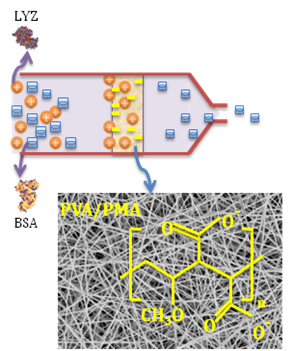
Functionalized Electrospun Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Nanofibrous Membranes with Poly(Methyl Vinyl Ether-Alt-Maleic Anhydride) for Protein Adsorption
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
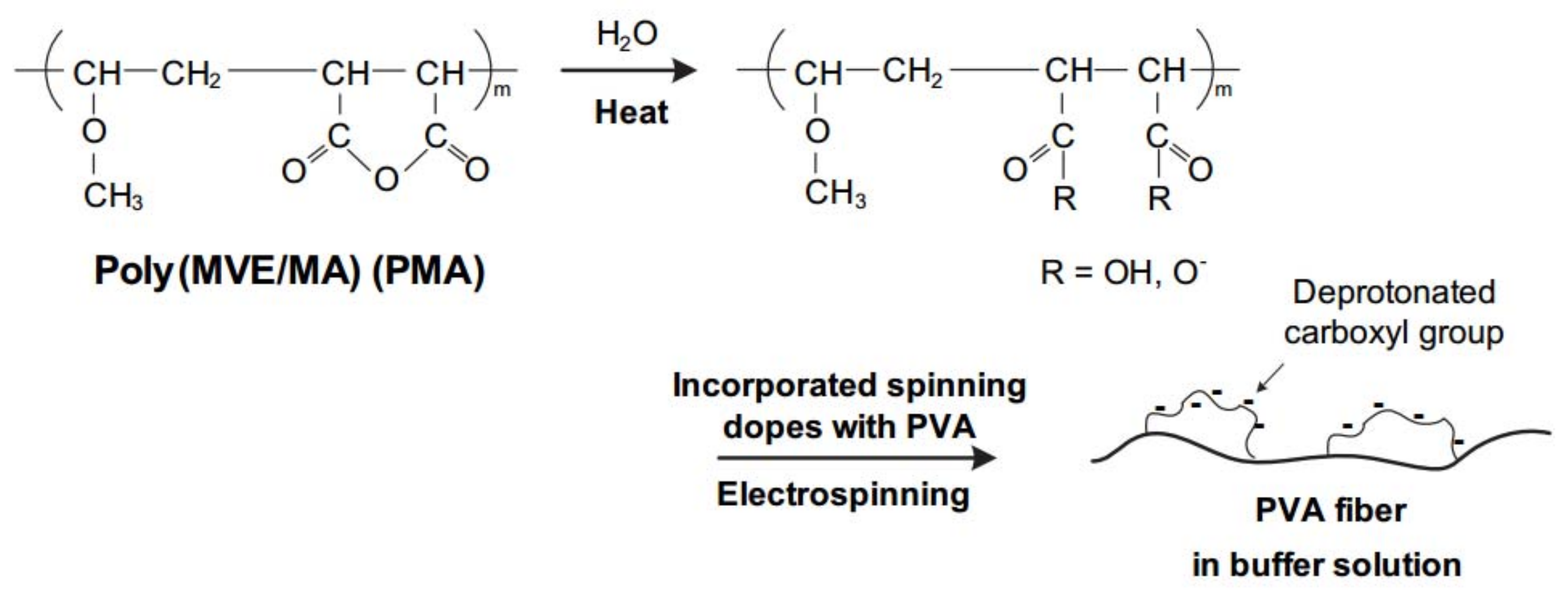
2.1. Electrospinning
2.2. Heat Treatment
2.3. Adsorption Experiment
2.4. Membrane Characterization
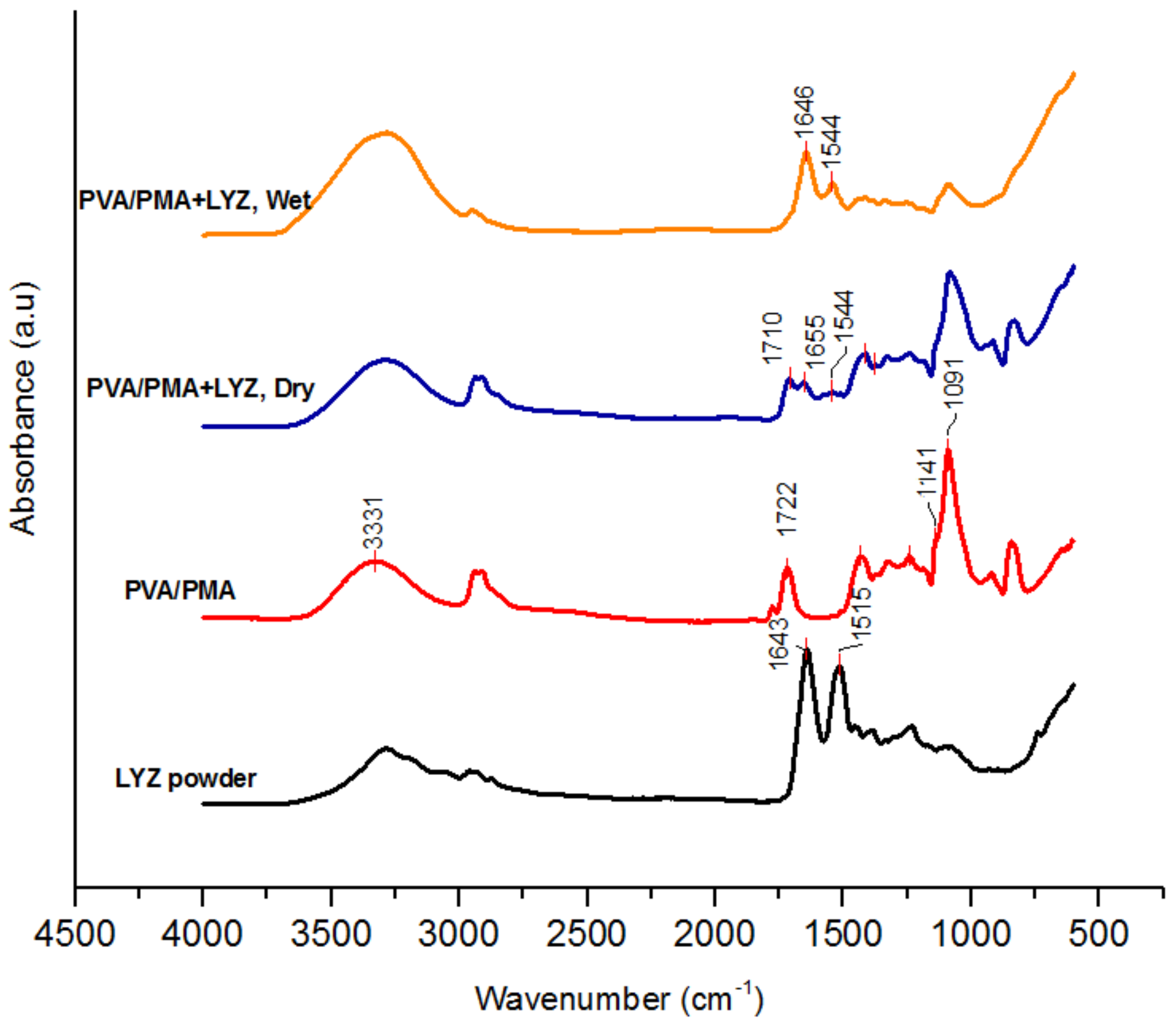
2.4.1. FTIR Spectroscopy
2.4.2. FESEM Imaging
Statistical Analysis
2.4.3. BET Surface Area
2.5. Adsorption Selectivity
3. Results and Discussion
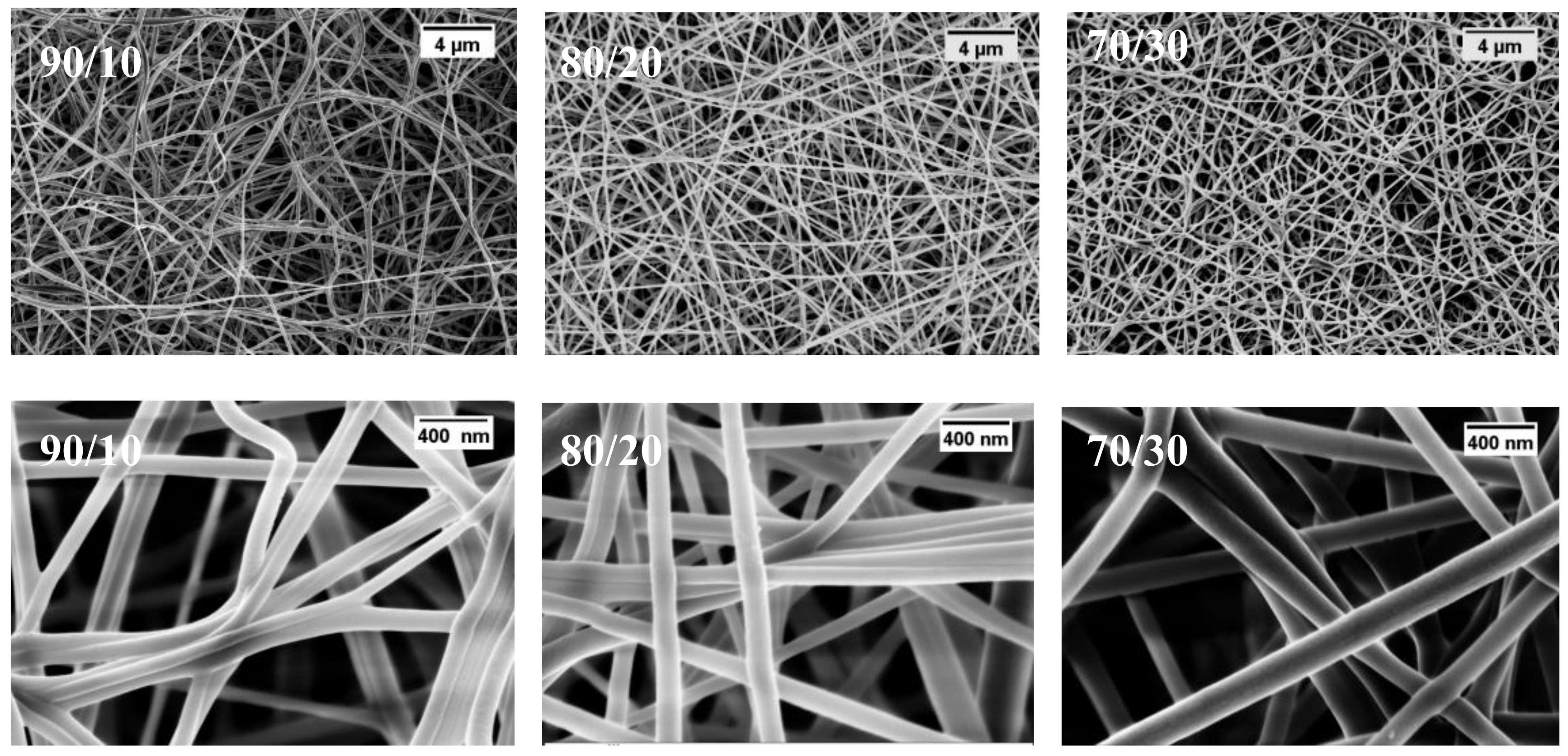
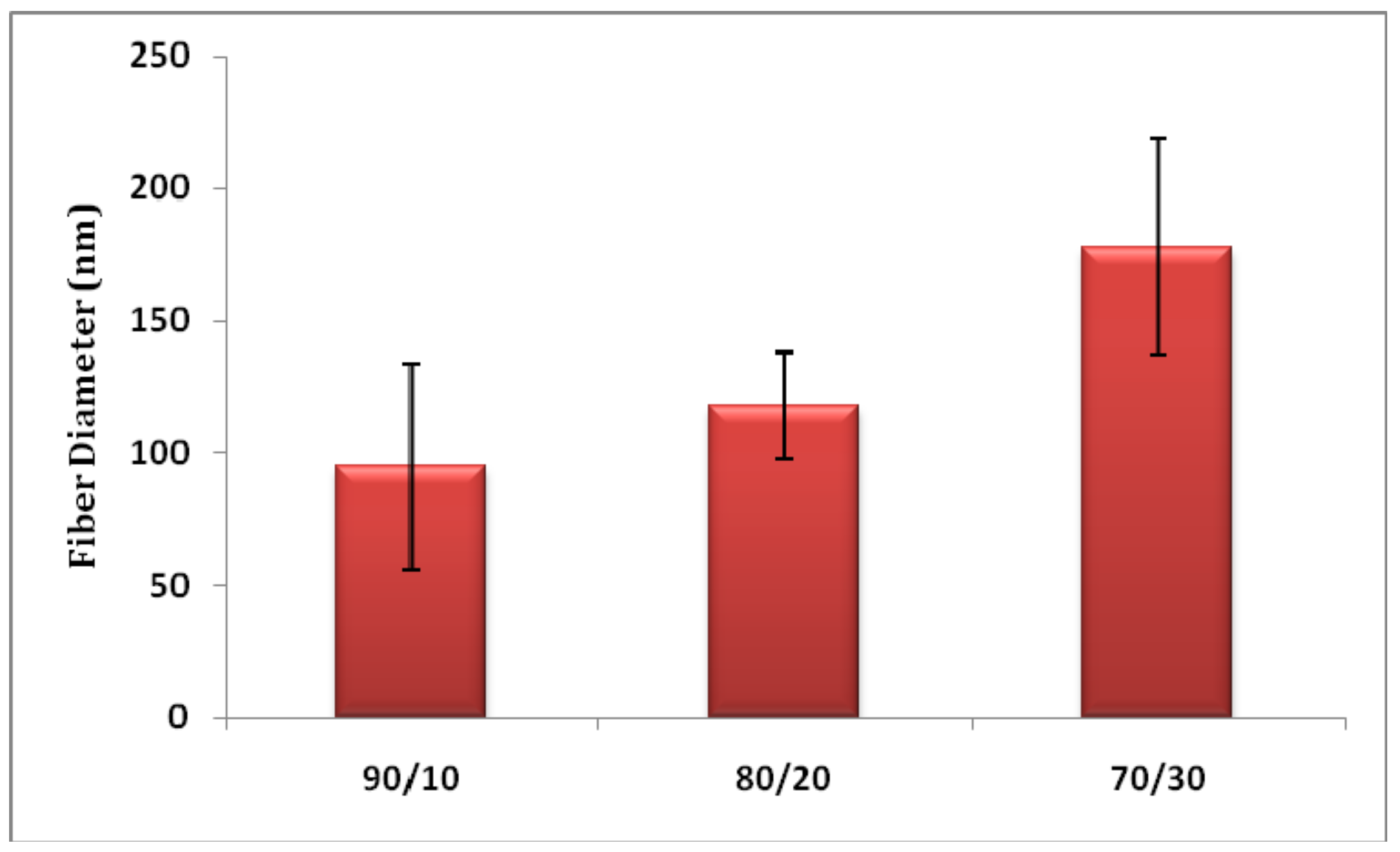
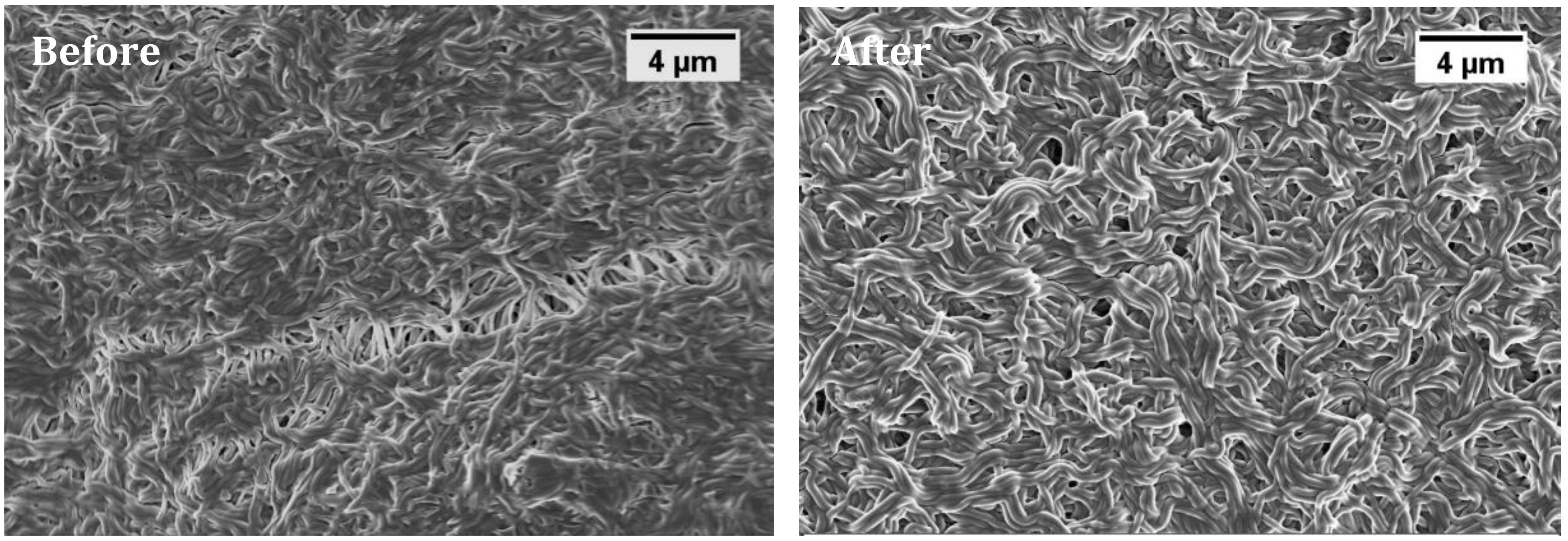
3.1. Nanofiber Morphology and Structure
3.2. Adsorption Performance
3.3. Optimization of Adsorption Conditions
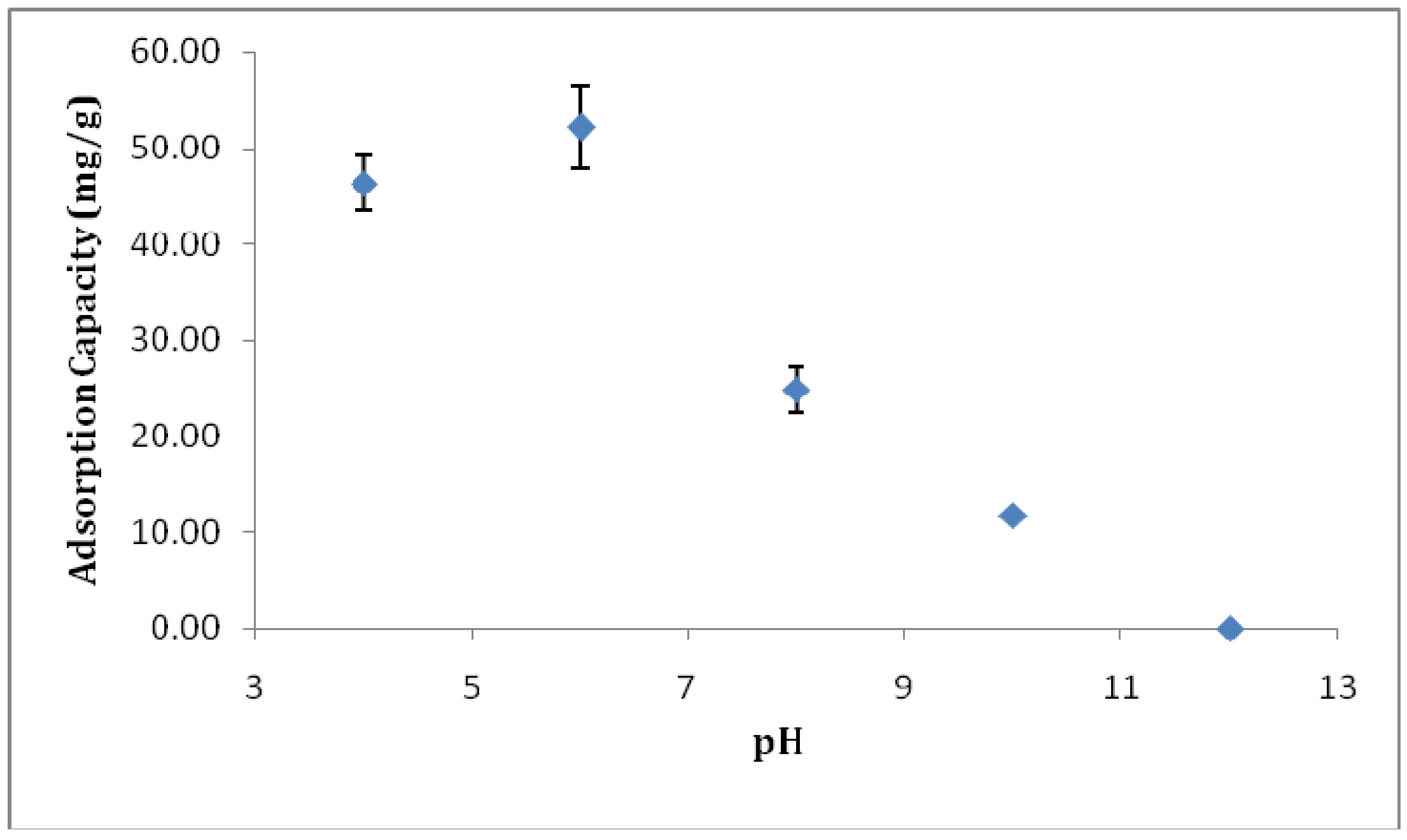
3.3.1. Effect of pH
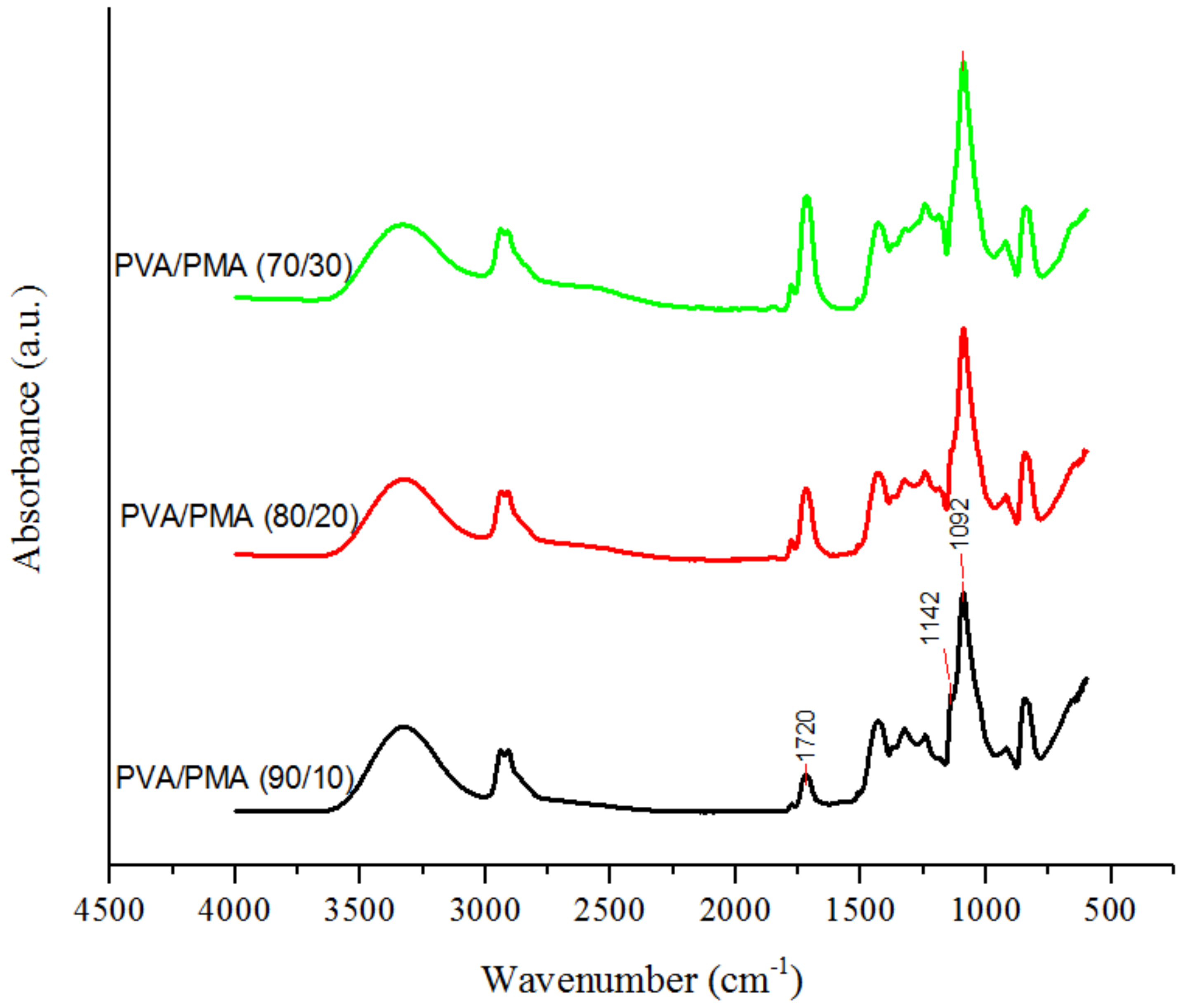
3.3.2. Effect of PMA Content
3.4. Membrane Reusability
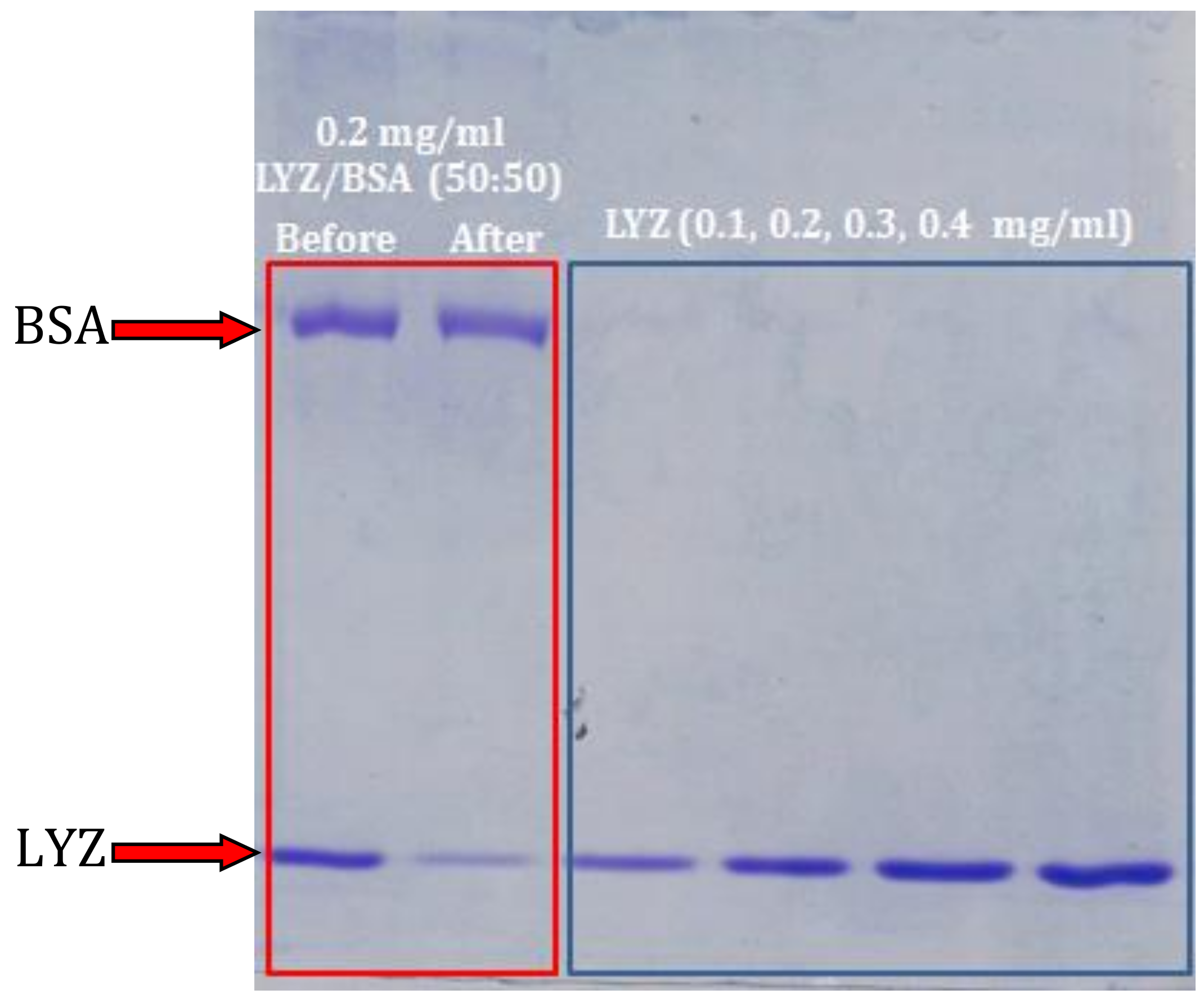
