Microstructure and Tensile Properties of AZ61 Alloy Sheets Processed by High-Ratio Extrusion with Subsequent Direct Aging Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
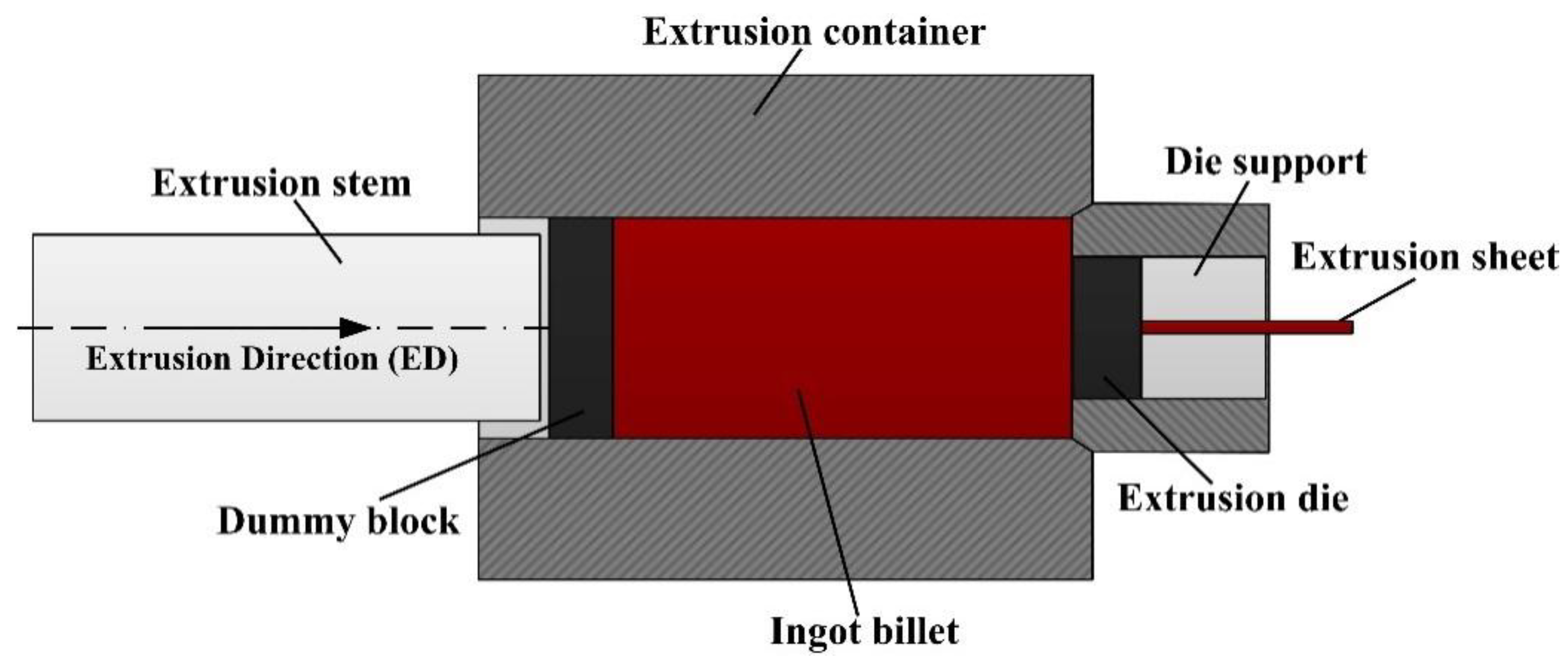
2. Experimental Procedure
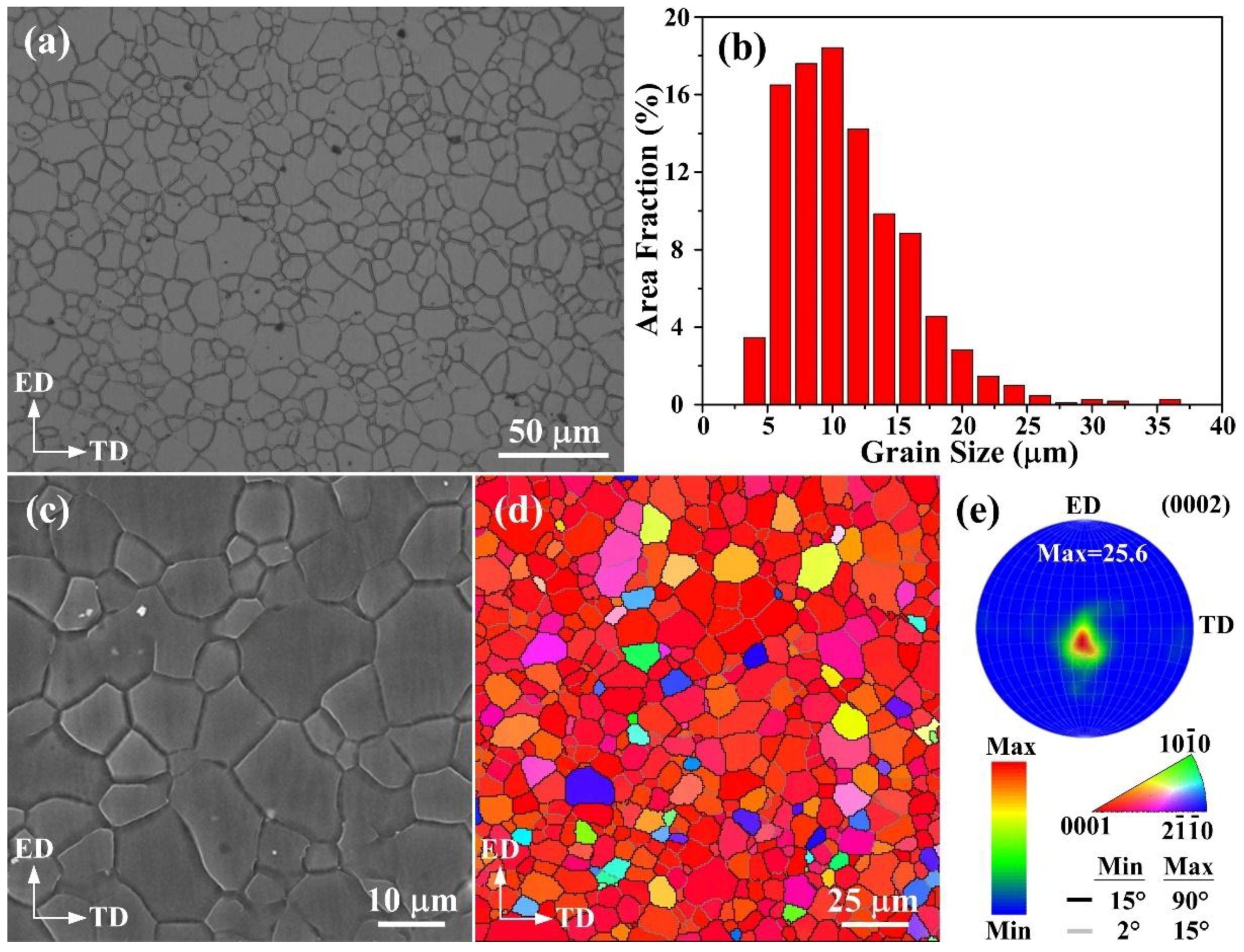
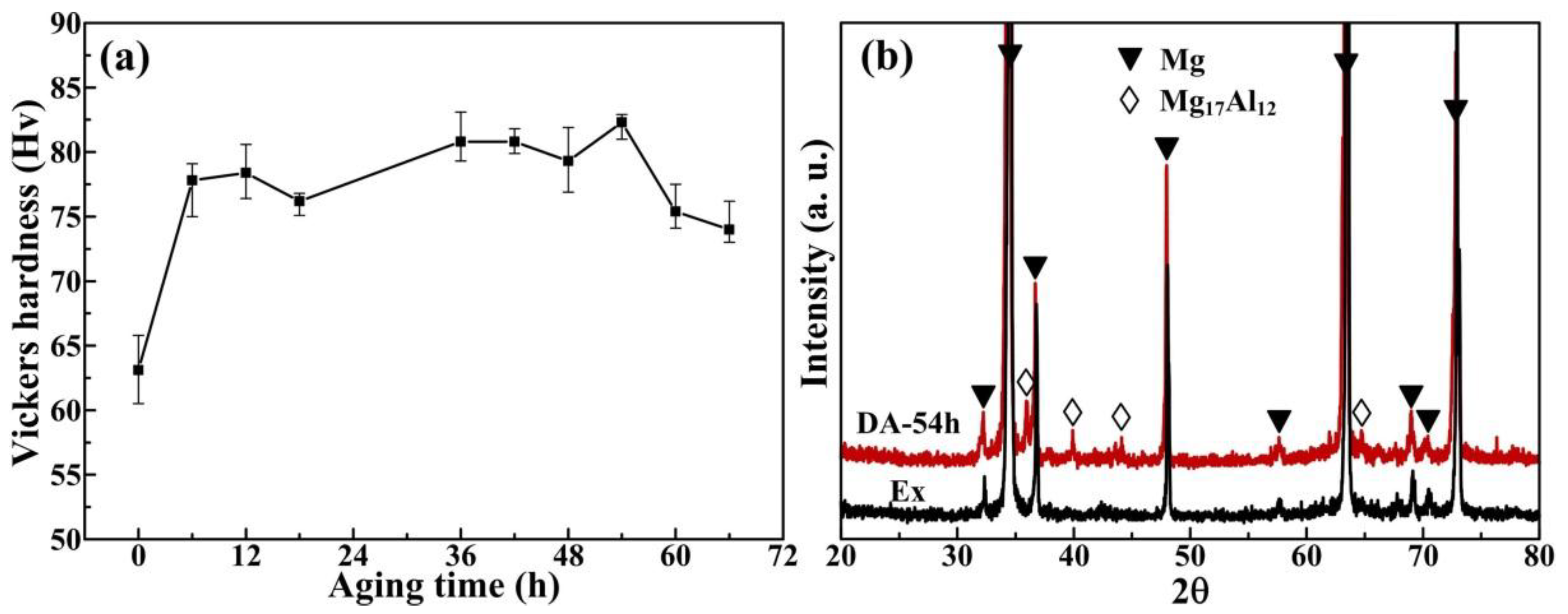
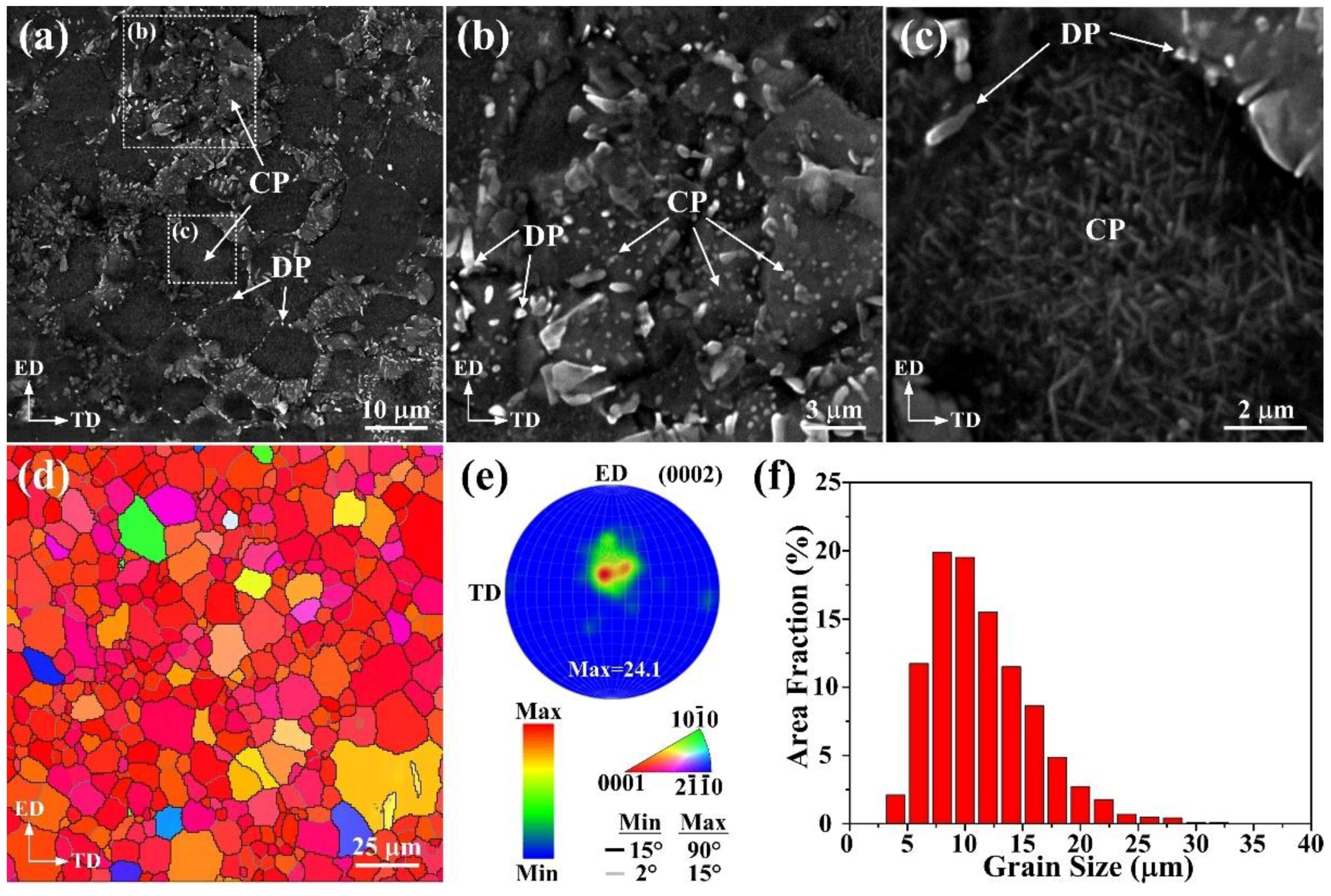
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhilyaev, A.P.; Nurislamova, G.V.; Kim, B.-K.; Baró, M.D.; Szpunar, J.A.; Langdon, T.G. Experimental parameters influencing grain refinement and microstructural evolution during high-pressure torsion. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 753–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, Y.; Arai, K.; Itoh, S.; Kamado, S.; Kojima, Y. Realization of high strength and high ductility for AZ61 magnesium alloy by severe warm working. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2005, 6, 185–194. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, W.J.; Hong, S.I.; Kim, Y.S.; Min, S.H.; Jeong, H.T.; Lee, J.D. Texture development and its effect on mechanical properties of an AZ61 Mg alloy fabricated by equal channel angular pressing. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 3293–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.G.; Yan, H.; Chen, R.S. Microstructure, texture and mechanical properties in an as-cast AZ61 Mg alloy during multi-directional impact forging and subsequent heat treatment. Mater. Des. 2015, 87, 891–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Shu, D.; Hu, C.; Zhao, Z.; Yuan, B. Grain refinement in an as-cast AZ61 magnesium alloy processed by multi-axial forging under the multitemperature processing procedure. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 541, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, Y.; Utsunomiya, H.; Tsuji, N.; Sakai, T. Novel ultra-high straining process for bulk materials-development of the accumulative roll-bonding (ARB) process. Acta Mater. 1999, 47, 579–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, N.; Saito, Y.; Utsunomiya, H.; Tanigawa, S. Ultra-fine grained bulk steel produced by accumulative roll-bonding (ARB) process. Scr. Mater. 1999, 40, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.B.; Wang, Q.D.; Peng, L.M.; Roven, H.J. Microstructure and high tensile ductility of ZK60 magnesium alloy processed by cyclic extrusion and compression. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 476, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiev, R.Z.; Langdon, T.G. Principles of equal-channel angular pressing as a processing tool for grain refinement. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2006, 51, 881–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, K.; Horita, Z.; Nemoto, M.; Langdon, T.G. Influence of channel angle on the development of ultrafine grains in equal-channel angular pressing. Acta Mater. 1998, 46, 1589–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.J.; Wang, Q.D.; Peng, J.G.; Zhai, C.Q.; Ding, W.J. Effects of extrusion ratio on the microstructure and mechanical properties of AZ31 Mg alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2007, 182, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murai, T.; Matsuoka, S.; Miyamoto, S.; Oki, Y. Effects of extrusion conditions on microstructure and mechanical properties of AZ31B magnesium alloy extrusions. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2003, 141, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabuchi, M.; Asahina, T.; Iwasaki, H.; Higashi, K. Experimental investigation of superplastic behaviour in magnesium alloys. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1997, 13, 825–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukai, T.; Watanabe, H.; Higashi, K. Grain refinement of commercial magnesium alloys for high-strain-rate-superplastic forming. Mater. Sci. Forum 2000, 350–351, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uematsu, Y.; Tokaji, K.; Kamakura, M.; Uchida, K.; Shibata, H.; Bekku, N. Effect of extrusion conditions on grain refinement and fatigue behaviour in magnesium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 434, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.K.; Huang, J.C. Fabrication of low temperature superplastic AZ91 Mg alloys using simple high-ratio extrusion method. Key Eng. Mater. 2003, 233–236, 875–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, H.; Mukai, T.; Ishikawa, K.; Higashi, K. High-strain-rate superplasticity in an AZ91 magnesium alloy processed by ingot metallurgy route. Mater. Trans. 