Effect of Polyacrylic Acid on Rheology of Cement Paste Plasticized by Polycarboxylate Superplasticizer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Test Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Cement
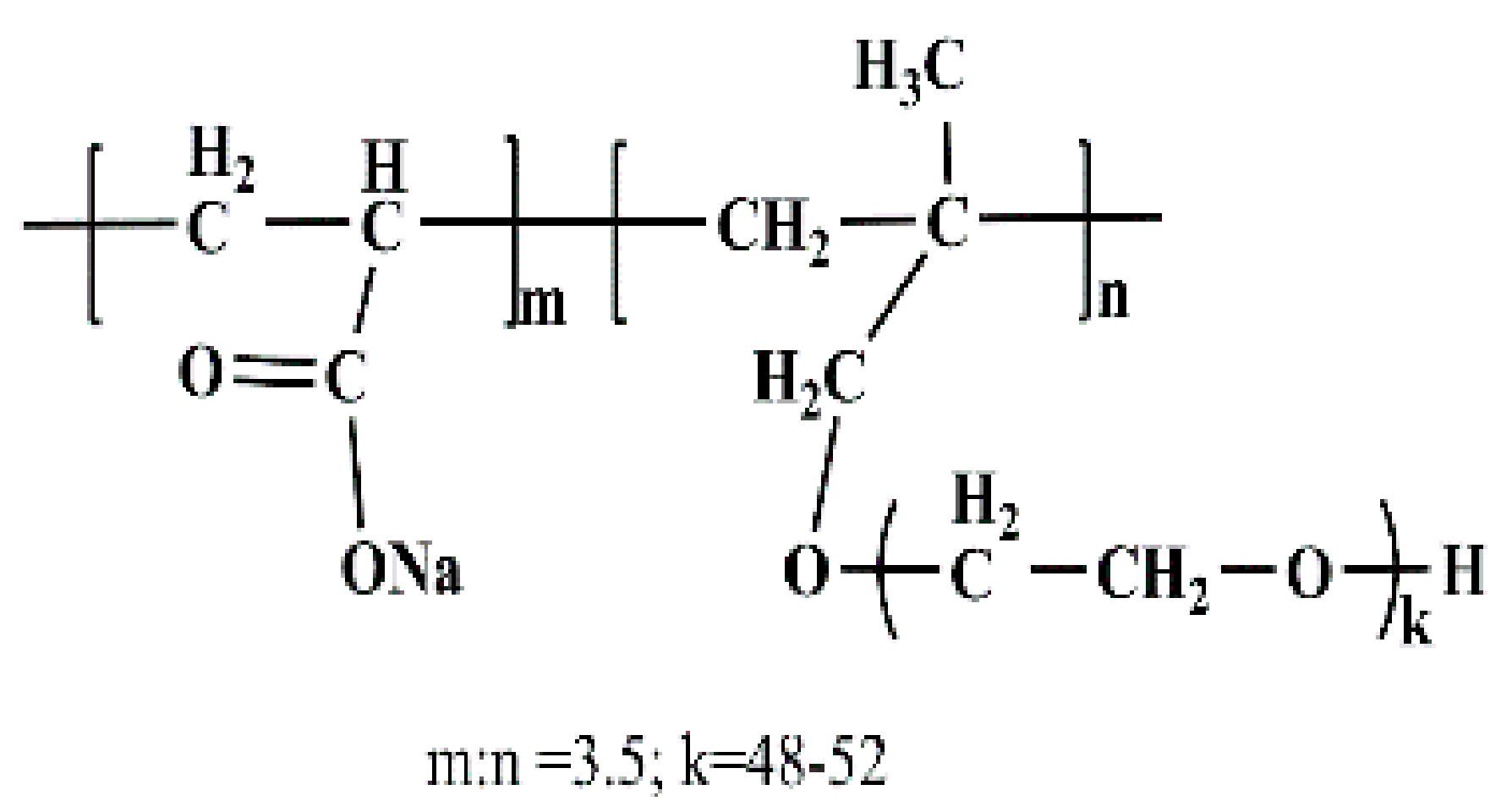
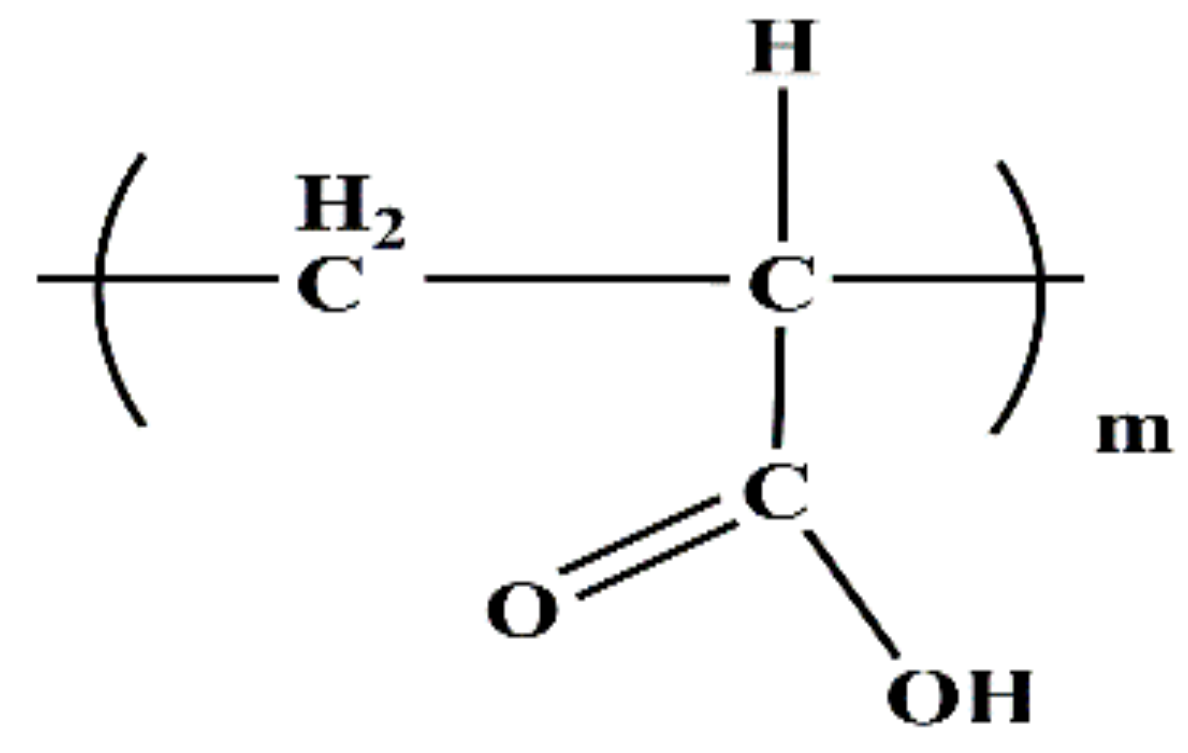
