| Mg-4Nd-3Zn | 87.9 (±2.8) | 226.3 (±6.7) | 9.0 (±0.9) |
| Mg-4Nd-5Zn | 88.9 (±1.3) | 283.1 (±5.0) | 13.7 (±1.0) |
| Mg-4Nd-8Zn | 115.0 (±1.6) | 311.9 (±4.4) | 13.0 (±1.7) |
| Solution Treated Tested at Room Temperature | |||
| Mg-4Nd | 87.1 (±2.4) | 285.0 (±20.6) | 14.4 (±2.1) |
| Mg-4Nd-3Zn | 80.9 (±2.4) | 285.1 (±6.2) | 11.3 (±1.2) |
| Mg-4Nd-5Zn | 69.0 (±5.1) | 356.6 (±14.1) | 13.9 (±1.2) |
| Mg-4Nd-8Zn | 78.9 (±3.7) | 375.4 (±3.7) | 13.2 (±0.2) |
| As-Cast Tested at 200 °C | |||
| Mg-4Nd | 99.5 (±7.1) | 198.8 (±13.1) | 10.2 (±1.0) |
| Mg-4Nd-3Zn | 68.8 (±3.2) | 203.7 (±10.9) | 12.3 (±1.1) |
| Mg-4Nd-5Zn | 67.8 (±1.9) | 218.7 (±9.4) | 25.8 (±2.1) |
| Mg-4Nd-8Zn | 89.7 (±0.4) | 230.1 (±0.3) | 26.4 (±1.0) |
| Solution Treated Tested at 200 °C | |||
| Mg-4Nd | 87.3 (±4.2) | 258.3 (±5.5) | 12.4 (±0.6) |
| Mg-4Nd-3Zn | 67.2 (±1.4) | 238.6 (±5.5) | 18.0 (±2.0) |
| Mg-4Nd-5Zn | 55.8 (±3.4) | 265.9 (±8.6) | 27.8 (±2.0) |
| Mg-4Nd-8Zn | 69.3 (±0.5) | 300.2 (±9.8) | 33.9 (±1.5) |
| 0.2% Proof Stress ± SD (MPa) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alloy (wt.%) | As-Cast at RT | As-Cast at 200 °C | Solution Treated at RT | Solution Treated at 200 °C |
| Mg-4Nd | 106.8 (± 5.2) | 80.4 (± 3.8) | 63.2 (±1.5) | 74.4 (±1.4) |
| Mg-4Nd-3Zn | 88.2 (±2.9) | 66.9 (±1.6) | 56.2 (±2.9) | 50.5 (±3.3) |
| Mg-4Nd-5Zn | 69.2 (±1.5) | 66.7 (±1.5) | 50.2 (±1.4) | 48.3 (±2.4) |
| Mg-4Nd-8Zn | 100.3 (±4.4) | 83.4 (±8.0) | 63.5 (±0.1) | 57.7 (±1.6) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gavras, S.; Buzolin, R.H.; Subroto, T.; Stark, A.; Tolnai, D. The Effect of Zn Content on the Mechanical Properties of Mg-4Nd-xZn Alloys (x = 0, 3, 5 and 8 wt.%). Materials 2018, 11, 1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071103
Gavras S, Buzolin RH, Subroto T, Stark A, Tolnai D. The Effect of Zn Content on the Mechanical Properties of Mg-4Nd-xZn Alloys (x = 0, 3, 5 and 8 wt.%). Materials. 2018; 11(7):1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071103
Chicago/Turabian StyleGavras, Serge, Ricardo H. Buzolin, Tungky Subroto, Andreas Stark, and Domonkos Tolnai. 2018. "The Effect of Zn Content on the Mechanical Properties of Mg-4Nd-xZn Alloys (x = 0, 3, 5 and 8 wt.%)" Materials 11, no. 7: 1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071103
APA StyleGavras, S., Buzolin, R. H., Subroto, T., Stark, A., & Tolnai, D. (2018). The Effect of Zn Content on the Mechanical Properties of Mg-4Nd-xZn Alloys (x = 0, 3, 5 and 8 wt.%). Materials, 11(7), 1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071103