2002, 43, 78–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uematsu, Y.; Tokaji, K.; Matsumoto, M. Effect of aging treatment on fatigue behaviour in extruded AZ61 and AZ80 magnesium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 517, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Feng, T.T.; Zhang, L.; Liu, C.G.; Pan, Y.; Zha, M.; Nan, X.L.; Wang, C.; Jiang, Q.C. Achieving a weak basal texture in a Mg–6Al–3Sn alloy by wave-shaped die rolling. Mater. Des. 2015, 88, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.S.; Chun, D.K.; Kim, H.K. Fatigue properties of fine grained magnesium alloys after severe plastic deformation. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2005, 19, 1441–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Morsy, A.; Ismail, A.; Waly, M. Microstructural and mechanical properties evolution of magnesium AZ61 alloy processed through a combination of extrusion and thermomechanical processes. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 486, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harai, Y.; Kai, M.; Kaneko, K.; Horita, Z.; Langdon, T.G. Microstructural and mechanical characteristics of AZ61 magnesium alloy processed by high-pressure torsion. Mater. Trans. 2008, 49, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiner, S.; Uggowitzer, P.J. Mechanical anisotropy of extruded Mg-6% Al-1% Zn alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 379, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaziz, M.H.; Paradis, M.; Samuel, A.M.; Doty, H.W.; Samuel, F.H. Effect of aluminum addition on the microstructure, tensile properties, and fractography of cast Mg-based alloys. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 2017, 7408641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.S.; Suzuki, K.; Saito, N. Textures and stretch formability of Mg-6Al-1Zn magnesium alloy sheets rolled at high temperatures up to 793 K. Scr. Mater. 2009, 60, 651–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.F. Precipitation and hardening in magnesium alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2012, 43, 3891–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.J.; Li, Y.Y.; Hsu, Y.F.; Trong, S.; Wang, W.H. Aging behaviour and precipitate morphologies in Mg-7.7Al-0.5Zn-0.3Mn (wt.%) alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 476, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.G.; Yan, H.; Chen, R.S. Enhanced mechanical properties due to grain refinement and texture modification in an AZ61 Mg alloy processed by small strain impact forging. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 621, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-H.; You, B.S.; Park, S.H. Effect of billet diameter on hot extrusion behavior of Mg-Al-Zn alloys and its influence on microstructure and mechanical properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 690, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyana, M.S.; Mutoh, Y.; McEvily, A.J. The influence of mechanical surface treatments on fatigue behavior of extruded AZ61 magnesium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 549, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashad, M.; Pan, F.; Lin, D.; Asif, M. High temperature mechanical behavior of AZ61 magnesium alloy reinforced with graphene nanoplatelets. Mater. Des. 2016, 89, 1242–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Zhang, J.X.; Jiang, Y.Y.; Li, Q.Z. Effect of strain ratio on cyclic deformation and fatigue of extruded AZ61A magnesium alloy. Int. J. Fatigue 2012, 44, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.T.; Zeng, X.Q.; Liu, L.F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.P.; Ding, W.J. Effect of cerium on microstructures and mechanical properties of AZ61 wrought magnesium alloy. J. Mater. Sci. 2004, 39, 7061–7066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.L.; Li, X.C.; Xu, W.T.; Wu, D.; Yang, M. Effects of process parameters on microstructural evolution and properties of AZ61 alloy during hot extrusion. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. IOP Publ. 2015, 103, 012037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajuri, Z.B.; Miyashita, Y.; Hosokai, Y.; Mutoh, Y. Effects of Mn content and texture on fatigue properties of as-cast and extruded AZ61 magnesium alloys. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2006, 48, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avvari, M.; Narendranath, S. Influence of Route-R on wrought magnesium AZ61 alloy mechanical properties through equal channel angular pressing. J. Magnes. Alloys 2014, 2, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.F.; Wang, Y.; Qu, J.J. Microstructure and mechanical properties of AZ61 alloys with large cross-sectional size fabricated by multi-pass ECAP. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 560, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.J.; Park, I.B.; Han, S.H. Formation of a nanocomposite-like microstructure in Mg-6Al-1Zn alloy. Scr. Mater. 2012, 66, 590–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, M.; Zhang, H.M.; Wang, C.; Wang, H.Y.; Zhang, E.B.; Jiang, Q.C. Prominent role of a high volume fraction of Mg17Al12 particles on tensile behaviors of rolled Mg-Al-Zn alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 728, 682–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.S.; Suzuki, K.; Chino, Y.; Mabuchi, M. Texture and stretch formability of AZ61 and AM60 magnesium alloy sheets processed by high-temperature rolling. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 632, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olguín-González, M.L.; Hernández-Silva, D.; García-Bernal, M.A.; Sauce-Rangel, V.M. Hot deformation behavior of hot-rolled AZ31 and AZ61 magnesium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 597, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, H.; Mukai, T.; Higashi, K. Influence of temperature and grain size on threshold stress for superplastic flow in a fine-grained magnesium alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2008, 39, 2351–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
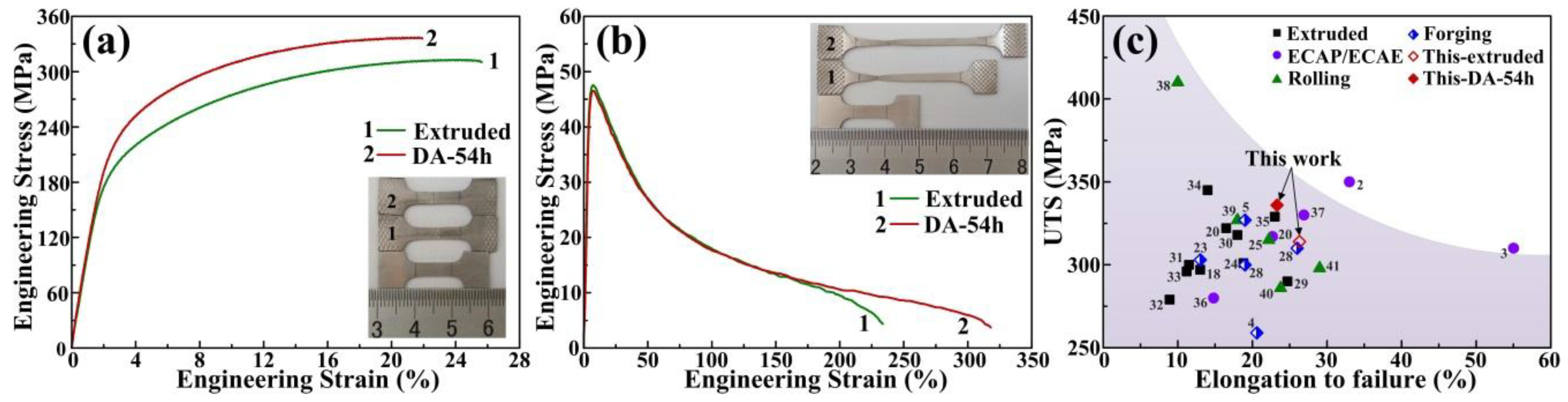
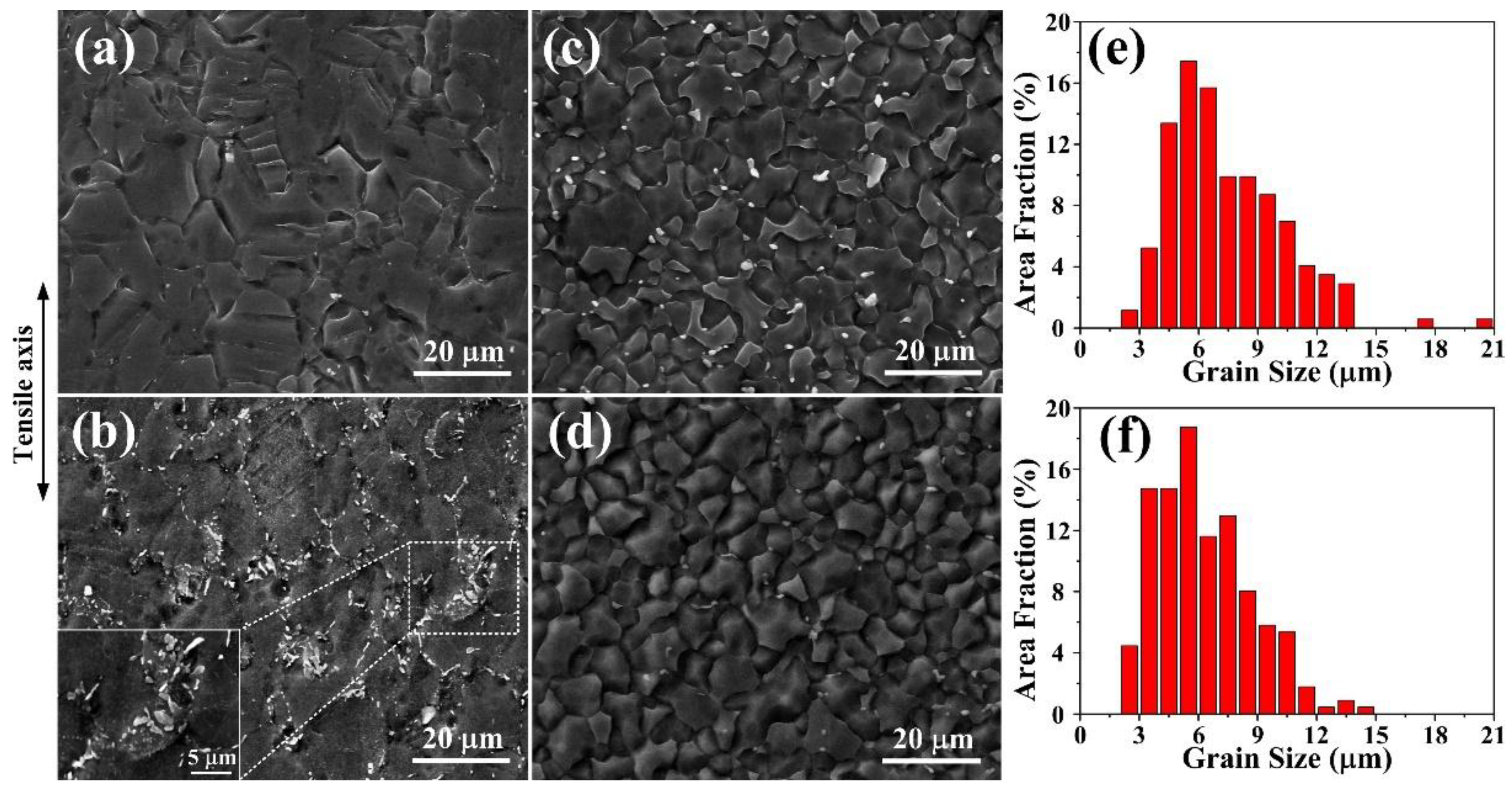
| Samples | Room Temperature | 300 °C | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength, σb/MPa | Yield Strength, σ0.2/MPa | Elongation to Failure, εf/% | Tensile Strength, σb/MPa | Elongation to Failure, εf/% | |