2.1.2. Additives
2.2. Test Methods
2.2.1. Fluidity Performance
2.2.2. Rheology Performance
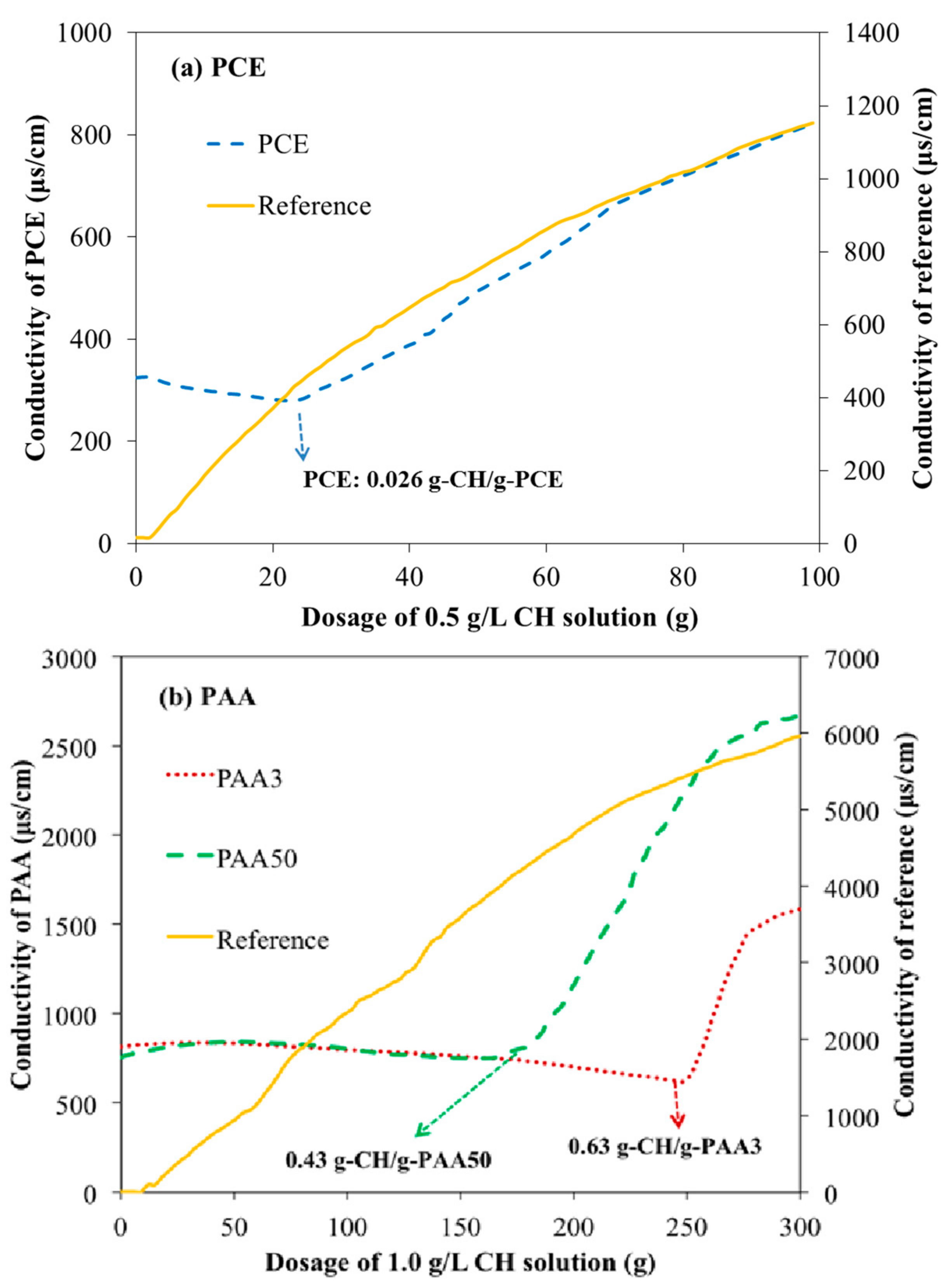
2.2.3. Adsorption Amount
2.2.4. Zeta Potential
2.2.5. Conductivity
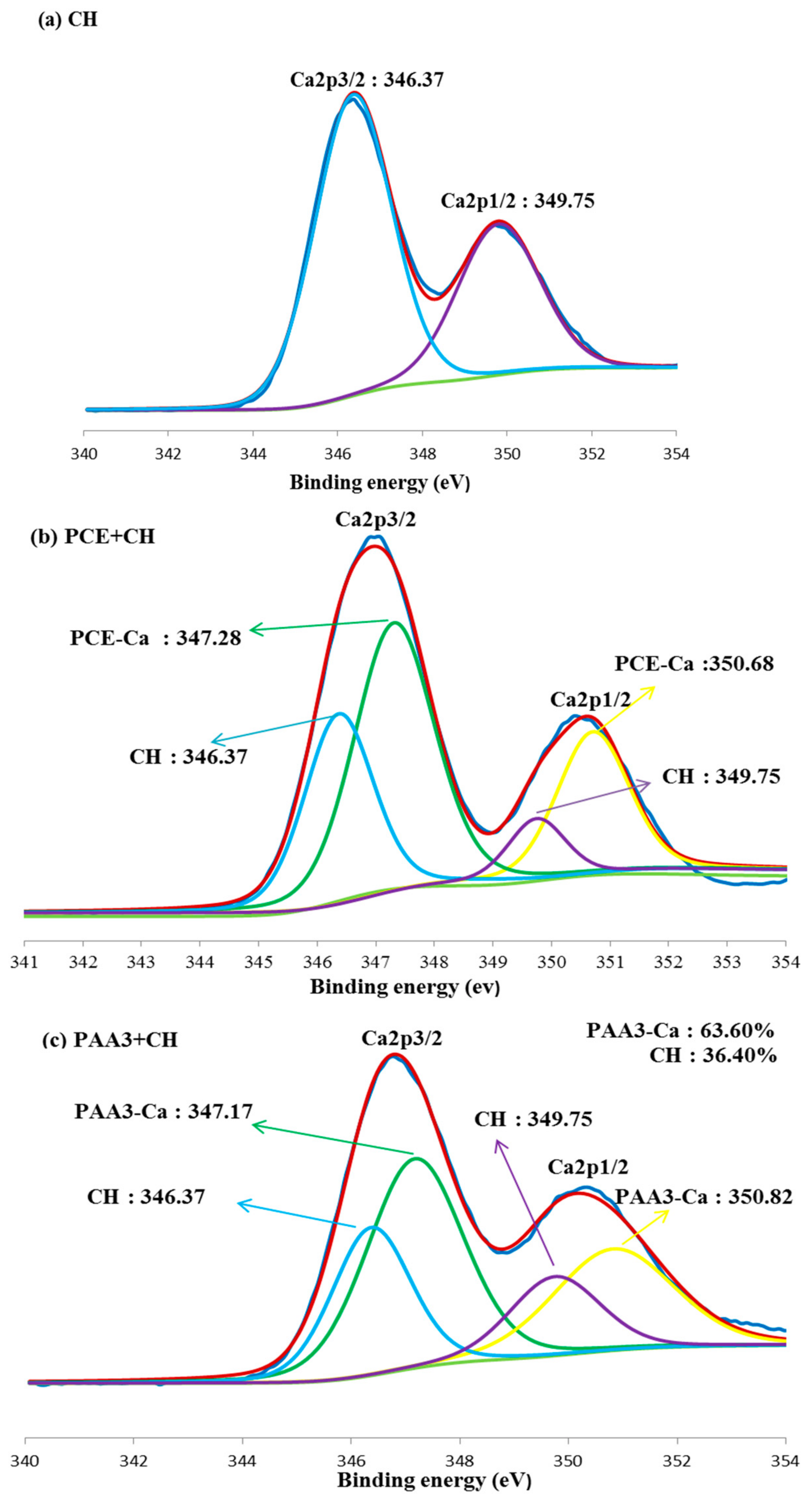
2.2.6. Binding Energy of Ca2+