3.5. Adsorption Selectivity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhakta, S.A.; Evans, E.; Benavidez, T.E.; Garcia, C.D. Protein adsorption onto nanomaterials for the development of biosensors and analytical devices: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 872, 7–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, S.; Dai, F.; Ma, Y.; Yan, T.; Si, Y.; Sun, G. Ultrafine Silk-Derived Nanofibrous Membranes Exhibiting Effective Lysozyme Adsorption. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 8777–8784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, T.; Li, Y.; An, L.; Li, W.; Zhang, Z. Preparation of pH-controllable nanofibrous membrane functionalized with lysine for selective adsorption of protein. Coll. Surf. A 2017, 531, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fu, Q.; Wang, X.; Si, Y.; Yu, J.; Wang, X.; Ding, B. In situ cross-linked and highly carboxylated poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofibrous membranes for efficient adsorption of proteins. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 7281–7290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Wang, X.; Si, Y.; Liu, L.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Scalable Fabrication of Electrospun Nanofibrous Membranes Functionalized with Citric Acid for High-Performance Protein Adsorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 11819–11829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matlock-Colangelo, L.; Colangelo, N.W.; Fenzl, C.; Frey, M.; Baeumner, A.J. Passive mixing capabilities of micro-and nanofibres when used in microfluidic systems. Sensors 2016, 16, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Lan, Z.; Matsuura, T.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospun polyethersulfone affinity membrane: Membrane preparation and performance evaluation. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2009, 877, 3686–3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voicu, S.I.; Condruz, R.M.; Mitran, V.; Cimpean, A.; Miculescu, F.; Andronescu, C.; Miculescu, M.; Thakur, V.K. Sericin Covalent Immobilization onto Cellulose Acetate Membrane for Biomedical Applications. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1765–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, H.-T.; Lin, J.-M.; Cheng, T.-H.; Chou, S.-Y.; Huang, C.-C. Direct purification of lysozyme from chicken egg white using weak acidic polyacrylonitrile nanofiber-based membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 125, 616–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Y.; White, C.J.B.; Xue, Y.; Nie, H.; Zhu, L. Elaboration, characterization and study of a novel affinity membrane made from electrospun hybrid chitosan/nylon-6 nanofibers for papain purification. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 2296–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneiderman, S.; Zhang, L.; Fong, H.; Menkhaus, T.J. Surface-functionalized electrospun carbon nanofiber mats as an innovative type of protein adsorption/purification medium with high capacity and high throughput. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 8989–8995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, M.; Chery, J.; Frey, M.W. Functionalization of Electrospun Poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) Nanofiber Membranes for Selective Chemical Capture. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matlock-Colangelo, L.; Cho, D.; Pitner, C.L.; Frey, M.W.; Baeumner, A.J. Functionalized electrospun nanofibers as bioseparators in microfluidic systems. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 1696–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matlock-Colangelo, L.; Coon, B.; Pitner, C.L.; Frey, M.W.; Baeumner, A.J. Functionalized electrospun poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofibers for on-chip concentration of E. coli cells. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 1327–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, D.; Matlock-Colangelo, L.; Xiang, C.; Asiello, P.J.; Baeumner, A.J.; Frey, M.W. Electrospun nanofibers for microfluidic analytical systems. Polymer 2011, 52, 3413–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, D.; Lee, S.; Frey, M.W. Characterizing zeta potential of functional nanofibers in a microfluidic device. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 372, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.W.; Lee, K.H.; Khil, M.S.; Ho, Y.S.; Kim, H.Y. The effect of molecular weight and the linear velocity of drum surface on the properties of electrospun poly(ethylene terephthalate) nonwovens. Fibers Polym. 2004, 5, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akar, E.; Altinişik, A.; Seki, Y. Preparation of pH- and ionic-strength responsive biodegradable fumaric acid crosslinked carboxymethyl cellulose. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 90, 1634–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Liu, W.; Yu, Y.; Du, J.; Li, N.; Xu, L. Synthesis of mono-dispersed mesoporous SBA-1 nanoparticles with tunable pore size and their application in lysozyme immobilization. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 37470–37478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
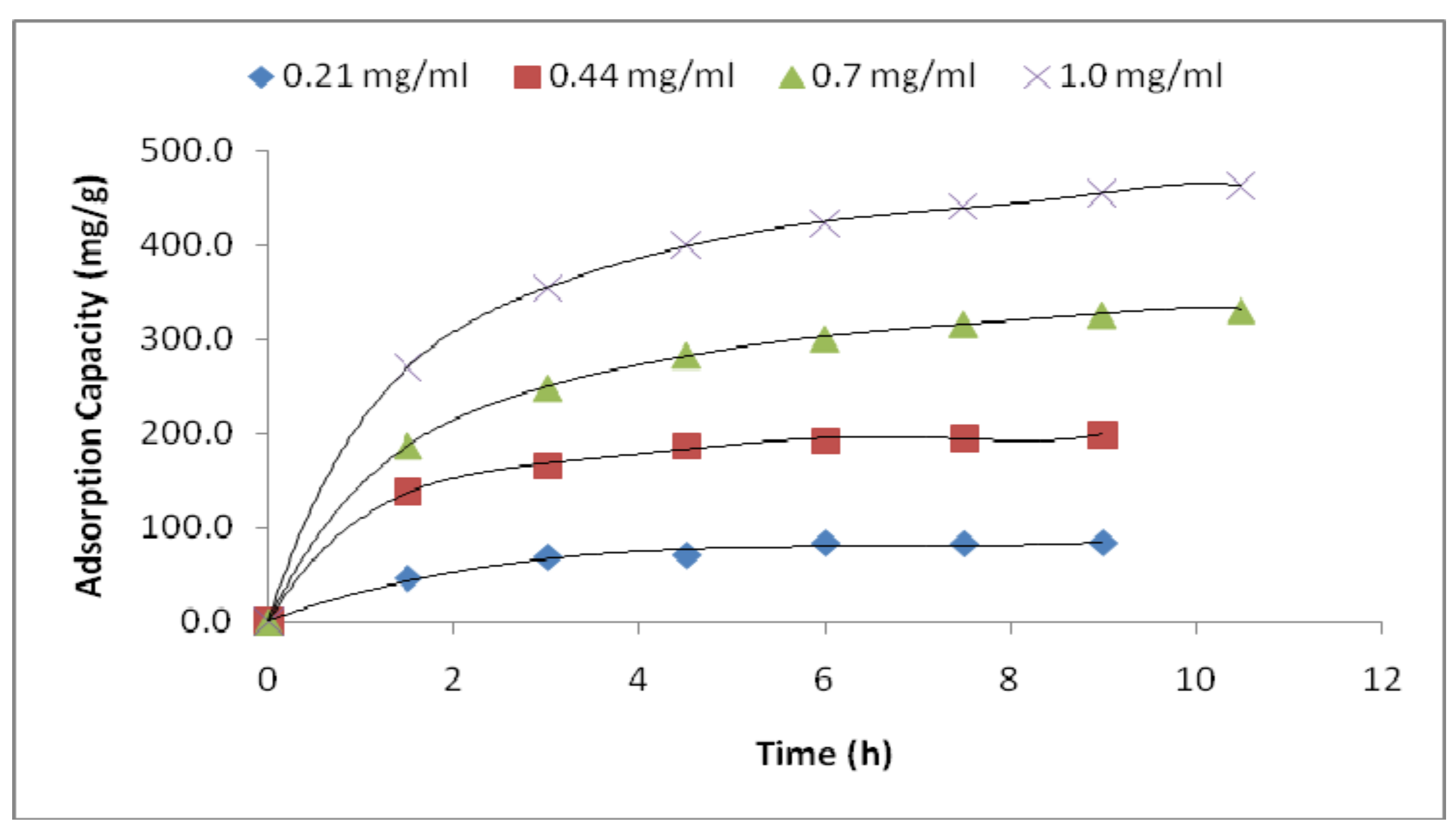
| LYZ Conc. (mg/mL) | 0.21 | 0.44 | 0.7 | 1.0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qe (mg/g) | 86.29 ± 3.89 | 207.88 ± 13.12 | 326 ± 7.35 | 476.53 ± 19.48 |
| PVA/PMA | C | Qe |
|---|---|---|
| w/w (%) | (mg/mL) | (mg/g) |
| 70:30 | 0.22 | 81.94 ± 2.09 |
| 80:20 | 0.21 | 80.07 ± 3.71 |
| 90:10 | 0.21 | 44.75 ± 2.53 |
| PVA/PMA | C=O/C-O | C-O-C/C-O |
|---|---|---|
| 90/10 | 0.16 | 0.54 |
| 80/20 | 0.29 | 0.46 |
| 70/30 | 0.43 | 0.38 |
| Solution | LYZ | Adsorption |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Conc. (mg/mL) | Capacity (mg/g) |
| Pristine LYZ solution | 0.18 | 0.0 |
| Effluent—1st LYZ Adsorption | 0.03 | 55.1 |
| Effluent—Base Elution | 0.17 | 14.1 |
| Effluent—2nd LYZ Adsorption | 0.02 | 59.6 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Najafi, M.; Chery, J.; Frey, M.M. Functionalized Electrospun Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Nanofibrous Membranes with Poly(Methyl Vinyl Ether-Alt-Maleic Anhydride) for Protein Adsorption. Materials 2018, 11, 1002. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11061002
Najafi M, Chery J, Frey MM. Functionalized Electrospun Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Nanofibrous Membranes with Poly(Methyl Vinyl Ether-Alt-Maleic Anhydride) for Protein Adsorption. Materials. 2018; 11(6):1002. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11061002
Chicago/Turabian StyleNajafi, Mesbah, Joronia Chery, and Margaret M. Frey. 2018. "Functionalized Electrospun Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Nanofibrous Membranes with Poly(Methyl Vinyl Ether-Alt-Maleic Anhydride) for Protein Adsorption" Materials 11, no. 6: 1002. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11061002
APA StyleNajafi, M., Chery, J., & Frey, M. M. (2018). Functionalized Electrospun Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Nanofibrous Membranes with Poly(Methyl Vinyl Ether-Alt-Maleic Anhydride) for Protein Adsorption. Materials, 11(6), 1002. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11061002