| Extruded | 314 ± 2 | 169 ± 6 | 26.5 ± 0.7 | 47 ± 1 | 231.8 ± 1.8 |
| DA-54h | 336 ± 1 | 191 ± 3 | 23.3 ± 1.3 | 48 ± 1 | 306.5 ± 11.5 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, C.-C.; Wang, H.-Y.; Zha, M.; Wang, C.; Li, J.-H.; Yang, Z.-Z.; Jiang, Q.-C. Microstructure and Tensile Properties of AZ61 Alloy Sheets Processed by High-Ratio Extrusion with Subsequent Direct Aging Treatment. Materials 2018, 11, 895. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11060895
Zhang C-C, Wang H-Y, Zha M, Wang C, Li J-H, Yang Z-Z, Jiang Q-C. Microstructure and Tensile Properties of AZ61 Alloy Sheets Processed by High-Ratio Extrusion with Subsequent Direct Aging Treatment. Materials. 2018; 11(6):895. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11060895
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Cheng-Cheng, Hui-Yuan Wang, Min Zha, Cheng Wang, Jie-Hua Li, Zhi-Zheng Yang, and Qi-Chuan Jiang. 2018. "Microstructure and Tensile Properties of AZ61 Alloy Sheets Processed by High-Ratio Extrusion with Subsequent Direct Aging Treatment" Materials 11, no. 6: 895. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11060895
APA StyleZhang, C.-C., Wang, H.-Y., Zha, M., Wang, C., Li, J.-H., Yang, Z.-Z., & Jiang, Q.-C. (2018). Microstructure and Tensile Properties of AZ61 Alloy Sheets Processed by High-Ratio Extrusion with Subsequent Direct Aging Treatment. Materials, 11(6), 895. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11060895