2.2.7. Conformation Behavior of PAA and PCE
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fluidity
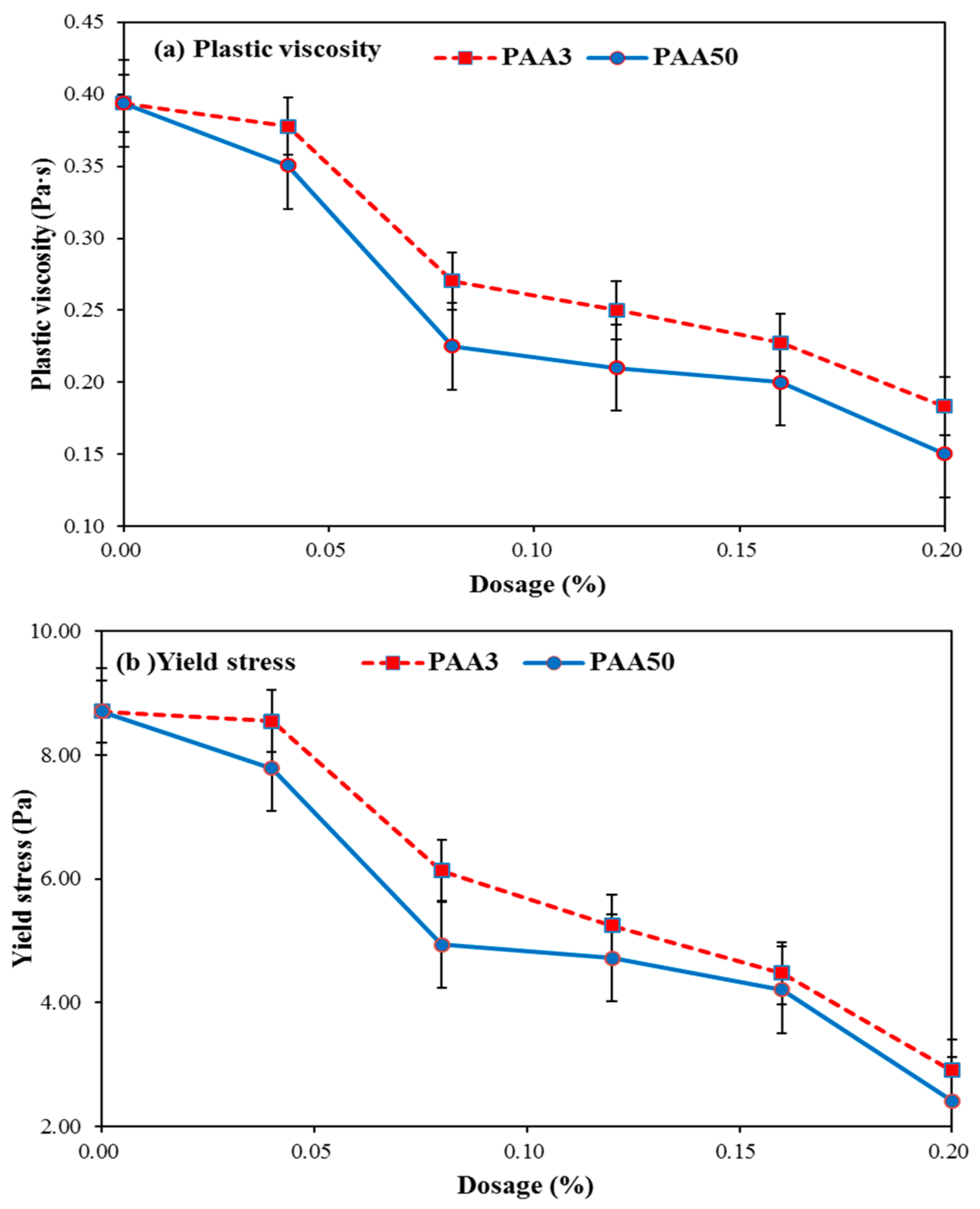
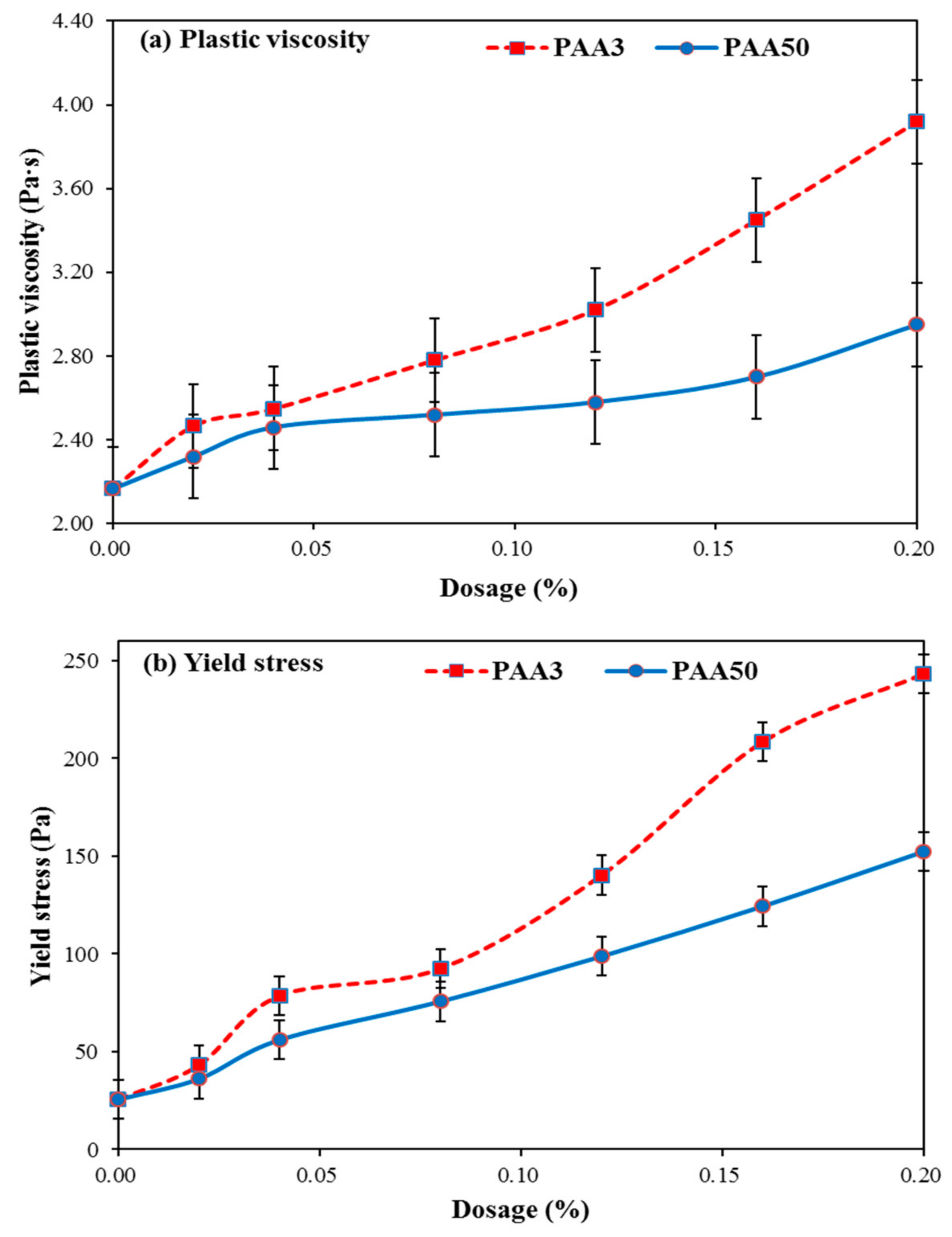
3.2. Rheology Performance
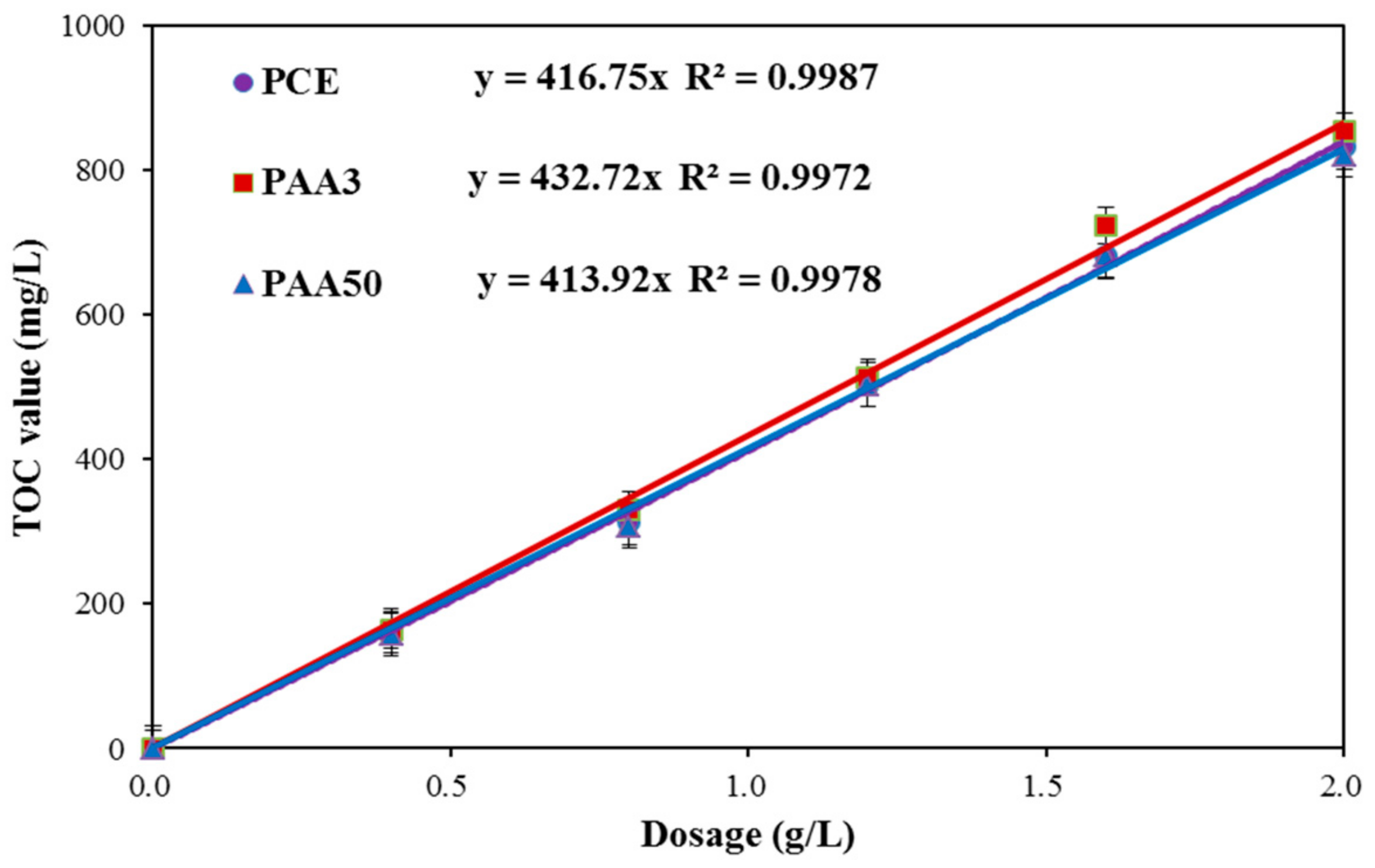
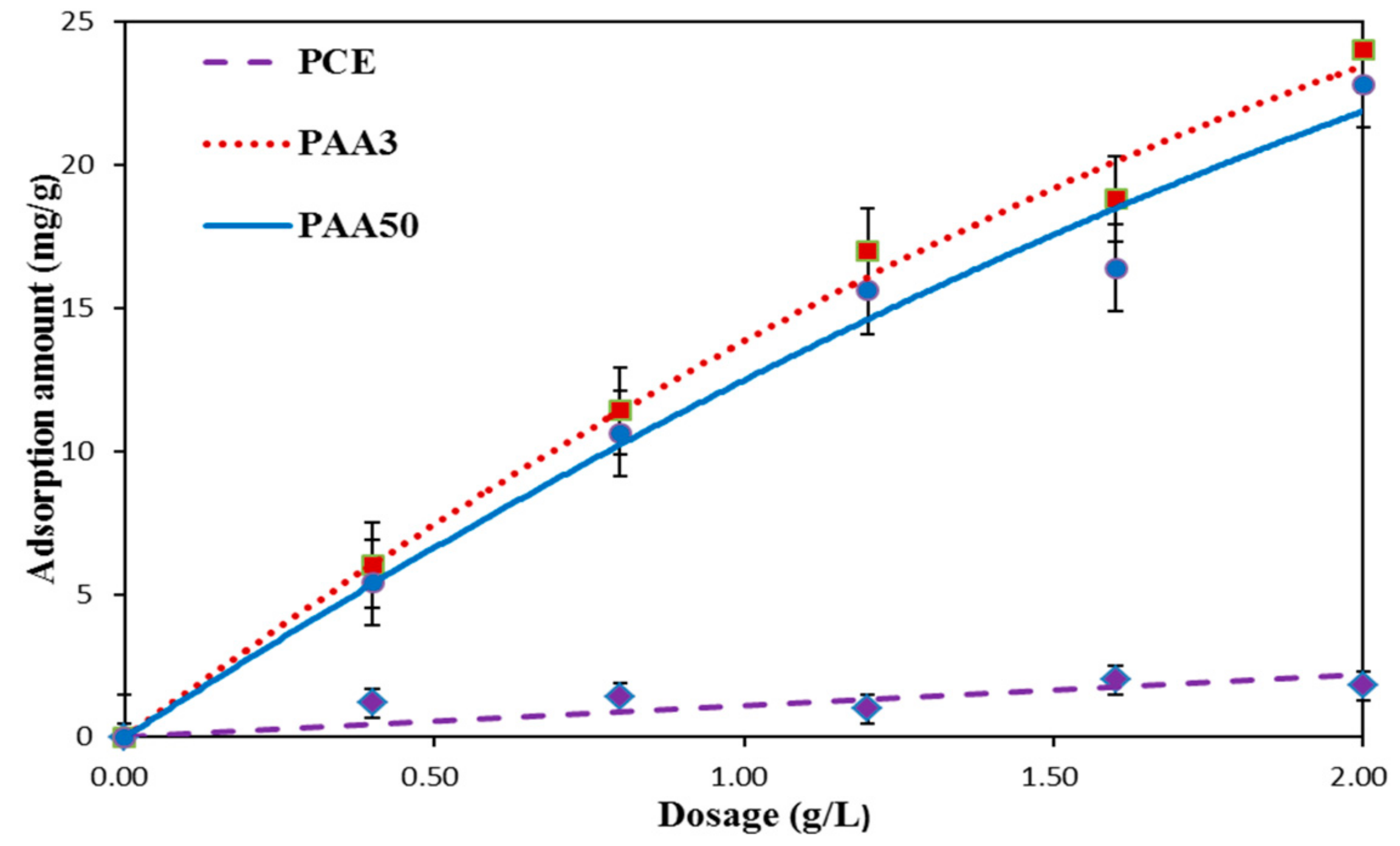
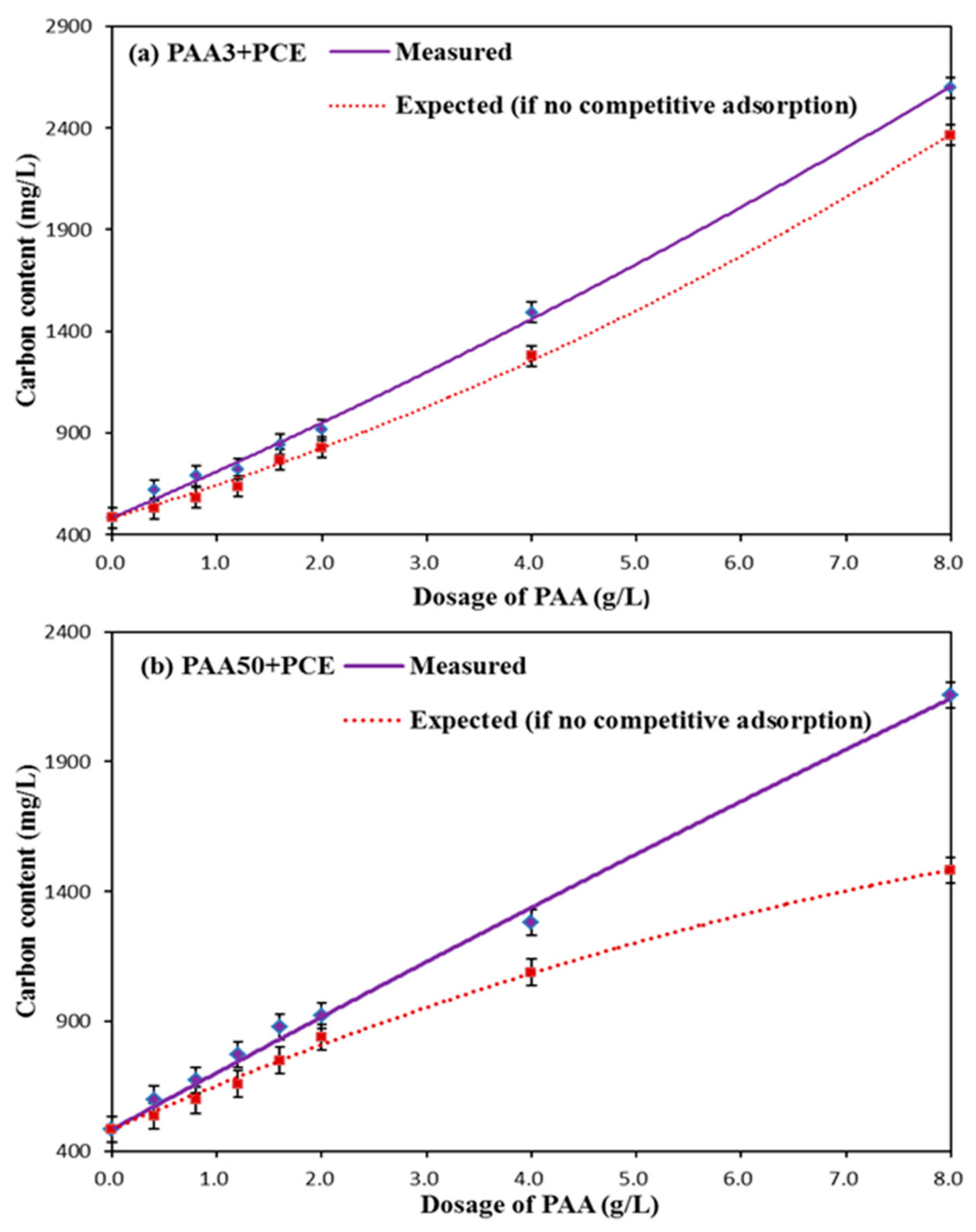
3.3. Adsorption Amount
- (1)
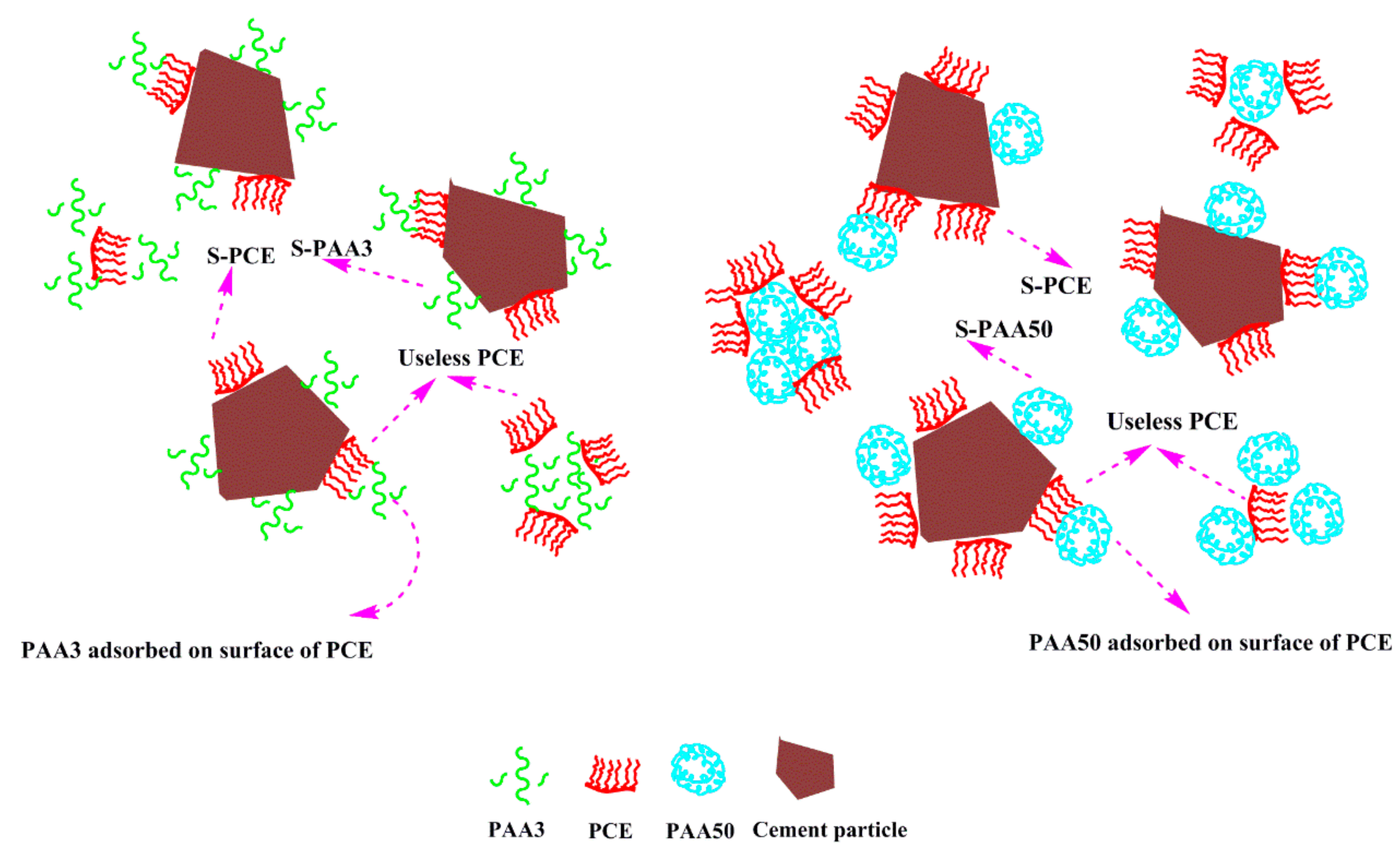
- Adsorption Behavior of PAA and PCE
- (2)
- Competitive Adsorption between PAA and PCE
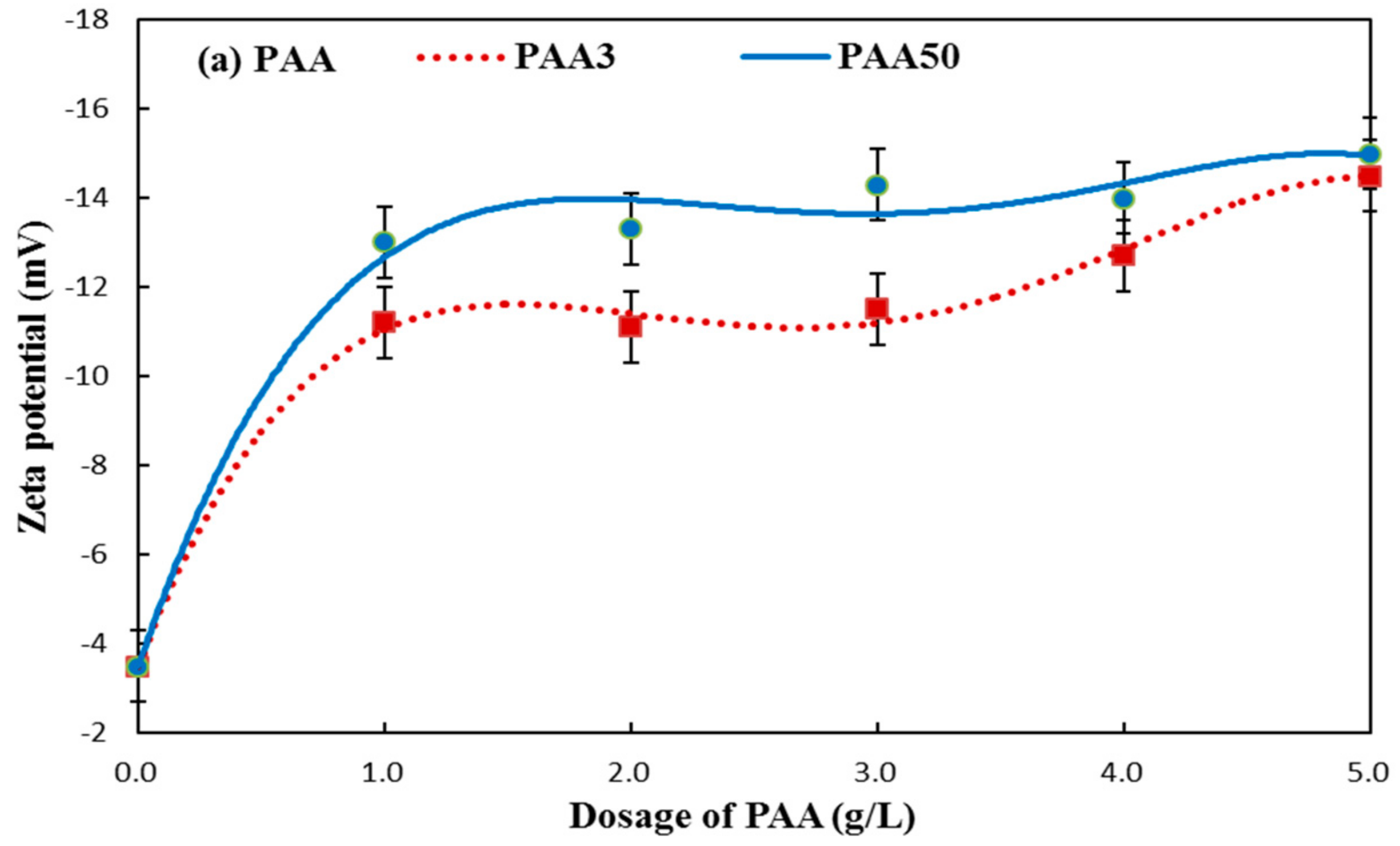
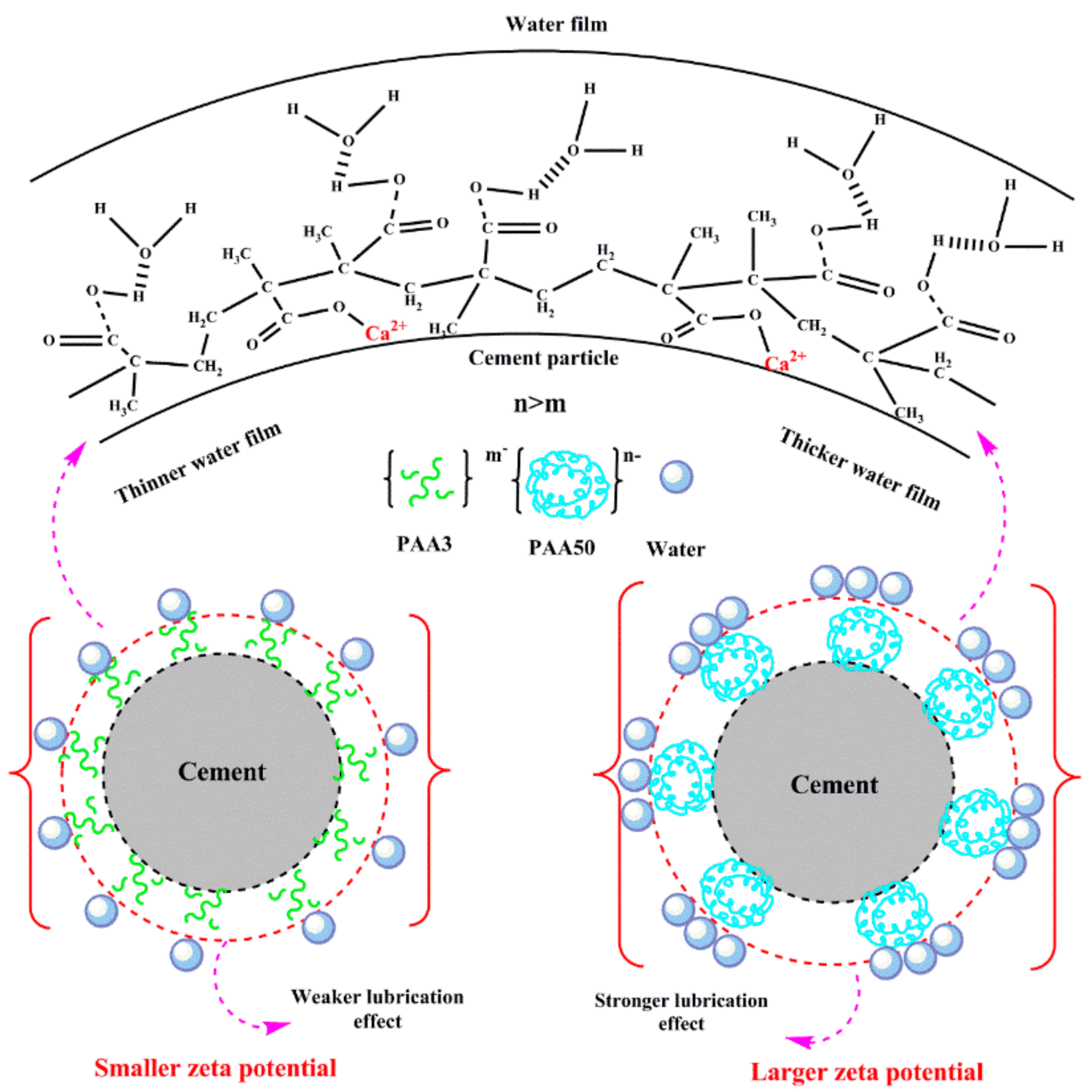
3.4. Zeta Potential
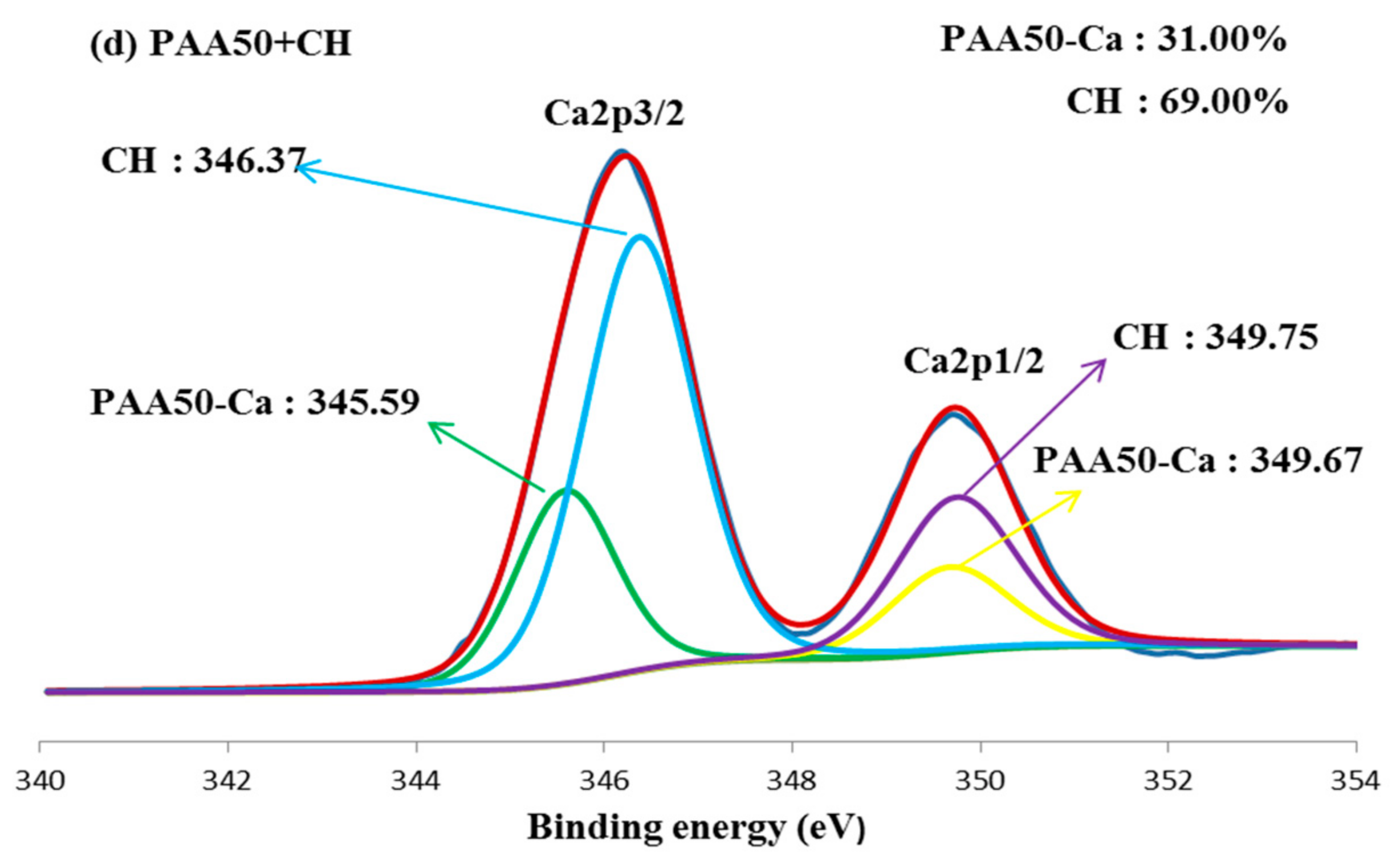
3.5. Combination of Carboxyl Groups with Ca2+
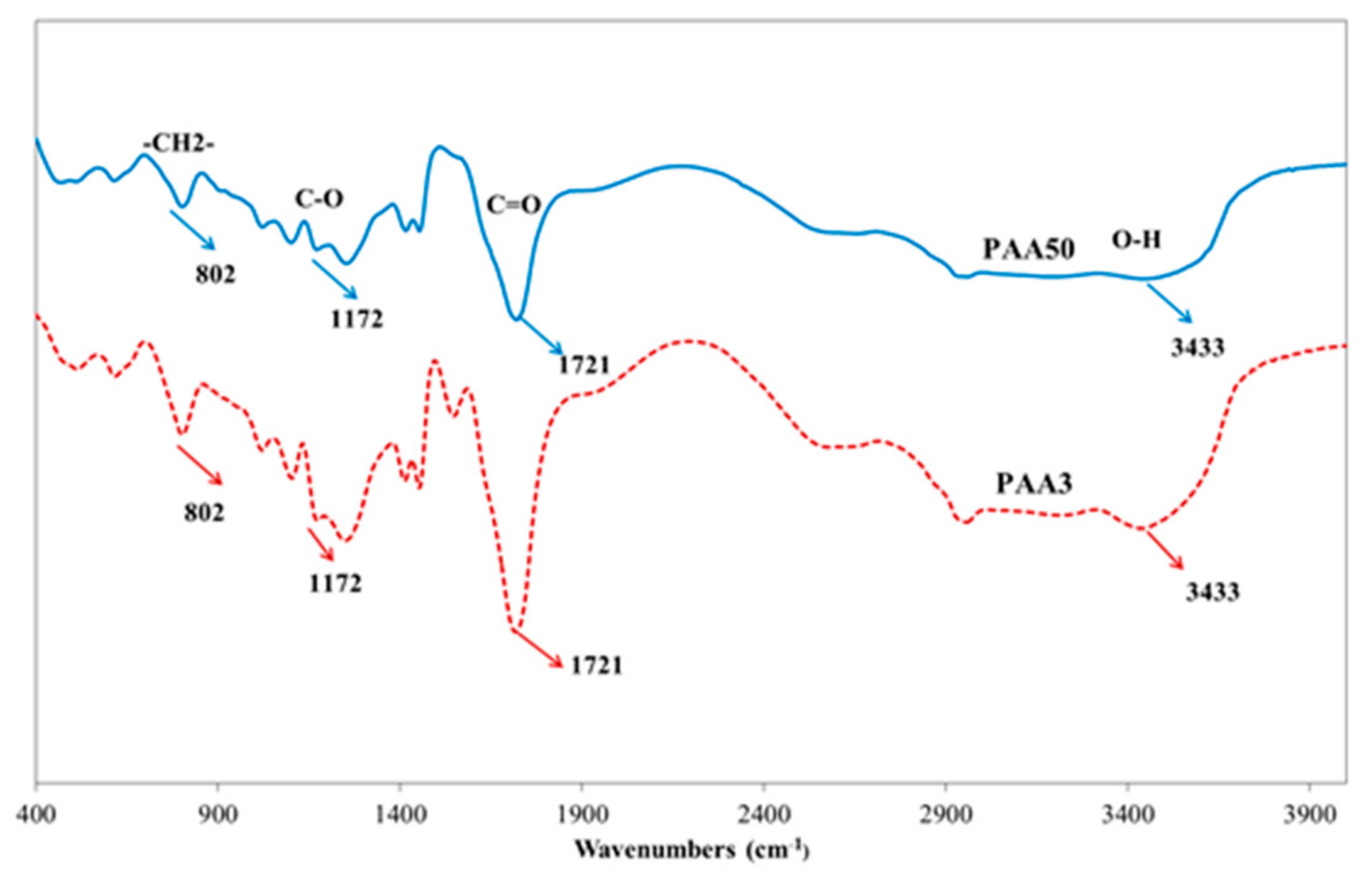
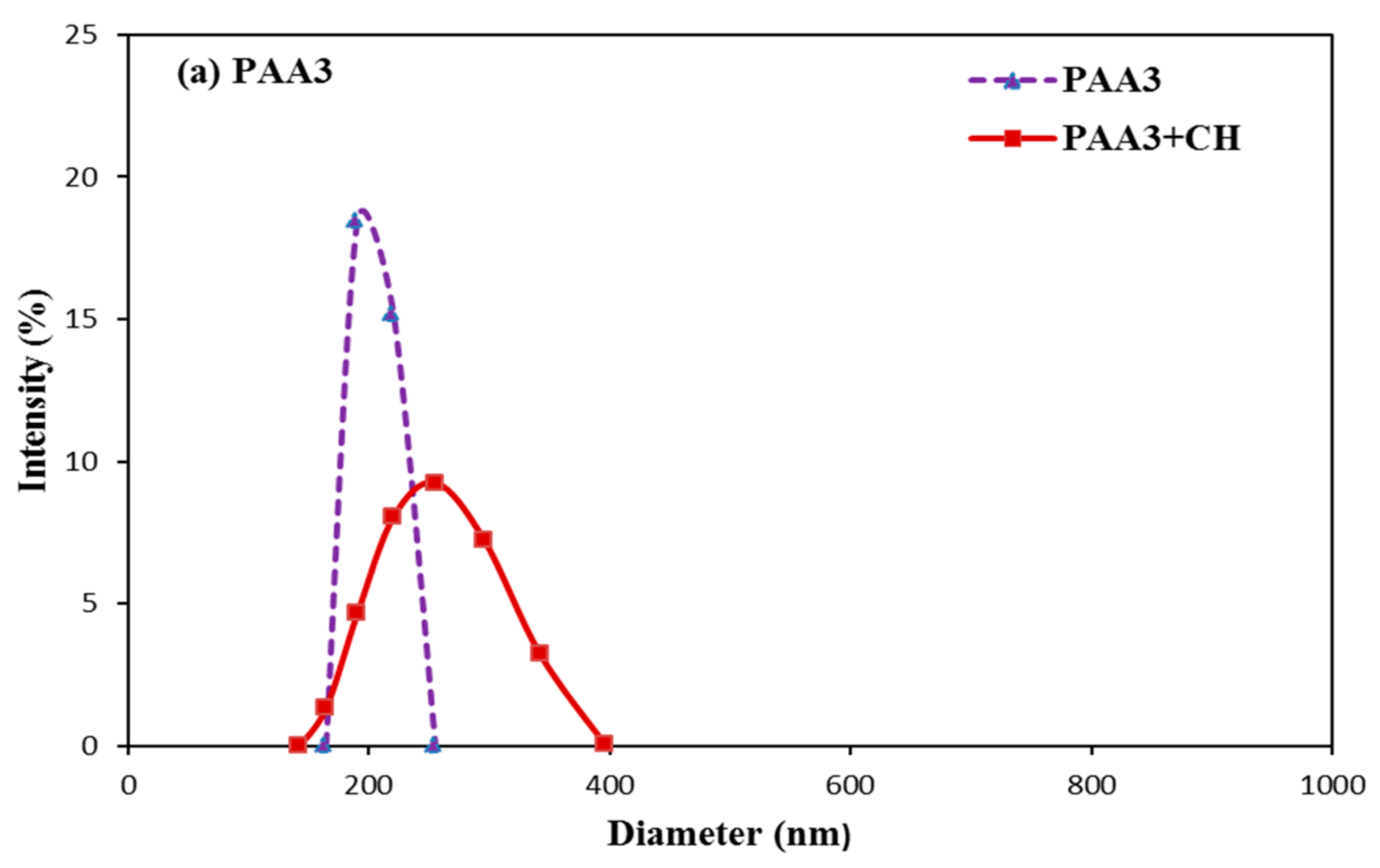
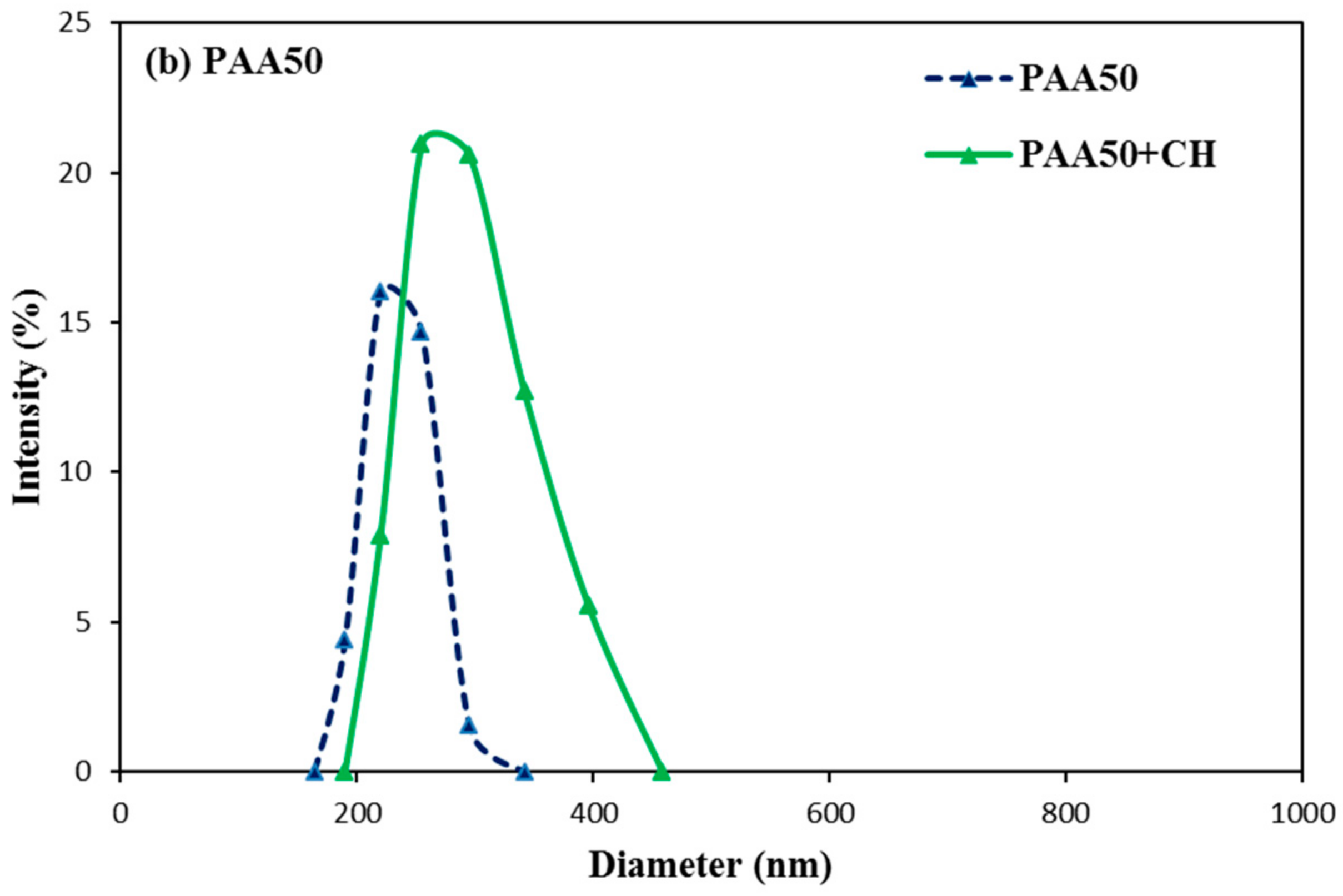
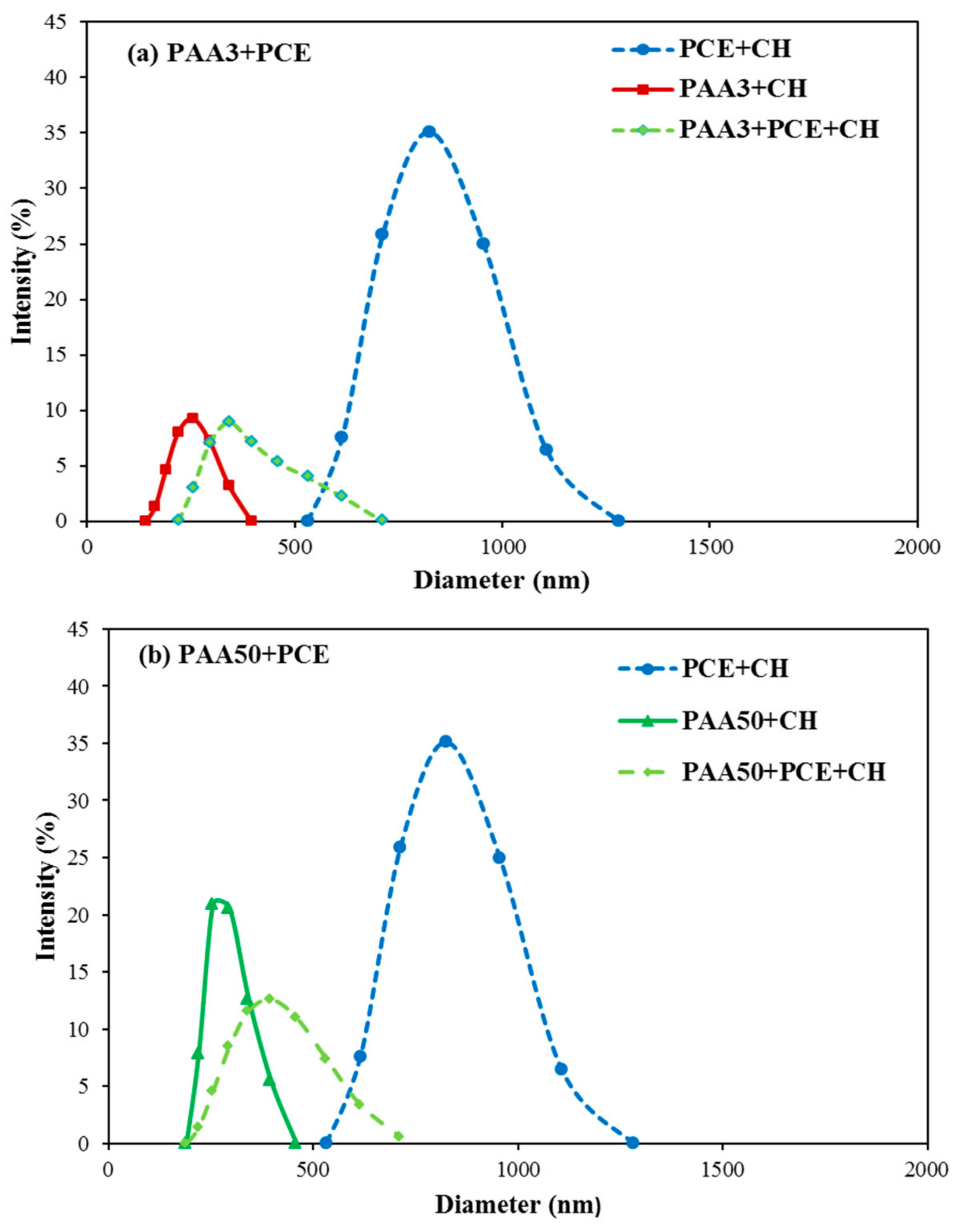
3.6. Aggregation Behavior of PAA and PCE
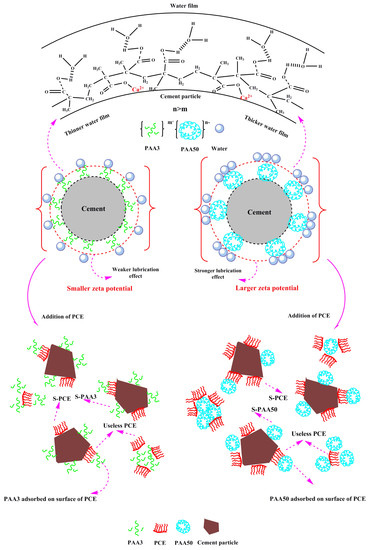
3.7. Mechanism
- (1)
- Effect of PAA on fluidity performance of cement paste
- (2)
- Effect of PAA on performance of PCE
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- PAA can adsorb onto the surface of cement particles, and smaller molecular weight of PAA has stronger adsorption ability. In the presence of Ca2+, PAA can be curled, as a result of the combination between carboxyl groups and Ca2+. PAA with greater molecular weight may be curled more obviously, and form a spherical structure in the presence of Ca2+.
- (2)
- PAA can plasticize cement paste, because of the lubricating effect and the increased zeta potential; greater molecular weight results in stronger plasticizing ability.
- (3)
- PAA has a negative effect on dispersion of PCE, and smaller molecular weight results in stronger negative effect. The main reason for this is due to the competitive adsorption effect.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schmidt, W.; Brouwers, H.J.H.; Kühne, H.-C.; Meng, B. Influences of superplasticizer modification and mixture composition on the performance of self-compacting concrete at varied ambient temperatures. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2014, 49, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Tan, Y.; Li, E.; Dai, Y.; Yang, M. High-Performance Grouting Mortar Based on Mineral Admixtures. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 2015, 425456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Peng, Y.; Tan, H.; Jian, S.; Zhi, Z.; Guo, Y.; Qi, H.; Zhang, T.; He, X. Effect of hydroxypropyl-methyl cellulose ether on rheology of cement paste plasticized by polycarboxylate superplasticizer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 160, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, R.; Zheng, S.; Farhan, S.; Yao, H.; Jiang, H. Research on the chemical mechanism in the polyacrylate latex modified cement system. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 76, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Ma, B.; Zhi, Z.; Tan, H.; Liu, M.; Jian, S.; Guo, Y. Effect of polyacrylic acid emulsion on fluidity of cement paste. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 535, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bey, H.B.; Hot, J.; Baumann, R.; Roussel, N. Consequences of competitive adsorption between polymers on the rheological behaviour of cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2014, 54, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiśniewska, M.; Nosal-Wiercińska, A.; Dąbrowska, I.; Szewczuk-Karpisz, K. Effect of the solid pore size on the structure of polymer film at the metal oxide/polyacrylic acid solution interface—Temperature impact. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 175, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-R.; Kong, X.-M.; Lu, Z.-B.; Lu, Z.-C.; Hou, S.-S. Effects of the charge characteristics of polycarboxylate superplasticizers on the adsorption and the retardation in cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 67, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalas, F.; Pourchet, S.; Nonat, A.; Rinaldi, D.; Sabio, S.; Mosquet, M. Fluidizing efficiency of comb-like superplasticizers: The effect of the anionic function, the side chain length and the grafting degree. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 75, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.-R.; Pan, L.-S.; Wang, C.-M.; Zhang, D.-L.; Xu, N. Effects of polycarboxylate superplasticizers with different molecular structure on the hydration behavior of cement paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 105, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Guo, Y.; Ma, B.; Li, X.; Gu, B. Adsorbing Behavior of Polycarboxylate Superplasticizer in the Presence of Ester Group in Side Chain. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2017, 38, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, F.; Tan, H.; Guo, Y.; Ma, B.; He, X.; Zhou, Y. Effect of sodium gluconate on dispersion of polycarboxylate superplasticizer with different grafting density in side chain. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 55, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Zou, F.; Ma, B.; Guo, Y.; Li, X.; Mei, J. Effect of competitive adsorption between sodium gluconate and polycarboxylate superplasticizer on rheology of cement paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 144, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Guo, Y.; Zou, F.; Jian, S.; Ma, B.; Zhi, Z. Effect of borax on rheology of calcium sulphoaluminate cement paste in the presence of polycarboxylate superplasticizer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 139, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Zou, F.; Ma, B.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Jian, S. Effect of sodium tripolyphosphate on adsorbing behavior of polycarboxylate superplasticizer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 136, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; He, T.; Hu, D.; Shi, C. Effects of two retarders on the fluidity of pastes plasticized with aminosulfonic acid-based superplasticizers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 26, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Gu, B.; Guo, Y.; Ma, B.; Huang, J.; Ren, J.; Zou, F.; Guo, Y. Improvement in compatibility of polycarboxylate superplasticizer with poor-quality aggregate containing montmorillonite by incorporating polymeric ferric sulfate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 162, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Gu, B.; Ma, B.; Li, X.; Lin, C.; Li, X. Mechanism of intercalation of polycarboxylate superplasticizer into montmorillonite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 139, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait-Akbour, R.; Boustingorry, P.; Leroux, F.; Leising, F.; Taviot-Gueho, C. Adsorption of PolyCarboxylate Poly(ethylene glycol) (PCP) esters on Montmorillonite (Mmt): Effect of exchangeable cations (Na+, Mg2+ and Ca2+) and PCP molecular structure. J. Colloids Interface Sci. 2015, 437, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, B.; Zeng, Z.; Ren, Q.; Chen, Y.; Liang, M.; Zou, H. Study on the performance of polycarboxylate-based superplasticizers synthesized by reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization. J. Mol. Struct. 2016, 1120, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessaies-Bey, H.; Baumann, R.; Schmitz, M.; Radler, M.; Roussel, N. Organic admixtures and cement particles: Competitive adsorption and its macroscopic rheological consequences. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 80, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, C.; Nadelman, E.; Washburn, N.R.; Kurtis, K.E. Lignopolymer Superplasticizers for Low-CO2 Cements. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 4041–4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Kong, X.; Zhang, C.; Xing, F.; Cai, Y.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, B. Effect of surface modification of colloidal particles in polymer latexes on cement hydration. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 155, 1147–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plank, J.; Hirsch, C. Impact of zeta potential of early cement hydration phases on superplasticizer adsorption. Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zingg, A.; Winnefeld, F.; Holzer, L.; Pakusch, J.; Becker, S.; Gauckler, L. Adsorption of polyelectrolytes and its influence on the rheology, zeta potential, and microstructure of various cement and hydrate phases. J. Colloids Interface Sci. 2008, 323, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, S.; Barbhuiya, S.A.; Charan, D.; Pandey, S.P. Characterising cement–superplasticiser interaction using zeta potential measurements. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 2517–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonapasta, A.A.; Buda, F.; Colombet, P. Interaction between Ca ions and poly (acrylic acid) chains in macro-defect-free cements: A theoretical study. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Tian, Y.; Li, Z. Interactions between organic and inorganic paste in PA and PA/PU modified cement based materials. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2011, 23, 1412–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şakar-Deliormanli, A. Flow behavior of hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose/polyacrylic acid interpolymer complexes in aqueous media. Polym. Int. 2012, 61, 1751–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yuan, R.; Ying, L. Study on the molecular behavior of hydrophobically modified poly (acrylic acid) in aqueous solution and its emulsion-stabilizing capacity. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 128, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AzariJafari, H.; Kazemian, A.; Ahmadi, B.; Berenjian, J.; Shekarchi, M. Studying effects of chemical admixtures on the workability retention of zeolitic Portland cement mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 72, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, J.; Zhao, P.; Dai, N.; Zhai, Z.; Ai, T. Improving cracking resistance of cement mortar by thermo-sensitive poly N-isopropyl acrylamide (PNIPAM) gels. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 176, 1292–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Li, G.; Li, Y. Effects of superplasticizers and retarders on the fluidity and strength of sulphoaluminate cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 126, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plank, J.; Winter, C. Competitive adsorption between superplasticizer and retarder molecules on mineral binder surface. Cem. Concr. Res. 2008, 38, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesage, K.; Cizer, Ö.; Desmet, B.; Vantomme, J.; De Schutter, G.; Vandewalle, L. Plasticising mechanism of sodium gluconate combined with PCE. Adv. Cem. Res. 2015, 27, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; He, T.; Song, X.; Liang, G. Effect of sodium gluconate on polynaphthalene sulfonate adsorption. Adv. Cem. Res. 2011, 23, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Flexural Strength (MPa) | Compressive Strength (MPa) | Setting Time (min) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 d | 28 d | 3 d | 28 d | Initial setting | Final setting |
| 4.6 | 7.6 | 25.6 | 45.5 | 238 | 291 |
| Cl− (%) | Alkali Content (%) | Water reducing Ratio (%) | pH Value | Solid Content (%) | Mw (g/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.03 | 3.75 | 30.1 | 7.2 | 40.0 | 67,500 |
| Solid Content (%) | pH Value | Mw (g/mol) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PAA3 | 30 | 3.0–3.5 | 3000 |
| PAA50 | 50 | 2.5–3.0 | 50,000 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, B.; Peng, Y.; Tan, H.; Lv, Z.; Deng, X. Effect of Polyacrylic Acid on Rheology of Cement Paste Plasticized by Polycarboxylate Superplasticizer. Materials 2018, 11, 1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071081
Ma B, Peng Y, Tan H, Lv Z, Deng X. Effect of Polyacrylic Acid on Rheology of Cement Paste Plasticized by Polycarboxylate Superplasticizer. Materials. 2018; 11(7):1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071081
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Baoguo, Yi Peng, Hongbo Tan, Zhenghang Lv, and Xiufeng Deng. 2018. "Effect of Polyacrylic Acid on Rheology of Cement Paste Plasticized by Polycarboxylate Superplasticizer" Materials 11, no. 7: 1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071081
APA StyleMa, B., Peng, Y., Tan, H., Lv, Z., & Deng, X. (2018). Effect of Polyacrylic Acid on Rheology of Cement Paste Plasticized by Polycarboxylate Superplasticizer. Materials, 11(7), 1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071081